Comparing Additionality of Tuberculosis Cases Using GeneXpert or Smear-Based Active TB Case-Finding Strategies among Social Contacts of Index Cases in Nepal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
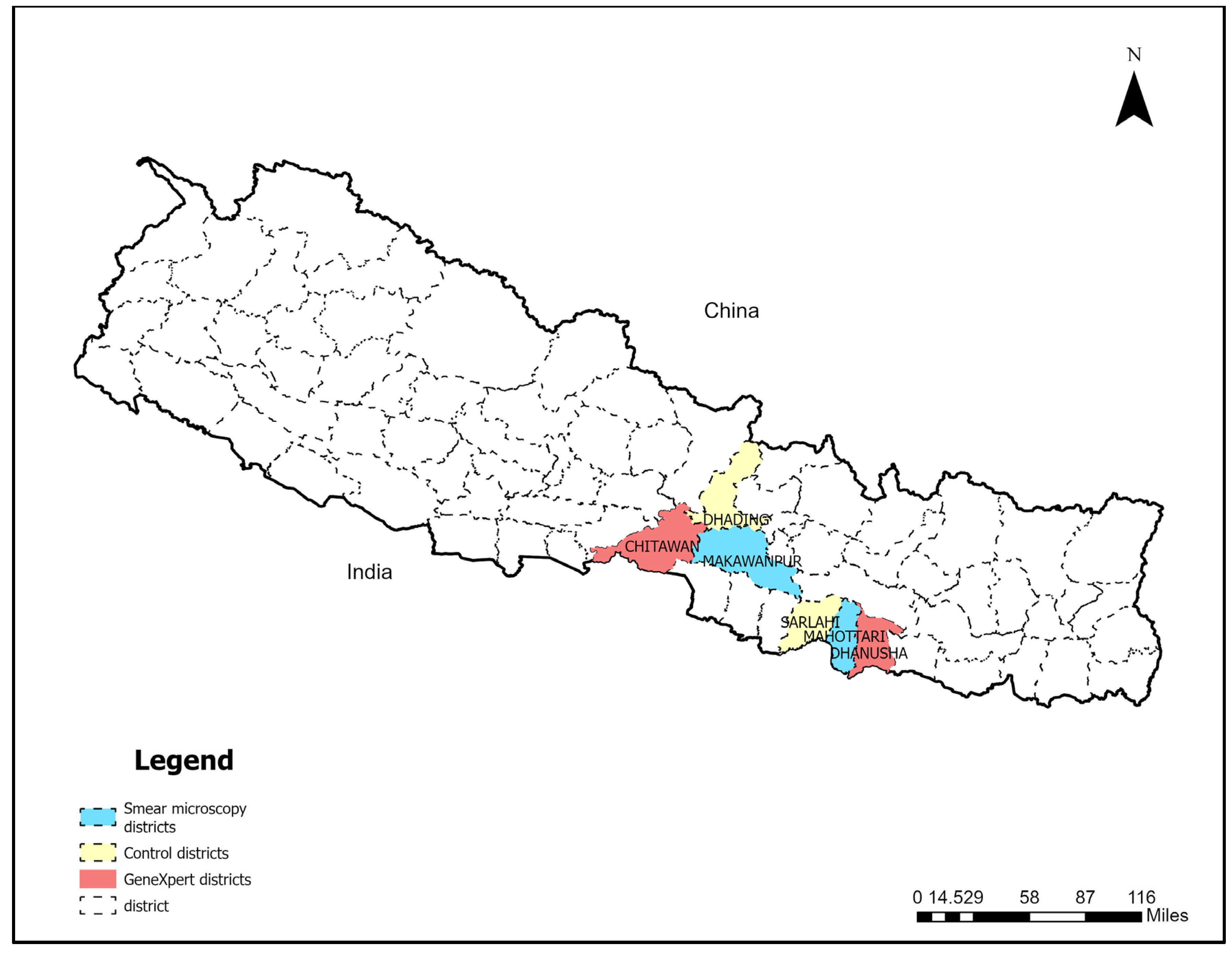
2.1. Study Setting
2.2. Intervention
2.2.1. Close-Community Contact Tracing
2.2.2. TB Case-Finding Camps
2.2.3. Door-to-Door Screening in High-Risk Areas
2.3. Ethical Approval
2.4. Data Management and Analysis
TB Yield and Additionality Analysis
3. Results
Comparison of Yield from GeneXpert versus Smear Microscopy
4. Additionality
5. Discussion
Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACF | Active case-finding |
| BNMT | Birat Nepal Medical Trust |
| CHV | Community health volunteer |
| DOTS | Directly observed treatment shortcourse |
| KNCV | Koninklijke Nederlandse Centrale Vereniging tot bestrijding der Tuberculose |
| LMIC | Low- and middle-income countries |
| MDR | Multidrug resistant |
| NNS | Number needed to screen |
| NNT | Number needed to test |
| NTP | National tuberculosis program |
| PCF | Passive case-finding |
| TB | Tuberculosis |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- World Health Organisation. Global Tuberculosis Report 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037021 (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Ho, J.; Fox, G.J.; Marais, B.J. Passive case finding for tuberculosis is not enough. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2016, 5, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golub, J.E.; Mohan, C.I.; Comstock, G.W.; Chaisson, R.E. Active case finding of tuberculosis: Historical perspective and future prospects. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2005, 9, 1183–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Waisbord, S. Behavioural Barriers in Tuberculosis Control: A Literature Review. 2006. Available online: https://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/Pnadf406.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- de Vries, S.G.; Cremers, A.L.; Heuvelings, C.C.; Greve, P.F.; Visser, B.J.; Belard, S.; Janssen, S.; Spijker, R.; Shaw, B.; Hill, R.A.; et al. Barriers and facilitators to the uptake of tuberculosis diagnostic and treatment services by hard-to-reach populations in countries of low and medium tuberculosis incidence: A systematic review of qualitative literature. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e128–e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steingart, K.R.; Ramsay, A.; Pai, M. Optimizing sputum smear microscopy for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2007, 5, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shewade, H.D.; Gupta, V.; Satyanarayana, S.; Pandey, P.; Bajpai, U.N.; Tripathy, J.P.; Kathirvel, S.; Pandurangan, S.; Mohanty, S.; Ghule, V.H.; et al. Patient characteristics, health seeking and delays among new sputum smear positive TB patients identified through active case finding when compared to passive case finding in India. