Emergence of Arboviruses in the United States: The Boom and Bust of Funding, Innovation, and Capacity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Arbovirus Emergence in the U.S.
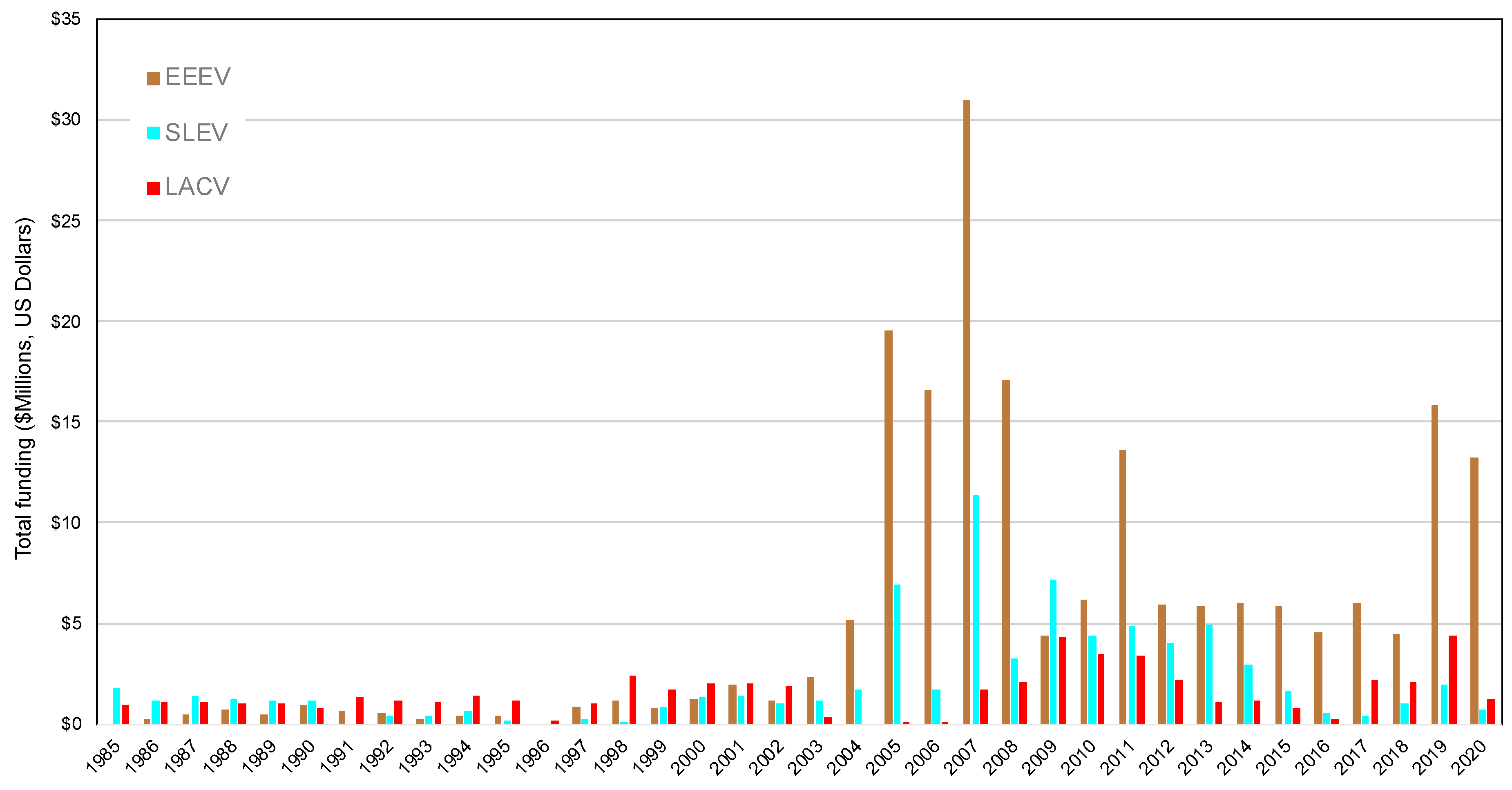
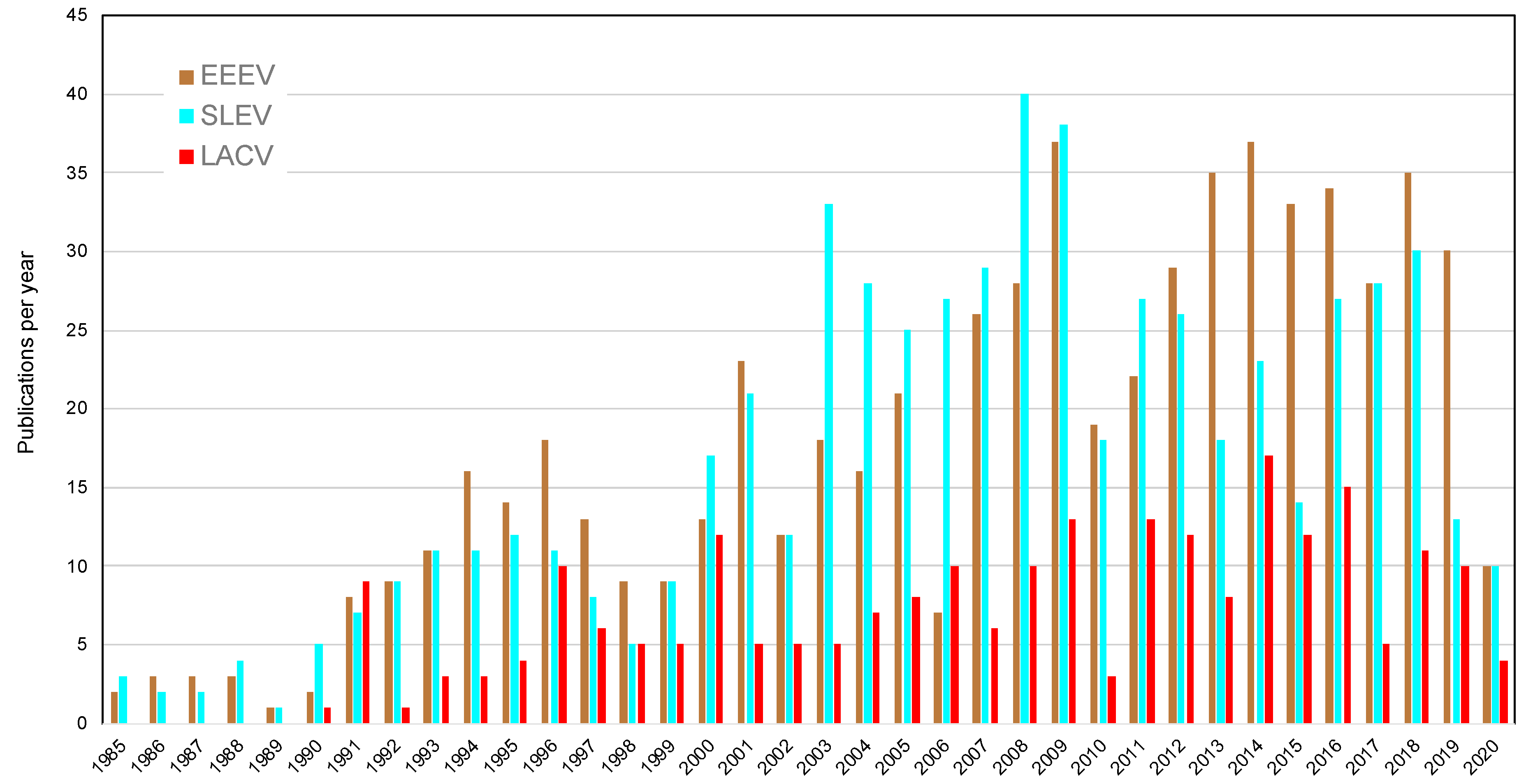
3. Federal Funding and Publications in Response to Arboviral Emergence
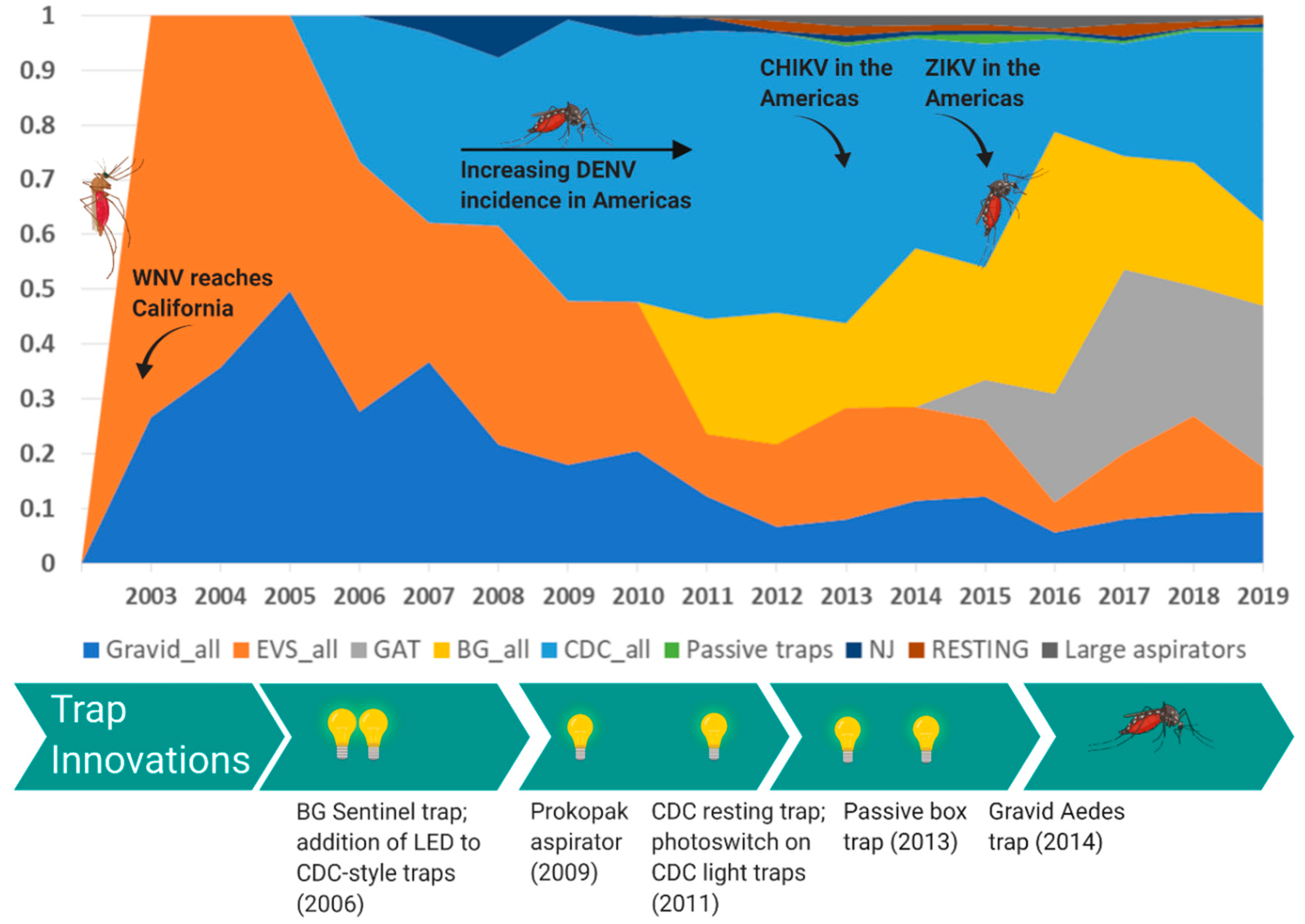
4. Innovation of Mosquito Surveillance Tools
4.1. Culex-Borne Virus Surveillance
4.2. Aedes-Borne Virus Surveillance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Houlihan, C.F.; Whitworth, J.A. Outbreak science: Recent progress in the detection and response to outbreaks of infectious diseases. Clin. Med. 2019, 19, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayabalisingham, B.; Hessen, M.; James, C. Infectious Disease Outbreak Research: Insights and Trends 2020 [Webinar] In Scopus Webinar Series. Available online: https://www.brighttalk.com/webcast/13703/391874. (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Pavlin, J.A.; Mostashari, F.; Kortepeter, M.G.; Hynes, N.A.; Chotani, R.A.; Mikol, Y.B.; Ryan, M.A.K.; Neville, J.S.; Gantz, D.T.; Writer, J.V.; et al. Innovative Surveillance Methods for Rapid Detection of Disease Outbreaks and Bioterrorism: Results of an Interagency Workshop on Health Indicator Surveillance. Am. J. Public Health 2003, 93, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USAID. Fighting Ebola: A Grand Challenge for Development. Available online: http://www.ebolagrandchallenge.net (accessed on 7 April 2020).
