A Closure Contact Model of Self-Affine Rough Surfaces Considering Small-, Meso-, and Large-Scale Stage Without Adhesive
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Single-Asperity Contact Model (JK Model with a Single Asperity)
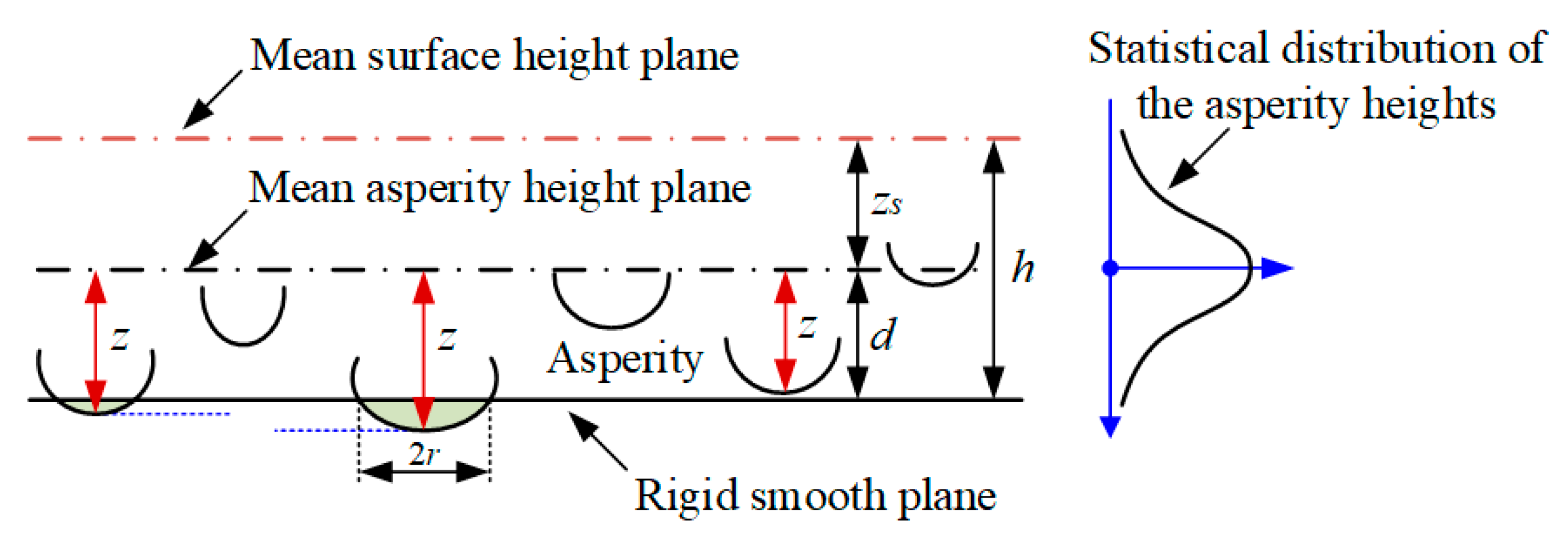
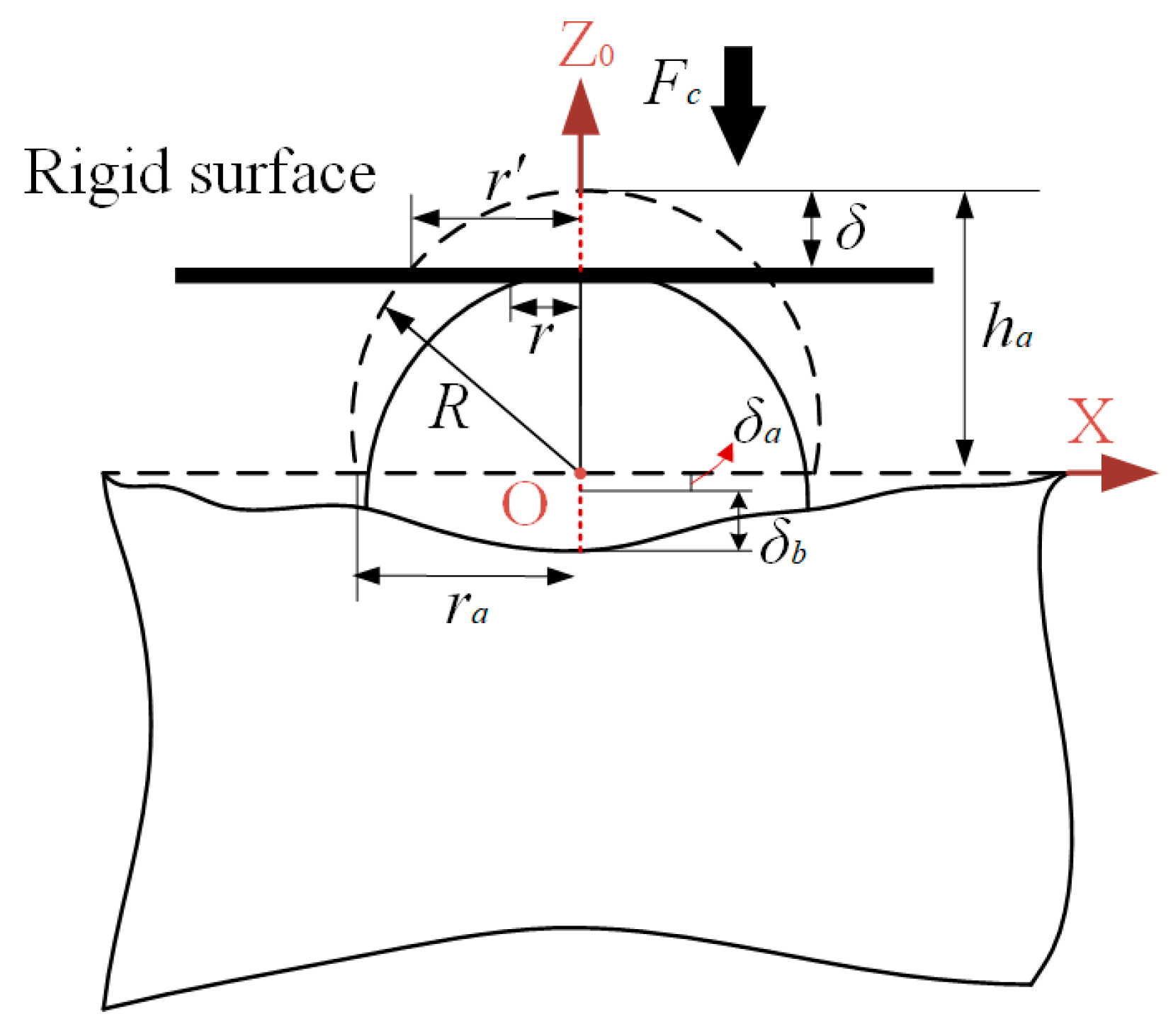
2.1. Problem Description
2.2. Asperity–Substrate Interaction
2.3. Asperity Contact Modeling in Elastic, Elastoplastic, and Full Plastic Deformation—JK Model
- Elastic deformation
- 2.
