Abstract
Text mining in big data analytics is emerging as a powerful tool for harnessing the power of unstructured textual data by analyzing it to extract new knowledge and to identify significant patterns and correlations hidden in the data. This study seeks to determine the state of text mining research by examining the developments within published literature over past years and provide valuable insights for practitioners and researchers on the predominant trends, methods, and applications of text mining research. In accordance with this, more than 200 academic journal articles on the subject are included and discussed in this review; the state-of-the-art text mining approaches and techniques used for analyzing transcripts and speeches, meeting transcripts, and academic journal articles, as well as websites, emails, blogs, and social media platforms, across a broad range of application areas are also investigated. Additionally, the benefits and challenges related to text mining are also briefly outlined.
1. Introduction
In recent years, we have witnessed an increase in the quantities of available digital textual data, generating new insights and thereby opening up opportunities for research along new channels. In this rapidly evolving field of big data analytic techniques, text mining has gained significant attention across a broad range of applications. In both academia and industry, there has been a shift towards research projects and more complex research questions that mandate more than the simple retrieval of data. Due to the increasing importance of artificial intelligence and its implementation on digital platforms, the application of parallel processing, deep learning, and pattern recognition to textual information is crucial. All types of business models, market research, marketing plans, political campaigns, or strategic decision-making are facing an increasing need for text mining techniques in order to address the competition.
Large amounts of textual data could be collected as a part of a research, such as scientific literature, transcripts in the marketing and economic sectors, speeches in the field of political discourse, such as presidential campaigns and inauguration speeches, and meeting transcripts. Furthermore, online sources, such as emails, web pages, blogs/micro-blogs, social media posts, and comments, provide a rich source of textual data for research [1]. Large amounts of data are also being collected in semi-structured form, such as log files containing information from servers and networks. As such, text mining analysis is useful for both unstructured and semi-structured textual data [1].
Data mining and text mining differ on the type of data they handle. While data mining handles structured data coming from systems, such as databases, spreadsheets, ERP, CRM, and accounting applications, text mining deals with unstructured data found in documents, emails, social media, and the web. Thus, the difference between regular data mining and text mining is that in text mining the patterns are extracted from natural language text rather than from structured databases of facts [2]. Since all the written or spoken information can be represented in textual form, data mining requires all kinds of text mining tools when it comes to the interpretation and analysis of sentences, words, phrases, speeches, claims, adverts, and statements. This paper conducts an extensive analysis of text mining applications in big data analytics as used in various commercial fields and academic studies. While the vast majority of the literature deals with the optimization of a specific text mining technique, this paper seeks to summarize the features of all text mining methods, thereby summarizing the state-of-the-art practices and approaches in all the possible fields of application. It is centered around seven key applications of text mining in transcripts and speeches, meeting transcripts, and academic journal articles, as well as websites, emails, blogs, and social media networking sites; for each of these, we, respectively, provide a description of the field, their functionality, the most commonly used methods, the associated problems, and the related and relevant references.
The remaining sections of this paper are organized in the following manner. In the Section 2, we introduce the topic of text mining in transcripts and speeches. We explain the different classification techniques used in, for instance, the analysis of political speeches that classify opinions or sentiments in a manner that allows one to infer from a text or speech the ideology that a speaker most probably espouses. Furthermore, we explain the methods used in classifying transcripts and speeches and identify the shortcomings of these methods, which are primarily related to the behavioral nature of human beings, such as ironic or ideological behavior. In the Section 3, we take a closer look at blog mining, the dominance of news-related content in blogs and micro-blogging, and present the methods used in this area. Most of the methods applied in blog mining are based on dimensionality reduction, which is also found in other fields of text mining applications. Additionally, the relationship between blog mining and cybersecurity—which is an interesting and novel application of blog mining—is also covered in this section. In the Section 4, we analyze email mining and the techniques commonly used in relation to it. A very specific feature of email mining is its noisy data, which has been discussed in this section. Moreover, we explain the challenges to the identification of the content of the email body and how email mining is used in business intelligence. The web mining techniques that are used in screening and analyzing websites are studied in the Section 5. The features of a website, such as links, links between websites, anchor text, and html tags, are also discussed. Moreover, the difficulty of capturing unexpected and dynamically generated patterns of data is also explored. Additionally, the importance of pattern recognition and text matching in e-commerce is highlighted. In the Section 6, we present studies conducted on the use of Twitter and Facebook and explain the role of text mining in marketing strategies based upon social media, as well as the use of social media platforms for the prediction of financial markets. In Section 7 and Section 8, we round up our extensive analysis of text mining applications by exploring the text mining techniques used for academic journal articles and meeting transcripts. Section 9 discusses the important issue of extract hidden knowledge from a set of texts and building hypotheses. Finally, in the concluding section, we highlight the advantages and challenges related to text mining and discuss its potential benefits to society and individuals.
2. Text Mining in Transcripts and Speeches
Text mining refers to the extraction of information and patterns that are implicit, previously unknown, and potentially valuable in an automatic or semi-automatic manner from immense unstructured textual data, such as natural-language texts [3].
There are two types of text mining algorithms: supervised learning and unsupervised learning (the two terms originated in machine learning methods). Supervised learning algorithms are employed when there is a set of predictors to predict a target variable. The algorithm uses the target’s observed values to train a prediction model. Support vector machines (SVMs) are a set of supervised learning methods used for classification and prediction. On the other hand, unsupervised learning methods do not use a target value to train their models. In other words, the unsupervised learning algorithms use a set of predictors (features) to reveal hidden structures in the data. Non-negative matrix factorization is an unsupervised learning method [4].
Transcripts are a written or printed version of material originally presented in another medium, such as in speeches. Therefore, the analysis of transcripts can be treated in the same manner as the analysis of speeches, as spoken words need to be pre-processed through, for instance, a voice-recognition API or manual transcription. Despite its extensive application in transcripts from other fields, such as marketing and political science, text mining as a technique in economics has historically been less explored. Bholat et al. [5] presented a comprehensive overview of the various text mining techniques used for research topics of interest to central banks for analyzing a corpus of documents, including, amongst others, the verbatim transcripts of meetings. Recently, three years of speeches, interviews, and statements of the Secretary General of Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) were analyzed using text-minin techniques [6].
The ideology, as a key factor affecting an individual’s system of beliefs and opinions that controls their acts, is an important feature in text mining when it comes to political (or religious) textual data. Ideology provides the “knowledge of what-goes-with-what” [7] and shapes each individual’s perception of any given issue [8]. However, the main issue in taking ideology as a feature for text and opinion mining is that, in many cases, the ideology of the speaker is not very clear, especially when it comes to politicians. To overcome the issue, one may use the texts with known ideological background and build a classification model to classify ideology behind a text, based on the textual data. Applying the trained classification model to a political text would help understand the ideology behind the speech or a text and, consequently, the opinion of a person.
Two approaches are extensively used in text mining: opinion classification and sentiment classification [9].
2.1. Opinion Classification
The main concern in opinion mining is to determine to what extent a text in-hand supports or opposes a specific subject. Although opinion mining is vastly used to analyze political texts, from speeches to short text on Twitter [8], it is very useful in other fields, too. For instance, one may use opinion mining to determine the opinion of the customers on features of a product, an audience’s opinion on a movie, or to find the people’s favorite asset in a market [10,11,12]. Most applications, in the context of political speeches, target the curation of general-purpose political opinion classifiers, given their potential and significant uses in e-rulemaking and mass media analysis [13,14,15,16]. The steps involved in the implementation of opinion mining are as follows [17]:
- Determining text polarity to decide whether a given text is factual in nature (i.e., it unbiasedly describes a particular situation or event and refrains from providing a positive or a negative opinion on it) or not (i.e., it comments on its subject matter and expresses specific opinions on it), which amounts to the categorization of binary texts into subjective and objective [18,19].
- Determining text polarity to decide if a given subjective text posits a positive or negative opinion on the subject matter [18,20].
- Determining the extent of text polarity to categorize the positive opinion extended by a text on its subject matter as weakly positive, mildly positive, or strongly positive [21,22].
The literature related to opinion mining is growing see [23,24]. A highly beneficial source for opinion classification is Wordnet [25] by Princeton University, a lexical database of the English language containing nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs grouped into 117,000 sets of cognitive synonyms (synsets), with each set expressing a distinct concept. A detailed description of Wordnet can be found in an article by Miller et al. [26].
2.2. Sentiment Classification
Sentiment classification is closely related to opinion mining and is mainly based on a technique called sentiment scoring. The basic idea behind the technique is to extract effective content from a text based on the appraisal, polarity, tone, and valence [27]. In order to build a sentiment score, one may use a set of predefined lists of terms with allocated quantitative weights for positive and negative connotations. Then, counting the positive and negative terms will get a score showing how much a text opposes or approves a given subject [28]:
Taking the weights into account (if weights already exist):
where is the sentiment weight for ith positive term, and is the sentiment weight for jth negative term.
This measure is subsequently interpreted as a relative gap between positively and negatively connoted language. In a seemingly convenient manner, it ranges between −1 and + 1, where a score of 0.5, for example, is interpreted as 50% points overweight for positively connoted language, implying a fairly positive sentiment guiding the text [27].
However, despite its strengths, such as implementation transparency, relevance, replicability, intuitiveness, and a high level of human supervisory, sentiment classification also bears some drawbacks, such as context dependence, which might hold a positive connotation in their original context (e.g., commercial reviews) but convey a negative tone in political contexts, or vice versa. Furthermore, estimating the positive and negative weights is not always straightforward.
According to Rauh [27], the more technically advanced literature has recently explored context-specific machine-learning approaches (e.g., Ceron et al. [29], Hopkins et al. [30], Oliveira et al. [31], and van Atteveldt et al. [32]). They also addressed its challenges, such as oversimplification, irony, and negation.
2.3. Functionality
One interesting application of opinion and sentiment classification is to use them for predicting someone’s opinion or their system of beliefs and ideology based on their speech or written messages (e.g., text on social media, books, articles, etc.). Klebanov et al. [33] were the first researchers in the area of text classification to examine whether two people hold differing opinions or the same opinion but phrase it differently [34]. Moreover, they offered some insight into the conceptual structure that governs political ideologies, such as how these ideologies succeed in creating coherent belief systems, and determine (for the benefit of those who follow them) what goes with what. However, the results obtained in this manner provide a negligible amount of information regarding the structure of ideologies or the extent to which they are cohesive or convincing. In contrast, the studies conducted by Lakoff [35], Lakoff and Johnson [36], and Klebanov et al. [33] identify the underlying belief systems based on the cognitive structure and metaphors of liberal and conservative ideologies by employing an automatic lexical cohesion detector on Margaret Thatcher’s 1977 speech for the Conservative Party Conference. The identification of the underlying belief systems requires the pre-processing of the text. Miner et al. [37] proposed a pre-processing method by removing stopwords (e.g., “the”, “a”, “an”, etc.), prefixes (e.g., “re”, “pre”, etc.), and suffixes (e.g., “ing”, “ation”, “fy”, “itis”, etc.). Unifying words’ spellings and typesettings (lower and upper cases) and correcting misspelled words is another step in their pre-processing scheme. The pre-processing will make the words normalized in the text and reduce the noise in unstructured text data. Sarkar et al. [38] described a classification algorithm based on a SVM, which allows for 80–89% accuracy.
Sentiment and opinion classification is used for classification of discussion treads and reviews, too. Lu et al. [39] used the opinion classification methods to automatically discover the opposed opinion and build an opposing opinion network for a social thread. In order to build the network, they analyzed the agree/disagree relations between posts in a social network platform (i.e., a forum). The sentiment and opinion classification methods are developed based on machine learning methods (e.g., SVM, neural networks, naive Bayes, maximum entropy, and stochastic gradient descent) to classify the large number of online reviews [40,41]. Kennedy and Inkpen [40] and Tripathy et al. [41] applied classification methods to classify the Internet Movie Database (IMDB) movie reviews, though they did not build a network of opinions on the movies.
A challenge in the classification of political speeches is that political speeches feature far fewer sentiment words—typically, adjectives or adverbs—that have been identified to be most indicative of opinions, as in the case of movie reviews. Instead, political speeches tend to express opinions in the choice of the nouns. Moreover, nouns that hold no political connotations in common usage may come across as heavily-laden with political intentions when expressed in the context of a specific debate [8].
Acharya et al. [34] used classification algorithms that, by comparing the performance of logistic regression, SVM, and naive Bayes models (NB), analyzes the speech of a given United States (U.S.) presidential candidate from 1996–2016 to predict the candidate’s political party affiliation, as well as the region and year in which the speech was delivered. They found a superior performance of the logistic regression, followed by SVM and NB methods. These results are supported by the work conducted by Joachims [42], who found that logistic regression classifies a presidential candidate’s speech as democratic or republican most accurately. Thus, predicting the candidate’s political party and the year in which the speech was delivered is relatively easy, while predicting the location in which the speech was delivered, proves to be significantly more difficult.
