Investigation of Novel Piecewise Fractional Mathematical Model for COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
3. Piecewise Existence and Uniqueness of Solution
- (C1)
- ∃; ∀ we have
- (C2)
- ∃&;
Stability Analysis
- (H1)
- For each and a constant , we obtain
- (H2)
- For each and constant , we obtain
4. Numerical Scheme
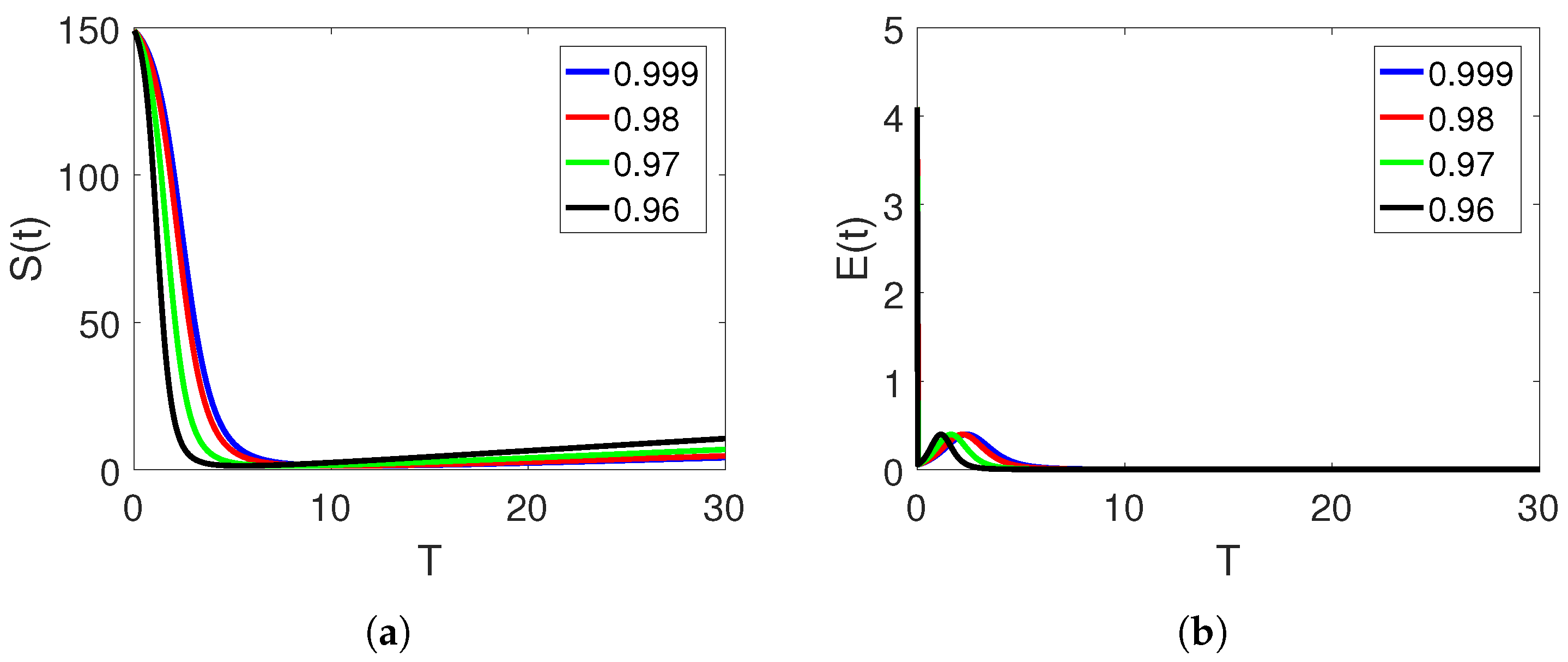
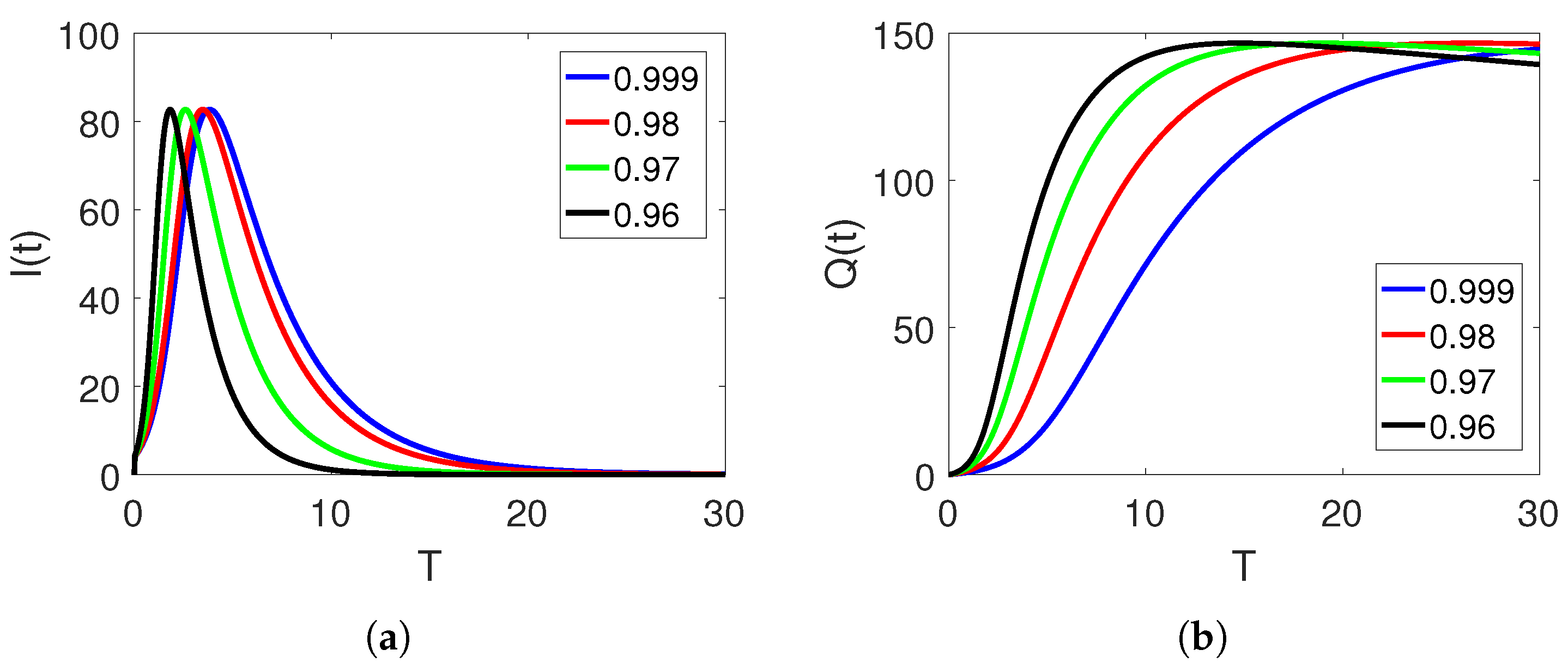
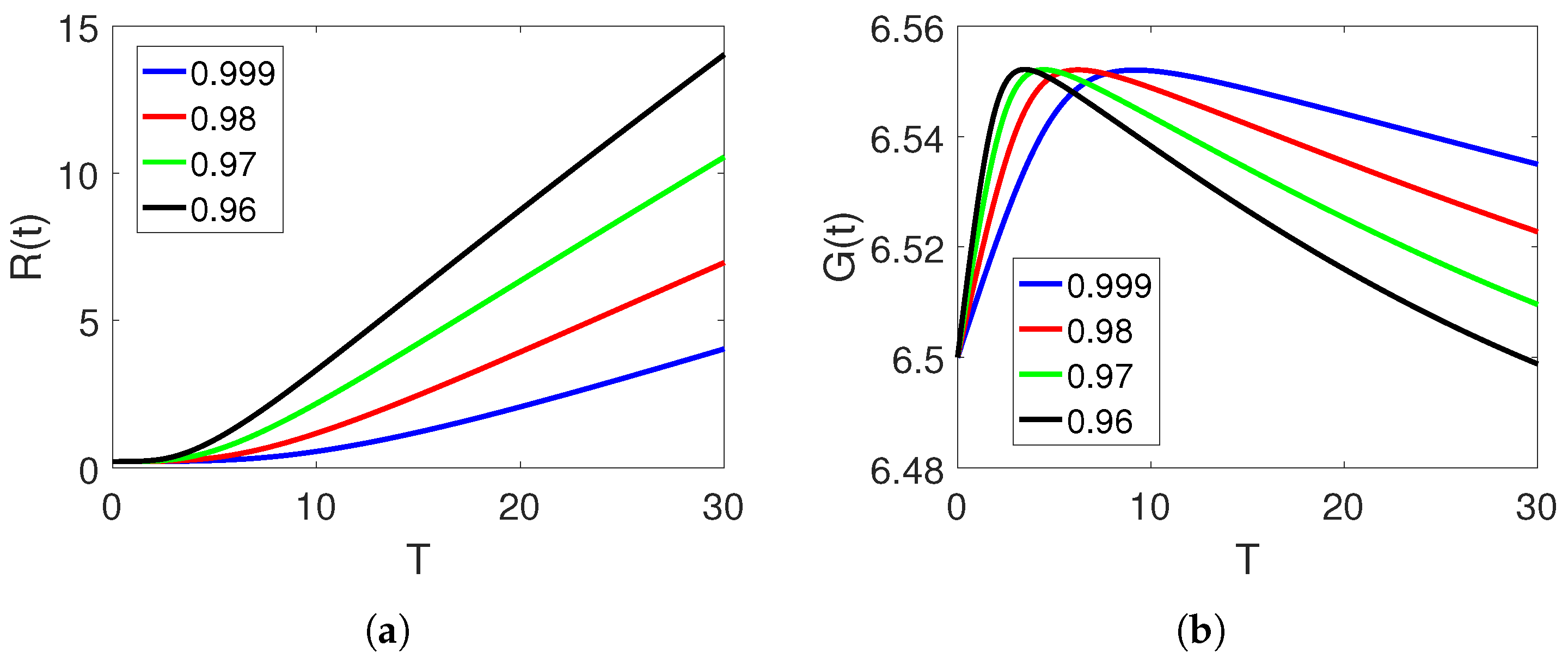
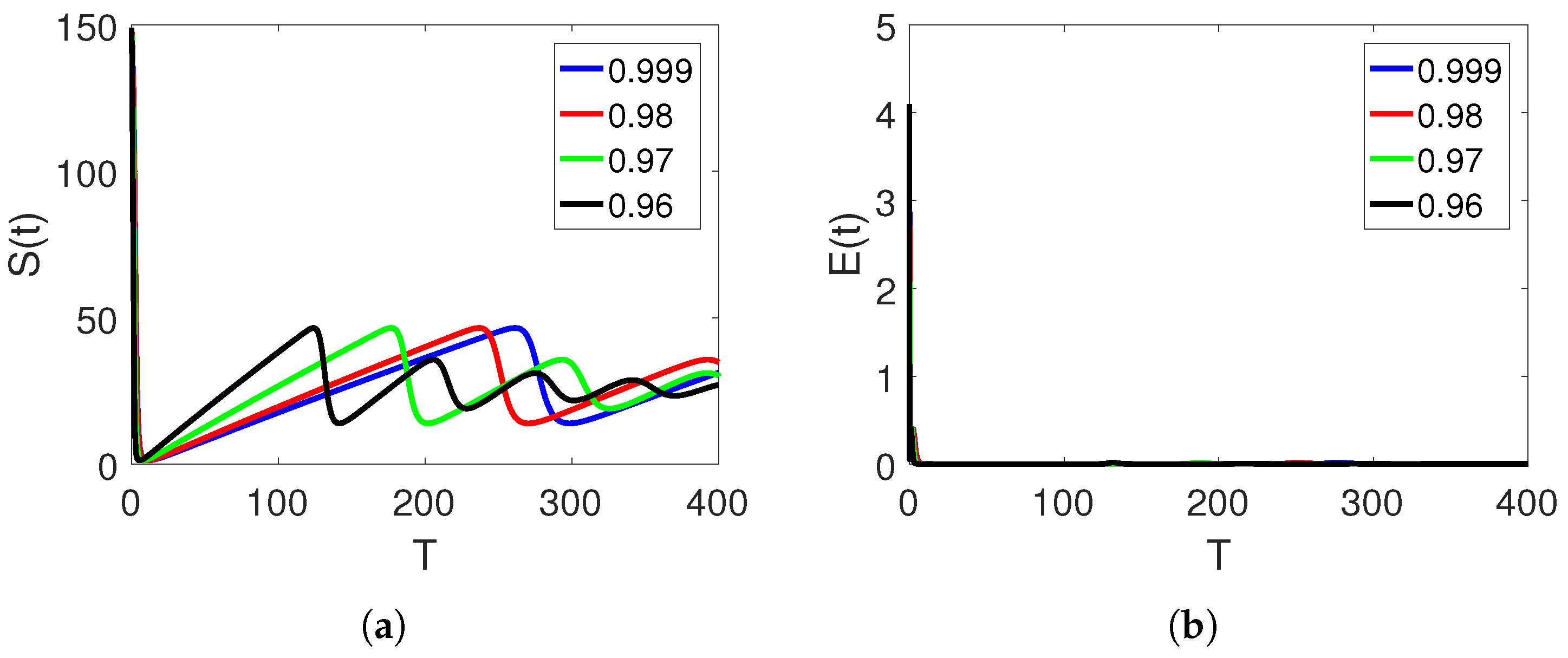
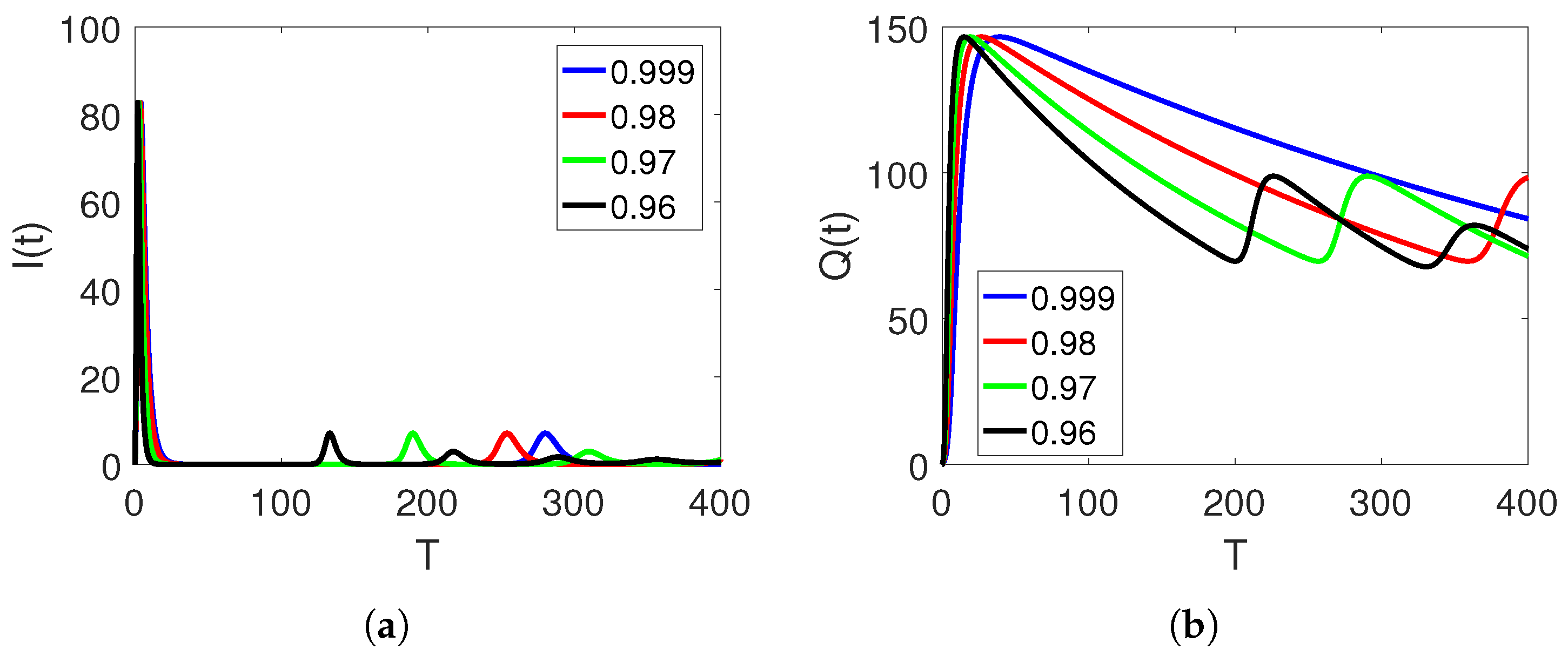
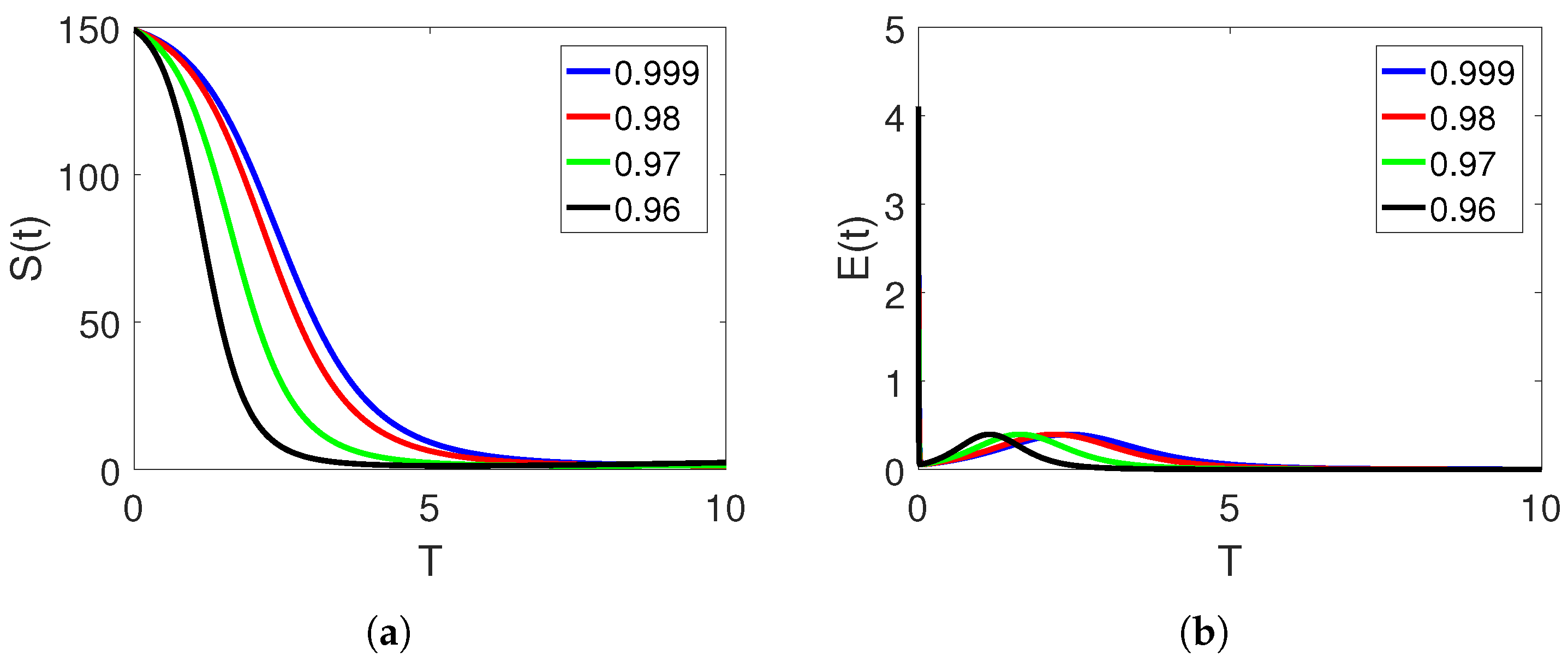
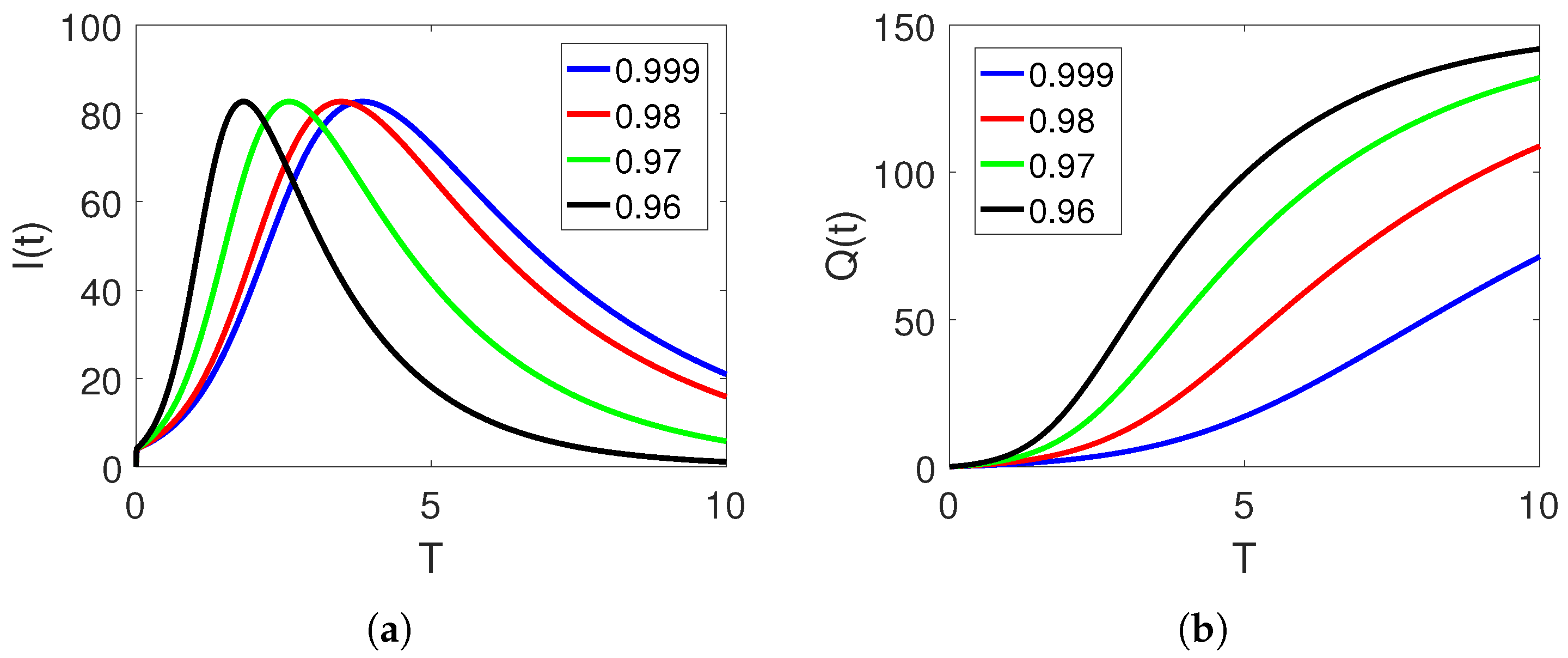
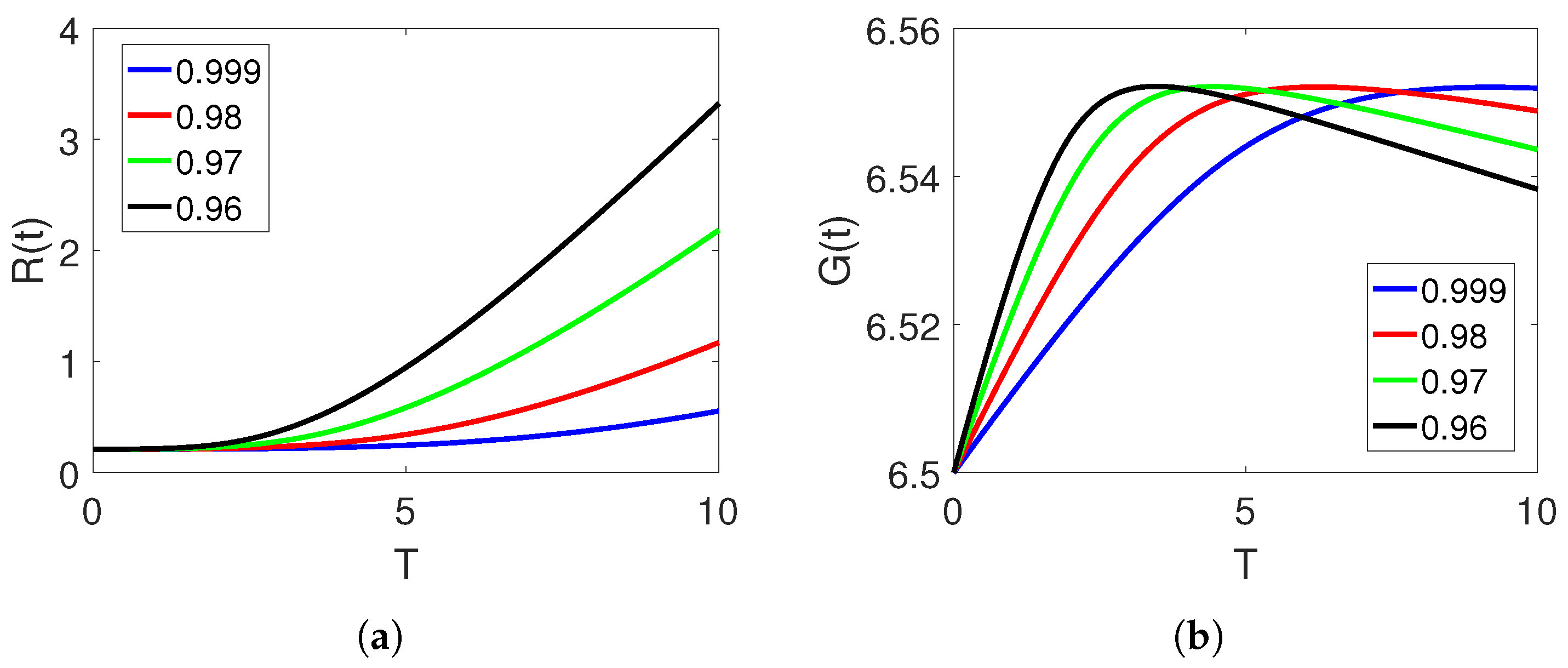
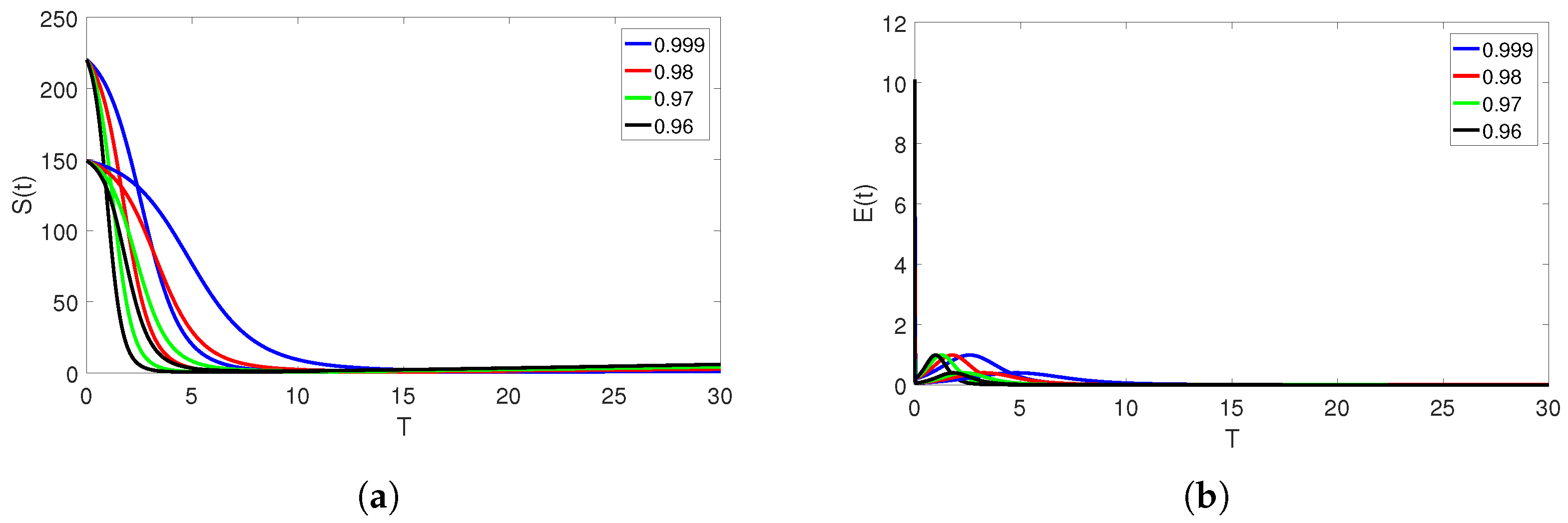
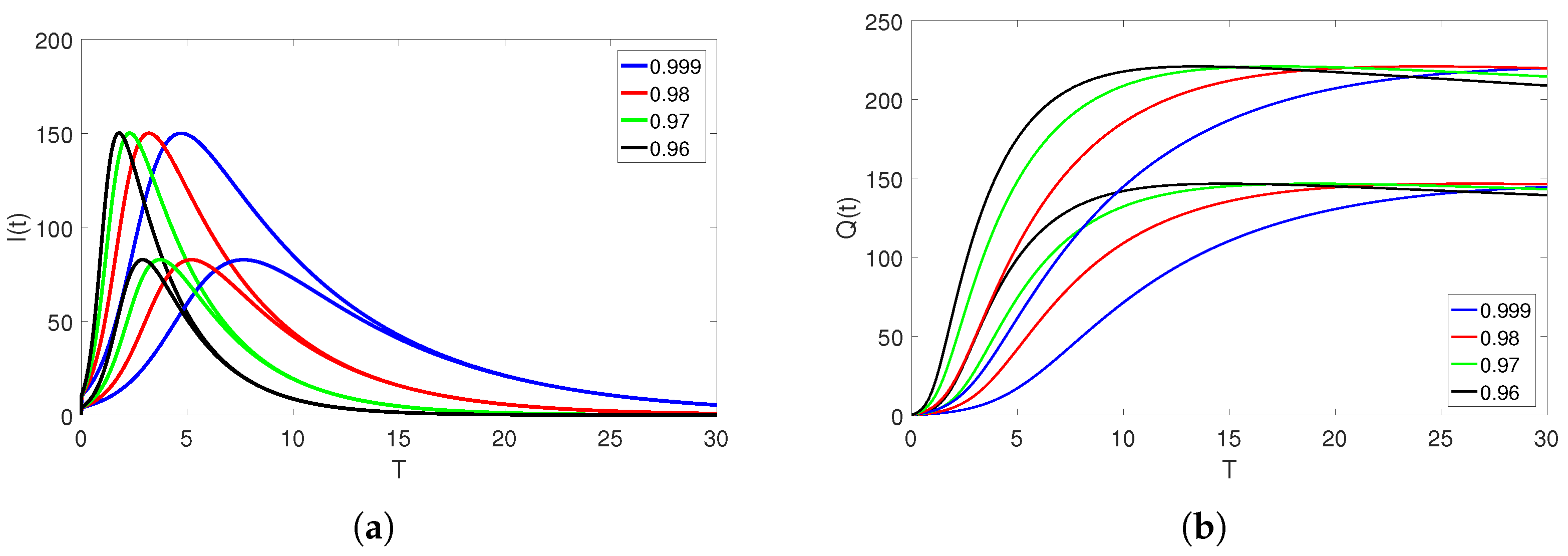
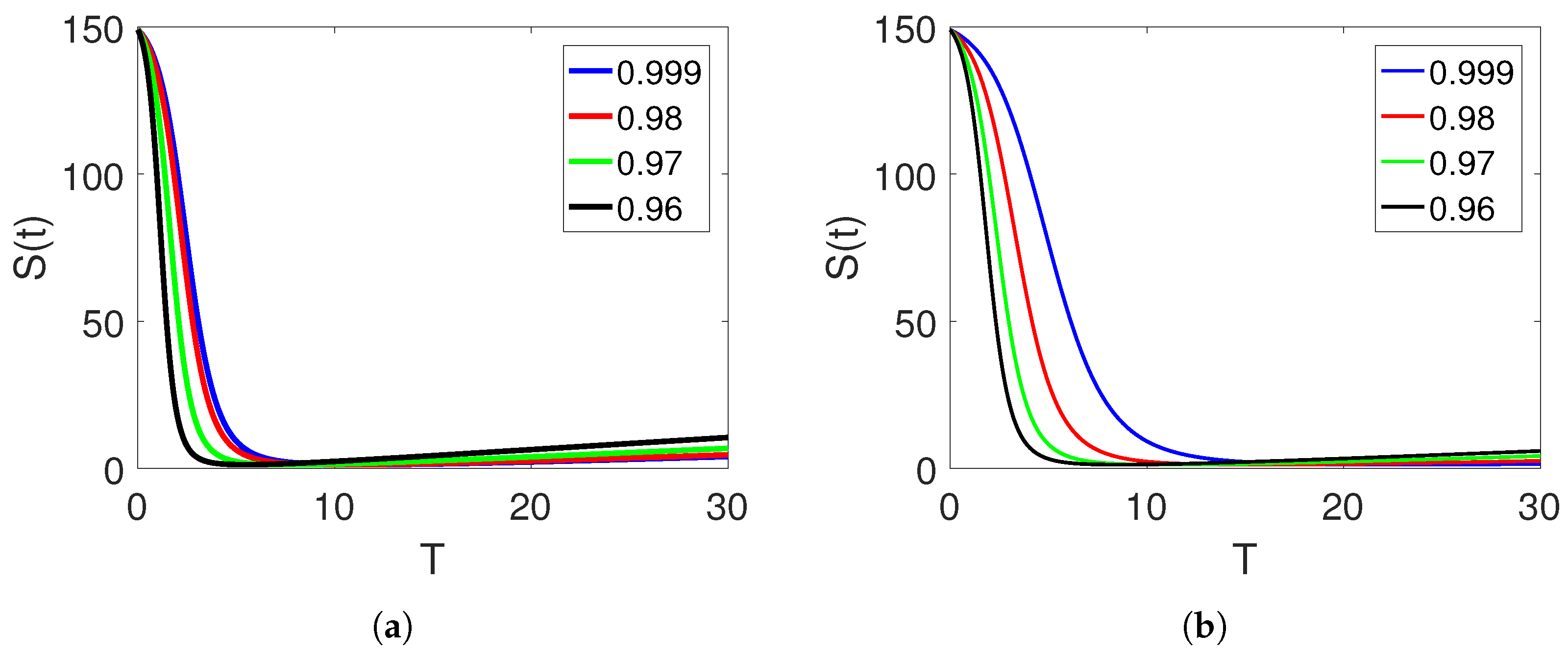
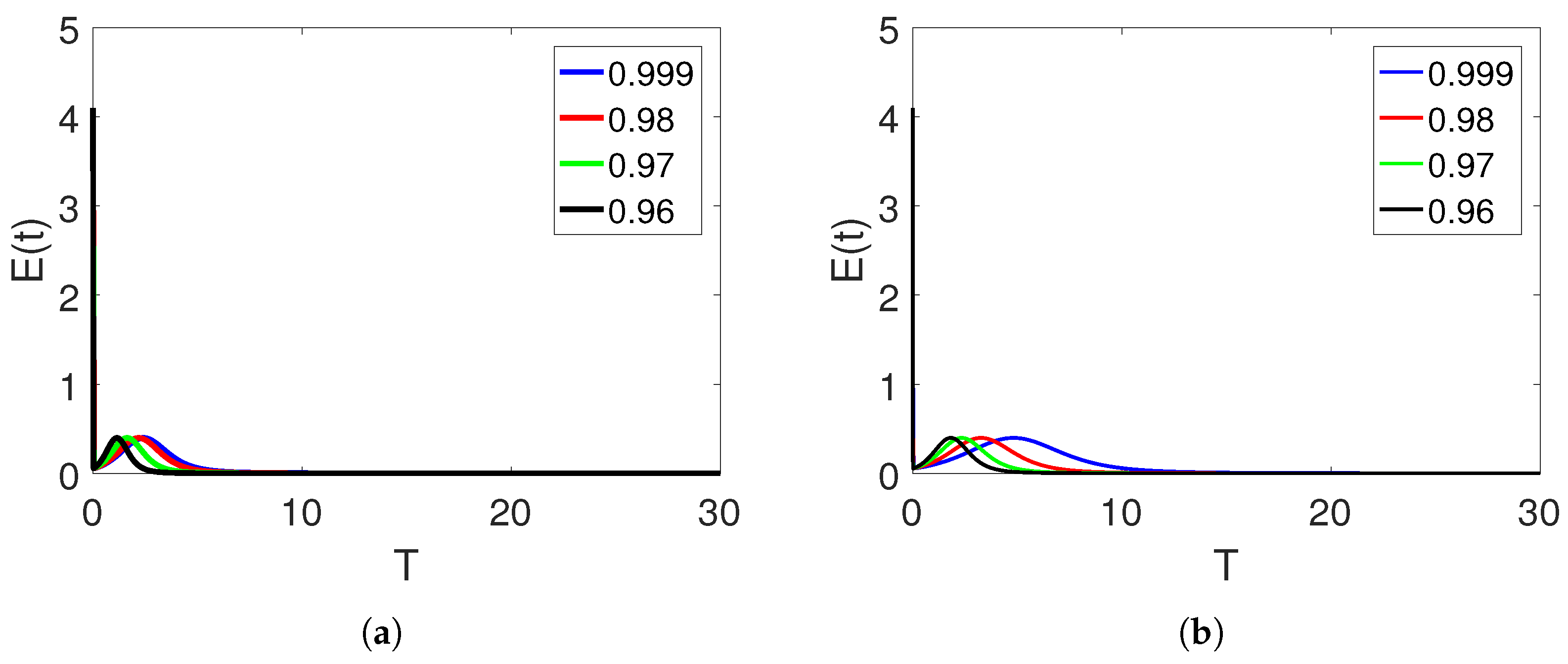
5. Numerical Simulation and Discussion
Convergence and Comparison
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.; Lau, E.H.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, S.; Ahmed, A.; Khan, M.S.; Javed, M.A. Stability analysis and solutions of dynamical models for Dengue. Punjab Univ. J. Math. 2018, 50, 45–67. