Rational Approximations for the Oscillatory Two-Parameter Mittag–Leffler Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
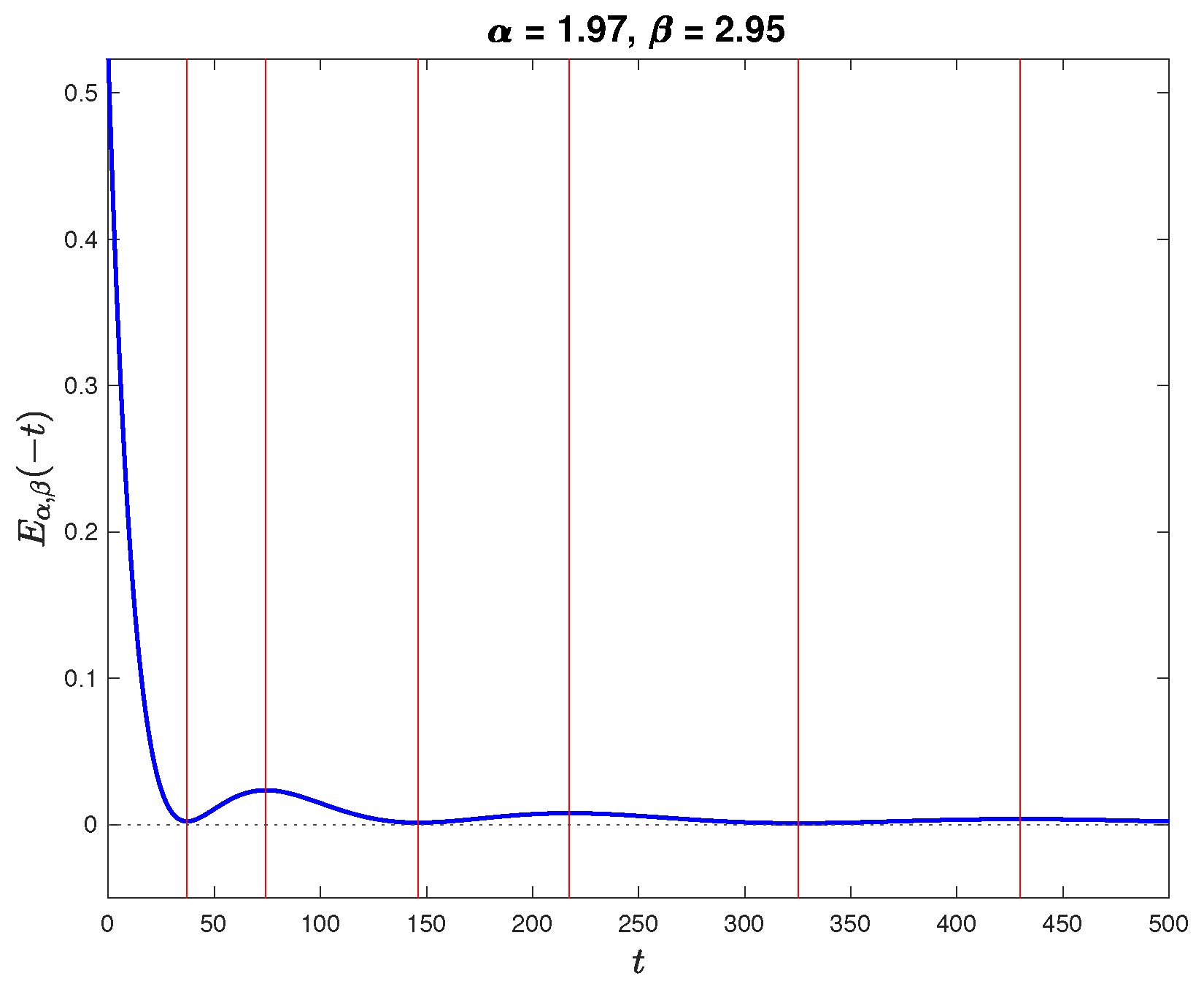
2. Monotonicity and Oscillatory Properties
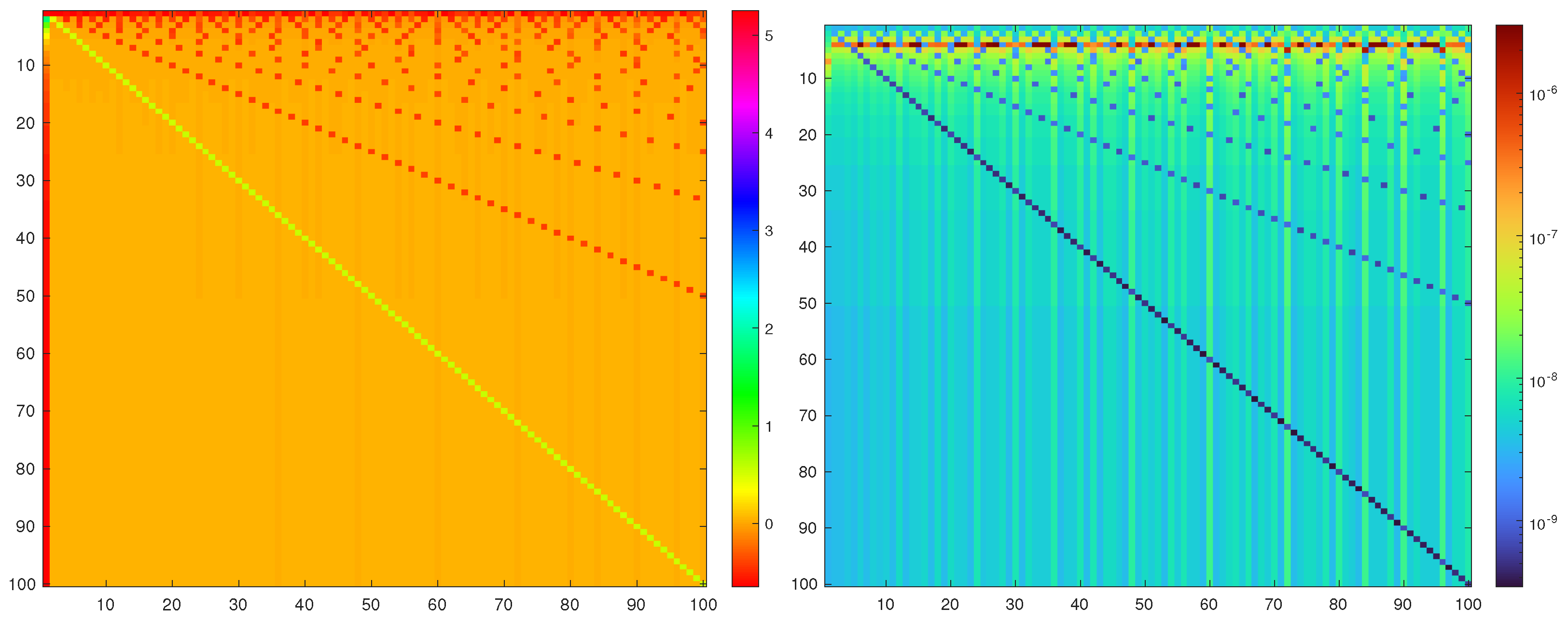
3. Derooting Decomposition
4. Rational Approximation
4.1. Global Padé Approximation
