Association between Rhesus Blood Groups and Malaria Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection of Studies and Data Extraction
2.3. Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Search Results and Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.2. Reporting Quality of the Included Studies and Qualitative Synthesis
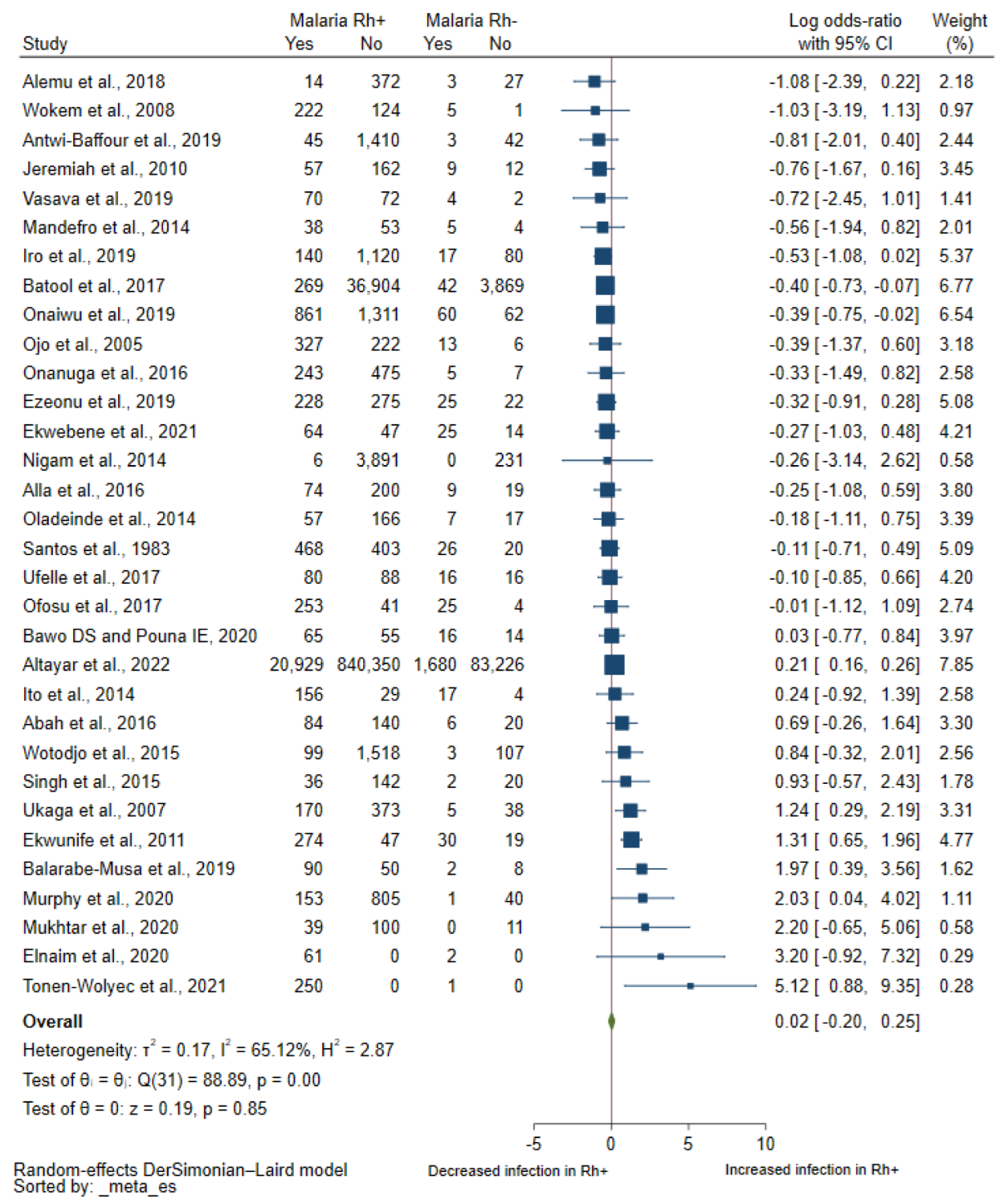
3.3. Association between Rhesus Blood Groups and Malaria
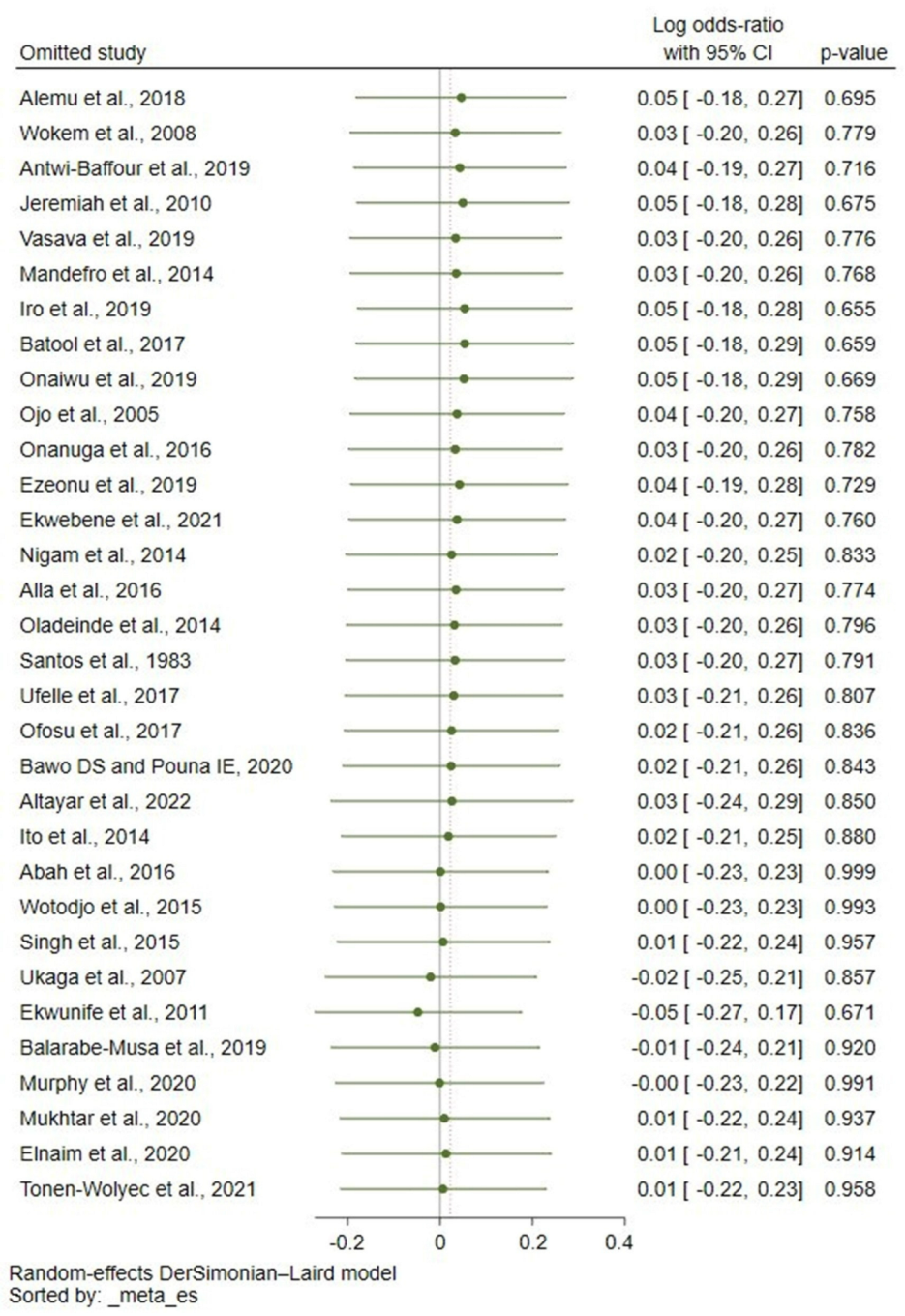
