Semantic Ontology-Based Approach to Enhance Arabic Text Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Previous Work
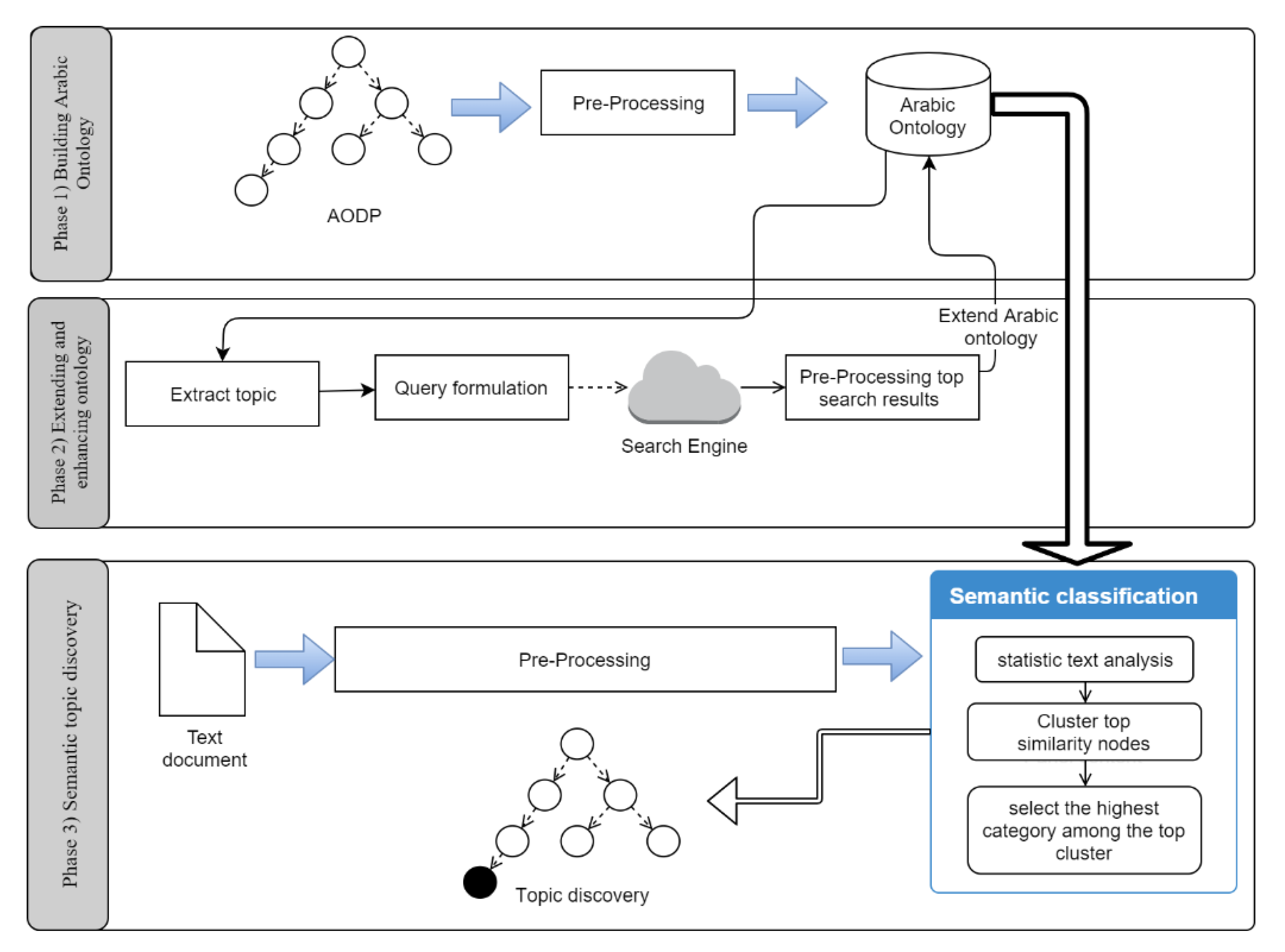
3. Enhanced Arabic Topic-Discovery Architecture (EATA)
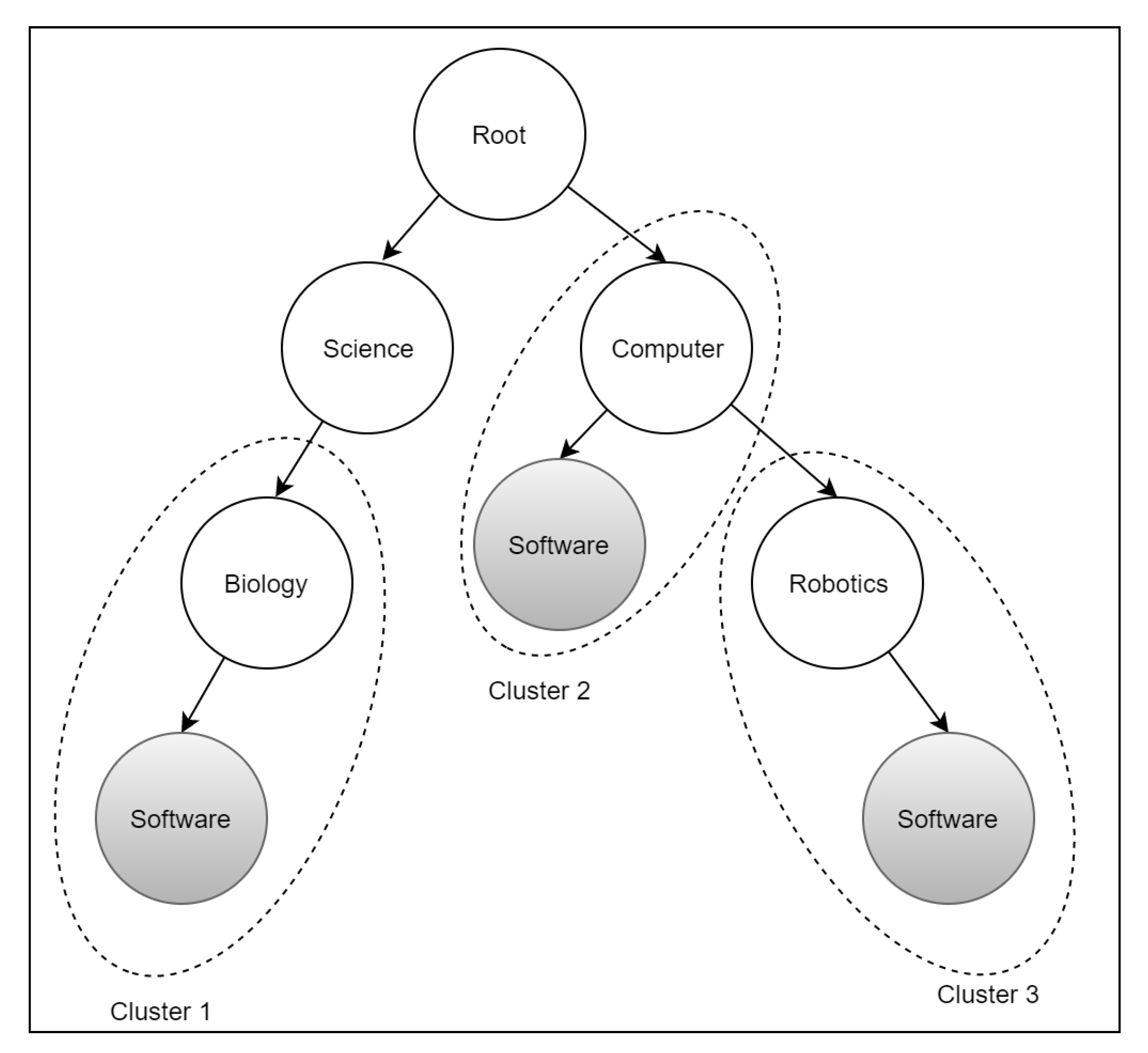
Phase 3: Semantic Topic Discovery
| Algorithm 1: Semantic Clustering Mechanism. |
 |
4. Evaluation
4.1. Step 1: Dataset Preparation
- –
- Replacing آ, أ, and إ with ا.
- –
- Replacing ى, ئ with ي.
- –
- Replacing ة with ه.
- –
- Removing the prefixes: ف، ك، ب، ل، ال، بال، وال، كال، لل، فال.
- –
- Removing the suffixes: ين، ان، ية، يه، ، ون.
4.2. Step 2: Evaluation Metrics
- –
- Accuracy measure: is the number of correct classifications divided by the total number of classifications, and it can be calculated as follows:
- –
- Precision measure: is the ratio of the accurate data among the retrieved data, and it can be calculated as follows:
- –
- Recall measure: is the ratio of relevant data among the retrieved data, and it can be calculated as follows:
- –
- F1 measure: is a combination of the precision and recall, and can be calculated as follows:where:
- –
- TP: true positive.
