Abstract
The influence of Mg2+ doping (3 mol %) on structural and humidity sensing properties of (Ba0.5,Sr0.5)TiO3 (BST) perovskite nanocomposite were studied in details. Microstructural properties revealed the particle size, surface area, and average pore volume diminished for doped sample. For the MgO doped BST sensor, the film resistance and total impedance are changed more than four orders of magnitude in the 20–95% RH range, while BST sensor shows three orders change. The 3 mol % MgO doped sample with maximum hysteresis of 6.1 RH% and response/recovery time of about 30/80 s exhibits faster characteristics compare to pure BST sample with 6.8 RH% hysteresis and response/recovery of 41 s and 98 s, respectively. Transduction mechanism was found based on the proton transfer and further confirmed by a Bode plot and Nyquist complex impedance plane plot.
1. Introduction
Humidity measurement determines the amount of water vapor available in a gaseous mixture such as air, oxygen, nitrogen, etc. Humidity sensors have application in various fields such as meteorology, medicines, biochemical, air conditioning, warehouse, chemical gas purification and nutritional products manufacturing [1]. Today number of researches are growing more focused on derivation of novel composite materials applicable as humidity sensing element for elimination of undesirable characteristics such as hydrophilicity, poor sensitivity, signal drift hence low detection range, and defective physical robustness at rough conditions. Moisture sensors are classifying to two types of relative and absolute sensors. This assortment is based on the sensing principle and mechanism of module, i.e., capacitive, resistive, electrolytic (old fashioned), thermal conductivity (thermoelemental), mechanical, optical and oscillating types [2].
Inorganic materials based on metal oxides have revealed practical promising properties in comparison to organic polymer films from viewpoints of hydrophobicity and shelf life for chemical humidity sensor applications. Development of perovskite-based humidity sensitive nanocomposites with insight into the influence of addition of dopant nanoparticles on the structural and electrophysical properties of humidity sensors is an important study [3]. Substitution or doping or both of these actions with the positive ions in A or B site of the complex perovskite structures (ABX3), can be resulted in widely different humidity sensitive properties [4,5]. Among others, (Bax,Sr1-x)TiO3 as a well-known mixed dielectric perovskite has been extensively applied for electrochemical applications, e.g., solid oxide fuel cells, biosensing, capacitive transducers, gas and humidity sensing. Variations of Ba2+ and Sr2+ atoms in A site, or addition of other external atoms as surcharge cations to A, B or both sites have been reported for improvement of the water-induced polarization effects [6]. Next to the ionic size and mobility contribution, morphology and microstructural control of the perovskite film are deemed as most determinative factors [7]. In this paper, influence of the addition of Mg2+ alkaline ions on the structural and humidity sensitive properties of the nanoscale (Ba0.5,Sr0.5)TiO3 perovskite are presented. Nanocomposites were synthesized and doped through solid state reaction, and devices were fabricated through thick film technology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Synthesis and Characterization
Perovskite metal oxide powders were synthesized by solid state reaction method from BaCO3 (99.999%), SrCO3 (≥99.9%), and TiO2 (≥99%) precursors (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The basic powders were mixed and ultrasonically bathed in water. The composites were wet milled for 8 h using mono miller with zirconia balls, and dried inside of oven at 50 °C overnight. Final product as (Ba0.5,Sr0.5)TiO3 nanocomposite was obtained after 3 h calcination of the dried powders at 1000 °C in air using of the horizontal tubular furnace. (1 − x)(Ba0.5,Sr0.5)TiO3-(x)MgO (x = 0, 0.03) nanocomposites of this research were produced by addition of the 3 mol % MgO (particle size < 50 nm, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) as dopants to the parent (Ba0.5,Sr0.5)TiO3 perovskites following the above process. Particle morphology, average particle size, and presence of the smaller dopants in calcined powders have been observed by energy filtered transmission electron microscopy (EFTEM). Surface area analyzer has determined the surface area and total pore volume of the nanocomposites by multi point BET and BJH methods, respectively. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) has been employed for determination of the cured ceramic films surface morphology.
