Abstract
The Edge Intelligence (EI) paradigm has recently emerged as a promising solution to overcome the inherent limitations of cloud computing (latency, autonomy, cost, etc.) in the development and provision of next-generation Internet of Things (IoT) services. Therefore, motivated by its increasing popularity, relevant research effort was expended in order to explore, from different perspectives and at different degrees of detail, the many facets of EI. In such a context, the aim of this paper was to analyze the wide landscape on EI by providing a systematic analysis of the state-of-the-art manuscripts in the form of a tertiary study (i.e., a review of literature reviews, surveys, and mapping studies) and according to the guidelines of the PRISMA methodology. A comparison framework is, hence, provided and sound research questions outlined, aimed at exploring (for the benefit of both experts and beginners) the past, present, and future directions of the EI paradigm and its relationships with the IoT and the cloud computing worlds.
1. Introduction
The International Data Corporation (IDC) forecasts that, by 2025, over 150 billion devices will be connected across the globe [1], with the majority of them generating data in real-time. In the same year, the source forecasts also that Internet of Things (IoT) devices located at the network edge will generate over 90 Zettabytes of data, namely more than the half of the Global Datasphere (i.e., the amount of data created, captured, and replicated in any given year across the world).
This shift in the digital landscape, from centralized data centers to a network of dispersed ubiquitous devices, requires a reassessment of the current methods of data analysis and processing to keep pace with the burgeoning volume and velocity of data. Currently, cloud-based data analysis and learning systems enable organizations to store and process vast amounts of data, making them readily accessible from any location at any time [2]. This enables organizations to make rapid and informed decisions, optimize operations, and reduce costs. However, with the increasing volume of data being generated and the high-expectations of IoT services’ QoS/QoE [3], there is a growing need for more efficient methods for data processing/analysis and for system management, to be implemented closer to the source of data collection. This is where Edge Intelligence (EI) comes in, as it allows for the processing and analysis of data as much as possible at the network’s edge, instead of solely relying on centralized data centers. This truly distributed and pervasive computing approach not only reduces latency and data traffic, but it also enables real-time decision-making, improves scalability, privacy, and reliability, and ultimately, leads to more efficient and effective data analysis.
Being recognized as an extremely promising enabler for many next-generation IoT services in different smart-* domains, in a few years, the EI has become the centerpiece of a wide literature, spanning from very narrow technical contributions to comprehensive studies and informative analysis. As a result, currently, EI looks like a container of so many entangled concepts (astride IoT, AI, edge and cloud computing, data science) that are complex to approach and even more challenge to productively apply. Therefore, in order to offer an extensive and in-depth understanding of the theoretical basis, architectures, technologies, and application scenarios of the novel and multidisciplinary field of EI, this survey provides an overview of the research efforts made so far, by exploring the literature in accordance with two key principles:
- Comprehensiveness: The research methodology we applied to perform our systematic EI literature review followed the PRISMA guidelines [4], a formal protocol consisting of well-defined and reproducible steps centered on clear criteria for the selection of the target articles, aiming at high level of homogeneity and quality [5];
- Effectiveness: Given the infeasibility of an exhaustive study of the whole EI literature, we opted for a systematic review performed in the form of a tertiary study, a well-established approach, also known as meta-analysis [6], which has the purpose of aggregating and generalizing the main results from large collections of thematically related secondary studies (reviews, surveys, roadmaps, white papers, etc.).
The joint exploitation of these two distinct, but highly compatible, approaches to the research synthesis is a novelty in the EI literature (precisely, only [7] provided a systematic review) but as demonstrated in many other fields [8], it allows summarizing wide bodies of knowledge, quantifying the size, strength, and trend of research directions, and generating new valuable insights. Ultimately, this survey sets out to serve as a valid resource for anyone looking to stay current in this rapidly evolving field and to gain insights into the potential future developments in EI.
This manuscript is organized as follows. In Section 2, we introduce the main concepts to approach the EI paradigm, its diffusion in the IoT scenario, and its relationships with other mainstream paradigms such as edge and cloud computing, AI, etc. In Section 3, we provide a detailed report of the research objectives we pursued and of the search methodology we adopted, thus reviewing the obtained literature in Section 4. Final remarks conclude the manuscript in Section 5.
2. Background
EI has witnessed a significant surge in growth lately, being intrinsically tied to the progression of edge computing. However, at the beginning of the ubiquitous and pervasive computing era, there was a significant deficiency of intelligence at the network’s edge in favor of a “remote” intelligence. For example, the primary function of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) [9] was to gather and transmit data according to the “sense-and-forward” paradigm, by means of dumb sensors that were relatively simplistic and resource limited. Therefore, cloud computing emerged as a prevalent enabler for supporting WSNs due to its ability to provide scalable data storage and management, remote monitoring and control, and ease of use. Both WSNs and cloud computing have started, hence, to take advantage of one another: the former found the necessary computing power for implementing intelligent solutions to be fed with a huge amount of real-time data provided by the latter.
As the IoT has gained traction [10], a plethora of more sophisticated devices, known as “smart objects”, emerged at the periphery of the network. These devices, such as smart thermostats, security cameras, and connected appliances, promised to make our lives easier by automating daily tasks and providing valuable insights. However, despite their improved capabilities, these devices continued to be heavily reliant on cloud-based infrastructure [11]: indeed, devices still remained unable to take actions without the assistance of the cloud since both the volume and the heterogeneity of the data increased dramatically, and consequently, only simple processing tasks and limited storage operations could be performed locally.
Only in the last decade, a number of issues about the IoT–cloud duo has emerged and pushed for a paradigm shift: indeed, while cloud-based infrastructure does provide the necessary scalability and flexibility for IoT devices, it also introduces a number of challenges. One major concern is the potential for data breaches and privacy violations, as sensitive information is transmitted to and stored on remote servers. Additionally, the reliance on cloud-based infrastructure can also result in unacceptably high latency in field-to-cloud and back transmissions, as well as exorbitant energy and bandwidth consumption. To address these issues, new computing paradigms such as edge and fog computing have emerged, with the intent to carry not only data processing, but more broadly, intelligence (intended as “Interacting, Interoperate, Cooperation, Communicating and Perception” capabilities [12]) as close as possible to the data sources, in the place of remote servers accessed over the Internet.
