Personalised Fractional-Order Autotuner for the Maintenance Phase of Anaesthesia Using Sine-Tests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
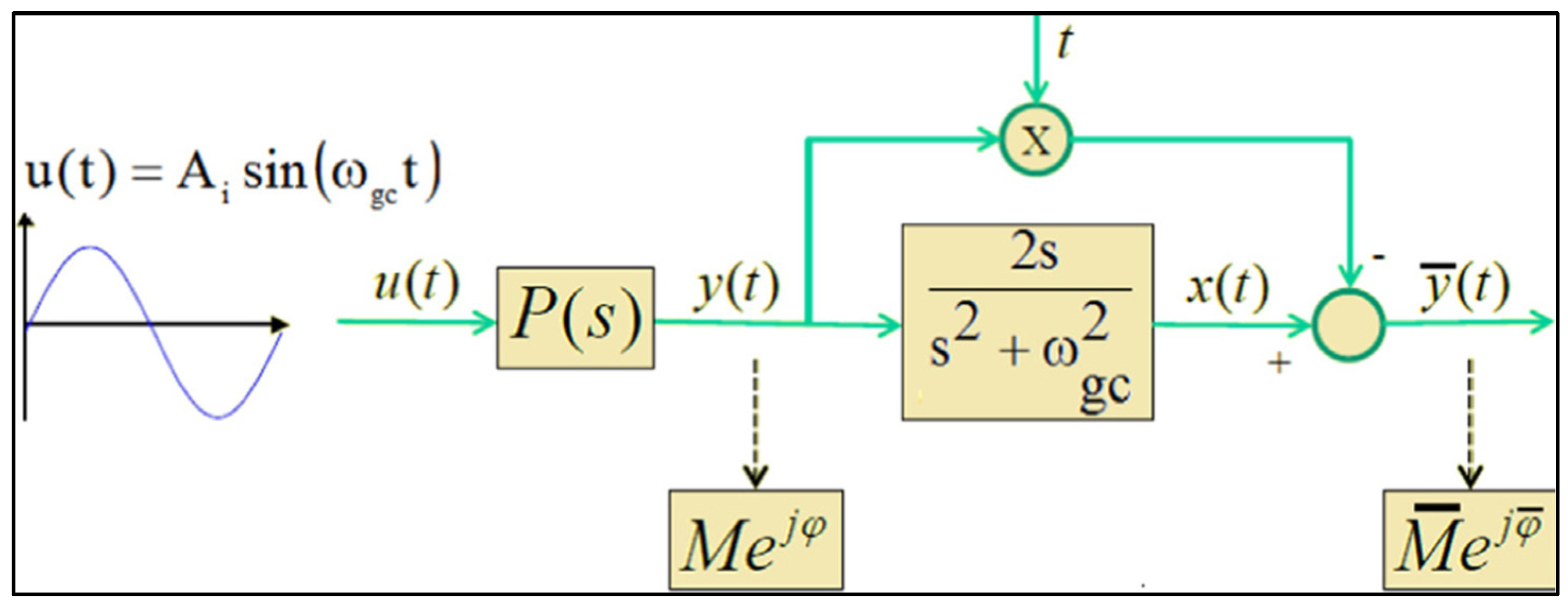
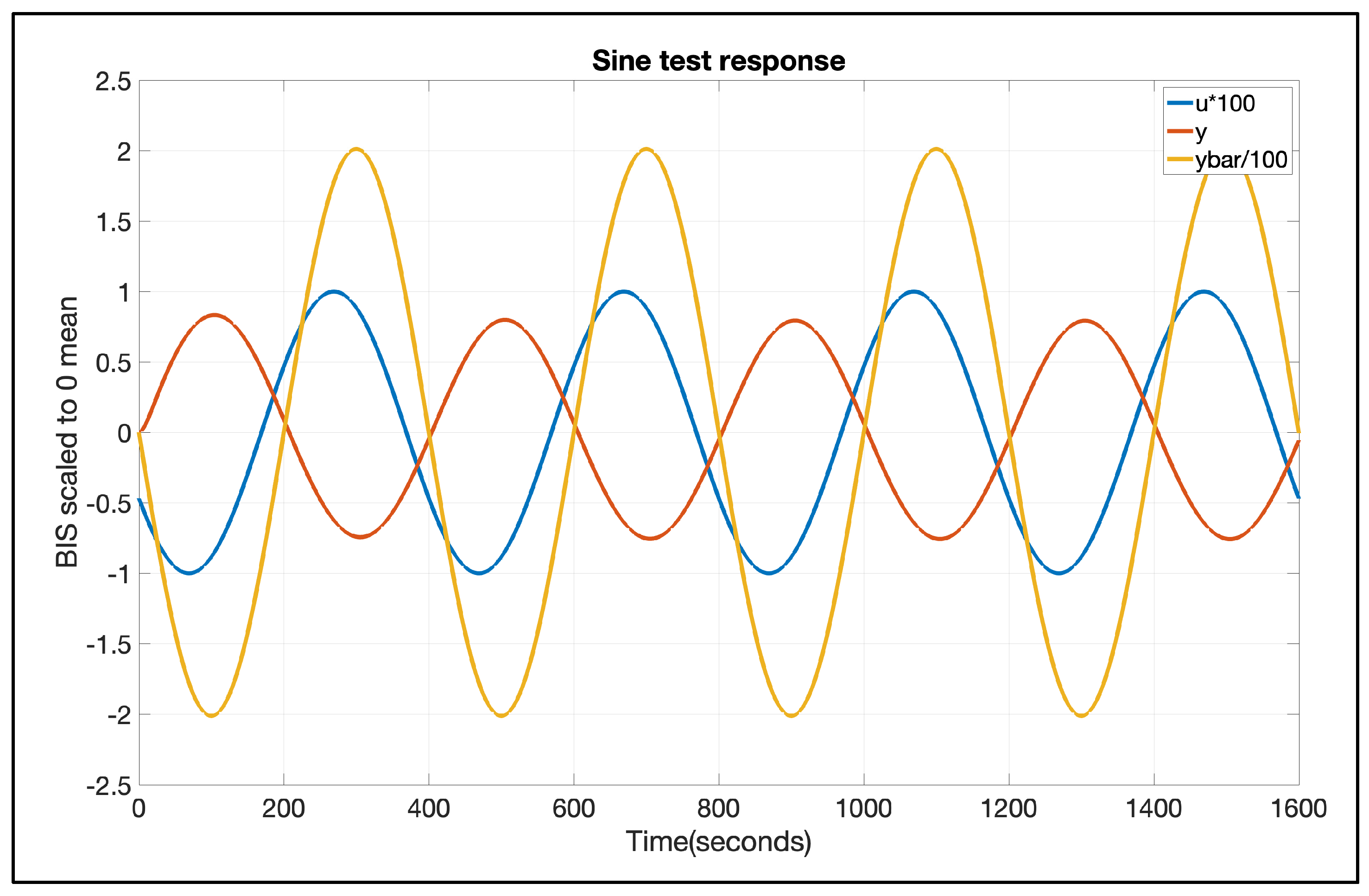
2.1. Sine Test Method
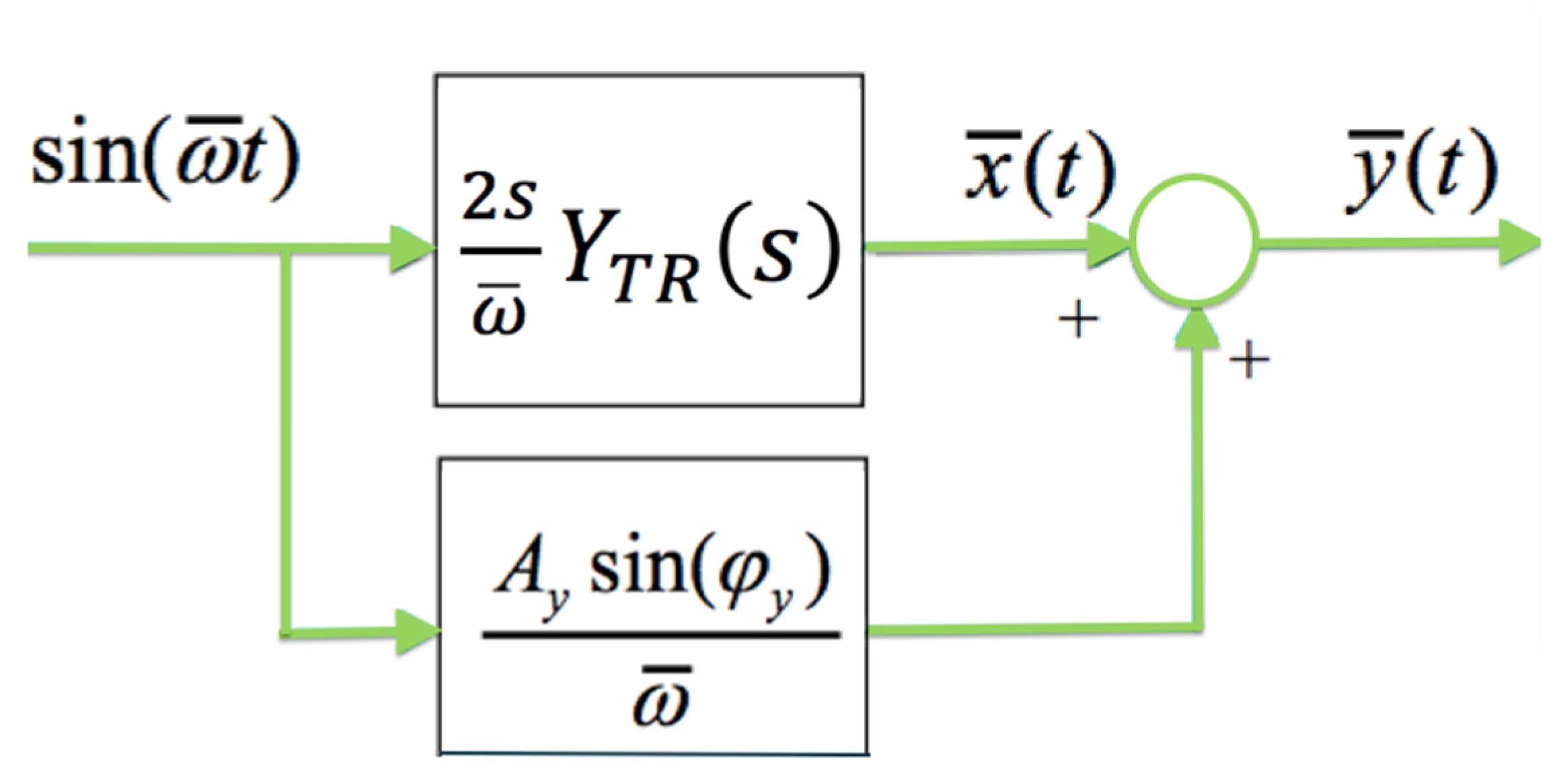
2.2. Autotuning Mathematical Background
2.3. Algorithm Description
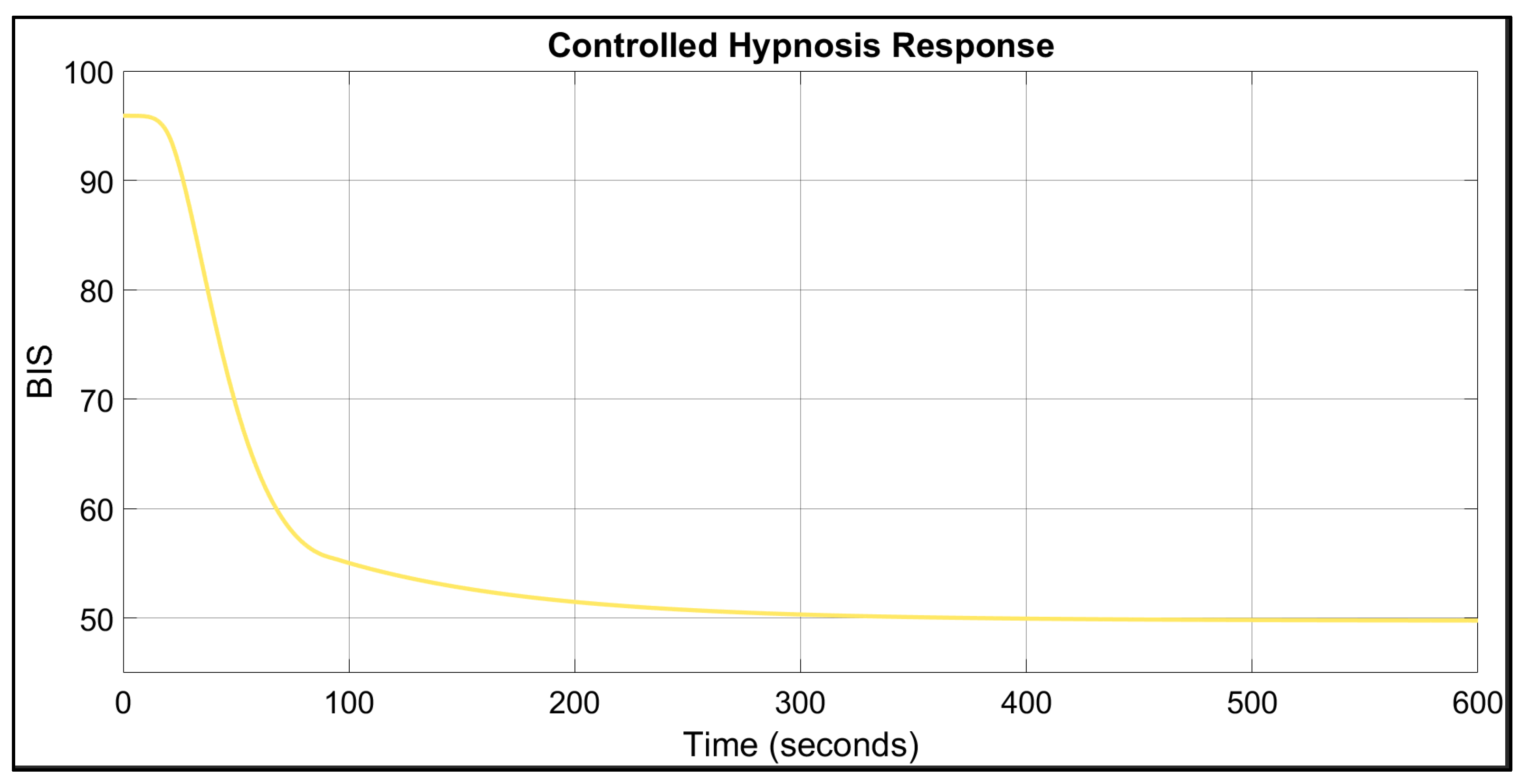
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TCI | Target-controlled infusion |
| BIS | Bispectral Index |
| TIVA | Total Intravenous Anaesthesia |
| PK | Pharmacokinetic |
| PD | Pharmacodynamic |
| FO | Fractional order |
| PID | Proportional-integrative-derivative |
| Prop | Propofol progression rate |
| TT | Time-to-target |
| EEG | Electroencephalographic |
| EMG | Electromyographic |
Appendix A

- Perform a sine-test on the system using as the input signal a sine of the form . The sampling period for data acquisition is Ts, and the total number of measured samples is N.
- Analyse the steady-state oscillation of y(t) to determine the amplitude Ay and phase using (42)
- Calculate the transient part yTR(t) as: , with
- Calculate the complex number .
- Calculate the frequency response of the process and the frequency response slope at the frequency as: and .
References
- Casas-Arroyave, F.D.; Fernández, J.M.; Zuleta-Tobón, J.J. Evaluation of a closed-loop intravenous total anesthesia delivery system with BIS monitoring compared to an open-loop target-controlled infusion (TCI) system: Randomized controlled clinical trial. Colomb. J. Anesthesiol. 