Pore Structure Characterization and Fractal Characteristics of Tight Limestone Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Adsorption and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Samples
2.1. Experimental Samples
2.2. LTNA Experiment
2.3. NMR Experiment
3. Fractal Dimension Calculation Method
4. Results and Discussion
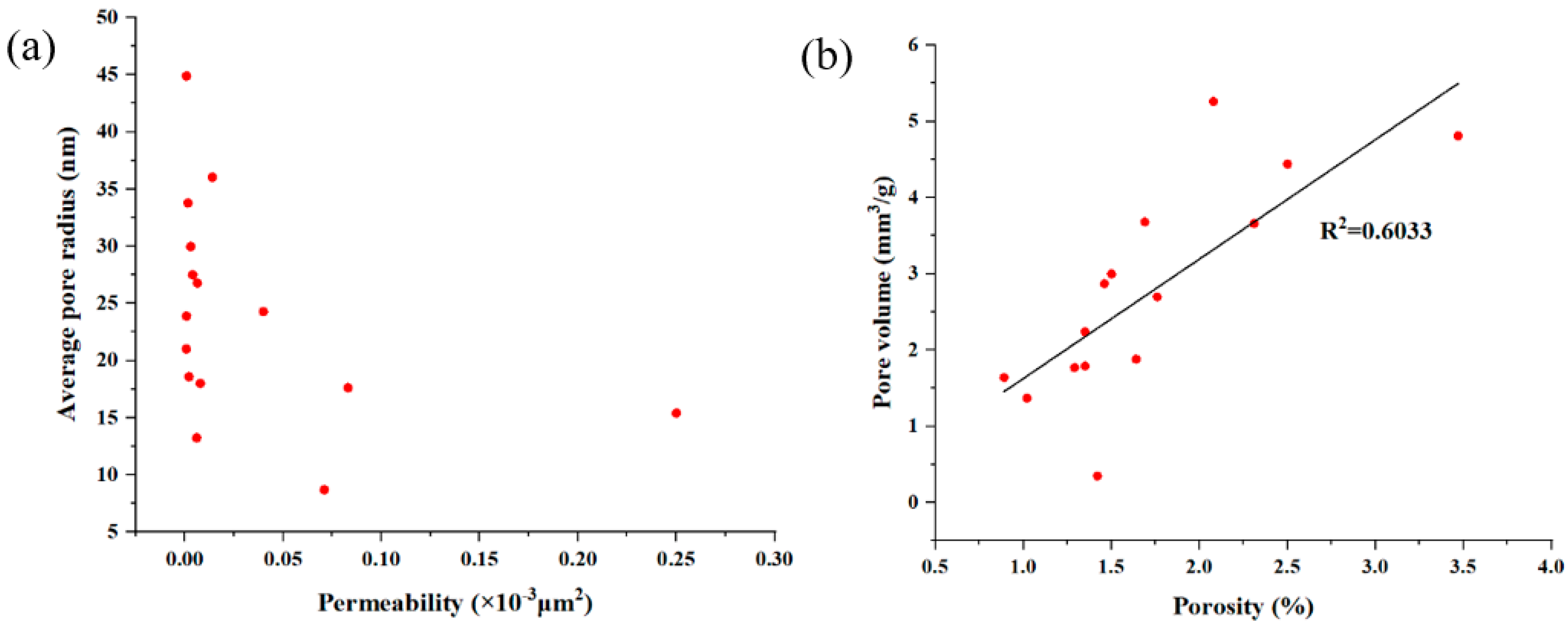
4.1. LTNA Characterization
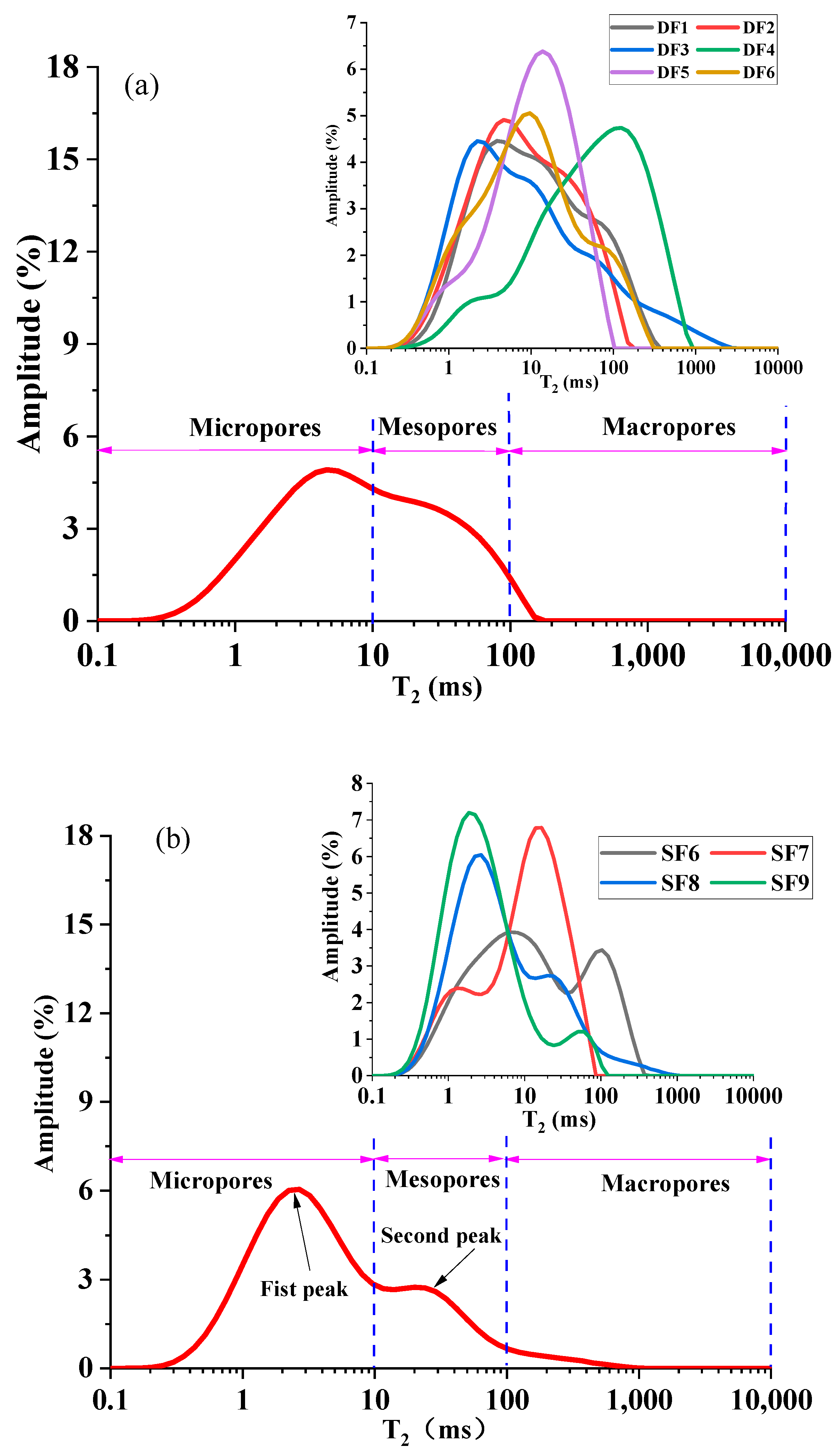
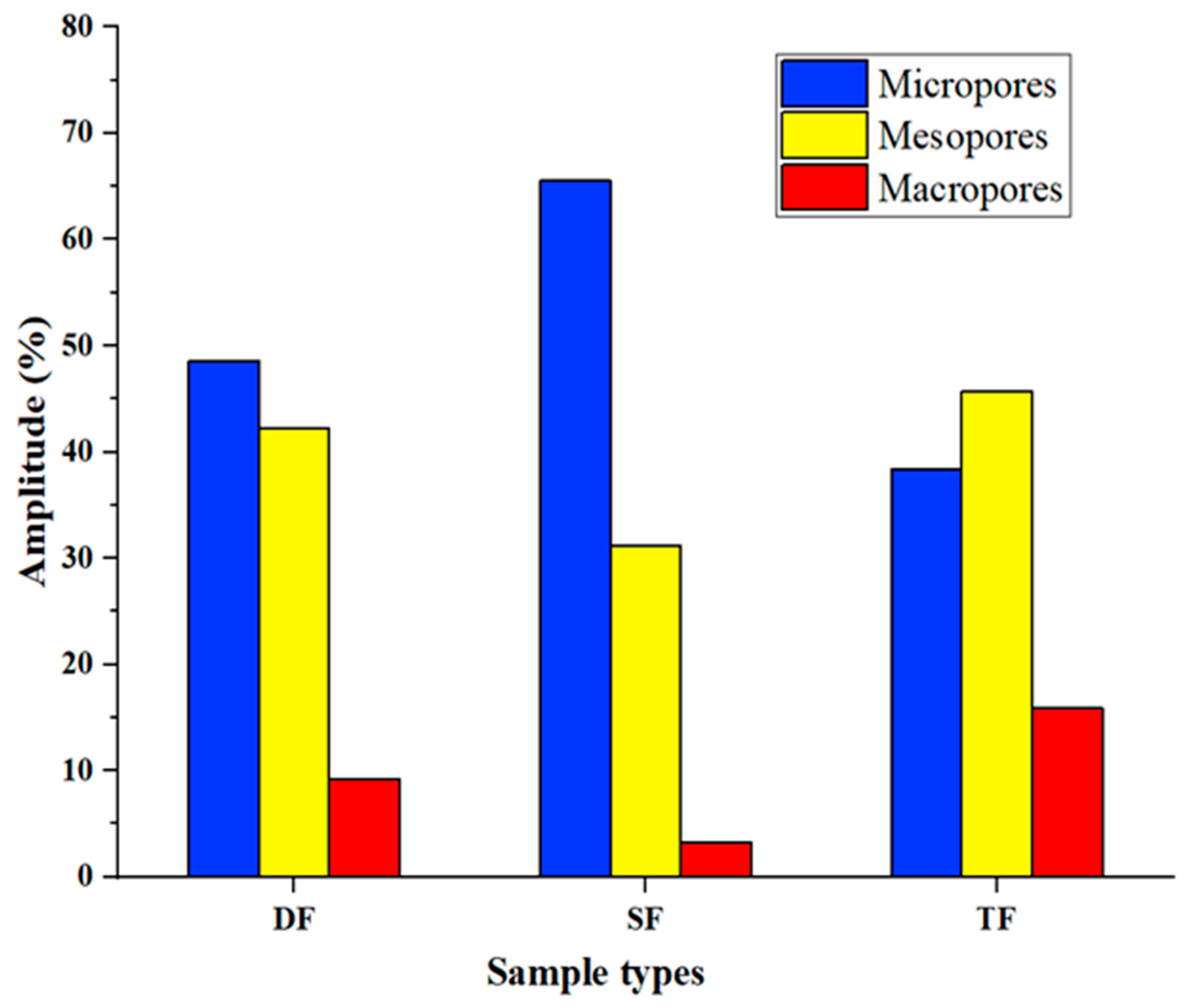
4.2. NMR Characterization
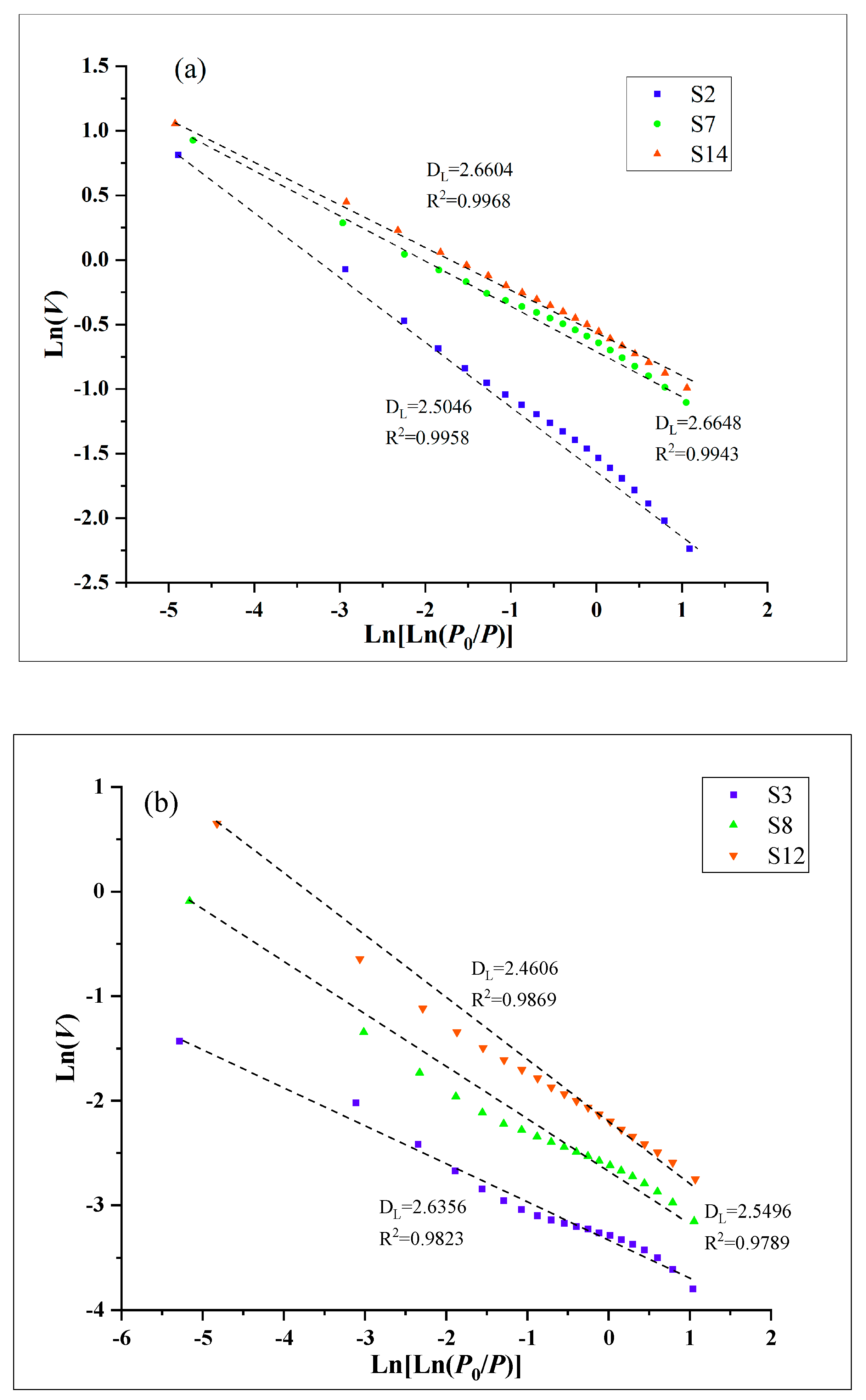
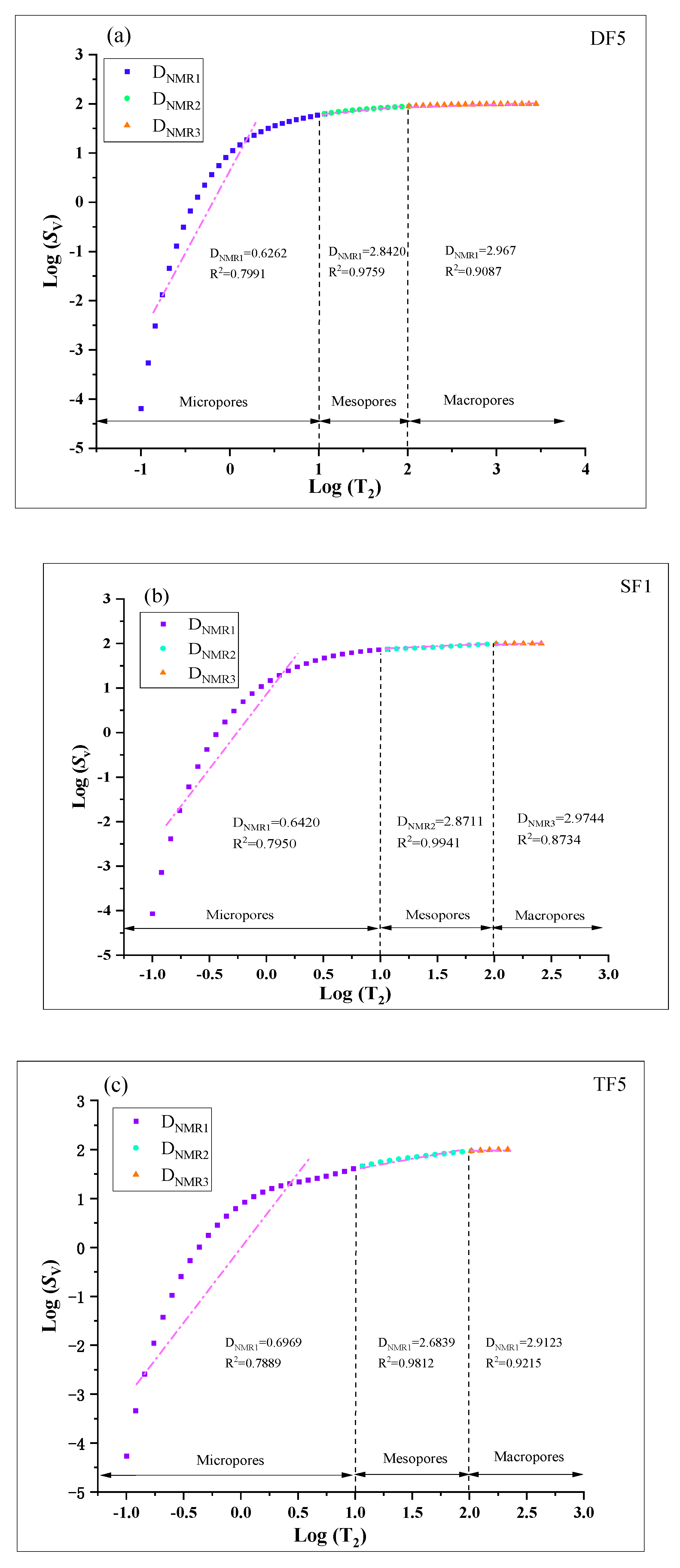
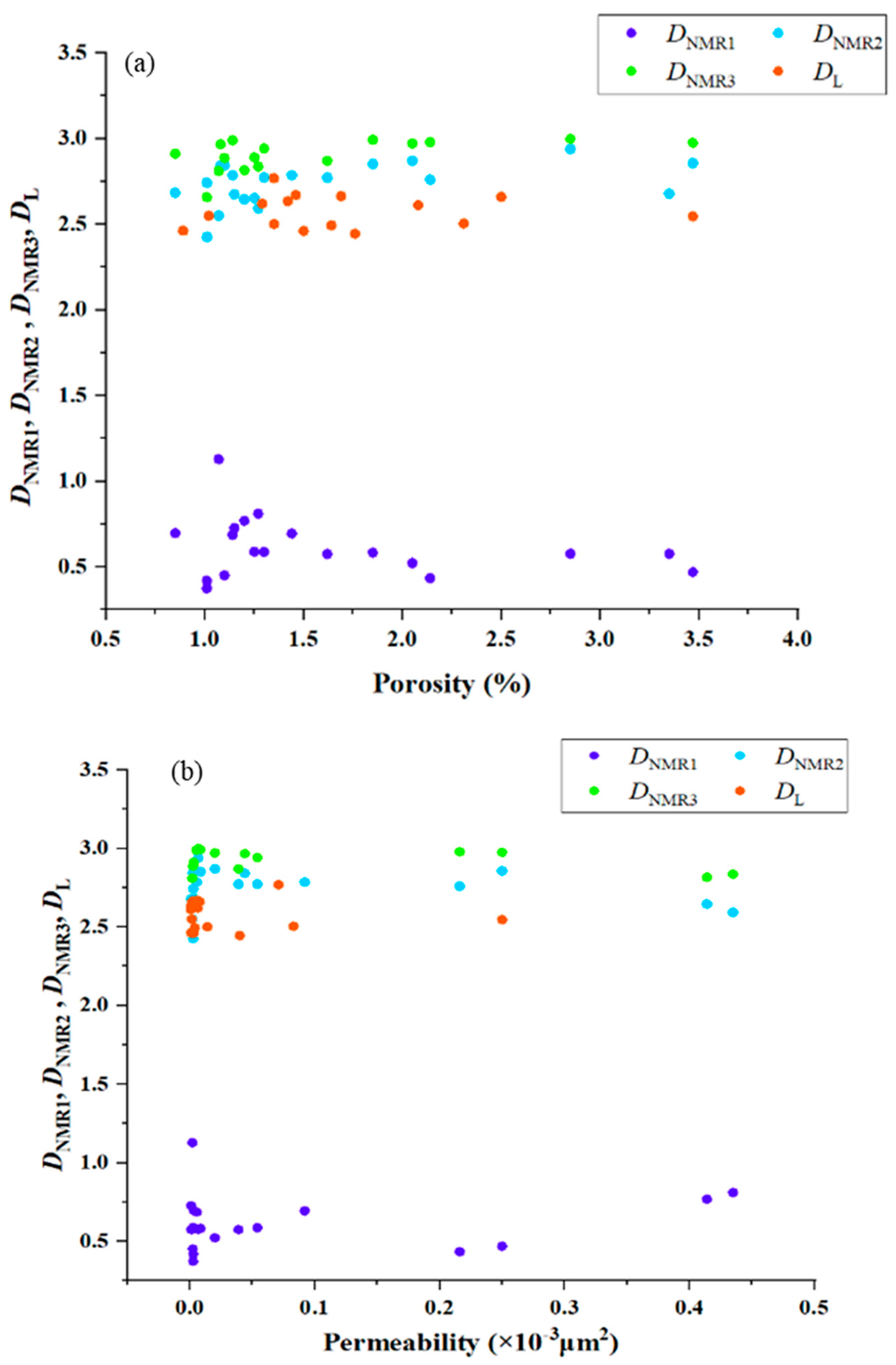
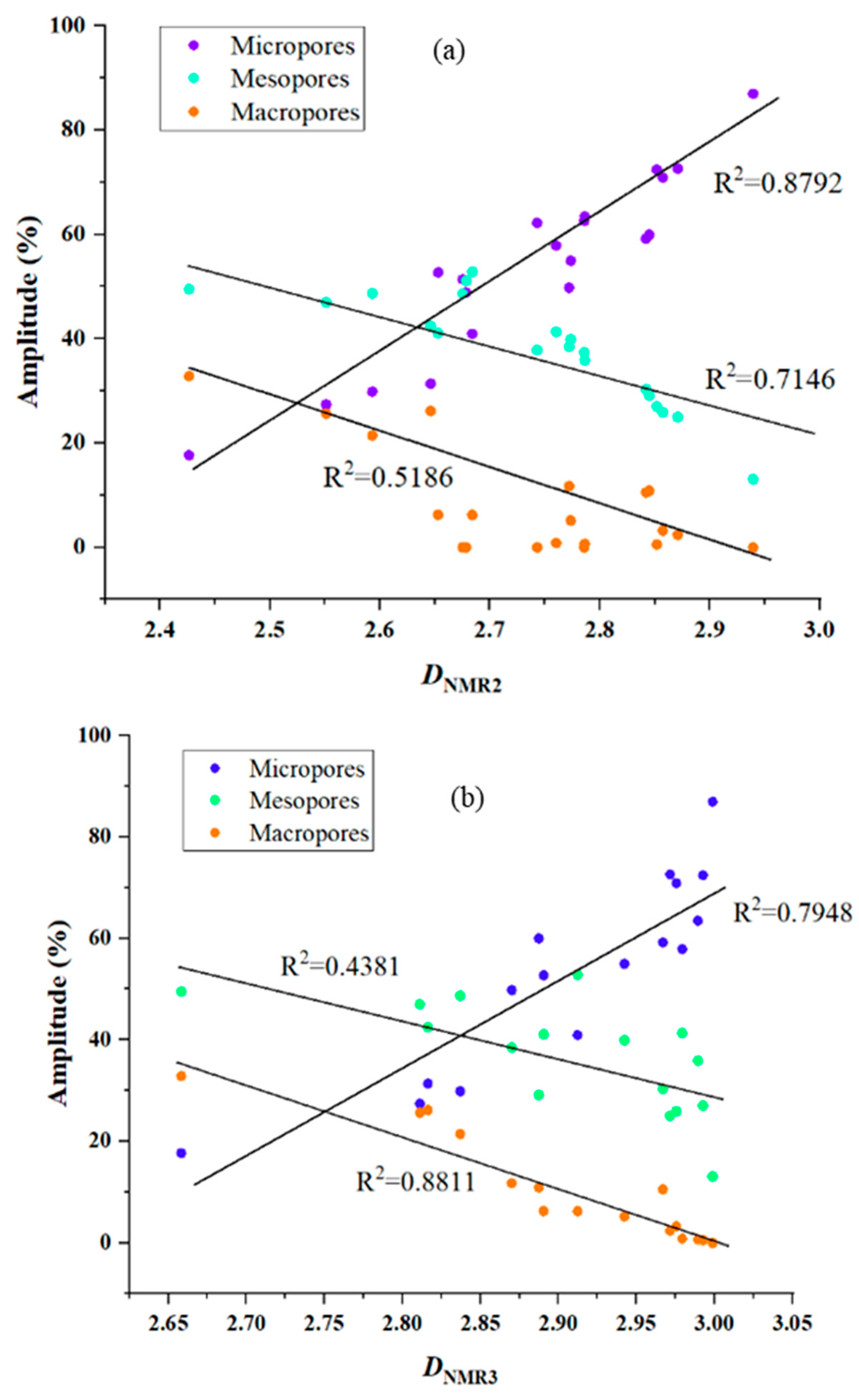
4.3. Fractal Characterization
5. Conclusions
- (1)
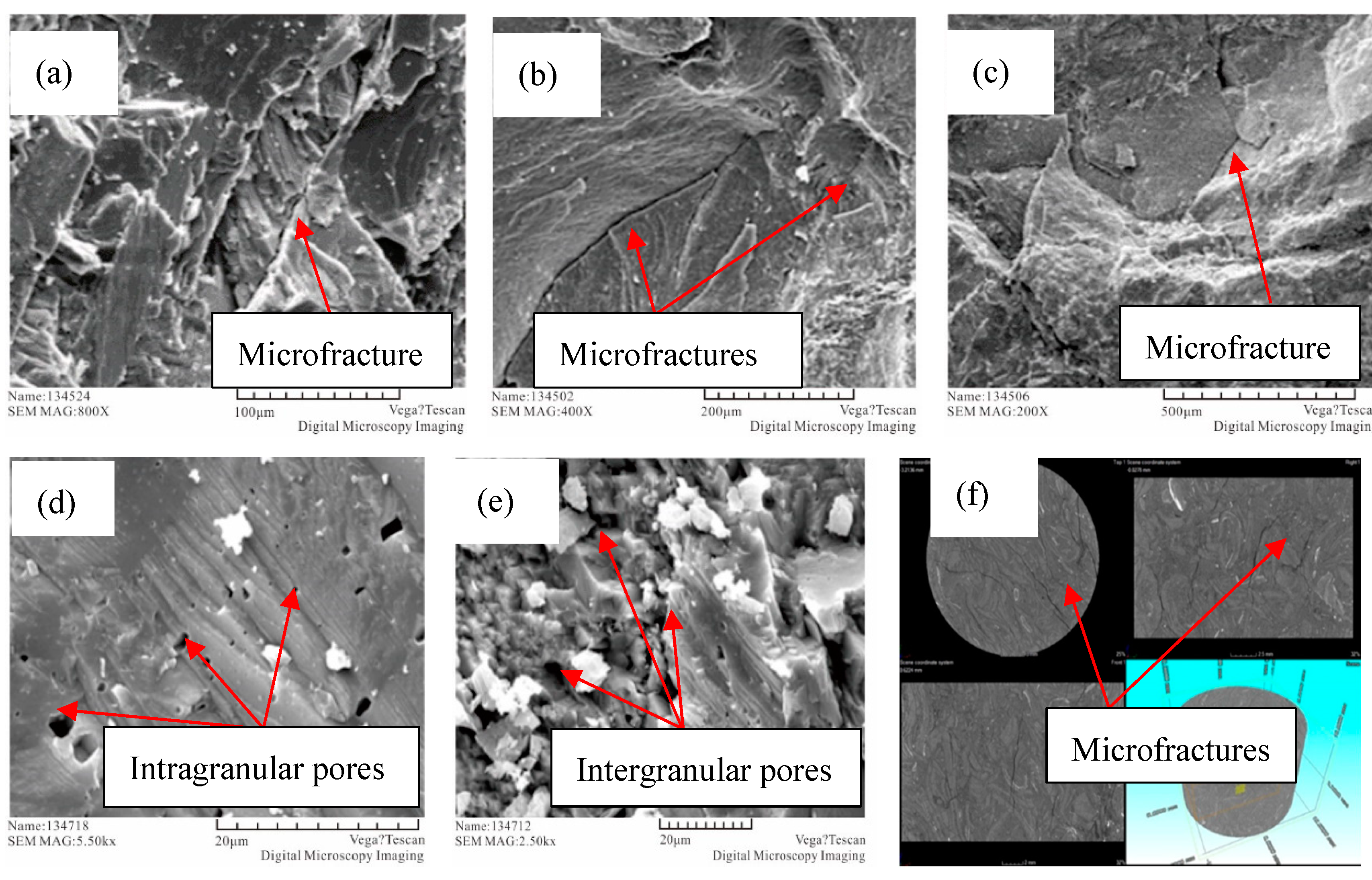
- The tight limestones have intergranular pores, intragranular pores, and microfractures. Their LTNA test data indicate that the pores of tight limestone have H3 and H4 types, and the pore radius of tight limestone is between 8.71 nm and 44.89 nm, with an average of 23.99 nm.
- (2)
- The NMR results of tight limestone show that there are three types of T2 distribution curves, namely, DF, SF, and TF, and the contents of micropores, mesopores, and macropores of the three types of cores are different. Among them, the SF-type tight limestone core has the highest micropore content, with an average of 65.52%. In addition, the average content of macropores in the TF-type tight limestone is 45.68%.
- (3)
- The fractal dimension of LTNA (DL) is between 2.4446 and 2.7688, with an average of 2.5729. There is a good positive correlation between DL and the specific surface area of tight limestone, and there is a good positive correlation between DNMR2, DNMR3, and the content of micropores of tight limestone, which shows that with the increase in micropore content, the surface roughness of the pores in tight limestone is more complex.