In this direction, more recently, EI has emerged in order to support the new and ambitious services and scenarios of the IoT. It incorporates both emerging and well-established approaches from edge and cloud computing, AI, data science, and networking to bring intelligence outside the boundaries of the cloud. This approach, also referred to as “Edge AI”, pushes as much as possible for local operations, even better if directly on edge devices, such as smartphones, IoT devices, and industrial equipment, rather than in the cloud or a centralized data center. As illustrated in Figure 1, this strategy effectively reduces the amount of data transmitted from the device monitoring a target phenomenon to a remote server, thus reducing the time and the communication that pass between the operations of sensing and actuation. However, the challenge of EI involves not only embedding the characteristics of massive computing systems into tiny, restricted devices, as if trying “to fit an elephant into a small box” [13], but indeed, a full-fledged infrastructure to allow EI, at its extreme, to transform Big Data into intelligent data and to enable real-time device management, system performance, decision-making, and operation monitoring, thus improving overall responsiveness, privacy, effectiveness, and productivity [12,14,15,16]. Although EI holds the potential to rival the cloud, it cannot maximize its capabilities when employed alone. EI and cloud computing can complement each other seamlessly, with the optimum approach being a synergistic relationship, exemplified by the IoT–edge–cloud continuum [17]. This harmonious connection is crucial in today’s technological arena, resulting in enhanced resource utilization, heightened efficiency, and the best outcomes.
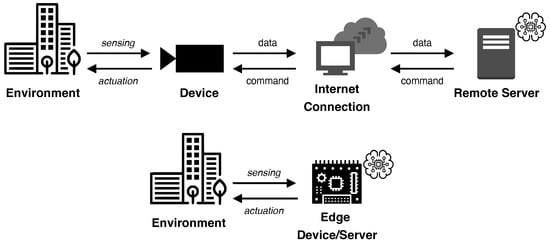
Figure 1.
From remote (e.g., cloud-based) to local (e.g., EI) data processing.
3. Research Methodology
We undertook an initial informal search, which, together with personal knowledge, confirmed that there exist a relevant number of contributions on the EI topic and that a systematic review would be appropriate. It also provided the information needed to guide the manual search process. Accordingly, a survey of articles regarding EI spanning 13 years (from January 2011 to February 2023) was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the PRISMA statement. After the record screening and the report selection processing, we analyzed a total of 50 works. However, they refer to specific domains (e.g., robotics [18] or cyber-security [19]) or technology (e.g., embedded intelligence for FPGA [20]), to narrow contributions (e.g., a novel version of an algorithm or an optimized model [21,22]), and to broader surveys/review papers outlining definitions, goals, and roadmaps for EI. We decided to focus specifically on the latter and performed a further hand-made selection, which produced a systematic analysis literature in the form of a tertiary study of 14 publications. The undertaken search plan is summarized in Table 1, while Figure 2 depicts the flow-chart of the PRISMA-based selection process, detailed in the following subsections.

Table 1.
Search plan.
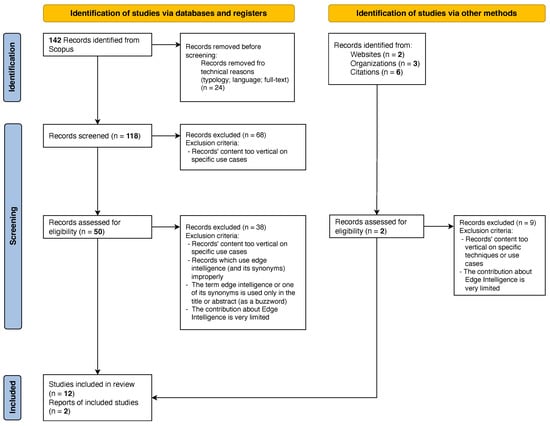
Figure 2.
Flow-chart of the literature review selection process according to the PRISMA guidelines.
3.1. Objectives
This review aimed to identify the state-of-the-art on EI, at the confluence of AI, cloud, and edge computing, to bring intelligence as close as possible to the data sources. The survey was conducted to identify the current research trend and research challenges related to EI and to answer the following Research Questions (RQs):
- (RQ1) What are current definitions or interpretations of EI?
- (RQ2) Are there specific reference architectures that help to enable intelligence at the edge?
- (RQ3) What are the main topics (intended as broad subjects or themes) addressed by EI?
- (RQ4) What are the key techniques (intended as enabling, implementation methods) of EI?
- (RQ5) What are the pursued goals, the on-going efforts, and the future challenges for EI?
3.2. Search Strategy
An exhaustive search of the articles regarding EI was performed in February 2023 by two of the authors on the following digital libraries: ScienceDirect, Scopus, IEEEXplore, ACM Digital Library, and Web of Science. The search focused on retrieving scientific publications proposing solutions (i.e., models, techniques, approaches, architectures) that aim to understand how to bring intelligence as close as possible to the data sources. The keyword search string was defined according to three key concepts: (i) edge intelligence; (ii) embedded intelligence; (iii) on-device intelligence. Considering such key terms and their synonyms, the following search string was identified:
To find relevant results, we applied the search string to articles’ titles, and we forced a distance of a maximum of two words between the key terms. Later on, since the object of our work was specifically on EI’s secondary studies, we applied the following search string to manuscripts’ abstracts:
It is worth noting that the search string (2) incorporates the wildcard symbol “*”, and this allows for the stemming task over key terms such as “survey”, “review”, and “discussion”.
3.3. Eligibility Criteria
The articles were eligible for selection if they met all of the following inclusion criteria:
- The work is a literature review, survey, or mapping study that specifically delves into the EI realm;
- A model or at least a formal definition of EI is proposed or adopted;
- The work uses EI as the main element of the proposed solution;
- Either EI-based or EI-enabling architectures or techniques are presented.
The articles were excluded from the selection if they met one of the following exclusion criteria:
- The work is too vertical on use cases (ranging from individual domains such as autonomous vehicles [23] and the smart grid [24] to general IoT-based applications [25]), techniques (e.g., information fusion for EI [26], neural-network-based self-learning architecture [27]), algorithm customization (e.g., combination of blockchain and k-means algorithm [28]), or model/platform optimization [20,29];
- The terms “edge intelligence” and “embedded intelligence” or one of their synonyms are contained only in the title, abstract, or keywords and are missing in the main body of the article [21,30,31];
- The concept of EI or one of its synonyms is either defined or used improperly [32,33];
- The work is a pre-print and/or its extension has been already included (as for [34] with respect to [35]).
