Inter-observer Variability in the Analysis of CO-RADS Classification for COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. CT Chest Imaging
2.3. Imaging Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report-1; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, E.K.U.N.; Loureiro, B.M.C.; Strabelli, D.G.; de Pádua Gomes de Farias, L.; Garcia, J.V.R.; Gama, V.A.A.; Ferreira, L.C.; Chate, R.C.; Assunção, A.N.; Sawamura, M.V.Y.; et al. Evaluating the RSNA and CORADS classifications for COVID-19 on chest computed tomography in the Brazilian population. Clinics 2021, 76, e2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penha, D.; Pinto, E.G.; Matos, F.; Hochhegger, B.; Monaghan, C.; Taborda-Barata, L.; Irion, K.; Marchiori, E. CO-RADS: Coronavirus Classification Review. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2021, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, A.; Yılmaz, S.; Erol, Ö.Ö.; Kaygusuz, S.; Göncüoğlu, A.; Kömürcü, S.P.; Erkmen, İ.K.; Kaçmaz, B.; Gül, S. Interobserver Agreement in the Analysis of the Different Radiological Classification of COVID-19 on Computed Tomography. Mediterr. J. Infect. Microb. Antimicrob. 2021, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Shen, C.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Xing, L.; Wei, J.; et al. Evaluating the accuracy of different respiratory specimens in the laboratory diagnosis and monitoring the viral shedding of 2019-nCoV infections. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.; Kay, F.U.; Abbara, S.; Bhalla, S.; Chung, J.H.; Chung, M.; Henry, T.S.; Kanne, J.P.; Kligerman, S.; Ko, J.P.; et al. Radiological Society of North America Expert Consensus Document on Reporting Chest CT Findings Related to COVID-19: Endorsed by the Society of Thoracic Radiology, the American College of Radiology, and RSNA. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.D.; Ryerson, C.J.; Haramati, L.B.; Sverzellati, N.; Kanne, J.P.; Raoof, S.; Schluger, N.W.; Volpi, A.; Yim, J.-J.; Martin, I.B.K.; et al. The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multinational Consensus Statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2020, 296, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, S.T.; Awan, M.W.; Farid, S.; Aziz, H.; Arshad, W.; Ahmad, M. COVID-19 Reporting and Data System (CO-RADS) for Assessment of Pulmonary Involvement and CT Severity Score in Predicting Disease Severity. J. Bahria Univ. Med. Dent. Coll. 2022, 12, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.X.; Hsieh, B.; Xiong, Z.; Halsey, K.; Choi, J.W.; Tran, T.M.L.; Pan, I.; Shi, L.