2.4. Arguments Extraction
As another application, text mining is used to extract facts and arguments, specifically from political speeches and documents. An argument, in a certain context, usually consists of two main parts: a claim and a series of minor and major premises to support the claim. The premises are known and already proven facts. Argument extraction is closely related to opinion mining and belief classifications. Extracting the arguments from a large amount of textual data, not only helps building a knowledge base for a given subject or a task, it also helps to reexamine different arguments, with different common bases, and produce new ones in large scale. Extracting arguments requires distinguishing between the claims and the fact, which will result in extracting the arguments, along with the underlying facts. The big potential of argument extraction in political textual data has attracted many researchers in text mining. For instance, Sardianos et al. [43] proposed a supervised technique, based on conditional random fields, to extract arguments and their underlying facts. They applied the method to web pages containing news and tagged speeches. Florou et al. [44] applied a variate of argument extraction methods to Greek language social media to estimate the public support for an unannounced (unpublished or unfinished) policies. They took into account the structure of the sentences and discourse markers, like connectives, as well as the tense and mood of the verbal construction, and showed the importance of verbal construction in argument extraction. Goudas et al. [45] developed a two-stage approach to extract the arguments made by bloggers and others in social media related to the arguments made by policymakers, as well as new arguments in social media. The proposed model is applied to a vast number of Greek language social media contents. Their method has a high accuracy rate in extracting arguments and building relational links between arguments and policies. Lippi and Torroni [46] used the machine learning methods to extract arguments from seven party leaders’ debates during the 2015 UK general election. Their results show the importance of using voice features, along with textual data, when it comes to extracting claims and facts from a speech.
2.5. Methods
Generally, the first step in text mining (after cleansing the textual data and reducing the noise) is to represent the text using a proper model. A common text representation model represents a document as a vector of features. The feature vector represents text with its frequent words or phrases, or grammatical structure of the sentences [47]. Most simple vector representations of text consider a text as a Bag-of-Words (BOW) or combination of BOW with Bag-of-Characters. More advanced versions look at the text as a Bag-of-Features [48]. Another common text representation method is to use a graph or a diagram to represent the relation of the words and segments in a document [49]. The diagram representation can be used to demonstrate the relation between terms in a text and use these terms to classify/categorize the text [48]. The next problem in text mining is to find a similarity measure and a classification function to properly classify the texts. One approach is to employ semantic similarity measures [50]. In addition to similarity measures, one may use machine or statistical learning models to classify textual data. The logistic regression is a binary classification algorithm that applies the logistic function as the hypothesis. The model subsequently locates the optimal that minimizes the associated cost function that will then determine a separating sigmoid curve between the two classes [34]. SVM is a statistical classification method that was suggested by Cortes and Vapnik [51]. SVM, exploiting the structural risk minimization principle of computational learning theory, seeks a decision surface to categorize the training data points into two classes and forms decisions based on the SVMs which are identified as the only competent elements in the training set. According to Vinodhini and Chandrasekaran [52], SVMs separate the classes by building a margin in an effort to minimize the distance between each class and that margin.
NB models learn probabilities based on prior distribution across classes from the training data, under the assumption that all the features are independent; this specifically holds true when predicting a class based on training [34].
Yu et al. [8] tested the party classifiers for congressional speech data. They found that the classifiers which were trained on the house speeches are more efficient with processing senate speeches than vice versa and that the best overall classifier is SVM, which has equally weighted features.
In addition to the application of logistic regression, SVM, and NB, other statistical methods are also available for classification in natural language processing, such as maximum entropy and maximum likelihood [53], which use Candide, an automatic machine translation system developed by IBM, to test the performance of both the methods. These methods find a significant efficacy of maximum entropy techniques for performing context-sensitive modeling.
Other evidence for detectable patterns associated with ideological orientation in the political speech were found by Diermeier et al. [54], Evans et al. [55], and Laver et al. [56], as these studies achieve a high classification accuracy. Piryani et al. [57] presented an extensive scientometric analysis of the research work undertaken on opinion mining and sentiment analysis during 2000–2016.
Wilson et al. [22] created a system called the OpinionFinder, which performs a subjectivity analysis. Thus, it can automatically identify texts with opinions, sentiments, speculations, and other private states. OpinionFinder seeks to identify subjective sentences and to highlight the various aspects of subjectivity in these sentences, including the source (holder) of the subjectivity and words that are included in phrases expressing positive or negative sentiments. It encompasses four components:
- An NB classifier that applies several lexical and contextual features to distinguish between subjective and objective sentences [58,59];
- A component for identifying speech events (e.g., “stated” and “according to”) and directing subjective expressions (e.g.,, “appalled” and “is sad”);
- A source identifier combining a conditional random field sequence tagging model [60] and extraction pattern learning [61] to determine the sources of the speech events and subjective expressions [62];
- A component that applies two classifiers to identify the words contained in phrases that express positive or negative sentiments [63].
2.6. Shortcomings
Sentiment analysis, however, faces a predominant challenge with its classification of text under one particular sentiment polarity, whether positive, negative or neutral [24,64,65,66,67]. In order to solve this problem, Fang [68] proposed a general process for the categorization of sentiment polarity.
Another field of application is the detection of offensive language in the so-called hate speech, which refers to submitting to stereotypes to express and propagate an ideology of hate [69,70].
A key problem in speech recognition is that transcripts with high word error rate are obtained for documented speeches in poor audio conditions and spontaneous speech recorded in actual conditions, as pointed out by the NIST Rich Transcription Meeting program [71]. Recordings from Call centers and telephone surveys are of poor audio quality due to the use of cell phones and/or surrounding noise, unconstrained speech, variable utterance length, and various disfluencies, such as pauses, repetitions, and rectifications. Consequently, speech mining is extremely difficult on this type of corpora [72]. Camelin et al. [72] proposed a sampling and information extraction strategy as the solution to these problems. In order to evaluate the accuracy, as well as the representativeness, of the extracted information, they suggested several solutions based on the Kullback-Leibler divergence.
3. Blog Mining
Blogs allow authors to maintain entries that are continuing and arranged in reverse chronology for an audience that can interact with the authors through the comments section. Blogs can belong to a broad variety of genres, ranging from diaries of personal and mundane musings to corporate business blogs; however, they tend to be associated with more personal and spontaneous forms of writing. Social researchers have capitalized on blogs as a source of data in several cases, from performing content analysis related to gender and language use to determining ethnographic participation in blogging communities [73]. After the creation of the very first blog, Links.net, in 1994 [74], the internet became home to hundreds of millions of blogs. Due to the large numbers of existing blog posts, the blogosphere content may seem haphazardly and chaotic [75]. Consequently, effective mining techniques are required to aid in the analysis and comprehension of blog data. Webb and Wang [76] reviewed the general methodological options that are frequently used when studying blogs and micro-blogs; the options investigated included both quantitative and qualitative analyzes, and the study was undertaken in an effort to offer practical guidance on how a researcher can reasonably sift through them.
Many of the blog mining techniques are similar to those used for text and web documents; however, the nature of blog content may lead to various linguistic and computational challenges [77,78]. Current research in blog mining reflects the prominence of news or news-related content and micro-blogging. Blog mining, furthermore, overlaps with features of social media mining [79,80].
Apart from the text content, blogs also provide other information, such as details regarding the title and author of the blog, its date and time of publication, and tags or category attributes, among others. Similar to other social media data, blog content also undergoes changes over time. New posts are uploaded, novel topics are deliberated over, perceptions change, and new communities spring up and mature. Identifying and understanding the topics that are trending in the blogosphere can provide credible information regarding product sales, political views, and potentially attention-garnering social areas [81,82].
Methods in blog mining that have gained popularity over the years include classification and clustering [83], probabilistic latent sentiment analysis (PLSA) or latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA), mixture models, time series, and stream methods [80]. Existing text mining methods and general dimensionality reduction methods have been used by a number of studies [75,77,84,85,86,87] on blog mining; however, the analysis that can be undertaken with these methods is limited to mono- or bi-dimensional blog data, while the general dimensionality methods may not be effective in preserving information retrieved from blogs [88]. Tsai [78] applied the tag-topic model for blog data mining. Dimensionality reduction was performed with the spectral dimensionality reduction technique Isomap to show the similarity plot of the blog content and tags. Tsai [88] presented an analysis of the multiple dimensions of blog data by proposing the unsupervised probabilistic blogger-link-topic (BLT) model to address the challenges in determining the parties most likely to blog about a specific topic and in identifying the associated links for a given blog post on a given topic and detect splog. The results indicated that BLT obtained the highest average precision for blog classification with respect to other techniques that used the blogger-date-topic (BDT), author-topic (AT), and LDA models. In the study of Tsai [89], the AT model based on the LDA was extended to the analyzes and visualization of blog authors, associated links, and time of publication, and a framework based on dimensionality reduction was suggested to visualize the dimensions of content, tags, authors, links, and time of publication. This study was the first to analyze the multiple dimensions of blogs by using dimensionality reduction techniques, namely multidimensional scaling (MDS), Isomap, locally linear embedding (LLE), and LDA, on a set of business blogs.
Sandeep and Patil [90], after conducting a brief review of the literature on blog mining, proposed a multidimensional approach to blog mining by defining a method that combines the blog content and blog tags to discern blog patterns. However, the proposed method can only be applied to text-based blogs.
Blogs can be categorized, influential blogs can be promoted, and new topics can be identified. It is also possible to ascertain perspectives or sentiments from the blogosphere through data mining techniques [81]. Although several solutions are available that can effectively handle information in small volumes, they are static in nature and usually do not scale up accurately owing to their high complexity. Moreover, such solutions have been designed to run once or in a fixed dataset, which is not sufficient for processing huge volumes of streamed data. In response to this issue, Tsirakis et al. [91] suggested a platform focusing on real-time opinion mining from news sites and blogs. Hussein [92] presented a survey on the challenges relevant to the approaches and techniques of sentiment analysis. Furthermore, the research of Chen and Chen [93] applied big data and opinion mining approaches to the analysis of investors’ sentiments in Taiwan. First, the authors reviewed previous studies related to sentiment mining and selection of features; subsequently, they analyzed financial blogs and news articles available online for creating a public mood dynamic prediction model exclusively for Taiwanese stock markets by taking into account the views of behavioral finance and the features of financial communities on the internet.
The filtering of spam blogs is another predominant theme in blog mining, and it can considerably misrepresent any estimation of the number of blog posts made [78] and the evaluation of cybersecurity threats. Most intelligence analysis studies have focused on analyzing the news or forums for security incidents, but few have concentrated on blogs. Tsai and Chan [85] analyzed blog posts for identifying posts made under various categories of cyber security threats related to the detection of cyber attacks, cybercrime, and terrorism. PLSA was used for detecting keywords from various cyber security blog entries pertaining to specific topics. Along similar lines, Tsai and Chan [94] proposed blog data mining techniques for assessing security threats. They used LDA-based probabilistic methods to detect keywords from security blogs with respect to specific topics. The research concluded that the probabilistic approach can enhance information retrieval related to blog search and keyword detection. Recognition of cyber threats from open threat intelligence can prove beneficial for incident response in very early stages. Lee et al. [95] proposed a free web service for examining emerging cybersecurity topics based on the mining of open threat intelligence, which is dedicated to locating various emerging topics in cyber threats (i.e., nearly zero-day attacks) and providing possible solutions for organizations. The demonstration showed that with information collected from experts on Twitter and specific targeted RSS blogs, Sec-Buzzer promptly recognizes the emerging information security threats and, subsequently, publishes related news, technical reports, and solutions in time.
Applications of blog mining vary and, among others, include opinion mining for agriculture [96], prospective industrial technologies [97], decision support in fashion buying processes [98], detection of major events [99], retrieval of information regarding popular tourist locations, and travel routes [100], the summarization of popular information from massive tourism blog data [101], summarization of news blogs and detecting the copy and reproduced multi-lingual contents [102,103,104] and detecting the fake news [105].
4. Email Mining
Email is a convenient and common means of textual communication. It is also intrinsically connected to the overall internet experience since an email account is required for signing up for any form of online activity, including to create accounts for social networking platforms and instant messaging. The Radicati Group, Inc., executive summary of email statistics report 2012–2019 [106] predicts that the total number of business and consumer emails sent and received daily will exceed 293 billion in 2019; this statistic is forecasted to increase to over 347 billion by the end of 2023. To optimize the use of emails and explore its business potential, email mining has been extensively undertaken and has observed commendable progress in terms of both research and practice.
Email mining is similar to text mining since they both pertain to textual data. However, specific characteristics of email data separate it from text mining. To begin with, email data can be highly noisy. More specifically, it may include headers, signatures, quotations, or program codes. It may also carry extra line breaks or spaces, special character tokens, or spelling and grammar mistakes. Moreover, spaces and periods may be mistakenly absent from it. Hence, the email data needs to be cleaned in depth before high quality mining [107]. In addition, an email is a data stream targeted towards a specific user and the concepts or distributions of the target audiences of the messages may vary over time with respect to the messages received by that user. It is also problematic to obtain public email data for experiments due to privacy issues [108].
Emails contain links to a vast social network with data on the person or organization in charge, thus making email mining more resourceful [109]. During email mining, the links can be exploited for their content and a better understanding of behavior. On the other hand, the techniques currently in use are not able to effectively handle the vast amount of data. There is heterogeneity, noise, and variety, and mining techniques cannot be easily modified to adjust to big data environments [110]. Another challenge in email mining is data visualization, which makes decision-making considerably harder. Hidden information cannot be extracted or visualized due to the lack of scalable visualization tools. If the data is not presented more comprehensibly, visualization and decision-making also become difficult for the data miners [111].
Initial studies on email mining predominantly focused on the existing tools for personal collection management since large and diverse collections were not accessible for research use [112]. That changed, most notably with the Enron Corporation email collection [113]. However, the LingSpam corpus, compiled by Androutsopoulos et al. [114], was one of the first publicly available datasets.
A number of email mining studies have focused on people-related tasks, including name recognition and reference resolution, contact information extraction, identity modeling and resolution, role discovery, and expert identification, as well as the generation of access to large-scale email archives from multiple viewpoints by using a faceted search [115]. Moreover, some significant applications of email mining include tasks, such as filtering emails based on priority and identifying spam and phishing emails, as well as automatic answering, thread summarization, contact analysis, email visualization, network property analysis, and categorization [116,117].
