Imaging in Gastroparesis: Exploring Innovative Diagnostic Approaches, Symptoms, and Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Gastric Neuromuscular Pathophysiology
3. Clinical Aspects and Overlap with Other Functional Diseases
4. Diagnostic Pathways in Gastroparesis
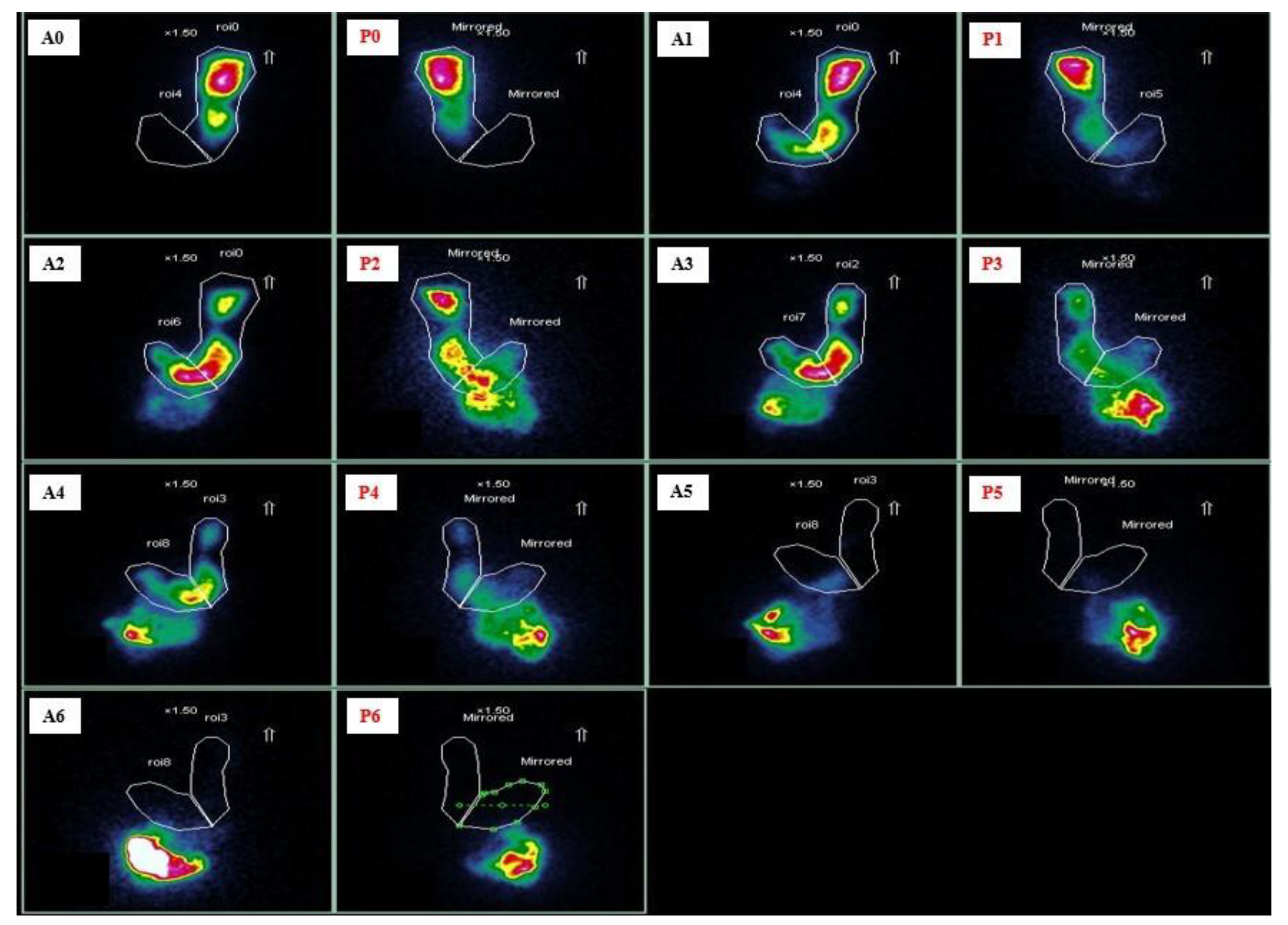
4.1. Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy
4.2. Wireless Motility Capsule
4.3. 13 Carbon-Gastric Emptying Breath Test
4.4. Other Diagnostic Techniques
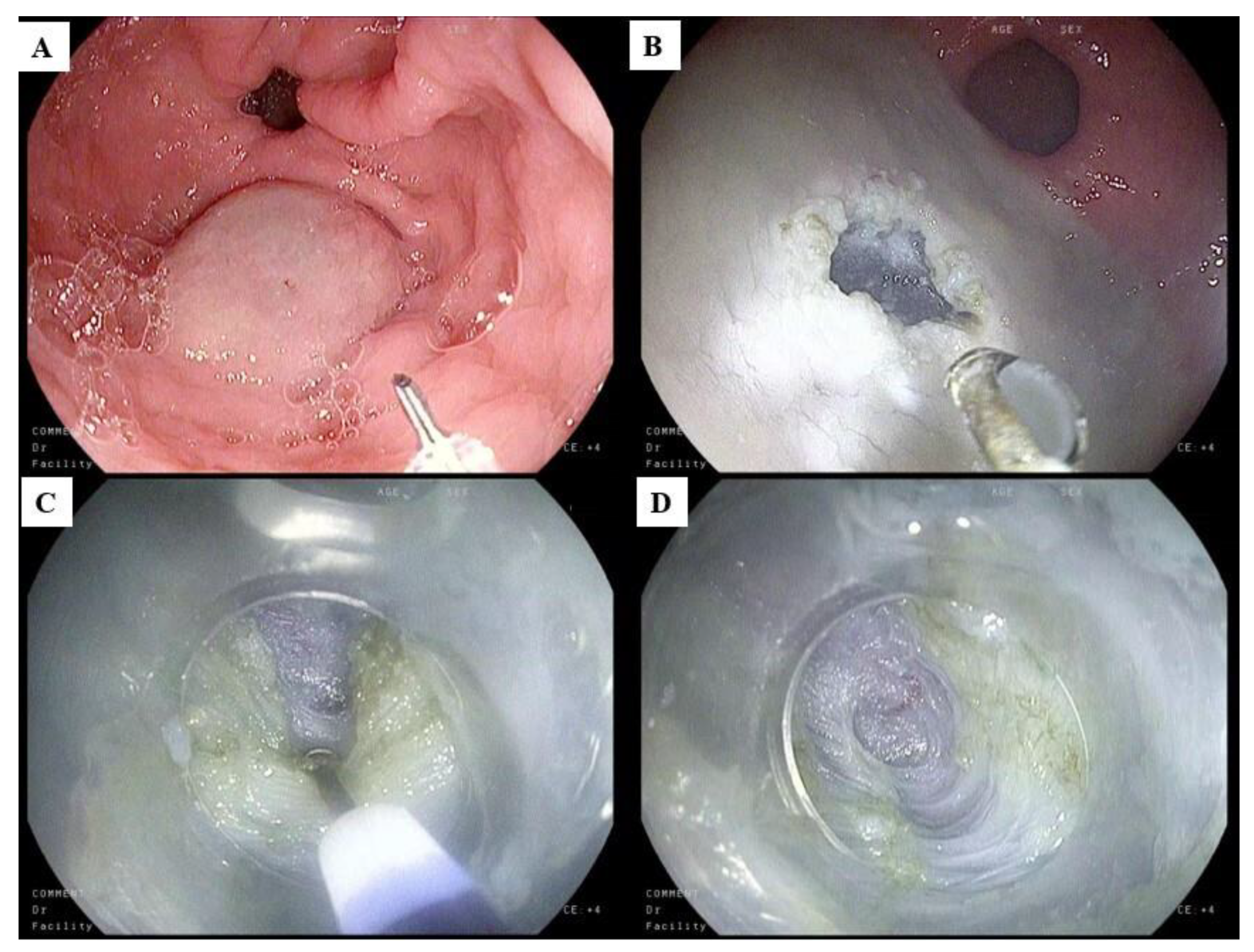
4.5. Endoluminal Functional Lumen Imaging Probe
5. Old and New Treatments
5.1. Dietary Adjustments
5.2. Medical Treatment
5.3. Surgical and Endoscopic Treatment
5.4. Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schol, J.; Wauters, L.; Dickman, R.; Drug, V.; Mulak, A.; Serra, J.; Enck, P.; Tack, J. ESNM Gastroparesis Consensus Group. United European Gastroenterology (UEG) and European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility (ESNM) consensus on gastroparesis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Coles, M.; Parkman, H.P. Gastroparesis in the 2020s: New treatments, new paradigms. Current Gastroenterol. Rep. 2020, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovezani Ramos, G.; Camilleri, M. Ten controversies in gastroparesis and a look to the future. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 35, e14494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, B.E.; Crowell, M.D.; Mathis, C.; Bauer, D.; Heinberg, L.J. Gastroparesis: Quality of life and health care utilization. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-K.; Choung, R.S.; Locke, G.R., 3rd; Schleck, C.D.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Szarka, L.A.; Mullan, B.; Talley, N.J. The incidence, prevalence, and outcomes of patients with gastroparesis in Olmsted County, Minnesota, from 1996 to 2006. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Jiang, B.; Manne, S.; Moses, P.L.; Almansa, C.; Bennett, D.; Dolin, P.; Ford, A.C. Epidemiology and outcomes of gastroparesis, as documented in general practice records, in the United Kingdom. Gut 2021, 70, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharucha, A.E. Epidemiology and natural history of gastroparesis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 44, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, E.; Choung, R.S.; Schleck, C.D.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Talley, N.J.; Locke, G.R., 3rd. Prevalence of hidden gastroparesis in the community: The gastroparesis “iceberg”. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 18, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, I.; Levesque, H.; Ducrotte, P.; Denis, P.; Hellot, M.F.; Benichou, J.; Cailleux, N.; Courtois, H. Gastric involvement in systemic sclerosis: A prospective study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botrus, G.; Baker, O.; Borrego, E.; Ngamdu, K.S.; Teleb, M.; Gonzales Martinez, J.L.; Maldonado, G., 3rd; Hussein, A.M.; McCallum, R. Spectrum of gastrointestinal manifestations in joint hypermobility syndromes. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 355, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, A.S.; Ordög, T.; Sanders, K.M. Neural regulation of slow-wave frequency in the murine gastric antrum. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G486–G495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashashati, M.; Moraveji, S.; Torabi, A.; Sarosiek, I.; Davis, B.R.; Diaz, J.; McCallum, R.W. Pathological findings of the antral and pyloric smooth muscle in patients with gastroparesis-like syndrome compared to gastroparesis: Similarities and differences. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2828–2833. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, M.; Farrugia, G.; Lurken, M.S.; Bernard, C.E.; Faussone-Pellegrini, M.S.; Smyrk, T.C.; Parkman, H.P.; Abell, T.L.; Snape, W.J.; Hasler, W.L.; et al. Cellular changes in diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faussone-Pellegrini, M.S.; Grover, M.; Pasricha, P.J.; Bernard, C.E.; Lurken, M.S.; Smyrk, T.C.; Parkman, H.P.; Abell, T.L.; Snape, W.J.; Hasler, W.L.; et al. Ultrastructural differences between diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, J.; Damjanov, I.; Lin, Z.; Sarosiek, I.; Wetzel, P.; McCallum, R.W. Absence of the interstitial cells of Cajal in patients with gastroparesis and correlation with clinical findings. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2005, 9, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, F.V.; Sinagra, E.; Barchi, A.; Verga, M.C.; Brinch, D.; Raimondo, D.; Danese, S. Gastroparesis: The Complex Interplay with Microbiota and the Role of Exogenous Infections in the Pathogenesis of the Disease. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, F.V.; Sinagra, E.; Raimondo, D.; Danese, S. The Role of Microbiota in Upper and Lower Gastrointestinal Functional Disorders. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimino, L.; Barchi, A.; Mandarino, F.V.; Spanò, S.; Lamparelli, L.A.; Vespa, E.; Passaretti, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Savarino, E.V.; Jairath, V.; et al. A multi-omic analysis reveals the esophageal dysbiosis as the predominant trait of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, M.A.; Pasricha, P.J. Post-surgical and obstructive gastroparesis. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2007, 9, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, T.L.; Camilleri, M.; Donohoe, K.; Hasler, W.L.; Lin, H.C.; Maurer, A.H.; McCallum, R.W.; Nowak, T.; Nusynowitz, M.L.; Parkman, H.P.; et al. American Neurogastroenterology and Motility Society and the Society of Nuclear Medicine. Consensus recommendations for gastric emptying scintigraphy: A joint report of the American Neurogastroenterology and motility society and the Society of Nuclear Medicine. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 753–763. [Google Scholar]