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
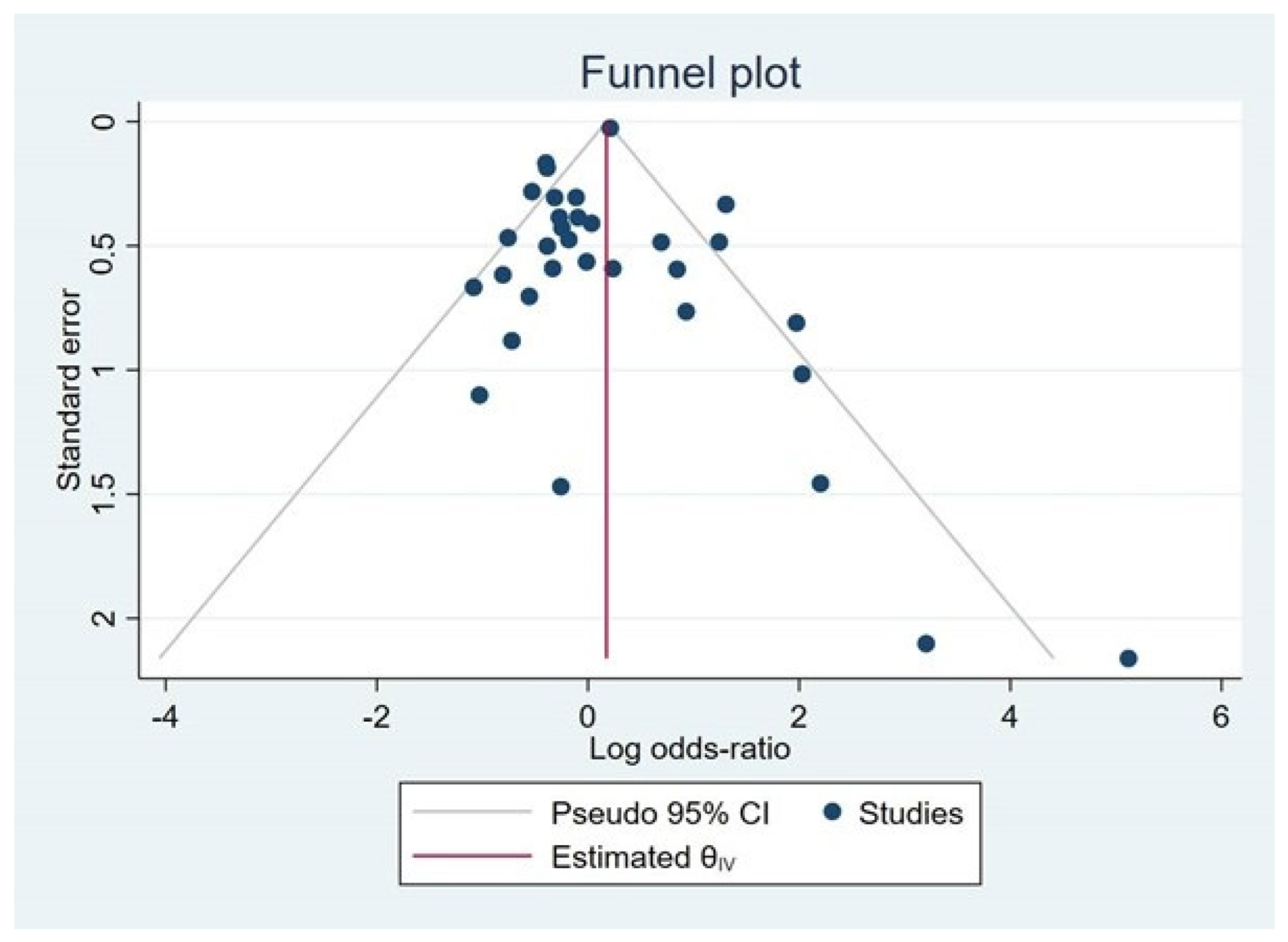
3.5. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laura, D. The Rh Blood Group; NCBI (US): Bethesda, ML, USA, 2006; pp. 1–10.
