Abstract
Scrub typhus and its etiological agents, Orientia species, have been around for a very long time. Historical reference to the rickettsial disease scrub typhus was first described in China (313 AD) by Hong Ge in a clinical manual (Zhouhofang) and in Japan (1810 AD) when Hakuju Hashimoto described tsutsuga, a noxious harmful disease in the Niigata prefecture. Other clinicians and scientists in Indonesia, Philippines, Taiwan, Australia, Vietnam, Malaysia, and India reported on diseases most likely to have been scrub typhus in the early 1900s. All of these initial reports about scrub typhus were from an area later designated as the Tsutsugamushi Triangle—an area encompassing Pakistan to the northwest, Japan to the northeast and northern Australia to the south. It was not until the 21st century that endemic scrub typhus occurring outside of the Tsutsugamushi Triangle was considered acceptable. This report describes the early history of scrub typhus, its distribution in and outside the Tsutsugamushi Triangle, and current knowledge of the causative agents, Orientia species.
1. Early History of Scrub Typhus and the Etiologic Agents of the Tsutsugamushi Triangle
1.1. Scrub Typhus Disease Presentation and Diagnosis
Scrub typhus, a febrile disease with mild to life-threatening manifestations, is characterized by rapid onset of fever, headache, chills, arthralgias and myalgias and often the presentation of eschar prior to and a macularpapular rash following initiation of disease [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The illness lasts approximately 3 weeks and ends without sequalae. Rapid response (24–72 h) to antibiotic treatment with tetracyclines, chloramphenicol, and azithromycin is characteristic and diagnostic [2,3,5,6]. In fatal cases, the disease is characterized by multi-organ failure, with pathologic lesions in lungs, kidneys, liver, and brain [3,5].
The lack of scrub typhus-specific signs and symptoms makes the clinical diagnosis very difficult [2,3,5]. Moreover, laboratory diagnosis at the time of illness is also very difficult, as antibodies do not reach detectable levels for 5–10 days after disease presentation, and the level of orientiae in the blood stream demonstrable by molecular methods only reaches detectable levels sporadically during acute illness and is unapparent after initial treatment with appropriate antibiotic treatment [7]. The specimen of choice, biopsy of eschar and/or rash, is unfortunately rarely obtained, though the level of Orientia DNA is in abundance, unaffected by prior antibiotic treatment, and maintained in the lesion for the life of the lesion [7].
1.2. Early History of Scrub Typhus
China
Historically, scrub typhus has been around for a very long time. Human historical reference to scrub typhus (Table 1) was first described in China’s Zhouhofang, a clinical manual, in 313 AD [8]. Subsequently, in 610, Yuan-Fang Chao described the epidemiology, clinical course, and treatment of the disease in a poem, which is considered medically accurate [8] and Shi-Zhen Li, a well-known physician, described the characteristics of the disease in a book entitled, “Ben Cao, Gang Mu” in 1596 [8]. In 1908, Ashburn and Craig reported that in China, “shashitsu,” the name for scrub typhus, occurred in old Chinese writings of more than a thousand years (Table 2). The authors also indicated that the Chinese recognized the disease as a distinct illness, and it was attributed to the bite of a mite which occurred in summer in certain districts that had been flooded by spring rains [1]. The red lice (sna ra) or mites had been associated with illness characterized by fever and a pustule at the site of injury. Moreover, they recognized that three days after the bite, high fever developed, and a pustule appeared at the site of the injury [1]. Clearly, the Chinese were well aware of scrub typhus (shashitsu) and for an extensive period of time.

Table 1.
Early History of Scrub Typhus.

Table 2.
Synonyms for Scrub Typhus.
Japan
In Japan, in 1810, Hakuju Hashimoto described “tsutsuga”, a noxious harmful disease in the Niigata prefecture of the main island of Japan [9]. However, according to Tanaka, as described in Ashburn and Craig [1], the name tsutsugamushi (tsutsuga = disease/illness and mushi (bug/insect)) has been around since the earliest historical times in Japan. Though reports of tsutsugamushi disease, from the northwest coast of the main island, Nippon (the two prefectures, Akito and Echigo, later changed to three prefectures, Akito, Yamagata and Niigata), and research associated with it was published in Japanese medical and science journals, it was not until Theobald Palm in 1878 [10] and Bälz and Kawakami in 1879 [11] that tsutsugamushi disease from Japan was reported in European journals.
The Etiology of Scrub Typhus in Japan
Up until the 1920s, the etiology of tsutsugamushi and, therefore, scrub typhus was unknown. In addition, multiple diseases which were later believed to be synonymous with tsutsugamushi were known as Japanese river fever, flood fever, island fever, Kedani (mite) disease, akamushi disease, shimamushi disease yochubio, and shashitsu [1] (Table 2). During the 1920s, the laboratories of Hayashi, Nagayo, Ogata, and Kawamura were working to discover the causative agent of tsutsugamushi. At this time, it was postulated that spirits, noxious air, parasites, bacteria, and viruses were possible causes of tsutsugamushi. In 1920, Hayashi indicated that the causative agent was a protozoan and named the agent Theileria tsutsugamushi [12]. However, by 1924, Hayashi indicated that the agent was not a protozoan, but most likely a rickettsia [13], as described by Kawamura et al. [8]. Hayashi, however, did not give his new agent a binomial name [8]. In the meantime, Nagayo demonstrated the causative agent of scrub typhus could be maintained in human and dog macrophages and that the agent could be passed to and cause disease in monkeys by intradermal and intracutaneous inoculations [14], as described by Kawamura [8]. In 1929, Ogata and Unno used a rabbit intratesticular inoculation technique to obtain the tsutsugamushi agent from a human blood sample and passed it to other rabbits (testis) [15]. This was the first time that the scrub typhus agent was isolated from a human following inoculation of the patient’s blood into rabbit testis and, subsequently, transferring the agent from that rabbit into another rabbit, showing the ability of the causative agent to be isolated and transferred [8]. Unfortunately, Ogata and Unno did not provide a binomial name for the agent in their report. However, they did provide the agent and the methodology to both Nagayo and Kawamura laboratories [8]. Ogata, subsequently, developed a new rabbit model for tsutsugamushi. This entailed infecting the anterior chamber of rabbits’ eyes. This proved to be a far more sensitive method of infection and, subsequently, Nagayo used this tsutsugamushi model in his laboratory [8]. Moreover, Nagayo utilized the agent from Ogata and the inoculation of the anterior chamber of rabbit eyes to grow a large number of rickettsiae. These organisms could, subsequently, be maintained in rabbit Descemet’s membrane cell cultures. The results and the proposed name for the agent of tsutsugamushi, Rickettsia orientalis, was reported in 1930 in the Japanese Journal of Experimental Medicine [16], as described by Kawamura et al. [8]. Ogata and Kawamura, also utilizing Ogata’s agent, reported on the etiology of tsutsugamushi in the German journal Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie in the same issue in 1931, naming the agent as Rickettsia tsutsugamushi and Rickettsia akamushi, respectively [17,18], as described by Kawamura et al. [8] (Table 3). In 1932, Hayashi concluded that his agent was the same as Ogata’s R. tsutsugamushi and Nagayo’s R. orientalis [19]. Further, also in 1932, Ogata reported a new laboratory animal model for tsutsugamushi—the intraperitoneal (IP) inoculation of mice for the growth of R. tsutsugamushi [20], as described by Kawamura et al. [8]. This is a scrub typhus laboratory animal model that is still used today [21]. In the 6th edition of Bergey’s manual, the name of the agent for scrub typhus was reported as O. tsutsugamushi. Though much controversy was associated with this name [8], it was not completely resolved until 1995 when R. tsutsugamushi was moved out of the genus Rickettsia and into its own genus Orientia, with the new species name, Orientia tsutsugamushi [22] (Table 3).

Table 3.
Previous and Current Names of the Scrub Typhus Agent from the Tsutsugamushi Triangle.