- Wise, J.L.; Vazquez-Roque, M.I.; McKinney, C.J.; Zickella, M.A.; Crowell, M.D.; Lacy, B.E. Gastric Emptying Scans: Poor Adherence to National Guidelines. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 2897–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, C.; Kuo, B.; Nguyen, L.; Vaughn, V.M.; Petrey, P.; Greer, K.; Yadlapati, R.; Abell, T.L. ACG Clinical Guideline: Gastroparesis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 1197–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.A.; Snape, W.J., Jr. Clinical presentation and pathophysiology of gastroparesis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 44, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, B.E.; Tack, J.; Gyawali, C.P. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Medically Refractory Gastroparesis: Expert Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Chedid, V.; Ford, A.C.; Haruma, K.; Horowitz, M.; Jones, K.L.; Low, P.A.; Park, S.Y.; Parkman, H.P.; Stanghellini, V. Gastroparesis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, M.; Bernard, C.E.; Pasricha, P.J.; Parkman, H.P.; Gibbons, S.J.; Tonascia, J.; Koch, K.L.; McCallum, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; Hasler, W.L.; et al. Diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis is associated with loss of CD206-positive macrophages in the gastric antrum. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e13018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Sanders, K.M. Gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 68–87.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, G.W.; Spencer, N.J.; Jokela-Willis, S.; Bayguinov, P.O.; Lee, H.T.; Ritchie, L.A.; Ward, S.M.; Smith, T.K.; Sanders, K.M. ICC-MY coordinate smooth muscle electrical and mechanical activity in the murine small intestine. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, e138–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ordög, T.; Ward, S.M.; Sanders, K.M. Interstitial cells of cajal generate electrical slow waves in the murine stomach. J. Physiol. 1999, 518 Pt 1, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Calderon, L.F.; Sanders, B.E.; Mccurdy, G.; Nasir, A.; Zheng, W.; Massaad, J.; Xie, M.; Luo, H.; Li, L.; et al. Quantification of Interstitial Cells of Cajal in the Gastric Muscle of Patients with Gastroparesis at Per-Oral Endoscopic Pyloromyotomy: A Novel Approach for Future Research in Pathogenesis of Gastroparesis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 4492–4499. [Google Scholar]
- Bayguinov, O.; Sanders, K.M. Role of nitric oxide as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the canine pyloric sphincter. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 264, G975–G983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.M.; Morris, G.; Reese, L.X.; Wang, Y.; Sanders, K.M. Interstitial cells of Cajal mediate enteric inhibitory neurotransmission in the lower esophageal and pyloric sphincters. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumshirn, M.; Bruninga, K.; Camilleri, M. Simplifying the evaluation of postprandial antral motor function in patients with suspected gastroparesis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 92, 1496–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Stanghellini, V.; Malagelada, J.R. Gastric manometric abnormalities in patients with dyspeptic symptoms after fundoplication. Gut 1983, 24, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mearin, F.; Camilleri, M.; Malagelada, J.R. Pyloric dysfunction in diabetics with recurrent nausea and vomiting. Gastroenterology 1986, 90, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivarao, D.V.; Mashimo, H.; Goyal, R.K. Pyloric sphincter dysfunction in nNOS-/- and W/Wv mutant mice: Animal models of gastroparesis and duodenogastric reflux. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, P.J.; Yates, K.P.; Nguyen, L.; Clarke, J.; Abell, T.L.; Farrugia, G.; Hasler, W.L.; Koch, K.L.; Snape, W.J.; McCallum, R.W.; et al. Outcomes and Factors Associated With Reduced Symptoms in Patients With Gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1762–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkman, H.P.; Hasler, W.L.; Fisher, R.S. American Gastroenterological Association. American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the diagnosis and treatment of gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1592–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revicki, D.A.; Rentz, A.M.; Dubois, D.; Kahrilas, P.; Stanghellini, V.; Talley, N.J.; Tack, J. Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI): Development and validation of a patient reported assessment of severity of gastroparesis symptoms. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 13, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revicki, D.A.; Rentz, A.M.; Dubois, D.; Kahrilas, P.; Stanghellini, V.; Talley, N.J.; Tack, J. Development and validation of a patient-assessed gastroparesis symptom severity measure: The Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkman, H.P.; Yates, K.; Hasler, W.L.; Nguyen, L.; Pasricha, P.J.; Snape, W.J.; Farrugia, G.; Koch, K.L.; Calles, J.; Abell, T.L.; et al. Similarities and differences between diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkman, H.P.; Hallinan, E.K.; Hasler, W.L.; Farrugia, G.; Koch, K.L.; Calles, J.; Snape, W.J.; Abell, T.L.; Sarosiek, I.; McCallum, R.W.; et al. Nausea and vomiting in gastroparesis: Similarities and differences in idiopathic and diabetic gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 1902–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snodgrass, P.; Sandoval, H.; Calhoun, V.D.; Ramos-Duran, L.; Song, G.; Sun, Y.; Alvarado, B.; Bashashati, M.; Sarosiek, I.; McCallum, R.W. Central Nervous System Mechanisms of Nausea in Gastroparesis: An fMRI-Based Case-Control Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkman, H.P.; Wilson, L.A.; Hasler, W.L.; McCallum, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; Koch, K.L.; Abell, T.L.; Schey, R.; Kuo, B.; Snape, W.J.; et al. Abdominal Pain in Patients with Gastroparesis: Associations with Gastroparesis Symptoms, Etiology of Gastroparesis, Gastric Emptying, Somatization, and Quality of Life. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 2242–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasler, W.L.; Wilson, L.A.; Parkman, H.P.; Koch, K.L.; Abell, T.L.; Nguyen, L.; Pasricha, P.J.; Snape, W.J.; McCallum, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; et al. Factors related to abdominal pain in gastroparesis: Contrast to patients with predominant nausea and vomiting. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, W.L.; Wilson, L.A.; Nguyen, L.A.; Snape, W.J.; Abell, T.L.; Koch, K.L.; McCallum, R.W.; Pasricha, P.J.; Sarosiek, I.; Farrugia, G.; et al. Opioid Use and Potency Are Associated With Clinical Features, Quality of Life, and Use of Resources in Patients With Gastroparesis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, P.J.; Colvin, R.; Yates, K.; Hasler, W.L.; Abell, T.L.