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, L.N.Q.; Forse, R.J.; Codlin, A.J.; Vu, T.N.; Le, G.T.; Do, G.C.; Van Truong, V.; Dang, H.M.; Nguyen, L.H.; Nguyen, H.B.; et al. A comparative impact evaluation of two human resource models for community-based active tuberculosis case finding in Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, E.; Kohli, M.; Weber, S.F.; Suresh, A.; Schumacher, S.G.; Denkinger, C.M.; Pai, M. Advances in Molecular Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01582-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, J.S.; Modi, S.; Musau, S.; McCarthy, K.; Alexander, H.; Burmen, B.; Heilig, C.M.; Shiraishi, R.W.; Cain, K. Comparative Yield of Different Diagnostic Tests for Tuberculosis among People Living with HIV in Western Kenya. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenteno-Cuevas, R. New molecular mechanisms related to drug resistance in tuberculosis. Microbes Infect. Chemother. 2022, 2, e1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Global Strategy and Targets for Tiberculosis Prevention, Care and Control after 2015: Report by the Sceretariat. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/172828 (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Houben, R.; Menzies, N.A.; Sumner, T.; Huynh, G.H.; Arinaminpathy, N.; Goldhaber-Fiebert, J.D.; Lin, H.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Mandal, S.; Pandey, S.; et al. Feasibility of achieving the 2025 WHO global tuberculosis targets in South Africa, China, and India: A combined analysis of 11 mathematical models. Lancet Glob. Health 2016, 4, e806–e815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis Module 2: Screening—Systematic Screening for Tuberculosis Disease. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240022676 (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- World Health Organisation. Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis. Module 3: Diagnosis—Rapid Diagnostics for Tuberculosis Detection 2021 Update. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240029415 (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- World Health Organization. Systematic Screening for Active Tuberculosis: Principles and Recommendations. 2013. Available online: https://www.who.int/tb/publications/Final_TB_Screening_guidelines.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Gurung, S.C.; Dixit, K.; Rai, B.; Dhital, R.; Paudel, P.R.; Acharya, S.; Budhathoki, G.; Malla, D.; Levy, J.W.; Lonnroth, K.; et al. Comparative Yield of Tuberculosis during Active Case Finding Using GeneXpert or Smear Microscopy for Diagnostic Testing in Nepal: A Cross-Sectional Study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Helath Organisation. Gear up to END TB: Introducing the END TB Stratgey. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/156394 (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Bohlbro, A.S.; Hvingelby, V.S.; Rudolf, F.; Wejse, C.; Patsche, C.B. Active case-finding of tuberculosis in general populations and at-risk groups: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, S.C.; Rai, B.; Dixit, K.; Worrall, E.; Paudel, P.R.; Dhital, R.; Sah, M.K.; Pandit, R.N.; Aryal, T.P.; Majhi, G.; et al. How to reduce household costs for people with tuberculosis: A longitudinal costing survey in Nepal. Health Policy Plan. 2021, 36, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, O.; Atkins, S.; Lonnroth, K.; Caws, M.; Viney, K. ‘Power plays plus push’: Experts’ insights into the development and implementation of active tuberculosis case-finding policies globally, a qualitative study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e036285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermann, O.; Kluppelberg, R.; Lonnroth, K.; Viney, K.; Caws, M.; Atkins, S. ‘A double-edged sword’: Perceived benefits and harms of active case-finding for people with presumptive tuberculosis and communities-A qualitative study based on expert interviews. PloS ONE 2021, 16, e0247568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, C.M.; Amanullah, F.; Dharmadhikari, A.; Nardell, E.A.; Seddon, J.A.; Vasilyeva, I.; Zhao, Y.; Keshavjee, S.; Becerra, M.C. Turning off the tap: Stopping tuberculosis transmission through active case-finding and prompt effective treatment. Lancet 2015, 386, 2334–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stop TB Partnership. The Global Plan to Stop TB: 2018–2022. The Paradigm Shift. 2019. Available online: https://stoptb.org/assets/documents/global/plan/GPR_2018-2022_Digital.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Saunders, M.J.; Tovar, M.A.; Collier, D.; Baldwin, M.R.; Montoya, R.; Valencia, T.R.; Gilman, R.H.; Evans, C.A. Active and passive case-finding in tuberculosis-affected households in Peru: A 10-year prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.H.; Dowdy, D.; Dye, C.; Murray, M.; Cohen, T. The impact of new tuberculosis diagnostics on transmission: Why context matters. Bull. World Health Organ. 2012, 90, 739–747A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermann, O.; Tran, P.B.; Forse, R.J.; Vo, L.N.Q.; Codlin, A.J.; Viney, K.; Caws, M.; Lonnroth, K. Capitalizing on facilitators and addressing barriers when implementing active tuberculosis case-finding in six districts of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam: A qualitative study with key stakeholders. Implement. Sci. 2021, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health and Population. National TB Prevalence Survey 2018/19. 2020. Available online: https://nepalntp.gov.np/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/NTPS-Report-Bodypages.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- National Tuberculosis Center. National Strategic Plan for Tuberculosis Prevention, Care and Control. Kathmandu. 2016. Available online: https://nepalntp.gov.np/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/NSP-report-english-revised.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Central Bureau of Statistics. National Population and Housing Census 2011 (National Report); Central Bureau of Statistics: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2012.
- National Tuberculosis Program Nepal. Annual Report 2075/76 (2018/19); Government of Nepal: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2020.