Tang et al. [116] conducted a brief but exhaustive survey on email mining. The authors introduced the feature-based and social structure-based representation approaches, which are often performed in the pre-processing phase. Following this, they identified five email mining tasks—spam detection, email categorization, contact analysis, email network property analysis, and email visualization. Later, the commonly used techniques for each task were discussed. These included NB, SVMs, rule-based and content-based models, and random forest (RF), as well as K-nearest neighbour (K-NN) classifiers (pertaining to the classification problem in the email content detection) and the K-means algorithm (pertaining to the semi-supervised clustering problem). The methods based on principal component analysis (PCA), LDA, and term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) were presented as well.
The study by Mujtaba et al. [117] comprehensively reviewed 98 articles published between 2006–2016 on email classification from the Web of Science core collection databases and the Scopus database. In this study, the methodological decision analysis was performed in the following five aspects: (1) email classification application areas, (2) the datasets used in each application area, (3) feature space utilized in each application area, (4) email classification techniques, and (5) the use of performance measures.
Sentiment analysis of online text documents has been a flourishing field of text mining among researchers and scholars. In contrast to the content of public data, the real sentiment is often expressed in personal communications. Emails are frequently used for sending emotional messages that reflect deeply meaningful events in the lives of people [118]. On the other hand, sentiment analysis on large business emails could reveal valuable patterns useful for business intelligence [119,120]. The study of Hangal et al. [118] proposed the use of sentiment analysis techniques on the personal email archives of users to aid the task of personal reflection and analysis. The authors built and publicly released the Muse email mining system. The system helps users to analyze, mine, and visualize their own long-term email archives. Moreover, Liu and Lee [120] proposed a framework for email sentiment analysis that uses a hybrid scheme of algorithms, combined with K-means clustering and SVM classifier, and is to be applied to the Enron email corpus. The evaluation for the framework is conducted by comparing three labeling methods, namely, SentiWordNet, K-means, and polarity, and five classifiers, namely, SVM, NB, logistic regression (LR), decision tree (DT), and OneR. The empirical results indicated that the combined K-means and SVM algorithm achieved high accuracy compared to other approaches. In continuation of their previous studies, Liu and Lee [121] conducted sentiment clustering on Enron email data with a novel sequential viewpoint. This involved the transformation of sentiment features into a trajectory representation for implementing the trajectory clustering (TRACLUS) algorithm, along with the combination of sentiment temporal clustering, so as to discover sentiment flow in email messages in the topical and temporal distribution.
While insider threats in cybersecurity are often associated with malicious activities, insider threat is one of the most significant threats faced in business espionage [122]. Chi et al. [123], focused on the detection of insider threats by combining linguistic analysis and K-means algorithm to analyze communications, such as emails, to ascertain whether an employee meets certain personality criteria and to deduce the risk level for each employee. Soh et al. [124] focused on an aspect-based sentiment analysis that can provide more detailed information. Moreover, they presented a novel employee profiling framework equipped with deep learning models for insider threat detection, which is based on aspect-based sentiment and social network information. The authors evaluated the new presented framework, ASEP, on the dataset of the augmented Enron emails, and demonstrated that the employee profiles retrieved from ASEP can effectively encode the implicit social network information and, more significantly, their aspect-based sentiments.
The continued growth in the number of email users has led to a massive increase in spam emails. The global average of the daily spam volume for June 2019 was 459.40 billion, while the corresponding average of the daily (legitimate) email volume was 79.82 billion [125]. The large volume of spam emails moving through computer networks has a debilitating effect on the memory space available to email servers, communication bandwidth, CPU power, and user time. On the other hand, if we consider the fact that the majority of cyber attacks start with a phishing email [126] into accounts, there can be no doubt that phishing is a high-risk attack vector for organizations and even government agencies. Therefore, a predominant challenge in the email mining process is to identify and isolate spam emails.
Two general approaches are adopted for mail filtering: knowledge engineering (KE) and machine learning (ML) [127]. Spam filtering techniques based on knowledge engineering use a set of predefined rules. These rules are implemented to identify the basic characteristics of the email message. The ML techniques construct a classifier by training it with a set of emails called the training dataset. Several filtering methods based on ML have been extensively adopted when addressing the problem of email spam.
Bhowmick and Hazarika [128] presented an exhaustive review of some of the frequently used content-based email spam filtering methods. They mostly focused on ML algorithms for spam filtering. The authors studied the significant concepts, efforts initiated, effectiveness, and trends in spam filtering. They comprehensively discussed the fundamentals of email spam filtering, the changing nature of spam, and spammers’ tricks to evade the spam filters of email service providers (ESPs). Moreover, they examined the popular machine learning techniques used in combating the menace of spam.
Dada et al. [129] examined the applications of ML techniques to the email spam filtering process of leading internet service providers (ISPs), such as Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook, and focused on revisiting the machine learning techniques used for filtering email spam over the 2004–2018 period, such as K-NN, NB, Neural Networks (NN), Rough set, SVM, NBTree classifiers, firefly algorithm (FA), C4.5/J48 decision tree algorithms, logistic model tree induction (LMT), and convolutional neural network (CNN). Stochastic optimization techniques, such as evolutionary algorithms (EAs), have also been explored by Dada et al. [129], as the optimization engines are able to enhance feature selection strategies within the anti-spam methods, such as the genetic algorithm (GA), particle swarm optimization (PSO), and ant colony algorithm (ACO).
Most of relevant works on this topic classify emails using the term “occurrence” in the email. Some works, additionally, focus on the semantic properties of the email text. In the study conducted by Bahgat et al. [130], the email filtering was based on the introduction of semantic modeling to address the high dimensionality of features by examining the semantic attributes of words. Various classifiers were studied to gauge their performance in segregating emails as spam or ham experiments on the Enron dataset. Correlation-based feature selection (CFS) which was introduced as a technique for feature selection, improved the accuracy of RF and radial basis function (RBF) network classifiers, while CFS ensured the accuracy of other classifiers, such as SVM and J48.
A phishing attack that uses sophisticated techniques that direct online customers to a new web page that has not yet been included in the black-list is called a zero-day attack [131]. Chowdhury et al. [132] in their overview of the work on the filtering of phishing emails and pruning techniques, proposed a multilayer hybrid strategy (MHS) for the zero-day filtering of phishing emails that emerge during a separate time span, which uses the training data collected previously during another time span. MHS was based on a new pruning method, the multilayer hybrid pruning (MHP). The empirical study demonstrated that MHS is effective and that the performance of MHP is better than that of other pruning techniques.
In a newer approach aimed at studying the detection of phishing emails, Smadi et al. [133] discussed the relevant work on protection techniques, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Moreover, they proposed a novel framework that combines a dynamic evolving neural network, based on reinforcement learning (RL), to detect phishing attacks in the online mode for the first time. The proposed model, phishing email detection system (PEDS), was also the first work in this field that used reinforcement learning to detect a zero-day phishing attack. NN was used as the core of the classification model, and a novel algorithm, called the dynamic evolving neural network, which used reinforcement learning (DENNuRL), was developed to allow the NN to evolve dynamically and build the best NN capable of solving the problem. It was demonstrated that the proposed technique can handle zero-day phishing attacks with high levels of performance and accuracy, while comparison with other similar techniques on the same dataset indicated that the proposed model outperformed the existing methods.
5. Web Mining
The World Wide Web (or the web) is at present a popular and interactive medium for disseminating information. The most commonly accessed type of information on websites is textual data, such as emails, blogs, social media, and web news articles. Web data differs from the data retrieved from other sources because of certain characteristics that make it more advantageous. In fact, website information is readily available to the public at large, is cost-effective in terms of access, and can be extensive with respect to coverage and the volume of data contained [134]. However, locating information on the web is a daunting and challenging task because of the immense volume of data and noise contained [135].
Etzioni [136] referred to web mining as the application of data mining techniques to automatically discover and extract knowledge in a website, while Cooley et al. [137] further highlighted the importance of considering the behavior and preferences of the users. Web mining has enabled the analysis of the increasing volume of data accessible on the web. Furthermore, it has indicated that conventional and traditional statistical approaches are inefficient in undertaking this task [138]. Besides, clean and consolidated data is closely connected to the quality and utility of the patterns discerned through these tools since they are directly dependent on the data to be used [139].
Web usage mining (WUM), web structure mining (WSM), and web content mining (WCM) are the three predominant categories of web mining [136,140,141]. WCM and WSM utilize the primary web data, while WUM mines the secondary data [136].
WCM adopts the concept and principles of data mining to discover information from the text and media documents [142]. WCM mainly focuses on web text mining and web multimedia mining. WSM emphasizes the hyperlink structure of the web to link the different objectives together [143]. A typical web graph is structured with web pages as nodes and hyperlinks as edges, establishing a connection between two related pages. WSM primarily works on link mining, internal structure mining and URL mining. In addition, WSM can be used for categorizing web pages and is useful for gathering information, such as that pertaining to the similarities and relationships between different websites. The typical applications of WSM are (a) link-based categorization of web pages, (b) ranking of web pages through a combination of content and structure, and (c) reverse engineering of website models [144]. Link-based classification pertains to the prediction of a web page category, which is based on the words on the page, links existing between the pages, anchor text, HTML tags, and other potential attributes on a web page. WUM is the process of applying data mining techniques to the discovery of usage patterns from the web data [145]. When a user interacts with a website, web log data is generated on a web server in the form of web server log files. Different types of usage log files, such as access log, error log, referrer log, and agent log, are created on a server [146]. Web logs are the type of data that prove the most resourceful when performing a behavioral analysis on a website user [137]. Web usage mining consists of three phases: (1) pre-processing, (2) discovery of usage patterns, and (3) analysis of the pattern. Typical applications are (a) the ones based on user modeling techniques, such as web personalization, (b) adaptive web sites, and (c) user modeling [144]. However, this personalization process that contains rebuilding a user’s session has raised important legal and ethical concerns. Velásquez [139] adopted an integrative approach based on the distinctive attributes of web mining to identify the harmful techniques.
Analyzing the patterns generated from a typical web user’s complex behavior is a daunting task since, most of the time, a user is responsible for the spontaneous and dynamic generation of patterns of data [147,148]. The exploration of the web for outliers, such as noise, deviation, incongruent observations, peculiarities, and exceptions, has received attention in the mining community. Chandola et al. [149] provided a general and broad overview of the extensive research conducted on anomaly detection techniques, spanning multiple research areas and application domains, including web applications and web attacks. Gupta and Kohli [148], Gupta and Kohli [150], Gupta and Kohli [151] made experimental attempts to identify outliers in regression algorithm outputs by using web-based datasets. In fact, various regression algorithms are extensively adopted by several online portals operating in varying application domains, especially e-commerce websites [148]. Specifically, Gupta and Kohli [151] formulated a framework with the help of ordered weighted operators (OWA) as a multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) problem. The results proved that the proposed framework can aid in considerably reducing the outliers; however, its testing was restricted to a static purpose and a small dataset and the data were scattered for over a year. This work was an extension of an earlier study by Gupta and Kohli [150] in which a small experiment was conducted on a web dataset through the application of an ordered weighted geometric averaging operator. A recent study by Gupta and Kohli [148] detected outliers based on the principle of multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) and utilized ordered weighted operators for the purpose of aggregation.
On a daily basis, news websites feature an overwhelming number of news articles. While several text mining techniques can be applied to web news articles, the constantly changing data characteristics and the real-time online learning environment can prove to be challenging.
Two recent studies, conducted by Iglesias et al. [152] and Za’in et al. [153], proposed a different approach based on evolving fuzzy systems (EFS). It allows the updating of the structure and parameters of an evolving classifier, aids in coping with huge volumes of web news, and enables the processing of data online and in real time, which is essential in real-time web news articles. Iglesias et al. [152] developed a web news mining based on eClass0 classifier, while Za’in et al. [153] proposed a web news mining framework built on fuzzy evolving type-2 classifier (eT2Class), which outperforms other consolidated algorithms.
With the effective use of e-commerce, the internet increases the accessibility of customers from all over the world without having to deal with any marketplace restrictions. Web mining research is emerging in many aspects of e-services with the aim of improving online transactions and making them more transparent and effective [154]. The owners of e-commerce websites depend considerably on the analysis and summarization of customer behaviors so as to invest efforts towards influencing user actions and optimizing the success metric. The application of web mining techniques on the web and e-commerce for the sake of improving profits is not new, and a significant amount of research has been conducted in this field, especially pertaining to usage data. Recently, Dias and Ferreira [155] proposed an all-in-one process, improved by the crossing of data secured from diverse sources, for collecting and structuring data from an e-commerce website’s content, structure, and users. Finally, they presented an information model for an e-commerce website which contained the recorded and structured information resulting from the intersection of various sources and tasks for pattern discovery. Moreover, Zhou et al. [156] proposed three new types of automatic data acquisition strategies, based on web crawlers and the Aho-Corasick algorithm, to improve the text matching efficiency by considering the Chinese official websites for agriculture, the wholesale market websites of agricultural products, and websites for agricultural product e-commerce.
In the current era of vibrant electronic and mobile commerce, the financial transactions conducted online on a daily basis are massive in number, which creates the potential for fraudulent activity. A common fraudulent activity is website phishing, which involves creating a replica of a trustworthy website for deceiving users and illegally obtaining their credentials. A report published by Symantec Corporation Inc. [157] substantiated that the number of malicious websites detected rose by 60% in 2018 with respect to 2017.