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Nguyen, L.; Farrugia, G.; Koch, K.L.; Parkman, H.P.; et al. Characteristics of patients with chronic unexplained nausea and vomiting and normal gastric emptying. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanghellini, V.; Chan, F.K.; Hasler, W.L.; Malagelada, J.R.; Suzuki, H.; Tack, J.; Talley, N.J. Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, G.R., 3rd; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Fett, S.L.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; Talley, N.J. Overlap of gastrointestinal symptom complexes in a US community. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2005, 17, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosiek, I.; Selover, K.H.; Katz, L.A.; Semler, J.R.; Wilding, G.E.; Lackner, J.M.; Sitrin, M.D.; Kuo, B.; Chey, W.D.; Hasler, W.L.; et al. The assessment of regional gut transit times in healthy controls and patients with gastroparesis using wireless motility technology. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanghellini, V.; Tack, J. Gastroparesis: Separate entity or just a part of dyspepsia? Gut 2014, 63, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasler, W.L.; May, K.P.; Wilson, L.A.; Van Natta, M.; Parkman, H.P.; Pasricha, P.J.; Koch, K.L.; Abell, T.L.; McCallum, R.W.; Nguyen, L.A.; et al. Relating gastric scintigraphy and symptoms to motility capsule transit and pressure findings in suspected gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolar, G.J.; Camilleri, M.; Burton, D.; Nadeau, A.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Prevalence of colonic motor or evacuation disorders in patients presenting with chronic nausea and vomiting evaluated by a single gastroenterologist in a tertiary referral practice. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkman, H.P.; Sharkey, E.; McCallum, R.E.; Hasler, W.L.; Koch, K.L.; Sarosiek, I.; Abell, T.L.; Kuo, B.; Shulman, R.J.; Grover, M.; et al. Constipation in patients with symptoms of gastroparesis: Analysis of symptoms and gastrointestinal transit. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehangir, A.; Parkman, H.P. Rome IV Diagnostic Questionnaire Complements Patient Assessment of Gastrointestinal Symptoms for Patients with Gastroparesis Symptoms. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, P.J.; Grover, M.; Yates, K.P.; Abell, T.L.; Bernard, C.E.; Koch, K.L.; McCallum, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; Kuo, B.; Bulat, R.; et al. Functional Dyspepsia and Gastroparesis in Tertiary Care are Interchangeable Syndromes With Common Clinical and Pathologic Features. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.H.; Schol, J.; Carbone, F.; Chen, Y.J.; Van den Houte, K.; Balsiger, L.M.; Broeders, B.; Vanuytsel, T.; Tack, J. Prevalence of delayed gastric emptying in patients with gastroparesis-like symptoms. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkman, H.P.; Hallinan, E.K.; Hasler, W.L.; Farrugia, G.; Koch, K.L.; Nguyen, L.; Snape, W.J.; Abell, T.L.; McCallum, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; et al. Early satiety and postprandial fullness in gastroparesis correlate with gastroparesis severity, gastric emptying, and water load testing. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e12981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tougas, G.; Eaker, E.Y.; Abell, T.L.; Abrahamsson, H.; Boivin, M.; Chen, J.; Hocking, M.P.; Quigley, E.M.; Koch, K.L.; Tokayer, A.Z.; et al. Assessment of gastric emptying using a low fat meal: Establishment of international control values. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayvargiya, P.; Jameie-Oskooei, S.; Camilleri, M.; Chedid, V.; Erwin, P.J.; Murad, M.H. Association between delayed gastric emptying and upper gastrointestinal symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2019, 68, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; O’Connor, M.; Neja, B.; Delaney, K.; Camilleri, M.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Bharucha, A.E. Reproducibility of gastric emptying assessed with scintigraphy in patients with upper GI symptoms. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, M.; Farrugia, G.; Stanghellini, V. Gastroparesis: A turning point in understanding and treatment. Gut 2019, 68, 2238–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M. Clinical practice. Diabetic gastroparesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkman, H.P.; Camilleri, M.; Farrugia, G.; McCallum, R.W.; Bharucha, A.E.; Mayer, E.A.; Tack, J.F.; Spiller, R.; Horowitz, M.; Vinik, A.I.; et al. Gastroparesis and functional dyspepsia: Excerpts from the AGA/ANMS meeting. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boltin, D.; Zvidi, I.; Steinmetz, A.; Bernstine, H.; Groshar, D.; Nardi, Y.; Boaz, M.; Niv, Y.; Dickman, R. Vomiting and dysphagia predict delayed gastric emptying in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. J. Diabetes Res. 2014, 2014, 294032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, K.; Kawabe, J.; Kawamura, E.; Kawano, N.; Emoto, M.; Yoshida, A.; Higashiyama, S.; Morioka, T.; Inaba, M.; Shiomi, S. Clinical assessment of delayed gastric emptying and diabetic complications using gastric emptying scintigraphy: Involvement of vascular disorder. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2014, 34, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, E.; Enomoto, M.; Kotani, K.; Hagihara, A.; Fujii, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Iwai, S.; Morikawa, H.; Kawabe, J.; Tominaga, K.; et al. Effect of mosapride citrate on gastric emptying in interferon-induced gastroparesis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.M.; Benezech, A.; Vitton, V.; Barthet, M. G-POEM with antro-pyloromyotomy for the treatment of refractory gastroparesis: Mid-term follow-up and factors predicting outcome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonlachanvit, S.; Maurer, A.H.; Fisher, R.S.; Parkman, H.P. Regional gastric emptying abnormalities in functional dyspepsia and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2006, 18, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orthey, P.; Yu, D.; Van Natta, M.L.; Ramsey, F.V.; Diaz, J.R.; Bennett, P.A.; Iagaru, A.H.; Salas Fragomeni, R.; McCallum, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; et al. Intragastric meal distribution during gastric emptying scintigraphy for assessment of fundic accommodation: Correlation with symptoms of gastroparesis. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedid, V.; Halawi, H.; Brandler, J.; Burton, D.; Camilleri, M. Gastric accommodation measurements by single photon emission computed tomography and two-dimensional scintigraphy in diabetic patients with upper gastrointestinal symptoms. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandarino, F.V.; Testoni, S.G.G.; Barchi, A.; Pepe, G.; Esposito, D.; Fanti, L.; Viale, E.; Biamonte, P.; Azzolini, F.; Danese, S. Gastric emptying study before gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM): Can intragastric meal distribution be a predictor of success? Gut 2023, 72, 1019–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, B.; McCallum, R.W.; Koch, K.L.; Sitrin, M.D.; Wo, J.M.; Chey, W.D.; Hasler, W.L.; Lackner, J.M.; Katz, L.A.; Semler, J.R.; et al. Comparison of gastric emptying of a nondigestible capsule to a radio-labelled meal in healthy and gastroparetic subjects. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.A.; Rao, S.; Nguyen, L.A.; Moshiree, B.; Sarosiek, I.; Schulman, M.I.; Wo, J.M.; Parkman, H.P.; Wilding, G.E.; McCallum, R.W.; et al. Validation of Diagnostic and Performance Characteristics of the Wireless Motility Capsule in Patients With Suspected Gastroparesis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 1770–1779.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A. The use of wireless motility capsule in the diagnosis and monitoring of gastroparesis. In Gastroparesis; McCallum, R.W., Parkman, H.P., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Camilleri, M.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Burton, D.D.; Choi, M.G.; Nair, K.S.; Verlinden, M. Toward office-based measurement of gastric emptying in symptomatic diabetics using [13C]octanoic acid breath test. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 2751–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, K.; Zhang, L.; Nugent Liegl, M.; Pawela, L.; Simpson, P.; Sood, M.R. Gastric emptying in healthy children using the Spirulina breath test: The impact of gender, body size, and pubertal development. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braden, B.; Adams, S.; Duan, L.P.; Orth, K.H.; Maul, F.D.; Lembcke, B.; Hör, G.; Caspary, W.F. The [13C]acetate breath test accurately reflects gastric emptying of liquids in both liquid and semisolid test meals. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.D.Z.; Nojkov, B. Diagnostic Methods for Evaluation of Gastric Motility-A Mini Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szarka, L.A.; Camilleri, M.; Vella, A.; Burton, D.; Baxter, K.; Simonson, J.; Zinsmeister, A.R. A stable isotope breath test with a standard meal for abnormal gastric emptying of solids in the clinic and in research. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viramontes, B.E.; Kim, D.Y.; Camilleri, M.; Lee, J.S.; Stephens, D.; Burton, D.D.; Thomforde, G.M.; Klein, P.D.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Validation of a stable isotope gastric emptying test for normal, accelerated or delayed gastric emptying. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2001, 13, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Hammer, H.F.; Hauser, B. 13 C-gastric emptying breath tests: Clinical use in adults and children. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibans, A.A.; Kim, S.; Kunkel, D.; Coleman, T.P. High-Resolution Electrogastrogram: A Novel, Noninvasive Method for Determining Gastric Slow-Wave Direction and Speed. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzana, R.J.; Koch, K.L.; Bingaman, S. Gastric myoelectrical activity in patients with gastric outlet obstruction and idiopathic gastroparesis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Lin, Z.; Pan, J.; McCallum, R.W. Abnormal gastric myoelectrical activity and delayed gastric emptying in patients with symptoms suggestive of gastroparesis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1996, 41, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, T.R.; Cheng, L.K.; Du, P.; Wang, T.H.; Bernard, C.E.; Vannucchi, M.G.; Faussone-Pellegrini, M.S.; Lahr, C.; Vather, R.; Windsor, J.A.; et al. Loss of Interstitial Cells of Cajal and Patterns of Gastric Dysrhythmia in Patients With Chronic Unexplained Nausea and Vomiting. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 56–66.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, D.A.; O’Grady, G.; Du, P.; Gharibans, A.A.; Andrews, C.N. Body surface mapping of the stomach: New directions for clinically evaluating gastric electrical activity. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Elzen, B.D.; Bennink, R.J.; Wieringa, R.E.; Tytgat, G.N.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. Fundic accommodation assessed by SPECT scanning: Comparison with the gastric barostat. Gut 2003, 52, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilja, O.H.; Lunding, J.; Hausken, T.; Gregersen, H. Gastric accommodation assessed by ultrasonography. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 2825–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, N.; Nakamoto, Y.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F.; Kido, A.; Ishimori, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Yamada, T.; Sato, M.; Aoyama, A.; Date, H.; et al. Gastric motility and emptying assessment by magnetic resonance imaging after lung transplantation: Correlation with gastric emptying scintigraphy. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarakji, A.M.; Morales, F.; Rovito, P. Hepatobiliary scintigraphy as a diagnostic modality for gastroparesis of the bypassed stomach after gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.A.; Kou, W.; Lin, Z.; Hinchcliff, M.; Thakrar, A.; Falmagne, S.; Prescott, J.; Dorian, E.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Pandolfino, J.E. Normal Values of Esophageal Distensibility and Distension-Induced Contractility Measured by Functional Luminal Imaging Probe Panometry. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 674–681.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, J.; Pagnon, L.; Hure, F.; Legros, R.; Crepin, S.; Fauchais, A.L.; Palat, S.; Ducrotté, P.; Marin, B.; Fontaine, S.; et al. Peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy is efficacious and safe for refractory gastroparesis: Prospective trial with assessment of pyloric function. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desprez, C.; Melchior, C.; Wuestenberghs, F.; Zalar, A.; Jacques, J.; Leroi, A.M.; Gourcerol, G. Pyloric distensibility measurement predicts symptomatic response to intrapyloric botulinum toxin injection. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 90, 754–760.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, L.; Wo, J.; DeWitt, J.; Yim, B.; Siwiec, R.; Nowak, T.; Mendez, M.; Gupta, A.; Dickason, D.; Stainko, S.; et al. Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of refractory gastroparesis: A prospective single-center experience with mid-term follow-up (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosoughi, K.; Ichkhanian, Y.; Jacques, J.; Aadam, A.A.; Benias, P.C.; Law, R.; Hasler, W.L.; Canakis, A.; Ragi, O.; Triggs, J.; et al. Role of endoscopic functional luminal imaging probe in predicting the outcome of gastric peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olausson, E.A.; Störsrud, S.; Grundin, H.; Isaksson, M.; Attvall, S.; Simrén, M. A small particle size diet reduces upper gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with diabetic gastroparesis: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olausson, E.A.; Alpsten, M.; Larsson, A.; Mattsson, H.; Andersson, H.; Attvall, S. Small particle size of a solid meal increases gastric emptying and late postprandial glycaemic response in diabetic subjects with gastroparesis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 80, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S.; Ferrie, S.; Carey, S. Nutrition management in patients with chronic gastrointestinal motility disorders: A systematic literature review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanculete, M.F.; Chiarioni, G.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Dumitrascu, D.I.; Popa, S.L. Disorders of the brain-gut interaction and eating disorders. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3668–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayvargiya, P.; Camilleri, M.; Chedid, V.; Mandawat, A.; Erwin, P.J.; Hassan Murad, M. Effects of Promotility Agents on Gastric Emptying and Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkman, H.P.; Carlson, M.R.; Gonyer, D. Metoclopramide nasal spray is effective in symptoms of gastroparesis in diabetics compared to conventional oral tablet. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abell, T.L.; Bernstein, R.K.; Cutts, T.; Farrugia, G.; Forster, J.; Hasler, W.L.; McCallum, R.W.; Olden, K.W.; Parkman, H.P.; Parrish, C.R.; et al. Treatment of gastroparesis: A multidisciplinary clinical review. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2006, 18, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S.; Camilleri, M. Review article: Metoclopramide and tardive dyskinesia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saffar, A.; Lennernäs, H.; Hellström, P.M. Gastroparesis, metoclopramide, and tardive dyskinesia: Risk revisited. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Khan, K.S.; Du, M.C.; Du, W.W.; Ouyang, Y.Q. Efficacy and Safety of Domperidone and Metoclopramide in Breastfeeding: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Breastfeed. Med. 2021, 16, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvers, M.; Kipnes, V.; Broadstone, A.; Patterson, D.; Quigley, E.M.; McCallum, R.; Leidy, N.K.; Farup, C.; Liu, Y.; Joslyn, A. Domperidone in the management of symptoms of diabetic gastroparesis: Efficacy, tolerability, and quality-of-life outcomes in a multicenter controlled trial. Clin. Ther. 1998, 20, 438–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.M.; Jeong, H.E.; Lee, H.; Shin, J.Y. Association between domperidone use and adverse cardiovascular events: A nested case-control and case-time-control study. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2020, 29, 1636–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelik, E.; Masarwa, R.; Perlman, A.; Rotshild, V.; Muszkat, M.; Matok, I. Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and network meta-analysis of the cardiovascular safety of macrolides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00438-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testoni, P.A.; Bagnolo, F.; Fanti, L.; Passaretti, S.; Tittobello, A. Longterm oral cisapride improves interdigestive antroduodenal motility in dyspeptic patients. Gut 1990, 31, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, W.; Shatin, D.; Wysowski, D.K.; Gurwitz, J.; Andrade, S.E.; Goodman, M.; Chan, K.A.; Platt, R.; Schech, S.D.; Ray, W.A. Contraindicated use of cisapride: Impact of Food and Drug Administration regulatory action. JAMA 2000, 284, 3036–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; Van den Houte, K.; Clevers, E.; Andrews, C.N.; Papathanasopoulos, A.; Holvoet, L.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Caenepeel, P.; Arts, J.; Vanuytsel, T.; et al. Prucalopride in gastroparesis: A randomized placebo-controlled crossover study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tack, J.; Rotondo, A.; Meulemans, A.; Thielemans, L.; Cools, M. Randomized clinical trial: A controlled pilot trial of the 5-HT4 receptor agonist revexepride in patients with symptoms suggestive of gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, B.; Barnes, C.N.; Nguyen, D.D.; Shaywitz, D.; Grimaldi, M.; Renzulli, C.; Canafax, D.; Parkman, H.P. Velusetrag accelerates gastric emptying in subjects with gastroparesis: A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 53, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chedid, V.; Brandler, J.; Arndt, K.; Vijayvargiya, P.; Jing Wang, X.; Burton, D.; Harmsen, W.S.; Siegelman, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Randomised study: Effects of the 5-HT(4) receptor agonist felcisetrag vs placebo on gut transit in patients with gastroparesis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 53, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.W.; Chun, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Jung Lee, H.; Chung, H.; Cho, S.J.; Pil Im, J.; Gyun Kim, S.; Sung Kim, J. Efficacy and safety of ghrelin agonists in patients with diabetic gastroparesis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Liver 2020, 14, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M.; McCallum, R.W.; Tack, J.; Spence, S.C.; Gottesdiener, K.; Fiedorek, F.T. Efficacy and safety of Relamorelin in diabetics with symptoms of gastroparesis: A randomized, placebo-controlled study. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1240–1250.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, P.; Vos, R.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Tack, J. Influence of the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist ondansetron on gastric sensorimotor function and nutrient tolerance in healthy volunteers. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 444–449. [Google Scholar]