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.M.; May, R.M. Population biology of infectious diseases: Part I. Nature 1979, 280, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thieme, H.R. Princeton series in theoretical and computational biology. In Mathematics in Population Biology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Feng, S.; Yang, J.; Peng, X.L.; Cao, X.; Zhang, J.; Yao, M.; Zhu, H.; Li, M.Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Analysis of potential risk of COVID-19 infections in China based on a pairwise epidemic model. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Yang, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhuge, C.; Hong, L. Epidemic analysis of COVID-19 in China by dynamical modeling. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.06563. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, N.; Zhong, M.; Yan, Y.; Pan, H.S.; Cheng, J.; Chen, W. Dynamic models for Coronavirus Disease 2019 and data analysis. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2020, 43, 4943–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.F.W.; Yuan, S.; Kok, K.H.; To, K.K.W.; Chu, H.; Yang, J.; Xing, F.; Liu, J.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Poon, R.W.S.; et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet 2020, 395, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.T.; Leung, K.; Leung, G.M. Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: A modelling study. Lancet 2020, 395, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Lin, Q.; Ran, J.; Musa, S.S.; Yang, G.; Wang, W.; Lou, Y.; Gao, D.; Yang, L.; He, D.; et al. Preliminary estimation of the basic reproduction number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in China, from 2019 to 2020: A data-driven analysis in the early phase of the outbreak. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 92, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Li, Q.; Tang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, J. An updated estimation of the risk of transmission of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCov). Infect. Dis. Model. 2020, 5, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, M. Estimation of the final size of the COVID-19 epidemic. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Character 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.M.; May, R.M. Directly transmitted infections diseases: Control by vaccination. Science 1982, 215, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, K. The incidence of infectious diseases under the influence of seasonal fluctuations. In Mathematical Models in Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1976; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Tang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, J. Estimation of the transmission risk of the 2019-nCoV and its implication for public health interventions. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Atangana, A.; Alzahrani, E. The dynamics of COVID-19 with quarantined and isolation. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, Z.; Qureshi, S.; Memon, B.R. Memon, Assessing the role of quarantine and isolation as control strategies for COVID-19 outbreak: A case study. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 144, 110655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javeed, S.; Anjum, S.; Alimgeer, K.S.; Atif, M.; Khan, M.S.; Farooq, W.A.; Hanif, A.; Ahmad, H.; Yao, S.W. A novel mathematical model for COVID-19 with remedial strategies. Results Phys. 2021, 27, 104248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A.; Baleanu, D. New fractional derivatives with non-local and non-singular kernel. Theory Appl. Heat Transf. Model Therm. Sci. 2016, 20, 763–769. [Google Scholar]
- Goufo, E.F.D. Application of the Caputo-Fabrizio fractional derivative without singular kernel to Korteweg-de Vries-Burgers equation. Math. Model. Anal. 2016, 21, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goufo, E.F.D. A bio mathematical view on the fractional dynamics of cellulose degradation. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2015, 18, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A. Extension of rate ofchange concept:from local to nonlocal operators with applications. Results Phys. 2020, 19, 103515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A.; Araz, S.I. Nonlinear equations with global differential and integral operators: Existence, uniqueness with application to epidemiology. Results Phys. 2020, 20, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabunga, S.K.; Goufo, E.F.D.; Tuong, V.H. Analysis and simulation of a mathematical model of tuberculosis transmission in democratic Republic of the Congo. