Abstract
International students play a crucial role in China’s talent development strategy. Thus, predicting overseas talent mobility is essential for formulating scientifically reasonable talent introduction policies, optimizing talent cultivation systems, and fostering international talent cooperation. In this study, we proposed a novel fractional-order grey model based on the Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) and Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) algorithm to forecast the movement of overseas talent, namely MGDFGM(1,1). Compared to the traditional grey model FGM(1,1), which utilizes the same fractional order at all time points, the proposed MGDFGM(1,1) model dynamically adjusts the fractional-order values based on the time point. This dynamic adjustment enables our model to better capture the changing trends in the data, thereby enhancing the model’s fitting capability. To validate the effectiveness of the MGDFGM(1,1) model, we primarily utilize Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) as the evaluation criteria for the prediction accuracy, as well as standard deviation (STD) as an indicator of the model stability. Furthermore, we perform experimental analysis to evaluate the predictive performance of the MGDFGM(1,1) model in comparison to NAÏVE, ARIMA, GM(1,1), FGM(1,1), LSSVR, MLP, and LSTM. The research findings demonstrate that the MGDFGM(1,1) model achieves a remarkably high level of prediction accuracy and stability for forecasting overseas talent mobility in China. The implications of this study offer valuable insights and assistance to government departments involved in overseas talent management.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
With the reform and opening-up policy, and the continued globalization of China’s economy and the increasing importance of education within Chinese families, a notable rise in the number of individuals pursuing overseas studies can be observed [1,2]. In the context of fierce global competition for international talents and the tide of anti-globalization, an increasing number of overseas students have demonstrated their intention to return to their home country for development. Talents, especially high-level talents, are important for China’s innovative development [3]. Their return to China significantly impacts technological advancement and economic development [4]. Therefore, attracting more overseas students to contribute to the development of the motherland has become an urgent focus for China’s pursuit of high-quality development. It is worth noting that government departments and companies increasingly prioritize managing overseas talents, aiming to comprehensively understand their mobility patterns [5,6].
1.2. Overseas Talent Mobility Prediction
Accurate overseas talent prediction is essential for relevant decision-makers to understand the future trends in overseas talent mobility and develop appropriate policies. Specifically, it can be beneficial for government departments to understand the trends in talent mobility so that they can formulate and adjust policies related to studying abroad, introducing talent, and retaining talent [7]. In addition, understanding the trends in international talent mobility can work in favor of relevant organizations, universities, and enterprises in making effective plans for international exchanges and collaborations [8,9]. Furthermore, since most of the overseas study talent is a high-level talent, accurately predicting talent mobility can help relevant departments to plan the allocation of human resources effectively, thereby rationalizing industrial layouts and developing economic growth [3].
Currently, there are two main categories of research on overseas talent flow trends. In the first instance, some studies analyze the factors that drive talent flow [10], the factors affecting students’ willingness to study abroad [11,12], and how to attract [7] and retain talent [13]. A second aspect is to develop models of talent mobility, although this field is relatively understudied.
In the field of overseas talent mobility prediction, the grey model is the most popular model. Based on the limited data available on the number of Chinese students studying abroad, Ke and Wu utilized the GM(1,1) model to establish a prediction model for the number of Chinese students studying abroad [14]. Li employed the GM(1,1) model to forecast Chinese overseas students’ development trends [15]. For the prediction of Chinese overseas talent mobility, Ren and Jiang apply four form models of GM(1,1) to predict the number of students studying abroad and returned students [16]. Jiang et al. further proposed a fractional-order grey prediction model based on change-point detection [17]. Additionally, some scholars have applied statistical or machine learning models. For example, Feng and Yu utilized an ARIMA(2,2,2) model to predict the trend of Chinese talent mobility [18]. Olesia constructed five linear trend models based on the different destination countries for Ukrainian students studying abroad [19]. Yang and Duan developed a quadratic curve trend model for predicting the number of Chinese students studying abroad [20]. Yang et al. proposed a hybrid approach, FSDESVR, combining feature selection (FS) and support vector regression (SVR) with differential evolution (DE) for predicting the number of Taiwanese students studying abroad [21]. Bijak et al. compared multiple forecasting models, including AR, ARIMA, Bayesian models, and Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ADL) models. The research findings revealed that no single forecasting method could effectively suit different sets of forecast data [22]. Therefore, some scholars have used combined modeling to predict overseas talent mobility. For instance, Li proposes a combination model combining multiple linear regression, ARIMA, and support vector regression models, which outperformed individual forecasting models [23]. Hu constructs a combined model based on the L1 norm to build the GM(1,3) model and BP neural network model [24]. Also, Wei proposed a combined prediction model integrating GM(1,1) and BP neural networks [25].
Although combination models are superior to single models, single models serve as the foundation for forecast combination [26]. Currently, there are relatively few models for predicting the flow of overseas talent, making it still highly necessary to construct a single predictive model with high accuracy for forecasting the movement of overseas talent. Based on the above analysis, considering the good performance of the grey model in predicting the flow of overseas talent [8], as well as the complexity and limited sample size of China’s overseas talent mobility, this paper aims to develop a new grey forecasting model for the flow of overseas talent in China, encompassing the number of Chinese students studying abroad and those returning to China.