The phishing phenomena, which mostly focused on web-based phishing detection methods than email-based detection methods, were discussed in detail by the study of Mohammad et al. [158], which provided a comprehensive evaluation of the blacklist-based, whitelist-based, and the heuristics-based detection approaches. The study concluded that, despite only heuristics-based detection approaches having the ability to recognize these websites, their accuracy may reduce considerably in case of change in the environmental features. A successful phishing detection model should also be adept at adapting its knowledge and structure in a continuous, self-structuring, and interactive manner in response to the changing environment that is characteristic of phishing websites. Yi et al. [159] proposed a class of deep neural network, namely the deep belief model (DBN), to detect web phishing. They evaluated the effectiveness of the detection model on DBN based on the true positive rate (TPR) with different parameters. The TPR was found to be approximately 90%.
Diverse disciplines have been interested in and have extensively undertaken the analysis of human behavior. Therefore, a broad theoretical framework is available with remarkable potential for application in other areas, particularly in the analysis of web user browsing behavior. With respect to web user browsing behavior, a prominent source of data is web logs that store every website visitor’s actions [160]. A recent study by Apaolaza and Vigo [161] addressed the challenges of mining web logs and proposed a set of functionalities into workflows that addresses these challenges. The study indicated that assisted pattern mining is perceived to be more useful and can produce more actionable knowledge for discovering interactive behaviors on the web. The requirement for more accurate and objective data for describing the navigation and preferences of web users led the researchers to study a combination of different data sources, from web and biometric data to traditional WUM research or experiments. Slanzi et al. [162] provided an extensive overview of the biometric information fusion applied to the WUM field.
6. Social Media
With the advent of social media, information related to various issues started going viral. Dealing with this flow has become an indispensable societal daily routine [163]. Moreover, social media creates new ways for people from various communities to engage with each other [164]. Social media is a perfect platform for the public to transfer opinions, thoughts, and views on any topic in a manner that significantly affects their opinions and decisions. Many companies simultaneously analyze the information available on social media platforms to collect the opinions of their customers and implement market research. Additionally, social media has started attracting researchers from several fields, including sociology, marketing, finance, and computer [24].
6.1. Twitter
Twitter is a social media platform where users can share their opinions, follow others, and comment on their opinions. In recent years, several researchers have focused on Twitter. With over 140 million tweets being posted in a day, Twitter serves as a valuable pool of data for many researchers [165]. Studies on topics ranging from the prediction of box office results of a movie to the changes in the stock market are based on Twitter data. Nisar and Yeung [166] collected a sample of 60,000 tweets made over a six-day period before, during, and after the local elections in the United Kingdom to investigate the relationship between their content and the changes in the London FTSE100 index [166]. Similarly, many other researchers use the information available on Twitter to make stock market predictions [167,168,169,170,171,172,173,174,175]. Öztürk and Ayvaz [163] studied Turkish and English tweets for evaluating their sentiments towards the Syrian refugee crisis and found that Turkish tweets are remarkably different from English tweets [163]. A study on the Arabic Twitter feed is proposed by Alkhatib et al. [176] with the objective of offering a novel framework for events and incidents management in smart [176]. Gupta et al. [177] presented a research framework to examine the cybersecurity attitudes, behavior, and their relationship by applying sentiment analysis and text mining techniques on tweets for gauging people’s cybersecurity actions based on what they say in their texts.
Regarding tourist sentiment analysis, Philander and Zhong [178] expounded on the application of tourist sentiment series from Twitter data for building low-cost and real-time measures of hospitality customer attitudes/perceptions.
Twitter data has also been studied by researchers from various fields to analyze (a) the Twitter usage behaviors of journalists [179] and cancer patients [180], (b) the sentiments of political tweets during the 2012 U.S. presidential election [181], (c) the effects of Twitter on brand management [182] and a given smartphone brand’s supply chain management [183], (d) the opinions held by people on the issue of terrorism [184], (e) the social, economic, environmental, and cultural factors pertaining to the sustainable care of both the environment and public health which most concern Twitter users [185], and (f) the tweet posting comments of academic libraries [186].
6.2. Facebook
Facebook is an American social media platform that is considered to be one of the biggest technology companies besides Amazon, Apple, and Google. According to Social Times, Facebook has 1.59 billion monthly active users. The Pew Research Center [187] determined that Facebook is the most extensively used social media platform. Facebook allows its users to express their thoughts, views, and ideas in the form of comments, wall posts, and blogs [187].
Kim and Hastak [188] analyzed Facebook data during the 2016 Louisiana flood, when parishes in Louisiana used their Facebook accounts to share information with people affected by the disaster. They discussed the critical role played by social media in emergency plans with the aim of helping emergency agencies in creating better mitigation plans for disasters [188].
In the context of business, companies need to monitor customer-generated content, not only on their personal social media page but also on the page of their competitors, to increase their competitive advantages. In this regard, He et al. [189] apply text mining to the Facebook and Twitter pages of three of the largest pizza chains in the U.S. pizza industry in order to help businesses in utilizing social media knowledge for decision-making [189].
Salloum et al. [190] classified the Facebook posts of Arabic newspapers through different text mining techniques. They found that the UAE is a country that shares the most number of posts on Facebook and also that videos are the most attracting part of the Facebook pages of Arabic newspapers [190].
Text mining on Facebook is also used to help institutions with their marketing strategies. Al-Daihani and Abrahams [191] implemented a text analysis on the Facebook posts of the academic libraries of the top 100 English-speaking universities. Their findings can be applied by academic libraries to develop their marketing, engagement, and visibility strategies.
6.3. Other Social Media Platforms
Text mining on social media is also utilized to improve transport and tourism planning. In this regard, Serna and Gasparovic [192] conducted a study on transportation modes using TripAdvisor comments and proposed a dashboard platform with graphical items that analyzes this data. This dashboard would facilitate the results collected from social media and its effect on tourism would be discussed [192]. Furthermore, Sezgen et al. [193] investigated the primary drivers of customer satisfaction and dissatisfaction of both full-service and low-cost carriers and of economy and premium class cabins using TripAdvisor passenger reviews for fifty (50) airlines. Text mining in social media platforms has been used to automatically rank different brands and make recommendations. Suresh et al. [194] applied opinion mining to the real life reviews from Yelp. They used the reviews given by restaurants’ customers to build a recommendation list. Saha and Santra [195] applied a similar idea to textual feedback from Zomato.
Existing literature on text mining on social media have predominantly discussed English texts and semantics [196] since most of the available packages have been developed for English-speaking users. However, several studies have focused on Chinese social media and semantics. Liu et al. [197] used discussion forums related to the Chinese stock market, namely the East Money forum, and opinion classification to predict stock volatilities [197].
Chen et al. [198] focused on Sina Weibo, a Chinese social media platform, to predict stock market volatilities. Moreover, they used the deep recurrent neural network [198].
A study by Liu et al. [199] sought to assess social media effects in the big data era. They used Chinese platforms, such as Hexun and Sina Weibo, and considered the stock index from 77 corporate companies in Shanghai and Shenzhen. The experimental results highlighted the positive relationship between the trading volumes/financial turnover ratios and the media activities [199].
The axis of the work of Zhang et al. [200] is Xueqiu, a Chinese platform that is similar to Twitter but specifically for investors. In their study, they classified the tweets by polarity, implementing the naive Bayes network, and predicted the stock price movements by using SVM and the perceptron network [200].
Recently, Pejic-Bach et al. [201] applied text mining on publicly accessible job advertisements on LinkedIn—one of the most influential social media networks for business—and developed a profile of Industry 4.0 job advertisements.
7. Published Articles
The enormous number of scientific publications provides an extremely valuable resource for researchers; however, their exponential growth represents a major challenge. On the other hand, a literature review is an essential component of almost any research project. Text mining enhanced the review of academic literature, and more papers are being published over the years using this technique. Text mining techniques can identify, group, and classify the key themes of a particular academic domain and highlight recurrence and popularity of topics over a period of time.
In the field of business, management, and information technology contexts, Moro et al. [202] performed topic detection on 219 articles between 2002 and 2013 through text mining when detecting terms pertaining to business intelligence in banking literature. They used the Bayesian topic model LDA and a dictionary of terms to group articles in several relevant topics. A similar study by Amado et al. [203], based on the study of Moro et al. [202], outlined a research literature analysis based on the text mining approach over a total of 1560 articles framed in the 2010–2015 period with the objective of identifying the primary trends on big data in marketing. Furthermore, Moro et al. [204] summarized the literature collected on ethnic marketing in the period 2005–2015 using LDA.
Cortez et al. [205] focused on analyzing 488 research articles published on a specific journal within a 17-year timeline on the domain of expert systems. The authors adopted LDA and followed a methodology similar to that applied by Moro et al. [202] and Moro and Rita [206] for branding strategies on social media platforms in the hospitality and tourism field. Guerreiro et al. [207] used the topic model cluster algorithm Correlated Topic Model (CTM), which is based on LDA, to conduct an analysis of 246 articles published in 40 different journals between 1988 and 2013 on the subject of cause-related marketing (CRM). The study revealed the most discussed topics on CRM. The study of Loureiro et al. [208] explored a text-mining approach using LDA to conduct an exhaustive analysis of 150 articles on virtual reality in 115 marketing-related journals, indexed in Web of Science. Galati and Bigliardi [209] implemented text mining methodologies for conducting a comprehensive literature review of Industry 4.0 to identify the main overarching themes discussed in the past and track their evolution over time.
Literature review articles on text mining have also recently emerged in the field of operations management, thus providing a framework for identifying the predominant topics and terms in the field. Guan et al. [210] used latent semantic analysis (LSA) to identify the core areas of production research based on the abstracts of all articles published in a specific journal since its inception and revealed how the focus extended on topics has evolved over time. Demeter et al. [211] applied two text mining tools on 566 papers in 12 special issues of a specific journal between 1994 and 2016 to gather a comprehensive review of the entire field of inventory research.
Literature reviews within several domains have also benefited from text mining. Grubert [212] investigated the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) literature by applying unsupervised topic modeling to more than 8200 environment-related LCA journal article titles and abstracts published between 1995 and 2014. Yang et al. [213] mined 1000 abstracts from the Google Scholar database for search results for technology infrastructure of solar forecasting, classified the concepts of solar forecasting on the full texts of 249 papers from Science Direct, and also undertook the keyword analysis and topic modeling on six handpicked papers on emerging technologies related to the subject. Moro et al. [214] performed text mining over the whole textual contents of papers, excluding only the references and authors’ affiliations, published in a tourism-related journal from 1996 to 2016. In the field of agriculture, Contiero et al. [215] analyzed through text mining the abstracts of 130 peer-reviewed papers that were published between 1970 and 2017 dealing with the pain issue in pig production and its correlation with the welfare in pigs.
Text mining was further employed as a tool in literature review-based studies in public health and medical sciences for various key themes, such as the adolescent substance and depression [216], cognitive rehabilitation and enhancement through neurostimulation [217], the protein factors related to the different cancer types [218], and diseases and syndromes in neurology [219].
Text mining methods are also employed to extract metadata from published articles. Kayal et al. [220] developed a method to automatically extract funding information from scientific articles. Yousif et al. [221] developed a model based on deep learning to extract the purpose of a citation to an article. Coupling this information with the number of citation and the applications of the articles results gives good measure to evaluate the efficiency of the funding.
However, text mining comes under the microscope of copyright, contracts, and licenses. Invoking the fundamental principles of copyright in the context of new technologies, Sag [222] explains that copying expressive works for non-expressive purposes should not be considered as infringement and should instead be labeled as fair use. In his article, Sag deals with the U.S.’s current legal framework and the feasibility of its adjustment to the text data mining processes, especially in the aftermath of the decisions in the cases of Authors Guild v. HathiTrust and Authors Guild Inc. v. Google. Recently, the European’s parliament voted in favor of a copyright exception (Directive (EU) 2019/790) on text and data mining for research purposes, as well as for individuals and institutions with legal access to protected works [223].
8. Meeting Transcripts
Most of the time, the meeting transcripts are too long, making reading and analyzing the core content infeasible; therefore, providing a framework that can extract the keywords automatically from the meeting transcripts is instrumental. Towards this end, Sheeba and Vivekanandan [224] proposed a model in which the keywords and key phrases are extracted from meeting transcripts. They claimed that the difficulty of this work is tied to the occurrence of synonyms, homonyms, hyponymy, and polysemy in the transcripts. Keywords were extracted by using the MaxEnt and SVM classifiers, and the extraction of bigram and trigram keywords was ensured through the N-gram-based approach.
The way meeting transcripts are written varies in terms of their style and details compared to the written text style. Liu et al. [225] presented a list with the differences that could negatively impact a keyword extraction system, such as the low lexical density, the lack of a perfect structure, the poor structure, and the varied speaking styles and word usage of a multiplicity of participants.
Liu et al. [225] extended the previous work of [226] by proposing a supervised framework for the extraction of keywords from meeting transcripts based on various features, such as decision-making sentence features, speech-related features, and summary features, that reflect the meeting transcripts more efficiently. The authors conducted experiments using the ICSI meeting corpus for both human transcripts and different automatic speech recognition (ASR) outputs, and they showed that the method suggested outperforms the TF-IDF weighting and a predominant state-of-the-art phrase extraction system.