2019, 47, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neckebroek, M.; Ionescu, C.M.; van Amsterdam, K.; De Smet, T.; De Baets, P.; Decruyenaere, J.; De Keyser, R.; Struys, M.M.R.F. A comparison of propofol-to-BIS post-operative intensive care sedation by means of target controlled infusion, Bayesian-based and predictive control methods: An observational, open-label pilot study. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2018, 33, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, E.; Cyr, S.; Kazan, R.; Giunta, F.; Hemmerling, T.M. Clinical performance and Safety of Closed-Loop Systems: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 124, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.G.; Eckert, D.J. Effects of hypnotics on obstructive sleep apnea endotypes and severity: Novel insights into pathophysiology and treatment. Sleep Med. Rev. 2021, 58, 101492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, N.; Kalra, Y.; Panwar, S.; Arora, M.K.; Dhingra, U. Comparison of target concentration of propofol during three phases of live donor liver transplant surgery using a target-controlled infusion of propofol total intravenous anaesthesia—A prospective, observational pilot study. Indian J. Anaesth. 2024, 68, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fahlenkamp, A.V.; Peters, D.; Biener, I.; Billoet, C.; Apfel, C.; Rossaint, R.; Coburn, M. Evaluation of bispectral index and auditory evoked potentials for hypnotic depth monitoring during balanced xenon anaesthesia compared with sevoflurane. Br. J. Anaesth. 