Indonesia
During the early 1900s, other clinicians and scientists in Asia, Australia, and Islands of the Indian and Pacific Oceans reported on local diseases most likely to have been scrub typhus (Table 2). Dr. Schüffner of Deli, Sumatra, Indonesia, described a disease, pseudotyphoid, that resembled scrub typhus as early as 1902 [23]. Later, he indicated that this disease was similar to Kedani fever (later determined to be scrub typhus) in Japan [24]. Subsequently, scrub typhus was discovered to be endemic for many islands throughout the Indonesian archipelago [25,26,27,28,29,30].
Taiwan
In 1908, Japanese clinicians reported that eastern Taiwan had a febrile disease with a rash that was reported as a tsutsugamushi disease-like ailment and was confirmed in 1914 to be a tsutsugamushi disease but with a lower fatality rate (approximately 3%), which was significantly different to the high mortality rate (~20–40%) seen with tsutsugamushi in Japan at this time [31]. Scrub typhus continues to be associated with the main island of Taiwan [32,33] as well as the highly endemic Pescadores Islands of the South China Sea [34,35,36].
The Philippines
Further, also in 1908, two cases of tsutsugamushi disease were described for two US military personnel, stationed at Camp Connell, Samar, the Philippines, based upon clinical records [1]. Ashburn had just returned from Japan where he had seen many cases of tsutsugamushi that Japanese clinicians had shown him prior to reviewing the clinical records for these two cases and reporting about the cases and tsutsugamushi disease [1]. During the repatriation of the Philippines in WWII, 284 cases of scrub typhus occurred in the month of November, 1944 [37,38]. One of the isolates from a US soldier deployed to the Guinan region of Samar Island, Volner strain, was used to develop a lyophilized rat lung-spleen vaccine. This was the first US scrub typhus vaccine ever tested in a field trail, that was unfortunately unsuccessful [39]. Subsequently, studies showed evidence of scrub typhus throughout the Philippines [37,40].
Australia
In 1910, Mossman fever, later described as endemic glandular fever and, subsequently, determined to be scrub typhus, was reported in North Queensland, Australia [41,42,43,44]. The endemic region of scrub typhus in Australia now includes Queensland [45,46], the islands of the Torres Strait [46], the Northern Territory [47], and western Australia [48,49].
Vietnam
In 1915, a fever of unknown etiology among two individuals was reported in Saigon, Vietnam [50] to be a disease similar to that described in Deli, Sumatra (i.e., pseudotyphoid), that was later determined to be scrub typhus [24]. Subsequently, the presence of scrub typhus throughout Vietnam was confirmed [38,51,52,53,54,55,56,57].
Korea
In 1915, a “mild” rickettsial disease called paratyphus was reported among 15 patients (no deaths) in the spring of 1913–1914 from Jemulpo, Incheon, Korea by Weir, a medical missionary [58]. Because only mild disease presentations with no deaths were associated with paratyphus, it was thought not to be epidemic typhus, which was endemic for Korea at the time. Moreover, the disease only developed during March–June and, in retrospect, it was assumed not to be murine typhus (seen year round and most commonly in the fall) or tsutsugamushi disease (seen in summer and fall). Thus, Chung and Kang believe it could have been Brill–Zinsser disease and not scrub typhus [59].
During the period of 1910–1945, there was some evidence of endemic scrub typhus in Korea. A study of mites attached to wild rats collected in Suwon were similar to Trombicula akamshi. In addition, rickettsial diseases with mild presentations and low OX19 titers may not have been murine typhus but scrub typhus [59]. During Japanese occupation, the Japanese physicians considered tsutsugamushi disease a severe disease with a 15–60% mortality rate. Thus, they may have overlooked a milder form of scrub typhus in Korea. In addition, the Weil–Felix test with OXK was not often utilized [59]. Following 1945, evidence increased for the presence of scrub typhus in Korea [59] and consequently the endemicity of scrub typhus became obvious by detection of infected mites, rodents and humans [60,61,62,63]. In recent years, there has been an ever-increasing number of scrub typhus cases reported in South Korea (2637 cases in 2001 to 10,485 cases in 2013) [59,64].
Malaysia
In 1900, the Institute of Medical Research (IMR) in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, was established as the Pathological Institute with the aim to promote the health status of the local population. In 1924, the institute began research on “tropical typhus” in the Federated Malay States. In the annual IMR Bulletin in 1925, Fletcher and Lesslar described tropical typhus as containing two components—an urban or shop typhus and a rural or scrub typhus [65].
Due to the fortuitous change in the composition of the Weil–Felix test, “tropical typhus” could be divided into two unique diseases. The Weil–Felix test initially utilized the strain of Bacillus proteus X.19 (Proteus vulgaris) that was isolated from the urine of a patient with epidemic typhus [66]. The P. vulgaris agent was not the cause of the disease but was found to be agglutinated by antibodies developed during epidemic typhus. The cross-reactivity of the antibodies to the P. vulgaris antigens (OX19) has been successfully used since 1916 to serologically diagnose epidemic typhus and murine typhus. Subsequently, another strain of P. vulgaris (OX2) was identified that reacted with the sera of spotted fever patients [7]. These patients also reacted to the OX19 to varying degrees. A third agglutinin (OXK) was, subsequently, identified in 1926 [67]. It was the Proteus mirabilis Kingsbury strain which reacted with sera from scrub typhus patients but not with sera from typhus or spotted fever patients [68,69]. With that new development, Fletcher and Lessar concluded that the rural tropical typhus or scrub typhus was the same as or similar to tsutsugamushi and unique from urban or shop typhus and other rickettsial diseases [70,71]. Moreover, it was determined that the urban or shop typhus form of tropical typhus was clinically the same as Brill’s disease and had the same Weil–Felix results. This disease was later referred to as murine typhus and the causative agent identified as Rickettsia typhi [72]. Throughout the subsequent history of the IMR scrub typhus, research continued with major advances in O. tsutsugamushi isolations, diagnostics, treatment/prophylaxis, vaccine and immunology research, and vector and ecology research [38]. Scrub typhus research is not limited to the IMR as indicated by recent publications [73,74,75,76,77,78].
India, Burma, Ceylon, and the Maldives
In 1932, Christian reported OXK-positive typhus cases that he believed were due to tick bites [79]. Due to the serologies conducted, they were most likely the first cases of scrub typhus reported from India. Similarly, in 1934, scrub typhus (OXK+) was reported among personnel from Simla Hills, India [80]. An investigation by Mehta reported the presence of Trombicula deliensis on rodents and shrews in the Simla Hills, suggesting that similar to the reports from Malaya, that these mites may be the vectors of scrub typhus [81]. Boyd reported on the presence of typhus among 110 cases in 1935, utilizing clinical presentations and Weil–Felix OXK serologies [82]. Interestingly, none of the OXK-positive cases in India presented with eschars [83]. In 1944, a report of two outbreaks of scrub typhus, which occurred during the period of 1937–1938 (n = 11) and 1939–1942 (n = 30), that were confirmed by Weil–Felix serology also indicated no presence of eschars [84]. One case from Boyd’s 110 cases was an individual who was OXK+ from Burma [82]. Subsequently, a study by Maitra and Sen Gupta showed the presence of scrub typhus and murine typhus (OXK and OX19 positive, respectively) in Burma [85]. The famous prototype, O. tsutsugamushi Gilliam, was contracted by Dr. Gilliam in 1944 on the equally famous Stillwell Road, in Burma [67]. Nicholls reported OXK-positive cases of tsutsugamushi (rural typhus) in nearby Ceylon [86]. Similarly, in Maldives, outbreaks of scrub typhus among British troops struck during the period of 1941–1944 [87]. Scrub typhus outbreaks occurred again in the period of 2002–2003 among the inhabitants of the Maldives, indicating the endemic nature of this disease [88]. This is certainly the case for India, where numerous publications have shown the breadth of scrub typhus throughout the subcontinent [89,90,91,92,93].
