Abstract
The conducted research concerned the effect of a magnetic field (MF) on the removal of iron compounds. The tested process was filtration through a quartz sand bed with a grain size of 0.4–0.8 mm. Another examined material was activated alumina. The obtained results proved that the MF had a significant impact on the efficiency of iron removal from a water filtrated trough than activated alumina. It was proven that the effect of the magnetic field on the filtration process using other filtration materials, was insignificant.
1. Introduction
The magnetic field (MF) is a physical process whose influence on different liquids is examined by researchers in many scientific centers. New applications of MF are still being sought. It is suspected that a magnetic field could modify water properties, aqueous solutions and changes in suspended solids structure as well. It may be related to, among others, changes in the conformation of the liquid and the phenomena of polarization [1]. Water is a dipole and has an uneven electric charge distribution in the molecule. An MF affects water in a certain manner and changes its properties. Transformation in the character of water, such as liquid viscosity, surface tension, and enthalpy of vaporization, transfigure into a modification of interactions between water molecules and molecules or ions of other compounds present in aqueous solutions [2,3,4]. Water technology seeks to remove these as water pollutants to conform with legal requirements or standards. The common process used for separation of particular components from the water is filtration and adsorption. During those processes, water contaminants are retained on the outer surface of filtration material grains or inside their pores. Different molecules present in the water are adsorbed on the surface of the material. The group of the most common adsorbents includes mainly activated carbon. One of the inorganic sorbents rarely used for removing the contaminants present in water is activated alumina (Al2O3) [5,6]. This material is not chemically inert and has amphoteric properties. Our research tested the mechanism governing the phenomenon of a components adsorption from aqueous solutions and its susceptibility to a magnetic field. The experiments explored the effectiveness of iron compound removal in the magnetic field-assisted filtration process through quartz sand and activated alumina. Obtained results proved that it is possible to apply a constant external magnetic field as an additional elementary process for improvement of the efficiency of filtration and adsorption.
2. Material and Methods
The conducted research involved determining the effect of a magnetic field on the efficiency of iron (Fe) removal from single component liquid solutions. The experiment was carried out on a laboratory scale. The research stand consisted of four laboratory columnar separators. The volume of a single column was 1 dm3. They were filled with the tested filtration materials: Quartz sand with a grain size of 0.4–0.8 mm into the first two columns and active alumina with granulation of 3–5 mm in the other two. The first column of each pair of devices filled with the same filtration material was the control stand (intended for control samples) and another one was for magnetized samples. The weight of filtration material in each was 750 g/dm3 [1].
Distilled water was used to prepare the solutions. It allowed elimination of the influence of other factors disturbing the testing of the MF (magnetic field) on the efficiency of iron removal. The water samples were prepared by adding to the distilled water an appropriate amount of concentrated iron standard solution. A series of Fe solutions were prepared with the concentrations: 1; 2; 5; and 10 mg Fe /dm3. Static ferrite magnets with a magnetic induction of B = 118 mT were used for the magnetization process. Table 1 shows the properties of the used magnets.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the magnets used for the experiment [1].
Magnets surrounded a tank with raw water made of PET (polyethylene terephthalate) and conducted an MF. The time of the raw water magnetizing was 10 minutes. The control samples were not subjected to a magnetic field. The magnetic induction was measured using the HGS-10A gaussmeter. The magnetic induction measured through the bottle wall was 57 mT. Such a course of action was taken to eliminate the possible influence of adsorption of the tested water components on the tank walls. Next, the solutions of magnetized and non-magnetized water were filtered through prepared filter columns filled with quartz sand and activated alumina. The water not treated with PM was filtered through the first of a pair of each column and magnetized through another one [1]. The experiment was replicated several times to reach reliable results.
The concentration of iron in the solution flowing into the columns and water samples after the filtration process was determined by the atomic absorption method with flame atomization using a Thermo Scientific iCE3500 atomic absorption spectrometer with a deuterium background correction.
3. Results and Discussion
Table 2 presents the obtained results with the standard deviation of iron removal using the filtration process supported by the magnetic field.

Table 2.
Obtained results comparison for samples, including Fe.
The model water samples, with a primary concentration of Fe about 0.95 mg/dm3, were subjected to a magnetic field and filtered by the studied filtration materials (Table 2). It was noted that only in the magnetized water, which ran through activated alumina, the iron concentration was lower than in the control sample. The calculated efficiency of iron removal from the raw water with Al2O3 was low and reached about 20% in the control samples. In samples subjected to the MF, the Fe removal effect was about 30% (Figure 1). Other research groups have conducted research on filtration efficiency using other tested filtration materials. Skoczko et al. proved that the lowest tested iron concentration was about 89% for quartz sand and up to 93% for activated carbon. Investigating the effectiveness of iron removal through various commercial filtration masses, they achieved an efficiency of iron removal from 82.59% to 97.61% with the GreenSandPlus [7].
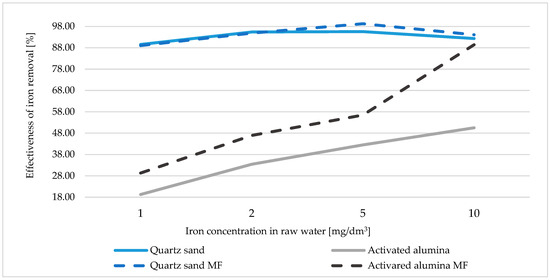
Figure 1.
Graph of the dependence of the iron removal efficiency on initial concentration in raw water.
4. Conclusions
- The filter material more susceptible to the influence of the MF was activated alumina, in comparison to the quartz sand.
- In the process of removing iron compounds from the model water, comparable results were achieved both with magnetized and control water by quartz sand.
- The influence of the MF on the efficiency of iron removal increased with the increase of the initial concentration of iron in the water before the process, in the case of the filtration process on the activated alumina.
Author Contributions
Ewa Szatyłowicz and Iwona Skoczko conceived and designed the experiments; Ewa Szatyłowicz performed the experiments; Ewa Szatyłowicz and Iwona Skoczko analyzed the data; Ewa Szatyłowicz contributed materials; Ewa Szatyłowicz wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Skoczko, I.; Szatyłowicz, E. Removal of heavy metal ions by filtration on activated alumina-assisted magnetic field. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 117, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Qin, H.; Qiao, J.; Guan, X. The enhancing effect of weak magnetic field on degradation of Orange II by zero-valent iron. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szcześ, A.; Chibowski, E.; Hołysz, L.; Rafalski, P. Effects of static magnetic field on water at kinetic condition. Chem. Eng. Process. 2011, 50, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, E.J.L.; Ramalho, T.C.; Magriotis, Z.M. Influence of magnetic field on physical–chemical properties of the liquid water: Insights from experimental and theoretical models. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 888, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoczko, I.; Szatyłowicz, E. Studies on the efficiency of groundwater treatment process with adsorption on activated alumina. J. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 18, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.S.; Pant, K.K. Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic studies for adsorption of As(III) on activated alumina. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 36, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoczko, I.; Piekutin, J.; Roszczenko, A. Removal of iron and manganese compounds from water. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2015, 17, 1587–1608. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).