Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Rickettsia spp. from Wild Small Mammals in Public Parks and Urban Areas of Bangkok Metropolitan, Thailand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Small Mammal Trapping
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction and Detection of Rickettsial DNA
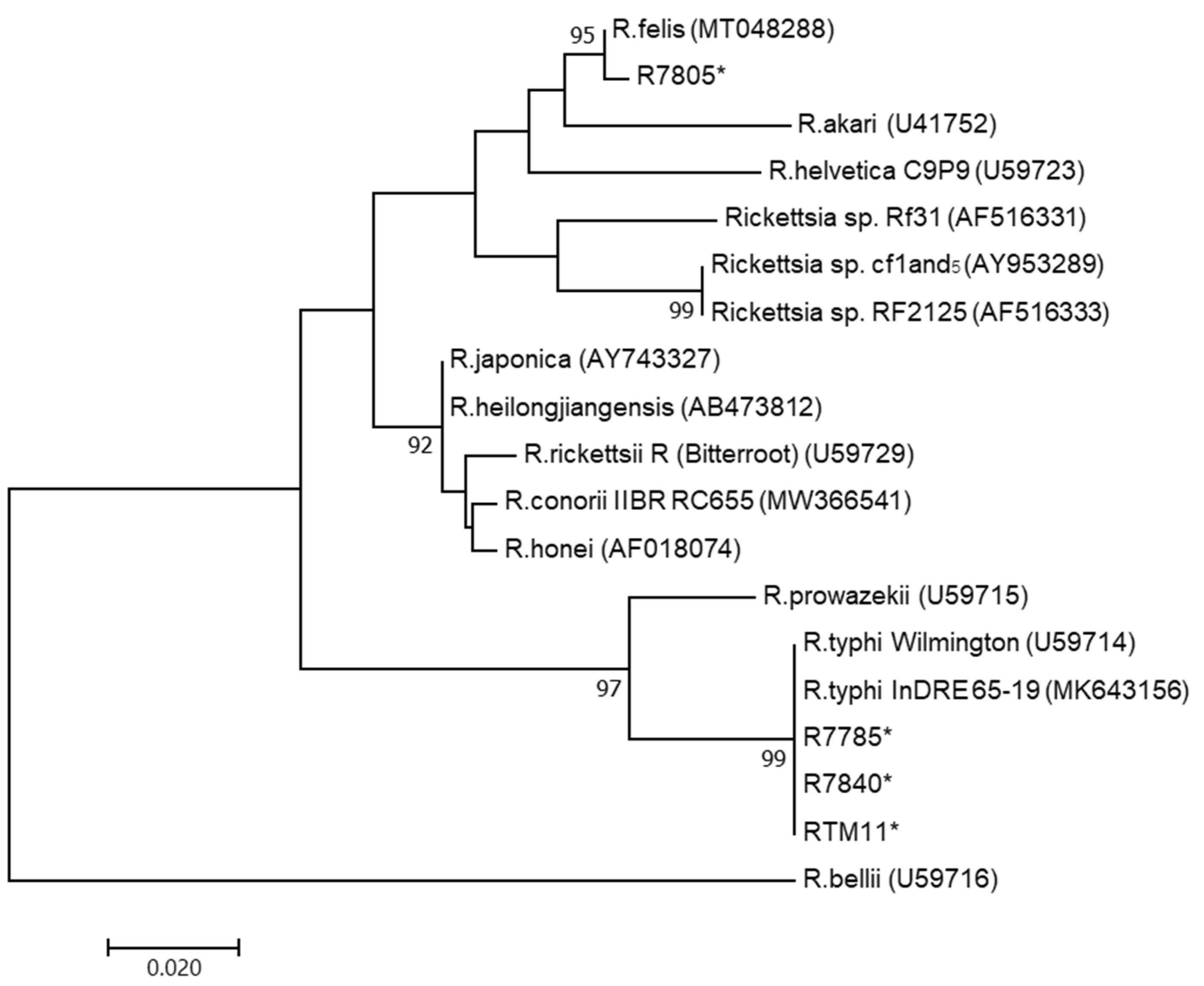
2.3. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sampling
3.2. PCR and DNA Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merhej, V.; Raoult, D. Rickettsial evolution in the light of comparative genomics. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2011, 86, 379–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, P.V. Emerging and re-emerging rickettsial infections. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 36, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, S.; Rauch, J.; Kuehl, S.; Richardt, U.; Keller, C.; Osterloh, A. Comparative evaluation of two Rickettsia typhi-specific quantitative real-time PCRs for research and diagnostic purposes. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 206, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, M.P.; Qin, X.; Karpathy, S.E.; Gioia, J.; Highlander, S.K.; Fox, G.E.; McNeill, T.Z.; Jiang, H.; Muzny, D.; Jacob, L.S.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Rickettsia typhi and comparison with sequences of other Rickettsiae. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azad, A.F. Epidemiology of murine typhus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1990, 35, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, T.E. Murine and epidemic typhus rickettsiae: How close is their relationship? Yale J. Biol. Med. 1982, 55, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.H. Rickettsiae. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas, Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK7624/ (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Fang, R.; Blanton, L.S.; Walker, D.H. Rickettsiae as emerging infectiousagents. Clin. Lab. Med. 2017, 37, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.H.; Ismail, N. Emerging and re-emerging rickettsioses: Endothelial cell infection and early disease events. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoosangwalthong, P.; Hii, S.F.; Kamyingkird, K.; Kengradomkij, C.; Pinyopanuwat, N.; Chimnoi, W.; Traub, R.J.; Inpankaew, T. Cats as potential mammalian reservoirs for Rickettsia sp. genotype RF2125 in Bangkok, Thailand. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2018, 13, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongkol, N.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; Taweethavonsawat, P.; Foongladda, S. Molecular evidence of Rickettsia in human and dog blood in Bangkok. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P.; Paddock, C.D.; Raoult, D. Tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: Emerging diseases challenging old concepts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 719–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whiley, H.; Custance, G.; Graves, S.; Stenos, J.; Taylor, M.; Ross, K.; Gardner, M.G. Rickettsia detected in the reptile tick Bothriocroton hydrosauri from the lizard Tiliqua rugosa in South Australia. Pathogens 2016, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novakova, M.; Literak, I.; Chevez, L.; Martins, T.F.; Ogrzewalska, M.; Labruna, M.B. Rickettsial infections in ticks from reptiles, birds and humans in Honduras. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2015, 6, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornok, S.; Kováts, D.; Csörgő, T.; Meli, M.L.; Gönczi, E.; Hadnagy, Z.; Takács, N.; Farkas, R.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R. Birds as potential reservoirs of tick-borne pathogens: First evidence of bacteraemia with Rickettsia helvetica. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kmetiuk, L.B.; Krawczak, F.S.; Machado, F.P.; Paploski, I.A.D.; Martins, T.F.; Teider-Junior, P.I.; Serpa, M.C.A.; Barbieri, A.R.M.; Bach, R.V.W.; Barros-Filho, I.R.; et al. Ticks and serosurvey of anti-Rickettsia spp. antibodies in wild boars (Sus scrofa), hunting dogs and hunters of Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Legendre, K.P.; Macaluso, K.R. Rickettsia felis: A review of transmission mechanisms of an emerging pathogen. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Rickettsia felis, an emerging flea-borne rickettsiosis. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2016, 3, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reif, K.E.; Kearney, M.T.; Foil, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Acquisition of Rickettsia felis by cat fleas during feeding. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parola, P.; Miller, R.S.; McDaniel, P.; Telford, S.R., 3rd; Rolain, J.-M.; Wongsrichanalai, C.; Raoult, D. Emerging rickettsioses of the Thai-Myanmar border. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edouard, S.; Bhengsri, S.; Dowell, S.F.; Watt, G.; Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Two human cases of Rickettsia felis infection, Thailand. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1780–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delaney, M.A.; Treuting, P.M.; Rothenburger, J.L. Rodentia. In Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals; Terio, K.A., McAloose, D., Leger, J.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 499–515. [Google Scholar]