1.3. The Tsutsugamushi Triangle
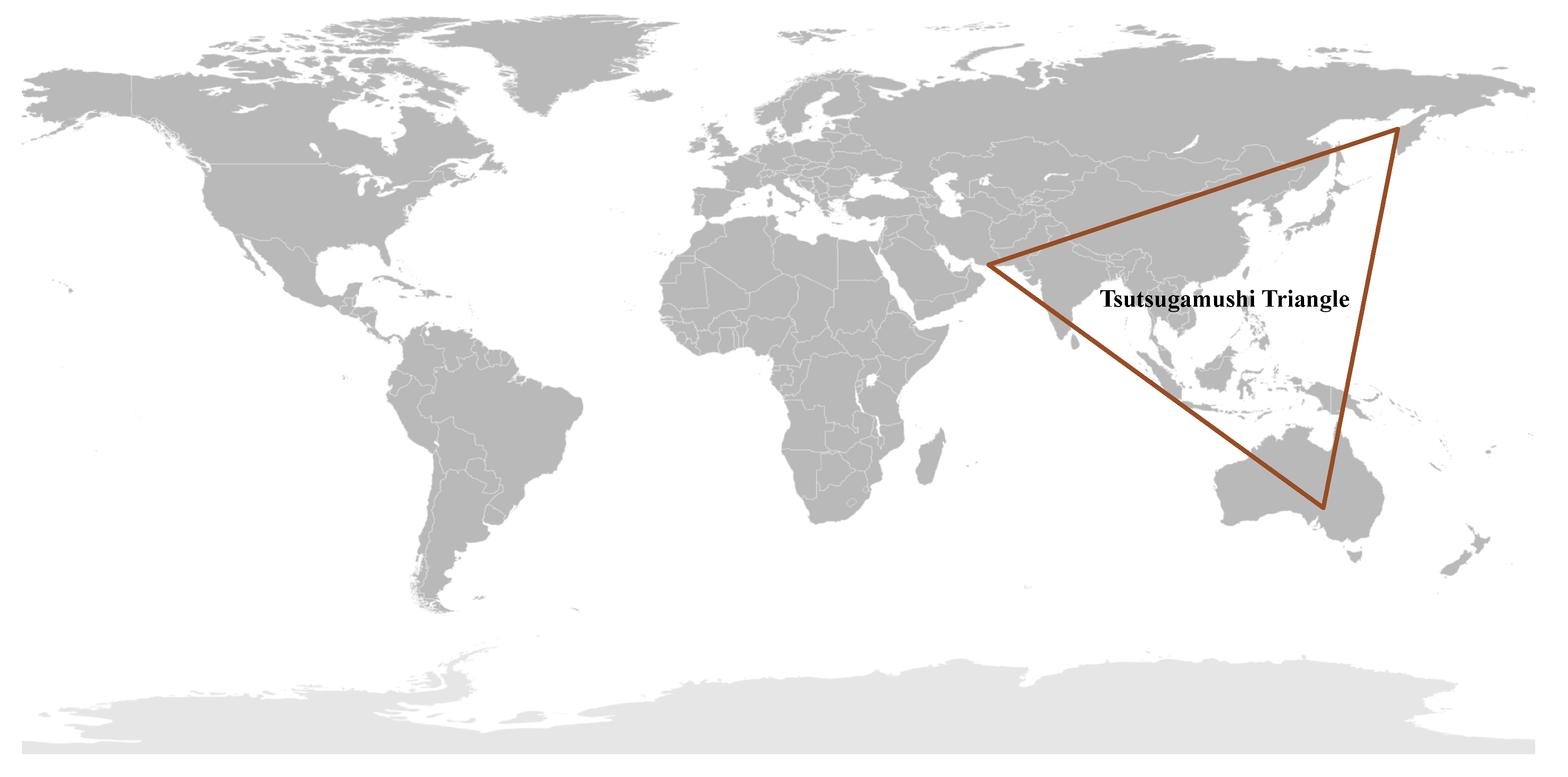
All of these reports of scrub typhus or diseases very similar to them throughout the Asia–Pacific region prior to WWII led to the assumption of a single rickettsial disease for a very large endemic region where many people were at risk of disease. Unfortunately, this assumption of a very large endemic area of scrub typhus was reinforced during WWII, where approximately 18,000 cases occurred among the allied forces and a similar number among the Japanese forces in the islands of Ceylon, Maldives, New Britain, Goodenough, and the Schouten Islands, and in the countries of China, Thailand, Japan, Australia, Lao, Cambodia, Vietnam, and Taiwan [25,37,38,83]. Contemporary reviews indicated the extent of scrub typhus distribution throughout the Tsutsugamushi Triangle [4,6,83,94,95,96,97,98], which included countries in the west (Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Nepal, India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Maldives), northeast (China, Russia, Republic of Korea, Japan, and Taiwan), south (Australia, Papua New Guinea, Indonesia, and the islands of the southwestern Pacific), and middle (Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Malaysia, Vietnam, and Philippines) (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
The Tsutsugamushi Triangle: Geographical Distribution of Scrub Typhus Caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi.
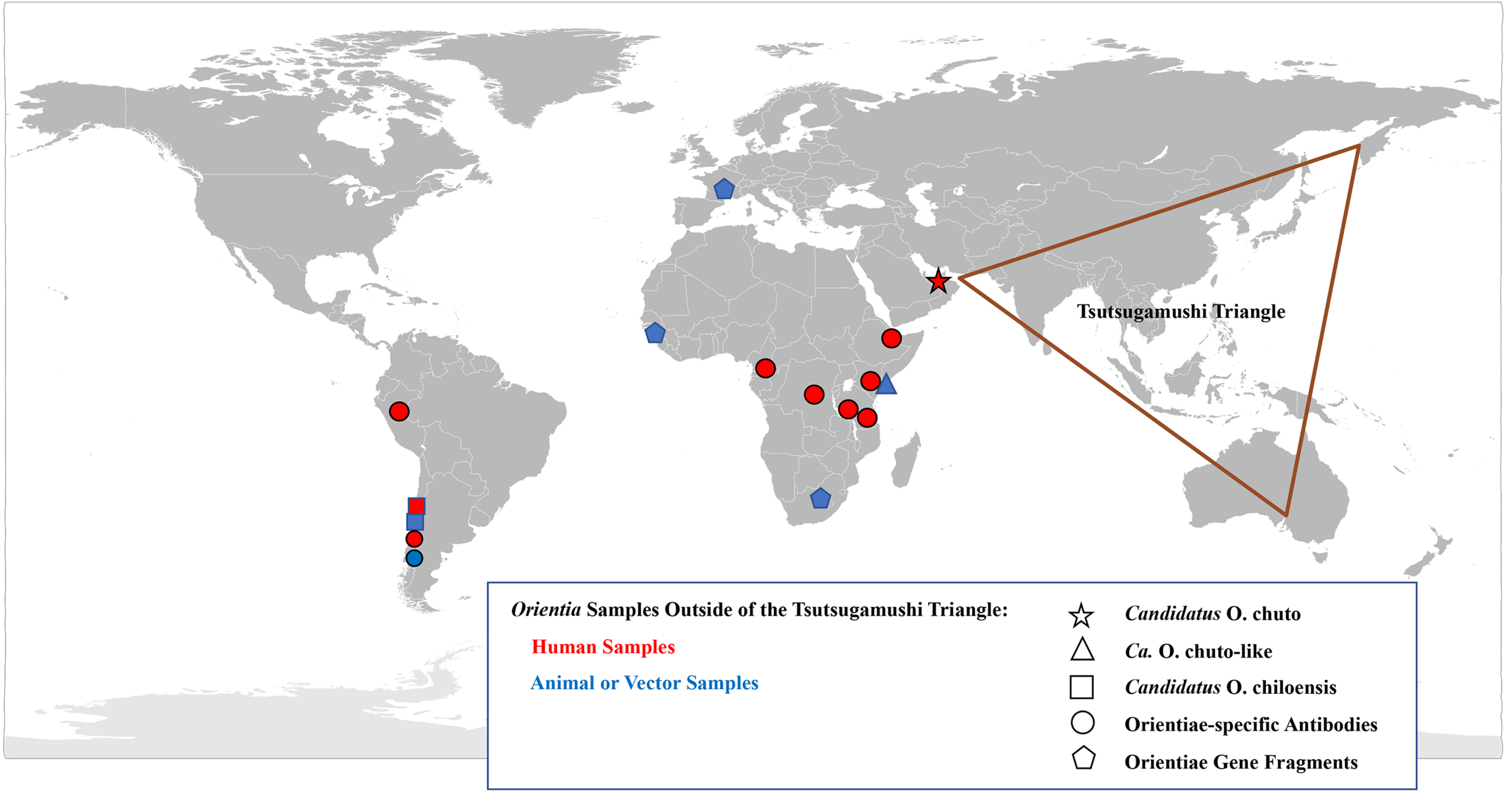
Consistent within the Tsutsugamushi Triangle has been the presence of a single species of Orientia which was identified within human cases, vector mites and mammalian hosts [8,83,94,98]. This species, O. tsutsugamushi, has a diversity of antigenic phenotypes and genetic genotypes found not only between countries but within countries [94,99,100]. However, as early as 1951, reports suggesting that scrub typhus occurred outside of the Tsutsugamushi Triangle began to emerge (Figure 2).