3.4. Study Selection
Figure 2 depicts the flow-chart of the approach adopted to select the articles according to the PRISMA guidelines [4]. The search in the digital libraries using the search string provided a total of 142 articles. In order to discard studies not relevant to our review, we removed the papers due to the following technical criteria, based on: (1) the type of publication, by eliminating materials such as editorials, short papers, posters, theses, dissertations, brief communications, commentaries, and unpublished works; (2) articles partially or wholly not written in English; (3) papers with text unavailable in full. In this step, a total of 24 papers were removed, obtaining 118 publications. To select the appropriate studies for this review, in the first screening task, only the records (title, abstract, and keyword) of each article were analyzed independently by two of the authors. Each researcher evaluated the title and the abstract according to the eligibility criteria to decide if that paper should be included in the next screening phase. A paper included by one of the researchers resulted in a full-text assessment in the next phase, so 50 papers were selected by the reviewers in this phase. In the last phase, all the researchers read the full papers and decided whether to include the work in the review based on the eligibility criteria and on criteria of relevance, rigorousness, credibility, and quality. Most of the papers were excluded in this phase because EI was used only in the title or abstract (as a buzzword) [36,37,38,39] or only in the related works Section [40], and therefore, it did not represent a fundamental element of the solution proposed in the manuscript [41,42]. To guarantee the high quality of the selected studies, final inclusion of a paper in the review was reached by consensus among the researchers (i.e., only if the majority of the researchers evaluated it as suitable for the review, or in case of parity, a discussion between the researchers took place to decide about the inclusion). In this phase, the researchers selected and analyzed a total of 20 papers. In parallel, we performed also an extensive snowballing search to identify other eligible studies (relevant, but not found by our query) according to the references’ lists (back-in-time search) and citations (forward-in-time search) of the included studies. In particular, we repeated our query by including the term “intelligence continuum”, which is sometimes used to refer to smart solutions distributed across all the architectural levels, hence including the edge. Finally, for the sake of maximum comprehensiveness, we also attempted to search for gray literature, thus covering relevant documents, unlisted in electronic databases since they are usually provided by both government and professional organizations, such as technical reports, Ph.D. theses, patents, company’s white papers, etc. Lastly, 14 secondary studies specifically related to EI were analyzed in more detail, and they are reported and compared in the framework of Table 2.
4. Literature Review
Already from an initial screening of our search results, we observed that the literature related to EI is not well consolidated. Although the term EI occasionally appears in older EI-related works such as [16,41], only in the last decade has the research established clearer boundaries of the domain, and only in the last four years (2019–2023) have more systematic studies been published in conference proceedings and journals, mostly. From a deep study of all the analyzed works, indeed, we were able to identify a clear classification of the studies under the general umbrella of EI: the majority of them are truly narrowed on specific techniques and domains (e.g., [18,19,43,44,45]), while few horizontal studies seek to explore the fundamentals, perspectives, and trends of EI (whereas with coarse-grained [42,46] or fine-tuned [12,14,35] analysis). However, as previously pointed out, the specific aim of this survey was to methodically shed light on the state-of-the-art of EI by performing a systematic analysis (interesting and somewhat surprisingly, there is only a systematic literature review [7] and a systematic classification [35]) in the form of a tertiary study, thus centering our analysis on comprehensive reviews, surveys, roadmaps, etc. In this direction, given the time of writing, milestone works are [12,35,47], which provide key contributions by discussing core components and concepts, designing theoretical frameworks, and analyzing technology drivers, exploring capabilities, benefits, opportunities, gaps, and use cases for current EI scenarios, as well as for the next decade. These three manuscripts are the most-cited ones (with more than 200+ citations in a short period of time), but obviously, many other interesting and relevant findings came from the other works identified adopting the research methodology discussed in Section 3 and whose comparative analysis is summarized in Table 2. Therefore, driven by the Research Questions (RQs) outlined in Section 3.1, we carried out an accurate literature analysis, whose research directions and main findings (enclosed in dotted boxes) are concisely presented in Figure 3.

Table 2.
Comparison framework for the analyzed literature.
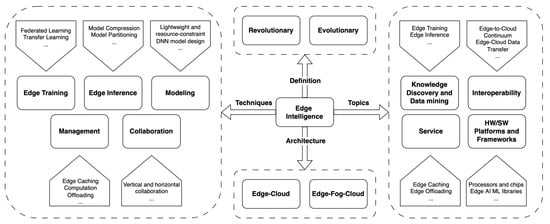
Figure 3.
Directions and main findings (enclosed in dotted boxes) of the performed study on EI.
Referring to RQ1, albeit almost twelve years have passed since the first appearance of the term [16] (also referred to as “Edge AI” in [41]), there is still not a formal definition of EI. All the surveyed works promote similar definitions of EI in which the terms edge computing and AI appear, naturally side-by-side. With a deeper look, however, these definitions can be classified into two groups:
- Evolutionary EI definitions, which “simply” mean EI as the next stage of current edge computing [14,48,49,50], where edge nodes self-process their own data, being empowered through lightened AI algorithms (individually measured in terms of <accuracy, latency, energy, memory footprint> [48]) or pre-trained models (intended as “pluggable AI capabilities for edge computers” [51]);
- Revolutionary EI definitions, which propose EI as a new paradigm combining (“the amalgam”, “the marriage”, “the confluence”) both novel and existing approaches, techniques, and tools from different areas (mainly from edge computing and AI, but also approximate computing, cognitive science, etc.) and realizing a fully distributed intelligence among end devices, edge nodes, and cloud servers [12,15,35,47,51,52,53,54].