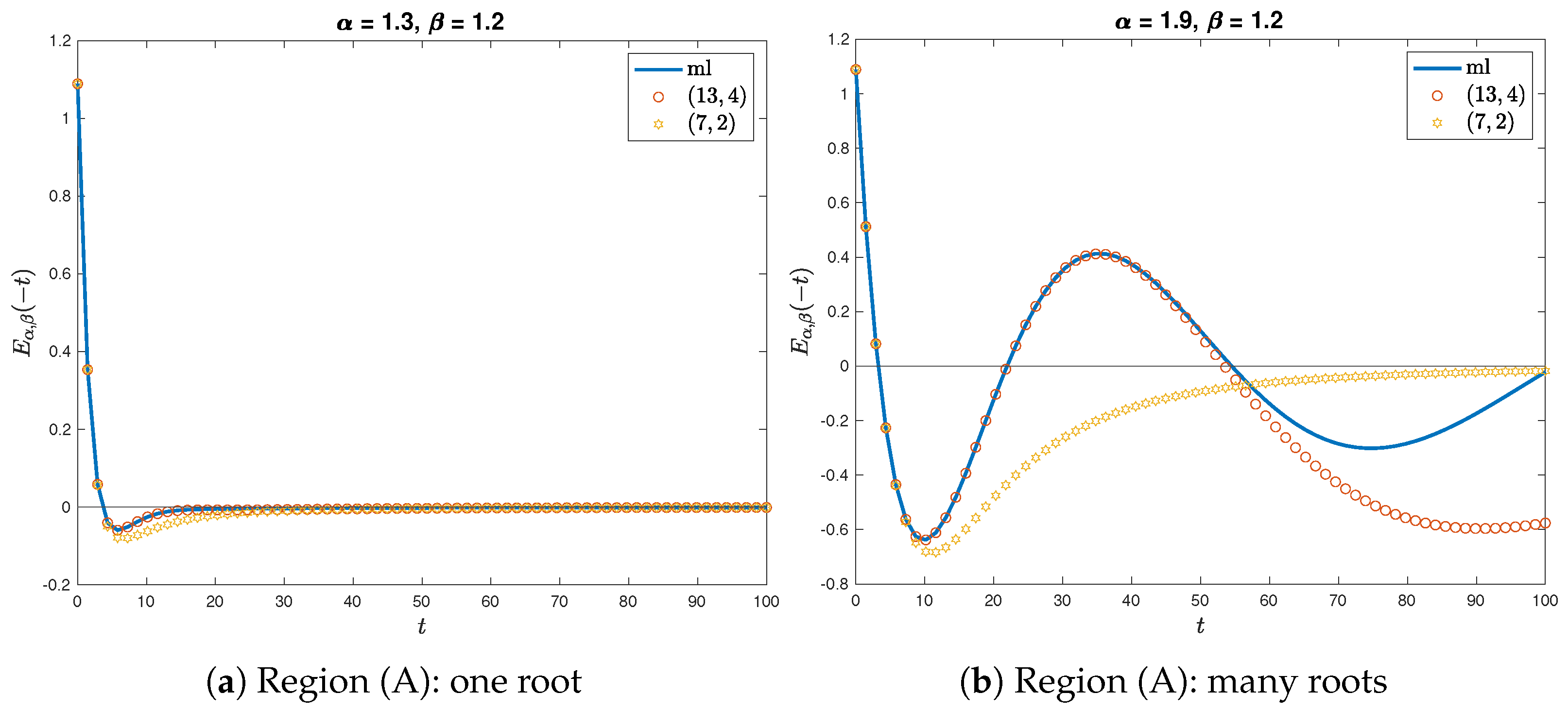
- When is in region (A), the existing global Padé approximants are not effective over extended intervals due to the existence of roots.
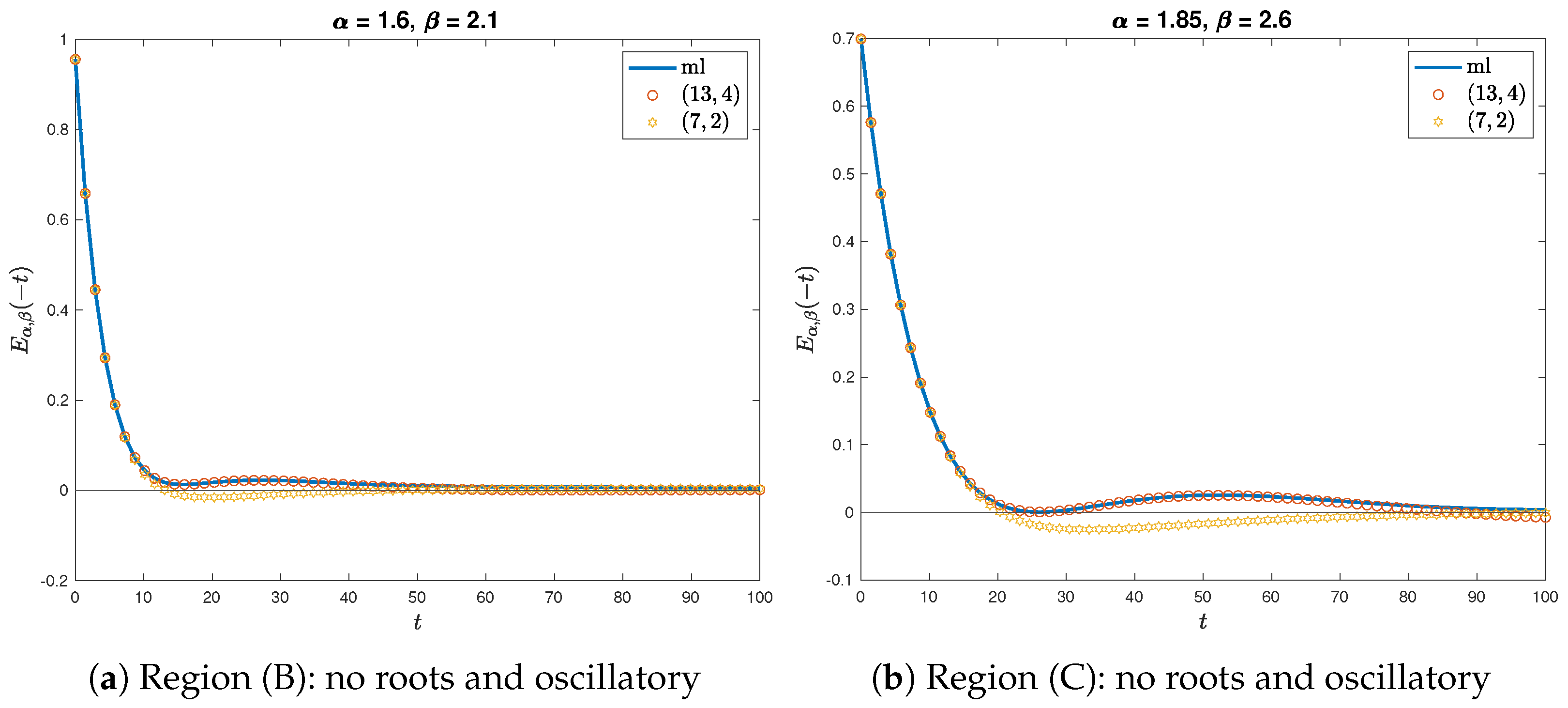
- When is in region (B) or (C), more accurate approximants should be used due to the oscillatory behavior of the MLF.