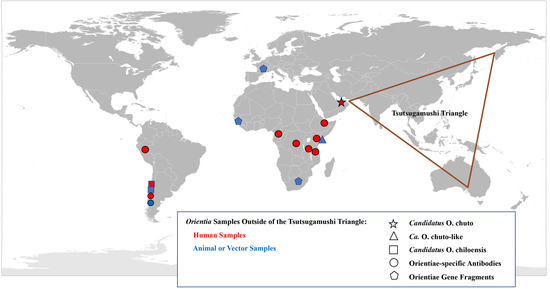
Figure 2.
Geographical Distribution of Orientia spp. and the Scrub Typhus: A Worldwide Disease.
2. Scrub Typhus Outside the Tsutsugamushi Triangle
2.1. Case Investigations
Africa
In 1951, Giroud and Jadin published a report that indicated that scrub typhus occurred outside the Tsutsugamushi Triangle. This report described an outbreak of a febrile disease among native Africans from Ruanda-Urundi working on constructing a factory building in Musha Hill, Belgian Congo (now Rwanda and Burundi) [101]. To investigate the outbreak, the authors utilized tests/reagents available at the time to determine whether the illness was due to rickettsiae or coxiella infections. Due to the existence of R. orientalis (O. tsutsugamushi) antigens, the authors included scrub typhus in the panel of rickettsial diseases to assess. Among the ill Africans, several were positive for the various rickettsial antigens, including two individuals who reacted to the R. orientalis antigens. To confirm the skin tests, blood from the two Orientia-positive patients were tested for complement-fixing antibodies to O. tsutsugamushi and were found to be positive, with titers of 80 and 320. To assess the reactivity to the scrub typhus assays in other populations who lived closely with native Africans in Musha Hill, healthy individuals, including nine people born in Muscat, Oman, five born in Bombay, India, and two born in Africa, with parents who were born in Bombay, were tested using the same skin and blood tests for evidence of previous O. tsutsugamushi infection. The authors considered Muscat and Bombay as scrub typhus-endemic regions and thought that people from those areas may be antibody positive to O. tsutsugamushi and may, therefore, act as positive controls. Of the nine individuals, originally from Muscat, three had strong, weak, and negative skin reactivity and antibodies against O. tsutsugamushi were detected with titers of 1280 (four individuals) and 640 (three individuals) in eight. Of the five people born in Bombay, three displayed positive skin reactivity to O. tsutsugamushi antigens and, interestingly, the two people whose parents were from Bombay, but who were born in and never traveled outside of eastern Africa, were also positive. These results suggested the presence of scrub typhus in eastern Africa. The authors indicated that a similar study they conducted among natives in western Africa showed that they were negative for evidence of scrub typhus [101].
In the 1990s, three case reports insinuated, but could not confirm, the presence of scrub typhus in Africa. The first described an individual from Japan visiting the Republic of Congo, who presented with fever six days after his return from Africa [102]. The disease was identified as scrub typhus, though the possibility could not be ruled out that the patient had contracted scrub typhus in Japan, within the Tsutsugamushi Triangle, during the six days prior to disease presentation. The second case involved a US missionary who visited Cameroon [103]. Within two weeks of his visit, the missionary noted a lesion on his leg and he had a fever and a rash three days later. Two weeks later, the missionary returned to the US and was, subsequently, admitted to a hospital in which he was treated for a rickettsial disease. He recovered within 24 h with doxycycline treatment and he had a four-fold rise in titer from 256 to 1024 of antibodies against O. tsutsugamushi. Unfortunately, no molecular or culture evidence confirmed the case of scrub typhus. The third case was of an individual who had visited Tanzania [104]. She had noted a lesion on her right foot and had a three-day history of fever and headache after returning to the Netherlands. Her acute and convalescent sera showed a seroconversion against O. tsutsugamushi antigens from <16 to 1024 by an indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA). Regrettably, none of these three cases had produced a culture of Orientia or had molecular evidence of the causative agents, thus, they were considered presumptive scrub typhus cases.
These results collectively implied that scrub typhus was endemic to Africa (Table 4) and the first study similarly implied the presence of scrub typhus in Arabia, both locations outside the Tsutsugamushi Triangle. Nevertheless, this notion of scrub typhus outside the Tsutsugamushi Triangle was not generally accepted and, therefore, scrub typhus was still considered an Asian-Australian-Pacific disease [94].

Table 4.
Evidence of Scrub Typhus Outside of the Tsutsugamushi Triangle.
United Arab Emirates
Conversely, the concept of scrub typhus as endemic outside of the Tsutsugamushi Triangle was firmly established with a 2010 report of a case contracted in Dubai, United Arab Emirates [105]. Not only was there serological evidence, but also molecular evidence and a culture of the infecting agent (Figure 3). The data substantiated the presence of scrub typhus on the Arabian Peninsula and the existence of a unique Orientia species other than O. tsutsugamushi (Table 5). The incompletely characterized agent has the proposed name of Candidatus Orientia chuto [105].