The definitions of the first groups aim to stress the achieved independence of edge nodes from the cloud, but, in this way, they definitively narrow down the scope of EI; the EI definition of the second group, instead, exposes a holistic perspective (not centered on the algorithmic capabilities of single edge nodes), reasoning in terms of a seamless edge–cloud ecosystem [35], promoting a continuum between the two domains and all their actors, technology enablers, etc. [53]. Indeed, for example, in [12], six EI levels are defined, and they form a collaborative hierarchy to be integrated for the design of efficient EI solutions. Far from providing the umpteenth EI definition, we adhered to the latter definition, and we believe that the “evolutionary” one limits the potential of EI: indeed, in order to enable novel IoT services or to optimize the overall system performance, all the available system’s data and resources should be fully and opportunistically exploited. Just in the direction of such a full-fledged EI vision, Refs. [47,51] provide an interesting interpretation, by identifying two complementary contributions, namely “AI for Edge” (or Intelligent Edge) and “AI on Edge”, also referred to in [55] as “AI for Operations” and “Operations for AI”. The former focuses on providing optimal solutions to solve key problems in edge computing (e.g., data offloading, energy management, nodes coordination) with the help of popular AI techniques, while the latter studies how (i.e., which hardware platforms, programming framework, methods, and tools) to perform the whole process of AI model building, i.e., training, inference, and optimization, on edge devices despite their intrinsic resource limitations.
Referring to RQ2, it was found that a reference architecture purposely designed for EI is still missing. Indeed, even if the international community is actively working towards the development of a comprehensive edge computing reference architecture [56,57,58,59] with a relevant portion of “intelligence” located on edge devices, the full development of an “Edge-native AI system” is currently far away, being only sketched in [27,35]. With respect to the analyzed works, half of them (7 out of 14 [7,47,48,50,52,53,55]) do not deal with such a point, while the remaining ones discuss a multi-level architecture, which is, implicitly or explicitly, strongly influenced by the IoT and by the ETSI MEC reference architecture [14,60]; indeed, these edge computing architectures look tailored to conform and mirror the IoT’s layered structure, which generally consists of various and closely intertwined layers that manage different system functionalities, such as data collection, processing, and management [61]. Notably, the majority of surveyed works (5 out of 7 [12,15,35,51,54]) expose two-layer architectures (i.e., edge and cloud layers), while only [14,49] include a third, intermediate layer, which is mainly responsible for networking (from LAN to WAN) and interoperability (protocol conversion) tasks. Therefore, it emerges that the fog computing layer is losing attractiveness, being embedded in the so-called “thick Edge” (including, exactly, gateways and other specific-purpose devices), except for some industrial use cases demanding particular requirements. This can be due to the ever-increasing power and miniaturization and lowering cost of IoT boards and micro-computers, which, most of the time, can perform typical fog computing duties (caching, pre-processing, etc.). Such a trend is especially noticeable in [51], whose authors define an “Edge Computing network” layer by distinguishing, from one side, devices such as base stations and gateways and, from the other side, tablets, smartphones, smartwatches, etc. Interestingly, only [55] and, primarily, [7] markedly stress the importance of a seamless interaction between the architectures, by presenting ad hoc methods, libraries, and frameworks for machine learning and data analytics on the edge-to-cloud continuum, in the spotlight today thanks to the recent initiative “European Cloud, Edge and IoT Continuum” led by the European Commission [62].
Referring to RQ3, an examination of the selected works revealed a common focus on EI’s general objectives, applications, and use cases (especially [14,50,51,53,54,55]), while key technical topics can be grouped primarily into four categories we purposely grounded:
- Knowledge Discovery and Data mining (KDD), which encompasses all aspects pertaining to the extraction of valuable insights and patterns from the vast data generated by end devices;
- Hardware platforms and software frameworks, namely those commercial devices and software tools that concretely allow enabling intelligence at the network edge;
- Service, which encompasses all non-functional aspects (from service placement, composition, and orchestration to mobility, offloading, caching, etc.) related to the support and maintenance of IoT services at the edge layer;
- Interoperability, which focuses on those methods and mechanisms enabling different devices, systems, and networks to be readily connected and exchange information.
A preponderance of the reviewed literature (8 out of 14 [7,12,35,47,49,51,52,54]) concentrated on the category KDD, thereby shedding light on techniques pertaining to data cleaning and preprocessing, feature selection and extraction, and model building and evaluation. Notably, within this category, the subjects of edge training and edge inference have garnered significant interest among researchers, as they pertain to the key methods and techniques that address the challenges of implementing intelligent systems at the edge of the network. Additionally, over half of the works (8 out of 14, [7,12,48,49,50,51,54]) also address topics related to HW platforms and SW frameworks, enumerating the mainstream legacy of EI software and hardware tools. One of the key findings was the prevalent use of GPU, FPGA, and ASIC hardware chips in supporting intelligence at the edge of the network. These chips are favored for their ability to provide the necessary computational power and flexibility for real-time data processing and analysis, leading to the development of various hardware platforms based on them that are widely used in current Edge AI applications. Examples include the Nvidia Jetson family (GPU-based), the Google Coral Edge TPU (ASIC-based), and the Horizon Sunrise (FPGA-based), all of which are known for their high performance and energy efficiency. Additionally, the machine learning libraries that are most-frequently referenced in the analyzed works include TensorFlow Lite, Core ML, and Pytorch Mobile. These libraries are widely used for developing and deploying models on edge devices, and some of them, such as TensorFlow Lite, have been specifically optimized to run natively on hardware configurations such as the Google Coral family. An intriguing discovery is the introduction of an open framework for EI, also known as OpenEI, presented in the paper [48]. This lightweight software platform imbues the edge with sophisticated processing and data-sharing capabilities. OpenEI comprises a deep learning package that is specifically optimized for resource-constrained edge devices, including a plethora of refined AI models, providing a streamlined solution for the deployment of EI applications. Then, we found that approximately half of the examined literature (5 out of 14 [35,47,49,51,52]) focuses on the primary techniques that seek to sustain and preserve the added value of IoT services. Within this category, edge caching and edge offloading have been the most-extensively researched [35,51,52], as they address the critical need for efficient data management and processing at the edge of the network, followed by ever-green (well-explored in the past, yet still crucial) topics such as service placements, user mobility, topology management, etc. [47,49]. Finally, an intriguing discovery is that only a minority of the reviewed papers (4 out of 14 [7,14,15,48]) reserves an adequate discussion on the interoperability topic, whereas its centrality has been widely recognized in the IoT ecosystem: these works agree that a rapid adoption of EI technologies by vendors and industry go through IoT gateways and unified interfaces for the system life-cycle (e.g., cross-platform software and RESTful AP for requirements assessment, authentication, resource discovery, system configuration, and deployment), but additionally, they focus on different aspects. For example, Ref. [48] delves into the transfer of data between edge nodes and cloud servers, emphasizing the importance of seamless collaboration; instead, Ref. [7] conducts an in-depth analysis of the collaborative aspect of the edge-to-cloud continuum, while, finally, Ref. [15] primarily concentrates on standardization, but from an industry perspective (by shedding light on requirements, potentials, and gaps in multiple use cases and domains, such as manufacturing, smart cities, and smart buildings). Conversely, there is no reference (if not as an open point in [12,35]) about semantic technologies.