- Midani, D.; Parkman, H.P. Granisetron transdermal system for treatment of symptoms of gastroparesis: A prescription registry study. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 22, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, P.J.; Yates, K.P.; Sarosiek, I.; McCallum, R.W.; Abell, T.L.; Koch, K.L.; Anh, B.; Nguyen, L.; Snape, W.J.; Hasler, W.L.; et al. Aprepitant has mixed effects on nausea and reduces other symptoms in patients with gastroparesis and related disorders. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, J.L.; Lieberman, V.R.; Dahal, A.; Keefe, M.S.; Xiao, C.; Birznieks, G.; Abell, T.L.; Lembo, A.; Parkman, H.P.; Polymeropoulos, M.H. Efficacy and safety of tradipitant in patients with diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shada, A.L.; Dunst, C.M.; Pescarus, R.; Speer, E.A.; Cassera, M.; Reavis, K.M.; Speer, E.A.; Cassera, M.; Reavis, K.M.; Swanstrom, L.L. Laparoscopic pyloroplasty is a safe and effective first-line surgical therapy for refractory gastroparesis. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zihni, A.M.; Dunst, C.M.; Swanström, L.L. Surgical Management for Gastroparesis. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 29, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro, J.P.; Lytle, N.W.; Patel, A.D.; Davis, S.S.; Christie, J.A.; Waring, J.P.; Sweeney, J.F.; Lin, E. Efficacy of laparoscopic pyloroplasty for the treatment of gastroparesis. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2014, 218, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, S.A.; Angelo, J.L.; Peckler, Z.; Philp, F.H.; Farah, K.F. Pyloroplasty for refractory gastroparesis. Am. Surg. 2015, 81, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbard, M.L.; Dunst, C.M.; Swanström, L.L. Laparoscopic and Endoscopic Pyloroplasty for Gastroparesis Results in Sustained Symptom Improvement. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2011, 15, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandarino, F.V.; Barchi, A.; D’Amico, F.; Fanti, L.; Azzolini, F.; Viale, E.; Esposito, D.; Rosati, R.; Fiorino, G.; Bemelman, W.A.; et al. Endoscopic Vacuum Therapy (EVT) versus Self-Expandable Metal Stent (SEMS) for Anastomotic Leaks after Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2023, 13, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, F.V.; Barchi, A.; Fanti, L.; D’Amico, F.; Azzolini, F.; Esposito, D.; Biamonte, P.; Lauri, G.; Danese, S. Endoscopic vacuum therapy for post-esophagectomy anastomotic dehiscence as rescue treatment: A single center case series. Esophagus 2022, 19, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, F.V.; Esposito, D.; Spelta, G.N.E.; Cavestro, G.M.; Rosati, R.; Parise, P.; Gemma, M.F.; Fanti, L. Double layer stent for the treatment of leaks and fistula after upper gastrointestinal oncologic surgery: A retrospective study. Updates Surg. 2022, 74, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, F.V.; Barchi, A.; Biamonte, P.; Esposito, D.; Azzolini, F.; Fanti, L.; Danese, S. The prophylactic use of endoscopic vacuum therapy for anastomotic dehiscence after rectal anterior resection: Is it feasible for redo surgery? Tech. Coloproctol. 2022, 26, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, F.V.; Barchi, A.; Leone, L.; Fanti, L.; Azzolini, F.; Viale, E.; Esposito, D.; Salmeri, N.; Puccetti, F.; Barbieri, L.; et al. Endoscopic vacuum therapy versus self-expandable metal stent for treatment of anastomotic leaks < 30 mm following oncologic Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy: A matched case-control study. Surg. Endosc. 2023. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, M.; Mandarino, F.V.; Di Saverio, S.; Gori, D.; Lugaresi, M.; Duchi, A.; Argento, F.; Cavallari, G.; Wheeler, J.; Nardo, B. Post-operative outcomes and predictors of mortality after colorectal cancer surgery in the very elderly patients. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzeddine, D.; Jit, R.; Katz, N.; Gopalswamy, N.; Bhutanil, M.S. Pyloric injection of botulinum toxin for treatment of diabetic gastroparesis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 55, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, J.; Holvoet, L.; Caenepeel, P.; Bisschops, R.; Sifrim, D.; Verbeke, K.; Janssens, J.; Tack, J. Clinical trial: A randomized-controlled crossover study of intrapyloric injection of botulinum toxin in gastroparesis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedenberg, F.K.; Palit, A.; Parkman, H.P.; Hanlon, A.; Nelson, D.B. Botulinum toxin A for the treatment of delayed gastric emptying. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleski, R.; Anderson, M.A.; Hasler, W.L. Factors Associated with Symptom Response to Pyloric Injection of Botulinum Toxin in a Large Series of Gastroparesis Patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, J.; Scott, B.; Kundu, S.; Stuart, P.; Koch, K.L. Effect of endoscopic pyloric therapies for patients with nausea and vomiting and functional obstructive gastroparesis. Auton. Neurosci. 2017, 202, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashab, M.A.; Besharati, S.; Ngamruengphong, S.; Kumbhari, V.; El Zein, M.; Stein, E.M.; Tieu, A.; Mullin, G.E.; Dhalla, S.; Nandwani, M.C.; et al. Refractory gastroparesis can be successfully managed with endoscopic transpyloric stent placement and fixation (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.O.; Sharaiha, R.Z.; Kord Valeshabad, A.; Lee, L.A.; Kalloo, A.N.; Khashab, M.A. Through-the-scope transpyloric stent placement improves symptoms and gastric emptying in patients with gastroparesis. Endoscopy 2013, 45, E189–E190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weusten, B.L.A.M.; Barret, M.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Familiari, P.; Gonzalez, J.M.; van Hooft, J.E.; Ishaq, S.; Lorenzo-Zúñiga, V.; Louis, H.; van Meer, S.; et al. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal motility disorders–part 1: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 498–515. [Google Scholar]