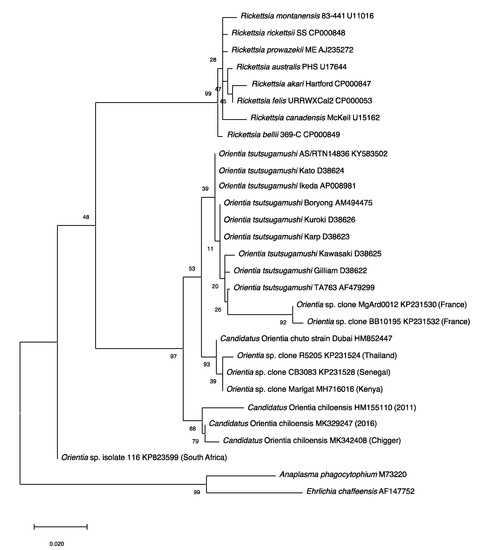
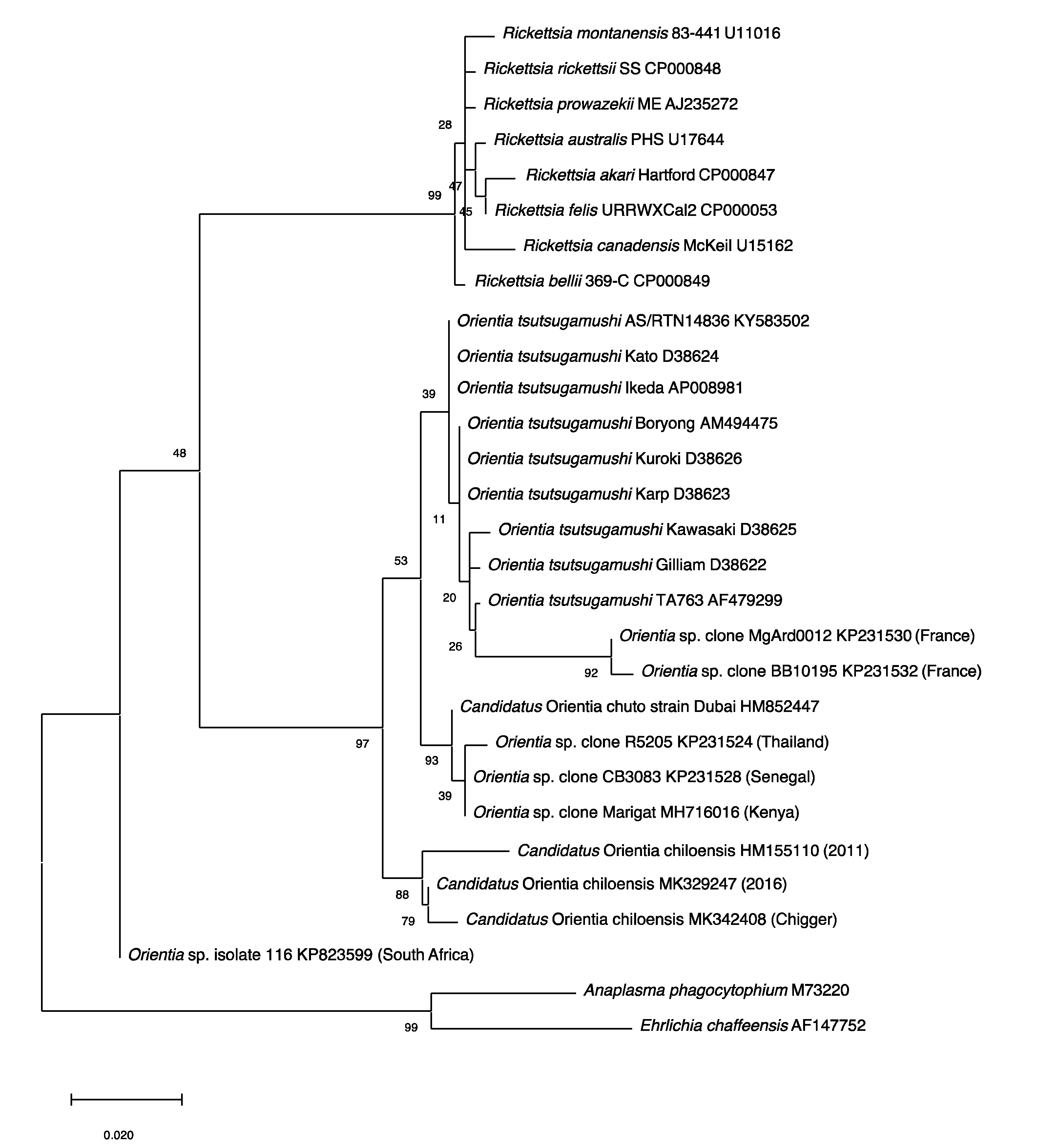
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic Tree. The evolutionary relationships of Orientia species detected outside of the Tsutsugamushi Triangle were compared with Orientia tsutsugamushi strains, Rickettsia species and other bacteria. The tree was constructed with the 560 bp rrs gene fragments using the Maximum Likelihood method and the Tamura–Nei model in MEGAX. The values of the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) were shown next to the branches.

Table 5.
Current Known and Proposed Agents of Scrub Typhus.
Chile
Subsequently, in 2011, a report of a scrub typhus case in Chile appeared that proved the existence of scrub typhus worldwide [106].
Unfortunately, an isolate was not recovered, though the limited molecular characterization of the Orientia DNA indicated, like the Ca. O. chuto, that this Orientia was not O. tsutsugamushi or for that matter Ca. O. chuto [106] (Figure 3).
2.2. Serological Evidence of Scrub Typhus Outside the Tsutsugamushi Triangle
Following these two astounding reports, investigators looked to confirm and expand upon these results, utilizing current serological and molecular assays for evidence of Orientia spp. infections outside of the Tsutsugamushi Triangle. Serological assays previously used for detecting rickettsial diseases outside of the Tsutsugamushi Triangle did not include those for scrub typhus group orientiae (STGO). Similarly, molecular assays for orientiae were not used to investigate the presence in mammalian hosts and/or arthropod vectors of orientiae outside of the Tsutsugamushi Triangle. This paradigm was changed with the two reports of scrub typhus in the United Arab Emirates and Chile. Thus, scientists included scrub typhus serological and molecular assays to conduct surveillance studies of rickettsial diseases in areas of Africa, South America, and Europe (Table 4). This resulted in the substantiation of scrub typhus outside of the Tsutsugamushi Triangle. In 2015, the first of these reports was of a seroprevalence study of fever patients from hospitals in Kenya. It was determined that 70 of 1401 (5%) patients had antibodies against O. tsutsugamushi that was confirmed by Western blot assays [107]. In an unrelated investigation conducted in western Kenya among sick children, paired acute and convalescent serum samples were tested, and it was determined that 15 of 281 patients (5.8%) had antibodies against O. tsutsugamushi ELISA antigens and 10 of these children seroconverted to O. tsutsugamushi antigens (3.6%). The seroreactivity was confirmed by Western blot analysis [108]. In Djibouti, a 20 week serosurvey of abattoir workers was conducted to determine their exposure to infectious disease agents. From multiple serum samples, it was ascertained that 3 of 49 workers had antibodies against O. tsutsugamushi ELISA antigens and one individual who reported a history of a febrile disease during the period of the study seroconverted to O. tsutsugamushi antigens by ELISA, IFA and Western blot tests [109].
2.3. Molecular Evidence of Scrub Typhus Outside the Tsutsugamushi Triangle
In addition to the serological data, molecular evidence for the presence of orientiae in Africa was conveyed in three separate reports (Figure 3). In 2015, Cosson et al. reported the presence of Orientia DNA among tissues of rodents from West Africa and Europe [110]. In South Africa, DNA preparation from the blood of a healthy dog from Mpumalanga Province had a 16S rRNA sequence that was 96.1% (247/257 bp) similar to that of Orientia spp. [111]. In East Africa, a rodent survey was conducted in a village where individuals who resided there had tested positive for antibodies against O. tsutusgamushi. Trombiculid mites were collected from the trapped rodents to assess them for molecular evidence of Orientia. DNA preparations provided evidence of Orientia species from sequences of gene fragments of the rrs and htrA that were most closely aligned to but not identical with Ca. O. chuto (Figure 3; Table 5) [112].
2.4. Endemic Scrub Typhus in South America
Two serological surveys were conducted in South America for rickettsial agents. The first, in Peru, assessed the role of rickettsial diseases in fever patients in the city of Iquitos on the Amazon river. It was determined that of 1124 individuals enrolled in the febrile surveillance study, 60 (5.3%) were seropositive against O. tsutsugamushi ELISA antigens and one person had a four-fold rise in titer, which suggested that he had scrub typhus. The ELISA results of this sample were confirmed by IFA [113]. The second survey involved a cross-sectional survey of dogs from Chiloé Island, the initial scrub typhus focus center in Chile [106,114]. It was revealed that of 202 dogs surveyed, 43 (21.3%) had immunoglobulin gamma (IgG) antibodies against O. tsutsugamushi antigens, with higher prevalence levels among dogs from rural areas and older dogs, and it was reported that dogs are a good sentinel animal for scrub typhus [115].
Since the initial scrub typhus case reported in 2011 [106], additional cases of scrub typhus (n > 40) [116] have been described from Chiloé Island [114,117] and from continental Chile [117,118]. The agents have been molecularly very much the same (Figure 3) from all cases from Chile [119], except for an imported case from the Republic of Korea, which was determined to be O. tsutsugamushi [120]. This is quite surprising when considering the extreme variation seen among the O. tsutsugamushi found throughout the Tsutsugamushi Triangle [94,99,100]. Similarly, characterization of orientiae from trombiculid mites of the genus Herpetacarus from Chiloé Island found the same orientiae as that associated with scrub typhus cases [121]. Thus, the molecular characterization of the agents both from human eschar/blood samples and trombiculid mites suggest a new scrub typhus agent, Candidiatus Orientia chiloensis (Figure 3; Table 5) [119,121].
The conservation of genetic variation in Chile orientiae may be related to the limitations placed on identifying cases and characterizing the agents—for the most part, utilizing clinical characteristics to identify cases (e.g., fever, headache, and eschar) and serological and molecular assays based upon O. tsutsugamushi antigens and sequences. Thus, as we identify more unique cases and develop better assays that are more sensitive and more generous in recognizing rare antibodies and sequences, with time, the antigenic and genetic variability of Chile orientiae may be discovered to be greater than current discoveries.