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, J.D. Energy: A reality check on the shale revolution. Nature 2013, 494, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, S.; Wu, X. New advances in the assessment of tight oil resource in China. Pet. Res. 2017, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhu, R.; Wu, S.; Bai, B.; Yang, Z.; Cui, J. Exploration and development of continental tight oil in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Su, H.; Liang, X.; Meng, L.; Yuan, L.; Li, X.; Liang, T. Integrated hydraulic fracturing techniques to enhance oil recovery from tight rocks. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Guo, W.; Zhou, S.; Wan, Y. Experimental study and isotherm models of water vapor adsorption in shale rocks. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 52, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Song, F.; Hu, X.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, W. Experimental study on flow characteristics of gas transport in micro- and nanoscale pores. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Deng, M.; Ma, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, B.; Zhang, Y. Distribution and controlling factors of tight sandstone oil in Fuyu oil layers of Da’an area, Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y. Overpressure controlling factors for tectonic fractures in near-source tight reservoirs in the southwest Ordos Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 188, 106818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, S.; Chen, X. Assessment on tight oil resources in major basins in China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 178, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zou, C.; Hou, L.; Wu, S.; Lin, S.; Luo, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, J.; Pan, S. Division of fine-grained rocks and selection of “sweet sections” in the oldest continental shale in China: Taking the coexisting combination of tight and shale oil in the Permian Junggar Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 109, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Tao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.; Fan, J.; Yuan, M. Enrichment factors and sweep spot evaluation of Jurassic