- Khashab, M.A.; Stein, E.; Clarke, J.O.; Saxena, P.; Kumbhari, V.; Chander Roland, B.; Kalloo, A.N.; Stavropoulos, S.; Pasricha, P.; Inoue, H. Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy for refractory gastroparesis: First human endoscopic pyloromyotomy (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 78, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Lee, J.; Gromski, M.A.; Kato, M.; Rodriguez, S.; Chuttani, R.; Matthes, K. Assessment of the length of myotomy in peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy (G-POEM) using a submucosal tunnel technique (video). Surg. Endosc. 2015, 29, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashab, M.A.; Ngamruengphong, S.; Carr-Locke, D.; Bapaye, A.; Benias, P.C.; Serouya, S.; Dorwat, S.; Chaves, D.M.; Artifon, E.; de Moura, E.G.; et al. Gastric per-oral endoscopic myotomy for refractory gastroparesis: Results from the first multicenter study on endoscopic pyloromyotomy (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 85, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vosoughi, K.; Ichkhanian, Y.; Benias, P.; Miller, L.; Aadam, A.A.; Triggs, J.R.; Law, R.; Hasler, W.; Bowers, N.; Chaves, D.; et al. Gastric per-oral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) for refractory gastroparesis: Results from an international prospective trial. Gut 2022, 71, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamal, F.; Khan, M.A.; Lee-Smith, W.; Sharma, S.; Acharya, A.; Jowhar, D.; Farooq, U.; Aziz, M.; Kouanda, A.; Dai, S.C.; et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: One-year outcomes of gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy for refractory gastroparesis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 55, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Luo, H.; Vachaparambil, C.; Mekaroonkamol, P.; Abdelfatah, M.M.; Xu, G.; Chen, H.; Xia, L.; Shi, H.; Keilin, S.; et al. Gastric peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy versus gastric electrical stimulation in the treatment of refractory gastroparesis: A propensity score-matched analysis of long term outcomes. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pioppo, L.; Reja, D.; Gaidhane, M.; Bareket, R.; Tawadros, A.; Madrigal Méndez, A.L.; Nieto, J.; Zamarripa, F.; Martínez, M.G.; Carames, M.C.; et al. Gastric per-oral endoscopic myotomy versus pyloromyotomy for gastroparesis: An international comparative study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 3177–3182. [Google Scholar]
- Spandorfer, R.; Zhu, Y.; Abdelfatah, M.M.; Mekaroonkamol, P.; Dacha, S.; Galt, J.R.; Halkar, R.; Cai, Q. Proximal and Distal Gastric Retention Patterns in Gastroparesis and the Impact of Gastric Per-Oral Endoscopic Myotomy: A Retrospective Analysis Using Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2020, 48, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinek, J.; Hustak, R.; Mares, J.; Vackova, Z.; Spicak, J.; Kieslichova, E.; Buncova, M.; Pohl, D.; Amin, S.; Tack, J. Endoscopic pyloromyotomy for the treatment of severe and refractory gastroparesis: A pilot, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Gut 2022, 71, 2170–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.; Mohan, B.P.; Aggarwal, M.; Ponnada, S.; Singh, A.; Thota, P.N.; Sanaka, M.R. Peroral Pyloromytomy is Effective and Safe for Postsurgical Gastroparesis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farha, J.; Fayad, L.; Kadhim, A.; Şimşek, C.; Badurdeen, D.S.; Ichkhanian, Y.; Itani, M.I.; Kalloo, A.N.; Khashab, M.A.; Kumbhari, V. Gastric Per-Oral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) for the Treatment of Gastric Stenosis Post-Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG). Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2350–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Camilleri, M. Selecting optimal patients with gastroparesis for G-POEM procedure. Gut 2022, 71, 659–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, L.S.; Baker, J.R.; Lee, A.A.; Harer, K.; Bowers, N.; Law, R.; Hasler, W.L. Impact of gastric per-oral endoscopic myotomy on static and dynamic pyloric function in gastroparesis patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Diagnostic Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Gastric emptying scintigraphy (GES) | The gold standard method to assess gastric emptying Increases diagnostic yield by 50% with the addition of a 4 h timepoint Evaluation of regional dysmotility patterns (IMD and RI) increases diagnostic accuracy | Poor standardization of diagnostic items across different centers Low-calorie and low-fat egg white meal, which does not mimic a normal meal Forbidden for childbearing women due to radiation exposure Low availability of nuclear medicine departments |
| Wireless motility capsule (WMC) | Non-invasive technique Good performance versus GES Whole gut transit time, including separated evaluations for the stomach and small intestine | High costs Contraindicated for recent abdominal surgery and swallowing disorders |
| Carbon (13C)-gastric emptying breath test (GEBT) | No requirement of detection No radiation exposure Onsite evaluation with remote analysis | Indirect assessment Liver, lung, and malabsorptive diseases affect accuracy |
| High-resolution electrogastrography (HR-EGG) | Non-invasive technique Detection of gastric myoelectrical activity | Difficult interpretation of electric signals High costs and low availability |
| Endoluminal Functional Lumen Imaging Probe (EndoFLIP) | Assesses pylorus integrity | Invasive and time-consuming with high costs No standardized cut-off measures |
| Study Design | Patients (n) | GP Subtype | Drug and Posology | Mechanism of Action | Outcomes | Side Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silvers et al. (1998) [112] | RCT Domperidone vs. PBO | 286 | NA | Domperidone 20 mg QID OS for 4 weeks | D2 receptor antagonist | ↓ GCSI from 10.32 to 3.79 in the single masked phase | AEs in 60.1% of patients: diarrhea, headache, abdominal pain, sinusitis, infection |
| Testoni et al. (1990) [115] | Prospective | 20 | NA | Cisapride 10 mg QID OS for 15 days | 5-HT4 receptor agonist | ↓ severity symptoms (p = 0.049) and ↑ IDMCs recorded (p = 0.022) | NA |