Song et al. [227] published two different articles on the extraction of keywords from meeting transcripts. The authors proposed a just-in-time keyword extraction method by considering two factors that make their work different from that of others. These factors are (1) the temporal history of preceding utterance, which gives more importance to recent utterance, and (2) the topic relevance, which considers only the preceding utterances that are relevant to the current ones. Their method was applied on two English and Korean datasets, including the National Assembly transcripts in Korean and the ICSI meeting corpus. The results indicated that including these factors can enhance keyword extraction. Furthermore, in a more recent study [228], they added the participant factor to their graph-based keyword extraction method.
Xie end Liu [229] applied a framework on the ICSI meeting corpus to summarize meeting transcripts. In this framework, only the noteworthy sentences are selected to form the summary. Therefore, to specify whether a sentence should be included in the summary or not, they used supervised classification. Moreover, various sampling methods were implemented for avoiding the problem of imbalanced data.
Sharp and Chibelushi [230] presented an algorithm for the text classification of meeting transcripts. This study focused on the analysis of spoken meeting transcripts of discussions on software development, with the aim to determine the topics discussed in these meetings and, thereby, extract the decisions made and issues discussed. The authors suggested an algorithm that is appropriate for segmenting meeting transcripts that are spoken by combining semantically complex lexical relations with speech cue phrases to build lexical chains in determining topic boundaries. They argue that the results can help project managers in avoiding rework actions.
9. Knowledge Extraction
As the number of digital documents has grown exponentially, almost on any topic, automated knowledge extraction methods have become popular in many sections, from science to marketing and business. Many text mining techniques deal with extracting knowledge authors represented in their texts, e.g., extracting arguments [43,44,45,46] and extracting opinions [13,14,15,16]. Knowledge extraction is usually concerned with finding and extracting the key elements from textual data (e.g., articles, short notes, tweets, blogs, etc.) to extract hidden knowledge or build new hypotheses. For instance, a set of articles by an author, (or group of authors) contains knowledge about writing style, reasoning methodology, etc. [231,232,233]. For another example, the set comments on the problem may contain information about different aspects of an issue and possible (proposed) solutions [234]. Extracting such knowledge requires the modeling of the relational structure of textual data, i.e., the relation between words, paragraphs, and other fractions of texts. Networks, as a powerful tool, have been used to demonstrate relational structure of textual data in many knowledge extraction applications.
The idea of using networks to represent the structure of a given text (or set of texts) has been a practical one in literary analysis. For instance, Amancio et al. [231] used a complex network to quantify characteristics of a text (e.g., intermittency, burstiness, and words’ co-occurrence) to authorship attribution. Although the method successfully classified eight authors from the nineteenth century, they concluded that the accuracy of the results may depend on the text database, features extracted from the network, and the attribution algorithm. They suggest that different algorithms and features should be tested before engaging the real application. Amancio [233] employed the same idea and combined it with Fuzzy classification and traditional stylometry methods to classify texts based on authors’ writing style. The results show improvement in authorship attribution and genre identification when a hybrid algorithm is used to classify texts. Although Amancio et al. [231] shade light on authorship attribution using networks and made it possible to think about automated author attribution, their study did not take the structural changes into account. It is very common among authors to change style over time due to change in socio-economic characteristics, personal changes, etc. Amancio et al. [232] employed a similar idea of using networks to detect and model the literary movements through time. The used the books published between 1590 to 1922 to draw the literary movements in five centuries.
Nuzzo et al. [235] developed a set of tools to discover new relations between genes and between genes and diseases so it can be used to build more likely hypotheses on gene-disease associations. In order to find new possibilities, they applied an algorithm with the following steps on the abstracts of published articles from ”PubMed“ databases:
- Extract concepts on terms describing genes and diseases from abstracts.
- Derive genes-disease annotation.
- Use similarity metrics to demonstrate the relevance between genes, which measures the terms shared between genes to identifies the possible relations.
- Summarize the resulting annotation network as a graph.
The method shows its power to identify new possible gene-disease relations and builds possible hypotheses, as well as extracts the existing knowledge from the abstracts. Although their method is effective, it cannot be easily used for other applications since it uses an already existing structured knowledge base (e.g., Unified Medical Language system) to extract concepts. In many applications, such a knowledge base either does not exist or is very limited.
Wang et al. [234] used a multilayer network structure to systematically characterize a social network conversations based on their contents. The study targets a large set of Twitter messages exchanged between people with Eating Disorder (ED) to determine the type of content discussed on the online community, determine the flow pattern for different types of contents, and show how the contents are correlated. Their use of multilayer network provides the ability to represent the nature of discussion and multiplex interactions (presenting each topic in a separated layer), as well as to incorporate multidimensional information. Furthermore, analyzing the multilayer networks for a period of time reveals the structural changes in connections, correlation between topics, etc. Their results show that engagement in pro-recovery and pro-ED discussion is highly correlated, as well as the number of entries and exits to a communication when there is pro-ED sharing. The flexibility of the model developed by Wang et al. [234] provides a powerful tool for extracting knowledge hidden in social network conversations (messages, comments, etc.).
10. Conclusions
New technologies have facilitated access to immense quantities of digital text, recording an ever increasing share of human interaction, communication, and culture [236]. Text mining provides a framework to maximize the value of information within large quantities of text; thereby, the use of text mining technologies has increased steadily in recent years and has become highly diverse.
This study has summarized the academic research efforts on text mining and its applications by examining the published literature developed over the recent past few years. Figure 1 shows the methods and applications discussed in this study. More than 200 academic journal articles on the subject were included and discussed in this review, alongside the state-of-the-art text mining approaches used for analyzing transcripts and speeches, meeting transcripts, and academic journal articles, as well as websites, emails, blogs/micro-blogs, and social media networking sites across a broad range of application areas.
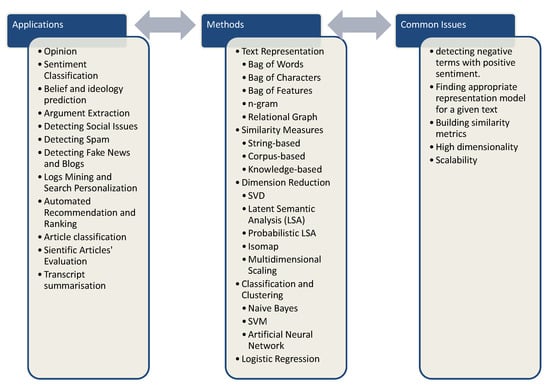
Figure 1.
The methods and application discussed in this study.
In practice, text mining enables the efficient exploitation of textual data on a broad range of real-world applications, such as (a) supporting large companies in faster and better decision-making by providing insights on the performance of marketing/sales strategies, enhancing customer experience, monitoring and enhancing the product/service, and gaining better customer engagement, (b) analyzing documents and verbatim transcripts in the economics sector, (c) analyzing political discourse streams that may provide valuable insights into critical discourse analysis, (d) creating more reliable and effective filtering methods for emails and websites, and (e) identifying relationships between users and certain products for social media purpose, as well as examining opinions on particular topics or sentiments on certain events. At the same time, by mining immense amounts of information in scientific literature, researchers can discover patterns and links between resources that cannot be detected through usual human viewing and reading, provide more meaningful answers to complex research questions, and even support scientific discovery in various domains.
There is a push, however, towards applications of text mining technologies on emerging crucial issues. One of the major serious issues is the relatively recent phenomenon of cybercrime [237,238,239,240] with strong impact on citizens, societies, and economies [241,242,243,244]. There are several ways in which text mining can be utilized for security analytics. Emails can be analyzed for discerning patterns in words and phrases, which may help identify a phishing attack. Websites can be scraped and analyzed to locate trends in themes that are related to security, such as the latest botnet threats, malware, and other Internet hazards [1]. More interestingly, social media offers a repository for intelligence-led policing operations; thereby, the law enforcement community is increasingly turning to social media monitoring to prevent and investigate crimes. Techniques, such as text mining, NLP, and sentiment analysis, provide a varied toolset that may assist in this direction [245]. Without pausing to address the approaches of previous studies regarding cybersecurity here in this paper, it is relevant to note that there is no universally agreed upon classification scheme that would contribute towards our understanding of cybercrime and serve as a useful tool for cybercrime stakeholders [246]. Recently, Donalds and Osei-Bryson [246] designed a new cybercrime classification scheme. Nevertheless, they also pointed out, the use of text mining and artificial intelligence technologies on this new ontology should be explored.
Another emerging, serious issue is the identification and detection of the widespread misinformation on social media and websites. In fact, the use of mega-platforms, such as Facebook and Twitter, as vectors for widespread misinformation spreading, e.g., during tragedies, national crises, or political campaigns, has been the subject of collective anxiety and a growing field of research [247,248,249,250,251]. Moreover, while one of the most beneficial values of text mining in big data analytics for businesses and governments is derived from the monitoring of human behavior and its predictive potential, the massive collection, instantaneous transmission, and combination and reuse of personal information for unforeseen purposes have placed new strains on strictly following the principles of data protection, which calls for a thorough consideration of their applications [252]. Serious ethical concerns and legal aspects have been raised when text mining is executed over data of a personal nature [139,253,254].
As it was noted earlier in this paper, there are pertinent challenges to the text mining process. First, the problem of ambiguity that the natural language faces is an issue. It can also be argued that what are conventionally referred to as languages exhibit immense internal variability across geographical and social space [255]. Moreover, many textual data sources are rife with abbreviations, acronyms, and specialized language. Second, the world of emails and online social networking sites can be very noisy. It may contain a large number of non-words, unknown words, and grammatically poor or incoherent sentences, as well as bots and trolls. Furthermore, text mining also carries limitations with respect to copyright, contracts, and licenses.
Another challenge in text mining arises when the method is employed in big textual data analysis. Since the size of big textual data rapidly grows, the text mining methods should be compatible with scalable data platforms. In other words, the employed text mining methods should have the ability to reduce the dimension of analyzed data and/or be compatible with the distributed computational systems and databases [256,257].
In summary, text mining carries immense potential as a tool for retrieving and analyzing large-scale and complex data and also allows spanning across a range of fields, disciplines, cultures, and languages. Not only are the cutting-edge of text mining technologies making significant improvements in terms of performance and accuracy within the framework of artificial intelligence and deep learning, mining in big data analytics is an evolving field, hence its having immense potential to advance science, encourage business growth in multiple industries, and ensure job growth. Moreover, text mining professionals are increasingly becoming high in demand. Furthermore, text mining may have the power to deliver significant insights to society and individuals, especially with respect to public health [258,259], healthcare [260,261], and education [262,263,264,265], and help evaluate social issues, such as crime (including cybercrime) [245,266,267], child abuse [268], and poverty [269]. Nevertheless, actions must be taken in time to efficiently solve the legal, ethical, and privacy concerns contained in the use of personal data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.H., C.B., S.U., M.T.M., M.R.Y.; investigation, H.H., C.B., S.U., M.T.M., M.R.Y.; writing–original draft preparation, H.H., C.B., S.U., M.T.M., M.R.Y.; writing–review and editing, H.H., C.B., S.U., M.T.M., M.R.Y.; supervision, H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Talabis, M.R.M.; McPherson, R.; Miyamoto, I.; Martin, J.L.; Kaye, D. Security and text mining. In Information Security Analytics; Talabis, M.R.M., McPherson, R., Miyamoto, I., Martin, J.L., Kaye, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearst, M.A. Text Data Mining. In The Oxford Handbook of Computational Linguistics; Mitkov, R., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 616–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumais, S. Using SVMs for text categorization, Microsoft research. IEEE Intell. Syst. Mag. 1998, 13, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Guduru, N. Text Mining with Support Vector Machines and Non-Negative Matrix Factorization Algorithms. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Rhodes Island, Rhodes Island, Greece, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bholat, D.; Hansen, S.; Santos, P.; Schonhardt-Bailey, C. CCBS Handbook No. 33, Text Mining For Central Banks; Bank of England: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- OPEC Bulletin. Language Lessons, July–August 2019. Available online: https://www.opec.org/opec_web/static_files_project/media/downloads/publications/OB07_082019.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Poole, K.T. Changing minds? Not in Congress! Public Choice 2007, 131, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Kaufmann, S.; Diermeier, D. Classifying party affiliation from political speech. J. Inf. Technol. Polit. 2008, 5, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esuli, A. A Bibliography on Sentiment Classification. 2006. Available online: http://liinwww.ira.uka.de/bibliography/Misc/Sentiment.html (accessed on 27 June 2019).