- World Health Organization. WHO Operational Handbook on Tuberculosis. Module 2: Screening—Systematic Screening for Tuberculosis Disease [M/OL]; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, J.; Sahu, S.; Blok, L.; Bakker, M.I.; Stevens, R.; Ditiu, L. A multi-site evaluation of innovative approaches to increase tuberculosis case notification: Summary results. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, C.; Gage, A.; Kim, M.K.; Kapoor, N.R.; Akweongo, P.; Amponsah, F.; Aryal, A.; Asai, D.; Awoonor-Williams, J.K.; Ayele, W.; et al. COVID-19 and resilience of healthcare systems in ten countries. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.E.; Ross, J.M.; Yao, M.; Schiller, I.; Kohli, M.; Dendukuri, N.; Steingart, K.R.; Horne, D.J. Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert Ultra assays for screening for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults, irrespective of signs or symptoms. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 3, CD013694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zifodya, J.S.; Kreniske, J.S.; Schiller, I.; Kohli, M.; Dendukuri, N.; Schumacher, S.G.; Ochodo, E.A.; Haraka, F.; Zwerling, A.A.; Pai, M.; et al. Xpert Ultra versus Xpert MTB/RIF for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults with presumptive pulmonary tuberculosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2, CD009593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Tuberculosis Profile: Nepal. Available online: https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/tb_profiles/?_inputs_&entity_type=%22country%22&lan=%22EN%22&iso2=%22NP%22 (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Pai, M.; Kasaeva, T.; Swaminathan, S. COVID-19’s Devastating Effect on Tuberculosis Care—A Path to Recovery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1490–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheda, K.; Perumal, T.; Moultrie, H.; Perumal, R.; Esmail, A.; Scott, A.J.; Udwadia, Z.; Chang, K.C.; Peter, J.; Pooran, A.; et al. The intersecting pandemics of tuberculosis and COVID-19: Population-level and patient-level impact, clinical presentation, and corrective interventions. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhwald, M.; Carmona, S.; Pai, M. Learning from COVID-19 to reimagine tuberculosis diagnosis. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e169–e170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, A.J.; Klinton, J.S.; Oga-Omenka, C.; Heitkamp, P.; Nawina Nyirenda, C.; Furin, J.; Pai, M. Tuberculosis in times of COVID-19. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2022, 76, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, T. Global tuberculosis progress reversed by COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, e118–e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, K.; Biermann, O.; Rai, B.; Aryal, T.P.; Mishra, G.; Teixeira de Siqueira-Filha, N.; Paudel, P.R.; Pandit, R.N.; Sah, M.K.; Majhi, G.; et al. Barriers and facilitators to accessing tuberculosis care in Nepal: A qualitative study to inform the design of a socioeconomic support intervention. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e049900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, S.C.; Dixit, K.; Rai, B.; Caws, M.; Paudel, P.R.; Dhital, R.; Acharya, S.; Budhathoki, G.; Malla, D.; Levy, J.W.; et al. The role of active case finding in reducing patient incurred catastrophic costs for tuberculosis in Nepal. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinvigorating Efforts to END TB in Nepal. Available online: https://www.who.int/nepal/news/detail/09-02-2022-Reinvigorating-efforts-to-end-Tuberculosis-in-Nepal (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- STOP TB Partnership. Global Plan to End TB 2023–2030. Available online: https://omnibook.com/embedview/dc664b3a-14b4-4cc0-8042-ea8f27e902a6/en?no-ui (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Burke, R.M.; Nliwasa, M.; Feasey, H.R.; Chaisson, L.H.; Golub, J.E.; Naufal, F.; Shapiro, A.E.; Ruperez, M.; Telisinghe, L.; Ayles, H. Community-based active case-finding interventions for tuberculosis: A systematic review. Lancet Public Health 2021, 6, e283–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Strategic Plan to End Tuberculosis (2021/22–2025/26); Government of Nepal, Ministry of Health and Population: Thimi, Nepal, 2022. Available online: https://nepalntp.gov.np/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/TB-National-Strategic-Plan-English-report-UPDATED-July-15-2022.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- STOP TB Partnership. Declaration of the Rights of People Affected by TB. May 2019. Available online: https://stoptb.org/assets/documents/communities/FINAL%20Declaration%20on%20the%20Right%20of%20People%20Affected%20by%20TB%2013.05.2019.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).