2010, 105, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, M.; Padula, F.; Latronico, N.; Paltenghi, M.; Visioli, A. Individualized PID tuning for maintenance of general anesthesia with propofol and remifentanil coadministration. J. Process Control 2021, 109, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltesz, K.; Van Heusden, K.; Dumont, G.A. In Automated Drug Delivery in Anesthesia; Models for control of intravenous anesthesia. Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 119–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, N.; van Heusden, K.; Görges, M.; Brodie, S.; Rollinson, A.; Petersen, C.L.; Dumont, G.A.; Ansermino, J.M.; Merchant, R.N. Design and evaluation of a Closed-Loop anesthesia system with robust control and safety system. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 127, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Agashe, S. Review of fractional PID controller. Mechatronics 2016, 38, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedus, E.T.; Birs, I.R.; Ghita, M.; Muresan, C.I. Fractional-Order Control Strategy for Anesthesia–Hemodynamic stabilization in patients undergoing surgical procedures. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, J.A.; Marrero, A.; Reboso, J.A.; León, A. Adaptive fuzzy predictive controller for anesthesia delivery. Control Eng. Pract. 2015, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, M.; Padula, F.; Latronico, N.; Paltenghi, M.; Visioli, A. Experimental results of an event-based PID control system for propofol and remifentanil coadministration. Control Eng. Pract. 