1.3. Grey Models
1.3.1. Basic Principles of Grey Forecasting Models
The grey forecasting model is one of the main contents of grey system theory proposed for handling uncertain information [27]. Compared to statistical models requiring data to conform to statistical assumptions, machine learning models require a large sample size for fitting [28]. Grey prediction models achieve nonlinear mapping using a limited number of samples without requiring the data to possess any statistical assumptions [26]. Therefore, grey prediction models are widely used in energy, transportation, water conservancy, economy, tourism, and population [29,30,31,32]. The grey prediction model stands out from other prediction models due to its unique approach of utilizing data modeling through the accumulative generation operation (AGO), rather than directly estimating and modeling the original data [33]. The basic grey prediction model, GM(1,1), is primarily based on the first-order AGO (1-AGO). This method generates cumulative sequences, constructs difference models, and derives the final equation for the time response using the least squares method and the inverse 1-AGO [27].
In the GM(1,1) model, the first-order accumulation assigns equal weight to all time point data, which does not comply with the new information priority principle for grey forecasting models [27]. To address the problem of information priority in the accumulation sequence, Wu et al. proposed a grey forecasting model based on fractional-order accumulation, namely FGM(1,1) [34]. The weighting of data during the process of accumulation is influenced by the fractional order, . As the value of increases, the weight assigned to old data increases proportionally, while the weight assigned to new data decreases correspondingly, and vice versa [34]. Compared to the integer order, the fractional order can better reveal the intrinsic characteristics and behaviors of objects. Therefore, the grey prediction model based on fractional-order accumulation has gradually attracted the attention of researchers and has been applied in various fields [35,36,37].
1.3.2. Advancements in Fractional-Order Grey Prediction Models
Improving the forecasting accuracy of the FGM(1,1) model is a primary research focus that entails proposing various fractional-order forms [38,39,40], constructing prediction models with different fractional-order structures [41,42,43,44], investigating the optimal number of modeling samples [17,45], and integrating other optimization algorithms to determine the optimal fractional order of the model [28,39,46], among other approaches. Although existing research has conducted in-depth discussions on the fractional-order grey prediction model, almost all of them have used a fixed fractional-order value. As mentioned above, the fractional order assigns different weights to the accumulated data [34]. While the accumulated data grow over time, the weights determined by the fractional order are also likely to change in accordance with the growth of the data. Thus, the fractional-order values should be dynamically adjusted according to the development of the data. Although there have been several papers discussing the dynamic change in relevant parameters in response to changes in time to improve prediction accuracy [47,48], there is scarce literature exploring the relationship between the time points and the fractional order during the modeling process to adjust the fractional order dynamically. Therefore, we propose a novel FGM(1,1) model in which the fractional order is dynamically adjusted based on different time points.
There are two problems that must be solved in order to achieve a dynamic fractional order. The first is how to determine the fractional order for each time point, and the second is how to determine the fractional order for future time points.
For the first problem, the current method for determining fractional-order values is based on the metaheuristic algorithm [39], and the method is also used in this study in order to calculate the optimal dynamic fractional order. There is no doubt that dynamic fractional optimization with multiple values to optimize is more difficult and complex than fixed fractional-order optimization with only one parameter to optimize. The GWO algorithm has the characteristics of simplicity and flexibility and achieves a proper balance between global search and local optimization [49]. It has been proven to perform well in solving parameters for grey prediction models [39,50]. Therefore, the GWO algorithm is adopted to optimize and solve the dynamic fractional-order values for the proposed model.
For the second problem, we can construct a model based on dynamic fractional-order values and datasets, which can be used to predict future fractional orders. Due to the nonlinear relationship between the optimal fractional order determined by grey wolf optimization and the given dataset, this model should be a nonlinear model. Given that the MLP is renowned as a leading nonlinear time series prediction model for its proficiency in forecasting nonlinear time series [51], the MLP model was thus employed to predict the fractional-order values based on the given dataset.
Basically, this study aims to propose a dynamic fractional-order grey prediction model based on the GWO and MLP, namely MGDFGM(1,1), for the flow of overseas talent in China. The proposed MGDFGM(1,1) model features an adaptive fractional order that adjusts as the time series data changes. It employs the GWO to optimize the dynamic fractional order in order to create the most suitable fitting model, and the MLP to make predictions about future fractional-order parameters in order to prepare an ex-post forecast of overseas talent in China.
1.4. Contributions
The main contribution of this work is that we have proposed a novel grey model MGDFGM(1,1) with a dynamic fractional order based on the MLP and GWO. Compared to the traditional grey model FGM(1,1), which utilizes the same fractional order at all time points, the fractional-order values of MGDFGM(1,1) are dynamically adjusted with the change in the dataset. With the dynamic adjustment, MGDFGM(1,1) is better able to capture the changing trends in the dataset. In addition, the GWO is used in this study for optimizing the dynamic fractional-order values to build the best fitting model. The MLP is applied to predict the fractional-order values to make an ex-post forecast of overseas talents in China. Furthermore, this work takes the flow of Chinese overseas talents as the experimental subject. In comparing different statistical models, grey models, and artificial intelligence models, it is demonstrated that MGDFGM(1,1) has a high degree of predictive accuracy and good predictive stability for predicting Chinese overseas talent mobility, thus offering a novel approach to predict overseas talent mobility.