Author Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to the conceptualization, development and writing of the manuscript. All authors have read and agree to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Part of this material was presented at the 2nd Asia Pacific Rickettsia Conference, Chiang Rai, Thailand, 3–6 November 2019.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ashburn, P.M.; Craig, C.F. A comparative study of tsutsugamushi disease and spotted or tick fever of Montana. Boston Med. Surg. J. 1908, 158, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, G.; Kantipong, P. Orientia tsutsugamushi and scrub typhus. In Rickettsial Diseases; Raoult, D., Parola, P., Eds.; Informa Healthcare USA, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 237–256. [Google Scholar]
- Paris, D.H.; Shelite, T.R.; Day, N.P.; Walker, D. Unresolved Problems Related to Scrub Typhus: A Seriously Neglected Life-Threatening Disease. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.J.; Foley, D.; Richards, A.L. A spatiotemporal database to track human scrub typhus using the VectorMap application. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, S.; Weeratunga, P.; Sivayoganathan, S.; Fernando, S.D. Clinical manifestations of scrub typhus. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 111, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdad, M.Y.; Abdallah, R.A.; Fournier, P.-E.; Stenos, J.; Vasoo, S. A Concise Review of the Epidemiology and Diagnostics of Rickettsioses: Rickettsia and Orientia spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luce-Fedrow, A.; Mullins, K.; Kostik, A.P.; John, H.K.S.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L. Strategies for detecting rickettsiae and diagnosing rickettsial diseases. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 537–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, A., Jr.; Tanaka, H.; Tamura, A. Tsutsugamushi Disease; Univ. Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Yoshimoto, T. Scrub typhus in Japan. Am. J. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrobiol. 2019, 2, 1042. [Google Scholar]
- Palm, T.A. Some account of a disease called Shima Mushi or Island Insect Diseases by the natives of Japan. Edin. Med. J. 1878, 24, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Bälz, E.; Kawakami. Die Japanische Fluss-oder Ueber-schwemmungsfieber. Virchow’s Arch. 1879, 78, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N. Etiology of Tsutsugamushi disease. J. Parasitol. 1920, 7, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N. On Ricketts’ corpuscles. Trans. Japan. Pathol. Soc. 1924, 22, 569–576. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Nagayo, M.; Miyagawa, Y.; Mitamura, T.; Imamura, A.; Tamiya, T.; Sato, K. On the experimental Tsutsugamushi disease in monkeys by intracutaneous inoculation of the virus. Sci. Rep. Gov. Inst. Infect. Dis. 1923, 2, 371–373. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ogata, N.; Unno, Y. On the transfer of causative agent of Tsutsugamushi disease to the rabbit testis and microorgansims appearing in the testis. J. Chiba Med. Soc. 1929, 7, 1215–1222. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Nagayo, M.; Tamiya, T.; Mitamura, T.; Sato, K. On the virus of Tsutsugamushi disease and its demonstration by a new method. Trans. Japan Pathol. Soc. 1930, 20, 556–566. [Google Scholar]
- Ogata, N. Aetiology der Tsutsugamushikrankheit: Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Zbl f Bakt 1931, 122, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, R.; Imagawa, Y. Die Feststellung des Erregers bei der Tsutsugamushikrankheit. Zbl f Bakt 1931, 122, 261. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, N. On Tsutsugamushi disease. Trans. Japan Pathol. Soc. 1932, 22, 689–690. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ogata, N.; Nakajima, G.; Kajima, S. Animals employed for experimental infection by pathogenic rickettsiae in laboratory—Especially recommendation to use mouse for the detection of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Tokyo Med. J. 1932, 2760, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Luce-Fedrow, A.; Lehman, M.L.; Kelly, D.J.; Mullins, K.; Maina, A.N.; Stewart, R.L.; Ge, H.; John, H.S.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L. A Review of Scrub Typhus (Orientia tsutsugamushi and Related Organisms): Then, Now, and Tomorrow. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Ohashi, N.; Urakami, H.; Miyamura, S. Classification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in a New Genus, Orientia gen. nov., as Orientia tsutsugamushi comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüffner, W. Geneesk. Tijdschr. Med. Indie 1909, 49, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Schüffner, W. Pseudotyphoid fever in Deli, Sumatra (a variety of Kedani fever). Philipp. J. Sci. 1915, 10, 345. [Google Scholar]
- Logue, J.B. Scrub typhus. Report of epidemic in the Southwest Pacific. US Nav. Med. Bull. 1944, 43, 645–649. [Google Scholar]
- Hadi, T.R.; Nalim, S.; Sukaeri, S.; Dennis, D.T. Scrub typhus survey of Biak and Owi islands: ectoparasites of small mammals and rickettsial isolations. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1980, 11, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dennis, D.T.; Hadi, T.R.; Brown, R.J.; Sukaeri, S.; Leksana, B.; Cholid, R. A survey of scrub and murine typhus in the Ancol section of Jakarta, Indonesia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1981, 12, 574–580. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, A.L.; Soeatmandji, D.W.; Widodo, M.A.; Sardjono, T.W.; Yanuwiadi, B.; Hernowati, T.E.; Baskoro, A.D.; Roebiyoso, E.; Hakim, L.; Soendoro, M. Seroepidemiological evidence for murine and scrub typhus in Malang, Indonesia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 57, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.K.D. The Real Enemy: Scrub Typhus and the Invasion of Sansapor. Am. Entomol. 2009, 55, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Widjaja, S.; Williams, M.; Winoto, I.; Farzeli, A.; Stoops, C.A.; Barbara, K.A.; Richards, A.L.; Blair, P.J. Geographical Assessment of Rickettsioses in Indonesia. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatori, J. On the endemic tsutsugamushi disease in Formosa. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasit. 1919, 13, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, J.L.; Irving, G.S.; Wang, H.C.; Lien, J.C.; Chen, W.F.; Cross, J.H. Scrub typhus in Eastern Taiwan, 1970. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1974, 23, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Kuo, K.-C.; Sun, W.; Lin, J.-N.; Lai, C.-H.; Lee, C.-H. Clinicoepidemiologic characteristics of scrub typhus and murine typhus: A multi-center study in southern Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamiya, C.; Honda, S. Observations on tsutsugamushi disease of the Pescadores. J. Formosan Med. Assoc. 1933, 32, 1803–1804. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, W.C.; Chen, W.F.; Lien, J.C.; Hsu, S.H. Scrub Typhus in the Pescadores Islands: An Epidemiologic and Clinical Study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 13, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, J.; Ho, C.; Van Peenen, P.; Santana, F. Isolation of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi from mammals and chiggers (Fam. Trombiculidae) in the Pescadores Islands, Taiwan. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1978, 72, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, C.B.; Woodward, T.E.; Sullivan, R.R. Tsutsugamushi Disease (Scrub or Mite-Borne Typhus) in the Philippine Islands during American Re-Occupation in 1944–45. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1946, 26, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J.; Richards, A.L.; Temenak, J.; Strickman, D.; Dasch, G. The Past and Present Threat of Rickettsial Diseases to Military Medicine and International Public Health. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34 (Suppl. 4), s145–s169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, T.O.; Gauld, R.L.; Kitaoka, M. A field trial of a vaccine prepared from the Volner strain of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1949, 50, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.H.; Basaca-Sevilla, V. Seroepidemiology of scrub typhus and murine typhus in the Philippines. Philipp. J. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1981, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Smithson, O. Mossman Fever. J. Trop. Med. 1910, 13, 351. [Google Scholar]
- Breinl, A.; Priestley, H.; Fielding, J.W. On the occurrence and pathology of endemic glandular fever, a specific fever, occurring in the Mossman District of North Queensland. Med. J. Aust. 1914, 1, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breinl, A.; Priestley, H.; Fielding, J.W. On the occurrence and pathology of endemic glandular fever, a specific fever, occurring in the Mossman District of North Queensland. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1915, 30–33, Abstracted from the Med. J. Aust. 1914, 1, 391–395.. [Google Scholar]