2.2. Device Fabrication and Characterization
Two types of fine nanocomposites, i.e., (Ba0.5,Sr0.5)TiO3 or (BST) and BST doped 3 mol % MgO as active layers were mixed with organic vehicle to form sensitive inks. Organic compound was synthesized by solving of the ethyl cellulose (48% ethoxyl, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) in α-terpineol and m-Xylene (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) with 1:12:12 ratio. Conducting platinum electrodes with 7 pairs of interdigital fingers were printed utilizing screen printing machine on alumina substrates then dried according to the datasheet and followed by annealing at 1000 °C for 15 min inside of the furnace. Aqua sensitive inks were deposited on top of the first layer and coated samples were dried at 150 °C for 15 min, then annealed at 1100 °C for half an hour. Humidity sensors were wire bonded and placed inside of the laboratory-made temperature and humidity simulation chamber and tested at room temperature and continuous range of 20% to 95% RH. The AC and DC electrical characterizations were conducted via computer controlled precision LCR meter at frequency range of 20 Hz to 2 MHz and 500 mVp-p (4 wire type Kelvin clip lead connection with two-point probe).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructural Properties
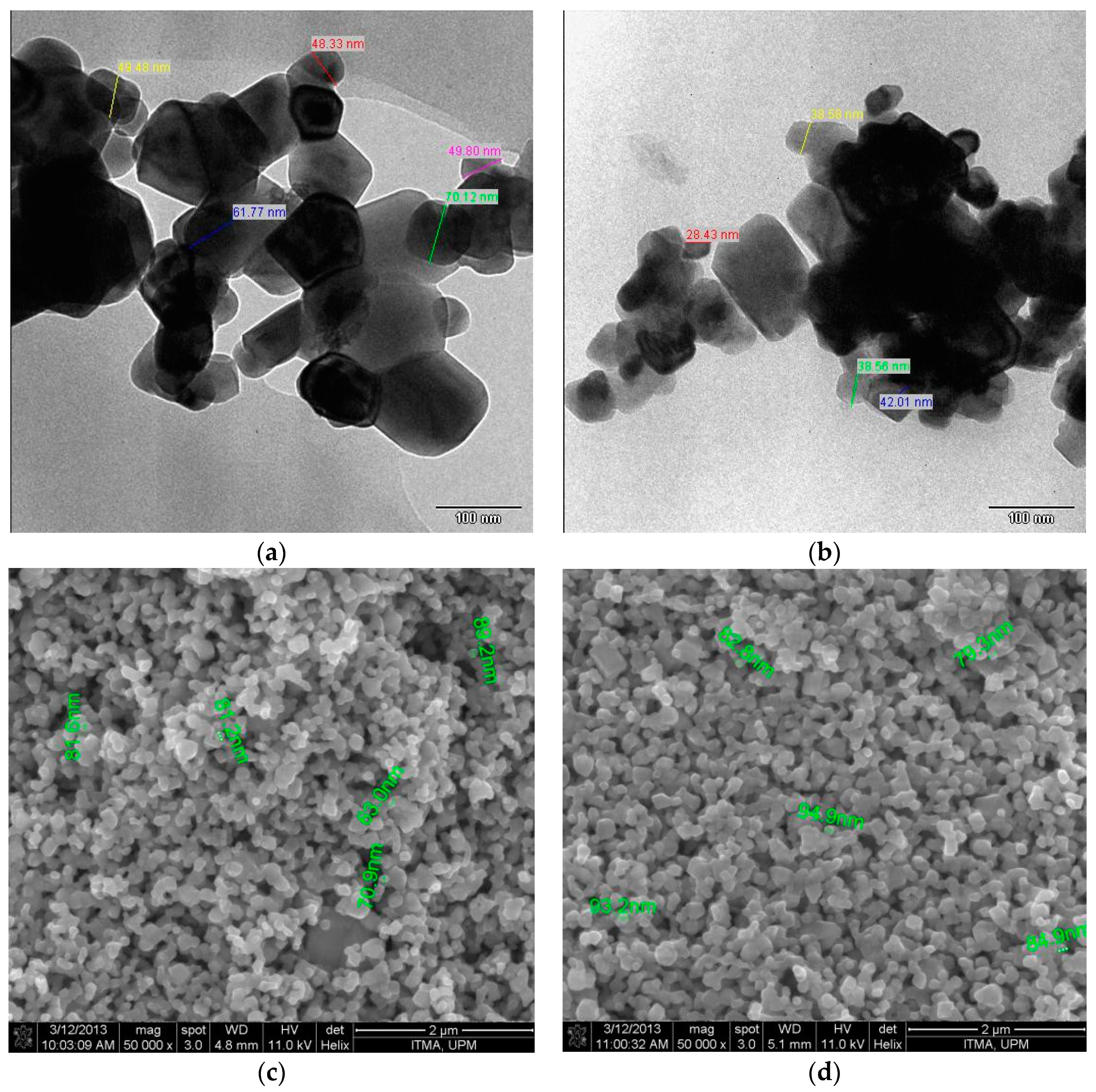
TEM images of the BST and 3 mol % MgO-BST nanocomposites are illustrated in Figure 1a,b. Average particle size of the powder samples was obtained from processing of the pictures and lists in Table 1. Analysis provides a good correlation between the calculated crystallite sizes (XRD) and particles. Morphologies demonstrate agglomeration of the smaller roundish particles as MgO on the surface of BST particles (Figure 1b). FESEM photographs of the