The remainder of this work is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the FGM(1,1), GWO algorithm, and MLP method, as well as the proposed MGDFGM(1,1) model. Section 3 examines the proposed model for predicting the flow of overseas talent in China. Section 4 discusses the predictions of MGDFGM(1,1) compared to other grey model predictions and analyzes the advantages of the MGDFGM(1,1) model. The conclusion and future work are briefed in Section 5.
2. Methodology
2.1. FGM(1,1)
The modeling steps for the FGM(1,1) are as follows:
(1) Set as an original non-negative sequence:
(2) Convert to the fractional-order accumulation sequence by Hausdorff r-order accumulated generating operation (r-AGO):
(3) Set as an immediately adjacent mean generating the sequence of
(4) The fractional grey differential equation is constructed as
(5) Estimate the parameters a and b by the least squares method
where
(6) Obtain the time response series of the grey differential equation,
(7) The final prediction value is obtained by reverse r-order AGO:
The FGM(1,1) model follows the principle of prioritizing new information when falls within the range of 0 to 1. The FGM(1,1) model is equivalent to the GM(1,1) model when is equal to one [34].
2.2. GWO
The GWO algorithm is a metaheuristic optimization algorithm proposed by Mirjalili et al. in 2014, inspired by the social hierarchy and hunting behavior of grey wolves [52].
In the mathematical model of the GWO algorithm, is considered as the optimal solution, followed by , , and in order. The mathematical model equation is as follows:
where represents the distance between the grey wolves and the prey, and are vector parameters, represents the current position vector of the prey, represents the current position vector of the grey wolves, denotes the current iteration number. is the convergence factor, which linearly decreases from 2 to 0 during the iteration process. and are random vectors in the range [0,1].
During the hunting process, grey wolves can identify and surround the prey’s location. Let us assume α, β, and δ know the potential prey’s location. Based on α, β, and δ, the prey’s location can be determined during the hunting process, assisting other grey wolves in updating their positions and gradually approaching the prey. The mathematical model for this phenomenon is expressed below:
where , , and represent the distances between , , and and other grey wolves, respectively. , , and are the current positions of , , and . The grey wolves adjust their positions based on the three current best solutions, continuously approaching the prey. The average value is used as the new position update target. The formula is as follows:
When the prey stops moving, the grey wolves begin their attack. If , then the grey wolves launch their attack. Otherwise, the grey wolves leave the prey and seek an optimal position. At the same time, in the model, is a random number within the range of [0,2], and this randomness prevents the model from becoming trapped in local optimal solutions, thus obtaining the global optimal solution [53].
2.3. MLP
The MLP is a widely utilized feedforward artificial neural network [54]. The structure of a three-layer MLP comprises an input layer, a hidden layer, and an output layer. The input layer usually consists of a group of nodes through which data are fed into the network. The hidden layer also includes a group of nodes connected to all nodes in the input layer. These nodes apply activation functions to the input data, resulting in nonlinear transformations. The output layer typically contains a node connected to all nodes in the hidden layer, representing the potential output values of the MLP. The mathematical model of the MLP can be represented as:
where represents the predicted value, is the number of hidden-layer nodes, is the input vector dimension, represents the activation function, and are the weights from the input layer to the hidden layer and from the hidden layer to the output layer, respectively.
2.4. Proposed MGDFGM(1,1)
This study proposes a novel grey model MGDFGM(1,1) with a dynamic fractional order based on MLP and GWO. The main modeling process of MGDFGM(1,1) is as follows:
Step I: Establish a dynamic FGM(1,1). Dynamic parameter adjustment enhances the adaptability of the grey model and improves the accuracy of its predictions [47]; hence, we have established a grey prediction model with dynamic fractional-order parameter adjustment. In the traditional FGM(1,1), the fractional order is the same at different time points during fractional-order accumulation [34]. However, in the proposed MGDFGM(1,1) model, the fractional order is associated with the actual values at different time points. The fractional order at each time point is denoted as , where . Thus,
The final prediction result can be obtained through a reverse dynamic fractional order,
Step II: Solve the fractional order . Implement the GWO algorithm to find the optimal by minimizing MAPE as the loss function [39]. The obtained optimal is then used to construct the fitting model in the dynamic FGM(1,1) model. We implement the GWO algorithm using the EvoloPy framework [49]. The GWO algorithm is configured with several search agents = 1000, the maximum number of iterative steps = 1000, and dim = 15. The operator search range is set between the highest value of 1 and the lowest value of 0. Therefore, ranges from 0 to 1, following the principle of prioritizing new information in the proposed model [24].
Step III: Fractional-order prediction. Because the fractional order is related to the data at the corresponding time point, it is not possible to solve the fractional order of the prediction stage by the previous modeling stage. Here, represents the number of prediction time points. Hence, the MLP method is employed to predict the fractional order in the prediction stage. The input of the MLP is represented as , and the corresponding output is denoted as . Here, represent the predicted values of the case data, and { denote the predicted values of the fractional order. The MLP consists of an input layer, a hidden layer, and an output layer, implemented using Python. The optimal parameters of the MLP are determined using grid search with time series five-fold cross-validation. The “lbfgs” solver is used to optimize the weights. The activation functions can be “identity”, “logistic”, “tanh”, or “relu”; the number of nodes in the hidden layer are set from 2 to 12; the maximum number of iterations are set to 3000.
