A Variational Level Set Image Segmentation Method via Fractional Differentiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. The LIF Model
2.2. Texture Features
2.3. Structural Features
3. The Proposed Model
3.1. Energy Functional of the NFD-LIF Model
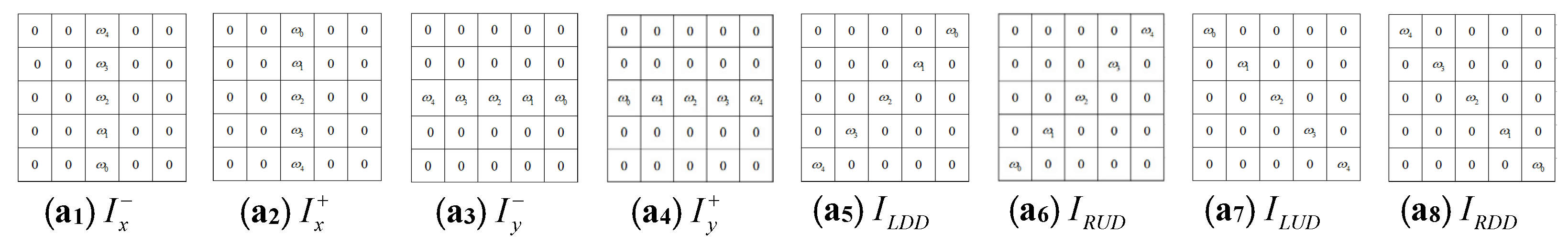
3.2. Energy Functional Solution
3.3. Regular Term Constraints
3.4. Validation of the NFD-LIF Model
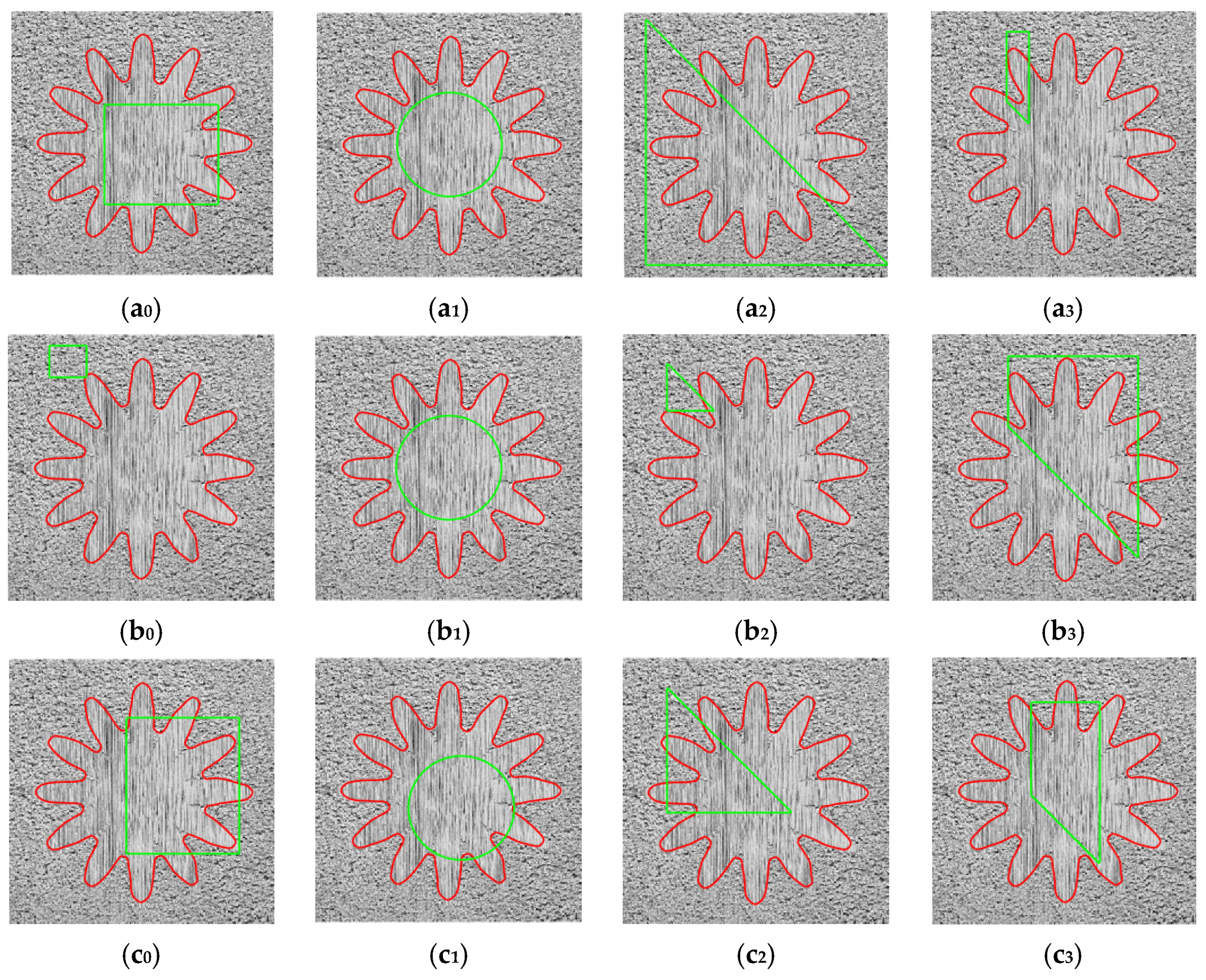
3.4.1. Verifying the Robustness of NFD-LIF Model to the Initial Contours
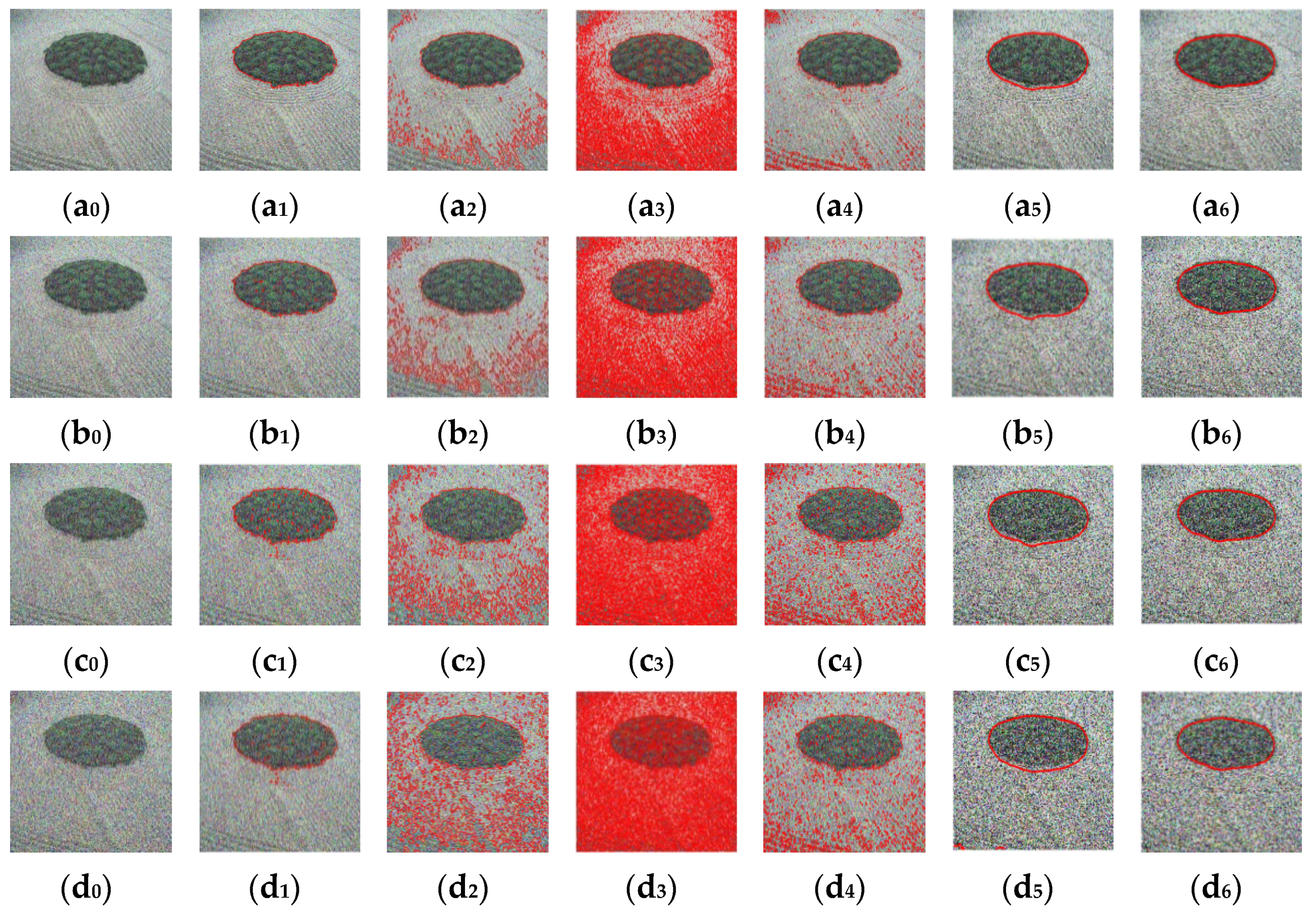
3.4.2. Verifying the Robustness of NFD-LIF Model to Noise
4. Comparative Experimental Results and Analysis
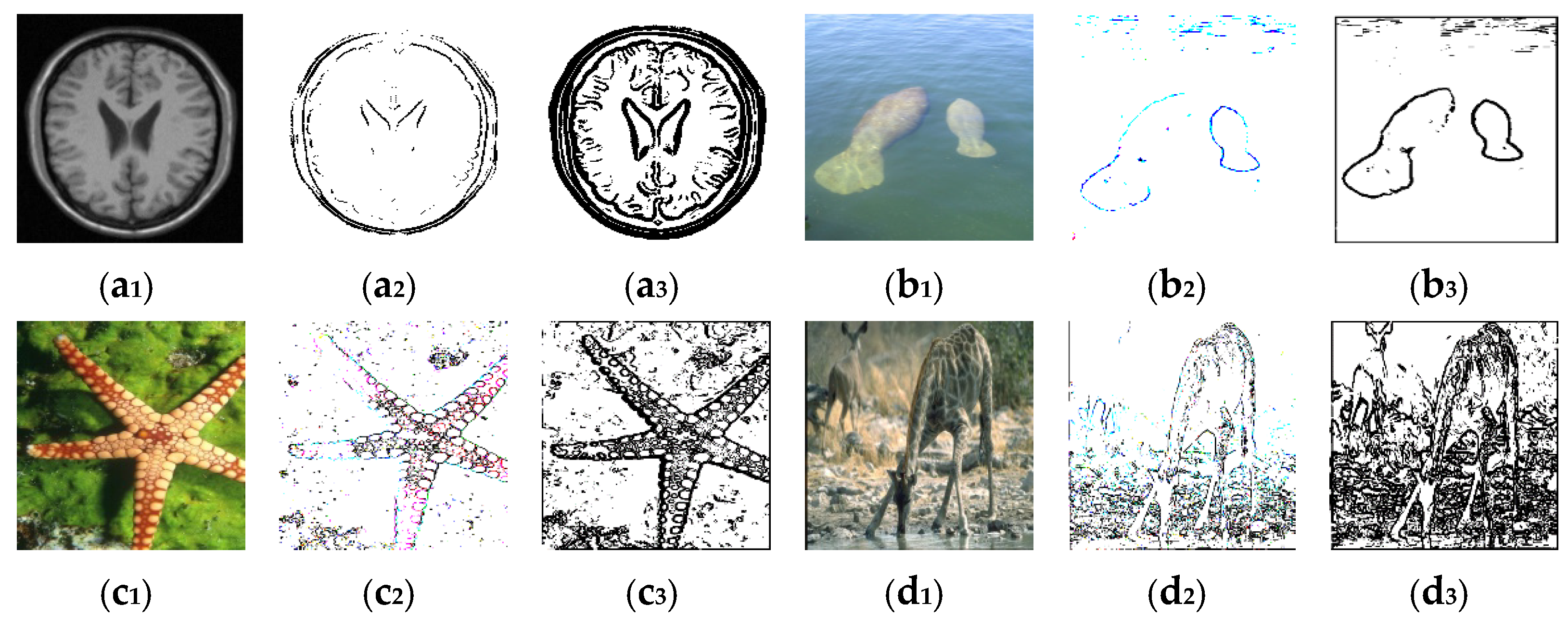
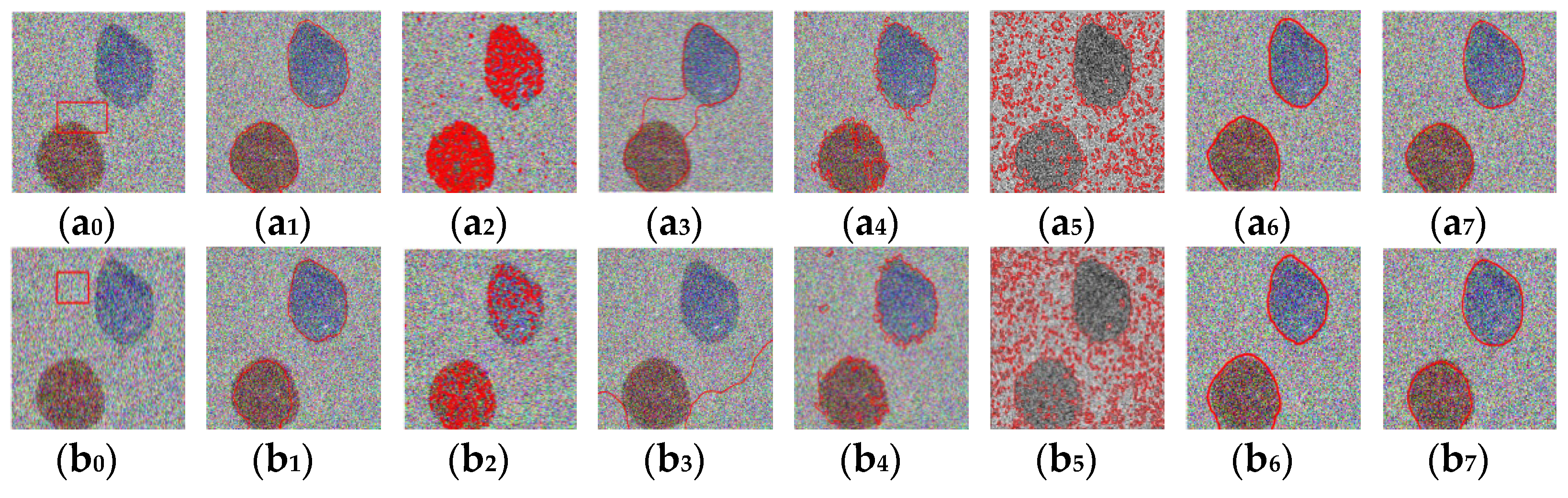
4.1. Segmentation Results of the Model for Structurally Information-Rich Images
4.2. Segmentation Results of the Model for Texture Information-Rich Images
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, J.; He, K.; Sun, J. Instance-aware semantic segmentation via multi-task network cascades. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3150–3158. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected CRFs. Comput. Sci. 2014, 4, 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 851–859. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Williams, B.M.; Vallabhaneni, S.R.; Czanner, G.; Zheng, Y. Learning active contour models for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 1–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, D.; Ying, Z.; Amjad, A.; Jiao, F.X.; Thill, D.M.S.; Li, X.A. Automatic contour refinement for deep learning auto-segmentation of complex organs in MRI-guided adaptive radiotherapy. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 7, 100968. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Yeh, W.C.; Hao, Z.; Yang, Z. A cooperative honey bee mating algorithm and its application in multi-threshold image segmentation. Inf. Sci. 2016, 369, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, R.; Pang, M. Lung segmentation based on random forest and multi-scale edge detection. IET Image Processing 2019, 13, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.M.A.; Jose, C.; Supriya, M.H. Hardware realization of canny edge detection algorithm for underwater image segmentation using field programmable gate arrays. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2017, 12, 2536–2550. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Liu, W.; Xing, W. A weighted edge-based level set method based on multi-local statistical information for noisy image segmentation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent 2019, 59, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.H.; Shen, H.B. Saliency driven region-edge-based top down level set evolution reveals the asynchronous focus in image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 80, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.W.; Hasan, A.M.; Jalab, H.A. A new deformable model based on fractional wright energy function for tumor segmentation of volumetric brain MRI scans. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 163, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, P.; Guo, D.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Dan, G. Liver MRI segmentation with edge preserved intensity inhomogeneity correction. Signal Image Video Process 2018, 12, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, L.; Verma, K.; Singh, B.K. Hybrid segmentation method based on multi-scale Gaussian kernel fuzzy clustering with spatial bias correction and region-scalable fitting for breast US images. IET Comput. Vis 2018, 12, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, G.; Dong, B.; Lei, Y. A level set method based on additive bias correction for image segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 185, 115633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, M.; Witkin, A.; Terzopoulos, D. Snakes: Active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1988, 1, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cselles, V.; Kimmel, R.; Sapiro, G. Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1997, 22, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.F.; Vese, L.A. Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Processing 2001, 10, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Kao, C.Y.; Gore, J.C.; Ding, Z.H. Minimization of region-scalable fitting energy for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Processing 2008, 17, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Song, H.; Zhang, L. Active contours driven by local image fitting energy. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; In Cho, S. Spatial color histogram-based image segmentation using texture-aware region merging. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 24573–24600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; Jia, W.; Wang, X.F.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, R.X.; Luo, Y.T.; Xue, F.; Lu, J.T. An intensity-texture model based level set method for image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fan, S.; Ning, X.; Liao, L. An efficient level set model with self-similarity for texture segmentation. Neurocomputing 2017, 266, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subudhi, P.; Mukhopadhyay, S. A novel texture segmentation method based on co-occurrence energy-driven parametric active contour model. Signal Image Video Process 2018, 12, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, D.; Cheriyadat, A.M. Factorization-based texture segmentation. Image Processing IEEE Trans. 2015, 24, 3488–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Chen, H.; Zheng, S.; Fang, B. A factorization based active contour model for texture segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 4309–4313. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Wang, H.; Wen, C.; Xu, L. Texture image segmentation using statistical active contours. J. Electron. Imaging 2018, 27, 051211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, Z.H.; Kim, D.G.; Hussain, M.; Sajawal, R.M.B.K. Low-rank estimation for image denoising using fractional-order gradient-based similarity measure. Circuits Syst. Signal Processing 2021, 40, 4946–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbaghi, F.K.; Rezghi, M.; Eslahchi, M.R. A hybrid image denoising method based on integer and fractional-order total variation. Iran. J. Sci. Technology. Trans. A Sci. 2020, 44, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Zhang, F.; Li, B.Z.; Tao, R. Fractional domain varying-order differential denoising method. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ullah, A.; Khan, S.; Ali, M.; Ali, J. A novel fractional-order variational approach for image restoration based on fuzzy membership degrees. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 43574–43600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yu, J.; Yan, H.; Mou, J. A new image encryption scheme based on fractional-order hyperchaotic system and multiple image fusion. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Yan, H.; He, H. Multi-focus image fusion based on fractional-order derivative and intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2020, 21, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zou, Q.H.; Chen, W.S.; Li, Y. A fast region-based segmentation model with Gaussian kernel of fractional order. Adv. Math. Phys. 2013, 2013, 501628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y. A new active contour medical image segmentation method based on fractional varying-order differential. Mathematics 2022, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Li, B.Z. A novel active contour model for noisy image segmentation based on adaptive fractional order differentiation. IEEE Trans. Image Processing 2020, 29, 9520–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Wang, R. Fractional differentiation-based active contour model driven by local intensity fitting energy. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 6098021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbelaez, P.; Maire, M.; Fowlkes, C.; Malik, J. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.P.; Srivastava, H.M. Fractional calculus operators and their applications involving power functions and summation of series. Appl. Math. Comput. 1997, 81, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.F.; Zhou, J.L. A novel approach for multi-scale texture segmentation based on fractional differential. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2011, 88, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritpal, S.; Surya, S.B. A quantum-clustering optimization method for COVID-19 CT scan image segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 185, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, B. Adaptive segmentation model for liver CT images based on neural network and level set method. Neurocomputing 2021, 453, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saman, S.; Narayanan, S.J. Active contour model driven by optimized energy functionals for MR brain tumor segmentation with intensity inhomogeneity correction. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 21925–21954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
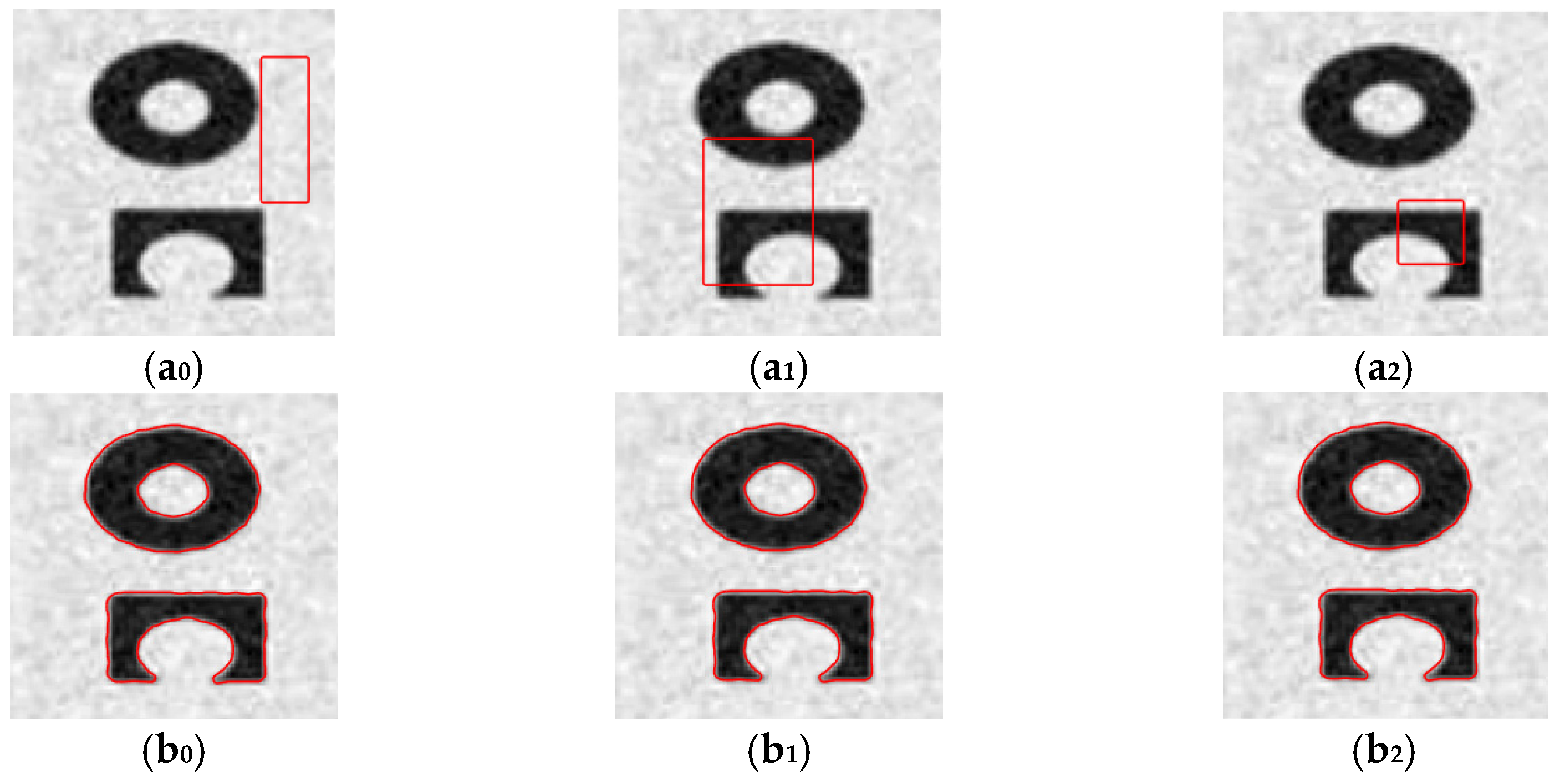



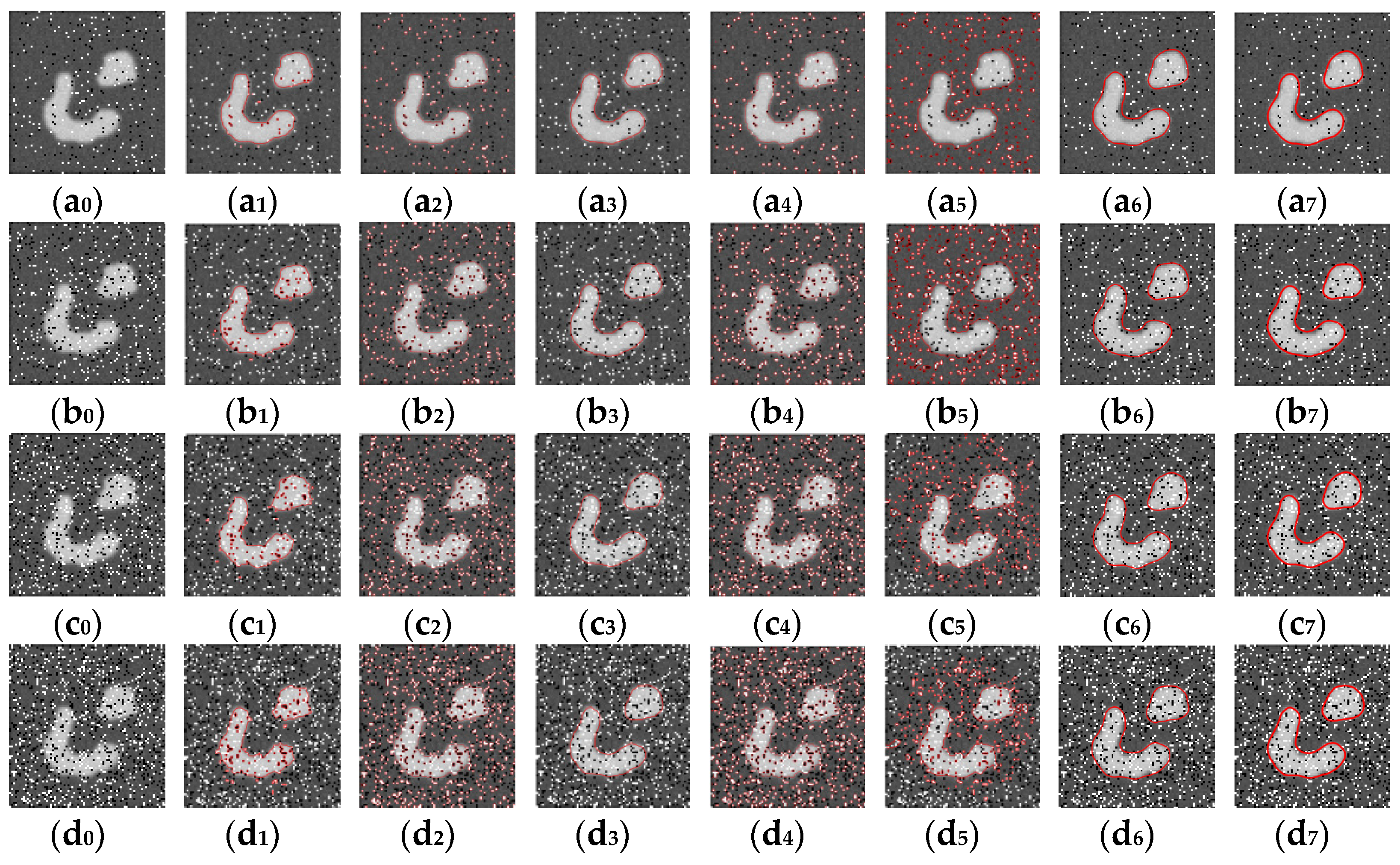