- Dave, K.; Lawrence, S.; Pennock, D.M. Mining the peanut gallery: Opinion extraction and semantic classification of product reviews. In Proceedings of the 12th international conference on World Wide Web (WWW2003), Budapest, Hungary, 20–24 May 2003; pp. 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Liu, B. Mining and summarizing customer reviews. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD’2004), Seattle, WA, USA, 22 August 2004; pp. 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Lee, L.; Vaithyanathan, S. Thumbs up? Sentiment classification using machine learning techniques. In Proceedings of the ACL-02 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP’02), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 6–7 July 2002; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Rajagopalan, S.; Srikant, R.; Xu, Y. Mining newsgroups using networks arising from social behavior. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW2003), Budapest, Hungary, 20 May 2003; pp. 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, N.; Zhou, L.; Hovy, E.; Shulman, S.W. Identifying and classifying subjective claims. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research: Bridging Disciplines & Domains, New York, NY, USA, 20–23 May 2007; Digital Government Society of North America: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Shulman, S.W. E-rulemaking: Issues in current research and practice. Int. J. Public Adm. 2015, 28, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Pang, B.; Lee, L. Get out the vote: Determining support or opposition from Congressional floor-debate transcripts. In Proceedings of the 2006 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP’06), Sydney, Australia, 22–23 July 2006; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Esuli, A.; Sebastiani, F. SENTIWORDNET: A Publicly Available Lexical Resource for Opinion Mining. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’06), Genoa, Italy, 22 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, B.; Lee, L. A sentimental education: Sentiment analysis using subjectivity summarization based on minimum cuts. In Proceedings of the 42nd Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain, 21–26 July 2004; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Hatzivassiloglou, V. Towards answering opinion questions: Separating facts from opinions and identifying the polarity of opinion sentences. In Proceedings of the 2003 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Sapporo, Japan, 11 July 2003; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Turney, P.D. Thumbs up or thumbs down? Semantic orientation applied to unsupervised classification of reviews. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Lee, L. Seeing stars: Exploiting class relationships for sentiment categorization with respect to rating scales. In Proceedings of the 43rd Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 25–30 June 2005; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.; Wiebe, J.; Hwa, R. Just how mad are you? Finding strong and weak opinion clauses. In Proceedings of the 21st Conference of the American Association for Artificial Intelligence, Boston, MA, USA, 16–20 July 2006; AAAI Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 761–769. [Google Scholar]
- Baccianella, S.; Esuli, A.; Sebastiani, F. SENTIWORDNET 3.0: An enhanced lexical resource for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, LREC, Valletta, Malta, 17–23 May 2010; pp. 2200–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, B.; Lee, L. Opinion Mining and Sentiment Analysis. Found. Trends Inf. Retr. 2008, 2, 1–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wordnet. 2019. Available online: https://wordnet.princeton.edu/ (accessed on 28 June 2019).
- Miller, G.A.; Beckwith, R.; Fellbaum, C.; Gross, D.; Miller, K.J. Introduction to WordNet: An On-line Lexical Database. Int. J. Lexicogr. 1990, 3, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauh, C. Validating a sentiment dictionary for German political language—A workbench note. J. Inf. Technol. Polit. 2018, 15, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.; Soroka, S. Affective news: The automated coding of sentiment in political texts. Polit. Commun. 2012, 29, 205–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron, A.; Curini, L.; Iacus, S.M. iSA: A fast, scalable and accurate algorithm for sentiment analysis of social media content. Inf. Sci. 2016, 367–368, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, D.; King, G. A method of automated nonparametric content analysis for social science. Am. J. Polit. Sci. 2010, 54, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.J.S.; Bermejo, P.H.D.S.; dos Santos, P.A. Can social media reveal the preferences of voters? A comparison between sentiment analysis and traditional opinion polls. J. Inf. Technol. Polit. 2017, 14, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Atteveldt, W.; Kleinnijenhuis, J.; Ruigrok, N.; Schlobach, S. Good news or bad news? Conducting sentiment analysis on Dutch text to distinguish between positive and negative relations. J. Inf. Technol. Polit. 2008, 5, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebanov, B.B.; Diermeier, D.; Beigman, E. Lexical cohesion analysis of political speech. Polit. Anal. 2008, 16, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, A.; Crawford, N.; Maduabum, M. A Nation Divided: Classifying Presidential Speeches; Stanford Univesity: Stanford, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lakoff, G. Moral Politics: How Liberals and Conservatives Think, 2nd ed.; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakoff, G.; Johnson, M. Metaphors We Live By; The Chicago University Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Miner, G.; Elder, J.; Fast, A.; Hill, T.; Nisbet, R.; Delen, D. Practical Text Mining and Statistical Analysis for Non-Structured Text Data; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Anurag, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Das, W.; Datta, D. Text Classification using Support Vector Machine. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2015, 4, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhai, C.; Roth, D. Unsupervised discovery of opposing opinion networks from forum discussions. In Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Maui, HI, USA, 2 November 2012; pp. 1642–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, A.; Inkpen, D. Sentiment classification of movie reviews using contextual valence shifters. Comput. Intell. 2006, 22, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, A.; Agrawal, A.; Rath, S.K. Classification of sentiment reviews using n-gram machine learning approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 57, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachims, T. Text categorization with Support Vector Machines: Learning with many relevant features. In Machine Learning: ECML-98; Nédellec, C., Rouveirol, C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 1398, pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardianos, C.; Katakis, I.M.; Petasis, G.; Karkaletsis, V. Argument extraction from news. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Argumentation Mining, Denver, CO, USA, 4 June 2015; pp. 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florou, E.; Konstantopoulos, S.; Koukourikos, A.; Karampiperis, P. Argument extraction for supporting public policy formulation. In Proceedings of the 7th Workshop on Language Technology for Cultural Heritage, Social Sciences, and Humanities, Sofia, Bulgaria, 8 August 2013; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Goudas, T.; Louizos, C.; Petasis, G.; Karkaletsis, V. Argument extraction from news, blogs, and social media. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Tools 2015, 24, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, M.; Torroni, P. Argument Mining from Speech: Detecting Claims in Political Debates. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12 February 2016; pp. 2979–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, F. Machine learning in automated text categorization. ACM Comput. Surv. 2002, 34, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumya, G.K.; Shibily, J. Text classification by augmenting Bag of Words (BOW) representation with co-occurrence feature. OSR J. Comput. Eng. 2014, 16, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulos, G.; Mavridi, P.; Paliouras, G.; Papadakis, G.; Tserpes, K. Representation models for text classification: A comparative analysis over three web document types. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Web Intelligence, Mining and Semantics, Craiova, Romania, 13 June 2012; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, W.H.; Fahmy, A.A. A survey of text similarity approaches. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 68, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinodhini, G.; Chrasekaran, R.M. Sentiment Analysis and Opinion Mining: A Survey. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. Softw. Eng. 2012, 2, 282–292. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, A.L.; Brown, P.F.; Della Pietra, S.A.; Della Pietra, V.J.; Gillett, J.R.; Lafferty, J.D.; Mercer, R.L.; Printz, H.; Ureš, L. The Candide system for machine translation. In HLT ’94 Proceedings of the Workshop on Human Language Technology; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 1994; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diermeier, D.; Godbout, J.-F.; Yu, B.; Kaufmann, S. Language and ideology in Congress. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Midwest Political Science Association (MPSA’07), Chicago, IL, USA, 4 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.; Wayne, M.; Cates, C.L.; Lin, J. Recounting the court? Toward a text-centered computational approach to understanding they dynamics of the judicial system. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Midwest Political Science Association, Chicago, IL, USA, 7 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Laver, M.; Benoit, K.; Garry, J. Extracting policy positions from political texts using words as data. Am. Polit. Sci. Rev. 2003, 97, 311–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piryani, R.; Madhavi, D.; Singh, V.K. Analytical mapping of opinion mining and sentiment analysis research during 2000–2015. Inf. Process. Manag. 2017, 53, 122–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riloff, E.; Wiebe, J. Learning extraction patterns for subjective expressions. In Proceedings of the 2003 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-2003), Sapporo, Japan, 11–12 July 2003; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riloff, E.; Wiebe, J. Exploiting subjectivity classification to improve information extraction. In Proceedings of the 20th National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 9–13 July 2005; AAAI Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 1106–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty, J.; McCallum, A.; Pereira, F. Conditional random fields: Probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Machine Learning, Williams College, MA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2001; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Riloff, E. An empirical study of automated dictionary construction for information extraction in three domains. Artif. Intell. 1996, 85, 101–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Cardie, C.; Riloff, E.; Patwardhan, S. Identifying sources of opinions with conditional random fields and extraction patterns. In Proceedings of the Conference on Human Language Technology and Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Sydney, Australia, 22–23 July 2006; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.; Wiebe, J.; Hoffmann, P. Recognizing contextual polarity in phrase-level sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the Conference on Human Language Technology and Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–8 October 2005; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesley, P.; Vincent, B.; Xu, L.; Srihari, R.K. Using verbs and adjectives to automatically classify blog sentiment. In AAAI Spring Symposium: Computational Approaches to Analyzing Weblogs (2006); AAAI: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Cardie, C. Adapting a polarity lexicon using integer linear programming for domain-specific sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the 2009 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Singapore, 6–7 August 2009; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2009; Volume 2, pp. 590–598. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Yu, M.; Zhou, M.; Liu, X.; Zhao, T. Target-dependent twitter sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the 49th, Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Portland, OR, USA, 19–24 June 2011; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.K.-W.; Na, J.-C.; Theng, Y.-L.; Chang, K. Sentence-Level Sentiment Polarity Classification Using a Linguistic Approach. In Digital Libraries: For Cultural Heritage, Knowledge Dissemination, and Future Creation; Xing, C., Crestani, F., Rauber, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 7008, pp. 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhan, J. Sentiment analysis using product review data. J. Bigdata 2015, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nockleby, J.T. Hate Speech. In Encyclopedia of the American Constitution, 2nd ed.; Levy, L.W., Karst, K.L., Winkler, A., Eds.; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 1277–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, W.; Hirschberg, J. Detecting Hate Speech on the World Wide Web. In Proceedings of the 2012 Workshop on Language in Social Media (LSM 2012), Montréal, QC, Canada, 7 June 2012; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Fiscus, J.G.; Ajot, J.; Garofolo, J.S. The Rich Transcription 2007 Meeting Recognition Evaluation. In Multimodal Technologies for Perception of Humans. RT 2007, CLEAR 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Stiefelhagen, R., Bowers, R., Fiscus, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 4625, pp. 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camelin, N.; Béchet, F.; Damnati, G.; De Mori, R. Speech Mining in Noisy Audio Message Corpus. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2007, Antwerp, Belgium, 27–31 August 2007; pp. 2401–2404. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Speech-mining-in-noisy-audio-message-corpus-Camelin-Béchet/9d59c1f2d228fce67c5c6fac7f04cc1a2b29b532 (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Hookway, N. Entering the blogosphere: Some strategies for using blogs in social research. Qual. Res. 2008, 8, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C. The Early Years. New York Magazine, 10 February 2006; 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, F.S.; Chen, Y.; Chan, K.L. Probabilistic Techniques for Corporate Blog Mining. In PAKDD 2007: Emerging Technologies in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining; Washio, T., Zhou, Z.-H., Huang, J.Z., Hu, X., Li, J., Xie, C., He, J., Zou, D., Li, K.-C., Freire, M.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, L.M.; Wang, Y. Techniques for analyzing blogs and micro-blogs. In Advancing Research Methods with New Technologies; Sappleton, N., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 206–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.S. Dimensionality reduction techniques for blog visualization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 2766–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.S. A tag-topic model for blog mining. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 5330–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafarani, R.; Abbasi, M.; Liu, H. Social Media Mining: An Introduction; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendt, B. Text mining for news and blogs analysis. In Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining; Sammut, C., Webb, G.I., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, G.; Liu, H. Data Mining in social media. In Social Network Data Analytics; Aggarwal, C.C., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 327–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Zafarani, R.; Abbasi, M.; Barbier, G.; Liu, H. Convergence of influential bloggers for topic discovery in the blogosphere. In Advances in Social Computing. SBP 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Chai, S.K., Salerno, J., Mabry, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6007, pp. 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leban, G.; Fortuna, B.; Brank, J.; Grobelnik, M. Event registry: Learning about world events from news. In WWW ’14 Companion Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on World Wide Web; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.S.; Chan, K.L. Dimensionality reduction techniques for data exploration. In Proceedings of the 2007 6th International Conference on Information, Communications and Signal Processing, Singapore, 10–13 December 2007; pp. 1568–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.S.; Chan, K.L. Detecting Cyber Security Threats in Weblogs using Probabilistic Models. In PAISI 2007: Intelligence and Security Informatics; Yang, C.C., Zeng, D., Chau, M., Chang, K., Yang, Q., Cheng, X., Wang, J., Wang, F.-Y., Chen, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4430, pp. 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Tsai, F.S.; Kdwee, A.T. Detecting novel business blogs. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information, Communications and Signal Processing, Macau, China, 8–10 December 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.S. A data-centric approach to feed search in blogs. Int. J. Web Eng. Technol. 2012, 7, 228–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.S. Blogger-Link-Topic Model for Blog Mining. In New Frontiers in Applied Data Mining. PAKDD 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Cao, L., Huang, J.Z., Bailey, J., Koh, Y.S., Luo, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.S. Dimensionality reduction framework for blog mining and visualisation. Int. J. Data Mining Model. Manag. 2012, 4, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seep, K.S.; Patil, N. A Multidimensional Approach to Blog Mining. In Progress in Intelligent Computing Techniques: Theory, Practice, and Applications; Sa, P., Sahoo, M., Murugappan, M., Wu, Y., Majhi, B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirakis, N.; Poulopoulos, V.; Tsantilas, P.; Varlamis, I. Large scale opinion mining for social, news and blog data. J. Syst. Softw. 2017, 127, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, D.M.E.-D.M. A survey on sentiment analysis challenges. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 30, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-Y.; Chen, T.-H. Modeling public mood and emotion: Blog and news sentiment and socio-economic phenomena. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 96, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.S.; Chan, K.L. Blog Data Mining for Cyber Security Threats. In Data Mining for Business Applications; Cao, L., Yu, P.S., Zhang, C., Zhang, H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-C.