tight oil in central Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Res. 2019, 4, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, D. Reservoir and development characteristics of the Da’anzhai tight oil in Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Res. 2019, 4, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, Z.; He, F.; Liu, X.; Deng, W. Analysis of limestone reservoir forming geological conditions of Taiyuan formation in central and eastern Ordos basin. Pet. Geol. Eng. 2022, 36, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, C.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.; Lin, J.; Hou, G.; Wang, Y. Characteristics and Development Patterns of Tight Limestone Reservoirs: A Case Study of the Daanzhai Formation in the Central Sichuan Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2015, 27, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Ran, Q.; Liu, B.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y. Classification of lacustrine tight limestone considering matrix pores or fractures: A case study of Da’anzhai Member of Jurassic Ziliujing Formation in central Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ning, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, T.; Niu, T.; Zeng, Y. Petrophysical characterization of tight oil reservoirs using pressure-controlled porosimetry combined with rate-controlled porosimetry. Fuel 2015, 154, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; Ji, Y.; Liu, R.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. An Improved Method of Characterizing the Pore Structure in Tight oil Reservoirs: Integrated NMR and Constant-Rate-Controlled Porosimetry Data. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 166, 778–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Z.; Lin, W.; Xiong, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, T.; Xia, D.; Wu, Z. Study on pore structures of tight sandstone reservoirs based on nitrogen adsorption, high-pressure mercury intrusion and rate-controlled mercury intrusion. J. Energy Resour. Technol.