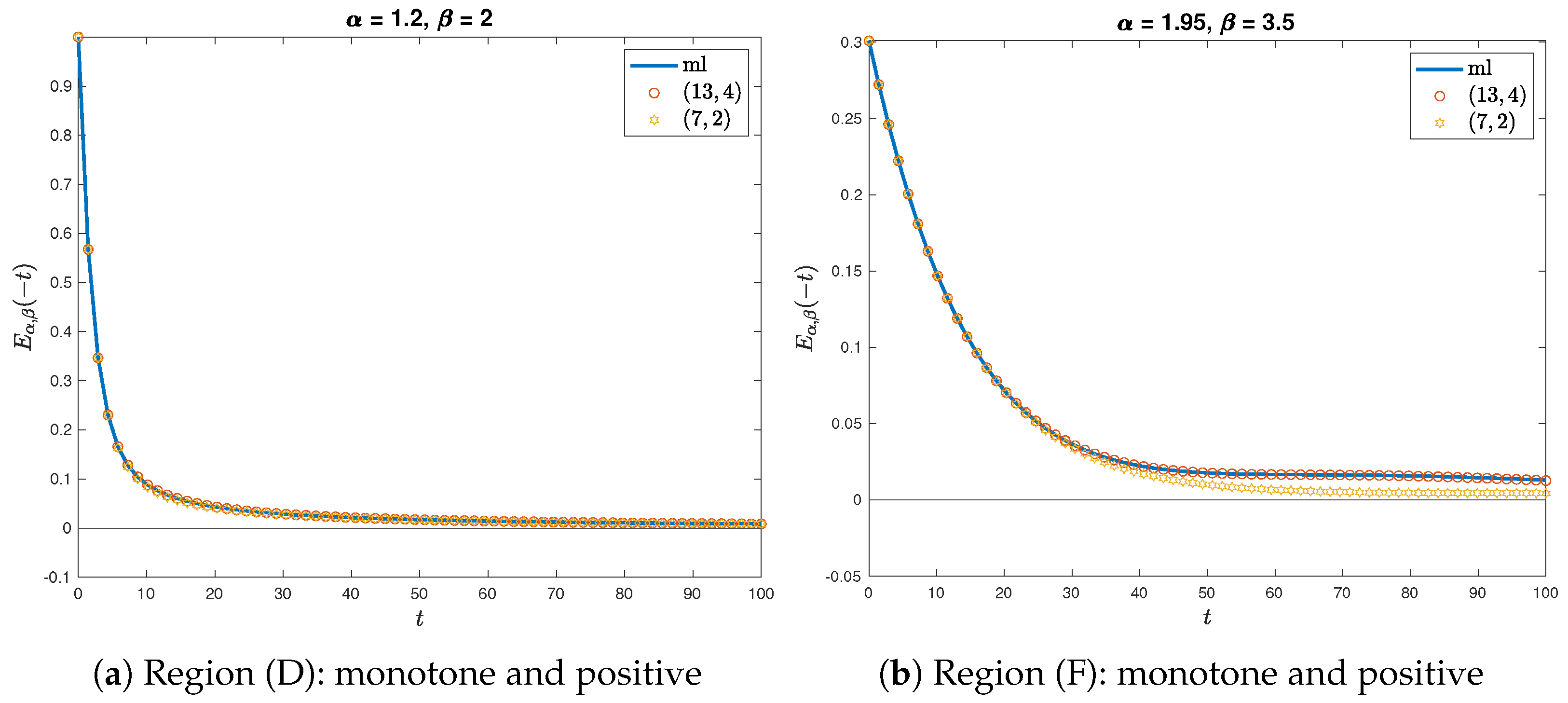
- When is in region (D) or (F), the approximant is sufficiently accurate since the MLF is globally monotone.
