Relationship between Physicochemical Characteristics and Pathogenic Leptospira in Urban Slum Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
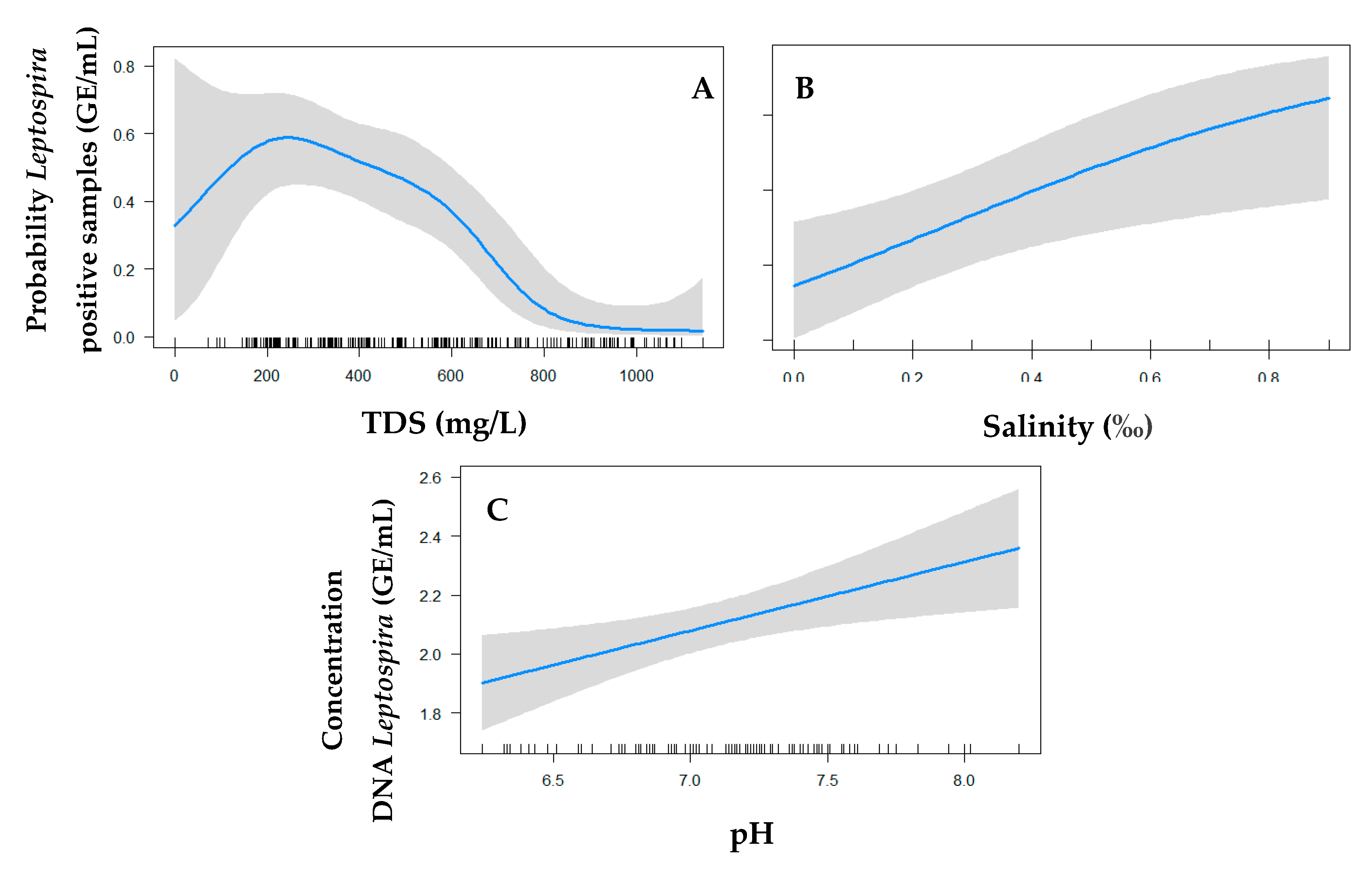
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torgerson, P.R.; Hagan, J.E.; Costa, F.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Goris, M.G.; Stein, C.; Ko, A.I.; Abela-Ridder, B. Global Burden of Leptospirosis: Estimated in Terms of Disability Adjusted Life Years. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.; Hagan, J.E.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Torgerson, P.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Stein, C.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Ko, A.I. Global Morbidity and Mortality of Leptospirosis: A Systematic Review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, A.I.; Goarant, C.; Picardeau, M. Leptospira: The dawn of the molecular genetics era for an emerging zoonotic pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, A.J.; Athanazio, D.A.; Reis, M.G.; Ko, A.I. Leptospirosis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 18, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganoza, C.A.; Matthias, M.A.; Collins-Richards, D.; Brouwer, K.C.; Cunningham, C.B.; Segura, E.R.; Gilman, R.H.; Gotuzzo, E.; Vinetz, J.M. Determining risk for severe leptospirosis by molecular analysis of environmental surface waters for pathogenic Leptospira. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.L.; Buckingham, M.; Taylor, M.P. Studies on Leptospira icterohaemorrhagiae; survival in water and sewage; destruction in water by halogen compounds, synthetic detergents, and heat. J. Infect. Dis. 1948, 82, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, W.; Ringen, L.M. Some effects of various environmental conditions on the survival of Leptospira pomona. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1957, 18, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, J.; Walker, M. Survival of a pathogenic Leptospira serovar in response to combined in vitro pH and temperature stresses. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrino, M.G.; Doetsch, R.N. ‘Viscotaxis’, a new behavioural response of Leptospira interrogans (biflexa) strain B16. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1978, 109, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueba, G.; Zapata, S.; Madrid, K.; Cullen, P.; Haake, D. Cell aggregation: A mechanism of pathogenic Leptospira to survive in fresh water. Int. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Agampodi, S.B.; Dahanayaka, N.J.; Bandaranayaka, A.K.; Perera, M.; Priyankara, S.; Weerawansa, P.; Matthias, M.A.; Vinetz, J.M. Regional differences of leptospirosis in Sri Lanka: Observations from a flood-associated outbreak in 2011. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, A.I.; Galvao Reis, M.; Ribeiro Dourado, C.M.; Johnson, W.D., Jr.; Riley, L.W. Urban epidemic of severe leptospirosis in Brazil. Salvador Leptospirosis Study Group. Lancet 1999, 354, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevejo, R.T.; Rigau-Perez, J.G.; Ashford, D.A.; McClure, E.M.; Jarquin-Gonzalez, C.; Amador, J.J.; de los Reyes, J.O.; Gonzalez, A.; Zaki, S.R.; Shieh, W.J.; et al. Epidemic leptospirosis associated with pulmonary hemorrhage-Nicaragua, 1995. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corburn, J.; Riley, L. Slum Health: From the Cell to the Street, 1st ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hagan, J.E.; Moraga, P.; Costa, F.; Capian, N.; Ribeiro, G.S.; Wunder, E.A., Jr.; Felzemburgh, R.D.; Reis, R.B.; Nery, N.; Santana, F.S.; et al. Spatiotemporal Determinants of Urban Leptospirosis Transmission: Four-Year Prospective Cohort Study of Slum Residents in Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanovas-Massana, A.; Costa, F.; Riediger, I.N.; Cunha, M.; de Oliveira, D.; Mota, D.C.; Sousa, E.; Querino, V.A.; Nery, N., Jr.; Reis, M.G.; et al. Spatial and temporal dynamics of pathogenic Leptospira in surface waters from the urban slum environment. Water Res. 2018, 130, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Method for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21th ed.; APHA, Ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Allaire, J. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio Team: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; p. 394. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.V.; Lall, C.; Raj, R.V.; Vedhagiri, K.; Vijayachari, P. Coexistence and survival of pathogenic leptospires by formation of biofilm with Azospirillum. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoro, M.A.; Okoh, O.O.; Adefisoye, M.A.; Okoh, A.I. Physicochemical Properties of Wastewater in Three Typical South African Sewage Works. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, J.; Lo, M.; Bulach, D.M.; Zuerner, R.L.; Adler, B.; Haake, D.A. Response of Leptospira interrogans to physiologic osmolarity: Relevance in signaling the environment-to-host transition. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faine, S. Leptospira and Leptospirosis; CRC Press Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Viau, E.J.; Boehm, A.B. Quantitative PCR-based detection of pathogenic Leptospira in Hawai’ian coastal streams. J. Water Health 2011, 9, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.E.; Turner, L.H. The effect of pH on the survival of leptospires in water. Bull. World Health Organ. 1961, 24, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.J.; Self, H.R. Observations on the survival of Leptospira australis A in soil and water. Epidemiol. Infect. 1955, 53, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Wunder, E.A., Jr.; De Oliveira, D.; Bisht, V.; Rodrigues, G.; Reis, M.G.; Ko, A.I.; Begon, M.; Childs, J.E. Patterns in Leptospira Shedding in Norway Rats (Rattus norvegicus) from Brazilian Slum Communities at High Risk of Disease Transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.G.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Hacker, K.P.; Wunder, E.A., Jr.; Begon, M.; Reis, M.G.; Childs, J.E.; Costa, F.; Lindow, J.C.; Ko, A.I. Quantification of pathogenic Leptospira in the soils of a Brazilian urban slum. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanovas-Massana, A.; Pedra, G.G.; Wunder, E.A., Jr.; Diggle, P.J.; Begon, M.; Ko, A.I. Quantitative survival of Leptospira interrogans in soil and water microcosms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairani-Bejos, S.; Bahaman, A.R.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Mutalib, A.R. The survival of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo in the Malaysian Environment. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2004, 3, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Thibeaux, R.; Geroult, S.; Benezech, C.; Chabaud, S.; Soupé-Gilbert, M.