| Test Image | DSC | Precision | Recall | JSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 6(b0) | 0.9804 | 0.9701 | 0.9908 | 0.9615 |
| Figure 6(b1) | 0.9850 | 0.9721 | 0.9982 | 0.9704 |
| Figure 6(b2) | 0.9916 | 0.9870 | 0.9963 | 0.9834 |
| Figure 6(b3) | 0.9787 | 0.9856 | 0.9718 | 0.9582 |
| Figure 6(b4) | 0.9803 | 0.9636 | 0.9978 | 0.9614 |
| Figure 6(b5) | 0.9775 | 0.9890 | 0.9662 | 0.9559 |
| Model | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.13 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (s) | Iterations | Time (s) | Iterations | Time (s) | Iterations | Time (s) | Iterations | |
| LIC | 2.763 | 50 | 4.103 | 70 | 5.393 | 100 | 7.792 | 150 |
| LBF | 3.107 | 70 | 3.731 | 90 | 5.122 | 120 | 8.788 | 200 |
| Model from [16] | 0.934 | 50 | 1.142 | 70 | 1.417 | 100 | 1.782 | 150 |
| Model from [27] | 4.228 | 60 | 5.134 | 60 | 6.184 | 100 | 6.201 | 100 |
| NFD-LIF | 2.580 | 17 | 2.924 | 25 | 3.165 | 30 | 3.435 | 30 |
| Model | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.20 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (s) | Iterations | Time (s) | Iterations | Time (s) | Iterations | Time (s) | Iterations | |
| LBF | 34.074 | 40 | 41.697 | 50 | 59.556 | 70 | 60.451 | 70 |
| CV | 2.408 | 80 | 2.728 | 100 | 3.466 | 150 | 5.565 | 300 |
| Model from [16] | 1.018 | 50 | 1.199 | 80 | 1.433 | 120 | 1.129 | 150 |
| LIF | 4.682 | 600 | 4.987 | 700 | 5.082 | 700 | 5.875 | 800 |
| LSACM | 5.438 | 300 | 6.808 | 400 | 8.728 | 600 | 11.139 | 800 |
| Model from [27] | 14.507 | 290 | 14.545 | 300 | 14.512 | 300 | 16.479 | 350 |
| NFD-LIF | 2.748 | 17 | 3.183 | 20 | 3.260 | 25 | 3.272 | 25 |