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A.; Araz, S.I. Mathematical model of COVID-19 spread in Turkey and South Africa: Theory, methods and applications. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A.; Araz, S.I. New concept in calculus: Piecewise differential and integral operators. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfan, M.; Shah, K.; Ullah, A.; Salahshour, S.; Ahmadian, A.; Ferrara, M. A novel semi-analytical method for solutions of two dimensional fuzzy fractional wave equation using natural transform. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 2022, 15, 315–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rahman, M.; Arfan, M.; Shah, Z.; Kumam, P.; Shutaywi, M. Nonlinear fractional mathematical model of tuberculosis (TB) disease with incomplete treatment under Atangana-Baleanu derivative. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 2845–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfan, M.; Alrabaiah, H.; Rahman, M.U.; Sun, Y.L.; Hashim, A.S.; Pansera, B.A.; Ahmadian, A.; Salahshour, S. Investigation of fractal-fractional order model of COVID-19 in Pakistan under Atangana-Baleanu Caputo (ABC) derivative. Results Phys. 2021, 24, 104046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlubny, I. Geometric and physical interpretation of fractional integration and fractional differentiation. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2002, 5, 367–386. [Google Scholar]
- Verhulst, P.F. Notice sur la loi que la population suit dans son accroissement. Corresp. Math. Phys. 1838, 10, 113–121. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Fabiano, N.; Radenovic, S. Geometric Brownian motion and a new approach to the spread of covid-19 in Italy. Gulf J. Math. 2021, 10, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiano, N.; Radenovic, S. On COVID-19 diffusion in italy: Data analysis and possible Vojnotehni? Vojnoteh. Glas./Mil. Tech. Cour. 2020, 68, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, P.; Konwar, N.; Radenovic, S. Metric Fixed Point Theory, Applications in Sciences, Engineering and Behavioural Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Baleanu, D.; Arshad, S.; Jajarmi, A.; Shokat, W.; Ghassabzade, F.A.; Wali, M. Dynamical behaviours and stability analysis of a generalized fractional model with a real case study. J. Adv. Res. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]


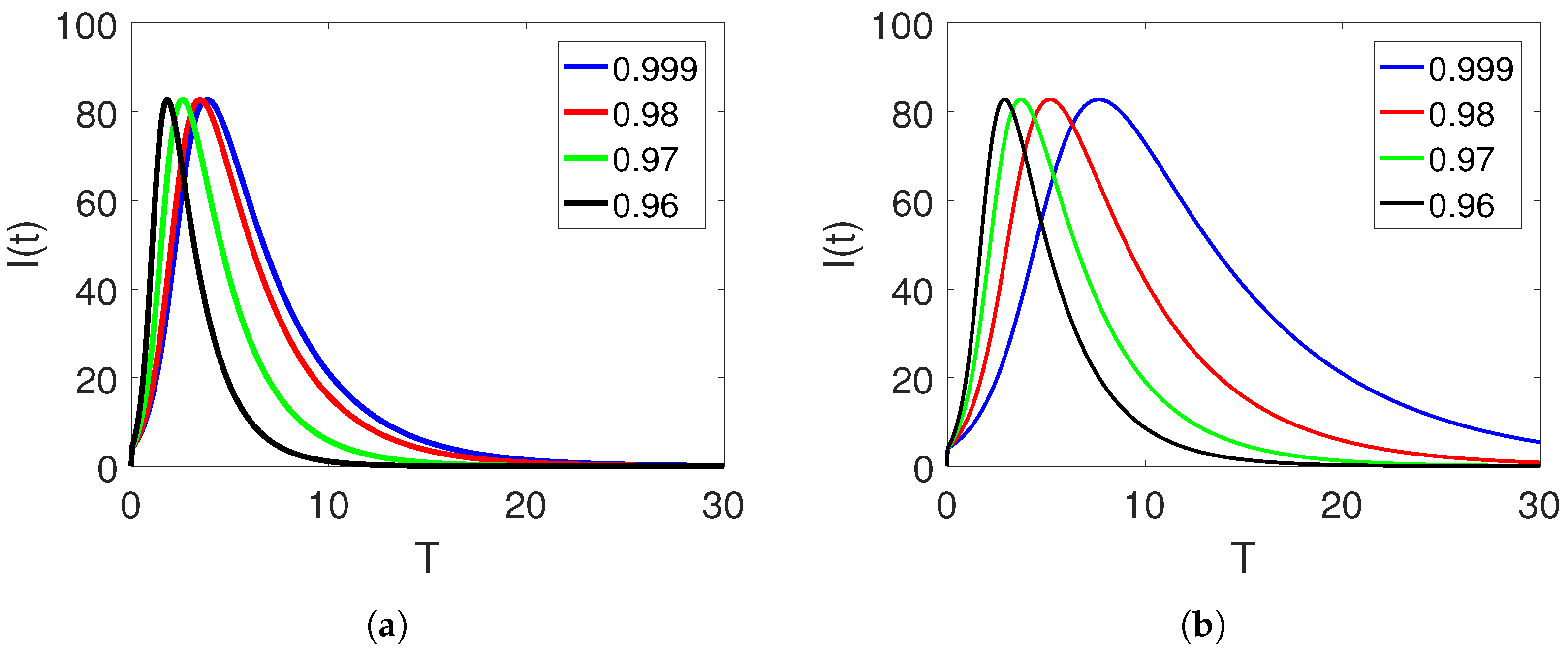