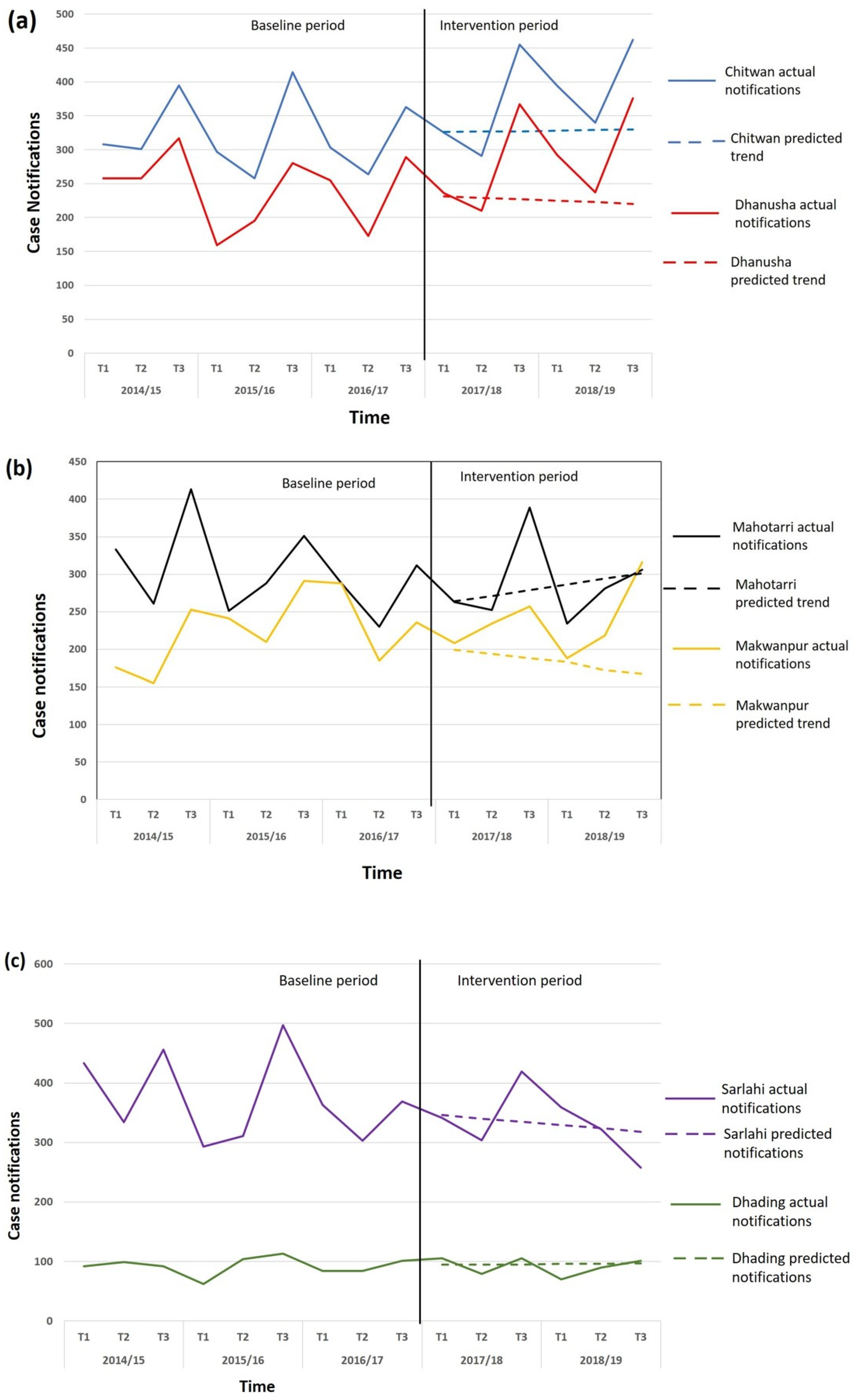
| Category | District | Baseline | Intervention | Base-Line Total | Inter-Vention Total | % Change | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015/16 | 2016/17 | 2017/18 | 2018/19 | |||||||||||||
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | |||||
| Evaluation—Xpert | ||||||||||||||||
| Chitwan | 297 | 258 | 414 | 303 | 264 | 363 | 325 | 291 | 455 | 394 | 340 | 462 | 1899 | 2267 | +19.4 | |
| Dhanusha | 159 | 195 | 280 | 255 | 173 | 289 | 236 | 210 | 367 | 292 | 237 | 376 | 1351 | 1718 | +27.2 | |
| Total | 456 | 453 | 694 | 558 | 437 | 652 | 561 | 501 | 822 | 686 | 577 | 838 | 3250 | 3985 | +22.6 | |
| Evaluation—Smear | ||||||||||||||||
| Mahottari | 251 | 288 | 351 | 288 | 230 | 312 | 263 | 252 | 389 | 234 | 281 | 306 | 1720 | 1725 | +0.3 | |
| Makwanpur | 241 | 201 | 291 | 288 | 185 | 236 | 208 | 234 | 257 | 188 | 218 | 316 | 1442 | 1421 | −1.5 | |
| Total | 492 | 489 | 642 | 576 | 415 | 548 | 471 | 486 | 646 | 422 | 499 | 622 | 3162 | 3146 | −0.5 | |
| Control | ||||||||||||||||
| Sarlahi | 293 | 311 | 497 | 363 | 303 | 369 | 341 | 304 | 419 | 359 | 322 | 258 | 2136 | 2003 | −6.2 | |
| Dhading | 62 | 104 | 113 | 84 | 84 | 101 | 105 | 79 | 105 | 70 | 90 | 101 | 548 | 550 | +0.4 | |
| Total | 355 | 415 | 610 | 447 | 387 | 470 | 446 | 383 | 524 | 429 | 412 | 559 | 2648 | 2553 | −3.6 | |
| Predicted | Actual Notified Cases in Intervention Period | Predicted Total | Inter-Vention Total | % Difference | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District | 2017/18 | 2018/19 | 2017/18 | 2018/19 | |||||||||||
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | ||||
| Evaluation—GeneXpert | |||||||||||||||
| Chitwan | 326 | 327 | 327 | 328 | 329 | 330 | 325 | 291 | 455 | 394 | 340 | 462 | 1967 | 2267 | +15.3 |
| Dhanusha | 231 | 229 | 227 | 225 | 223 | 220 | 236 | 210 | 367 | 292 | 237 | 376 | 1355 | 1718 | +26.8 |
| Total | 557 | 556 | 554 | 553 | 552 | 550 | 561 | 501 | 822 | 686 | 577 | 838 | 3322 | 3985 | +20.0 |
| Evaluation—Smear | |||||||||||||||
| Mahotarri | 199 | 194 | 188 | 183 | 172 | 167 | 263 | 252 | 389 | 234 | 281 | 306 | 1103 | 1725 | +56.4 |
| Makwanpur | 264 | 271 | 279 | 286 | 294 | 301 | 208 | 234 | 257 | 188 | 218 | 316 | 1695 | 1421 | −16.2 |