films surface are seen in Figure 1c,d. Average grain size of the samples from 150 points measurement are provided in Table 1. Addition of MgO doping agents led to a slight increase of grain size. Specific surface area, pore volume and radius of the nanocomposites based on surface area analyzer are listed in Table 1.
Figure 1.
TEM images of nanocomposites calcined at 1000 °C: (a) BST; (b) 3 mol % MgO doped BST. SEM photograph of films fired at 1100 °C: (c) BST; (d) 3 mol % MgO doped BST.

Table 1.
Detailed properties of the nanocomposites in this research before and after doping.
3.2. Humidity Sensitive Properties
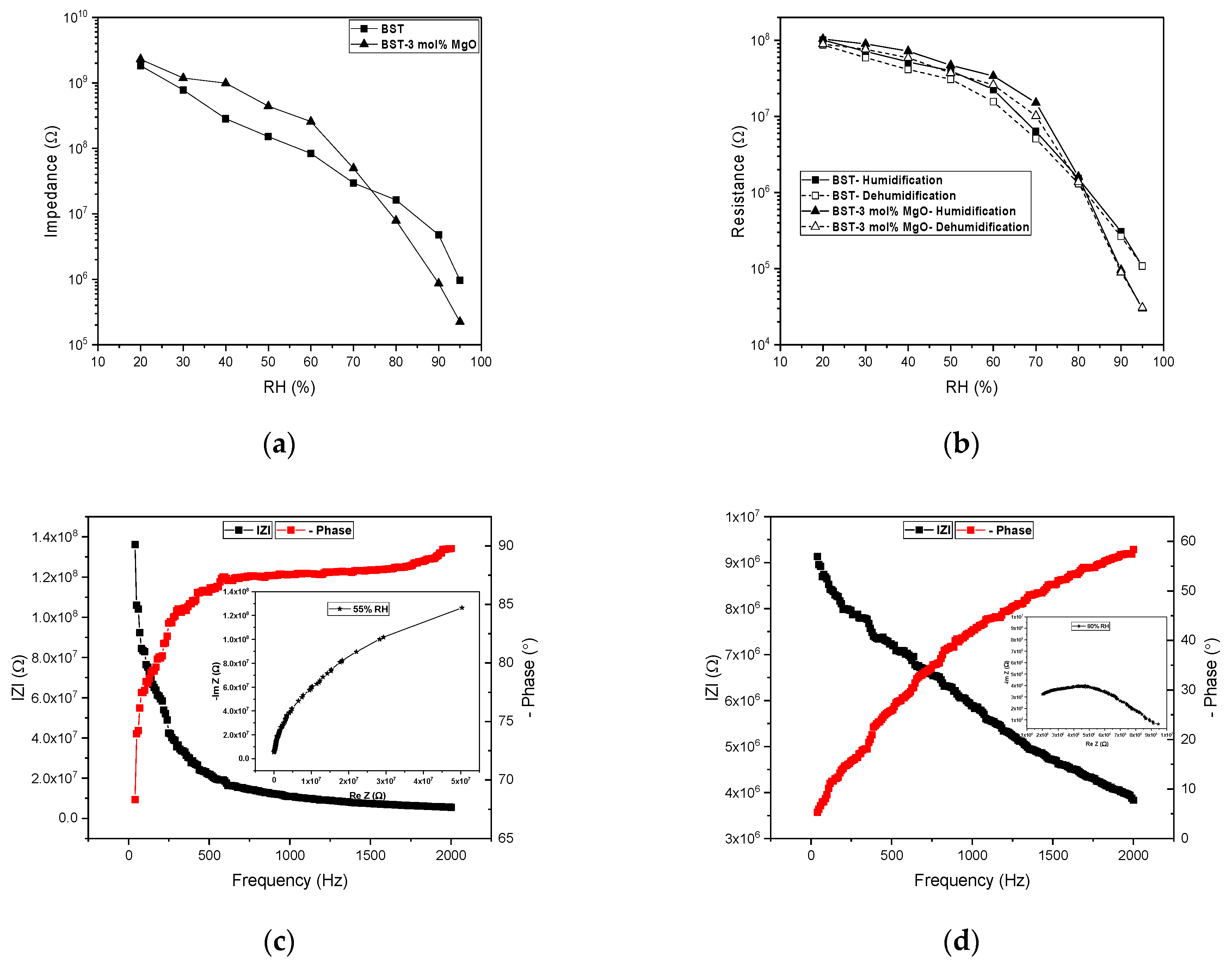
Sensitivity as total impedance change of the sensors shows in Figure 2a. MgO added BST with more than four orders of magnitude change exhibits higher sensitivity. Figure 2b shows hysteresis characteristics as resistance change of the sensors which is 6.1 RH% and 6.8 RH% for the doped and pure BST sensors, respectively. BSTM3 with response time of 30 s showed faster response than the BST with 41 s. Bode and Nyquist plots based on the complex impedance spectra at different RH levels confirm that sensors operate based on the protonic conduction mechanism (Figure 2c,d). Sensor contains of BST added 3 mol % MgO exhibits remarkable improved humidity sensitive performance for almost all humidity ranges compared to that contains of pure BST.
Figure 2.
(a) Comparison of impedance change of the sensors; (b) hysteresis characteristics of the sensors measured at 10 KHz; (c) Bode and Inset Nyquist plot of the real and imaginary part of the impedance at 55% RH; (d) Bode and Inset Nyquist plot of the sensor at 80% RH.