2023, 131, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, T.; Badau, N.; Mihai, M.; Hegedus, E.; Birs, I.; Copot, D.; Dulf, E.H.; Muresan, C.I. Advancing Anesthesia Education: Training on Modeling and Control for Enhanced Patient Care. In Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on Internet Based Control Education (IBCE), Ghent, Belgium, 18–20 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Parvinian, B.; Pathmanathan, P.; Daluwatte, C.; Yaghouby, F.; Gray, R.A.; Weininger, S.; Morrison, T.M.; Scully, C.G. Credibility evidence for computational patient models used in the development of physiological Closed-Loop controlled devices for critical care medicine. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleveld, D.J.; Colin, P.; Absalom, A.R.; Struys, M.M.R.F. Pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic model for propofol for broad application in anaesthesia and sedation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 942–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, J.P.; Vereecke, H.E.M.; Proost, J.H.; Eleveld, D.J.; Wietasch, J.K.G.; Absalom, A.R.; Struys, M.M.R.F. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions in anaesthesia. A review of current knowledge and how it can be used to optimize anaesthetic drug administration. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 118, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linassi, F.; Zanatta, P.; Spano, L.; Burelli, P.; Farnia, A.; Carron, M. Schnider and Eleveld Models for Propofol Target-Controlled Infusion Anesthesia: A Clinical comparison. Life 2023, 13, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Keyser, R.; Muresan, C.I.; Ionescu, C.M. A novel auto-tuning method for fractional order PI/PD controllers. ISA Trans. 