- Abramowicz, K.F.; Rood, M.P.; Krueger, L.; Eremeeva, M.E. Urban focus of Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia felis in Los Angeles, California. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgo, M.P.; Telzak, E.E.; Currie, B.; Perlman, D.C.; Litman, N.; Levi, M.; Nathenson, G.; Benach, J.L.; Al-Hafidh, R.; Casey, J. A focus of rocky mountain spotted fever within New York City. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M. Rickettsialpox in New York City. Am. J. Med. 1948, 4, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, L.S.; Walker, D.H.; Bouyer, D.H. Rickettsiae and ehrlichiae within a city park: Is the urban dweller at risk? Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, F.; Ciccozzi, M.; Lo Presti, A.; Cella, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Di Luca, M.; Toma, L.; Bianchi, R.; Khoury, C.; Rezza, G.; et al. Characterization of spotted fever group Rickettsiae in ticks from a city park of Rome, Italy. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2015, 51, 284–290. [Google Scholar]
- Schorn, S.; Pfister, K.; Reulen, H.; Mahling, M.; Silaghi, C. Occurrence of Babesia spp., Rickettsia spp. and Bartonella spp. in Ixodes ricinus in Bavarian public parks, Germany. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paladsing, Y.; Boonsri, K.; Saesim, W.; Changsap, B.; Thaenkham, U.; Kosoltanapiwat, N.; Sonthayanon, P.; Ribas, A.; Morand, S.; Chaisiri, K. Helminth fauna of small mammals from public parks and urban areas in Bangkok Metropolitan with emphasis on community ecology of infection in synanthropic rodents. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3675–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Shu, P.-Y.; Mu, J.-J.; Wang, H.-C. High prevalence of Rickettsia spp. infections in small mammals in Taiwan. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, M.; Bazin, E.; Galan, M.; Chaval, Y.; Claude, J.; Herbreteau, V.; Michaux, J.; Piry, S.; Morand, S.; Cosson, J.F. Cytonuclear discordance among Southeast Asian black rats (Rattus rattus complex). Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosoy, M.; Khlyap, L.; Cosson, J.-F.; Morand, S. Aboriginal and invasive rats of genus Rattus as hosts of infectious agents. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagès, M.; Chaval, Y.; Herbreteau, V.; Waengsothorn, S.; Cosson, J.-F.; Hugot, J.-P.; Morand, S.; Michaux, J. Revisiting the taxonomy of the Rattini tribe: A phylogeny-based delimitation of species boundaries. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerburg, B.G.; Singleton, G.R.; Kijlstra, A. Rodent-borne diseases and their risks for public health. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 221–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Li, F.; Liao, Y.; Shen, J.-J.; Xu, J.-M.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Li, J.