Referring to RQ4, a noteworthy outcome is that 5 papers [14,15,52,53,55] out of the 14 did not provide insights on any specific enabling techniques for EI, but rather, focused on imparting a general overview of their principal contribution. As for the remaining nine works [7,12,35,47,48,49,50,51,54], a thorough analysis resulted in the classification of EI’s key technologies into the following categories:
- Edge inference, which covers all techniques for near-real-time inference, i.e., as close as possible to the data sources;
- Edge training, which encompasses all techniques that aid in training complex ML models on constrained and resource-limited devices;
- Modeling, which encompasses all techniques that aid in designing ML models’ architectures suitable for resource-limited devices;
- Management, which encompasses all techniques that aid in managing the vast amount of real-time data at the edge layer;
- Collaboration, which includes techniques that aim to improve the interoperability between nodes across the edge-to-cloud continuum.
The categories that the majority of the analyzed works center on are edge inference [7,12,35,47,48,49,50,51] and edge training [7,12,35,49,51,54] (respectively, 8 and 6 out of 9). This is indicative of ongoing research efforts aimed at understanding the most-efficient ways to train ML models and provide timely predictions and analyses as close as possible to both end-devices and end-users. Edge inference pertains to the utilization of a pre-trained model or algorithm to make predictions or classify new data on edge devices or servers. The majority of current AI models are optimized for deployment on devices with ample computational resources, making them unsuitable for edge environments. The reviewed literature, however, identifies two main challenges in enabling efficient edge inference [12,35,48,51]: designing models that are suitable for deployment on resource-constrained edge devices or servers and accelerating inference to provide real-time responses. One widely discussed approach to addressing these challenges is model compression (for reducing the size and computational requirements of existing models without affecting their accuracy) and, especially, its techniques of network pruning and parameter quantization. Another prominent approach discussed in the literature is model partitioning, which involves transferring the computationally intensive portions of a model to an edge server or neighboring mobile device, thus reducing the workload on the endpoint device and significantly enhancing inference performance: in this regard, the technique of model early exit has garnered much attention, as it enables the use of output data from early layers of a DNN to achieve a classification result, thus enabling the inference process to be completed using only a subset of the full DNN model. Unlike traditional centralized training methods that are executed on powerful servers or computing clusters, edge training is typically performed in a decentralized manner by using a training dataset located on devices with less computational power at the network’s edge. This poses several challenges such as selecting the appropriate training architecture, increasing the training speed, and optimizing performance. The surveyed works propose various techniques to address these issues. The most-commonly used architectures in the literature are “solo training” [35,51], where tasks are performed on a single device, and “collaborative training” [35,49,51], where multiple devices work together to train a shared model or algorithm. It is noteworthy that solo training has higher hardware requirements, which are often unavailable, and as consequence, several works focus on collaborative training architectures and techniques such as Federated Learning (FL) (which has been proposed in several variations such as communication-efficient FL, resource-optimized FL, security-enhanced FL and hierarchical FL [35,51]) and knowledge transfer learning. The latter method involves training a primary network (referred to as the “teacher network”) on a base dataset and then transferring the acquired knowledge, in the form of learned features, to a secondary network (referred to as the “student network”) for further training on a target dataset. This technique promises to drastically reduce the energy costs of model training on both end devices and edge servers. Approximately half of the papers (4 out of 9 [7,35,48,49]) also deal with modeling techniques for the design of ML models aimed at fully leveraging the limited resources of edge devices. According to the literature reviewed [7,12,35,47,49,51,54], it was noticed that deep learning outperformed other machine learning methods in a variety of tasks, including image classification, object detection, and face recognition. These deep learning models are commonly referred to as Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) due to their layered architecture. Despite the fact that DNNs can take on a variety of structures [12,49,51], such as Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), the surveyed works primarily focus on the general DNN architecture. The increasing complexity and computational demands of modern DNN models make it challenging to run them on edge devices with limited resources, such as mobile devices, IoT terminals, and embedded devices. To address this challenge, recent works such as [7,35,48,49] focus on designing lightweight and resource-constraint DNN models that are more suitable for edge environments. According to [35], this approach can significantly improve the performance of training and inference tasks on edge devices. The categories of management and collaboration received relatively less attention in the analyzed works, with only 3 [35,47,51] and 2 [7,51] papers, respectively, out of 9 addressing these topics. The management techniques primarily focus on optimizing data retrieval and processing speed and on minimizing power consumption and thermal stress on the edge device. Edge caching and computation offloading are widely used techniques to achieve these goals [35,51,52]: the former involves storing frequently accessed data on edge devices, reduces latency, and increases data retrieval speed; the latter, on the other hand, distributes the computational workload among a group of edge devices and encompasses various strategies such as Device-to-Cloud (D2C), Device-to-Edge (D2E), Device-to-Device (D2D), and hybrid offloading [35,52]. The collaboration category delves into methods for fostering cooperation and coordination among edge devices and other network entities such as vertical and horizontal collaboration and integral and partial task offloading [51]. It is particularly notable to observe the survey [7] through its extensive citation and analysis of a plethora of works, making a significant, albeit indirect, contribution to all the categories outlined, except for “management”.