- Langan, A.M.; Mathew, R.Y. The establishment of “Mossman,” “coastal” and other previously unclassified fevers of north Queensland as endemic typhus. Med. J. Aust. 1935, 2, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carley, J.G.; Doherty, R.L.; Derric, E.H.; Pope, J.H.; Emanuel, M.L.; Ross, C.H. The investigation of fevers in North Queensland by mouse inoculation, with particular reference to scrub typhus. Aust. Ann. Med. 1955, 4, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faa, A.G.; McBride, W.; Garstone, G.; Thompson, R.E.; Holt, P. Scrub Typhus in the Torres Strait Islands of North Queensland, Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odorico, D.M.; Graves, S.R.; Currie, B.; Catmull, J.; Nack, Z.; Ellis, S.; Wang, L.; Miller, D.J. New Orientia tsutsugamushii strain from scrub typhus in Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1998, 4, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, M.L.; Chappell, T.; Golledge, C.L. Scrub typhus in Western Australia. Commun. Dis. Intel. 1993, 17, 570–571. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, S.; Wang, L.; Nack, Z.; Jones, S. Rickettsia serosurvey in Kimberley, Western Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noc, F.; Gautron, P. Deux cas de fièvre indéterminée rappelant le pseudo-typhus de Delhi observés à Saigon. Bull. Soc. Med. Chir d’ Indoch. 1915, 6, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Beytout, D. Rickettsioses Diagnostiquées Par Microagglutination De Janvier 1962 A Juin 1963 A Saigon. Bull. Société Pathol. Exot. 1964, 57, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, V.; May, T.T.X.; Blasdell, K.; Lo, L.V.; Morvan, C.; Lay, S.; Anukool, W.; Wongprompitak, P.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; Laurent, D.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Cambodia and Central Vietnam reveals a broad region-wide genetic diversity. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 15, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, S.; Cuong, N.C.; Tra, D.T.; Doan, Y.H.; Shimizu, K.; Tuan, N.Q.; Yoshida, L.M.; Mai, L.Q.; Duc-Anh, D.; Ando, S.; et al. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of scrub typhus and murine typhus among hospitalized patients with acute undifferentiated fever in Northern Vietnam. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Pham, H.T.; Nguyen, T.V.; Hoang, P.V.; Le, M.T.; Takemura, T.; Hasebe, F.; Hayasaka, D.; Yamada, A.; Miura, K. The genotypes of Orientia tsutsugamushi, identified in scrub typhus patients in northern Vietnam. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 111, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Viet, N.; Laroche, M.; Pham, H.L.T.; Viet, N.L.; Mediannikov, O.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Use of eschar swabbing for the molecular diagnosis and genotyping of Orientia tsutsugamushi causing scrub typhus in Quang Nam province, Vietnam. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, N.V.; Hoi, L.T.; Toan, T.K.; Hoa, T.M.; Fox, A.; Van Kinh, N.; Van Doorn, H.R.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Bryant, J.E.; Nadjm, B.; et al. Seroprevalence of Scrub Typhus, Typhus, and Spotted Fever Among Rural and Urban Populations of Northern Vietnam. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trung, N.V.; Hoi, L.T.; Cuong, D.D.; Ha, D.T.; Hoa, T.M.; Lien, V.N.; Hoa, N.T.; Hoa, L.N.M.; Huong, D.T.; Bich, V.T.N.; et al. Analysis of the 56-kDa type specific antigen gene of Orientia tsutsugamushi from northern Vietnam. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, H.H. A continued fever of Korea. China Med. J. 1915, 29, 307–315. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, M.H.; Kang, J.S. History of tsutsugamushi disease in Korea. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 51, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.Y.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Seo, J.H.; Lim, J.W.; Yong, T.S.; Klein, T.A.; Lee, W.J. Geographical distribution and relative abundance of vectors of scrub typhus in the Republic of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Guinn, M.L.; Klein, T.A.; Lee, J.S.; Richards, A.L.; Kim, H.-C.; Ha, S.J.; Shim, S.H.; Baek, L.J.; Song, K.-J.; Chong, S.-T.; et al. Serological Surveillance of Scrub Typhus, Murine Typhus, and Leptospirosis in Small Mammals Captured at Firing Points 10 and 60, Gyeonggi Province, Republic of Korea, 2001–2005. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Kang, J.S. Isolation of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi from Korean patients. J. Korean Med. Assoc. 1987, 30, 999–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Myers, T.E.; Rozmajzl, P.J.; Graf, P.C.; Chretien, J.-P.; Gaydos, J.C.; Richards, A.L. Seroconversions to Rickettsiae in US Military Personnel in South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1073–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-W.; Cho, P.Y.; Moon, S.-U.; Na, B.-K.; Kang, Y.-J.; Sohn, Y.; Youn, S.-K.; Hong, Y.; Kim, T.-S. Current situation of scrub typhus in South Korea from 2001−2013. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, W.; Lesslar, J.E. “Tropical typhus” in the Federated Malay States; Bulletin Institute of Medical Research: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Cruikshank, R. The Weil-Felix reaction in typhus fever. J. Hyg. (Lond.) 1927, 27, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.J.; A Fuerst, P.; Richards, A.L. Origins, Importance and Genetic Stability of the Prototype Strains Gilliam, Karp and Kato of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, W.; Lessar, J.E. Tropical typhus in the Federated Malay States; Bulletin Institute of Medical Research: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1926. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, W.; Field, J.W. The Tsutsugamushi Disease in the Federated Malay States; Bulletin Institute Medical Research: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, W.; Lessar, J.E.; Lewthwaite, R. The aetiology of tsutsugamushi disease and tropical typhus in Federated Malay States: A preliminary note. Part, I. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1928, 22, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, W.; Lessar, J.E.; Lewthwaite, R. The aetiology of the tsutsugamushi disease and tropical typhus in Federated Malay States. Part II. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1929, 23, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, W. Tropical Typhus. BMJ 1932, 2, 1140–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, T.S.; Devi, S.; A Suan, K.; Chun, S.S.; Ming, H.T.; Yasin, R.M.; Kamalanathan, M. Seroepidemiologic survey of Orientia tsutsugamushi, Rickettsia typhi, and TT118 spotted fever group rickettsiae in rubber estate workers in Malaysia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 61, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tay, S.T.; Ho, T.M.; Rohani, M.Y.; Shamala, D. Antibody prevalence of Orientia tsutsugamushi, Rickettsia typhi and TT118 spotted fever group rickettsiae among febrile patients in rural areas of Malaysia. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 94, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwa, B.H. Environmental change, development and vector borne disease: Malaysia’s experience with filariasis, scrub typhus and dengue. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2006, 10, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, S.T.; Mohamed Zan, H.A.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Ngui, R. Antibody prevalence and factors associated with exposure to Orientia tsutsugamushi in different aboriginal subgroups in West Malaysia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed Zan, H.A.; Ponnampalavanar, S.; Faridah, S.O.S.; Savithiri, P.D.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Tay, S.T. Genetic variants of Orientia tsutsugamushi identified from scrub typhus cases in Malaysia. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 33, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Low, V.L.; Tan, T.K.; Khoo, J.J.; Lim, F.S.; Abubakar, S. An overview of rickettsiae in Southeast Asia: Vector-animal-human interface. Acta Trop. 2020, 202, 105282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, C.R. A case of typhus due to tick bite. J. R. Army Med. 1932, 59, 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- MacNamara, C.V. An epidemic of typhus (vector unknown) in the Simla Hills. J. R. Army Med. Corps 1934, 64, 174–186. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, D.R. Studies on typhus in Simla Hills. VIII. Ectoparasites of rats and shrews with special reference to their possible role in the transmission of typhus. Indian J. Med. Res. 1936, 25, 353–365. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, J.S.K. Fevers of typhus group in Inda: Analysis of 110 cases reported in 1934. J. R. Army Med. Corps 1935, 65, 289–305. [Google Scholar]
- Farner, D.S.; Katsampes, C.P. Tsutsugamushi disease. US Naval Med. Bull. 1944, 43, 800–836. [Google Scholar]