- –
- TN: true negative.
- –
- FP: false positive.
- –
- EN: false negative.
4.3. Step 2: Evaluation Process
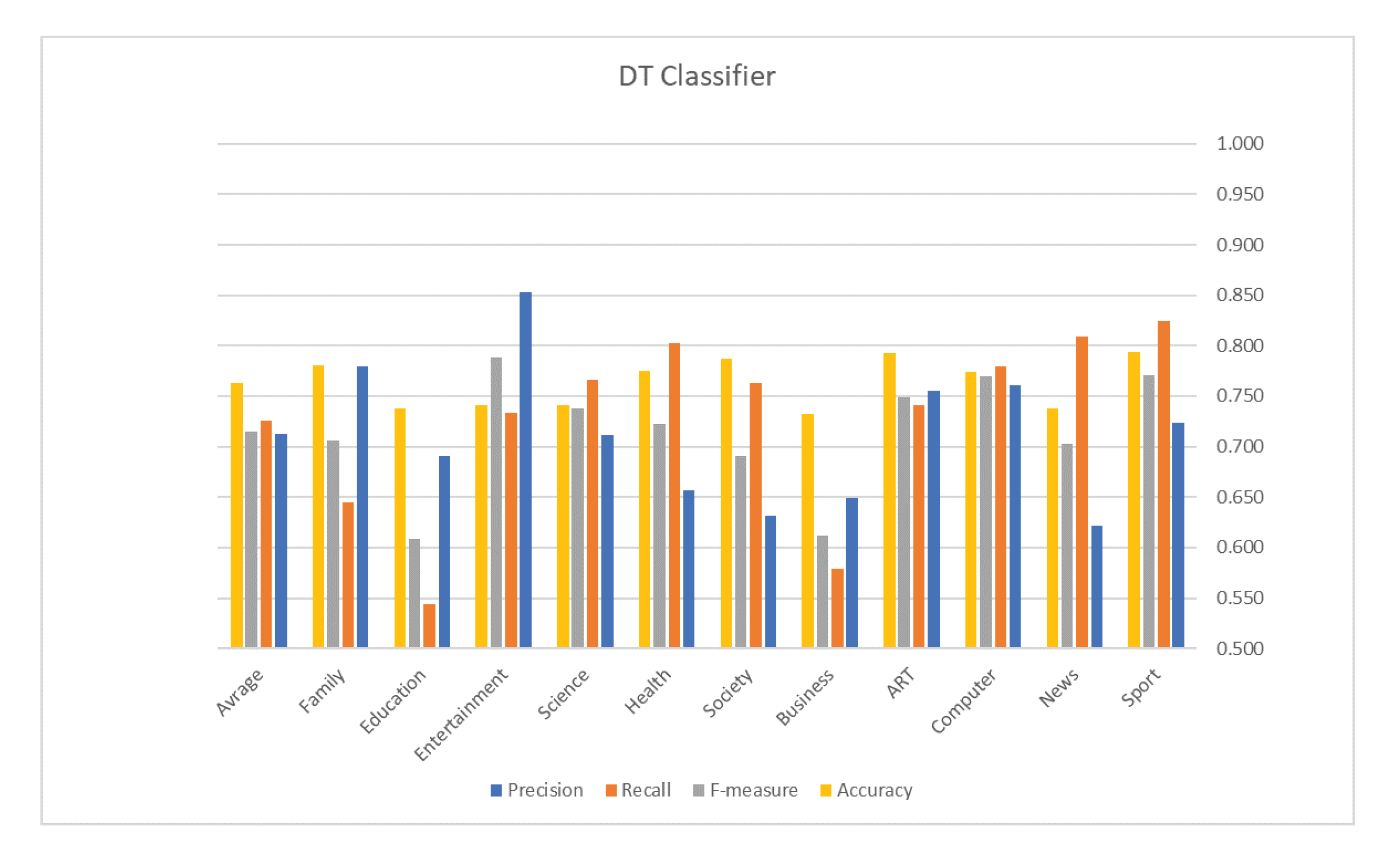
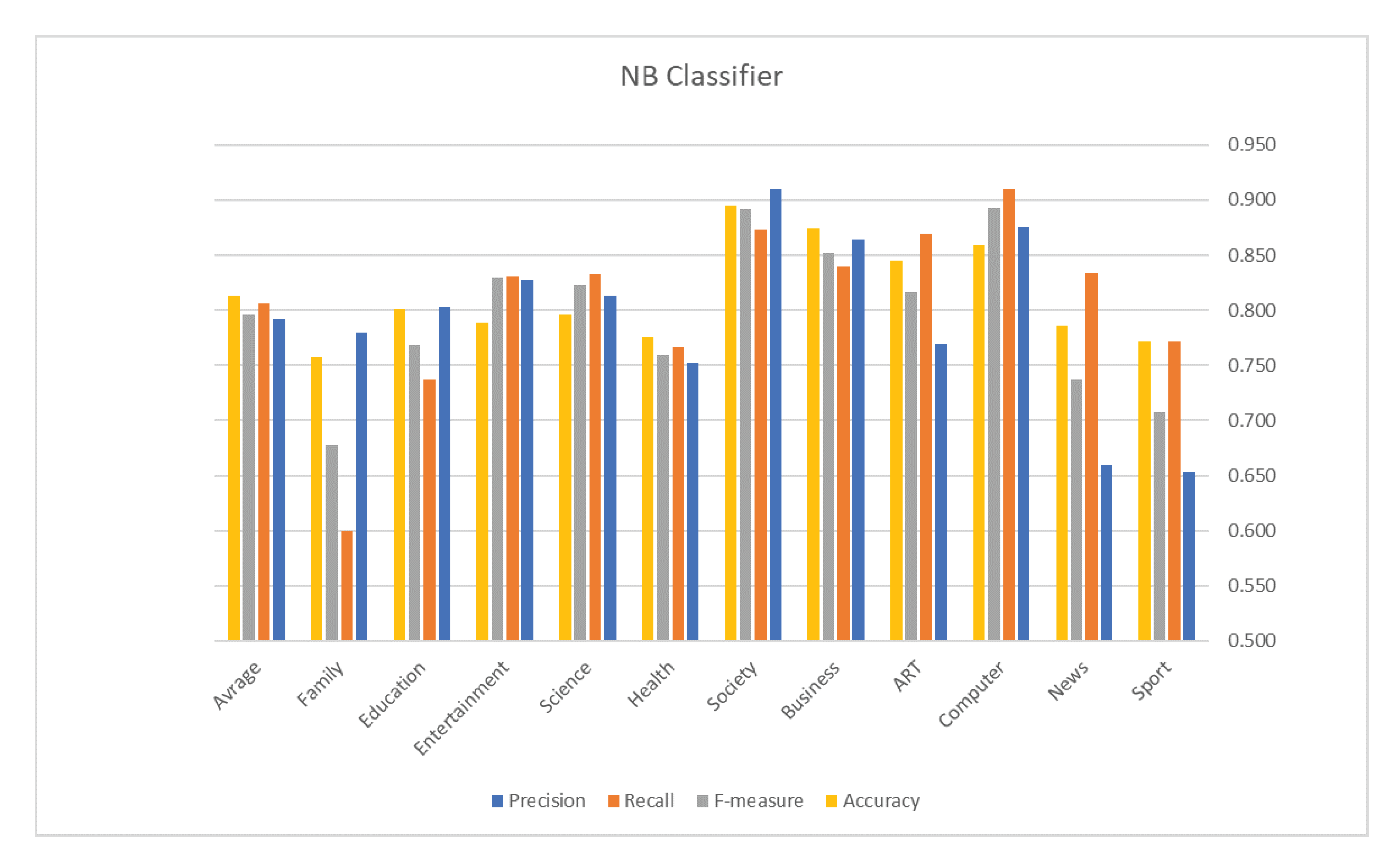
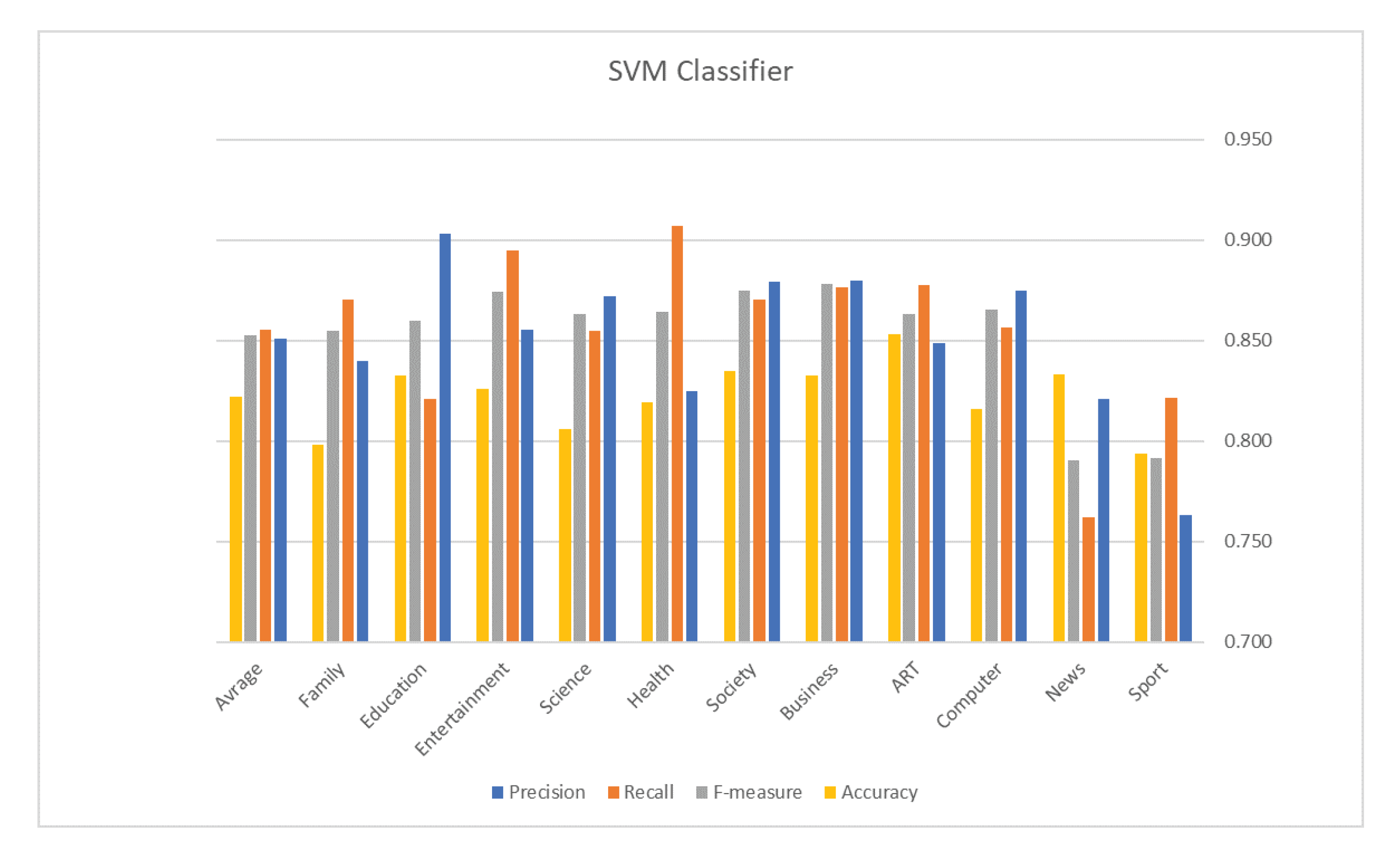
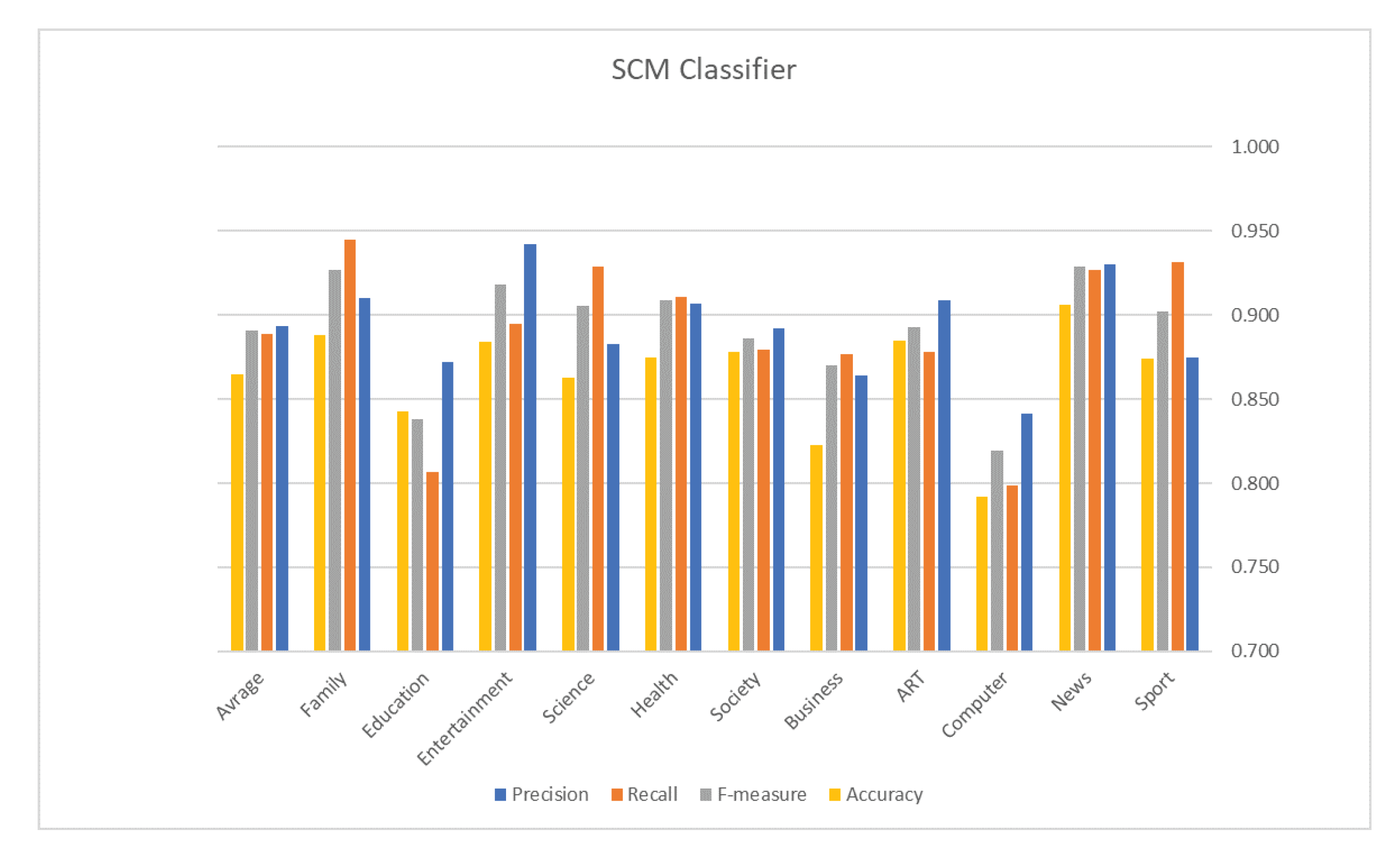
5. Evaluation Results
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.J. Semantics Processing for Search Engines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, Union, NJ, USA, 15–17 August 2018; pp. 124–126. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, T.A.; Calais, P.H.; de Castro Reis, D.; Lemos, A.P. An anatomy for neural search engines. Inf. Sci. 2019, 480, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtipour, K.; Hussain, A.; Gelbukh, A. Adaptation of sentiment analysis techniques to Persian language. In International Conference on Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, K.; Srivastava, P.; Chakrabarti, P. Exploring Structure Oriented Feature Tag Weighting Algorithm for Web Documents Identification. In International Conference on Soft Computing Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Hawalah, A.; Fasli, M. Using user personalized ontological profile to infer semantic knowledge for personalized recommendation. In International Conference on Electronic Commerce and Web Technologies; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 282–295. [Google Scholar]
- Hawalah, A. Modelling Dynamic and Contextual User Profiles for Personalized Services. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Essex, Colchester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hawalah, A.; Fasli, M. Utilizing contextual ontological user profiles for personalized recommendations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 4777–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magara, M.B.; Ojo, S.O.; Zuva, T. A comparative analysis of text similarity measures and algorithms in research paper recommender systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Information Communications Technology and Society (ICTAS), Durban, South Africa, 8–9 March 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dashtipour, K.; Hussain, A.; Zhou, Q.; Gelbukh, A.; Hawalah, A.Y.; Cambria, E. PerSent: A freely available Persian sentiment lexicon. In International Conference on Brain Inspired Cognitive Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 310–320. [Google Scholar]