-B.; Wang, D.-C.; Mei, J.; et al. Performance of Radiologists in Differentiating COVID-19 from Non-COVID-19 Viral Pneumonia at Chest CT. Radiology 2020, 296, E46–E54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; Zhang, N.; Diao, K.; Lin, B.; Zhu, X.; Li, K.; et al. Chest CT Findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Relationship to Duration of Infection. Radiology 2020, 295, 200463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessmann, N.; Sánchez, C.I.; Beenen, L.; Boulogne, L.H.; Brink, M.; Calli, E.; Charbonnier, J.-P.; Dofferhoff, T.; van Everdingen, W.M.; Gerke, P.K.; et al. Automated Assessment of COVID-19 Reporting and Data System and Chest CT Severity Scores in Patients Suspected of Having COVID-19 Using Artificial Intelligence. Radiology 2021, 298, E18–E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwee, R.M.; Adams, H.J.A.; Kwee, T.C. Diagnostic Performance of CO-RADS and the RSNA Classification System in Evaluating COVID-19 at Chest CT: A Meta-Analysis. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2021, 3, e200510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, T.; Yang, Z.; Hou, H.; Zhan, C.; Chen, C.; Lv, W.; Tao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Xia, L. Correlation of Chest CT and RT-PCR Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Report of 1014 Cases. Radiology 2020, 296, E32–E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokop, M.; Van Everdingen, W.; van Rees Vellinga, T.; Quarles van Ufford, H.; Stöger, L.; Beenen, L.; Geurts, B.; Gietema, H.; Krdzalic, J.; Schaefer-Prokop, C.; et al. COVID-19 Standardized Reporting Working Group of the Dutch Radiological Society. CO-RADS: A Categorical CT Assessment Scheme for Patients Suspected of Having COVID-19-Definition and Evaluation. Radiology 2020, 296, E97–E104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, D.; Panvini, N.; Rengo, M.; Vicini, S.; Lichtner, M.; Tieghi, T.; Ippoliti, D.; Giulio, F.; Orlando, E.; Iozzino, M.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver variability of CO-RADS in patients with suspected coronavirus disease-2019: A multireader validation study. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleiss, J.L.; Cohen, J. The equivalence of weighted kappa and the intraclass correlation coefficient as measures of reliability. Educational and psychological measurement. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1973, 33, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cömert, R.G.; Cingöz, E.; Meşe, S.; Durak, G.; Tunacı, A.; Ağaçfidan, A.; Önel, M.; Ertürk, Ş.M. Radiological Imaging of Viral Pneumonia Cases Identified Before the COVİD-19 Pandemic Period and COVİD-19 Pneumonia Cases Comparison of Characteristics. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.M.H.; Talari, H.; Gholamrezanezhad, A.; Farhood, B.; Rahimi, H.; Razzaghi, R.; Mehri, N.; Rajebi, H. A low-dose chest CT protocol for the diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia: A prospective study. Emerg. Radiol. 2020, 27, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.J.; Mahajan, A.; Rane, S.; Bhattacharjee, A. Assessment of COVID-19 severity using computed tomography imaging: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Res. Stat. Treat. 2021, 4, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka, T.; Takahashi, M.; Mori, M.; Tsuchiya, J.; Yamaga, E.; Horii, T.; Yamada, H.; Kimura, M.; Kimura, K.; Kitazume, Y.; et al. Evaluation of the Usefulness of CO-RADS for Chest CT in Patients Suspected of Having COVID-19. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheha, A.S.; Mohamed, N.H.; Eid, Y.M.; Sheha, D.S.; El-Shayeb, M.; Amin, M.M.; Saeed, A.M.; Abdou, D.; Osman, A.M. Comparison of the RSNA chest CT classification system and CO-RADS system in reporting COVID-19 pneumonia in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. Egypt J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2022, 53, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawab, M.; Basha, M.A.A.; Mohamed, I.A.I.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Zaitoun, M.M.A.; Elsayed, S.B.; Mahmoud, N.E.M.; El Sammak, A.A.; Yousef, H.Y.; Aly, S.A.; et al. Comparison of the CO-RADS and the RSNA chest CT classification system concerning sensitivity and reliability for the diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.V.; McInnes, M.; Jacob, B.; Kumar, D.; Soman, D.K.; Subair, H.S.V.; Mahajan, P.S.; Shah, M.A.H.; Sabawi, M.A.S.; Al-Heidous, M. Diagnostic accuracy and inter-observer agreement with the CO-RADS lexicon for CT chest reporting in COVID-19. Emerg. Radiol. 