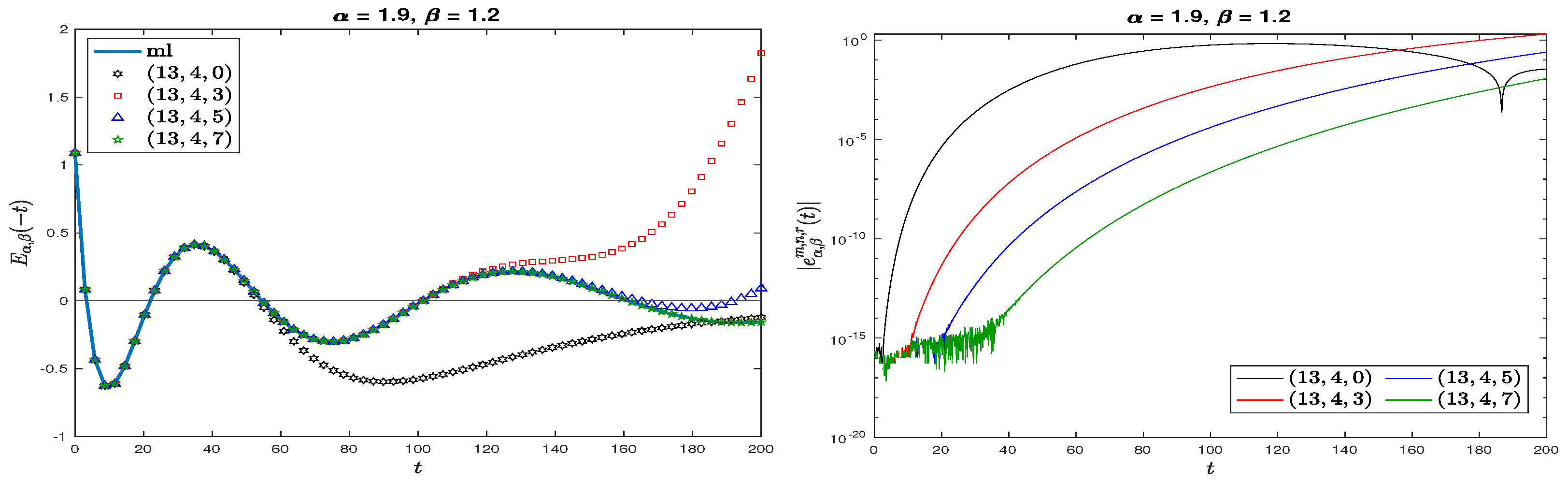
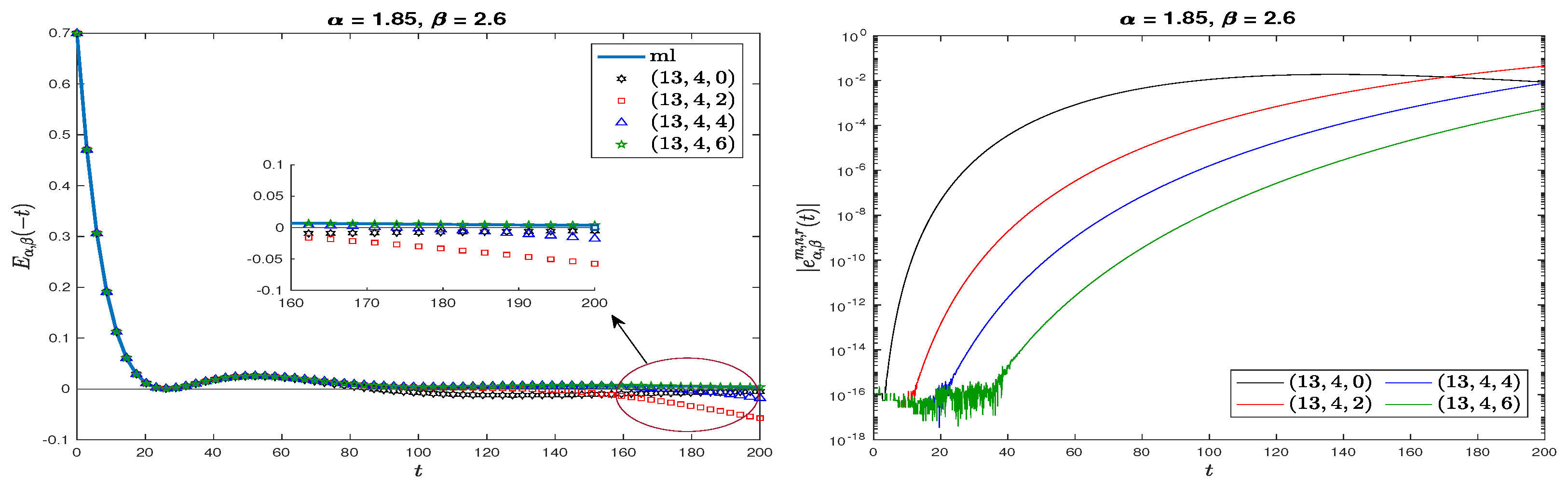
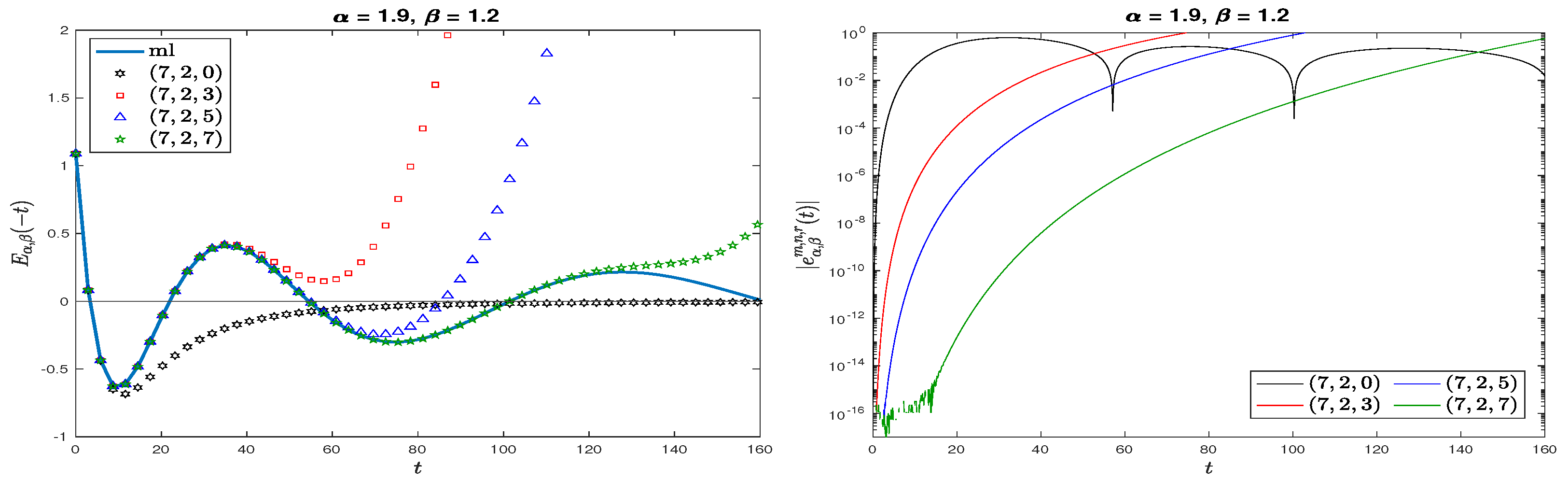
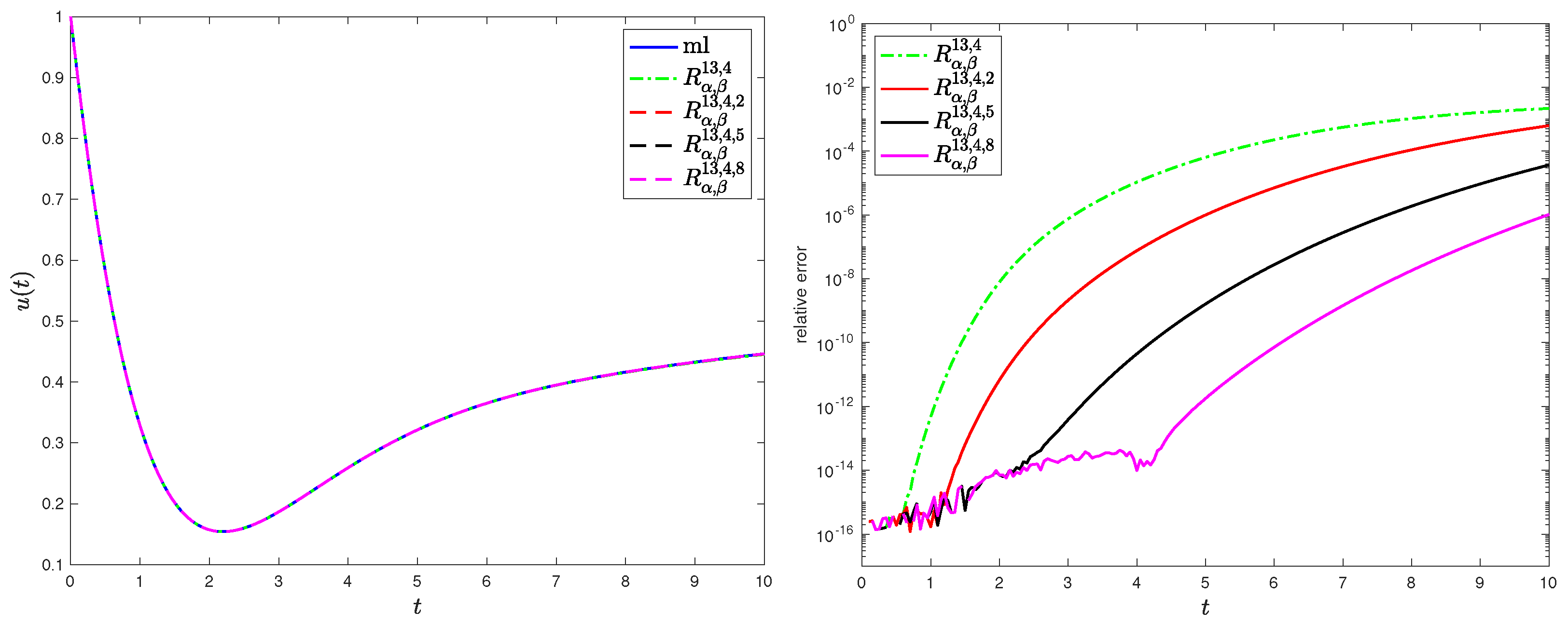
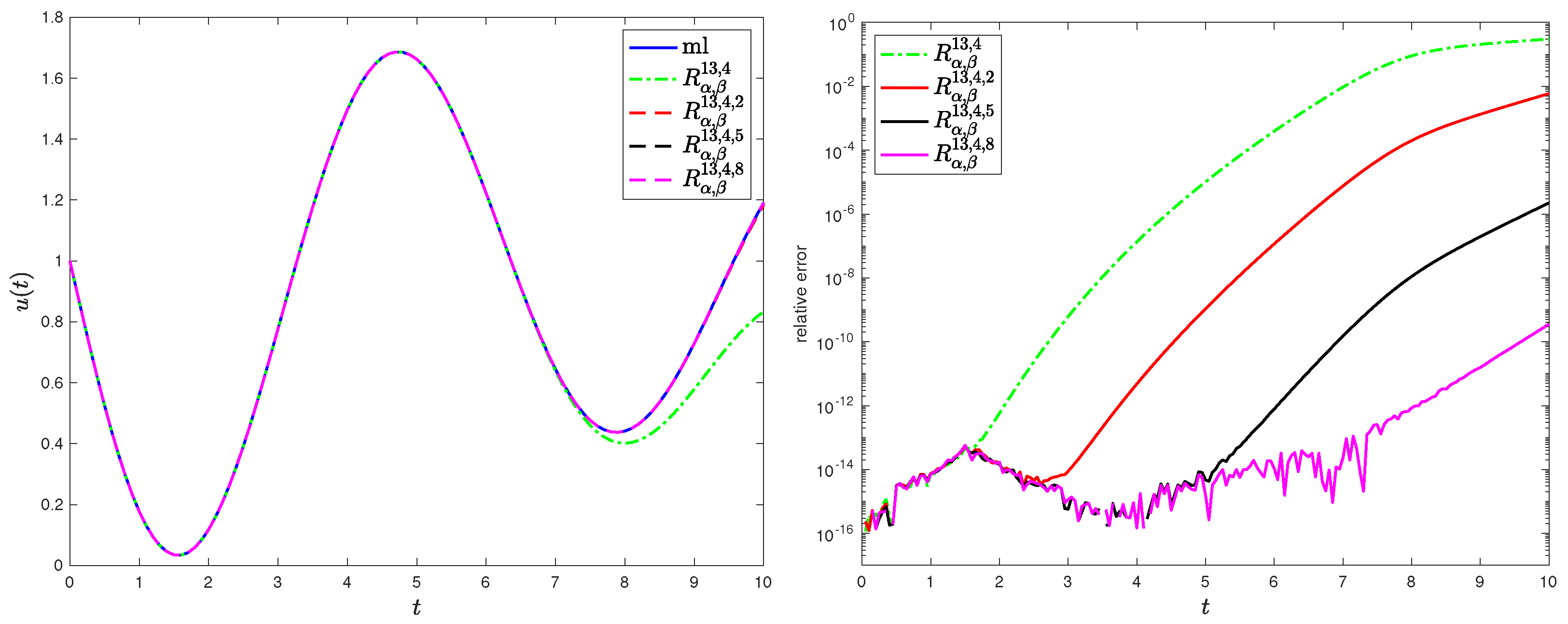
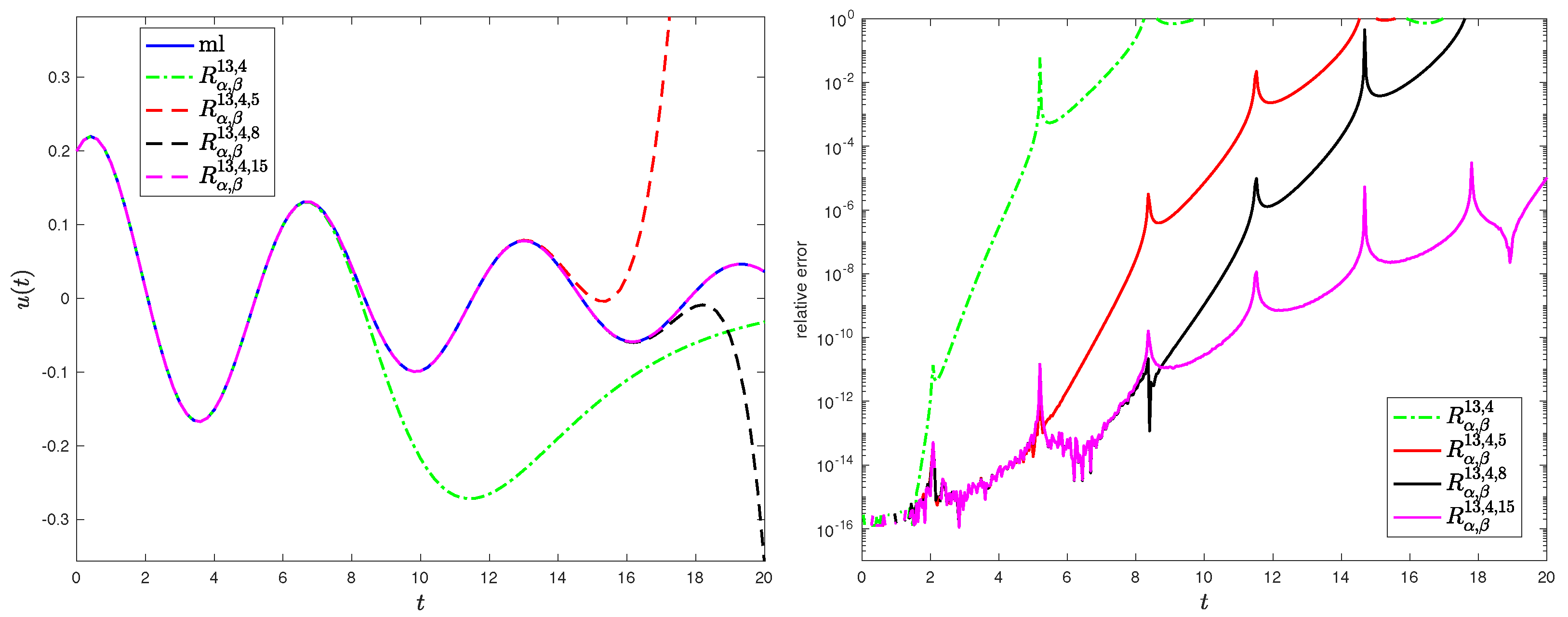
4.2. Rational Approximation for Oscillatory MLFs
4.3. Asymptotic Behavior of the Approximation Error
5. Approximation of the Matrix Mittag–Leffler Function
- 1.
- Linear system approachA straightforward approach is to evaluate and using efficient methods for the evaluation of matrix polynomials, such as the Paterson–Stockmeyer method and Horner’s method (nested multiplication) [28]. Additionally, the powers , can be precomputed and used in the computation of both and to minimize the overall cost. It is noteworthy that research in the field of matrix polynomial evaluation is increasingly active. In particular, a new family of methods for evaluating matrix polynomials, which are more efficient than the established Paterson–Stockmeyer method, was proposed in [29]. This area could be a subject of future research for us, as this section concentrates on introducing general techniques for approximating the MLF matrix using rational approximation, aiming for a general comparison.Using this approach, the approximant is obtained by solving the matrix systemThis requires solving N systems for an matrix.