- USAID. Combating Zika | Grand Challenge for Development | U.S. Agency for International Development. Available online: https://www.usaid.gov/grandchallenges/zika (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Bashir, N. James Dyson Designed a New Ventilator in 10 days. He’s Making 15,000 for the Pandemic Fight. Available online: https://www.cnn.com/2020/03/26/tech/dyson-ventilators-coronavirus/index.html (accessed on 7 April 2020).
- Bhatt, K.; Pourmand, A.; Sikka, N. Targeted Applications of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (Drones) in Telemedicine. Telemed. E-Health 2018, 24, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roblin, S. Will Blood-Bearing Delivery Drones Transform Disaster Relief and Battlefield Medicine? Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/sebastienroblin/2019/10/22/will-blood-bearing-delivery-drones--transform-disaster-relief-and-battlefield-medicine/ (accessed on 7 April 2020).
- Shapiro, G. How Innovation Is Helping Mitigate the Coronavirus Threat; STAT: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, A.; Meyer, D.; Ritchie, S. Searching for the proverbial needle in a haystack: Advances in mosquito-borne arbovirus surveillance. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohnstaedt, L.; Ladner, J.; Campbell, L.; Busch, N.; Barrera, R. Determining Mosquito Distribution from Egg Data: The Role of the Citizen Scientist. Am. Biol. Teach. 2016, 78, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esperança, P.M.; Blagborough, A.M.; Da, D.F.; Dowell, F.E.; Churcher, T.S. Detection of Plasmodium berghei infected Anopheles stephensi using near-infrared spectroscopy. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.N.; Dos Santos, L.M.B.; Chouin-Carneiro, T.; Pavan, M.G.; Garcia, G.A.; David, M.R.; Beier, J.C.; Dowell, F.E.; Maciel-De-Freitas, R.; Sikulu-Lord, M.T. Rapid, noninvasive detection of Zika virus in mosquitoes by near-infrared spectroscopy. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat0496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, D.; Ray, A.; Guda, T.; Keogh, E.; Singh, S.; Zhu, Y.; Debboun, M.; Reyna, M.; Vigilant, M.; Carpi, G.; et al. Project premonition project: Field trials of a robotic smart trap for mosquito identification and bionomics. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 610–611. [Google Scholar]
- Curren, E.J.; Lehman, J.; Kolsin, J.; Walker, W.L.; Martin, S.W.; Staples, J.E.; Hills, S.L.; Gould, C.V.; Rabe, I.B.; Fischer, M.; et al. West Nile Virus and Other Nationally Notifiable Arboviral Diseases—United States, 2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaensbauer, J.T.; Lindsey, N.P.; Messacar, K.; Staples, J.E.; Fischer, M. Neuroinvasive arboviral disease in the United States: 2003 to 2012. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e642–e650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krow-Lucal, E.R.; Lindsey, N.P.; Fischer, M.; Hills, S.L. Powassan Virus Disease in the United States, 2006–2016. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastula, D.M.; Hoang Johnson, D.K.; White, J.L.; Dupuis, A.P.; Fischer, M.; Staples, J.E. Jamestown Canyon Virus Disease in the United States-2000–2013. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsey, N.P.; Martin, S.W.; Staples, J.E.; Fischer, M. Notes from the Field: Multistate Outbreak of Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus—United States, 2019. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Gallagher, K.; Jajosky, R.A.; Ward, J.; Sharp, P.; Anderson, W.; Abellera, J.; Aranas, A.; Mayes, M.; Wodajo, M.; et al. Summary of Notifiable Diseases—United States, 2010. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2010, 59, 1–111. [Google Scholar]
- Robb, L.L.; Hartman, D.A.; Rice, L.; deMaria, J.; Bergren, N.A.; Borland, E.M.; Kading, R.C. Continued Evidence of Decline in the Enzootic Activity of Western Equine Encephalitis Virus in Colorado. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Staples, J.E. Arboviral Diseases Branch, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, CDC Notes from the field: Chikungunya virus spreads in the Americas—Caribbean and South America, 2013–2014. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2014, 63, 500–501. [Google Scholar]
- Zanluca, C.; de Melo, V.C.A.; Mosimann, A.L.P.; Santos, G.I.V.D.; Santos, C.N.D.D.; Luz, K. First report of autochthonous transmission of Zika virus in Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmaseda, A.; Standish, K.; Mercado, J.C.; Matute, J.C.; Tellez, Y.; Saborío, S.; Hammond, S.N.; Nuñez, A.; Avilés, W.; Henn, M.R.; et al. Trends in patterns of dengue transmission over 4 years in a pediatric cohort study in Nicaragua. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brathwaite, D.O.; San Martín, J.L.; Montoya, R.H.; del Diego, J.; Zambrano, B.; Dayan, G.H. The history of dengue outbreaks in the Americas. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, T.S.; da Encarnação Sá-Guimarães, T.; de Alvarenga, E.S.L.; Guimarães-Ribeiro, V.; de Meneses, M.D.F.; de Castro-Salles, P.F.; Dos Santos, C.R.; do Amaral Melo, A.C.; Soares, M.R.; Ferreira, D.F.; et al. History, epidemiology and diagnostics of dengue in the American and Brazilian contexts: A review. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PAHO. Number of Reported Cases of Dengue and Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF), Region of the Americas (by Country and Subregion) 1980–2018. Available online: https://www.paho.org/data/index.php/en/mnu-topics/indicadores-dengue-en/dengue-nacional-en/252-dengue-pais-ano-en.html (accessed on 7 April 2020).
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Reiner, R.C.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Gilbert, M.; Pigott, D.M.; Yi, D.; Johnson, K.; Earl, L.; Marczak, L.B.; et al. Past and future spread of the arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pless, E.; Gloria-Soria, A.; Evans, B.R.; Kramer, V.; Bolling, B.G.; Tabachnick, W.J.; Powell, J.R. Multiple introductions of the dengue vector, Aedes aegypti, into California. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, S.J.; Carlson, C.J.; Mordecai, E.A.; Johnson, L.R. Global expansion and redistribution of Aedes-borne virus transmission risk with climate change. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, L.A.; Fox, S.J.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Bellan, S.E.; Dimitrov, N.B.; Galvani, A.P.; Meyers, L.A. Assessing real-time Zika risk in the United States. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florida State Health Department. Department of Health Daily Zika Update | Florida Department of Health. Available online: http://www.floridahealth.gov/newsroom/2017/01/012717-zika-update.html (accessed on 18 April 2020).