- Bardhan, P.N. Typhus in the United Provinces of India. Being a contribution to the study of typhus fever. Indian Med. Gaz. 1944, 79, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Maitra, G.C.; Gupta, P.N.S. A Note on Cases of Typhus Fever in Burma and Their Distribution. Indian Med. Gaz. 1936, 71, 572–574. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, L. A case of tsutsugamushi (rural typhus) in Ceylon. Br. Med. J. 1940, 2, 490. [Google Scholar]
- Audy, J.R. A summary topographical account of scrub typhus 1908–1946. In Bulletins from the Institute for Medical Research; Federation of Malaya, No.1 of 1949; Government Press: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, M.D.; Yousuf, A.A.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Razee, A.; Chandranoi, K.; Jones, J.W. Scrub Typhus Reemergence in the Maldives. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1638–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, G.M.; Janardhanan, J.; Mahajan, S.K.; Tariang, D.; Trowbridge, P.; Prakash, J.A.J.; David, T.; Sathendra, S.; Abraham, O.C. Molecular epidemiology and genetic diversity of Orientia tsutsugamushi from patients with scrub typhus in 3 regions of India. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahi, M.; Gupte, M.; Bhargava, A.; Varghese, G.M.; Arora, R. DHR-ICMR Guidelines for Diagnosis & Management of Rickettsial Diseases in India. Indian J. Med Res. 2015, 141, 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Bora, T.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L.; Dutta, P. Seroepidemiology of rickettsial infections in Northeast India. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Biswal, M.; Kumar, A.; Zaman, K.; Jain, S.; Bhalla, A. Scrub Typhus in a Tertiary Care Hospital in North India. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, R.; Thakur, C.K.; Gupta, N.; Sagar, T.; Bahadur, T.; Wig, N.; Sood, R.; Misra, M.C. Mortality due to scrub typhus—Report of five cases. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J.; Fuerst, P.A.; Ching, W.M.; Richards, A.L. Scrub typhus: The geographical distribution of phenotypic and genotypic variants of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, S203–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonell, A.; Lubell, Y.; Newton, P.N.; Crumb, J.A.; Paris, D.H. Estimating the burden of scrub typhus: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Walker, D.H.; Jupiter, D.; Melby, P.C.; Arcari, C.M. A review of the global epidemiology of scrub typhus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, M.; Zaman, K.; Suri, V.; Rao, H.; Kumar, A.; Kapur, G.; Sharma, N.; Bhalla, A.; Jayashree, M. Use of eschar for the molecular diagnosis and genotypic characterisation of Orientia tsutsugamushi causing scrub typhus. Indian J. Med Microbiol. 2018, 36, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, I.; Pearson, I.; Dahal, P.; Thomas, N.V.; Roberts, T.; Newton, P.N. Scrub typhus ecology: a systematic review of Orientia in vectors and hosts. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 513–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, E.M.; Chaemchuen, S.; Blacksell, S.D.; Richards, A.L.; Paris, D.; Bowden, R.; Chan, C.; Lachumanan, R.; Day, N.; Donnelly, P.; et al. Long-read whole genome sequencing and comparative analysis of six strains of the human pathogen Orientia tsutsugamushi. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleshman, A.C.; Mullins, K.E.; Sahl, J.W.; Hepp, C.M.; Nieto, N.C.; Wiggins, K.B.; Hornstra, H.; Kelly, D.J.; Chan, T.C.; Phetsouvanh, R.; et al. Comparative pan-genomic analyses of Orientia tsutsugamushi reveal an exceptional model of bacterial evolution driving genomic diversity. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroud, P.; Jadin, J. Presence des anticorps vis-a-vis de Rickettsia orientalis chez les indigenes et des Asiatiques vivant au Ruanda-urundi (Congo Belge). Bull. Société Pathol. Exotique 1951, 44, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Osuga, K.; Kimura, M.; Goto, H.; Shimada, K.; Suto, T. A case of tsutsugamushi disease probably contracted in Africa. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1991, 10, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, R.P.; Ghorbani, A.J.; Jain, M.K.; Walker, D.H. A case of scrub typhus probably acquired in Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 25, 1473–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.; Nur, Y.A.; Osterhaus, M.E. Scrub and murine typhus among Dutch travellers. Infection 1999, 27, 291–292. [Google Scholar]
- Izzard, L.; Fuller, A.; Blacksell, S.D.; Paris, D.H.; Richards, A.L.; Aukkanit, N.; Nguyen, C.; Jiang, J.; Fenwick, S.; Day, N.P.J.; et al. Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4404–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcells, M.E.; Rabagliati, R.; García, P.; Poggi, H.; Oddo, D.; Concha, M.; Abarca, K.; Jiang, J.; Kelly, D.J.; Richards, A.L.; et al. Endemic scrub typhus-like illness, Chile. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiga, J.W.; Mutai, B.; Eyako, W.; Ng’ang’a, Z.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L.; Waitumbi, J.N. High sero-prevalence and IgG titers for spotted fever and scrub typhus in patients with febrile illness in Kenya. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maina, A.N.; Farris, C.M.; Odhiambo, A.; Jiang, J.; Laktabai, J.; Armstrong, J.; Holland, T.; Richards, A.L.; O’Meara, W.P. Q fever, scrub typhus, and rickettsial diseases in children, 2011–2012 Kenya. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, K.C.; Jiang, J.; Maina, A.; Dueger, E.; Zayed, A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Pimentel, G.; Richards, A.L. Evidence of Rickettsia and Orientia infections among abattoir workers in Djibouti. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosson, J.F.; Galan, M.; Bard, E.; Razzauti, M.; Bernard, M.; Morand, S.; Brouat, C.; Dalecky, A.; Bâ, K.; Charbonnel, N.; et al. Detection of Orientia sp. DNA in rodents from Asia, West Africa and Europe. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolo, A.O.; Sibeko-Matjila, K.P.; Maina, A.N.; Richards, A.L.; Knobel, D.L.; Matjila, P.T. Molecular detection of zoonotic rickettsiae and Anaplasma spp. in domestic dogs and their ectoparasites in Bushbuckridge, South Africa. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masakhwe, C.; Linsuwanon, P.; Kimita, G.; Mutai, B.; Leepitakrat, S.; Yalwala, S.; Abuom, D.; Auysawasi, N.; Gilbreath, T.; Wanja, E.; et al. Identification and characterization of Orientia chuto in trombiculid chigger mites collected from wild rodents in Kenya. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01124-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, C.; Jiang, J.; Morrison, A.C.; Castillo, R.; Leguia, M.; Loyola, S.; Ampuero, S.; Bausch, D.G.; Richards, A.L. Scrub typhus in the Peruvian Amazon Basin. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1389–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzel, T.; Dittrich, S.; López, J.; Phuklia, W.; Martinez-Valdebenito, C.; Velásquez, K.; Blacksell, S.D.; Paris, D.H.; Abarca, K. Endemic scrub typhus in South America. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzel, T.; Jiang, J.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Martinez-Valdebenito, C.; Lopez, J.; Richards, A.L.; Abarca, K. Canine seroprevalence to Orientia species in southern Chile: A cross–sectional survey on the Chiloé Island. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, K.; Weitzel, T.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Acosta-Jamett, G. Scrub typhus, an emerging infectious disease in Chile. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2018, 35, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzel, T.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Richards, A.L.; Grobusch, M.P.; Abarca, K. Scrub typhus risk in travelers to southern Chile. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 29, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzel, T.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L.; Abarca, K. Scrub typhus in continental Chile, 2016–2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarca, K.; Martinez-Valdebenito, C.; Angulo, J.; Jiang, J.; Farris, C.M.; Richards, A.L.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Weitzel, T. Molecular description of a novel Orientia species causing scrub typhus in South America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Weitzel, T.; Aylwin, M.; Martinez-Valdebenito, C.; Jiang, J.; Munita, J.M.; Thompson, L.; Abarca, K.; Richards, A.L. Imported scrub typhus: First case in South America and review of the literature. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2018, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Jamett, G.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Beltrami, E.; Silva-de La Fuente, M.C.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L.; Weitzel, T.; Abarca, K. Identification of trombiculid mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) on rodents from Chiloé Island and molecular evidence of infection with Orientia species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).