- Dashtipour, K.; Poria, S.; Hussain, A.; Cambria, E.; Hawalah, A.Y.; Gelbukh, A.; Zhou, Q. Multilingual sentiment analysis: State of the art and independent comparison of techniques. Cogn. Comput. 2016, 8, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, S.; Farra, N.; Nakov, P. SemEval-2017 task 4: Sentiment analysis in Twitter. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2017), Vancouver, DC, Canada, 3–4 August 2017; pp. 502–518. [Google Scholar]
- Alqarafi, A.S.; Adeel, A.; Gogate, M.; Dashitpour, K.; Hussain, A.; Durrani, T. Toward’s arabic multi-modal sentiment analysis. In International Conference in Communications, Signal Processing, and Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ieracitano, C.; Adeel, A.; Gogate, M.; Dashtipour, K.; Morabito, F.C.; Larijani, H.; Raza, A.; Hussain, A. Statistical Analysis Driven Optimized Deep Learning System for Intrusion Detection. In International Conference on Brain Inspired Cognitive Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 759–769. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Moslmi, T.; Albared, M.; Al-Shabi, A.; Omar, N.; Abdullah, S. Arabic senti-lexicon: Constructing publicly available language resources for Arabic sentiment analysis. J. Inf. Sci. 2018, 44, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Radaideh, Q.A.; Al-Abrat, M.A. An Arabic text categorization approach using term weighting and multiple reducts. Soft Comput. 2018, 23, 5849–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtipour, K.; Gogate, M.; Adeel, A.; Algarafi, A.; Howard, N.; Hussain, A. Persian named entity recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 16th International Conference on Cognitive Informatics & Cognitive Computing (ICCI* CC), Oxford, UK, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Gogate, M.; Adeel, A.; Hussain, A. Deep learning driven