- Elastoplastic deformation
- 3.
- Full plastic deformation
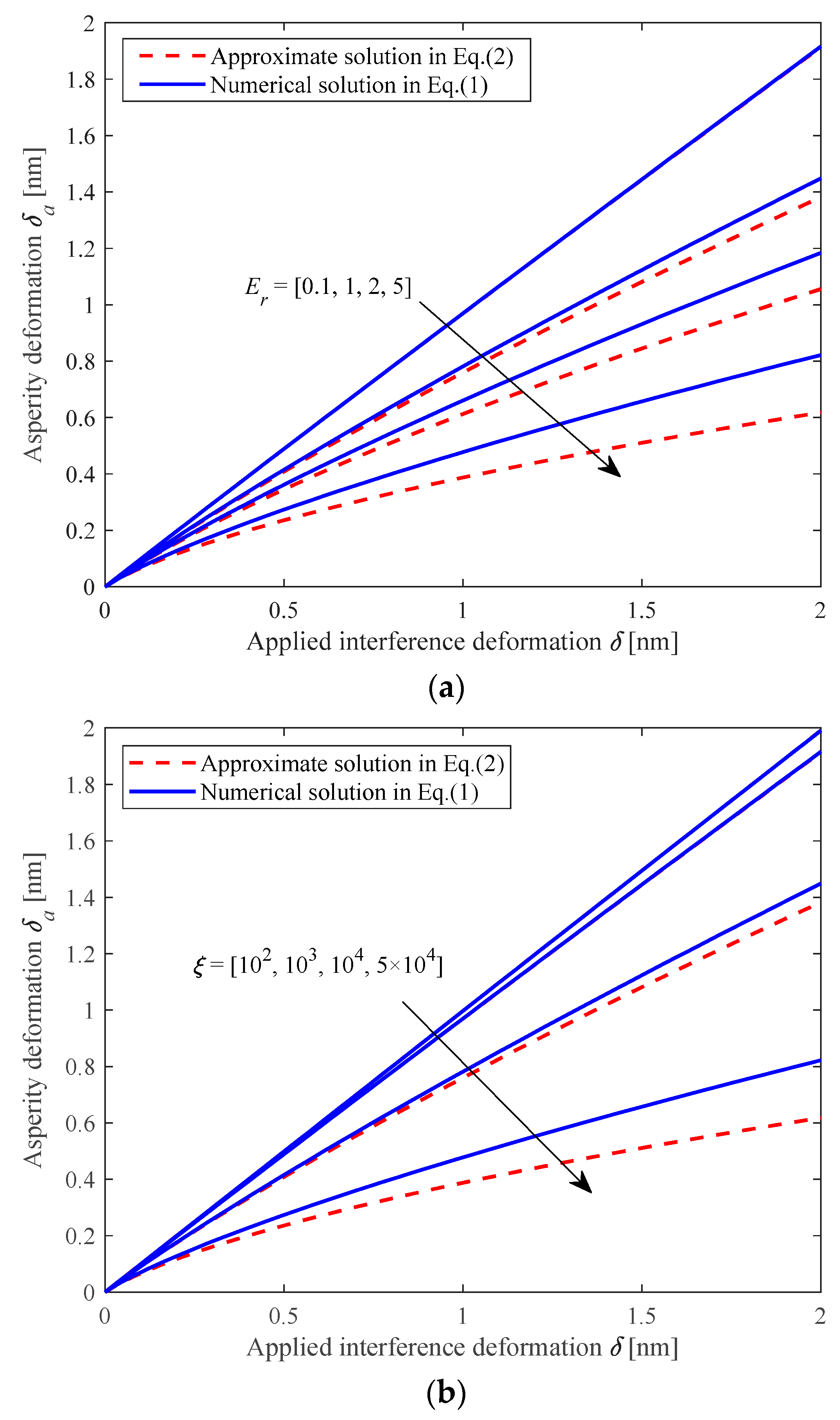
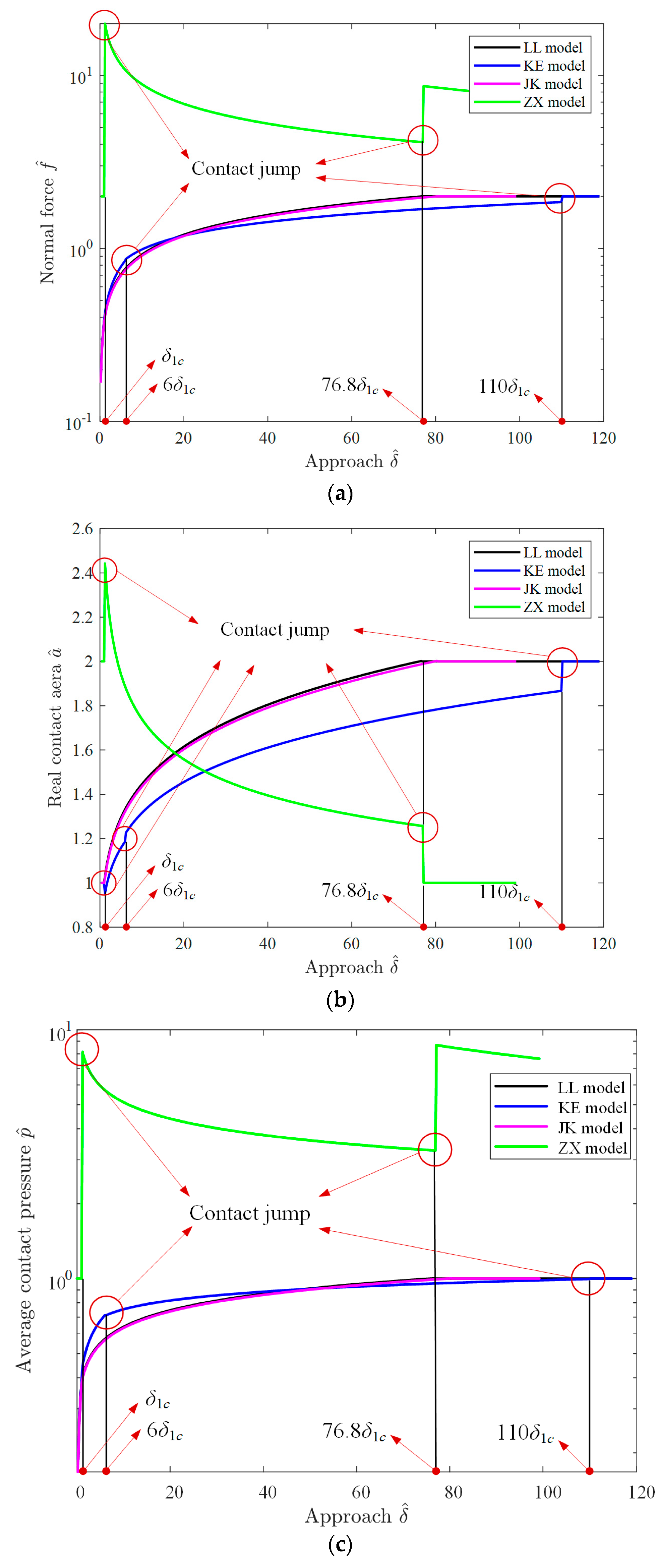
2.4. Analysis and Comparison of Different Single-Asperity Contact Models
3. Contact Model of Rough Surfaces (JK Model with Rough Surfaces)
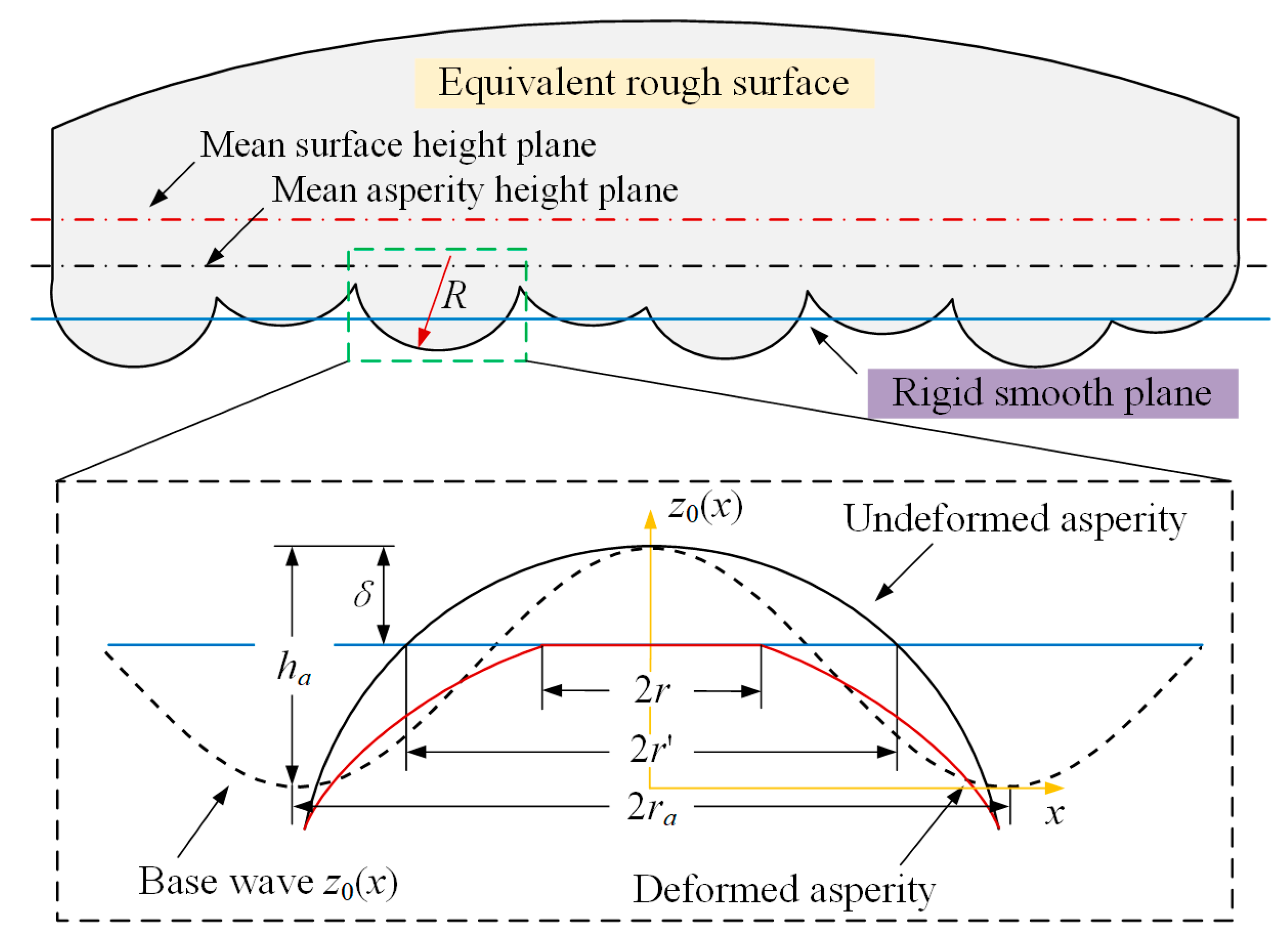
3.1. Island Distribution Function
3.2. Real Contact Area
3.3. Normal Contact Load
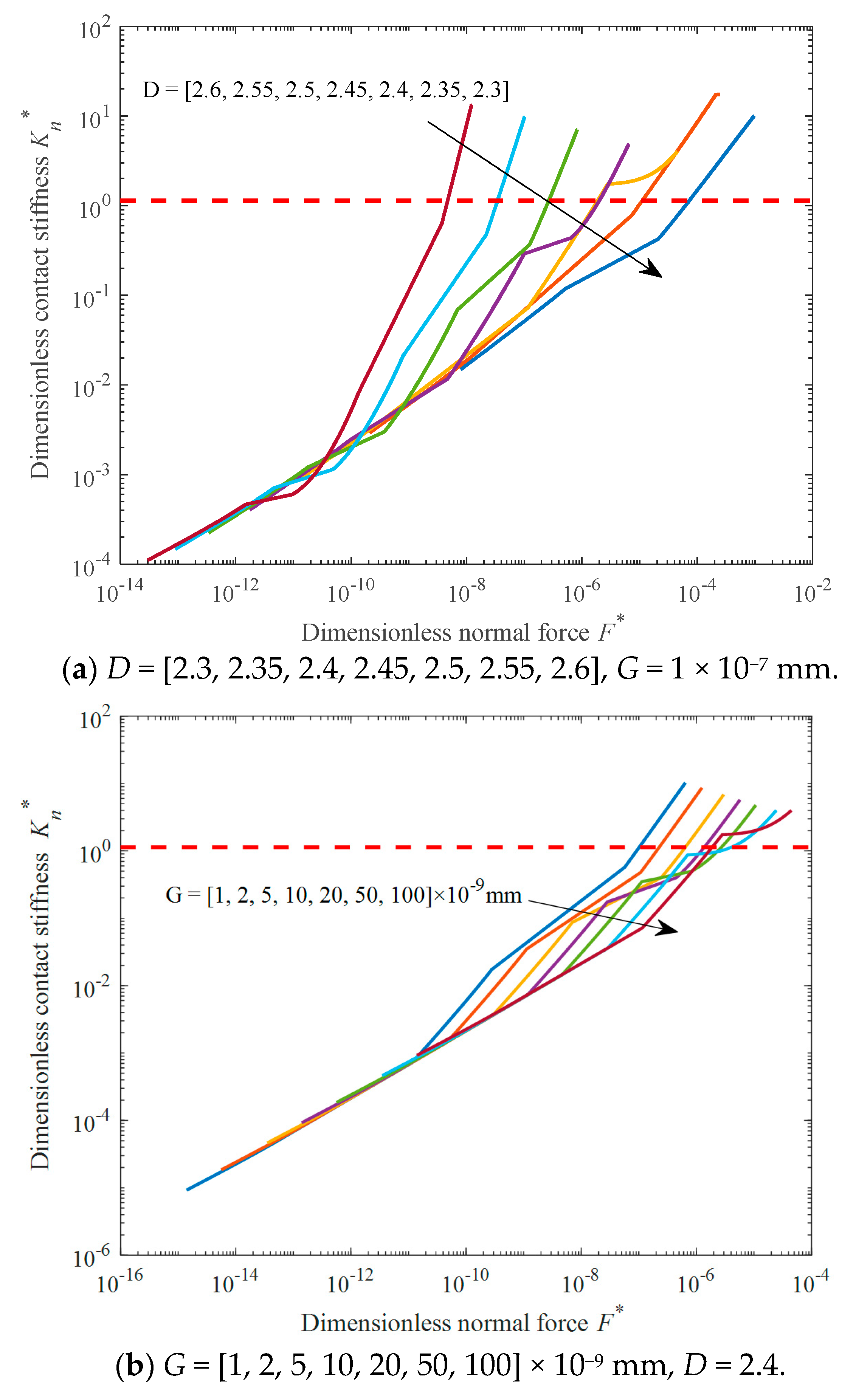
3.4. Normal Contact Stiffness
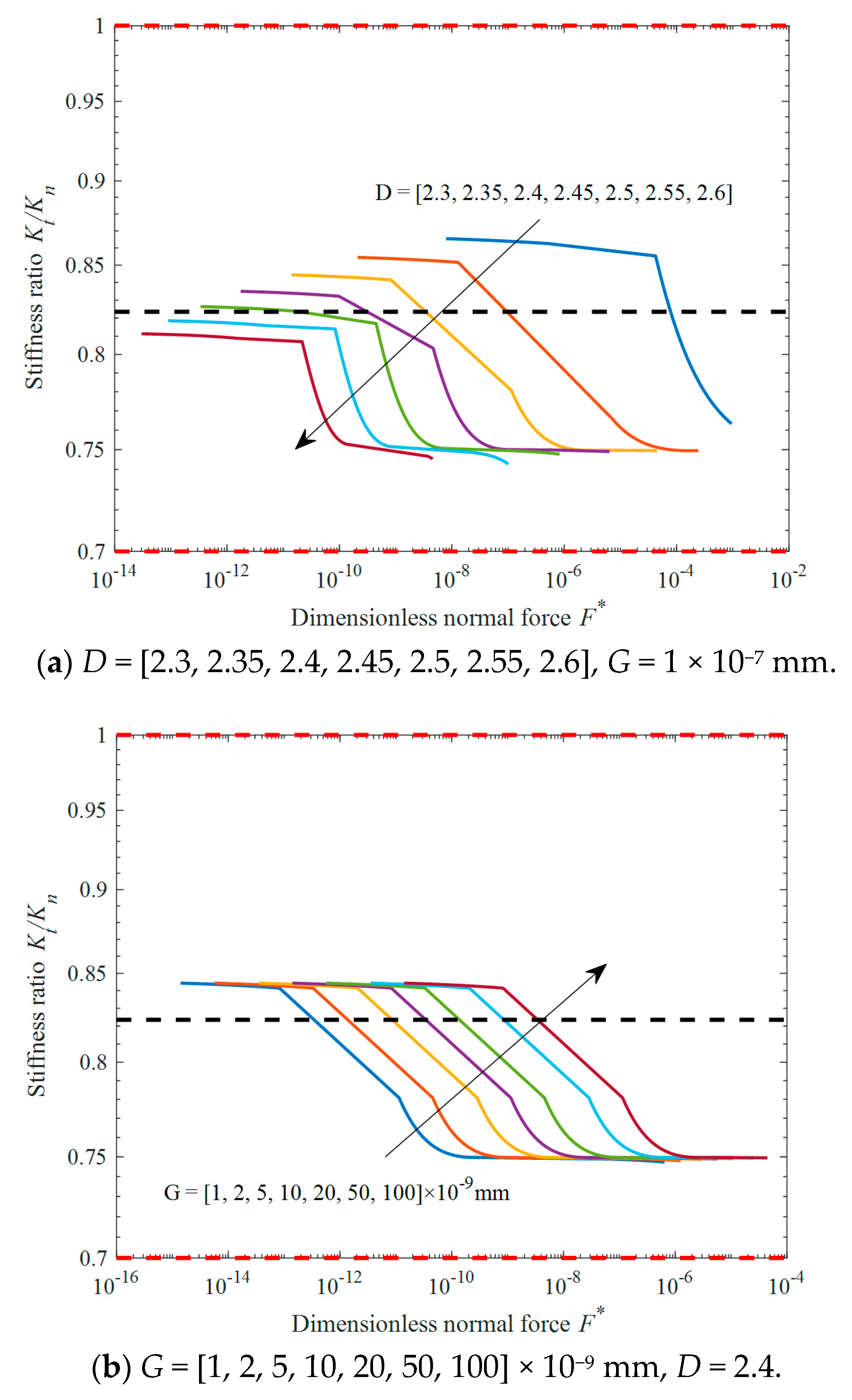
3.5. Tangential Contact Stiffness
3.6. Normal Contact Damping
3.7. Tangential Contact Damping
3.8. Numerical Analysis of JK Model on Rough Surfaces
4. Analysis and Verification
4.1. Theoretical Analysis
4.2. Experimental Validation
4.3. Comparison of the Results
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivation of Normal Contact Load
Appendix B. Derivation of Normal Contact Stiffness
Appendix C. Derivation of Tangential Contact Stiffness
Appendix D. Derivation of Normal Contact Damping
Appendix E. Derivation of Tangential Contact Damping
References
- Koshy, C.S.; Flores, P.; Lankarani, H.M. Study of the effect of contact force model on the dynamic response of mechanical systems with dry clearance joints: Computational and experimental approaches. Nonlinear Dyn. 2013, 73, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Liu, C.; Huang, G.; Qin, Z.; Zong, K.; Jiang, D. Trans-scale rough surface contact model based on molecular dynamics method: Simulation, modeling and experimental verification. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2023, 100, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Shao, Y.; Brennan, M.J. On the contact stiffness and nonlinear vibration of an elastic body with a rough surface in contact with a rigid flat surface. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2015, 49, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, F.P.; Tabor, D.; Palmer, F. The Friction and Lubrication of Solids; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Archard, J.F. Elastic deformation and the laws of friction. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1957, 243, 190–205. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Williamson, J.B.P. Contact of nominally flat surfaces. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1966, 295, 300–319. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, J.A. A simplified elliptic model of rough surface contact. Wear 2006, 261, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Tripp, J.H. The contact of two nominally flat rough surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1970, 185, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, D.J.; Archard, J.F. The properties of random surfaces of significance in their contact. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1970, 316, 97–121. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, A.W.; Gibson, R.D.; Thomas, T.R. The elastic contact of a rough surface. Wear 1975, 35, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, J.I. Comparison of models for the contact of rough surfaces. Wear 1986, 107, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, M.; Greenwood, J.A.; Paggi, M. Inclusion of “interaction” in the Greenwood and Williamson contact theory. Wear 2008, 265, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, M.; Delfine, V.; Demelio, G. A “re-vitalized” Greenwood and Williamson model of elastic contact between fractal surfaces. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2006, 54, 2569–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Vakis, A.; Liu, X.; Van der Giessen, E. Statistical model of rough surface contact accounting for size-dependent plasticity and asperity interaction. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2017, 106, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.L.; Green, I. A statistical model of elasto-plastic asperity contact between rough surfaces. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, G.; Bottiglione, F. Asperity contact theories: Do they predict linearity between contact area and load? J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2008, 56, 2555–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Wu, J.J. Surface roughness and contact: An apology. Meccanica 2001, 36, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J.R. Multiscale surfaces and Amontons’ law of friction. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 49, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müser, M.H.; Dapp, W.B.; Bugnicourt, R.; Sainsot, P.; Lesaffre, N.; Lubrecht, T.A.; Persson, B.N.J.; Harris, K.; Bennett, A.; Schulze, K.; et al. Meeting the contact-mechanics challenge. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzio, R.; Boragno, C.; Biscarini, F.; De Mongeot, F.B.; Valbusa, U. The contact mechanics of fractal surfaces. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.A.; Bhushan, B. Fractal Model of Elastic-Plastic Contact Between Rough Surfaces. J Tribol Trans Asme 1991, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Komvopoulos, K. A Fractal Theory of the Interfacial Temperature Distribution in the Slow Sliding Regime: Part II-Multiple Domains, Elastoplastic Contacts and Applications. J. Tribol. 1994, 116, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Komvopoulos, K. Contact analysis of elastic-plastic fractal surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.L.; Lin, J.F. A new microcontact model developed for variable fractal dimension, topothesy, density of asperity, and probability density function of asperity heights. J. Appl. Mech. 2007, 74, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Lan, G.; Wen, S.; Chen, Y. Tangential damping and its dissipation factor models of joint interfaces based on fractal theory with simulations. J. Tribol. 2014, 136, 011704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Cai, L.; Shi, W.; Liu, Z. Stiffness and damping model of bolted joint based on the modified three-dimensional fractal topography. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2017, 231, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, G.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Tan, W.; Li, X. A three-dimensional fractal model of the normal contact characteristics of two contacting rough surfaces. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 055023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y. A stiffness model of a joint surface with inclination based on fractal theory. Precis. Eng. 2020, 62, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, K.; Cheng, Z.; Han, G. An improved fractal model for tangential contact damping of high contact ratio gear considering friction effect. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 153, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.F.; Bower, A.F. Elastic–plastic contact of a rough surface with Weierstrass profile. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 462, 319–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, M.; Murolo, G.; Demelio, G.; Barber, J. Elastic contact stiffness and contact resistance for the Weierstrass profile. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2004, 52, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J. Elastoplastic contact between randomly rough surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 116101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, B.N.J. Theory of rubber friction and contact mechanics. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 3840–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tartaglino, U.; Persson, B.N.J. A multiscale molecular dynamics approach to contact mechanics. Eur. Phys. J. E 2006, 19, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morag, Y.; Etsion, I. Resolving the contradiction of asperities plastic to elastic mode transition in current contact models of fractal rough surfaces. Wear 2007, 262, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.L.; Lin, J.F. A modified fractal microcontact model developed for asperity heights with variable morphology parameters. Wear 2010, 268, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Huang, X. A complete contact model of a fractal rough surface. Wear 2014, 309, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afferrante, L.; Carbone, G.; Demelio, G. Interacting and coalescing Hertzian asperities: A new multiasperity contact model. Wear 2012, 278, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.L.; Streator, J.L. A multi-scale model for contact between rough surfaces. Wear 2006, 261, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedecke, A.; Jackson, R.L.; Mock, R. A fractal expansion of a three dimensional elastic–plastic multi-scale rough surface