Molecular Detection of Mutations in the penA and 23S rRNA Genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Related to Decreased Cephalosporin and Azithromycin Susceptibility in Rectal Specimens from Men Who Have Sex with Men (MSM) in Lima, Peru
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening of Rectal Clinical Samples Using Aptima Combo 2 Assay
2.2. DNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR Assay
2.3. Sanger Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Mutations in the 23S rRNA and penA Genes by MAMA-qPCR
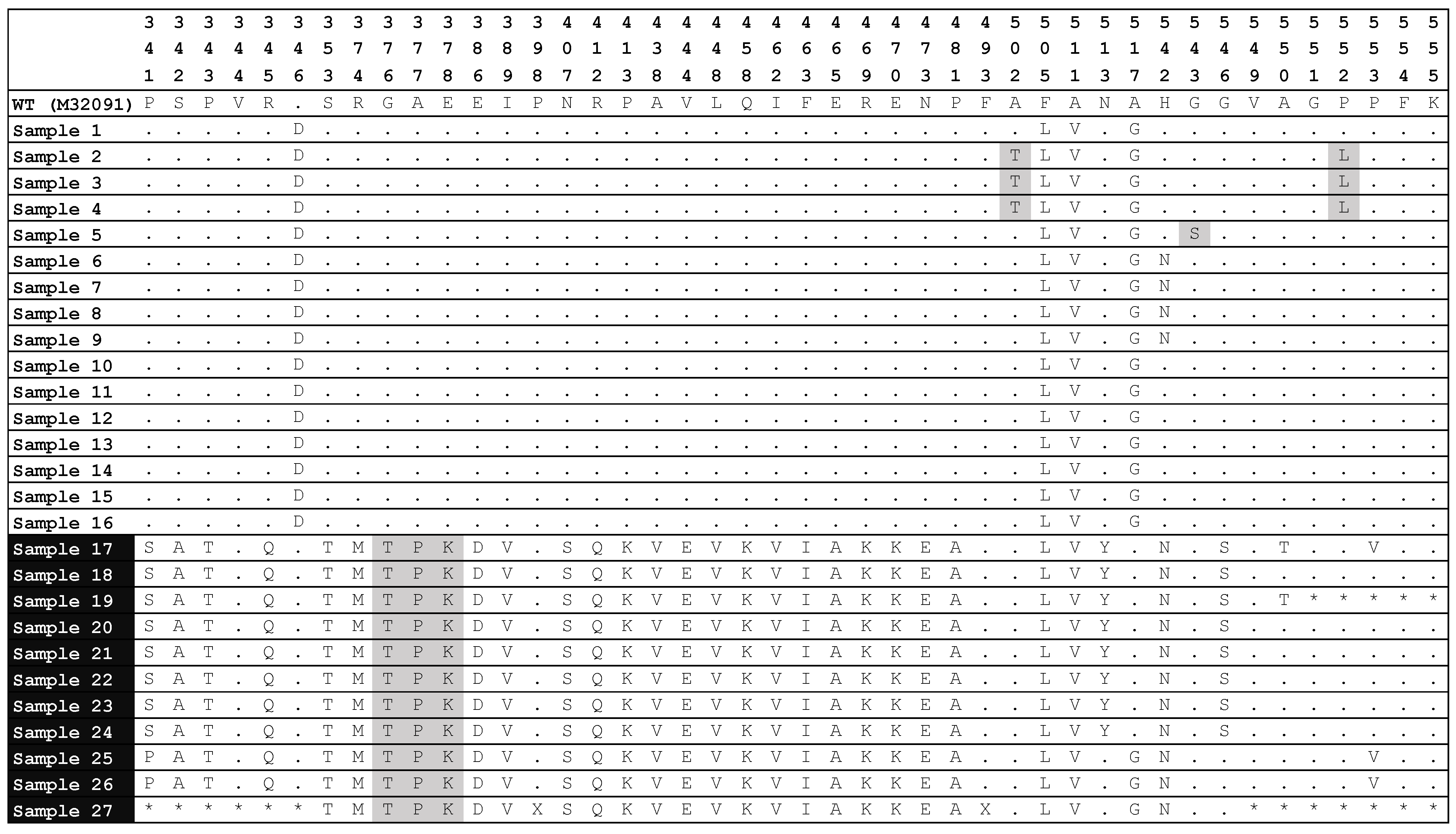
3.2. Analysis of Mutations in the 23S rRNA and penA Genes by Sanger Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Progress Report on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections, 2021. Accountability for the Global Health Sector Strategies 2016–2021: Actions for Impact; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240027077 (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Chan, P.A.; Robinette, A.; Montgomery, M.; Almonte, A.; Cu-Uvin, S.; Lonks, J.R.; Chapin, K.C.; Kojic, E.M.; Hardy, E.J. Extragenital Infections Caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis and Neisseria Gonorrhoeae: A Review of the Literature. Infect. Dis. Obs. Gynecol. 2016, 2016, 5758387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szetela, B.; Łapiński, Ł.; Giniewicz, K. Very High Incidence of Chlamydia Trachomatis, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae, and Treponema Pallidum among Low-Risk MSM in an Outpatient Clinic in Wroclaw, Poland in 2019–2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minetti, C.; Rocha, M.; Duque, L.M.; Meireles, P.; Correia, C.; Cordeiro, D.; João, I.; Manita, C.; Soeiro, S.; Santos, J.A.; et al. Orogenital and Anal Infection by Chlamydia Trachomatis, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae, Mycoplasma Genitalium, and Other Sexually Transmitted Infections in Men Who Have Sex with Men in Lisbon. Int. J. STD AIDS 2024, 35, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbee, L.A.; Dombrowski, J.C.; Kerani, R.; Golden, M.R. Effect of Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing on Detection of Extragenital Gonorrhea and Chlamydial Infections in Men Who Have Sex with Men Sexually Transmitted Disease Clinic Patients. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2014, 41, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-G.; Zhang, X.-H.; Zhao, P.-Z.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Ke, W.-J.; Ren, X.-Q.; Wang, L.-Y.; Chen, W.-Y.; Tucker, J.D. Gonorrhea and Chlamydia Prevalence in Different Anatomical Sites among Men Who Have Sex with Men: A Cross-Sectional Study in Guangzhou, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, S.R.; Segura, E.R.; Konda, K.A.; Flores, J.A.; Silva-Santisteban, A.; Galea, J.T.; Coates, T.J.; Klausner, J.D.; Caceres, C.F. High Prevalence of Chlamydia Trachomatis and Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Infections in Anal and Pharyngeal Sites among a Community-Based Sample of Men Who Have Sex with Men and Transgender Women in Lima, Peru. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e008245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unemo, M.; Shafer, W.M. Antimicrobial Resistance in Neisseria Gonorrhoeae in the 21st Century: Past, Evolution, and Future. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 587–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa-Lourenço, A.P.R.; Barros Dos Santos, K.T.; Moreira, B.M.; Fracalanzza, S.E.L.; Bonelli, R.R. Antimicrobial Resistance in Neisseria Gonorrhoeae: History, Molecular Mechanisms and Epidemiological Aspects of an Emerging Global Threat. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahata, S.; Senju, N.; Osaki, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Ida, T. Amino Acid Substitutions in Mosaic Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 Associated with Reduced Susceptibility to Cefixime in Clinical Isolates of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 3638–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gose, S.; Nguyen, D.; Lowenberg, D.; Samuel, M.; Bauer, H.; Pandori, M. Neisseria Gonorrhoeae and Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporins in California: Surveillance and Molecular Detection of Mosaic penA. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Le, W.; Genco, C.A.; Rice, P.A.; Su, X. Increase in Multidrug Resistant Neisseria Gonorrhoeae FC428-Like Isolates Harboring the Mosaic penA 60.001 Gene, in Nanjing, China (2017–2020). Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 4053–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianecini, R.A.; Poklepovich, T.; Golparian, D.; Cuenca, N.; Scocozza, L.; Bergese, S.; Canigia, L.F.; Vilches, V.; Lazzarino Elgart, M.J.; Unemo, M.; et al. Sustained Transmission of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Strains with High-Level Azithromycin Resistance (MIC ≥ 256 μg/mL) in Argentina, 2018 to 2022. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0097023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Berrocal, A.; Vargas-Herrera, N.; Benites, C.; Salazar-Quispe, F.; Mayta-Barrios, M.; Barrios-Cárdenas, Y.J.; Melano, R.G.; Yagui, M. Neisseria gonorrhoeae Surveillance Working Group Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Isolates from Peru, 2018 and 2019. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2022, 49, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qquellon, J.; Vargas, S.K.; Eguiluz, M.; Vasquez, F.; Durand, D.; Allan-Blitz, L.-T.; Konda, K.A.; Ochoa, T.J.; Caceres, C.F.; Klausner, J.D. Extra-Genital Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Infections with Genetic Mutations Conferring Ciprofloxacin Resistance among Men Who Have Sex with Men and Transgender Women in Lima, Peru. Int. J. STD AIDS 2023, 34, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.-K.; Martin, I.; Liu, G.; Bryden, L. Mutation in 23S rRNA Associated with Macrolide Resistance in Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3020–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; van der Veen, S. Neisseria Gonorrhoeae 23S rRNA A2059G Mutation Is the Only Determinant Necessary for High-Level Azithromycin Resistance and Improves in Vivo Biological Fitness. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, S.A.; Dave, J.; Ison, C.A. High-Level Azithromycin Resistance Occurs in Neisseria Gonorrhoeae as a Result of a Single Point Mutation in the 23S rRNA Genes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3812–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, V.G.; Mitterni, L.; Seah, C.; Rebbapragada, A.; Martin, I.E.; Lee, C.; Siebert, H.; Towns, L.; Melano, R.G.; Low, D.E. Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Treatment Failure and Susceptibility to Cefixime in Toronto, Canada. JAMA 2013, 309, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Laat, M.M.; Wind, C.M.; Bruisten, S.M.; Dierdorp, M.; de Vries, H.J.; Schim van der Loeff, M.F.; van Dam, A.P. Ceftriaxone Reduced Susceptible Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the Netherlands, 2009 to 2017: From PenA Mosaicism to A501T/V Nonmosaicism. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2019, 46, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameyama, S.; Onodera, S.; Takahata, M.; Minami, S.; Maki, N.; Endo, K.; Goto, H.; Suzuki, H.; Oishi, Y. Mosaic-like Structure of Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 Gene (penA) in Clinical Isolates of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae with Reduced Susceptibility to Cefixime. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3744–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Klausner, J.D. Six penA Codons Accurately and Reliably Predict Cefixime-Decreased Susceptibility in Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 851–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannigan, J.A.; Tirodimos, I.A.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Dowson, C.G.; Spratt, B.G. Insertion of an Extra Amino Acid Is the Main Cause of the Low Affinity of Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 in Penicillin-Resistant Strains of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. Mol. Microbiol. 