multimodal fusion for automated deception detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 November–1 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gogate, M.; Adeel, A.; Hussain, A. A novel brain-inspired compression-based optimised multimodal fusion for emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 November–1 December 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hussien, I.O.; Dashtipour, K.; Hussain, A. Comparison of Sentiment Analysis Approaches Using Modern Arabic and Sudanese Dialect. In International Conference on Brain Inspired Cognitive Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 615–624. [Google Scholar]
- Hawalah, A. A framework for building an arabic multi-disciplinary ontology from multiple resources. Cogn. Comput. 2018, 10, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.K.; Meng, H.; Yam, Y. Topic Discovery via Convex Polytopic Model: A Case Study with Small Corpora. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Infocommunications (CogInfoCom), Budapest, Hungary, 22–24 August 2018; pp. 000367–000372. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, L.; Hao, H.; Deng, J.; Sun, X.; Bai, X. Topic Discovery for Streaming Short Texts with CTM. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tellez, E.S.; Moctezuma, D.; Miranda-Jiménez, S.; Graff, M. An automated text categorization framework based on hyperparameter optimization. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2018, 149, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Dai, Y.; Xiang, Y. Feature selection based on feature interactions with application to text categorization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 120, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtipour, K.; Gogate, M.; Adeel, A.; Ieracitano, C.; Larijani, H.; Hussain, A. Exploiting deep learning for persian sentiment analysis. In International Conference on Brain Inspired Cognitive Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 597–604. [Google Scholar]
