Reducing Periprocedural Pain and Anxiety of Child Patients with Guided Relaxation Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment: A Clinical Research Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Virtual Reality (VR) in Acute Pain Management
2.2. Challenges of Using Medical VR Applications in Pediatrics
2.3. Virtual Natural Environment (VNE) in Pain and Anxiety Management
2.4. Guided Relaxation Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment (VNE)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Virtual Natural Environments (VirNE) Application
3.2. Research Methods
3.3. Measures
3.3.1. Measures from Interviews
3.3.2. Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED) Questionnaire
3.3.3. Adapted Visual Analog Scale for Anxiety (VAS-A) Questionnaire
3.3.4. Customized User Experience Questionnaire
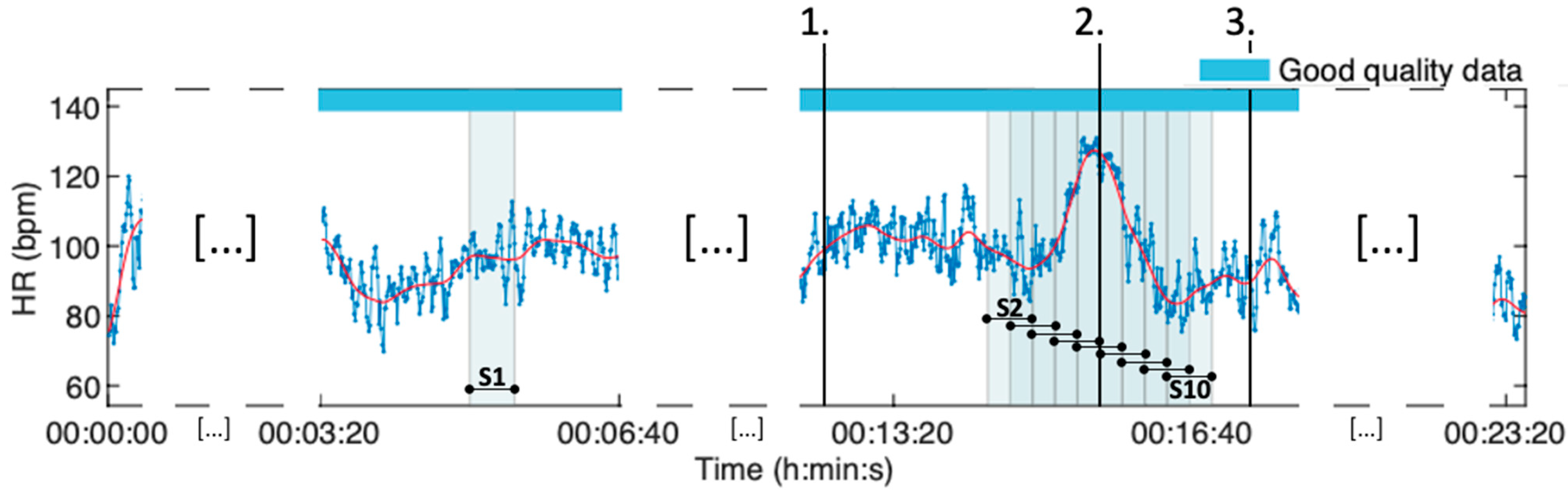
3.3.5. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Analyses
3.4. Statistical Analysis
3.5. Research Ethics Approval and Clinical Trials Registration
4. Results
4.1. Virtual Natural Environment (VNE) Selection
4.2. Interviews and Observations
4.2.1. Passive VNE Group
“It was pretty nice. I did not pay attention to the cannulation. The landscape was pretty nice, the sunshine and the rocks were nice.” [Participant, 11 years old]
“I liked the VR goggles, the picture, and the sounds, but since I’m not afraid of needles, it was not so useful for me.” [Participant, 12 years old]
4.2.2. Control Group
4.2.3. General Treatment Experience Between the Groups
4.3. Questionnaires
4.3.1. Adapted Visual Analog Scale for Anxiety (VAS-A) Questionnaires
4.3.2. Customized User Experience Questionnaire
4.4. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Analyses
4.4.1. The VR Intervention HRV Analysis of All Groups
4.4.2. The Periprocedural HRV Analysis of All Groups
5. Discussion
5.1. Main Findings
5.2. Related Work
5.3. Limitations and Recommendations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VR | Virtual reality |
| VNE | Virtual natural environment |
| VirNE | Virtual Natural Environments (The VR application used in the study) |
| HMD | Head-mounted display |
| HRV | Heart rate variability |
| HR | Heart rate |
| SDNN | Standard deviation of normal-to-normal intervals |
| RMSSD | Root mean square of successive differences between normal heartbeats |
| LF/HF ratio | Low frequency to high frequency ratio |
| SI | Stress index |
| IV | Peripheral intravenous (cannulation) |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
References
- McLenon, J.; Rogers, M.A.M. The Fear of Needles: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2019, 75, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelikol, Ş.; Tural Büyük, E.; Yıldızlar, O. Children’s Pain, Fear, and Anxiety During Invasive Procedures. Nurs. Sci. Q. 2019, 32, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orenius, T.; LicPsych; Säilä, H.; Mikola, K.; Ristolainen, L. Fear of Injections and Needle Phobia Among Children and Adolescents: An Overview of Psychological, Behavioral, and Contextual Factors. SAGE Open Nurs. 2018, 4, 237796081875944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncanson, E.; Le Leu, R.K.; Shanahan, L.; Macauley, L.; Bennett, P.N.; Weichula, R.; McDonald, S.; Burke, A.L.; Collins, K.L.; Chur-Hansen, A.; et al. The Prevalence and Evidence-Based Management of Needle Fear in Adults with Chronic Disease: A Scoping Review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röher, K.; Becke-Jakob, K.; Eich, C. Safety and Quality in Paediatric Procedural Sedation: What Really Matters? Curr. Opin. Anesthesiol. 2023, 36, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, S.; Thérond, A.; Cerda, I.H.; Studer, K.; Pan, A.; Tharpe, J.; Crowther, J.E.; Abd-Elsayed, A.; Gilligan, C.; Tolba, R.; et al. Virtual Reality in Acute and Chronic Pain Medicine: An Updated Review. Curr. Pain. Headache Rep. 2024, 28, 893–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, R.; Sekhar, P.; Hansen, C.J.; Peterson, L. Peripheral Intravenous Cannulation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyskä, I.; Turunen, M.; Chaychi Maleki, A.; Karppa, E.; Palmu, S.; Viik, J.; Mäkelä, J.; Puura, K. Effects of Using Guided Deep Breathing Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment to Reduce Stress during Pediatric Treatment. Healthcare 2023, 11, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyskä, I.; Turunen, M.; Chaychi Maleki, A.; Karppa, E.; Palmu, S.; Mäkelä, J.; Puura, K. Design and User Experience of VirNE Application: Deep Breathing Exercise in a Virtual Natural Environment to Reduce Treatment Anxiety in Pediatrics. Healthcare 2023, 11, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyskä, I.; Turunen, M.; Puura, K.; Chaychi Maleki, A.; Karppa, E.; Palmu, S.; Viik, J.; Mäkelä, J. Mindfulness-Based Guided Relaxation Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment to Reduce Periprocedural Pain and Anxiety in Pediatrics. Virtual Real. 2024; under review. [Google Scholar]