Step IV: Future value prediction. Bring the fractional-order predicted value obtained in the previous step into the dynamic FGM(1,1) model to obtain the future predicted values.
Based on the above steps, we refer to the dynamic fractional-order grey model that combines the MLP and GWO as MGDFGM(1,1). When all the fractional orders in MGDFGM(1,1) have the same value, MGDFGM(1,1) is equivalent to FGM(1,1). When all the fractional orders equal 1, MGDFGM(1,1) is equivalent to GM(1,1).
The proposed MGDFGM(1,1) model was compared with several forecasting models, including the classic and commonly used time series forecasting models NAÏVE and ARIMA [55], as well as the basic grey models GM(1,1) and FGM(1,1) [34], and three AI-based models, least squares support vector regression (LLSVR) [56], MLP [54], and long short-term memory networks (LSTM) [57], to demonstrate its superior performance. This study adopts NAÏVE as the baseline model for predicting overseas talent mobility. Compared to other models, Naïve forecasting is easier to implement and does not require any parameter optimization. Suppose more complex models perform worse than the Naïve model regarding the prediction performance. In this case, they cannot provide more useful information and are not recommended as predictive models for overseas talent mobility.
2.5. Model Evaluation Criteria
The MAPE is a widely used method for evaluating the prediction accuracy of grey models and is commonly employed to assess the overall performance of models [27,39]. However, relying solely on the MAPE as a performance metric may present certain risks [58]. Therefore, we also included the RMSE, another widely used metric for providing a comprehensive evaluation of model performance [59]. A lower value of the MAPE and RMSE signifies an enhanced predictive accuracy of the model. The respective formulas for the MAPE and RMSE are as follows:
According to the MAPE accuracy criterion [60], a model is deemed to have a high prediction accuracy if the error is below 10%, indicating its suitability for prediction, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Accuracy criteria for prediction models (MAPE).
This study applies STD as a measure to test the stability of the models utilized in this paper [30] as follows:
3. Empirical Results
3.1. Data Description
The main data used in this study include the number of Chinese students studying abroad and returning to China, which are the two most important predictors for predicting overseas talent mobility. This period covers 2000 to 2019 due to the constraints of data availability. The dataset is from the National Bureau of Statistics of China (https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01). Figure 1 presents the dataset employed in this study. Over the past decade, a noteworthy upsurge in the number of Chinese students pursuing education abroad and those repatriating to China has occurred.
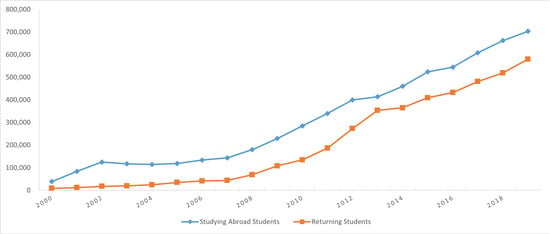
Figure 1.
Time series chart of overseas talent mobility (unit: person).
3.2. Experiment 1: Students Studying Abroad
Experiment 1 focuses on forecasting the number of students studying abroad. International students are chosen as the subject of study. The model is constructed using data from 2000 to 2016, and data from 2017 to 2019 are used to validate the predictive accuracy of the model. The specific calculation process using MGDFGM(1,1) in Experiment 1 is as follows.
The number of students studying abroad from 2000 to 2016 is the original sequence :
The GWO algorithm is used to optimize the fractional order of MGDFGM(1,1). After computation, the optimal order is determined to be
The corresponding accumulated sequence for the order is
Based on Formulas (5) and (6), parameters and are obtained through the least squares method. Therefore, it can be concluded that
Based on the above time response function, the inverse dynamic fractional order is used to calculate the fitting and predicted value .
Finally, using the MLP method for the fractional-order prediction of the next three years, we obtain , and thus, the final predicted values for 2017 to 2019 are .
Table 2 shows the predicted results of MGDFGM(1,1) and the comparative models. Figure 2 and Figure 3 represent the predicted performance of all the considered models during the fitting and forecasting stages of Experiment 1, respectively.

Table 2.
Comparison results of Experiment 1.
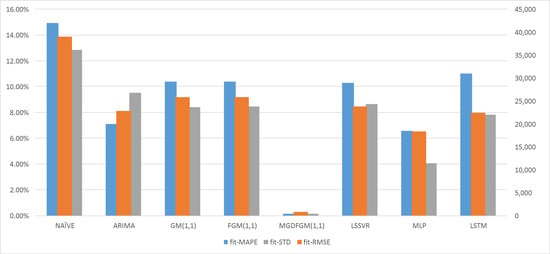
Figure 2.
The predicted performance of all considered models during the fitting stages of Experiment 1.
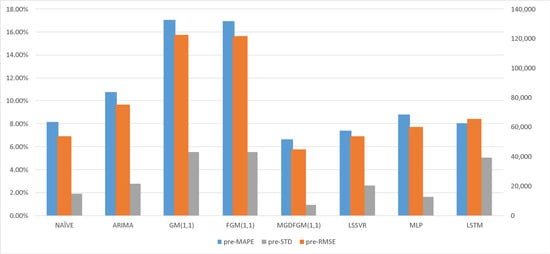
Figure 3.