- Kaplan, S. Congress Approves $1.1 Billion in Zika Funding. Available online: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/congress-approves-1-1-billion-in-zika-funding/ (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- MMWR. Assessing Capacity for Surveillance, Prevention, and Control of West Nile Virus Infection—United States, 1999 and 2004. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5506a2.htm (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Hadler, J.; Patel, D.; Bradley, K.; Hughes, J.; Blackmore, C.; Etkind, P.; Kan, L.; Getchell, J.; Blumenstock, J.; Engel, J. National Capacity for Surveillance, Prevention, and Control of West Nile Virus and Other Arbovirus Infections—United States, 2004 and 2012. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2014, 63, 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. Statistics & Maps | West Nile Virus | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/westnile/statsmaps/index.html (accessed on 18 April 2020).
- CDC. CDC Awards Nearly $184 Million to Continue the Fight against Zika. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2016/p1222-zika-funding.html (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- CDC. ELC 5-year Focus, Funding, and Impact | DPEI | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ncezid/dpei/elc/history-of-elc.html (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Rohe, D.L.; Fall, R.P. A miniature Battery Powered CO2 Baited Light Trap for Mosquito Borne Encephalitis Surveillance. Available online: https://eurekamag.com/research/000/583/000583985.php (accessed on 7 March 2019).
- Ritchie, S.A.; Cortis, G.; Paton, C.; Townsend, M.; Shroyer, D.; Zborowski, P.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Van Den Hurk, A.F. A simple non-powered passive trap for the collection of mosquitoes for arbovirus surveillance. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.B.; Johnson, B.J.; Fall, K.; Buhagiar, T.S.; Townsend, M.; Ritchie, S.A. Development, Optimization, and Field Evaluation of the Novel Collapsible Passive Trap for Collection of Mosquitoes. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panella, N.A.; Crockett, R.J.K.; Biggerstaff, B.J.; Komar, N. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention resting trap: A novel device for collecting resting mosquitoes. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2011, 27, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Service, M. Mosquito Ecology: Field Sampling Methods, 2nd ed.; Springer eBook Collection; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 1993; ISBN 978-94-015-8113-4. [Google Scholar]
- Maciel-de-Freitas, R.; Eiras, A.E.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R. Field evaluation of effectiveness of the BG-Sentinel, a new trap for capturing adult Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2006, 101, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiras, A.E.; Buhagiar, T.S.; Ritchie, S.A. Development of the gravid Aedes trap for the capture of adult female container-exploiting mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, A.J.; Amador, M.; Barrera, R. An improved autocidal gravid ovitrap for the control and surveillance of Aedes aegypti. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, P. A revised version of the CDC Gravid Mosquito Trap. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1987, 3, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Prokopec, G.M.; Galvin, W.A.; Kelly, R.; Kitron, U. A new, cost-effective, battery-powered aspirator for adult mosquito collections. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kompas, T.; Chu, L.; Pham, V.H.; Spring, D. Budgeting and portfolio allocation for biosecurity measures—Kompas. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2019, 63, 412–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompas, T.; Che, T.N.; Ha, P.V.; Chu, L. Cost–Benefit Analysis for Biosecurity Decisions. In Invasive Species: Risk Assessment and Management; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kading, R.C.; Cohnstaedt, L.W.; Fall, K.; Hamer, G.L. Emergence of Arboviruses in the United States: The Boom and Bust of Funding, Innovation, and Capacity. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020096
Kading RC, Cohnstaedt LW, Fall K, Hamer GL. Emergence of Arboviruses in the United States: The Boom and Bust of Funding, Innovation, and Capacity. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2020; 5(2):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020096
Chicago/Turabian StyleKading, Rebekah C., Lee W. Cohnstaedt, Ken Fall, and Gabriel L. Hamer. 2020. "Emergence of Arboviruses in the United States: The Boom and Bust of Funding, Innovation, and Capacity" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 5, no. 2: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020096
APA StyleKading, R. C., Cohnstaedt, L. W., Fall, K., & Hamer, G. L. (2020). Emergence of Arboviruses in the United States: The Boom and Bust of Funding, Innovation, and Capacity. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 5(2), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020096