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Wei, L.-J.; Mao, C.-H.; Dai, J.-H.; Kuang, Y.-T. Sec-Buzzer: Cyber security emerging topic mining with open threat intelligence retrieval and timeline event annotation. Soft Comput. 2017, 21, 2883–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsamidis, S.; Theodosiou, T.; Kazanidis, I.; Nikolaidis, M. A Framework for opinion mining in blogs for agriculture. Procedia Technol. 2013, 8, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Ju, J. Can media forecast technological progress? A text-mining approach to the on-line newspaper and blog’s representation of prospective industrial technologies. Inf. Process. Manag. 2019, 56, 1506–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti-Kashi, S.; Lùtjen, M.; Thoben, K.-D. Social media analytics for decision support in fashion buying processes. In Artificial Intelligence for Fashion Industry in the Big Data Era, Springer Series in Fashion Business; Thomassey, S., Zeng, X., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadoria, R.S.; Dixit, M.; Bansal, R.; Chauhan, A.S. Detecting and searching system for event on internet blog data using cluster mining algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems Design and Intelligent Applications 2012 (INDIA 2012), Visakhapatnam, India, 5–7 January 2012; Satapathy, S.C., Avadhani, P.S., Abraham, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Xu, H.; Qian, Y.; Li, Y. Make your travel smarter: Summarizing urban tourism information from massive blog data. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2016, 36, 1306–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yuan, H.; Ma, B.; Qian, Y. Where to go and what to play: Towards summarizing popular information from massive tourism blogs. J. Inf. Sci. 2019, 41, 830–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.K.; Klavans, J.L.; McKeown, K.R. Columbia newsblaster: Multilingual news summarization on the web. In Proceedings of the Demonstration Papers at HLT-NAACL, Boston, MA, USA, 2–7 May 2004; Available online: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/N04-3001 (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Li, Z.; Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Lu, H. Multimedia news summarization in search. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2016, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouris, P.; Alexandridis, G.; Stafylopatis, A. Abstractive text summarization based on deep learning and semantic content generalization. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July 2019; pp. 5082–5092. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Conroy, N.J.; Rubin, V.L. Misleading online content: Recognizing clickbait as false news. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM on Workshop on Multimodal Deception Detection, Seattle, WA, USA, 1 August 2015; pp. 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- The Radicati Group, Inc. Email Statistics Report, 2019–2023–Executive Summary February. February 2019. Available online: https://www.radicati.com/wp/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Email-Statistics-Report-2019-2023-Executive-Summary.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Palmer, D.D. Text preprocessing. In Handbook of Natural Language Processing, 2nd ed.; Indurkhya, N., Damerau, F.J., Eds.; Chapman & Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2010; pp. 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Katakis, I.; Tsoumakas, G.; Vlahavas, I. E-mail mining: Emerging techniques for E-Mail management. In Web Data Management Practices: Emerging Techniques and Technologies; Vakali, A., Pallis, G., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 220–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laclavík, M.; Dlugolinský, Š.; Šeleng, M.; Kvassay, M.; Gatial, E.; Balogh, Z.; Hluchý, L. Email analysis and information extraction for enterprise benefit. Comput. Inform. 2011, 30, 57–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Deng, P.; Wan, J.; Zhang, D.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Rong, X. Data mining for the internet of things: literature review and challenges. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2015, 431047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, M.A.; Jabin, S. Big Data: Issues, challenges, and techniques in business intelligence. In Big Data Analytics. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Aggarwal, V., Bhatnagar, V., Mishra, D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimt, B.; Yang, Y. Introducing the Enron corpus. In Proceedings of the CEAS 2004—First Conference on Email and Anti-Spam, Mountain View, CA, USA, 30–31 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Minkov, E.; Wang, R.C.; Cohen, W.W. Extracting personal names from emails: Applying named entity recognition to informal text. In Proceedings of the Conference on Human Language Technology and Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–8 October 2005; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsopoulos, I.; Koutsias, J.; Chrinos, K.V.; Paliouras, G.; Spyropoulos, C. An evaluation of naive Bayesian anti-spam filtering. In Proceedings of the 1th European Conference on Machine Learning in the New Information Age, Barcelona, Spain, 2 June 2000; pp. 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp, W.; Balog, K.; De Rijke, M. Using contextual information to improve search in email archives. In Proceedings of the 31th European Conference on IR Research on Advances in Information Retrieval, Toulouse, France, 6–9 April 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Pei, J.; Luk, W.S. Email mining: Tasks, common techniques, and tools. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2014, 41, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, G.; Shuib, L.; Raj, R.G.; Majeed, N.; Al-Garadi, M.A. Email classification research trends: review and open issues. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 9044–9064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangal, S.; Lam, M.S.; Heer, J. MUSE: Reviving memories using email archives. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 16–19 October 2011; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. Sentiment Analysis and Opinion Mining; Morgan & Claypool Publishers: Williston, VT, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lee, I. A Hybrid Sentiment Analysis Framework for Large Email Data. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering (ISKE), Taipei, Taiwan, 24–27 November 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lee, I. Discovering sentiment sequence within email data through trajectory representation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 99, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, B. Business Espionage: Risk, Threats, and Countermeasures; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Scarllet, C.; Prodanoff, Z.G.; Hubbard, D. Determining predisposition to insider threat activities by using text analysis. In Future Technologies Conference (FTC); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, C.; Yu, S.; Narayanan, A.; Duraisamy, S.; Chen, L. Employee profiling via aspect-based sentiment and network for insider threats detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisco Talos Intelligence Group Report. 2019. Available online: https://www.talosintelligence.com/ (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Osterman Research, Inc. Techniques for Dealing with Ransomware, Business Email Compromise and Spearphishing, An Osterman Research White Paper; Osterman Research, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tretyakov, K. Machine Learning Techniques in Spam Filtering. In Data Mining Problem-Oriented Seminar; MTAT: Beauvallon, France, 2004; pp. 60–79. Available online: https://courses.cs.ut.ee/2004/dm-seminarspring/uploads/Main/P06.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Bhowmick, A.; Hazarika, S.M. Machine learning for E-Mail spam filtering: review, techniques and trends. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.01042v1. [Google Scholar]
- Dada, E.G.; Bassi, J.S.; Chiroma, H.; Abdulhamid, S.M.; Adetunmbi, A.O.; Ajibuwa, O.E. Machine learning for email spam filtering: Review, approaches and open research problems. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, E.M.; Rady, S.; Gad, W.; Moawad, I.F. Efficient email classification approach based on semantic methods. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 3259–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almomani, A.; Wan, T.C.; Manasrah, A.; Altaher, A.; Baklizi, M.; Ramadass, S. An enhanced online phishing e-mail detection framework based on evolving connectionist system. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2013, 9, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.U.; Abawajy, J.H.; Kelarev, A.V.; Hochin, T. Multilayer hybrid strategy for phishing email zero-day filtering. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2016, 29, e3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smadi, S.; Aslam, N.; Zhang, L. Detection of online phishing email using dynamic evolving neural network based on reinforcement learning. Decis. Support Syst. 2018, 107, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gök, A.; Waterworth, A.; Shapira, P. Use of web mining in studying innovation. Scientometrics 2015, 102, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldherr, A.; Maier, D.; Miltner, P.; Günther, E. B Big Data, Big Noise: The Challenge of Finding Issue Networks on the Web. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2017, 35, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzioni, O. The world wide web: Quagmire or gold mine. Commun. ACM 1996, 39, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, R.; Mobasher, B.; Srivastava, J. Data preparation for mining World Wide Web browsing patterns. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 1999, 1, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, Z.; Larose, D.T. Data Mining the Web: Uncovering Patterns in Web Content, Structure and Usage; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Velásquez, J.D. Web mining and privacy concerns: Some important legal issues to be consider before applying any data and information extraction technique in web-based environments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 5228–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.; Levene, M. Data mining of user navigation patterns. In Web Usage Analysis and User Profiling. WebKDD 1999. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Masand, B., Spiliopoulou, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 92–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madria, S.K.; Bhowmick, S.S.; Ng, W.K.; Lim, E.P. Research Issues in Web Data Mining. In DataWarehousing and Knowledge Discovery. DaWaK 1999. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Mohania, M., Tjoa, A.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L. Web Mining and Social Networking; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanathey, K.; Thakur, R.S.; Jaloree, S. Ranking of web pages using aggregation of page rank and hits algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Stud. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2018, 7, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Facca, F.M.; Lanzi, P.L. Mining interesting knowledge from weblogs: A survey. Data Knowl. Eng. 2005, 53, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Cooley, R.; Deshpe, M.; Tan, P.-N. Web usage mining: Discovery and applications of usage patterns from web data. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2000, 1, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Keselj, V. Combined mining of web server logs and web contents for classifying user navigation patterns and predicting users’ future requests. Data Knowl. Eng. 2007, 61, 304–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, S.; Gupta, A. Fuzzy information retrieval in WWW: A survey. Int. J. Adv. Intell. Paradig. 2014, 6, 272–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kohli, S. FORA: An OWO based framework for finding Outliers in Web Usage Mining. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chola, V.; A Banerjee, A.; Kumar, V. Anomaly detection: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2009, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kohli, S. An analytical study of ordered weighted geometric averaging operator on Web data set as a MCDM problem. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Soft Computing for Problem Solving, Assam, India, 23 December 2014; Das, K., Deep, K., Pant, M., Bansal, J., Nagar, A., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kohli, S. OWA operator-based hybrid framework for outlier reduction in web mining. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2016, 31, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.A.; Tiemblo, A.; Ledezma, A.; Sanchis, A. Web news mining in an evolving framework. Inf. Fusion 2016, 28, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Za’in, C.; Pratama, M.; Lughofer, E.; Anavatti, S.G. Evolving type-2 web news mining. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 54, 200–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosala, R.; Blockeel, H. Web mining research: A survey. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2000, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.P.; Ferreira, H.S. Automating the extraction of static content and dynamic behaviour from e-commerce websites. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 109, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Cheng, C.; Kang, L.; Sun, R. Integration and Analysis of Agricultural Market Information Based on Web Mining. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symantec Corporation Inc. Internet Security Threat Report. 2019. Available online: https://resource.elq.symantec.com/LP=6819?CID=70138000001QvI4AAK (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Mohammad, R.M.; Thabtah, F.; McCluskey, L. Tutorial and critical analysis of phishing websites methods. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2015, 17, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Guan, Y.; Zou, F.; Yao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, T. Web Phishing Detection Using a Deep Learning Framework. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, P.E.; Dell, R.F.; Velásquez, J.D.; Loyola, P.S. Identifying User Sessions from Web Server Logs with Integer Programming. Intell. Data Anal. 2014, 18, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaolaza, A.; Vigo, M. Assisted pattern mining for discovering interactive behaviors on the web. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2019, 130, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slanzi, G.; Pizarro, G.; Velásquez, J.D. Biometric information fusion for web user navigation and preferences analysis: An overview. Inf. Fusion 2017, 38, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, N.; Ayvaz, S. Sentiment analysis on Twitter: A text mining approach to the Syrian refugee crisis. Telemat. Inf. 2018, 35, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, R.; King, C.K.; Grages, D.; Ewen, S.; Khan, S.U.; Madani, S.A.; Kolodziej, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Rayes, A.; et al. A survey on text mining in social networks. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 2015, 30, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, A.; Paroubek, P. Twitter as a corpus for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’10), Valletta, Malta, 17–23 May 2010; Calzolari, N., Choukri, K., Maegaard, B., Mariani, J., Odijk, J., Piperidis, S., Rosner, M., Tapias, D., Eds.; European Language Resources Association (ELRA): Luxembourg, 2010; pp. 1320–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Nisar, T.M.; Yeung, M. Twitter as a tool for forecasting stock market movements: A short-window event study. J. Financ. Data Sci. 2018, 4, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollen, J.; Mao, H.; Zeng, X. Twitter mood predicts the stock market. J. Comput. Sci. 2011, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.J.; Hristidis, V.; Castillo, C.; Gionis, A.; Jaimes, A. Correlating financial time series with micro-blogging activity. In Proceedings of the Fifth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, (WSDM’12), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 February 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenau, M.; Liebmann, M.; Neumann, D. Automated news reading: Stock price prediction based on financial news using context-capturing features. Decis. Support Syst. 2013, 55, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Sentiment Analysis on Twitter with Stock Price and Significant Keyword Correlation; The University of Texas: Austin, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, L.; Chan, K.C.; Ou, C. Public sentiment analysis in Twitter data for prediction of a company’s stock price movements. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 11th International Conference on e-Business Engineering, Guangzhou, China, 5–7 November 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, B.; Hu, W. Sentiment analysis of investor opinions on twitter. Soc. Netw. 2015, 4, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Behera, R.K.; Rath, S.K. Real-time sentiment analysis of Twitter streaming data for stock prediction. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkubaisi, G.A.A.J.; Kamaruddin, S.S.; Husni, H. Stock market classification model using sentiment analysis on twitter based on hybrid naive bayes classifiers. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018, 11, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadstock, D.C.; Zhang, D. Social-media and intraday stock returns: The pricing power of sentiment. Financ. Res. Lett. 2019, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, M.; El Barachi, M.; Shaalan, K. An Arabic social media based framework for incidents and events monitoring in smart cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Sharma, S.; Chennamaneni, A. Twitter Sentiment Analysis: An Examination of Cybersecurity Attitudes and Behavior. In Proceedings of the 2016 Pre-ICIS SIGDSA/IFIP WG8.3 Symposium: Innovations in Data Analytics, Dublin, Ireland, 11 December 2016; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Philer, K.; Zhong, Y. Twitter sentiment analysis: Capturing sentiment from integrated resort tweets. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2016, 55, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.Y.; Kim, Y.; Sang, Y. How do journalists leverage Twitter? Expressive and consumptive use of Twitter. Soc. Sci. J. 2017, 54, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crannell, W.C.; Clark, E.; Jones, C.; James, T.A.; Moore, J. A pattern-matched Twitter analysis of US cancer-patient sentiments. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 206, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Can, D.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Bar, F.; Narayanan, S. A system for real-time twitter sentiment analysis of 2012 US presidential election cycle. In Proceedings of the ACL 2012 System Demonstrations, Jeju Island, Korea, 8–14 July 2012; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Greco, F.; Polli, A. Emotional text mining: Customer profiling in brand management. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akundi, A.; Tseng, B.; Wu, J.; Smith, E.; Subbalakshmi, M.; Aguirre, F. Text mining to understand the influence of social media applications on smartphone supply chain. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 140, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S. Social Media Analysis of User’s Responses to Terrorism Using Sentiment Analysis and Text Mining. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 140, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Menendez, A.; Saura, J.R.; Alvarez-Alonso, C. Understanding #WorldEnvironmentDay user opinions in Twitter: A topic-based sentiment analysis approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daihani, S.M.; Abrahams, A. A text mining analysis of academic libraries’ Tweets. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2016, 42, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center, P.R. Social Media Fact Sheet; Pew Research Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Hastak, M. Social network analysis: Characteristics of online social networks after a disaster. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 38, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zha, S.; Li, L. Social media competitive analysis and text mining: A case study in the pizza industry. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2013, 33, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, S.A.; Mhamdi, C.; Al-Emran, M.; Shaalan, K. Analysis and classification of Arabic newspapers’ Facebook pages using text mining techniques. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Lang. Stud. 2017, 1, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Daihani, S.M.; Abrahams, A. Analysis of academic libraries’ facebook posts: Text and data analytics. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2018, 44, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, A.; Gasparovic, S. Transport analysis approach based on big data and text mining analysis from social media. Transp. Res. Procedia 2018, 33, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgen, E.; Mason, K.J.; Mayer, R. Voice of airline passenger: A text mining approach to understand customer satisfaction. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2019, 77, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, V.; Roohi, S.; Eirinaki, M. Aspect-based opinion mining and recommendation system for restaurant reviews. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM Conference on Recommender systems, Foster City, CA, USA, 1 October 2014; pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Santra, A.K. Restaurant rating based on textual feedback. In Proceedings of the 2017 International conference on Microelectronic Devices, Circuits and Systems (ICMDCS), Vellore, India, 10–12 August 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-Y.; Liao, C.-H.; Hsieh, R.-P. Modeling public mood and emotion: Stock market trend prediction with anticipatory computing approach. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Li, P.; Wan, T. Stock volatility prediction using recurrent neural networks with sentiment analysis. In International Conference on Industrial, Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intelligent Systems; Benferhat, S., Tabia, K., Ali, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yeo, C.K.; Lau, C.T.; Lee, B.S. Leveraging social media news to predict stock index movement using RNN-boost. Data Knowl. Eng. 2018, 118, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xia, X.; Li, A. Tweeting the financial market: Media effect in the era of Big Data. Pac. Basin Financ. J. 2018, 51, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, D.; Fang, B. Exploiting investors social network for stock prediction in China’s market. J. Comput. Sci. 2018, 28, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejic-Bach, M.; Bertoncel, T.; Meško, M.; Krstic, Ž. Text mining of industry 4.0 job advertisements. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, S.; Cortez, P.; Rita, P. Business intelligence in banking: A literature analysis from 2002 to 2013 using text mining and latent Dirichlet allocation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, A.; Cortez, P.; Rita, P.; Moro, S. Research trends on Big Data in Marketing: A text mining and topic modeling based literature analysis. Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2018, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, S.; Pires, G.; Rita, P.; Cortez, P. A text mining and topic modelling perspective of ethnic marketing research. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 103, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, P.; Moro, S.; Rita, P.; King, D.; Hall, J. Insights from a text mining survey on Expert Systems research from 2000 to 2016. Expert Syst. 2018, 35, e12280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, S.; Rita, P. Brand strategies in social media in hospitality and tourism. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 30, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, J.; Rita, P.; Trigueiros, D. A text mining-based review of cause-related marketing literature. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 139, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, S.M.C.; Guerreiro, J.; Eloy, S.; Langaro, D.; Panchapakesan, P. Understanding the use of virtual reality in marketing: A text mining-based review. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 100, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, F.; Bigliardi, B. Industry 4.0: Emerging themes and future research avenues using a text mining approach. Comput. Ind. 2019, 109, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Manikas, A.S.; Boyd, L.H. The at 55: A content-driven review and analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 57, 4667–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeter, K.; Szász, L.; Kö, A. A text mining based overview of inventory research in the ISIR special issues 1994-2016. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 209, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubert, E. Implicit prioritization in life cycle assessment: Text mining and detecting metapatterns in the literature. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 22, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kleissl, J.; Gueymard, C.A.; Pedro, H.T.C.; Coimbra, C.F.M. History and trends in solar irradiance and PV power forecasting: A preliminary assessment and review using text mining. Sol. Energy 2018, 168, 60–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, S.; Rita, P.; Cortez, P. A text mining approach to analyzing Annals literature. Ann. Tour. Res. 2017, 66, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contiero, B.; Cozzi, G.; Karpf, L.; Gottardo, F. Pain in Pig Production: Text Mining Analysis of the Scientific Literature. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2019, 32, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, W.; Huang, Y.-H.; Perkins, R.; Zou, W.; Chen, J.J. Text mining for identifying topics in the literatures about adolescent substance use and depression. BMC Public Health 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan, P.F.; Gerits, A.; Vuffel, W. A practical application of text mining to literature on cognitive rehabilitation and enhancement through neurostimulation. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.S.; Rodríguez, M.S.; Matthiesen, R. Review and literature mining on proteostasis factors and cancer. In Proteostasis. Methods in Molecular Biology; Matthiesen, R., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Ghasemi, M.; Sen, S.; Moraes, M.F.; Shah, V. Exploring diseases and syndromes in neurology case reports from 1955 to 2017 with text mining. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 109, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayal, S.; Afzal, Z.; Tsatsaronis, G.; Doornenbal, M.; Katrenko, S.; Gregory, M. A framework to automatically extract funding information from text. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Optimization, and Data Science, Volterra, Italy, 13 September 2018; pp. 317–328. [Google Scholar]
- Yousif, A.; Niu, Z.; Nyamawe, A.S.; Hu, Y. Improving citation sentiment and purpose classification using hybrid deep neural network model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, Cairo, Egypt, 26–28 October 2018; pp. 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Sag, M. The new legal landscape for text mining and machine learning. J. Copyr. Soc. USA 2019, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive (EU) 2019/790 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 April 2019 on Copyright in the Digital Single Market. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2019/790/oj (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Sheeba, J.; Vivekanan, K. Improved keyword and keyphrase extraction from meeting transcripts. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 52, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y. A supervised framework for keyword extraction from meeting transcripts. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2010, 19, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Pennell, D.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y. Unsupervised approaches for automatic keyword extraction using meeting transcripts. In NAACL’09 Proceedings of Human Language Technologies: The 2009 Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 620–628. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.-J.; Go, J.; Park, S.-B.; Park, S.-Y. A just-in-time keyword extraction from meeting transcripts. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–14 June 2013; Association for Computational Linguistics: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013; pp. 888–896. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.-J.; Go, J.; Park, S.-B.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, K.Y. A just-in-time keyword extraction from meeting transcripts using temporal and participant information. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2017, 48, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Liu, Y. Improving supervised learning for meeting summarization using sampling and regression. Comput. Speech Lang. 2010, 24, 495–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, B.; Chibelushi, C. Text segmentation of spoken meeting transcripts. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2008, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amancio, D.R.; Altmann, E.G.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Costa, L.F. Comparing intermittency and network measurements of words and their dependence on authorship. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 123024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amancio, D.R.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Costa, L.F. Identification of literary movements using complex networks to represent texts. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 043029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amancio, D.R. A complex network approach to stylometry. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Brede, M.; Ianni, A.; Mentzakis, E. Characterizing dynamic communication in online eating disorder communities: A multiplex network approach. Appl. Netw. Sci. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, A.; Mulas, F.; Gabetta, M.; Arbustini, E.; Zupan, B.; Larizza, C.; Bellazzi, R. Text mining approaches for automated literature knowledge extraction and representation. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2010, 160, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentzkow, M.; Kelly, B.T.; Taddy, M. Text As Data. NBER Work. Pap. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, R.; Xia, Y. Latent text mining for cybercrime forensics. Int. J. Future Comput. Commun. 2013, 2, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh-Lee, C.; Ju-Yeon, J.; Yoohwan, K. Text mining for security threat detection discovering hidden information in unstructured log messages. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 17–19 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, S. Text Mining for Modeling Cyberattacks. In Computational Analysis and Understanding of Natural Languages: Principles, Methods and Applications; Venkat, N., Gudivada, C.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 14; pp. 463–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Yuan, S.; Ou, H.; Liu, L. New Cyber Threat Discovery from Darknet Marketplaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Big Data and Analytics (ICBDA), Shanghai, China, 21–22 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.; Sharma, S.; Weinberg, A. Meeting the Cybersecurity Challenge. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/digital-mckinsey/our-insights/meeting-the-cybersecurity-challenge (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Aiken, M.; Mahon, C.; Haughton, C.; O’Neill, L.; O’Carroll, E. A consideration of the social impact of cybercrime: Examples from hacking, piracy, and child abuse material online. Contemp. Soc. Sci. 2015, 11, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponemon Institute. 2017 Cost of Data Breach Study: Global Overview (Research Report). Ponemon Institute. 2017. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/downloads/cas/ZYKLN2E3 (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- EC Horizon 2020, Secure Societies—Protecting Freedom and Security of Europe and Its Citizens. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/programmes/horizon2020/en/h2020-section/secure-societies-%E2%80%93-protecting-freedom-and-security-europe-and-its-citizens (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Bayerl, P.S.; Akhgar, B.; Brewster, B.; Domdouzis, K.; Gibson, H. Social media and its role for LEAs. In Cyber Crime and Cyber Terrorism Investigator’s Handbook; Akhgar, B., Staniforth, A., Bosco, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donalds, C.; Osei-Bryson, K.-M. Toward a cybercrime classification ontology: A knowledge-based approach. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 92, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C. An ontological approach to misinformation: Quickly finding relevant information. In Proceedings of the 50th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, (HICSS 2017), Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Attention-based convolutional approach for misinformation identification from massive and noisy microblog posts. Comput. Secur. 2019, 83, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gupta, A.; Kauten, C.; Deokar, A.V.; Qin, X. Detecting fake news for reducing misinformation risks using analytics approaches. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 279, 1036–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelke, S.; Attar, V. Source detection of rumor in social network—A review. Online Soc. Netw. Media 2019, 9, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondielli, A.; Marcelloni, F. A Survey on fake news and rumour detection techniques. Inf. Sci. 2019, 497, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Data Protection Supervisor. Meeting the Challenges of Big Data: A Call for Transparency, User Control, Data Protection by Design and Accountability, Opinion 7/2015. 2015. Available online: https://edps.europa.eu/sites/edp/files/publication/15-11-19_big_data_en.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Truyens, M.; van Eecke, P. Legal aspects of text mining. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2014, 30, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, R.; Yasin, A.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Afzal, W.; Yasin, A. Sharing information online rationally: An observation of user privacy concerns and awareness using serious game. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2019, 48, 102351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilton, P.A. Analysing Political Discourse: Theory and Practice; Routledge: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, S.A. MapReduce-based fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm: Implementation and scalability. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2015, 6, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontopoulos, I.; Giannakopoulos, G.; Varlamis, I. Distributing n-gram graphs for classification. Eur. Conf. Adv. Databases Inf. Syst. 2017, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.J.; Sarker, A.; Brownstein, J.S.; Nikfarjam, A.; Scotch, M.; Smith, K.L.; Gonzalez, G. Social media mining for public health monitoring and surveillance. In Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 2016, (PSB 2016); World Scientific Publishing Co.: Singapore, 2016; pp. 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.E.; Hovet, S.E.; Fung, I.C.-H.; Liang, H.; Fu, K.-W.; Tse, Z.T.H. Using Twitter for public health surveillance from monitoring and prediction to public response. Data 2018, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucini, F.R.; Fogliatto, F.S.; da Silveira, G.J.C.; Neyeloff, J.L.; Anzanello, M.J.; Kuchenbecker, R.S.; Schaan, B.D. Text mining approach to predict hospital admissions using early medical records from the emergency department. Int. J. Med Inform. 2017, 100, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsker, O.; Bolgova, E.; Yakovlev, A.; Funkner, A.; Kovalchuk, S. Pattern-based mining in electronic health records for complex clinical process analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 119, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, C.K.; Lee, Y.H.; Mak, W.K. Mining sentiments in SMS texts for teaching evaluation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 2584–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W. Examining students’ online interaction in a live video streaming environment using data mining and text mining. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2013, 29, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.W.; Isotani, S.; Zárate, L.E. Educational data mining: A review of evaluation process in the e-learning. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 1701–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Mello, R.; André, M.; Pinheiro, A.; Costa, E.; Romero, C. Text mining in education. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2019, e1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaeem, R.; Manoharan, M.; Yang, Y.; Barber, K.S. Modeling and analysis of identity threat behaviors through text mining of identity theft stories. Comput. Secur. 2017, 65, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Das, A.K. Graph-based clustering of extracted paraphrases for labelling crime reports. Knowl. Based Syst. 2019, 179, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrit, C.; Paauw, T.; Aly, R.; Lavric, M. Identifying child abuse through text mining and machine learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 88, 402–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, D.E.; Williams, B.J. Tracing poverty and inequality in international development discourses: An algorithmic and visual analysis of agencies’ annual reports and occasional white papers, 1978–2010. J. Soc. Policy 2014, 43, 173–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).