2021, 28, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, H.; Hasan, H.A.; Elmorshedy, R.; Gabr, A.; Abbas, W.A.; El-Barody, M.M. Validation of imaging reporting and data system of coronavirus disease 2019 lexicons CO-RADS and COVID-RADS with radiologists’ preference: A multicentric study. Egypt J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushentsev, N.; Bura, V.; Kotnik, M.; Shiryaev, G.; Caglic, I.; Weir-McCall, J.; Barrett, T. A head-to-head comparison of the intra- and interobserver agreement of COVID-RADS and CO-RADS grading systems in a population with high estimated prevalence of COVID-19. BJR Open 2020, 2, 20200053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwee, T.C.; Kwee, R.M. Chest CT in COVID-19: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Radiographics 2022, 40, 1848–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhotia, Y.; Mitra, K.; Onkar, P.; Dhok, A. Interobserver variability in CT severity scoring system in COVID-19 positive patients. Cureus 2022, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, N.; Cao, Y.; Alwalid, O.; Gu, J.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, C. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jaegere, T.M.H.; Krdzalic, J.; Fasen, B.A.C.M.; Kwee, R.M. COVID-19 CT Investigators South-East Netherlands (CISEN) study group. Radiological Society of North America Chest CT Classification System for Reporting COVID-19 Pneumonia: Interobserver Variability and Correlation with Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200213. [Google Scholar]
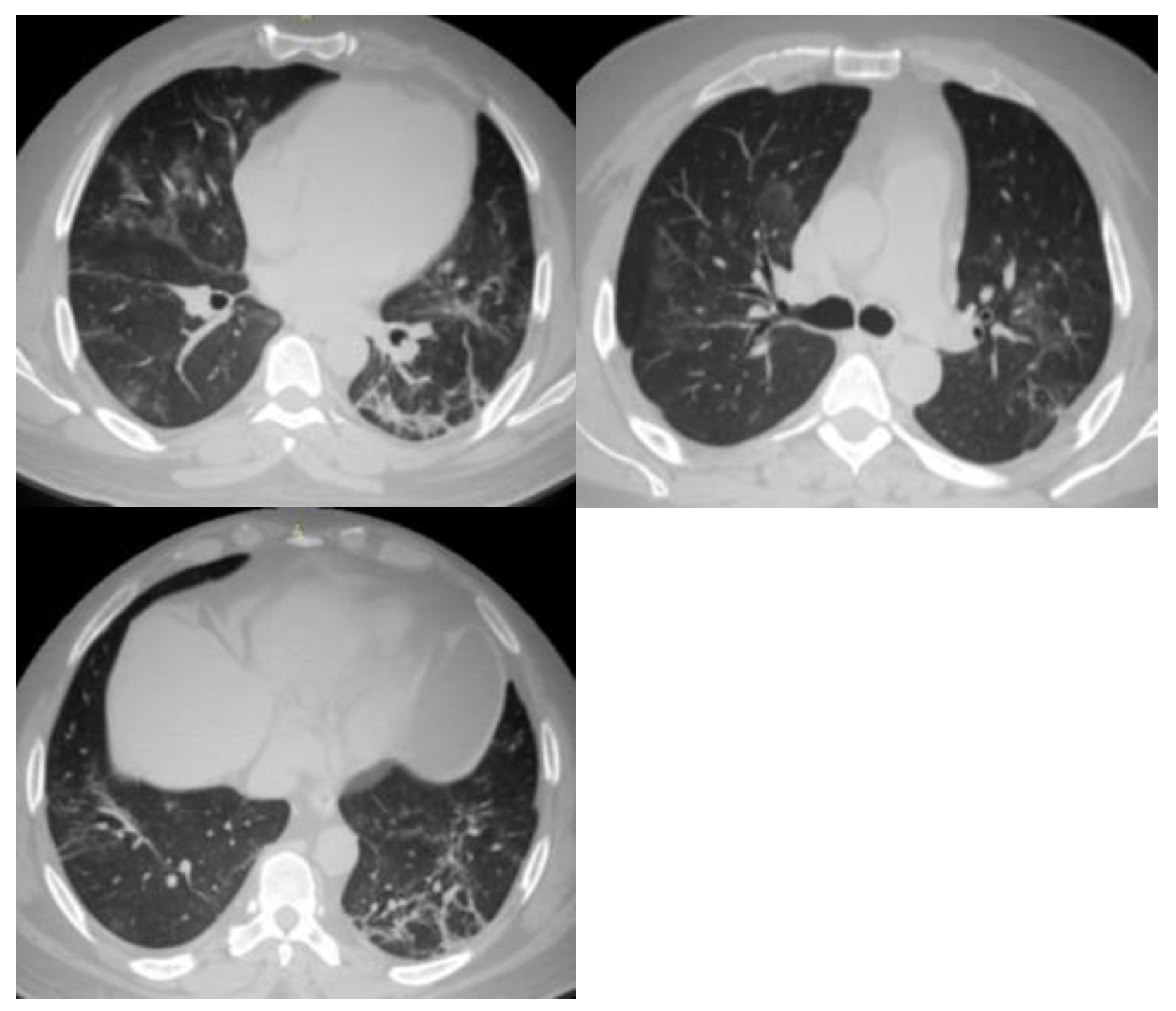
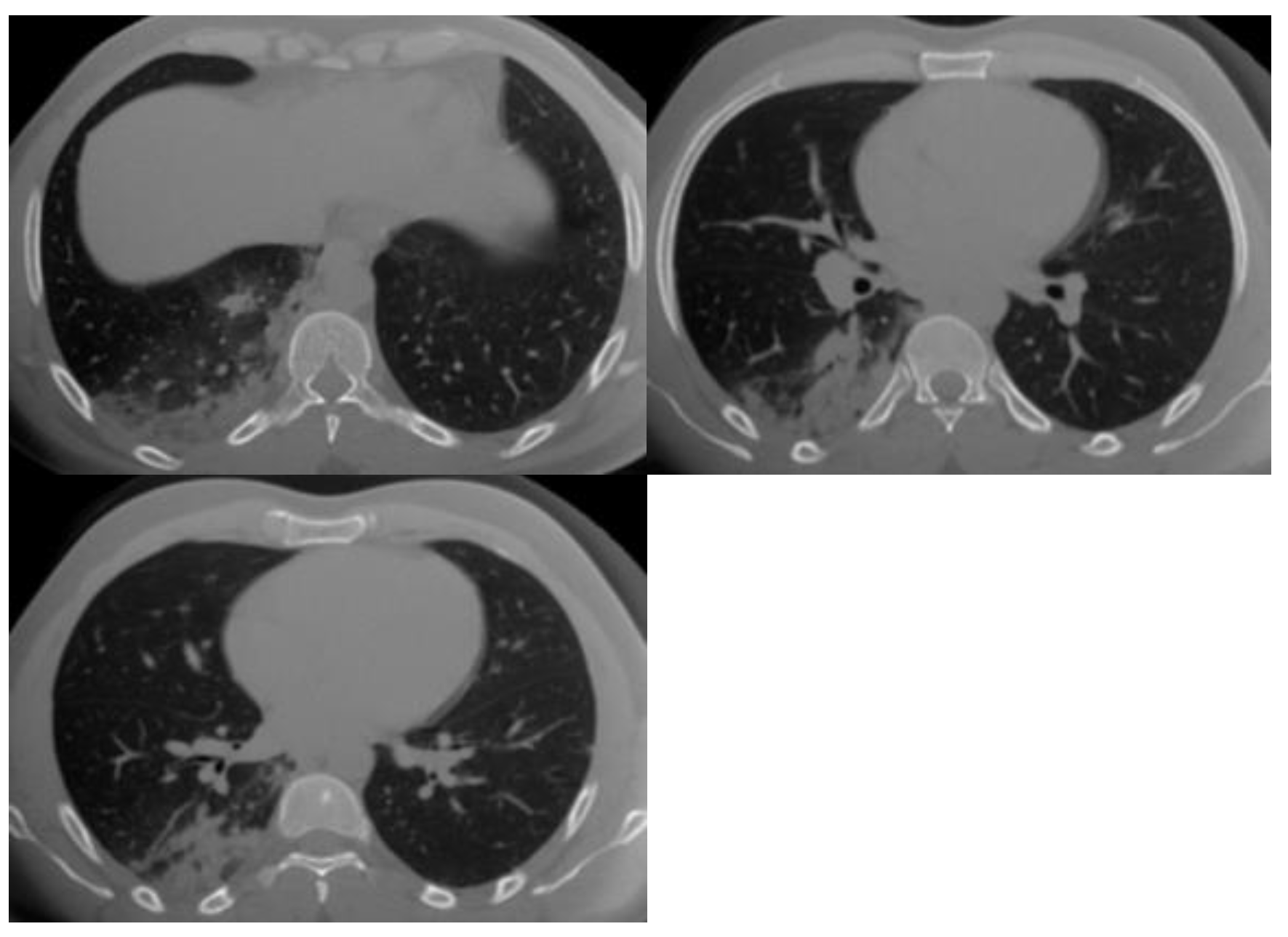

| CO-RADS | Level of Suspicion | CT Findings |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Very low | Normal or non-infectious CT findings. |
| 2 | Low | CT findings incompatible with COVID-19: bronchitis, infectious bronchiolitis, and bronchopneumonia. |
| 3 | Equivocal/uncertain | CT findings of other viral pneumonia or non-infectious results: perihilar GGO, homogenous extensive GGO, and GGO with smooth interlobular septal thickening. |
| 4 | High | CT findings are similar to those for CO-RADS 5, but a lack of contact with the visceral pleura, located unilaterally, in a peri-broncho vascular distribution, or when the findings are superimposed on pre-existing lung abnormalities. |
| 5 | Very high | Typical CT findings: ground-glass opacities with or without consolidations in lung regions close to visceral pleural surfaces and multifocal bilateral distribution. |
| Variable | n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 390 (61.9) |
| Female | 240 (38.1) | |