-Trans. ASME 2019, 141, 112903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Z.; Lin, W.; Xiong, S.; Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Xia, D. Fractal study on pore structure of tight sandstone based on full-scale map. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Technol. 2019, 22, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volery, C.; Davaud, E.; Durlet, C.; Clavel, B.; Charollais, J.; Caline, B. Microporous and tight limestones in the Urgonian Formation (late Hauterivian to early Aptian) of the French Jura Mountains: Focus on the factors controlling the formation of microporous facies. Sediment. Geol. 2010, 230, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. The pore structure of tight limestone—Jurassic Ziliujing Formation, Central Sichuan Basin, China. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 15, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Z.; Lin, W.; Xiong, S.; Wei, Y. Characteristics of microscopic pore-throat structure of tight oil reservoirs in Sichuan Basin measured by rate-controlled mercury injection. Open Phys. 2018, 16, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y. Study on Tight Sandstone Reservoir Characteristics and Development in Sichuan; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The Determination of Pore Volume and Area Distributions in Porous Substances. I. Computations from Nitrogen Isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haul, R. Adsorption, surface area and porosity. Z. Phys. Chem. 1969, 63, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, P.; Asif, M.; Ojha, K. Integrated fractal description of nanopore structure and its effect on CH4 adsorption on Jharia coals, India. Fuel 2018, 232, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Weller, A. Fractal dimension of pore-space geometry of an Eocene sandstone formation. Geophysics 2014, 79, D377–D387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, K.; Cai, J. Fractal characterization of tight oil reservoir pore structure using nuclear magnetic resonance and mercury intrusion porosimetry. Fractals 2018, 26, 1840017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, S. Fractal analysis of tight shaly sandstones using nuclear magnetic resonance measurements. AAPG Bull. 2018, 102, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yao, Y.; Liu, D.