- 2.
- Partial fraction approachPartial fraction decomposition is known to provide an efficient form for evaluating rational functions. For the global Padé approximants, it was discussed in [10,11] that these approximants have complex conjugate roots, which can contribute to efficient implementation. As an example, the approximant , admits the partial fraction decompositionwhere and are the non-conjugate residues and poles, respectively. This expression can be simplified asSo, for a matrix argument A, the approximant can be calculated aswhere I is the identity matrix.For example, in the implementation using the partial fraction approach, the partial fraction decompositions (22) are used to compute the matrix-vector products as outlined below.For a given square matrix A and a vector v, the matrix-vector product is computed using (20) aswhere the termis computed using the partial fraction decomposition approach. From (23), we use the approximationBy solving the systemswe obtainwhere , are the solutions of the linear systems (24). As such, no matrix inversion is required. Moreover, using the partial fraction decomposition of the rational approximations is considered an efficient and cost-effective alternative. As mentioned in [11], the poles and residues in the partial fraction decomposition (22) rely on and . Therefore, their computation can be achieved independently of the argument A. The Python or MATLAB “residue” function could be used for this purpose.
- 3.
- Matrix diagonalization approachWhen the matrix argument A is diagonalizable, a scenario frequently encountered in matrices derived from the semi-discretization of partial differential equations, then the factorization could be considered, where D is the diagonal matrix containing the eigenvalues, and the columns of Z are the corresponding eigenvectors. In this case, the matrix MLF can be computed as [28,30]Accordingly, the approximant can be computed asBy employing this approach, we only need to calculate the rational approximation for scalar arguments and perform matrix multiplications, which considerably reduces the computational time. We note that using the diagonalization approach is advisable only under the condition that the matrix is guaranteed to be well conditioned [28].