| Nationality | Egypt | 622 (98.7) |
| Italian | 3 (0.5) | |
| Indian | 1 (0.2) | |
| German | 2 (0.3) | |
| American | 1 (0.2) | |
| Ukrainian | 1 (0.2) | |
| Variable | Observer 1 | Observer 2 | Observer 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 107 | 104 | 103 |
| Emphysema | 16 | 13 | 13 |
| Peri-fissural nodule | 56 | 52 | 52 |
| Lung mass | 12 | 6 | 6 |
| Tree in bud | 7 | 2 | 3 |
| Centrilobular nodule | 53 | 49 | 44 |
| Consolidation | 68 | 63 | 63 |
| Cavitation | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| Smooth septal thickening with pleural effusion | 8 | 3 | 4 |
| Variable | Observer 1 | Observer 2 | Observer 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perihilar | 349 | 334 | 319 |
| Single focus | 20 | 403 | 13 |
| Centrilobular | 405 | 14 | 371 |
| Homogenous extensive | 18 | 109 | 11 |
| With smooth septal thickening | 113 | 2 | 114 |
| With smooth septal thickening and effusion | 5 | 149 | 2 |
| Small, not centrilobular, and not close to pleura | 152 | 4 | 143 |
| Organizing (scaring) pneumonia pattern without typical features | 9 | 366 | 4 |
| Multifocal bilateral | 375 | 396 | 370 |
| Multifocal unilateral close to pleural surface or fissure | 404 | 404 | 409 |
| Typical features on one side and unifocal other side | 15 | 15 | 14 |
| Unifocal bilateral | 6 | 6 | 3 |
| Variable | Observer 1 | Observer 2 | Observer 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical features: Multifocal bilateral GGOs, consolidation, close to the pleural surface or fissure, and pleural sparing | 385 | 382 | 369 |
| Typical features with organizing (scaring) pneumonia pattern | 291 | 283 | 292 |
| Typical features with crazy paving | 108 | 97 | 109 |
| Typical features with thickened vessels | 355 | 308 | 362 |
| Typical features with reversed halo | 39 | 35 | 34 |
| Variable | Observer 1 | Observer 2 | Observer 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO-RADS | 1 | 133 (21.1) | 133 (21.1) | 136 (21.6) |
| 2 | 15 (2.4) | 15 (2.4) | 14 (2.2) | |
| 3 | 36 (5.7) | 36 (5.7) | 32 (5.1) | |
| 4 | 66 (10.5) | 67 (10.6) | 52 (8.3) | |
| 5 | 380 (60.3) | 379 (60.2) | 396 (62.9) | |
| κ | 0.997 a (0.866–1.00) | 0.921 b (0.790–1.00) | 0.924 c (0.789–1.00) | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Variable | Observer 4 | Observer 5 | Observer 6 | Observer 7 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO-RADS | 1 | 137 (21.7) | 134 (21.3) | 145 (23) | 150 (23.8) | <0.001 |