-H.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Epidemiology and diversity of Rickettsiales bacteria in humans and animals in Jiangsu and Jiangxi provinces, China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, S.T.; Mokhtar, A.S.; Low, K.C.; Mohd Zain, S.N.; Jeffery, J.; Abdul Aziz, N.; Kho, K.L. Identification of rickettsiae from wild rats and cat fleas in Malaysia. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2014, 28 (Suppl. 1), 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chareonviriyaphap, T.; Leepitakrat, W.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Chao, C.C.; Ching, W.M. Dual exposure of Rickettsia typhi and Orientia tsutsugamushi in the field-collected Rattus rodents from Thailand. J. Vector Ecol. 2014, 39, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prompiram, P.; Poltep, K.; Pamonsupornvichit, S.; Wongwadhunyoo, W.; Chamsai, T.; Rodkvamtook, W. Rickettsiae exposure related to habitats of the oriental house rat (Rattus tanezumi, Temminck, 1844) in Salaya suburb, Thailand. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 13, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.D.; Abdad, M.Y.; Stenos, J. Serological evidence of Rickettsia spp. in Western Australian Dogs. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hii, S.F.; Kopp, S.R.; Abdad, M.Y.; Thompson, M.F.; O’Leary, C.A.; Rees, R.L.; Traub, R.J. Molecular evidence supports the role of dogs as potential reservoirs for Rickettsia felis. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eads, D.A.; Hoogland, J.L. Precipitation, climate change, and parasitism of prairie dogs by fleas that transmit plague. J. Parasitol. 2017, 103, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngeleja, R.C.; Luboobi, L.S.; Nkansah-Gyekye, Y. Plague disease model with weather seasonality. Math. Biosci. 2018, 302, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, V.; Londoño, A.F.; Miranda, J.; Mattar, S.; Acevedo-Gutiérrez, L.Y.; Diaz, F.J.; Rodas, J.D. Infection by Rickettsia felis in Ctenocephalides felis felis fleas from North of Colombia. J. Arthropod-Borne Dis. 2019, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panti-May, J.A.; Torres-Castro, M.; Hernández-Betancourt, S.; Dzul-Rosado, K.; Zavala-Castro, J.; López-Avila, K.; Tello-Martín, R. Detection of Rickettsia felis in wild mammals from three municipalities in Yucatan, Mexico. Ecohealth 2015, 12, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moonga, L.C.; Hayashida, K.; Nakao, R.; Lisulo, M.; Kaneko, C.; Nakamura, I.; Eshita, Y.; Mweene, A.S.; Namangala, B.; Sugimoto, C.; et al. Molecular detection of Rickettsia felis in dogs, rodents and cat fleas in Zambia. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbara, K.A.; Farzeli, A.; Ibrahim, I.N.; Antonjaya, U.; Yunianto, A.; Winoto, I.; Ester; Perwitasari, D.; Widjaya, S.; Richards, A.L.; et al. Rickettsial infections of fleas collected from small mammals on four islands in Indonesia. J. Med. Entomol. 2010, 47, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