-E.; Girault, D.; Bierque, E.; Goarant, C. Seeking the environmental source of Leptospirosis reveals durable bacterial viability in river soils. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Díaz, J.; García-Aljaro, C.; Pascual-Benito, M.; Galofré, B.; Blanch, A.R.; Lucena, F. Microcosms for evaluating microbial indicator persistence and mobilization in fluvial sediments during rainfall events. Water Res. 2017, 123, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre-Fontaine, G.; Aviat, F.; Fau-Thorin, C.; Thorin, C. Waterborne Leptospirosis: Survival and Preservation of the Virulence of Pathogenic Leptospira spp. in Fresh Water. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F.L.; Stensel, H.D. Metcalf & Eddy Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
| Physicochemical Parameters | Overall | Positive | Negative | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 25.7 ± 2.35 | 25.3 ± 2.44 | 26 ± 2.27 | <0.01 |
| pH | 7.2 ± 0.61 | 7.1 ± 0.60 | 7.3 ± 0.61 | 0.02 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 325 ± 284 | 352 ± 292 | 310 ± 279 | 0.23 |
| Total dissolved solids (TDS) (mg/L) | 533 ± 281 | 436 ± 209 | 592 ± 302 | <0.01 |
| Salinity (‰) | 0.28 ± 0.306 | 0.24 ± 0.35 | 0.30 ± 0.27 | 0.01 |
| Electrical conductivity (µS) | 0.99 ± 0.55 | 0.92 ± 0.60 | 1.04 ± 0.50 | 0.01 |
| Physicochemical Parameters | Logistic Model | Linear Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | 95% CI | Coefficient | 95% CI | |
| pH | 1.132 | 0.52–2.47 | 0.28 ** | 0.09–0.48 |
| Turbidity | 0.00 | −0.00–0.00 | ||
| TDS | 0.989 *** | 0.98–0.99 | ||
| Salinity | 10.097 * | 1.30–91.07 | −0.52 | −1.34–0.30 |
| Interaction terms | ||||
| pH * Water | 0.753 ** | 0.61–0.93 | ||
| TDS * Water | 1.005 *** | 1.00–1.01 | ||
| Salinity * Water | 0.37 | −0.15–0.89 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, D.; Airam Querino, V.; Sara Lee, Y.; Cunha, M.; Nery Jr., N., Jr.; Wessels Perelo, L.; Rossi Alva, J.C.; Ko, A.I.; Reis, M.G.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; et al. Relationship between Physicochemical Characteristics and Pathogenic Leptospira in Urban Slum Waters. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5030146
de Oliveira D, Airam Querino V, Sara Lee Y, Cunha M, Nery Jr. N Jr., Wessels Perelo L, Rossi Alva JC, Ko AI, Reis MG, Casanovas-Massana A, et al. Relationship between Physicochemical Characteristics and Pathogenic Leptospira in Urban Slum Waters. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2020; 5(3):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5030146
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Daiana, Vladimir Airam Querino, Yeonsoo Sara Lee, Marcelo Cunha, Nivison Nery Jr., Jr., Louisa Wessels Perelo, Juan Carlos Rossi Alva, Albert I. Ko, Mitermayer G. Reis, Arnau Casanovas-Massana, and et al. 2020. "Relationship between Physicochemical Characteristics and Pathogenic Leptospira in Urban Slum Waters" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 5, no. 3: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5030146
APA Stylede Oliveira, D., Airam Querino, V., Sara Lee, Y., Cunha, M., Nery Jr., N., Jr., Wessels Perelo, L., Rossi Alva, J. C., Ko, A. I., Reis, M. G., Casanovas-Massana, A., & Costa, F. (2020). Relationship between Physicochemical Characteristics and Pathogenic Leptospira in Urban Slum Waters. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 5(3), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5030146