- Adeel, A.; Gogate, M.; Farooq, S.; Ieracitano, C.; Dashtipour, K.; Larijani, H.; Hussain, A. A survey on the role of wireless sensor networks and IoT in disaster management. In Geological Disaster Monitoring Based on Sensor Networks; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mamoun, R.; Ahmed, M.A. A Comparative Study on Different Types of Approaches to the Arabic text classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 4777–4797. [Google Scholar]
- Hussien, F.M.I.; Olayah, F.; AL-dwan, M.; Shamsan, A. Arabic Text Classi- Fication Using SMO, Nave Bayesian, J48 Algorithms. Int. J. Res. Rev. Appl. Sci. 2011, 9, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Wahbeh, A.H.; Al-Kabi, M. Comparative Assessment of the Performance of Three WEKA Text Classifiers Applied to Arabic Text. Abhath Al-Yarmouk Basic Sci. Eng. 2012, 21, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Thwaib, E.; Al-Romimah, W. Support Vector Machine versus k-Nearest Neighbor for Arabic Text Classification. Int. J. Sci. 2014, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Al-diabat, M. Arabic Text Categorization Using Classification Rule Mining. Appl. Math. Sci. 2012, 6, 4033–4046. [Google Scholar]
- Sghaier, M.A.; Zrigui, M. Sentiment Analysis for Arabic e-commerce websites. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Engineering & MIS (ICEMIS), Agadir, Morocco, 22–24 September 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Alayba, A.M.; Palade, V.; England, M.; Iqbal, R. Arabic language sentiment analysis on health services. In Proceedings of the 2017 1st International Workshop on Arabic Script Analysis and Recognition (ASAR), Nancy, France, 3–5 April 2017; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Duwairi, R.M. Sentiment analysis for dialectical Arabic. In Proceedings of the 2015 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS), Amman, Jordan, 7–9 April 2015; pp. 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Hathlian, N.F.B.; Hafezs, A.M. Sentiment-subjective analysis framework for arabic social media posts. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th Saudi International Conference on Information Technology (Big Data Analysis) (KACSTIT), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 6–9 November 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulkareem, M.; Tiun, S. Comparative Analysis of ML POS on Arabic Tweets. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkey, L.S.; Ballesteros, L.; Connell, M.E. Light Stemming for Arabic Information Retrieval. In Arabic Computational Morphology; Soudi, A., Bosch, A.V.D., Neumann, G., Eds.; Number 38 in Text, Speech and Language Technology; Springer: Dutch, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 221–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khair, I.A. Effects of stop words elimination for Arabic information retrieval: A comparative study. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2006, 4, 119–133. [Google Scholar]
- Salton, G.; Wong, A.; Yang, C.S. A vector space model for automatic indexing. Commun. ACM 1975, 18, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza-Yates, R.; Ribeiro-Neto, B. Modern Information Retrieval: The Concepts and Technology behind Search, 2nd ed.; Addison-Wesley Professional: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Salton, G.; McGill, M.J. Introduction to Modern Information Retrieval; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Challam, V.; Gauch, S.; Chandramouli, A. Contextual search using ontology-based user profiles. In Proceedings of the Large Scale Semantic Access to Content (Text, Image, Video, and Sound), (RIAO ’07), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 30 May–1 June 2007; ACM: Paris, France, 2007; pp. 612–617. [Google Scholar]
- Castells, P.; Fernandez, M.; Vallet, D. An Adaptation of the Vector-Space Model for Ontology-Based Information Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2007, 19, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, A.; Abu-Errub, A.; Shambour, Q.; Turab, N. Arabic Text Categorization Algorithm using Vector Evaluation Method. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1501.01318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkova, J.; Gauch, S. Improving Ontology-Based User Profiles. In Proceedings of the Coupling Approaches, Coupling Media and Coupling Languages for Information Retrieval, Vaucluse, France, 26–28 April 2004; pp. 380–389. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, R.; Lima, C. Document Clustering Using an Ontology-Based Vector Space Model. Int. J. Inf. Retr. Res. 2015, 5, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, W.; Lv, X.; Peng, G. An improved focused crawler based on Semantic Similarity Vector Space Model. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 36, 392–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Domain | Number of Categories |
|---|---|
| Sport | 12 |
| News | 7 |
| Computer | 11 |
| ART | 6 |
| Business | 16 |
| Society | 14 |
| Health | 13 |
| Science | 10 |
| Entertainment | 8 |
| Education | 4 |
| Family | 6 |
| Dataset | Number of Documents |
|---|---|
| AODP | 5021 |
| Manual | 1060 |
| Classifier | Accuracy | Measures | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. Precision | 0.712 | ||
| Avg. Recall | 0.726 | ||
| DT | 0.763 | Avg. F1 | 0.714 |
| Avg. Precision | 0.792 | ||
| Avg. Recall | 0.806 | ||
| NB | 0.814 | Avg. F1 | 0.796 |
| Avg. Precision | 0.851 | ||
| Avg. Recall | 0.856 | ||
| SVM | 0.822 | Avg. F1 | 0.853 |
| C0C0C0Avg. Precision | 0.893 | ||
| Avg. Recall | 0.889 | ||
| SCM | 0.865 | Avg. F1 | 0.891 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hawalah, A. Semantic Ontology-Based Approach to Enhance Arabic Text Classification. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2019, 3, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc3040053
Hawalah A. Semantic Ontology-Based Approach to Enhance Arabic Text Classification. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2019; 3(4):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc3040053
Chicago/Turabian StyleHawalah, Ahmad. 2019. "Semantic Ontology-Based Approach to Enhance Arabic Text Classification" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 3, no. 4: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc3040053
APA StyleHawalah, A. (2019). Semantic Ontology-Based Approach to Enhance Arabic Text Classification. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 3(4), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc3040053