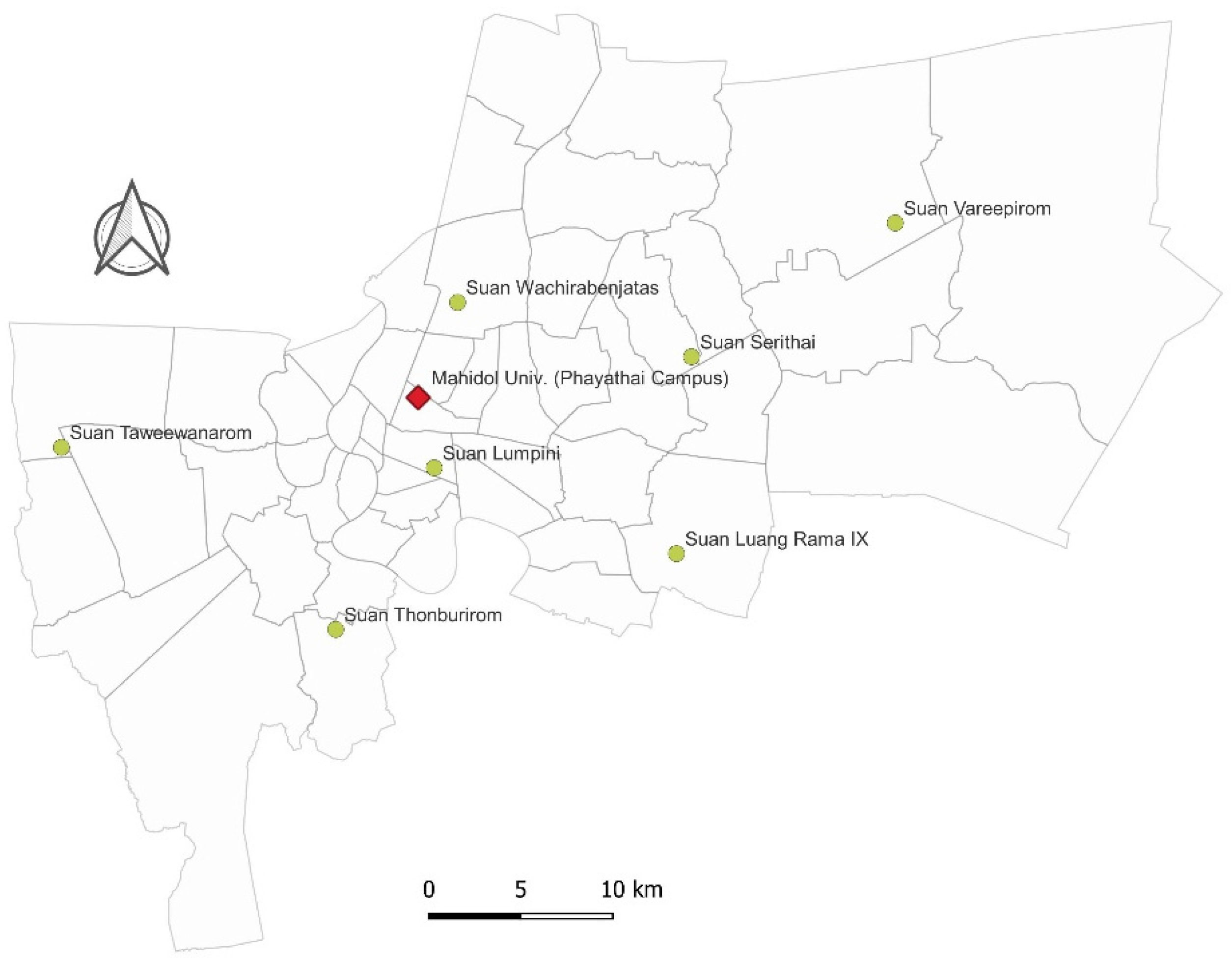
| Order | Family | Species | Suan Luang Rama IX | Suan Lumpini | Suan Serithai | Suan Taweevanarom | Suan Thonburirom | Suan Vareepirom | Suan Wachirabenjatas | Mahidol University Phyathai Campus | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rodentia | Muridae | R. exulans | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 12 (6.1) |
| Rodentia | Muridae | R. norvegicus | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 (1.0) |
| Rodentia | Muridae | R. rattus-complex | 31 | 2 | 13 | 11 | 5 | 23 | 48 | 29 | 162 (81.8) |
| Scandentia | Tupaiidae | T. belangeri | 7 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 19 (9.6) |
| Eulipotyphla | Soricidae | S. murinus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 (1.5) |
| Total | 38 (19.2) | 4 (2.0) | 17 (8.6) | 15 (7.6) | 12 (6.1) | 23 (11.6) | 55 (27.8) | 34 (17.2) | 198 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rungrojn, A.; Chaisiri, K.; Paladsing, Y.; Morand, S.; Junjhon, J.; Blacksell, S.D.; Ekchariyawat, P. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Rickettsia spp. from Wild Small Mammals in Public Parks and Urban Areas of Bangkok Metropolitan, Thailand. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6040199
Rungrojn A, Chaisiri K, Paladsing Y, Morand S, Junjhon J, Blacksell SD, Ekchariyawat P. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Rickettsia spp. from Wild Small Mammals in Public Parks and Urban Areas of Bangkok Metropolitan, Thailand. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2021; 6(4):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6040199
Chicago/Turabian StyleRungrojn, Artharee, Kittipong Chaisiri, Yossapong Paladsing, Serge Morand, Jiraphan Junjhon, Stuart D. Blacksell, and Peeraya Ekchariyawat. 2021. "Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Rickettsia spp. from Wild Small Mammals in Public Parks and Urban Areas of Bangkok Metropolitan, Thailand" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 6, no. 4: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6040199
APA StyleRungrojn, A., Chaisiri, K., Paladsing, Y., Morand, S., Junjhon, J., Blacksell, S. D., & Ekchariyawat, P. (2021). Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Rickettsia spp. from Wild Small Mammals in Public Parks and Urban Areas of Bangkok Metropolitan, Thailand. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 6(4), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6040199