The predicted performance of all considered models during the forecasting stages of Experiment 1.
During the model fitting stage, all the considered models demonstrated higher prediction accuracy compared to the naive model. However, only the ARIMA, MGDFGM(1,1), and MLP models achieved high prediction accuracy, with MAPE values less than 10%. In comparison, the prediction accuracy of the other models was considered good, with MAPE values ranging from 10% to 20%. In terms of prediction stability, the stability of the other seven models is also superior to that of the NAÏVE model. Therefore, considering the prediction accuracy and stability, the MGDFGM(1,1), ARIMA, and MLP models can be used as fitting models for the number of students studying abroad. However, the MGDFGM(1,1) model outperforms the other models in both aspects.
During the model forecasting stage, the ARIMA, GM(1,1), FM(1,1), and MLP models have a lower accuracy compared to the NAÏVE model. Among these models, the GM(1,1) model exhibits the lowest prediction accuracy and stability. Therefore, the traditional grey prediction models GM(1,1) and FGM(1,1) are not suitable for predicting the number of students studying abroad. In contrast, LSSVR, LSTM, and the proposed MGDFGM(1,1) model demonstrate superior prediction accuracy compared to the naive model, achieving a high level of precision. Specifically, the MGDFGM(1,1) model showcases the highest prediction accuracy. Moreover, regarding the model stability, the STD value of MGDFGM(1,1) is 0.915%, which is smaller than other models, indicating the highest level of prediction stability. Therefore, compared to the other comparative models, MGDFGM(1,1) demonstrates greater suitability for predicting the number of students studying abroad.
Figure 4 displays the trend prediction graphs of all the considered models to highlight the disparities in trend prediction among the models. During the fitting stage, all the models demonstrate highly accurate predictions that align closely with the actual values. However, in the prediction stage, the GM(1,1) and FGM(1,1) models produce overestimated predictions that deviate noticeably from the actual value curve. Conversely, the predicted values of the other six models are lower than the actual values, and the MGDFGM(1,1) curve exhibits the closest resemblance to the actual value curve. The predicted value curve of MGDFGM(1,1) demonstrates greater proximity to the actual value curve compared to the other comparative models in both the fitting and prediction stages.
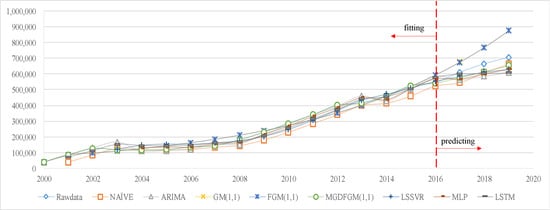
Figure 4.
The trend of actual and predicted values in Experiment 1 (unit: person).
In summary, based on the comprehensive comparative analysis of the model accuracy (MAPE and RMSE), model stability (STD), and model trend, it can be inferred that the proposed MGDFGM(1,1) model outperforms the non-grey models NAÏVE, ARIMA, LSSVR, MLP, and LSTM, as well as the grey models GM(1,1) and FGM(1,1) in predicting the number of students studying abroad. Hence, the proposed MGDFGM(1,1) proves to be an effective forecasting tool for the number of students studying abroad.
3.3. Experiment 2: Returned Overseas Students
Experiment 2 uses the number of returned overseas students for prediction to further validate the effectiveness of MGDFGM(1,1) in forecasting overseas talent mobility. The modeling and prediction process in Experiment 2 is similar to Experiment 1, using data from 2000 to 2016 to build the model, while data from 2017 to 2019 are used to validate the accuracy of the model’s predictions.
Using the GWO to optimize the order of the model, the calculated optimal order is
Thus, the obtained time response function is
We employed the MLP method for predicting the scores in the fractional order for the upcoming three years. The results revealed the values of {0.690, 0.724, 0.729}. Utilizing these outcomes, we derived the final projected values for the years 2017 to 2019 as .
Table 3 presents the predicted results of the MGDFGM(1,1) model and the comparison models for the number of returned overseas students. Figure 5 and Figure 6 represent the predicted performance of all the considered models during the fitting and forecasting stages of Experiment 2, respectively. For the fitting and forecasting data, the MGDFGM(1,1) model demonstrates lower MAPE and RMSE values compared to the other seven comparison models. Regarding model stability, the MGDFGM(1,1) model is slightly inferior to NAÏVE only during the prediction stage but exhibits the highest stability in all other scenarios.

Table 3.
Comparison results of Experiment 2.
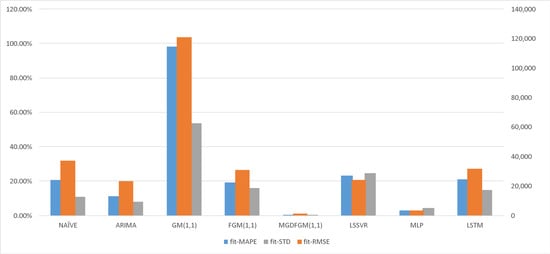
Figure 5.
The predicted performance of all considered models during the fitting stages of Experiment 2.