contact model. Tribol. Int. 2013, 59, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wu, S. A revised contact stiffness model of rough curved surfaces based on the length scale. Tribol. Int. 2021, 164, 107206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, S. Multi-stage contact model between fractal rough surfaces based on multi-scale asperity deformation. Appl. Math. Model. 2022, 109, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, L. A fractal contact model of rough surfaces considering detailed multi-scale effects. Tribol. Int. 2022, 176, 107920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ma, B.; Zhu, Y. A magnification-based multi-asperity (MBMA) model of rough contact without adhesion. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 133, 103724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, C.D.; Katta, R.R.; Polycarpou, A.A. Improved Elastic Contact Model Accounting for Asperity and Bulk Substrate Deformation. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 35, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Liu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, C. An estimation method of fractal parameters on rough surfaces based on the exact spectral moment using artificial neural network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 161, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Pharr, G.M. An improved relation for the effective elastic compliance of a film/substrate system during indentation by a flat cylindrical punch. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, L.; Etsion, I. Elastic-plastic contact analysis of a sphere and a rigid flat. J. Appl. Mech. 2002, 69, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.P.; Lin, J.F. An elastoplastic microasperity contact model for metallic materials. J. Trib. 2005, 127, 666–672. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature. Am. J. Phys. 1983, 51, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Kligerman, Y.; Kadin, Y. Unloading of an elastic–plastic loaded spherical contact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2005, 42, 3716–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B. On the Electric Contact Resistance. Tribol. Lett. 2022, 70, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharr, G.M.; Oliver, W.C.; Brotzen, F.R. On the generality of the relationship among contact stiffness, contact area, and elastic modulus during indentation. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindlin, R.D. Compliance of Elastic Bodies in Contact. J. Appl. Mech. 1949, 16, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putignano, C.; Ciavarella, M.; Barber, J.R. Frictional energy dissipation in contact of nominally flat rough surfaces under harmonically varying loads. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2011, 59, 2442–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Polycarpou, A.A. Investigation of Contact Stiffness and Contact Damping for Magnetic Storage Head-Disk Interfaces. J. Tribol. 2008, 130, 021901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
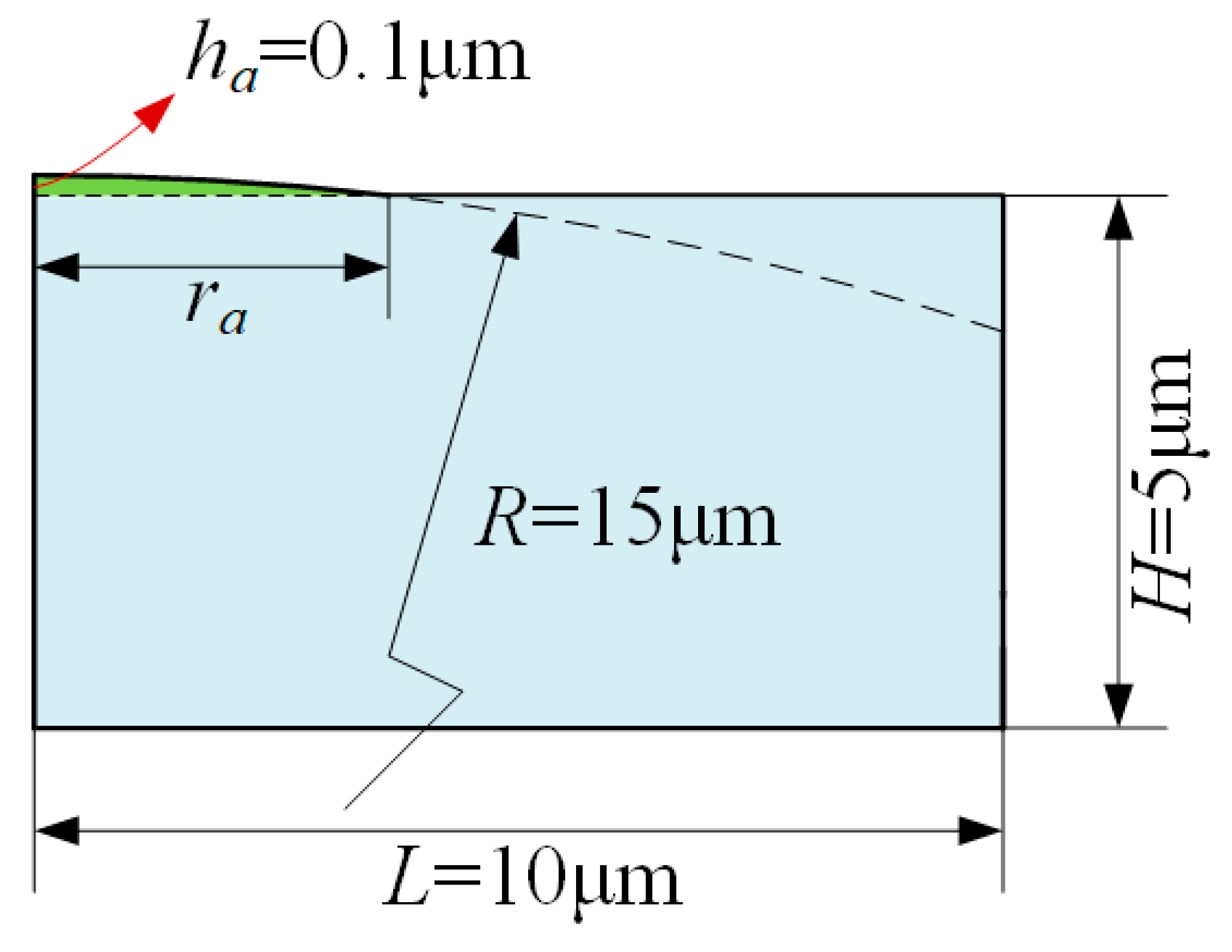




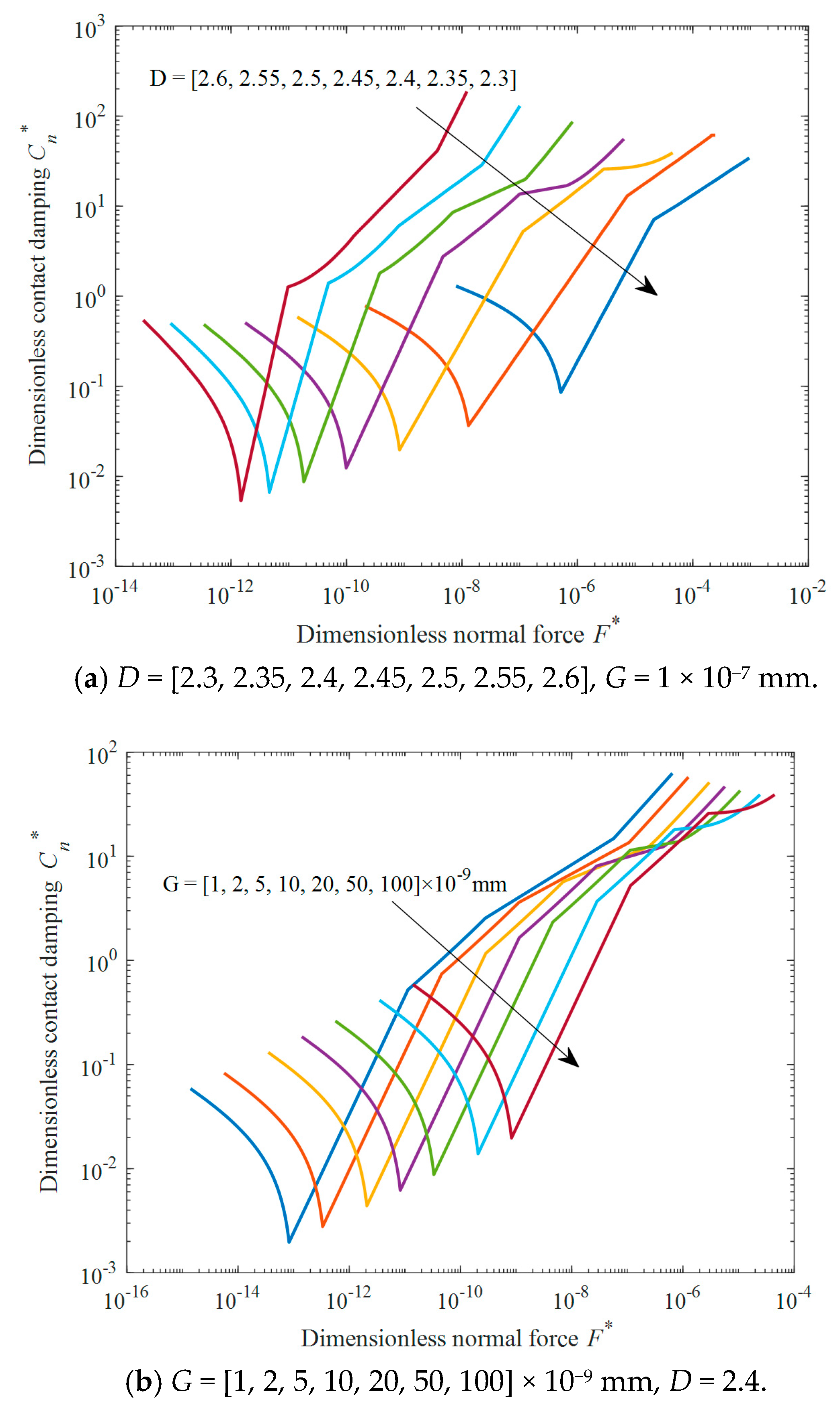


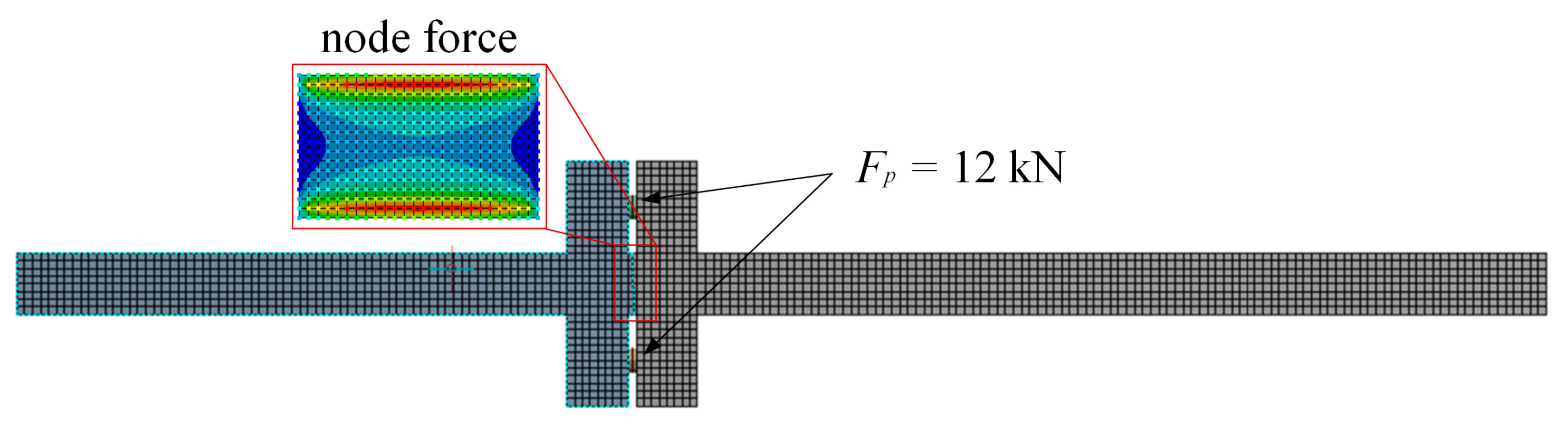
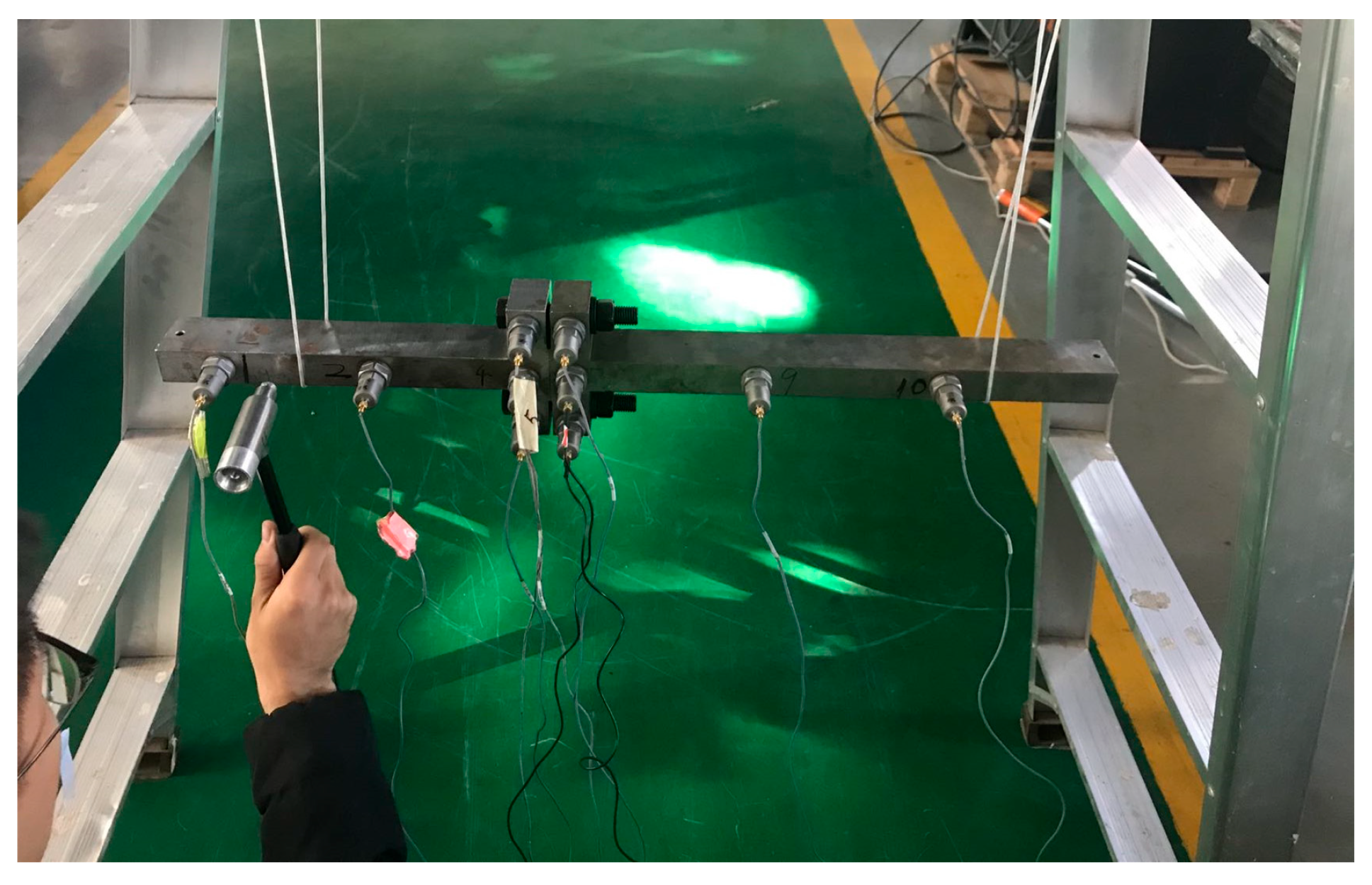

| No | R [μm] | ha [nm] | ra [μm] | D | G [×10−5 mm] | ξ [mm−0.5] | Ea [Gpa] | Eb [Gpa] | Er | FEA | JK Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F [×10−3 N] | A [×10−6 mm2] | F [×10−3 N] | A [×10−6 mm2] | ||||||||||
| #1 | 15 | 100 | 1.729 | 2.996 | 15.46 | 106.24 | 100 | 100 | 1 | 0.41 | 0.589 | 0.405 | 0.646 |
| 20 | 750 | 5.426 | 2.420 | 5.256 | 39.10 | 100 | 100 | 1 | 7.43 | 8.01 | 8.27 | 8.94 | |
| 40 | 3000 | 15.20 | 2.274 | 2.920 | 19.74 | 100 | 100 | 1 | 64.6 | 74.1 | 75.71 | 76.17 | |
| 80 | 6000 | 30.40 | 2.238 | 2.055 | 13.96 | 100 | 100 | 1 | 257.7 | 296.3 | 302.86 | 304.69 | |
| #2 | 15 | 100 | 1.729 | 2.996 | 15.46 | 106.24 | 150 | 100 | 1.5 | 0.43 | 0.589 | 0.402 | 0.629 |
| 20 | 750 | 5.426 | 2.420 | 5.256 | 39.10 | 150 | 100 | 1.5 | 7.70 | 8.01 | 8.70 | 9.05 | |
| 40 | 3000 | 15.20 | 2.274 | 2.920 | 19.74 | 150 | 100 | 1.5 | 70.1 | 74.2 | 75.07 | 75.52 | |
| 80 | 6000 | 30.40 | 2.238 | 2.055 | 13.96 | 150 | 100 | 1.5 | 279.4 | 296.6 | 300.77 | 302.59 | |
| #3 | 15 | 100 | 1.729 | 2.996 | 15.46 | 106.24 | 200 | 100 | 2 | 0.45 | 0.590 | 0.393 | 0.611 |