Finally, answering RQ5, the most-frequently mentioned application use cases in the reviewed literature pertain to the domains of smart cities [12,15], smart homes [48,51], smart factories [7,35], healthcare [49,50], entertainment [52,54], and automotive [47,51]. Notably, healthcare applications related to disease prediction [63,64], automotive applications exploiting connected and autonomous vehicles [65,66], as well as smart factory applications for the Industrial IoT [49,67] have been receiving significant attention from both industry professionals and researchers. The benefits of EI, such as low-latency communication, crucial in life-or-death situations, reduced bandwidth consumption, essential for energy efficiency in resource-limited devices, and enhanced privacy through the local storage of sensitive information, render these areas particularly appealing. Then, most of the surveyed works report some well-known, yet still unaddressed challenges typical of distributed computing and, hence, of the IoT [61], such as scalability [53,55], security and privacy [12,50,52], ethical issues [7,53], pervasiveness and ubiquity [7,14], resource optimization [48,52,54], heterogeneity [14,15,50,54], data scarcity and consistency [35,47,54], etc. However, these issues generally refer to the edge computing scenario rather than EI, whose main specific open challenges (and related future directions), instead, focus on:
- Understanding the performance of EI applications and finding a balance between effectiveness and efficacy [47,52], thanks to a targeted exploitation of HW/SW co-design techniques [48,68] and the development of novel, full-fledged simulators [69] specifically tailored to EI;
- Designing comprehensive architecture for EI [51], natively provided with the continuum concept and, possibly, with a standardized API, data model, workflow, and notations [14,15,50];
- Developing pervasive intelligent infrastructures that already consider the integration with 5G and 6G technology to facilitate EI solutions [15,27,29,35];
- Outlining engineering methodologies for resource-friendly EI models and situation-aware networking techniques [12,14,47,48,49], drawing from different computing, networking, and data science paradigms;
- Promoting programming and software platforms for EI [12,48], as well as lightweight OS for the edge devices [48]; with respect to the former, the most well-known are IoT Edge Microsoft Azure https://azure.microsoft.com/it-it/products/iot-edge/, accessed on 30 January 2023, Cisco Edge Intelligence https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/internet-of-things/edge-intelligence.html, accessed on 30 January 2023, AWS IoT Greengrass https://aws.amazon.com/greengrass/, accessed on 30 January 2023, IoT Core https://cloud.google.com/iot-core?hl=it, accessed on 30 January 2023, Google Coral https://coral.ai/, accessed on 30 January 2023, NVIDIA Jetson https://www.nvidia.com/it-it/autonomous-machines/embedded-systems/, accessed on 30 January 2023, and Open VINO https://docs.openvino.ai/latest/index.html, accessed on 30 January 2023, while obvious OS candidates for edge devices are open-source and Linux-based such as Wind River, Android Things, or RedHat (whereas there are others as well such as Azure RTOS, VxWorks, FreeRtos, etc.);
- Conceiving of innovative incentive and business models along with cutting-edge applications to promote the combination of theory and practice [35,49,51].
Although they all are relevant, some of the identified gaps in the EI literature are particularly challenging. For example, particular emphasis should be given to the preliminary evaluation of EI solutions under development; indeed, while there exist some simulators conceived for IoT and edge computing scenarios, only [70,71] specifically focus on EI and on the many orthogonal issues it leads across the edge–cloud continuum [72]. Then, open (horizontal, vertical, and specialty) standards [12,50], robust platform abstractions [51], and flexible programming approaches that are deployment-transparent [73,74] are also key to deal with the inherent heterogeneity, scalability, and dynamicity of EI scenarios. In particular, even if standardization processes are typically burdensome efforts of indefinite duration and results (as taught by the IoT), commonly accepted practices should be established, possibly integrating the existing de jure and de facto standards and operating frameworks. Finally, themes such as equal accessibility [53] and governance [29,55], trustworthiness, and explainability [27,75], which already have gained attention in conventional AI systems, are carefully observed by institutions, and therefore, they deserve further research efforts from both industry and academia.
5. Conclusions
IoT systems and related services need to be truly supported by a pervasive, reliable, and effective intelligence to unleash their disruptive potential in our daily lives. Cloudification has so far helped, but the latest candidate to burst onto the scene is EI, whose rich, though fresh, recent literature reflects its broad appeal and usefulness. This survey provided both a quantitative and qualitative analysis of the large body of knowledge related to EI and rapidly accumulated in the last decade by means of a systematic literature review of secondary study according to the well-known PRISMA guidelines.
As a final takeaway of this survey, we recognize that the ETSI MEC reference architecture provides a solid base for EI system engineering; however, the realization of AI functionalities is open, and intelligence has not yet been considered as a built-in capability of the edge system [14]. As result, it is still not completely clear how and where the EI capabilities should be built into the edge systems to achieve its maximum yield, while further specifications (mainly for standardized APIs, software constructs, interoperability mechanisms, supporting infrastructures) need to be developed. In particular, the latest concept of the edge–cloud continuum, at its extreme, may lead to isomorphic EI architectures, allowing the identical service provision among edge devices, gateways, and servers [14,76]; from such a perspective, data and computation can be transferred dynamically and performed on any level of the cloud–edge architecture that provides the optimal QoS/QoE, thus ultimately diluting or even dissolving the boundaries between the cloud and edge.