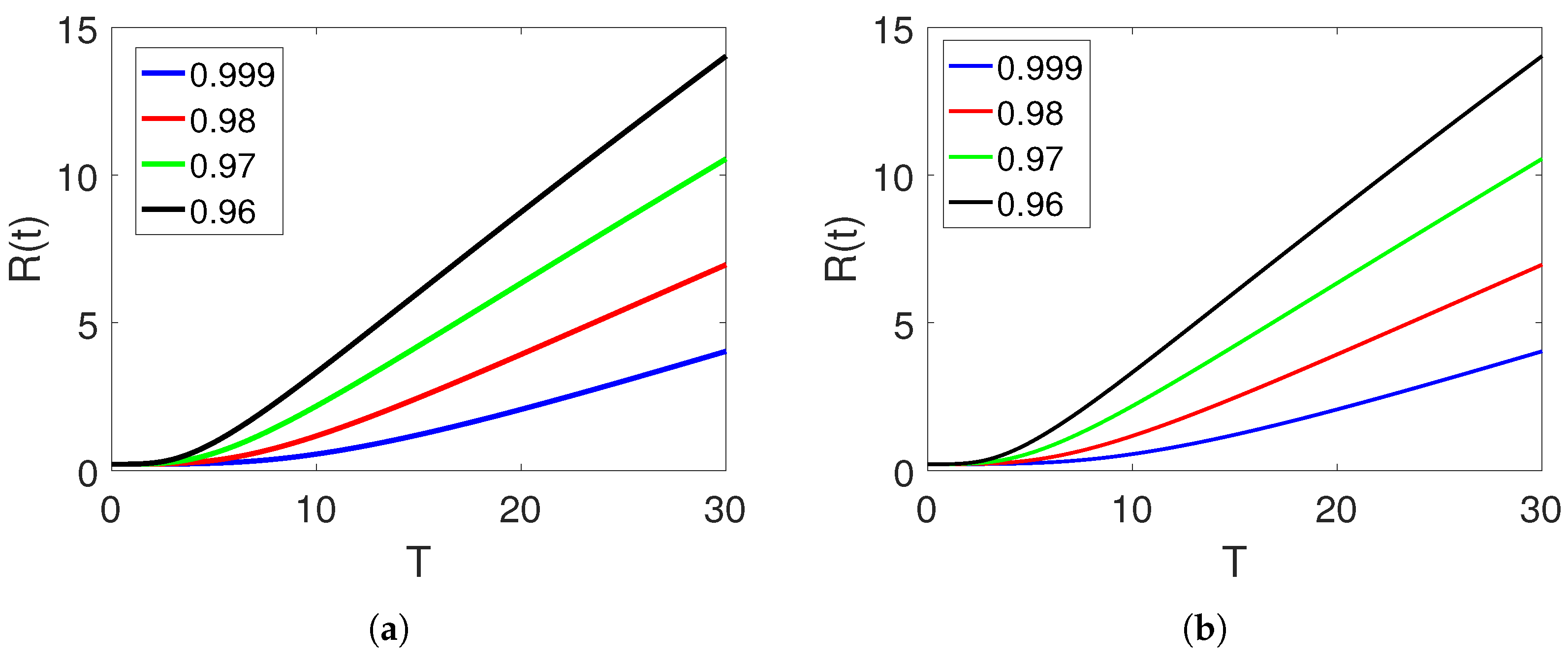
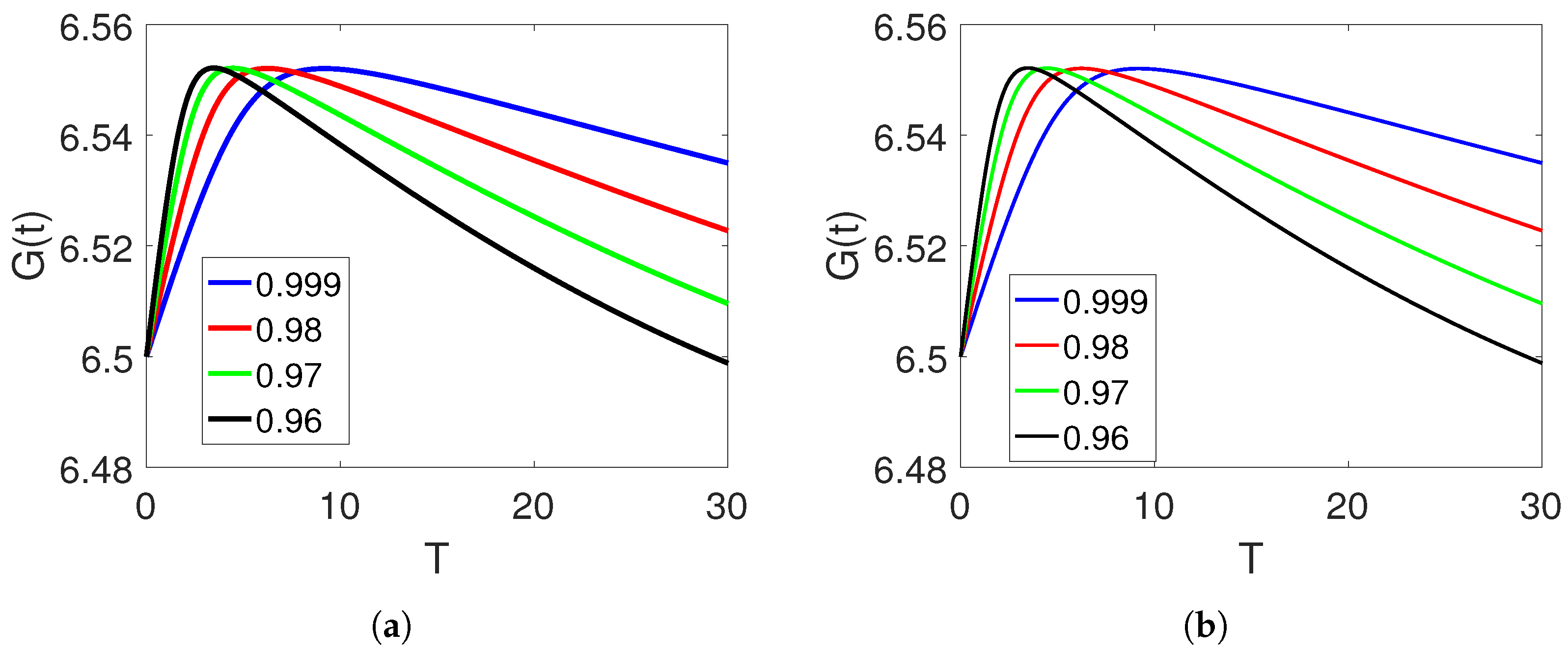
| Notation | Details |
|---|---|
| 27.530/1000 | |
| 0.004253392 | |
| 3.245065087 | |
| 0.003505 | |
| 6.884/1000 | |
| 0.0003551 | |
| 0.1597073 | |
| r | 0.058306850 |
| d | 0.00414502 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alazman, I.; Alkahtani, B.S.T. Investigation of Novel Piecewise Fractional Mathematical Model for COVID-19. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6110661
Alazman I, Alkahtani BST. Investigation of Novel Piecewise Fractional Mathematical Model for COVID-19. Fractal and Fractional. 2022; 6(11):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6110661
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlazman, Ibtehal, and Badr Saad T. Alkahtani. 2022. "Investigation of Novel Piecewise Fractional Mathematical Model for COVID-19" Fractal and Fractional 6, no. 11: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6110661
APA StyleAlazman, I., & Alkahtani, B. S. T. (2022). Investigation of Novel Piecewise Fractional Mathematical Model for COVID-19. Fractal and Fractional, 6(11), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6110661