| 20 | 750 | 5.426 | 2.420 | 5.256 | 39.10 | 200 | 100 | 2 | 7.82 | 8.01 | 8.92 | 9.07 | |
| 40 | 3000 | 15.20 | 2.274 | 2.920 | 19.74 | 200 | 100 | 2 | 72.6 | 74.2 | 74.47 | 74.92 | |
| 80 | 6000 | 30.40 | 2.238 | 2.055 | 13.96 | 200 | 100 | 2 | 290.0 | 296.8 | 298.84 | 300.65 | |
| Properties | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density ρ | 7800 | Kg/m3 |
| elastic modulus E | 2.0 × 105 | MPa |
| yield strength σs | 355 | MPa |
| Poisson’s ratio v | 0.3 | |
| hardness H | 994 | MPa |
| static friction coefficient μ | 0.25 |
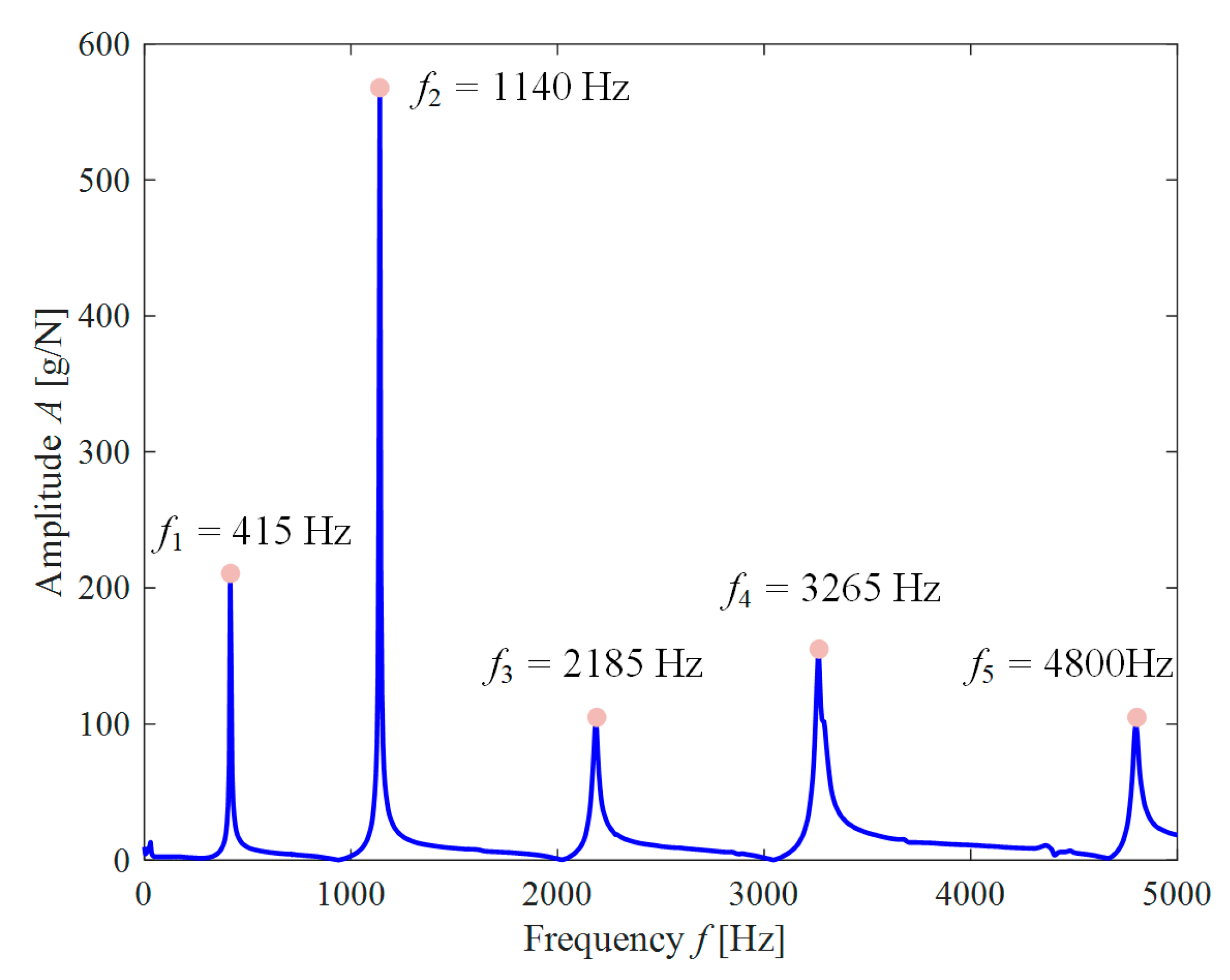
| Fp | Method | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 kN | JK model | 422.9 | 1153.2 | 2207.6 | 3307.7 | 4900.6 |
| Experiment 1 | 406 | 1126 | 2145 | 3249 | 4700 | |
| Error 1 | 3.89% | 2.35% | 2.81% | 1.76% | 4.09% | |
| 8 kN | JK model | 423.6 | 1154.1 | 2208.8 | 3311.7 | 4903.9 |
| Experiment 2 | 410 | 1135 | 2175 | 3285 | 4725 | |
| Error 2 | 3.21% | 1.65% | 1.53% | 0.81% | 3.65% | |
| 12 kN | JK model | 423.9 | 1154.6 | 2209.3 | 3313.78 | 4905.0 |
| Experiment 3 | 415 | 1140 | 2185 | 3265 | 4800 | |
| Error 3 | 2.10% | 1.26% | 1.10% | 1.47% | 2.14% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, K. A Closure Contact Model of Self-Affine Rough Surfaces Considering Small-, Meso-, and Large-Scale Stage Without Adhesive. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8100611
Zhang T, Wu Y, Liu X, Jiang K. A Closure Contact Model of Self-Affine Rough Surfaces Considering Small-, Meso-, and Large-Scale Stage Without Adhesive. Fractal and Fractional. 2024; 8(10):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8100611
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tao, Yiming Wu, Xian Liu, and Kai Jiang. 2024. "A Closure Contact Model of Self-Affine Rough Surfaces Considering Small-, Meso-, and Large-Scale Stage Without Adhesive" Fractal and Fractional 8, no. 10: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8100611
APA StyleZhang, T., Wu, Y., Liu, X., & Jiang, K. (2024). A Closure Contact Model of Self-Affine Rough Surfaces Considering Small-, Meso-, and Large-Scale Stage Without Adhesive. Fractal and Fractional, 8(10), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8100611