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y. Characterizations of full-scale pore size distribution, porosity and permeability of coals: A novel methodology by nuclear magnetic resonance and fractal analysis theory. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 196, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, H.; Deng, J.; Gao, R. Fractal Analysis of Pore Structure Development of Sandstone: A Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Investigation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47282–47293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, G.; Cao, Z.; Yuan, W.; Wang, P.; You, Y. Analysis of Petrophysical Characteristics and Water Movability of Tight Sandstone Using Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Nat. Resour. Res. 2019, 29, 2547–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tang, D.; Tao, S.; Ji, X.; Xu, H. Fractal analysis of the dynamic variation in pore-fracture systems under the action of stress using a low-field NMR relaxation method: An experimental study of coals from western Guizhou in China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 173, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Liu, K.; Tan, J.; Gao, F. Mechanism of shale gas occurrence: Insights from comparative study on pore structures of marine and lacustrine shales. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 104, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B.; Wheeler, J.A. The fractal geometry of nature. Am. J. Phys. 1998, 51, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.P.; Misra, S.; Tinni, A.; Sondergeld, C.; Rai, C. Pore connectivity and pore size distribution estimates for Wolfcamp and Eagle Ford shale samples from oil, gas and condensate windows using adsorption-desorption measurements. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 158, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.; Fu, J.; Shi, Y.; Mao, Z.; Xiao, D. Nuclear magnetic resonance surface relaxivity and its advanced application in calculating pore size distributions. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 111, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, X.; Cai, J.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Rabiei, M.; Li, C. Multifractal analysis of pore structure of Middle Bakken formation using low temperature N2 adsorption and NMR measurements. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 176, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Luo, Y.; Qi, D.; Lin, W.; Zhao, X. Waterflooding Huff-n-puff in Tight Oil Cores Using Online Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Energies 2018, 11, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zuo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, H.; Xi, S.; Shui, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Lin, J. Fractal analysis of pores and the pore structure of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang shale in northern Guizhou province: Investigations using NMR, SEM and image analyses. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 99, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, K.; Gao, Y.; Qin, Z. Fractal characteristics of the pore structures of fine-grained, mixed sedimentary rocks from the Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin: Implications for lacustrine tight oil accumulations. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 182, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Depth | Lithology | φ | K | Ap | Vc | ra | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2514.37~2516.06 | Limestone | 1.46 | 0.00600 | 1.15 | 2.87 | 13.25 | 2.6698 |
| S2 | 2517.56~2519.43 | Limestone | 2.31 | 0.08300 | 0.64 | 3.66 | 17.63 | 2.5046 |
| S3 | 2577.88~2579.35 | Limestone | 1.42 | 0.00084 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 23.90 | 2.6356 |