| Carbone et al. (2019) [117] | RCT Prucalopride vs. PBO | 34 | Diabetic (n = 6) Idiopathic (n = 28) | Prucalopride 2 mg OS for 4 weeks | 5-HT4 receptor agonist | ↓ GCSI and GES T½ compared to PBO (1.65 ± 0.19 vs. 2.28 ± 0.2, p < 0.0001, and 98 ± 10 vs. 126 ± 13 min, p= 0.005). | 18 AEs: volvulus (one case), diarrhea (nine cases), headache (eight cases) |
| Tack et al. (2016) [118] | RCT Revexepride (different dosages) vs. PBO | 62 | Diabetic (n = 30) Idiopathic (n = 32) | Revexepride 0.02 mg, 0.1 mg, 0.5 mg TID OS for 4 weeks | 5-HT4 receptor agonist | ↓ GCSI and PAGI-SYM for all dosage groups (p < 0.0001); no efficacy difference between drug dosages | 102 AEs (43.5% of patients): diarrhea, headache, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea |
| Kuo et al. (2021) [119] | RCT Velusetrag (different dosages) vs. PBO | 34 | Diabetic (n = 18) Idiopathic (n = 16) | Velusetrag 5 mg, 15 mg, 30 mg for 12 weeks | 5-HT4 receptor agonist | Higher rate of patients with ≥20% T1/2 reduction compared to PBO (52% vs. 5%, p = 0.002) | Mild and self-limiting AEs |
| Chedid et al. (2021) [120] | RCT Felcisetrag (different dosages) vs. PBO | 36 | Diabetic (n = 11) Idiopathic (n = 25) | Felcisetrag 0.1 mg, 0.2 mg, 1.0 mg IV for 3 days | 5-HT4 receptor agonist | ↓ mean GES T1/2 in all dosage groups compared to PBO (p < 0.001) | Two serious AEs, one discontinuation of the drug due to mild elevated pancreatic enzymes |
| Camilleri et al. (2017) [122] | RCT Relamoreline (different dosages) vs. placebo | 393 | Diabetic (n = 393) | Relamoreline 10 μg, 30 μg, or 100 μg TD SC for 12 weeks | GRL receptor agonist | ↓ GP symptoms and ↓ mean GES T1/2 in all dosage groups compared to PBO | Three diabetic ketoacidosis and two hyperglycemia events associated with concomitant infections |
| Carlin et al. (2021) [123] | RCT Tradipitant vs. PBO | 152 | Diabetic (n = 61) Idiopathic (n = 91) | Tradipitant 85 mg TD OS for 4 weeks | Antagonist of tachykinin receptor 1 | ↓ nausea compared to PBO; >1 point improvement in GCSI in 46.6% of patients (vs. 23.5% PBO) | 31 AEs: diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, dizziness, headache |
| Study Design | Patients (n) | Follow-Up | GP Subtype | Intervention | Outcomes | Adverse Events | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shada et al. (2016) [127] | Retrospective | 177 | 5 years | NA | Pyloroplasty | GP symptoms improvement (p < 0.001), except early satiety ↓ post-op median GES T1/2 (pre-op mean 167 min vs. post-op mean 74 min, p < 0.001). | Nine AEs: wound infection (four), leaks (two), bleeding (one), pulmonary embolism (one) |
| Toro et al. (2014) [128] | Retrospective | 50 | NA | NA | Pyloroplasty | Post-op clinical improvement in 82% of patients ↓ post-op median GES T1/2 (pre-op mean 180 min vs. post-op 60 min, p < 0.001) | No intra-operative AEs Five patients (10%) required other GE procedures |
| Hibbard et al. (2011) [130] | Retrospective | 142 | 3 months | Diabetic (n = 7) Idiopathic (n = 135) | Pyloroplasty | Improvement in all GP symptoms (p < 0.001); prokinetic use ↓ from 89% to 14% ↓ post-op median GES T1/2 (pre-op mean 320 min vs. post-op 112 min, p = 0.001) | One transient obstruction due to edema Four patients required reinterventions |
| Friedenberg et al. (2008) [140] | RCT Botulin injection versus PBO | 32 | 4 weeks | NA | Botulin injection | No difference in terms of improvement in symptoms and GE compared to PBO | No complications |
| Desprez et al. (2019) [142] | Prospective | 35 | 3 months | Diabetic (n = 11) Idiopathic (n = 18) Post-surgical (n = 6) | Botulin injection | Improvement in gastric fullness and bloating in cases with pre-op altered PD (EndoFLIP-assessed) ↓ median TSS from 13.5 to 10.5 (p < 0.01) | No complications |
| Kashab et al. (2015) [144] | Prospective | 30 | 49 days | Diabetic (n = 8) Idiopathic (n = 16) Post-surgical (n = 6) | Trans-pyloric stenting | Clinical response in 75% of patients (mainly in those with nausea and vomiting as predominant symptoms) Post-op GES normalized in six patients and improved in five patients. | Stent migrations in 59% of cases |
| Kashab et al. (2017) [146] | Prospective | 30 | 5.5 months | Diabetic (n = 11) Idiopathic (n = 7) Post-surgical (n = 12) | G-POEM | Clinical success in 26 patients (86%) Post-op GES normalized in 8/17 (47%) patients and improved in 6/17 (37%) patients | Two minor AEs: one pre-pyloric ulcer, one capno-peritoneum |
| Vosoghui et al. (2022) [147] | Prospective | 80 | 12 months | Diabetic (n = 19) Idiopathic (n = 33) Post-surgical (n = 28) | G-POEM | Clinical success in 45 patients (56%) GES retention > 20% at 4 h is a predictor of response | Mild AEs in five cases (6%): mucosotomy, capno-peritoneum |
| Martinek et al. (2022) [148] | RCT G-POEM vs. PBO | 41 | 6 months | Diabetic (n = 17) Idiopathic (n = 11) Post-surgical (n = 13) | G-POEM | Clinical success (decrease in GCSI by at least 50%) for 71% vs. PBO (22%) (p = 0.005) ↓ median GES retention at 4 h from 22% to 12% | Ten AEs, only three related to procedures: abdominal pain (one), mucosal injury (one), and delayed dumping syndrome (one) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandarino, F.V.; Testoni, S.G.G.; Barchi, A.; Azzolini, F.; Sinagra, E.; Pepe, G.; Chiti, A.; Danese, S. Imaging in Gastroparesis: Exploring Innovative Diagnostic Approaches, Symptoms, and Treatment. Life 2023, 13, 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13081743
Mandarino FV, Testoni SGG, Barchi A, Azzolini F, Sinagra E, Pepe G, Chiti A, Danese S. Imaging in Gastroparesis: Exploring Innovative Diagnostic Approaches, Symptoms, and Treatment. Life. 2023; 13(8):1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13081743
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandarino, Francesco Vito, Sabrina Gloria Giulia Testoni, Alberto Barchi, Francesco Azzolini, Emanuele Sinagra, Gino Pepe, Arturo Chiti, and Silvio Danese. 2023. "Imaging in Gastroparesis: Exploring Innovative Diagnostic Approaches, Symptoms, and Treatment" Life 13, no. 8: 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13081743
APA StyleMandarino, F. V., Testoni, S. G. G., Barchi, A., Azzolini, F., Sinagra, E., Pepe, G., Chiti, A., & Danese, S. (2023). Imaging in Gastroparesis: Exploring Innovative Diagnostic Approaches, Symptoms, and Treatment. Life, 13(8), 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13081743