| Total | 463 | 465 | 467 | 469 | 466 | 468 | 471 | 486 | 646 | 422 | 499 | 622 | 2798 | 3146 | +12.4 |
| Control | |||||||||||||||
| Sarlahi | 346 | 340 | 335 | 329 | 324 | 318 | 341 | 304 | 419 | 359 | 322 | 258 | 1992 | 2003 | +0.5 |
| Dhading | 95 | 95 | 95 | 96 | 96 | 97 | 105 | 79 | 105 | 70 | 90 | 101 | 574 | 550 | −4.2 |
| Total | 441 | 435 | 430 | 425 | 420 | 415 | 446 | 383 | 524 | 429 | 412 | 559 | 2566 | 2553 | −0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gurung, S.C.; Dixit, K.; Paudel, R.; Sah, M.K.; Pandit, R.N.; Aryal, T.P.; Khatiwada, S.U.; Majhi, G.; Dhital, R.; Paudel, P.R.; et al. Comparing Additionality of Tuberculosis Cases Using GeneXpert or Smear-Based Active TB Case-Finding Strategies among Social Contacts of Index Cases in Nepal. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8070369
Gurung SC, Dixit K, Paudel R, Sah MK, Pandit RN, Aryal TP, Khatiwada SU, Majhi G, Dhital R, Paudel PR, et al. Comparing Additionality of Tuberculosis Cases Using GeneXpert or Smear-Based Active TB Case-Finding Strategies among Social Contacts of Index Cases in Nepal. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(7):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8070369
Chicago/Turabian StyleGurung, Suman Chandra, Kritika Dixit, Rajan Paudel, Manoj Kumar Sah, Ram Narayan Pandit, Tara Prasad Aryal, Shikha Upadhyay Khatiwada, Govind Majhi, Raghu Dhital, Puskar Raj Paudel, and et al. 2023. "Comparing Additionality of Tuberculosis Cases Using GeneXpert or Smear-Based Active TB Case-Finding Strategies among Social Contacts of Index Cases in Nepal" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 7: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8070369
APA StyleGurung, S. C., Dixit, K., Paudel, R., Sah, M. K., Pandit, R. N., Aryal, T. P., Khatiwada, S. U., Majhi, G., Dhital, R., Paudel, P. R., Shrestha, G., Rai, B., Budhathoki, G., Khanal, M., Mishra, G., Levy, J., Van de Rest, J., Thapa, A., Ramsay, A., ... Caws, M. (2023). Comparing Additionality of Tuberculosis Cases Using GeneXpert or Smear-Based Active TB Case-Finding Strategies among Social Contacts of Index Cases in Nepal. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(7), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8070369