- Das, S. Hemolytic Disease of The Fetus and Newborn. In Blood Groups; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, R.; Ranjan, V.; Kumar, N. Association of ABO and Rh blood group in susceptibility, severity, and mortality of Coronavirus disease 2019: A hospital-based study from Delhi, India. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 767771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaylaci, S.; Dheir, H.; Issever, K.; Genc, A.B.; Senocak, D.; Kocayigit, H.; Guclu, E.; Suner, K.; Ekerbicer, H.; Koroglu, M. The effect of abo and rh blood group antigens on admission to intensive care unit and mortality in patients with COVID-19 infection. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras 2020, 66 (Suppl. S2), 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, K.; Aulin, L.B.S.; Freij, U.; Ellerstad, M.; Bruckle, L.; Hillmering, H.; Svae, T.E.; Broliden, K.; Gustafsson, R. Prevalence of parvovirus B19 viraemia among German blood donations and the relationship to ABO and Rhesus blood group antigens. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, jiac456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoodi, L.; Razavi, A.; Jafarpour, H.; Heshmati, M.; Soleymani, E.; Ghasemian, R. Relationship between the prevalence of blood groups and severity of Leptospirosis: A case-control study. Infect. Dis. 2020, 13, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tess, B.H.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Newell, M.L.; Dunn, D.T.; Lago, T.D. Breastfeeding, genetic, obstetric and other risk factors associated with mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 in Sao Paulo State, Brazil. Sao Paulo collaborative study for vertical transmission of HIV-1. AIDS 1998, 12, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiango, J.S.; Missingo, R.; Mzula, E. The relationship of blood groups and hepatitis B virus antigen carrier state. East. Afr. Med. J. 1982, 59, 816–818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahittikorn, A.; Masangkay, F.R.; Kotepui, K.U.; Milanez, G.J.; Kotepui, M. Comparison of Plasmodium ovale curtisi and Plasmodium ovale wallikeri infections by a meta-analysis approach. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazebew, B.; Munshea, A.; Nibret, E. Prevalence and association of malaria with ABO blood group and hemoglobin level in individuals visiting Mekaneeyesus primary hospital, Estie district, northwest Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerihun, T.; Degarege, A.; Erko, B. Association of ABO blood group and Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Dore Bafeno area, southern Ethiopia. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degarege, A.; Gebrezgi, M.T.; Ibanez, G.; Wahlgren, M.; Madhivanan, P. Effect of the ABO blood group on susceptibility to severe malaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Rev. 2019, 33, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afoakwah, R.; Aubyn, E.; Prah, J.; Nwaefuna, E.K.; Boampong, J.N. Relative susceptibilities of ABO blood broups to Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Ghana. Adv. Hematol. 2016, 2016, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, J.A.; Handel, I.G.; Thera, M.A.; Deans, A.M.; Lyke, K.E.; Kone, A.; Diallo, D.A.; Raza, A.; Kai, O.; Marsh, K.; et al. Blood group O protects against severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria through the mechanism of reduced rosetting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17471–17476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Lisy, K.; Tufanaru, C.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; Mu, P. Conducting systematic reviews of association (etiology): The Joanna Briggs Institute’s approach. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, S. The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp. Clin. Trials. 2015, 45 (Pt A), 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.; Rothstein, H.R. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abah, A.E.; Grey, A.; Onoja, H. Plasmodium malaria and ABO blood group among blood donors in Yenegoa, Bayelsa State, Nigeria. Prim. Health Care 2016, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Acquah, F.K.; Donu, D.; Bredu, D.; Eyia-Ampah, S.; Amponsah, J.A.; Quartey, J.; Obboh, E.K.; Mawuli, B.A.; Amoah, L.E. Asymptomatic carriage of Plasmodium falciparum by individuals with variant blood groups and haemoglobin genotypes in southern Ghana. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, G.; Mama, M. Asymptomatic malaria infection and associated factors among blood donors attending Arba Minch blood bank, southwest Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2018, 28, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alla, A.; Elfaki, T.E.M.; Elsadig, A.A.; Saad, M.B.E.A. Malaria infection and its relation to ABO blood grouping in Khartoum, Singa and Al Genaid, Sudan. Eur. Acad. Res. 2016, 3, 12938–12948. [Google Scholar]