To conclude, we attempted to disclose the wide research area of EI, and we hope that this survey can supply basic knowledge to enable new researchers to enter the area, current researchers to continue developments, and practitioners to apply the results, being confident that huge research efforts will be carried out to completely realize EI in the incoming years.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research leading to this work was carried out under the Italian MIUR, PRIN 2017 Project “Fluidware” (CUP H24I17000070001), and under the “MLSysOps Project” (Grant Agreement 101092912) funded by the European Community’s Horizon Europe Programme.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Reinsel, D.; Gantz, J.; Rydning, J. The Digitization of the World from Edge to Core. 2018. Available online: https://www.seagate.com/files/www-content/our-story/trends/files/idc-seagate-dataage-whitepaper.pdf?Tag=Sponsorships (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Biswas, A.R.; Giaffreda, R. IoT and cloud convergence: Opportunities and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 6–8 March 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 375–376. [Google Scholar]
- Fizza, K.; Banerjee, A.; Mitra, K.; Jayaraman, P.P.; Ranjan, R.; Patel, P.; Georgakopoulos, D. QoE in IoT: A vision, survey and future directions. Discov. Internet Things 2021, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Moher, D. Updating guidance for reporting systematic reviews: Development of the PRISMA 2020 statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramer, W.M.; De Jonge, G.B.; Rethlefsen, M.L.; Mast, F.; Kleijnen, J. A systematic approach to searching: An efficient and complete method to develop literature searches. J. Med Libr. Assoc. JMLA 2018, 106, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čehovin, G.; Bosnjak, M.; Lozar Manfreda, K. Meta-analyses in survey methodology: A systematic review. Public Opin. Q. 2018, 82, 641–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosendo, D.; Costan, A.; Valduriez, P.; Antoniu, G. Distributed intelligence on the Edge-to-Cloud Continuum: A systematic literature review. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2022, 166, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littell, J.H.; Corcoran, J.; Pillai, V. Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, F.L. Wireless Sensor Networks. In Smart Environments: Technologies, Protocols, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 11–46. [Google Scholar]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The internet of things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortino, G.; Guerrieri, A.; Russo, W.; Savaglio, C. Integration of agent-based and cloud computing for the smart objects-oriented IoT. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 18th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD), Hsinchu, Taiwan, 21–23 May 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, E.; Zeng, L.; Luo, K.; Zhang, J. Edge intelligence: Paving the last mile of artificial intelligence with edge computing. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1738–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Patgiri, R.; Waikhom, L.; Ahmed, A. A review on edge analytics: Issues, challenges, opportunities, promises, future directions, and applications. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, E.; Ahmad, I.; Aral, A.; Capobianco, M.; Ding, A.Y.; Gil-Castineira, F.; Gilman, E.; Harjula, E.; Jurmu, M.; Karvonen, T.; et al. The Many Faces of Edge Intelligence. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 104769–104782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge Intelligence. 2019. Available online: https://www.iec.ch/system/files/2019-09/content/media/files/iec_wp_edge_intelligence_en_lr.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Guo, B.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z. Living with internet of things: The emergence of embedded intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Internet of Things and 4th International Conference on Cyber, Physical and Social Computing, Dalian, China, 19–22 October 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Bittencourt, L.; Immich, R.; Sakellariou, R.; Fonseca, N.; Madeira, E.; Curado, M.; Villas, L.; DaSilva, L.; Lee, C.; Rana, O. The internet of things, fog and cloud continuum: Integration and challenges. Internet Things 2018, 3, 134–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Feng, X. Robot, Edge Intelligence and Data Survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Intl Conf on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, Intl Conf on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, Intl Conf on Cloud and Big Data Computing, Intl Conf on Cyber Science and Technology Congress (DASC/PiCom/CBDCom/CyberSciTech), AB, Canada, 25–28 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 843–848. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Qian, Y.; Hu, R.Q. Edge intelligence assisted gateway defense in cyber security. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, K.P.; Lee, P.J.; Ang, L.M. Embedded intelligence on FPGA: Survey, applications and challenges. Electronics 2021, 10, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalapura, V.S.; Amudha, J.; Satheesh, H.S. Recurrent neural networks for edge intelligence: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Model Optimization Techniques for Embedded Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Computing and Data Science (CDS), Stanford, CA, USA, 28–29 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cunneen, M.; Mullins, M.; Murphy, F. Autonomous vehicles and embedded artificial intelligence: The challenges of framing machine driving decisions. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 706–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molokomme, D.N.; Onumanyi, A.J.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Edge intelligence in Smart Grids: A survey on architectures, offloading models, cyber security measures, and challenges. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2022, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourechak, A.; Zedadra, O.; Kouahla, M.N.; Guerrieri, A.; Seridi, H.; Fortino, G. At the Confluence of Artificial Intelligence and Edge Computing in IoT-Based Applications: A Review and New Perspectives. Sensors 2023, 23, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Yue, B.; Wan, J.; Guizani, M. Information fusion for edge intelligence: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2022, 81, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Shi, G.; Li, Y.; Saad, W.; Poor, H.V. Toward self-learning edge intelligence in 6G. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Yao, D.; Kang, X.; Abulizi, A. Blockchain and K-means algorithm for edge AI computing. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1153208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raith, P.; Dustdar, S. Edge Intelligence as a Service. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Services Computing (SCC), Chicago, IL, USA, 5–10 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 252–262. [Google Scholar]
- Ciampi, L.; Gennaro, C.; Carrara, F.; Falchi, F.; Vairo, C.; Amato, G. Multi-camera vehicle counting using edge-AI. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 207, 117929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Mu, G.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, T. Benchmark analysis of yolo performance on edge intelligence devices. Cryptography 2022, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, F.; Guerreiro-Santalla, S.; Naya, M.; Duro, R.J. AI Curriculum for European High Schools: An Embedded Intelligence Approach. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2022, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandinetti, J. Examining embedded apparatuses of AI in Facebook and TikTok. AI Soc. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Su, X.; Tarkoma, S.; Jiang, T.; Crowcroft, J.; Hui, P. Edge intelligence: Architectures, challenges, and applications. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12172. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Su, X.; Tarkoma, S.; Jiang, T.; Crowcroft, J.; Hui, P. Edge intelligence: Empowering intelligence to the edge of network. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 1778–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welagedara, L.; Harischandra, J.; Jayawardene, N. Edge Intelligence Based Collaborative Learning System for IoT Edge. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 12th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 27–30 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 0667–0672. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; She, X.; Chakraborty, B.; Dash, S.; Mudassar, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Reliable edge intelligence in unreliable environment. In Proceedings of the 2021 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 1–5 February 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 896–901. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Ni, W.; Tao, X.; Zhang, P. Edge-intelligence-empowered, unified authentication and trust evaluation for heterogeneous beyond 5G systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, T.; Xu, L.; Mcardle, G. Edge intelligence for data handling and predictive maintenance in IIOT. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 49355–49371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaeri, M.; Afzal, A.; Shoaran, M. Challenges and opportunities of edge ai for next-generation implantable BMIs. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Circuits and Systems (AICAS), Incheon, Republic of Korea, 13–15 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 190–193. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, P. Artificial Intelligence Programming with Python, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ramya, R.; Ramamoorthy, S. Survey on Edge Intelligence in IoT-Based Computing Platform. In Ambient Communications and Computer Systems: Proceedings of RACCCS 2021; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2022; pp. 549–561. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, S.; Simoens, P.; Lootus, M.; Thakore, K.; Sharma, A. TinyMLOps: Operational Challenges for Widespread Edge AI Adoption. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW), Lyon, France, 30 May–3 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1003–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Seng, K.P.; Ang, L.M. Embedded intelligence: State-of-the-art and research challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 59236–59258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Letaief, K.B. Mobile edge intelligence and computing for the internet of vehicles. Proc. IEEE 2019, 108, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Anandaram, H.; Khanduja, M.; Kumar, R.; Saini, V.; Mohialden, Y.M. Recent Challenges on Edge AI with Its Application: A Brief Introduction. In Explainable Edge AI: A Futuristic Computing Perspective; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2022; pp. 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Zhao, H.; Fang, W.; Yin, J.; Dustdar, S.; Zomaya, A.Y. Edge intelligence: The confluence of edge computing and artificial intelligence. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 7457–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, L.; Shi, W. OpenEI: An open framework for edge intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 39th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Dallas, TX, USA, 7–10 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1840–1851. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Jiang, C. Edge intelligence: Challenges and opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer, Information and Telecommunication Systems (CITS), Hangzhou, China, 5–7 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sipola, T.; Alatalo, J.; Kokkonen, T.; Rantonen, M. Artificial Intelligence in the IoT Era: A Review of Edge AI Hardware and Software. In Proceedings of the 2022 31st Conference of Open Innovations Association (FRUCT), Helsinki, Finland, 27–29 April 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 320–331. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Leung, V.C.; Niyato, D.; Yan, X.; Chen, X. Convergence of edge computing and deep learning: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 869–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, B.; Amin, K. Edge Intelligence: A Robust Reinforcement of Edge Computing and Artificial Intelligence. In Innovations in Information and Communication Technologies (IICT-2020); Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021; pp. 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, A.Y.; Peltonen, E.; Meuser, T.; Aral, A.; Becker, C.; Dustdar, S.; Hiessl, T.; Kranzlmüller, D.; Liyanage, M.; Maghsudi, S.; et al. Roadmap for edge AI: A Dagstuhl perspective. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2112.00616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, J.; Bierzynski, K.; Cuéllar, M.; Morales, D.P. Edge Intelligence: Concepts, architectures, applications and future directions. ACM Trans. Embed. Comput. Syst. (TECS) 2022, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, T.; Dustdar, S. Edge intelligence: The convergence of humans, things, and Ai. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Engineering (IC2E), Prague, Czech Republic, 24–27 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar, A.; Ouyang, C. Edge Computing Architecture. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/cloud/architecture/architectures/edge-computing/reference-architecture/ (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Hallsten, J.; Viorel, P.; Petterson, S. IIC: Industrial IOT Reference Architecture. 2022. Available online: https://www.iiot-world.com/industrial-iot/connected-industry/iic-industrial-iot-reference-architecture/ (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Isaja, M. Reference Architecture for Factory Automation using Edge Computing and Blockchain Technologies. In The Digital Shopfloor-Industrial Automation in the Industry 4.0 Era; River Publishers: Aalborg, Denmark, 2022; pp. 71–101. [Google Scholar]
- Edge Computing Reference Architecture 2.0. Available online: http://en.ecconsortium.net/Lists/show/id/82.html (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Sabella, D.; Vaillant, A.; Kuure, P.; Rauschenbach, U.; Giust, F. Mobile-edge computing architecture: The role of MEC in the Internet of Things. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2016, 5, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortino, G.; Guerrieri, A.; Savaglio, C.; Spezzano, G. A Review of Internet of Things Platforms through the IoT-A Reference Architecture. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Intelligent and Distributed Computing, Bhubaneswar, India, 19–23 January 2022; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2022; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- De Majo, C.; Giuffrida, M. Understanding Cloud-Edge-IoT: Challenges and Opportunities—Webinar Highlights. 2022. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/7185383#.Y_7TRh9ByUl (accessed on 30 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Ooko, S.O.; Mukanyiligira, D.; Munyampundu, J.P.; Nsenga, J. Edge AI-based respiratory disease recognition from exhaled breath signatures. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Jordan International Joint Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information Technology (JEEIT), Amman, Jordan, 16–18 November 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Ooko, S.O.; Mukanyiligira, D.; Munyampundu, J.P.; Nsenga, J. Synthetic Exhaled Breath Data-Based Edge AI Model for the Prediction of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computing and Communications Applications and Technologies (I3CAT), Ipswich, UK, 15 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Tang, J.; Yu, B.; Wang, Y.; Shi, W. Edge computing for autonomous driving: Opportunities and challenges. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1697–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, N.; Yin, H. Integrated networking, caching, and computing for connected vehicles: A deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 67, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ota, K.; Dong, M. Deep learning for smart industry: Efficient manufacture inspection system with fog computing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4665–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, O.; Ecker, W.; Feldner, I.; Frischknecht, A.; Gerum, C.; Hämäläinen, T.; Hanif, M.A.; Klaiber, M.J.; Mueller-Gritschneder, D.; Bernardo, P.P.; et al. Automated HW/SW co-design for edge ai: State, challenges and steps ahead: Special session paper. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Hardware/Software Codesign and System Synthesis (CODES+ ISSS), Austin, TX, USA, 10–15 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Savaglio, C.; Campisano, G.; Di Fatta, G.; Fortino, G. IoT services deployment over edge vs cloud systems: A simulation-based analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 554–559. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, R.; Li, W.; Qiu, C.; Wang, X. SimEdgeIntel: A open-source simulation platform for resource management in edge intelligence. J. Syst. Archit. 2021, 115, 102016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaglio, C.; Fortino, G. A simulation-driven methodology for IoT data mining based on edge computing. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. (TOIT) 2021, 21, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, D.P.; Velasquez, K.; Curado, M.; Monteiro, E. A comparative analysis of simulators for the cloud to fog continuum. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2020, 101, 102029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, R.; Pianini, D.; Placuzzi, A.; Viroli, M.; Weyns, D. Pulverization in cyber-physical systems: Engineering the self-organizing logic separated from deployment. Future Internet 2020, 12, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, R.; Fortino, G.; Pianini, D.; Placuzzi, A.; Savaglio, C.; Viroli, M. A Methodology and Simulation-based Toolchain for Estimating Deployment Performance of Smart Collective Services at the Edge. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 20136–20148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corchado, J.M.; Ossowski, S.; Rodríguez-González, S.; De la Prieta, F. Advances in explainable artificial intelligence and edge computing applications. Electronics 2022, 11, 3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taivalsaari, A.; Mikkonen, T. A taxonomy of IoT client architectures. IEEE Softw. 2018, 35, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).