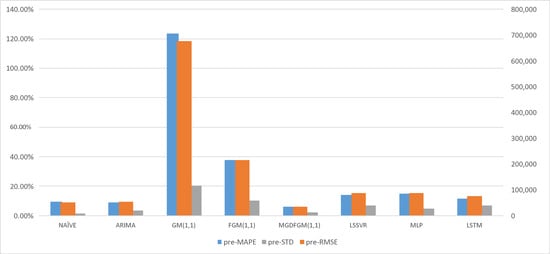
Figure 6.
The predicted performance of all considered models during the forecasting stages of Experiment 2.
Figure 7 displays the fitting and forecasting trends of all the considered models for the number of returned overseas students to highlight the differences in model prediction trends. The GM(1,1) model exhibits a significant deviation from the actual values even during the fitting stage. Although the FGM(1,1) model shows a relatively small deviation from the actual values during the fitting stage, it surpasses the actual value curve during the forecasting stage. On the other hand, the NAÏVE, ARIMA, LSSVR, MLP, LSTM, and MGDFGM(1,1) curves closely align with the actual value curve. The MGDFGM(1,1) curve consistently overestimates the values compared to the actual curve, while the other five models consistently underestimate the values. Additionally, the MGDFGM(1,1) curve most closely follows the actual value curve.
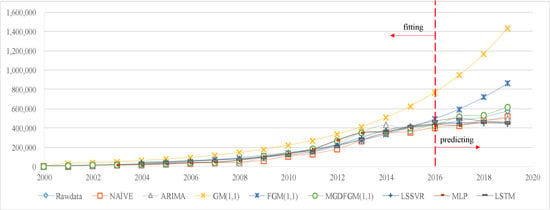
Figure 7.
The trend of actual and predicted values in Experiment 2(unit: person).
The comprehensive comparative analysis combining the model accuracy (MAPE and RMSE), model stability (STD), and model trend indicates that the proposed MGDFGM(1,1) model outperforms the other comparative models in predicting the number of returned overseas students. Therefore, the MGDFGM(1,1) model is shown to be effective in forecasting the count of returned overseas students.
4. Discussion
The results of Experiments 1 and 2 demonstrate that using a dynamic fractional-order grey forecasting model can effectively improve the prediction accuracy of grey forecasting models. In Experiment 1, compared to GM(1,1) and FGM(1,1), MGDFGM(1,1) has improved the MAPE values by 61.264% and 60.946%, and the RMSE values by 63.548% and 63.266%, respectively, elevating the prediction level from good to high accuracy. In Experiment 2, the performance of GM(1,1) in fitting and predicting the returnee students is poor, especially with an MAPE value exceeding 100% in the prediction stage. Although FGM(1,1) improved the prediction accuracy through the optimized fractional order (), it still falls short of the desired level and is only considered acceptable. However, with the dynamic accumulation of the fractional order based on the MLP and GWO, the grey prediction model significantly improved the accuracy of predicting returnee students. Compared to GM(1,1) and FGM(1,1), MGDFGM(1,1) has increased the MAPE values by 95.054% and 83.801%, and the RMSE values by 94.966% and 84.072% respectively, elevating the prediction accuracy from acceptable to high. Additionally, from the perspective of model stability, whether in the fitting or prediction stage, the MGDFGM(1,1) model remained stable compared to GM(1,1) and FGM(1,1). Therefore, the proposed dynamic fractional-order model can significantly enhance the prediction accuracy and stability of the grey prediction model.
The proposed MGDFGM(1,1) model has the following advantages compared to other traditional grey models: (1) The implementation of dynamic fractional-order accumulation enables the fitting of distinct trends within the data, enhancing the modeling capability with greater flexibility. (2) The model demonstrates high superiority in prediction accuracy and stability. However, the model still has some limitations, such as the need for assistance from other models for fractional-order prediction in the forecasting stage. In this study, the MLP is utilized for prediction, increasing the model’s complexity.
5. Conclusions
As a critical high-quality human resource, effective management of overseas talents is crucial for China’s talent strategy and labor internationalization. The accurate prediction of the flow of overseas talents can assist the government and enterprises in formulating more effective policies for talent attraction and retention, maximizing the potential of talents, and promoting sustainable economic and social development. Applying a univariate grey forecasting model is suitable given the limited data and unclear influencing factors in this study. We have introduced a dynamic fractional-order grey forecasting model, MGDFGM(1,1), for predicting the flow of overseas talent in China. In this model, the GWO method is used for fractional-order optimization, and the MLP model is employed for predicting the fractional order. The model exhibits exceptional accuracy in forecasting both studying abroad and returning to study in China, achieving an MAPE value below 7% and stability below 3%, outperforming other comparative models. Therefore, we can conclude that the proposed MGDFGM(1,1) is suitable for predicting the flow of overseas talent in China. In addition, the proposed fractional-order dynamic optimization method can improve the prediction accuracy of the traditional grey model by at least 60% in the case studies of this paper. Therefore, dynamically adjusting the fractional-order accumulation to enhance the prediction accuracy of the grey model has been proven to be effective.