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank International Graduate Academy (IGA) of the University of Freiburg for the Ph.D. funding of Hamid Farahani through LGFG scholarship. Furthermore, we would like to thank Jochen Kieninger for advise on the evaluation of the impedance data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Tripathy, A.; Pramanik, S.; Cho, J.; Santhosh, J.; Osman, N.A.A. Role of Morphological Structure, Doping, and Coating of Different Materials in the Sensing Characteristics of Humidity Sensors. Sensors 2014, 14, 16343–16422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenner, R.; Zdankiewicz, E. Micromachined Water Vapor Sensors: A Review of Sensing Technologies. IEEE Sens. J. 2001, 1, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enhessari, M.; Salehabadi, A. Perovskites-Based Nanomaterials for Chemical Sensors. In Progresses in Chemical Sensor; InTech: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, H.; Wagiran, R.; Urban, G. MgO-Doped (Zr,Sr)TiO3 Perovskite Humidity Sensors: Microstructural Effects on Water Permeation. In Proceedings; Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute: Basel, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 1, p. 408. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X. Humidity Sensing Properties of Bi0.5(Na0.85K0.15)0.5Ti0.97Zr0.03O3 Microspheres: Effect of A and B Sites Co-Substitution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, H. Synthesis and Fabrication of Nanocomposite Magnesia Doped Barium Strontium Titanate for Thick Film Humidity Sensor. Master’s Thesis, University Putra Malaysia (UPM), Selangor, Malaysia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.H.; Xu, H.J.; Hu, J.; Jiang, W.F.; Li, X.J. Structure and Humidity Sensing Properties of Barium Strontium Titanate/Silicon Nanoporous Pillar Array Composite Films. Thin Solid Films 2008, 517, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).