- Altayar, M.A.; Jalal, M.M.; Kabrah, A.; Qashqari, F.S.I.; Jalal, N.A.; Faidah, H.; Baghdadi, M.A.; Kabrah, S. Prevalence and association of transfusion transmitted infections with ABO and Rh blood groups among blood donors in the western region of Saudi Arabia: A 7-year retrospective analysis. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania) 2022, 58, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi-Baffour, S.; Kyeremeh, R.; Amoako, A.P.; Annison, L.; Tettehm, J.O.M.; Seidu, M.A. The incidence of malaria parasites in screened donor blood for transfusion. Malar. Res. Treat. 2019, 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balarabe-Musa, B.; Muhammad, H.R.; Momo, H.; Nnadike, F.A. Association of malaria parasitaemia with ABO/Rhesus blood group among out-patients of Township clinic Gwagwalada Abuja, Nigeria. J. Adv. Med. Med. Res. 2019, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamou, R.; Sevidzem, S.L. ABO/Rhesus blood group systems and malaria prevalence among students of the University of Dschang, Cameroon. Malar. World J. 2016, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Batool, Z.; Durrani, S.H.; Tariq, S. Association of ABO and Rh blood group types to hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV and syphilis infection, a five year’ experience in healthy blood donors in a tertiary care hospital. J. Ayub. Med. Coll. Abbottabad JAMC 2017, 29, 90–92. [Google Scholar]
- Bawo, D.S.; Pouna, I.E. Relationship between ABO blood groups and malaria infection in endemic regions of Nigeria. EKSU J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 5, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ekwebene, O.C.; Nnamani, C.P.; Edeh, C.G.; Obidile, C.V.; Tyotswame, Y.S. Prevalence of falciparum malaria in conjunction with age, gravidity, abo blood group/rhesus factor, and genotype among gravid women in south-eastern Nigeria. Int. J. Sci. Res. Dent. Med. Sci. 2021, 3, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ekwunife, C.A.; Ozumba, N.A.; Eneanya, C.I.; Nwaorgu, O.C. Malaria infection among blood donors in Onitsha urban, southeast Nigeria. SLJBR 2011, 3, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaim, E.G.; Amer, S.; Abdalmanan, M.; Abdullah, S.A.; Nageb, F.M.; Mutasem, M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Ali, S.A.; Hamed, H.A.A.; Mohammed, E.H.; et al. Association of thrombocytopenia, urine malaria antigens, and blood groups with malaria parasite density among Sudanese malaria patients at Sharg Al-Nile district in Khartoum State. Int. J. Adv. Res. Biol. Sci. 2020, 7, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ezeonu, C.M.; Adabara, N.U.; Garba, S.A.; Kuta, F.A.; Ewa, E.E.; Oloruntoba, P.O.; Atureta, Z. The risk of transfusion transmitted malaria and the need for malaria screening of blood donors in Abuja, Nigeria. Afr. J. Clin. Exp. Microbiol. 2019, 20, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.M.; Montoya, L.P.; Arboleda, M.; Ortiz, L.F. Association of severe malaria with ABO-blood group types in an endemic zone of Colombia. CES Med. 2009, 23, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Shettima, A.; Isa, T.; Askira, U.M.; Abbas, M.I. Strong linear correlation between parasite density and ABO-blood group among patients with malaria parasite infection. IJAM 2018, 5, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iro, A.; Lamine, M.M.; Lazoumar, R.H.; Alkassoum, I.; Maman, D.; Laouali, H.A.M.; Doutchi, M.; Maiguizo, S.; Laminou, I.M. Transfusional malaria and associated factors at the National Blood Transfusion Center of Niamey-Niger. J. Trop. Med. 2019, 2019, 7290852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, E.E.; Egwunyenga, A.O.; Ake, J.E.G. Prevalence of malaria and human blood factors among patients in Ethiope East, Delta State, Nigeria. IRJMBS 2014, 3, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremiah, Z.A.; Jeremiah, T.A.; Emelike, F.O. Frequencies of some human genetic markers and their association with Plasmodium falciparum malaria in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. J. Vector. Borne. Dis. 2010, 47, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mandefro, A.; Kelel, M.; Wessel, G. Association of ABO blood group and Rh factor with malaria and some gastrointestinal infectious disease in a population of Adet and Merawi, Ethiopia. GJBBR 2014, 9, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhtar, I.G.; Rahmat, S.; Salisu, A.I. Relationship between ABO And Rh D blood group phenotypes and malaria among a population of undergraduate students in Kano, Nigeria. Fudma J. Sci. 2020, 4, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, K.J.; Conroy, A.L.; Ddungu, H.; Shrestha, R.; Kyeyune-Byabazaire, D.; Petersen, M.R.; Musisi, E.; Patel, E.U.; Kasirye, R.; Bloch, E.M.; et al. Malaria parasitemia among blood donors in Uganda. Transfusion 2020, 60, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, J.S.; Singh, S.; Kaur, V.; Giri, S.; Kaushal, R.P. The prevalence of transfusion transmitted infections in ABO blood groups and Rh type system. Hematol. Rep. 2014, 6, 5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofosu, D.N.; Dotsey, C.; Debrekyei, Y.M. Association of asymptomatic malaria and ABO blood group among donors attending Asamankese Government Hospital. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2017, 6, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Ojo, D.A.; Mafiana, C.F. Prevalence of malaria and typhoid infections in endemic community of Ogun State, Nigeria. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2005, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Oladeinde, B.H.; Omoregie, R.; Osakue, E.O.; Onaiwu, T.O. Asymptomatic malaria among blood donors in Benin city Nigeria. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2014, 9, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Onaiwu, T.O.; Abechi, P.; Idemudia, N.L. Haemoglobin genotype, ABO/Rhesus blood groups and malaria among students presenting to a Private University Health Centre in Nigeria. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 11, 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- Onanuga, A.; Lamikanra, A. Association of ABO blood group and Plasmodium falciparum malaria among children in the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2016, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, S.E.B.; Salzano, F.M.; Helena, M.; Franco, L.P.; de Melo e Freitas, M.J. Mobility, genetic markers, susceptibility to malaria and race mixture in Manaus, Brazil. J. Hum. Evol. 1983, 12, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Urhekar, A.D.; Singh, R. A study on correlation of malaria infection with A, B, O, RH blood group system. J. Parasitol. Vector Biol. 2015, 7, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Tonen-Wolyec, S.; Batina-Agasa, S. High susceptibility to severe malaria among patients with A blood group versus those with O blood group: A cross-sectional study in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Trop. Parasitol. 2021, 11, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ufelle, S.A.; Onyekwelu, K.C.; Ikekpeazu, J.E.; Ezeh, R.C.; Esom, E.A.; Okoli, U.A. Influence of ABO blood groups in malaria infected pregnant women in Enugu, south-east, Nigeria. Biomed. Res. J. 2017, 28, 7248–7252. [Google Scholar]
- Ukaga, C.N.; Nwoke, B.E.; Udujih, O.S.; Ohaeri, A.A.; Anosike, J.C.; Udujih, B.U.; Nwachukwu, M.I. Placental malaria in Owerri, Imo state, south-eastern Nigeria. Tanzan J. Health Res. 2007, 9, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasava, S.; Lakhani, S.; Lakhani, J. Is there a relation between ABO blood group and malaria? IJCMAS 2019, 8, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wokem, G.N.; Okafor, R.A.; Nwachukwu, B.C. Some haematological profiles of children with malaria parasitaemia in Port Harcourt, Nigeria. Niger. J. Parasitol. 2008, 29, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotodjo, A.N.; Richard, V.; Boyer, S.; Doucoure, S.; Diagne, N.; Touré-Baldé, A.; Tall, A.; Faye, N.; Gaudart, J.; Trape, J.F.; et al. The implication of long-lasting insecticide-treated net use in the resurgence of malaria morbidity in a Senegal malaria endemic village in 2010–2011. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, J.; Wahlgren, M. Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte rosetting is mediated by promiscuous lectin-like interactions. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomsangpetch, R.; Todd, J.; Carlson, J.; Greenwood, B.M. The effects of hemoglobin genotype and ABO blood group on the formation of rosettes by Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 48, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournamille, C.; le van Kim, C.; Gane, P.; Cartron, J.-P.; Colin, Y. Molecular basis and PCR-DNA typing of the Fya/Fyb blood group polymorphism. Hum. Genet. 1995, 95, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournamille, C.; Colin, Y.; Cartron, J.P.; le van Kim, C. Disruption of a GATA motif in the Duffy gene promoter abolishes erythroid gene expression in Duffy–negative individuals. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, G. Blood group polymorphisms: Molecular approach and biological significance. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 1997, 4, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, I.W.; Eda, S.; Winograd, E. Cytoadherence and sequestration in Plasmodium falciparum: Defining the ties that bind. Microbes. Infect. 2003, 5, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserti, C.M.; Dzik, W.H. The ABO blood group system and Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Blood 2007, 110, 2250–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringwald, P.; Peyron, F.; Lepers, J.P.; Rabarison, P.; Rakotomalala, C.; Razanamparany, M.; Rabodonirina, M.; Roux, J.; Le Bras, J. Parasite virulence factors during falciparum malaria: Rosetting, cytoadherence, and modulation of cytoadherence by cytokines. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 5198–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, G.; Flegel, W.A.; Fletcher, A.; Garratty, G.; Levene, C.; Lomas-Francis, C.; Moulds, J.M.; Moulds, J.J.; Olsson, M.L.; Overbeeke, M.A.M.; et al. International society of blood transfusion committee on terminology for red cell surface antigens: Cape Town report. Vox Sang. 2007, 92, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, G.L.; Fletcher, A.; Garratty, G.; Henry, S.; Jorgensen, J.; Judd, W.J.; Levene, C.; Lomas-Francis, C.; Moulds, J.J.; Moulds, M.; et al. Blood group terminology 2004: From the International Society of Blood Transfusion committee on terminology for red cell surface antigens. Vox Sang. 2004, 87, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, R.; Das, N. Complement Receptor 1: Disease associations and therapeutic implications. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, J.A.; Moulds, J.M.; Newbold, C.I.; Miller, L.H. P. falciparum rosetting mediated by a parasite-variant erythrocyte membrane protein and complement-receptor 1. Nature 1997, 388, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Subgroups | Frequency (n) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Publication years | Before 2000 | 1 | 2.78 |
| 2000–2009 | 4 | 11.1 | |
| 2010–2019 | 23 | 63.9 | |
| 2020–2022 | 8 | 22.2 | |
| Study design | Cross-sectional studies | 29 | 80.6 |
| Case-control studies | 6 | 16.7 | |
| Not specified | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Country | Nigeria | 17 | 47.2 |
| Congo | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Cameroon | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Uganda | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Sudan | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Spain | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Niger | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Ghana | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Ethiopia | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Brazil | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Colombia | 1 | 2.78 | |
| India | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Pakistan | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Participants | Blood donors | 13 | 40.6 |
| Patients with malaria | 5 | 36.1 | |
| Malaria suspected patients | 4 | 11.1 | |
| Participants in community | 4 | 11.1 | |
| Patients in the hospital | 4 | 11.1 | |
| Pregnant women | 2 | 5.56 | |
| University’s staff | 1 | 2.78 | |
| University’s students | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Pregnant and nonpregnant women | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Students | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Plasmodium spp. | P. falciparum | 10 | 27.8 |
| P. falciparum, P. vivax | 5 | 13.9 | |
| P. falciparium, P. malariae | 2 | 5.56 | |
| Not specified | 19 | 52.8 | |
| Clinical status of malaria | Asymptomatic malaria | 24 | 66.7 |
| Uncomplicated malaria | 8 | 22.2 | |
| Asymptomatic and uncomplicated malaria | 2 | 5.56 | |
| Uncomplicated and severe malaria | 2 | 5.56 | |
| Age groups | Adult | 20 | 55.6 |
| All age ranges | 8 | 22.2 | |
| Children | 4 | 11.1 | |
| Not specified | 4 | 11.1 | |
| Method for malaria detection | Microscopy | 23 | 63.9 |
| RDT | 3 | 8.33 | |
| Microscopy, RDT | 2 | 5.56 | |
| Serology | 2 | 5.56 | |
| Microscopy/RDT/Molecular method | 1 | 2.78 | |
| Molecular method | 2 | 5.56 | |
| Not specified | 3 | 8.33 |
| Covariates | p Value | I-Squared Residual (%) | tau2 | R-Squared (%) | Number of Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Publication year | 0.51 | 58.13 | 0.24 | 0 | 32 |
| Study design | 0.47 | 64.02 | 0.21 | 0 | 31 |
| Continent | 0.76 | 64.11 | 0.26 | 0 | 32 |
| Country | 0.27 | 58.99 | 0.31 | 0 | 32 |
| Participants | 0.71 | 70.8 | 0.26 | 0 | 32 |
| Plasmodium spp. | 0.86 | 74.52 | 0.86 | 0 | 14 |
| Clinical status | 0.21 | 66.37 | 0.19 | 0 | 32 |
| Age group | 0.13 | 67.48 | 0.18 | 0 | 28 |
| Method for malaria detection | 0.48 | 60.98 | 0.35 | 0 | 30 |
| Reporting quality of the included studies | 0.96 | 61.52 | 0.26 | 0 | 32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rattanapan, Y.; Duangchan, T.; Wangdi, K.; Mahittikorn, A.; Kotepui, M. Association between Rhesus Blood Groups and Malaria Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040190
Rattanapan Y, Duangchan T, Wangdi K, Mahittikorn A, Kotepui M. Association between Rhesus Blood Groups and Malaria Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(4):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040190
Chicago/Turabian StyleRattanapan, Yanisa, Thitinat Duangchan, Kinley Wangdi, Aongart Mahittikorn, and Manas Kotepui. 2023. "Association between Rhesus Blood Groups and Malaria Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 4: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040190
APA StyleRattanapan, Y., Duangchan, T., Wangdi, K., Mahittikorn, A., & Kotepui, M. (2023). Association between Rhesus Blood Groups and Malaria Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(4), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040190