2016, 62, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiado, D.V.; Lemos, J.M.; Costa, B.A.; Paz, L.A.; Mendonca, T.F. A polynomial design approach to robust control of neuromuscular blockade of patients subject to general anesthesia. In Proceedings of the 52nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Firenze, Italy, 10–13 December 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, C.A.; Chen, Y.; Vinagre, B.M.; Xue, D.; Feliu, V. Fractional-Order Systems and Controls; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, J.; Caiado, D.V.; Costa, B.A.; Paz, L.A.; Mendonca, T.F.; Rabico, R.; Esteves, S.; Seabra, M. Robust control of Maintenance-Phase Anesthesia [Applications of control]. IEEE Control Syst. 2014, 34, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłowski, A.; Schiavo, M.; Latronico, N.; Paltenghi, M.; Visioli, A. Event-based MPC for propofol administration in anesthesia. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 229, 107289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghita, M.; Ghita, M.; Copot, D. In Automated Drug Delivery in Anesthesia; An overview of computer-guided total intravenous anesthesia and monitoring devices—Drug infusion control strategies and analgesia assessment in clinical use and research. Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 7–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, A.; Guirimand, A.; Szekely, B.; Michel-Cherqui, M.; Dumans, V.; Liu, N.; Chazot, T.; Fischler, M.; Le Guen, M. Does a hypnosis session reduce the required propofol dose during closed-loop anaesthesia induction? Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2018, 35, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnider, T.W.; Minto, C.F.; Gambus, P.L.; Andresen, C.; Goodale, D.B.; Shafer, S.L.; Youngs, E.J. The influence of method of administration and covariates on the pharmacokinetics of propofol in adult volunteers. Anesthesiology 1998, 88, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihai, M.; Birs, I.; Erwin, H.; Copot, D.; Neckebroek, M.; De Keyser, R.; Ionescu, C.M.; Muresan, C.I. First-Hand Design of a Fractional order PID for Controlling the Depth of Hypnosis during Induction. IFAC-Pap. 2024, 58, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åström, K.J.; Hägglund, T. Revisiting the Ziegler–Nichols step response method for PID control. J. Process Control 2004, 14, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghita, M.; Neckebroek, M.; Muresan, C.; Copot, D. Closed-Loop Control of Anesthesia: Survey on actual trends, challenges and perspectives. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 206264–206279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padula, F.; Ionescu, C.; Latronico, N.; Paltenghi, M.; Visioli, A.; Vivacqua, G. Optimized PID control of depth of hypnosis in anesthesia. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 144, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merigo, L.; Padula, F.; Latronico, N.; Paltenghi, M.; Visioli, A. Optimized PID control of propofol and remifentanil coadministration for general anesthesia. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2018, 72, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, G.A.; Martinez, A.; Ansermino, J.M. Robust control of depth of anesthesia. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2008, 23, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.; Martin, F.; Pollard, B. Delayed recovery of consciousness after general anaesthesia. BJA Educ. 2020, 20, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, N.; Schiavo, M.; Latronico, N.; Padula, F.; Paltenghi, M.; Visioli, A. On the Use of FOPID Controllers for Maintenance Phase of General Anesthesia. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Keyser, R.; Muresan, C.I.; Ionescu, C.M. Autotuning of a robust fractional order PID controller. IFAC-Pap. 2018, 51, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copot, C.; Muresan, C.; Ionescu, C.-M.; Vanlanduit, S.; De Keyser, R. Calibration of UR10 Robot Controller through Simple Auto-Tuning Approach. Robotics 2018, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Keyser, R.; Ionescu, C.M.; Festila, C. A one-step procedure for frequency response estimation based on a Switch-Mode transfer function analyzer. In Proceedings of the 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–15 December 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
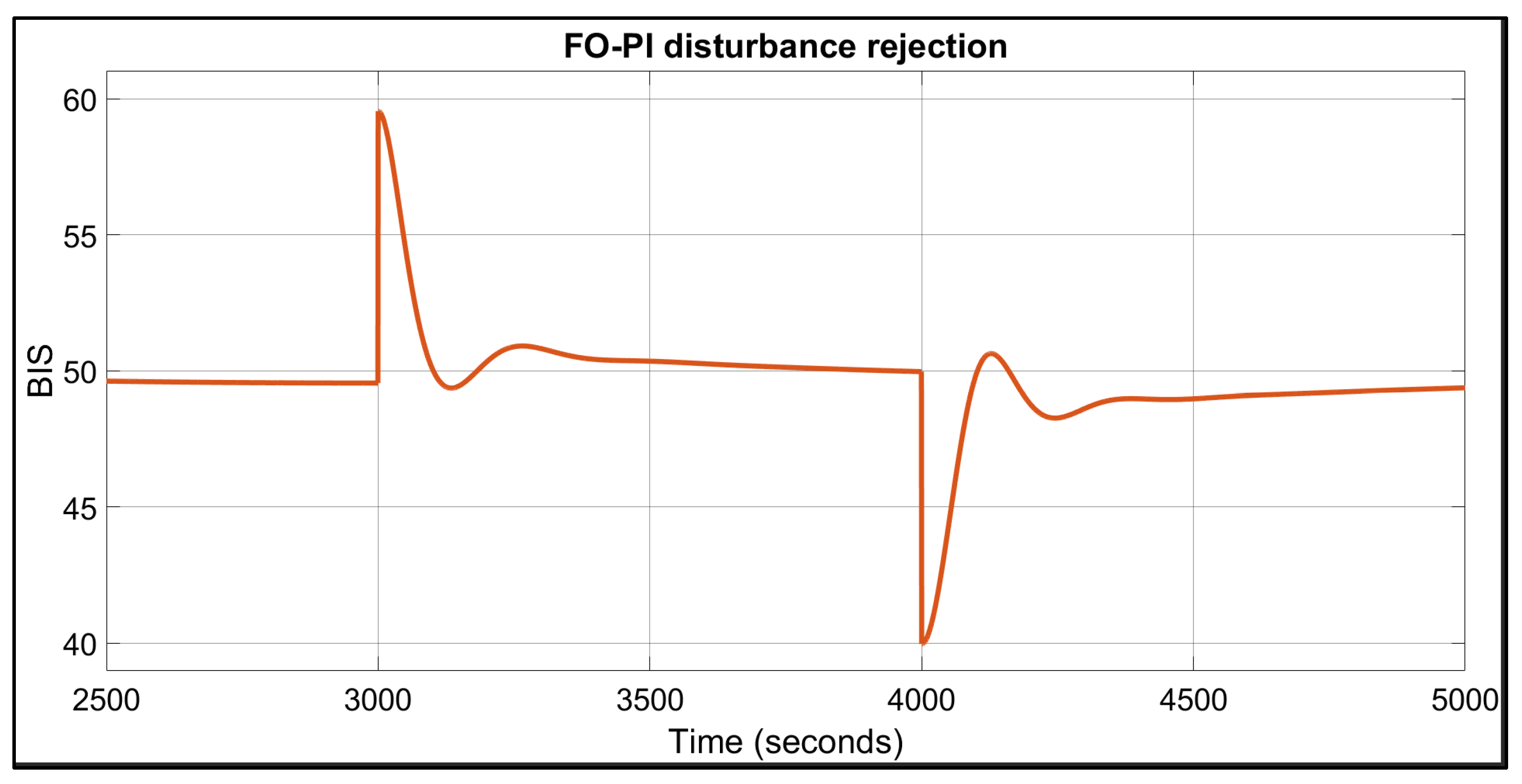

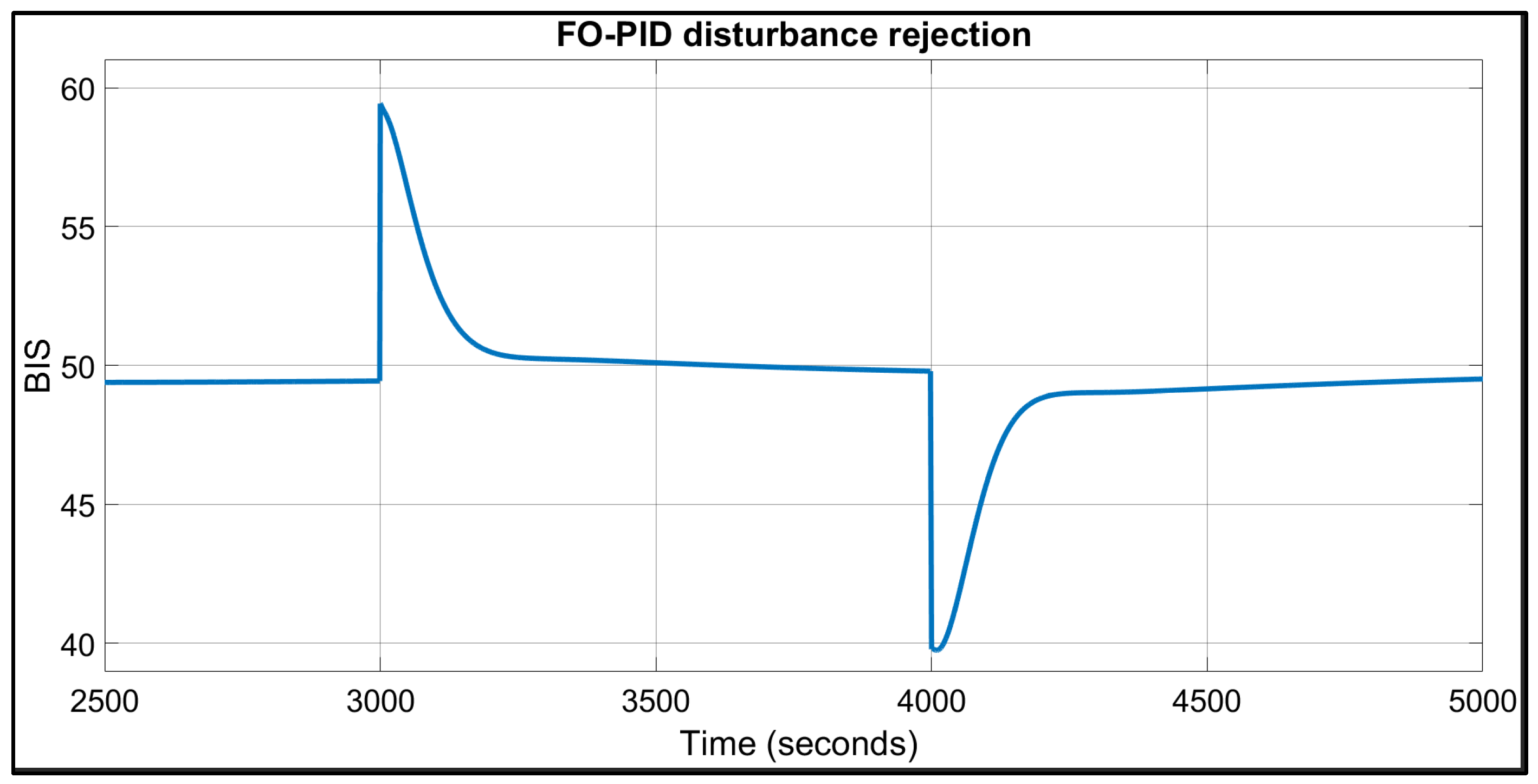


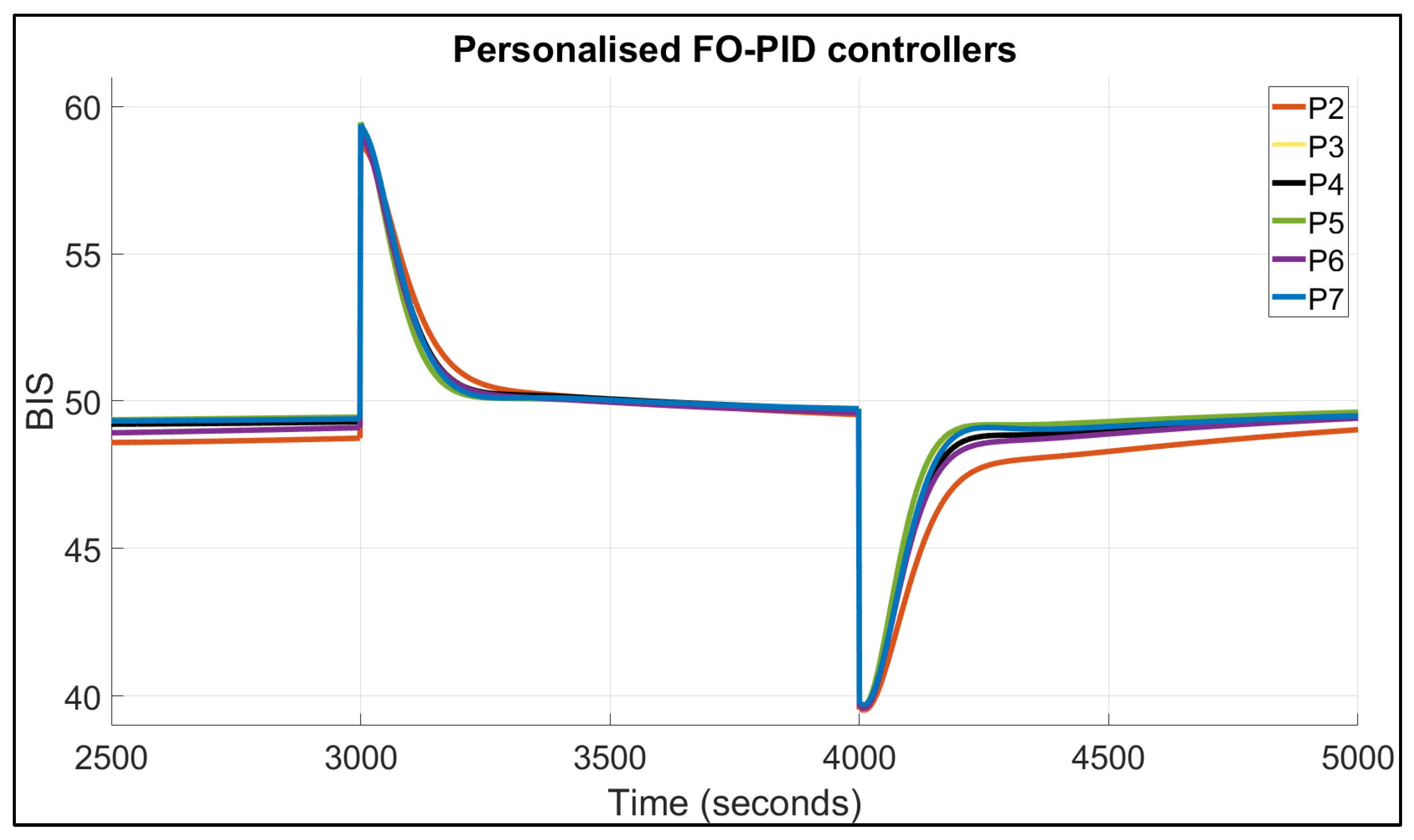
| Patient | TTs for FO-PI (Seconds) | TTs for FO-PID (Seconds) | IAE | BIS in Safe Range of 40–60? | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive Dist. | Negative Dist. | Positive Dist. | Negative Dist. | FO-PI | FO-PID | ||