1990, 4, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, A.J.; Tomberg, J.; Deacon, A.M.; Nicholas, R.A.; Davies, C. Crystal Structures of Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 from Penicillin-Susceptible and -Resistant Strains of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Reveal an Unexpectedly Subtle Mechanism for Antibiotic Resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Allan-Blitz, L.-T.; Klausner, J.D. Using the Genetic Characteristics of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Strains with Decreased Susceptibility to Cefixime to Develop a Molecular Assay to Predict Cefixime Susceptibility. Sex Health 2019, 16, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donà, V.; Smid, J.H.; Kasraian, S.; Egli-Gany, D.; Dost, F.; Imeri, F.; Unemo, M.; Low, N.; Endimiani, A. Mismatch Amplification Mutation Assay-Based Real-Time PCR for Rapid Detection of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae and Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants in Clinical Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00365-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal-Baron, P.; Salmerón, P.; García, J.N.; Trejo-Zahinos, J.; Sulleiro, E.; Lopez, L.; Jiménez de Egea, C.; Zarzuela, F.; Ruiz, E.; Blanco-Grau, A.; et al. Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Culture Growth Rates from Asymptomatic Individuals with a Positive Nucleic Acid Amplification Test. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, N.; Park, H.; Konda, K.A.; Joseph Davey, D.L.; Bristow, C.C.; Brown, B.; Leon, S.R.; Vargas, S.K.; Calvo, G.M.; Caceres, C.F.; et al. The PICASSO Cohort: Baseline Characteristics of a Cohort of Men Who Have Sex with Men and Male-to-Female Transgender Women at High Risk for Syphilis Infection in Lima, Peru. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordioli, M.; Gios, L.; Erbogasto, A.; Mirandola, M.; Sandri, A.; Padovese, V.; Caceres, C.; Vargas, S.; Blondeel, K.; Silva, R.; et al. Clinic-Based Evaluation of the Dual Xpert CT/NG Assay on the GeneXpert System for Screening for Extragenital Chlamydial and Gonococcal Infections amongst Men Who Have Sex with Men. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Deguchi, T.; Mizutani, K.-S.; Yasuda, M.; Yokoi, S.; Ito, S.-I.; Takahashi, Y.; Ishihara, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Ezaki, T. Emergence and Spread of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Clinical Isolates Harboring Mosaic-Like Structure of Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 in Central Japan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez, J.H.; Edwards, V.L.; Muniz Tirado, A.; Hardick, J.; Mehta, A.; Aluvathingal, J.; D’Mello, A.; Gaydos, C.A.; Manabe, Y.C.; Tettelin, H. Local emergence and global evolution of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with high-level resistance to azithromycin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2024, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unemo, M.; Shafer, W.M. Antibiotic Resistance in Neisseria Gonorrhoeae: Origin, Evolution, and Lessons Learned for the Future. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1230, E19–E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowler, L.D.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Riou, J.Y.; Spratt, B.G. Interspecies Recombination between the penA Genes of Neisseria Meningitidis and Commensal Neisseria Species during the Emergence of Penicillin Resistance in N. Meningitidis: Natural Events and Laboratory Simulation. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiley, D.M.; Goire, N.; Lambert, S.B.; Ray, S.; Limnios, E.A.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P.; Tapsall, J.W. Reduced Susceptibility to Ceftriaxone in Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Is Associated with Mutations G542S, P551S and P551L in the Gonococcal Penicillin-Binding Protein 2. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1615–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharat, A.; Demczuk, W.; Martin, I.; Mulvey, M.R. Effect of Variants of Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 on Cephalosporin and Carbapenem Susceptibilities in Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5003–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomberg, J.; Fedarovich, A.; Vincent, L.R.; Jerse, A.E.; Unemo, M.; Davies, C.; Nicholas, R.A. Alanine 501 Mutations in Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 from Neisseria Gonorrhoeae: Structure, Mechanism, and Effects on Cephalosporin Resistance and Biological Fitness. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Xie, Q.; Yin, X.; Li, X.; Xie, J.; Wu, X.; Tang, S.; Liu, M.; Zeng, L.; Pan, Y.; et al. penA Profile of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae in Guangdong, China: Novel penA Alleles Are Related to Decreased Susceptibility to Ceftriaxone or Cefixime. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) 1 | Product Size (bp) 2 | Target (Antibiotic Affected) 3 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2611_F C2611_R | AACGTCGTGAGACAGTTTGGTTT GAACTTAGCTACCCGGCTATGCA | 144 | 23S rRNA C2611T (moderate AZM resistance) | [26] |
| A2059_F A2059_R | TACAGTAAAGGTTCACGGGGTCAC TGGCCACACTGTCTCCTCCC | 100 | 23S rRNA A2059G (high AZM resistance) | [26] |
| 545_F 545_R | TGGTTAACGGTCGTTACGTCGATT GGCCCTGCCACTACACCGTT | 142 | Mosaic penA (decreased susceptibility/resistance to ESCs) | [26] |
| 345_F 345_R | GGCAAAGTGGATGCAACCGAT GATAAACGTGGGTATCTTGTACGG | 82 | Mosaic penA (decreased susceptibility/resistance to ESCs) | [26] |
| gonrRNA-F gonrRNA-R2 | ACGAATGGCGTAACGATGGCCACA TTCGTCCACTCCGGTCCTCTCGTA | 712 | 23S rRNA sequencing | [16] |
| rRNA_1 rRNA_2 rRNA_3 rRNA_4 | TCAGAATGCCACAGCTTACAAACT GCGACCATACCAAACACCCACAGG GATCCCGTTGCAGTGAAGAAAGTC AACAGACTTACTATCCCATTCAGC | 2054 2240 2217 1847 | 23S rRNA sequencing (Alleles 1–4) | [16] |
| PenA-A3 PenA-B3 | GCCGTAACCGATATGATCGA CGTTGATACTCGGATTAAGACG | 862 | penA sequencing | [30] |
| Gene | Position Number (Nucleotide or Codon) 1 | Wild Type Samples n (%) | Mutant Samples n (%) 2 | Mutation Detected |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23S rRNA | 2611 | 42 (100.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | C→T |
| 2059 | 62 (96.9%) | 2 (3.1%) | A→G | |
| penA | 345 | 39 (88.6%) | 5 (11.4%) | D345del |
| 545 | 58 (93.6%) | 4 (6.4%) | G545S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasquez, F.; Eguiluz, M.; Vargas, S.K.; Qquellon, J.; Caceres, C.F.; Klausner, J.D.; Konda, K.A. Molecular Detection of Mutations in the penA and 23S rRNA Genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Related to Decreased Cephalosporin and Azithromycin Susceptibility in Rectal Specimens from Men Who Have Sex with Men (MSM) in Lima, Peru. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080211
Vasquez F, Eguiluz M, Vargas SK, Qquellon J, Caceres CF, Klausner JD, Konda KA. Molecular Detection of Mutations in the penA and 23S rRNA Genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Related to Decreased Cephalosporin and Azithromycin Susceptibility in Rectal Specimens from Men Who Have Sex with Men (MSM) in Lima, Peru. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(8):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080211
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasquez, Francesca, Maria Eguiluz, Silver K. Vargas, Jazmin Qquellon, Carlos F. Caceres, Jeffrey D. Klausner, and Kelika A. Konda. 2025. "Molecular Detection of Mutations in the penA and 23S rRNA Genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Related to Decreased Cephalosporin and Azithromycin Susceptibility in Rectal Specimens from Men Who Have Sex with Men (MSM) in Lima, Peru" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 8: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080211
APA StyleVasquez, F., Eguiluz, M., Vargas, S. K., Qquellon, J., Caceres, C. F., Klausner, J. D., & Konda, K. A. (2025). Molecular Detection of Mutations in the penA and 23S rRNA Genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Related to Decreased Cephalosporin and Azithromycin Susceptibility in Rectal Specimens from Men Who Have Sex with Men (MSM) in Lima, Peru. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(8), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080211