| S4 | 2579.35~2580.68 | Limestone | 1.35 | 0.01400 | 0.20 | 1.79 | 36.04 | 2.5007 |
| S5 | 2825.99~2827.59 | Limestone | 1.76 | 0.04000 | 0.31 | 2.70 | 24.29 | 2.4446 |
| S6 | 2841.91~2843.56 | Limestone | 1.64 | 0.00400 | 0.25 | 1.88 | 27.51 | 2.4933 |
| S7 | 2666.12~2667.36 | Limestone | 1.69 | 0.00210 | 1.52 | 3.68 | 18.59 | 2.6648 |
| S8 | 2672.69~2674.56 | Limestone | 1.02 | 0.00160 | 0.21 | 1.37 | 33.79 | 2.5496 |
| S9 | 2679.78~2682.04 | Limestone | 1.29 | 0.00640 | 0.39 | 1.77 | 26.78 | 2.6208 |
| S10 | 2857.60~2858.60 | Limestone | 1.35 | 0.07100 | 2.06 | 2.24 | 8.71 | 2.7688 |
| S11 | 2874.00~2875.10 | Limestone | 0.89 | 0.00084 | 0.12 | 1.64 | 44.89 | 2.4628 |
| S12 | 2878.25~2879.43 | Limestone | 1.50 | 0.00300 | 0.32 | 3.00 | 29.98 | 2.4606 |
| S13 | 2151.53~2153.70 | Limestone | 3.47 | 0.25000 | 0.92 | 4.81 | 15.41 | 2.5464 |
| S14 | 1723.09~1725.29 | Limestone | 2.50 | 0.00790 | 1.65 | 4.44 | 18.01 | 2.6604 |
| S15 | 1725.29~1727.32 | Limestone | 2.08 | 0.00079 | 1.51 | 5.26 | 21.01 | 2.6114 |
| Sample | Lithology | φ/% | K/×10−3 μm2 | DNMR1 | DNMR2 | DNMR3 | Ω1/% | Ω2/% | Ω3/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF1 | Limestone | 1.25 | 0.00260 | 0.5897 | 2.6529 | 2.8905 | 52.71 | 41.05 | 6.24 |
| DF2 | Limestone | 2.14 | 0.21600 | 0.4347 | 2.7603 | 2.9794 | 57.87 | 41.30 | 0.83 |
| DF3 | Limestone | 1.08 | 0.04400 | 0.6262 | 2.8420 | 2.9670 | 59.18 | 30.31 | 10.51 |
| DF4 | Limestone | 1.01 | 0.00260 | 0.3744 | 2.4263 | 2.6582 | 17.66 | 49.50 | 32.84 |
| DF5 | Limestone | 3.35 | 0.00110 | 0.5769 | 2.6783 | / | 48.89 | 51.11 | 0.00 |
| DF6 | Limestone | 1.30 | 0.05400 | 0.5875 | 2.7735 | 2.9423 | 54.96 | 39.89 | 5.15 |
| SF1 | Limestone | 2.05 | 0.02000 | 0.5233 | 2.8709 | 2.9716 | 72.61 | 25.01 | 2.38 |
| SF2 | Limestone | 1.85 | 0.00850 | 0.5829 | 2.8517 | 2.9927 | 72.42 | 27.03 | 0.55 |
| SF3 | Limestone | 1.14 | 0.00540 | 0.6876 | 2.7863 | 2.9895 | 63.46 | 35.86 | 0.68 |
| SF4 | Limestone | 1.10 | 0.00240 | 0.4519 | 2.8449 | 2.8874 | 59.97 | 29.14 | 10.89 |
| SF5 | Limestone | 1.01 | 0.00260 | 0.4199 | 2.7429 | / | 62.19 | 37.81 | 0.00 |