Due to the impact of COVID-19, the Chinese government has not yet released data on the number of international students and returning personnel for 2020 and beyond. This lack of data poses significant challenges and opportunities for predicting the return of overseas talents. The focus of the research lies in obtaining data from recent years or using alternative indicators for forecasting the flow of overseas talent. Although some studies have explored factors influencing the flow of overseas talent, a consensus has not been reached. Therefore, this study adopts a univariate forecasting model to mitigate the influence of other factors on the model. However, exploring multivariate forecasting models that incorporate relevant influencing factors in predicting the flow of overseas talent would be a meaningful step. Therefore, a key research direction in the future will be the development of a multivariable grey forecasting model that incorporates the influence of exogenous variables on the flow of overseas talent.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.W. and P.J.; methodology, G.W. and H.F.; formal analysis, G.W. and R.C. (Rongjiang Cai); data curation, R.C. (Rui Chi); writing—original draft preparation, G.W. and P.J.; writing—review and editing, G.W. and P.J.; funding acquisition, P.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Humanities and Social Sciences Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China, GTANT No. 22YJC840012, the Application Strategies for the Philosophy and Social Science Planning of Zhejiang Province in 2023, GTANT No. 23BMHZ065YB, the Scientific Research Fund of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department, Grant No. Y202351610.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. These data can be found here as follows: (https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01, accessed on 10 January 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lin, D.; Zheng, W.; Lu, J.; Liu, X.; Wright, M. Forgotten or Not? Home Country Embeddedness and Returnee Entrepreneurship. J. World Bus. 2019, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Mok, K.H. Critical Reflections on Mainland China and Taiwan Overseas Returnees’ Job Searches and Career Development Experiences in the Rising Trend of Anti-Globalisation. High. Educ. Policy 2020, 33, 413–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, O.; Liu, X. Returnee Entrepreneurs and Firm Performance in Chinese High-Technology Industries. Int. Bus. Rev. 2009, 18, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sadowski-Smith, C.; Yu, W. Return Migration and Transnationalism: Evidence from Highly Skilled Academic Migration. Pap. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 4, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guan, J. Returnee Policies in China: Does a Strategy of Alleviating the Financing Difficulty of Returnee Firms Promote Innovation? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 164, 120509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, H. Dynamic Talent Flow Analysis with Deep Sequence Prediction Modeling. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2019, 31, 1926–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J. Trends in International Student Mobility: A Study of the Relationship between the UK and China and the Chinese Student Experience in the UK. Scott. Educ. Rev. 2006, 38, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, C.; Huang, J. Trends in Participation and Attainment of Chinese Students in UK Higher Education. Stud. High. Educ. 2014, 39, 805–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J. Student Mobility and Internationalization: Trends and Tribulations. Res. Comp. Int. Educ. 2012, 7, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Liu, J. Has Excess Epidemic Prevention Changed Chinese Students’ Willingness to Study Abroad: Three Rounds of the Same Volume Survey Based on the New “Push–Pull” Theory. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, K.H.; Xiong, W.; Ke, G.; Cheung, J.O.W. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on International Higher Education and Student Mobility: Student Perspectives from Mainland China and Hong Kong. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2021, 105, 101718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M. What Attracts Mainland Chinese Students to Australian Higher Education. Innov. Dev. 2007, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturgut, O. Best Practices in Recruiting and Retaining International Students in the U.S. Curr. Issues Educ. 2013, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, P.; Wu, G. Study on Prediction of the Number of Study Abroad Based on GM (1.1) Model. Value Eng. 2012, 31, 318–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. The Development of China’s Study Abroad Education and It’s Countermeasures. J. Syst. Sci. Inf. 2010, 8, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Jiang, P. Forecasting the Number of Students Studying Abroad and Returned Students Studying Abroad Based on Grey Forecasting Model. J. Manag. Decis. Sci. 2020, 3, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Wu, G.; Hu, Y.-C.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y. Novel Fractional Grey Prediction Model with the Change-Point Detection for Overseas Talent Mobility Prediction. Axioms 2022, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yu, D. Prediction of abroad Chinese students and its impact on household consumption. J. Nanjing Univ. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2014, 6, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totska, O. Modeling the migration of ukrainians to study abroad. Sci. J. Pol. Univ. 2018, 28, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Duan, X. Prediction of the number of students studying abroad in China: Based on the time series prediction method. Sci. Technol. Economy Mark. 2016, 1, 119–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Chen, H.-C.; Chen, W.-C.; Yang, C.-H. Forecasting Outbound Student Mobility: A Machine Learning Approach. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijak, J.; Disney, G.; Findlay, A.M.; Forster, J.J.; Smith, P.W.F.; Wiśniowski, A. Assessing Time Series Models for Forecasting International Migration: Lessons from the United Kingdom. J. Forecast. 2019, 38, 470–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Forecast and Analysis of Reasons for Changes in the Number of Students Studying Abroad. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 24, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z. Research on Combination Forecasting of the Number of Students Studying Abroad Based on L1 Norm. J. Chongqing Technol. Bus. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2022, 39, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y. Prediction of international students and returnees based on grey neural network model. Bus. Econ. 2010, 4, 4–6+122. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.-C.; Wu, G.; Jiang, P. Tourism Demand Forecasting Using Nonadditive Forecast Combinations. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2023, 47, 775–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Wang, R. A Historic Review of Grey Forecasting Models. J. Grey Syst. 2017, 29, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.; Xie, N. Parameter Estimation for Grey System Models: A Nonlinear Least Squares Perspective. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2021, 95, 105653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangmei, M.; Leping, T.; Chen, Y.; Lifeng, W. Forecast of Annual Water Consumption in 31 Regions of China Considering GDP and Population. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 713–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Cai, Y.; Yuan, H.; Deng, Y. Application of a Novel Hybrid Accumulation Grey Model to Forecast Total Energy Consumption of Southwest Provinces in China. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2023, 13, 629–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Xiao, X.; Gao, M.; Wang, X.; He, Q. Nonlinear Fractional Order Grey Model of Urban Traffic Flow Short-Term Prediction. J. Grey Syst. 2018, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Xie, N.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Analyzing the Aging Population and Density Estimation of Nanjing by Using a Novel Grey Self-Memory Prediction Model Under Fractional-Order Accumulation. J. Grey Syst. 2022, 34, 34–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y. Prediction of Energy-Related Carbon Emission Intensity in China, America, India, Russia, and Japan Using a Novel Self-Adaptive Grey Generalized Verhulst Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Yao, L.; Yan, S.; Liu, D. Grey System Model with the Fractional Order Accumulation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2013, 18, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Gao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X. Using a Novel Multi-Variable Grey Model to Forecast the Electricity Consumption of Shandong Province in China. Energy 2018, 157, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-C. Forecast Combination Using Grey Prediction with Fuzzy Integral and Time-Varying Weighting in Tourism. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2023, 13, 808–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Hua, L.; Wu, L. A Novel Method of Blockchain Cryptocurrency Price Prediction Using Fractional Grey Model. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Q.; Goh, M. A Novel Fractional Grey Riccati Model for Carbon Emission Prediction. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 124471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xie, M.; Wu, W.; Zeng, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X. The Novel Fractional Discrete Multivariate Grey System Model and Its Applications. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 70, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, B.; Nan, F.; Zhu, N.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, W. UFNGBM (1,1): A Novel Unbiased Fractional Grey Bernoulli Model with Whale Optimization Algorithm and Its Application to Electricity Consumption Forecasting in China. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 7405–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, K. Fractional Hausdorff Grey Model and Its Properties. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 138, 109915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifeng, W.U.; Sifeng, L.; Ligen, Y. Grey Model with Caputo Fractional Order Derivative. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2015, 35, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Wu, W.; Zeng, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Ye, L.; Ma, X.; Wu, W.; et al. A Novel Self-Adaptive Fractional Multivariable Grey Model and Its Application in Forecasting Energy Production and Conversion of China. Eng. Appl. Artif. InteL 2022, 115, 105319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-Z.; Pang, H.; Zheng, C.; Xie, W.; Liu, C. Predictive Analysis of Quarterly Electricity Consumption via a Novel Seasonal Fractional Nonhomogeneous Discrete Grey Model: A Case of Hubei in China. Energy 2021, 229, 120714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhicun, X.; Meng, D.; Lifeng, W. Evaluating the Effect of Sample Length on Forecasting Validity of FGM(1,1). Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 4687–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-C. Forecasting Tourism Demand Using Fractional Grey Prediction Models with Fourier Series. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 300, 467–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, T.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J. The Optimized Multivariate Grey Prediction Model Based on Dynamic Background Value and Its Application. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6663773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Tan, Y.; Xu, H.; Quan, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X. Forecasting the Electricity Consumption of Commercial Sector in Hong Kong Using a Novel Grey Dynamic Prediction Model. J. Grey Syst. 2018, 30, 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Mirjalili, S. Grey Wolf Optimizer: A Review of Recent Variants and Applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 30, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wu, W.-Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, T.; Dong, Z. Forecasting Fuel Combustion-Related CO2 Emissions by a Novel Continuous Fractional Nonlinear Grey Bernoulli Model with Grey Wolf Optimizer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 38128–38144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, K.; Sun, S.; Wang, S.; Wei, Y. A Secondary-Decomposition-Ensemble Learning Paradigm for Forecasting PM2.5 Concentration. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Riahi-Madvar, H.; Hooshyaripor, F.; Mosavi, A.; Shamshirband, S.; Zavadskas, E.; Chau, K. Prediction of Hydropower Generation Using Grey Wolf Optimization Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System. Energies 2019, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliyasu, A.M.; Fouladinia, F.; Salama, A.S.; Roshani, G.H.; Hirota, K. Intelligent Measurement of Void Fractions in Homogeneous Regime of Two Phase Flows Independent of the Liquid Phase Density Changes. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Sun, S.; Bi, D.; Guo, J.; Wang, S. Seasonal and Trend Forecasting of Tourist Arrivals: An Adaptive Multiscale Ensemble Learning Approach. J. Tour. Res. 2022, 24, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lai, K.K. Hybrid Approaches Based on LSSVR Model for Container Throughput Forecasting: A Comparative Study. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 2232–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, E.; Kim, G. Centralized Decomposition Approach in LSTM for Bitcoin Price Prediction. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Chang, P.-Y. Forecasting the Demand for Container Throughput Using a Mixed-Precision Neural Architecture Based on CNN–LSTM. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice, 3rd ed.; OTexts: Melbourne, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, C.D. Industrial and Business Forecasting Methods; Butterworth Scientific: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).