| 1 | 67 | 74 | 109 | 134 | 2138 | 2508 | Yes |
| 2 | 94 | 124 | 132 | 207 | 3002 | 3507 | Yes |
| 3 | 62 | 74 | 102 | 127 | 1977 | 2251 | Yes |
| 4 | 76 | 86 | 115 | 147 | 2304 | 2658 | Yes |
| 5 | 63 | 75 | 102 | 126 | 1987 | 2205 | Yes |
| 6 | 73 | 88 | 113 | 156 | 2285 | 2775 | Yes |
| 7 | 76 | 85 | 114 | 140 | 2238 | 2473 | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihai, M.D.; Birs, I.R.; Badau, N.E.; Hegedus, E.T.; Ynineb, A.; Muresan, C.I. Personalised Fractional-Order Autotuner for the Maintenance Phase of Anaesthesia Using Sine-Tests. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9050317
Mihai MD, Birs IR, Badau NE, Hegedus ET, Ynineb A, Muresan CI. Personalised Fractional-Order Autotuner for the Maintenance Phase of Anaesthesia Using Sine-Tests. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(5):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9050317
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihai, Marcian D., Isabela R. Birs, Nicoleta E. Badau, Erwin T. Hegedus, Amani Ynineb, and Cristina I. Muresan. 2025. "Personalised Fractional-Order Autotuner for the Maintenance Phase of Anaesthesia Using Sine-Tests" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 5: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9050317
APA StyleMihai, M. D., Birs, I. R., Badau, N. E., Hegedus, E. T., Ynineb, A., & Muresan, C. I. (2025). Personalised Fractional-Order Autotuner for the Maintenance Phase of Anaesthesia Using Sine-Tests. Fractal and Fractional, 9(5), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9050317