| SF6 | Limestone | 1.62 | 0.03900 | 0.5754 | 2.7721 | 2.8701 | 49.79 | 38.47 | 11.74 |
| SF7 | Limestone | 1.15 | 0.00098 | 0.7286 | 2.6752 | / | 51.36 | 48.64 | 0.00 |
| SF8 | Limestone | 3.47 | 0.25000 | 0.4694 | 2.8573 | 2.9756 | 70.90 | 25.87 | 3.23 |
| SF9 | Limestone | 2.85 | 0.00670 | 0.5774 | 2.9395 | 2.9989 | 86.94 | 13.06 | 0.00 |
| TF1 | Limestone | 1.27 | 0.43500 | 0.8115 | 2.5930 | 2.8371 | 29.86 | 48.70 | 21.44 |
| TF2 | Limestone | 1.07 | 0.00200 | 1.1293 | 2.5509 | 2.8111 | 27.38 | 46.99 | 25.63 |
| TF3 | Limestone | 1.20 | 0.41400 | 0.7702 | 2.6460 | 2.8163 | 31.37 | 42.47 | 26.16 |
| TF4 | Limestone | 1.44 | 0.09200 | 0.6950 | 2.7859 | / | 62.61 | 37.39 | 0.00 |
| TF5 | Limestone | 0.85 | 0.00300 | 0.6969 | 2.6839 | 2.9123 | 40.94 | 52.83 | 6.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Zhuang, Y. Pore Structure Characterization and Fractal Characteristics of Tight Limestone Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Adsorption and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8070371
Lin W, Zhao X, Li M, Zhuang Y. Pore Structure Characterization and Fractal Characteristics of Tight Limestone Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Adsorption and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Fractal and Fractional. 2024; 8(7):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8070371
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Wei, Xinli Zhao, Mingtao Li, and Yan Zhuang. 2024. "Pore Structure Characterization and Fractal Characteristics of Tight Limestone Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Adsorption and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance" Fractal and Fractional 8, no. 7: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8070371
APA StyleLin, W., Zhao, X., Li, M., & Zhuang, Y. (2024). Pore Structure Characterization and Fractal Characteristics of Tight Limestone Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Adsorption and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Fractal and Fractional, 8(7), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8070371