| Model | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (s) | Iterations | Time (s) | Iterations | Time (s) | Iterations | Time (s) | Iterations | |
| LIC | 84.187 | 200 | 93.161 | 220 | 109.747 | 260 | 168.315 | 400 |
| LIF | 269.597 | 300 | 371.972 | 400 | 469.276 | 500 | 683.124 | 700 |
| ACM-LPF | 247.853 | 200 | 251.804 | 200 | 261.478 | 300 | 273.04 | 400 |
| LSACM | 405.048 | 300 | 526.808 | 400 | 787.107 | 600 | 1057.725 | 800 |
| Model from [27] | 11.450 | 70 | 11.938 | 70 | 12.561 | 70 | 21.579 | 150 |
| NFD-LIF | 5.89 | 30 | 6.628 | 30 | 7.601 | 30 | 9.780 | 60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, R.; Peng, W. A Variational Level Set Image Segmentation Method via Fractional Differentiation. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6090462
Liu X, Liu G, Wang Y, Li G, Zhang R, Peng W. A Variational Level Set Image Segmentation Method via Fractional Differentiation. Fractal and Fractional. 2022; 6(9):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6090462
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiangguo, Guojun Liu, Yazhen Wang, Gengsheng Li, Rui Zhang, and Weicai Peng. 2022. "A Variational Level Set Image Segmentation Method via Fractional Differentiation" Fractal and Fractional 6, no. 9: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6090462
APA StyleLiu, X., Liu, G., Wang, Y., Li, G., Zhang, R., & Peng, W. (2022). A Variational Level Set Image Segmentation Method via Fractional Differentiation. Fractal and Fractional, 6(9), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6090462