| 2 | 5 (8) | 4 (0.6) | 13 (2.1) | 2 (0.3) | ||
| 3 | 54 (8.6) | 20 (3.2) | 32 (5.1) | 34 (5.4) | ||
| 4 | 71 (11.3) | 39 (6.2) | 55 (8.7) | 37 (5.9) | ||
| 5 | 363 (57.6) | 433 (68.8) | 385 (61.1) | 407 (64.6) | ||
| κ | 0.661 a (0.530–0.792) | 0.636 b (0.505–0.767) | 0.584 c (0.453–0.715) | 0.676 d (0.545–0.807) | 0.621 e (0.490–0.752) | 0.736 f (0.605–0.867) |
| Variable | Observer 1 | Observer 2 | Observer 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Observer 4 | 0.615 (0.484–0.746) | 0.613 (0.482–0.744) | 0.661 (0.530–0.792) |
| Observer 5 | 0.672 (0.541–0.803) | 0.669 (0.538–0.800) | 0.692 (0.561–0.823) |
| Observer 6 | 0.903 (0.772–1.00) | 0.900 (0.769–1.00) | 0.903 (0.772–1.00) |
| Observer 7 | 0.556 (0.425–0.687) | 0.554 (0.423–0.685) | 0.503 (0.371–0.634) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almalki, Y.E.; Basha, M.A.A.; Metwally, M.I.; Housseini, A.M.; Alduraibi, S.K.; Almushayti, Z.A.; Aldhilan, A.S.; Elzoghbi, M.M.; Gabr, E.A.; Manajrah, E.; et al. Inter-observer Variability in the Analysis of CO-RADS Classification for COVID-19 Patients. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8120523
Almalki YE, Basha MAA, Metwally MI, Housseini AM, Alduraibi SK, Almushayti ZA, Aldhilan AS, Elzoghbi MM, Gabr EA, Manajrah E, et al. Inter-observer Variability in the Analysis of CO-RADS Classification for COVID-19 Patients. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(12):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8120523
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmalki, Yassir Edrees, Mohammad Abd Alkhalik Basha, Maha Ibrahim Metwally, Ahmed Mohamed Housseini, Sharifa Khalid Alduraibi, Ziyad A. Almushayti, Asim S. Aldhilan, Mahmoud Mohamed Elzoghbi, Esraa Attia Gabr, Esaraa Manajrah, and et al. 2023. "Inter-observer Variability in the Analysis of CO-RADS Classification for COVID-19 Patients" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 12: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8120523
APA StyleAlmalki, Y. E., Basha, M. A. A., Metwally, M. I., Housseini, A. M., Alduraibi, S. K., Almushayti, Z. A., Aldhilan, A. S., Elzoghbi, M. M., Gabr, E. A., Manajrah, E., Hijazy, R. M. F., Akbazli, L. M. K., El Mokadem, A., Basha, A. M. A., & Mosallam, W. (2023). Inter-observer Variability in the Analysis of CO-RADS Classification for COVID-19 Patients. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(12), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8120523