6. Applications and Numerical Experiments
6.1. Application: Fractional Plasma Oscillations
6.1.1. Fractional Plasma Oscillation Model with a Static Electric Field
6.1.2. Fractional Plasma Oscillation Model with No Electric Field
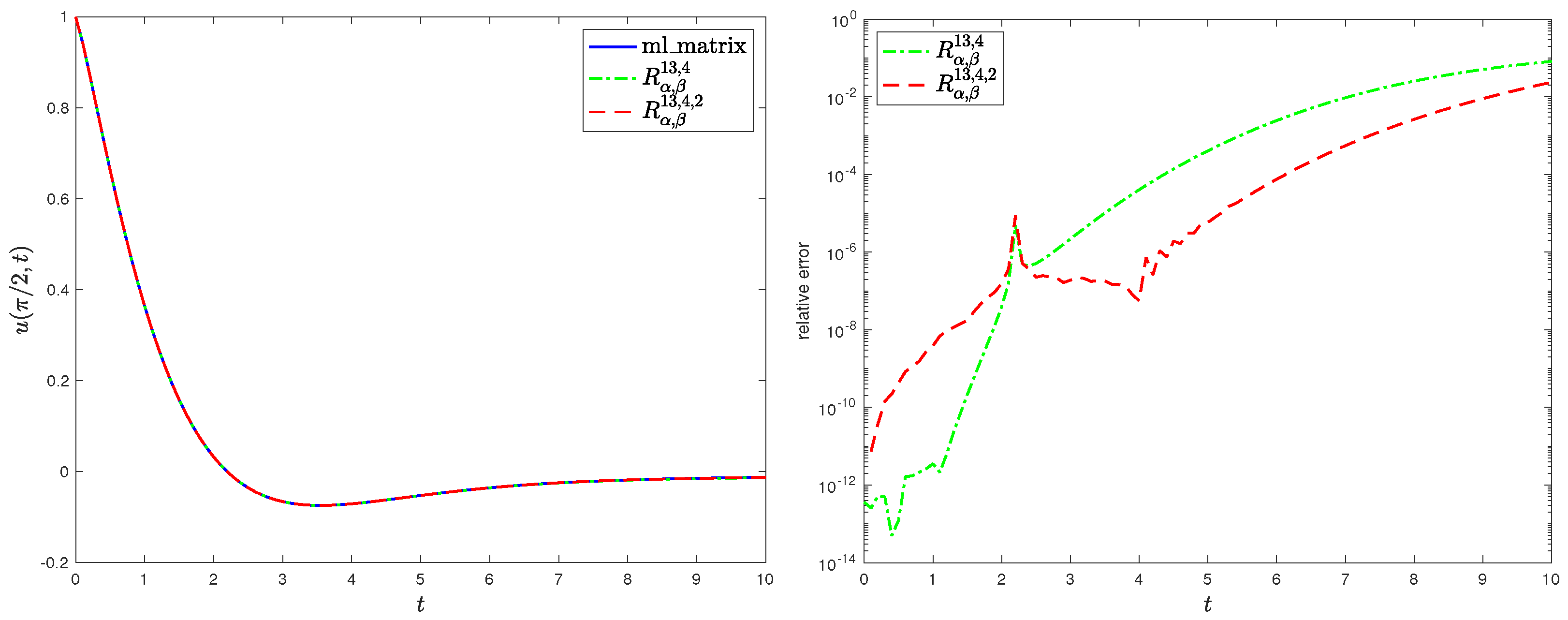
6.2. Application: Time-Fractional Diffusion-Wave Equation
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kilbas, A.; Srivastava, H.; Trujullo, J. Theory and Applications of Fractional Differential Equations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gorenflo, R.; Kilbas, A.A.; Mainardi, F.; Rogosin, S.V. Mittag-Leffler Functions. Related Topics and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gorenflo, R.; Mainardi, F. Fractional Oscillations and Mittag-Leffler Functions; Citeseer: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mainardi, F. Fractional relaxation-oscillation and fractional diffusion-wave phenomena. Chaos Solitons Fractals 1996, 7, 1461–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achar, B.N.; Hanneken, J.; Enck, T.; Clarke, T. Dynamics of the fractional oscillator. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2001, 297, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislavsky, A. Fractional oscillator. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 051103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanislavsky, A.A. Twist of fractional oscillations. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2005, 354, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenflo, R.; Loutchko, J.; Luchko, Y. Computation of the Mittag-Leffler function Eα,β(z) and its derivative. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2002, 5, 491–518. [Google Scholar]
- Garrappa, R. Numerical evalution of two and three parameter Mittag-Leffler functions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 2015, 53, 1350–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarumi, I.O.; Furati, K.M.; Khaliq, A.Q.M. Highly Accurate Global Padé Approximations of Generalized Mittag–Leffler Function and Its Inverse. J. Sci. Comput. 2020, 82, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarumi, I.O.; Furati, K.M.; Khaliq, A.Q.M.; Mustapha, K. Generalized Exponential Time Differencing Schemes for Stiff Fractional Systems with Nonsmooth Source Term. J. Sci. Comput. 2021, 86, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyiola, O.S.; Asante-Asamani, E.O.; Wade, B.A. A real distinct poles rational approximation of generalized Mittag-Leffler functions and their inverses: Applications to fractional calculus. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 330, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starovoitov, A.P.; Starovoitova, N.A. Padé approximants of the Mittag-Leffler functions. Sb. Math. 2007, 198, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhanifar, A.; Valizadeh, S. Mittag-Leffler-Padé approximations for the numerical solution of space and time fractional diffusion equations. Int. J. Appl. Math. Res. 2015, 4, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winitzki, S. Uniform Approximations for Transcendental Functions. In Computational Science and Its Applications, Proceedings of the ICCSA 2003: International Conference Montreal, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–21 May 2003; Kumar, V., Gavrilova, M.L., Tan, C.J.K., L’Ecuyer, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 780–789. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, C.; Osseiran, A. Rational solutions for the time-fractional diffusion equation. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2011, 71, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Chen, Y.Q. Global Padé approximations of the generalized Mittag-Leffler function and its inverse. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2015, 18, 1492–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingo, C.; Barrick, T.R.; Webb, A.G.; Ronen, I. Accurate Padé global approximations for the Mittag-Leffler function, its inverse, and its partial derivatives to efficiently compute convergent power series. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 2017, 3, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanneken, J.W.; Vaught, D.M.; Achar, B. Enumeration of the Real Zeros of the Mittag-Leffler Function Eα(z), 1<α<2. In Advances in Fractional Calculus; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hanneken, J.W.; Achar, B.; Vaught, D.M. An alpha-beta phase diagram representation of the zeros and properties of the Mittag-Leffler function. Adv. Math. Phys. 2013, 2013, 421685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.S.; Wang, Z.; Fu, S.Z. The zeros of the solutions of the fractional oscillation equation. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2014, 17, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrappa, R.; Popolizio, M. Computing the matrix Mittag-Leffler function with applications to fractional calculus. J. Sci. Comput. 2018, 77, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honain, A.H.; Furati, K.M. Rational Approximation for Oscillatory Mittag-Leffler Function. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2023 International Conference on Fractional Differentiation and Its Applications (ICFDA), Ajman, United Arab Emirates, 14–16 March 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Haubold, H.J.; Mathai, A.M.; Saxena, R.K. Mittag-Leffler functions and their applications. J. Appl. Math. 2011, 2011, 298628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Podlubny, I. 2009. Available online: www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/8738 (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Sadeghi, A.; Cardoso, J.R. Some notes on properties of the matrix Mittag-Leffler function. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 338, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, N.J. Functions of Matrices: Theory and Computation; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sastre, J. Efficient evaluation of matrix polynomials. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2018, 539, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrappa, R. Exponential integrators for time-fractional partial differential equations. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2013, 222, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.G.; Hernández, J.R.; Jiménez, R.E.; Astorga-Zaragoza, C.; Peregrino, V.O.; Fraga, T.C. Fractional electromagnetic waves in plasma. Proc. Rom. Acad. A 2014, 17, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo, J.Q.; Yuste, S.B. An explicit difference method for solving fractional diffusion and diffusion-wave equations in the Caputo form. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 2011, 6, 021014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
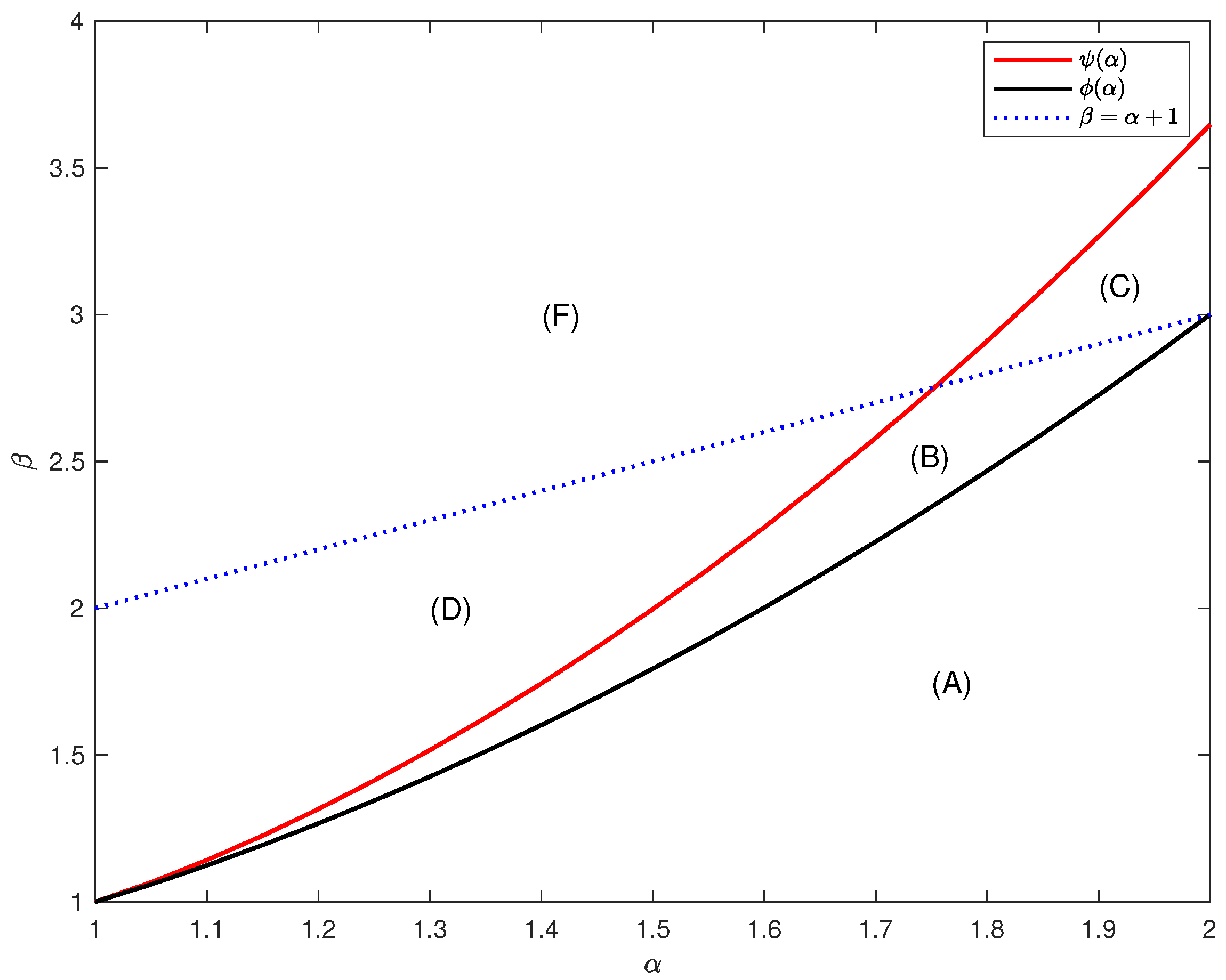

| Region | ||
|---|---|---|
| A | Finite number of roots | Finite number of roots |
| B | No real roots | Finite number of roots |
| C | No real roots | Finite number of roots |
| D | No real roots | No real roots |
| F | No real roots | No real roots |
| AE | RE | Runtime | AE | RE | Runtime | |
| Linear System | ||||||
| Partial Fraction | ||||||
| ml_matrix | ||||||
| RE | Runtime | |
|---|---|---|
| mL | - |
| Runtime | |
|---|---|
| ml_matrix |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Honain, A.H.; Furati, K.M.; Sarumi, I.O.; Khaliq, A.Q.M. Rational Approximations for the Oscillatory Two-Parameter Mittag–Leffler Function. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8060319
Honain AH, Furati KM, Sarumi IO, Khaliq AQM. Rational Approximations for the Oscillatory Two-Parameter Mittag–Leffler Function. Fractal and Fractional. 2024; 8(6):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8060319
Chicago/Turabian StyleHonain, Aljowhara H., Khaled M. Furati, Ibrahim O. Sarumi, and Abdul Q. M. Khaliq. 2024. "Rational Approximations for the Oscillatory Two-Parameter Mittag–Leffler Function" Fractal and Fractional 8, no. 6: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8060319
APA StyleHonain, A. H., Furati, K. M., Sarumi, I. O., & Khaliq, A. Q. M. (2024). Rational Approximations for the Oscillatory Two-Parameter Mittag–Leffler Function. Fractal and Fractional, 8(6), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8060319