- Stanney, K.M.; Nye, H.; Haddad, S.; Hale, K.S.; Padron, C.K.; Cohn, J.V. Extended Reality (Xr) Environments. In Handbook of Human Factors and Ergonomics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 782–815. ISBN 978-1-119-63611-3. [Google Scholar]
- McCaul, K.D.; Malott, J.M. Distraction and Coping with Pain. Psychol. Bull. 1984, 95, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefi Rad, A.; Wippert, P.-M. Insights into Pain Distraction and the Impact of Pain Catastrophizing on Pain Perception during Different Types of Distraction Tasks. Front. Pain Res. 2024, 5, 1266974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, K.A.; Chambers, C.T.; Spellman, C.M. Mechanisms of Distraction in Acute Pain Perception and Modulation. Pain 2017, 158, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Wang, X.; Xue, Q.; Chen, D. Active versus Passive Distraction for Reducing Procedural Pain and Anxiety in Children: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2023, 49, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.; Warty, R.R.; Sursas, J.A.; Payne, O.; Nair, A.; Krishnan, S.; da Silva Costa, F.; Wallace, E.M.; Vollenhoven, B. The Effectiveness of Virtual Reality in Managing Acute Pain and Anxiety for Medical Inpatients: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e17980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lier, E.J.; de Vries, M.; Steggink, E.M.; ten Broek, R.P.G.; van Goor, H. Effect Modifiers of Virtual Reality in Pain Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis. Pain 2023, 164, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.L.; Wang, Y.; Colloca, L. Impact of Virtual Reality Technology on Pain and Anxiety in Pediatric Burn Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Virtual Real. 2022, 2, 751735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.A.; Polhemus, A.H.; Haan Ospina, E.; Feller, H.; Zenni, M.; Deacon, M.; DeGrado, G.; Basnet, S.; Driscoll, M. The State of Science in the Use of Virtual Reality in the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Pain: A Systematic Scoping Review. Clin. J. Pain 2022, 38, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreesmann, N.J.; Su, H.; Thompson, H.J. A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality Therapeutics for Acute Pain Management. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2022, 23, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordgård, R.; Låg, T. The Effects of Virtual Reality on Procedural Pain and Anxiety in Pediatrics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Virtual Real. 2021, 2, 699383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, O.; Wrzeciono, A.; Rutkowska, A.; Guzik, A.; Kiper, P.; Rutkowski, S. Virtual Reality Interventions for Needle-Related Procedural Pain, Fear and Anxiety—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorz, J.E.; Czub, M.; Šulžickaja, B.; Kiliś-Pstrusińska, K. Mobile Virtual Reality Distraction Reduces Needle Pain and Stress in Children? Cyberpsychology J. Psychosoc. Res. Cyberspace 2020, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Shen, J.; Wheeler, K.K.; Patterson, J.; Lever, K.; Armstrong, M.; Shi, J.; Thakkar, R.K.; Groner, J.I.; Noffsinger, D.; et al. Efficacy of Smartphone Active and Passive Virtual Reality Distraction vs Standard Care on Burn Pain Among Pediatric Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2112082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz-Torres, M.; San Martín-Rodríguez, L.; García-Vivar, C.; Soto-Ruiz, N.; Escalada-Hernández, P. Passive or Interactive Virtual Reality? The Effectiveness for Pain and Anxiety Reduction in Pediatric Patients. Virtual Real. 2022, 26, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.; Delanerolle, G.; Zeng, Y.; Shi, J.Q.; Ebrahim, R.; Pang, J.; Hapangama, D.; Sillem, M.; Shetty, S.; Shetty, B.; et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Digital Application Use in Clinical Research in Pain Medicine. Front. Digit. Health 2022, 4, 850601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, N.; Fan, L. Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Intervention on Reducing the Pain, Anxiety and Fear of Needle-Related Procedures in Paediatric Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2023, 79, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, V.; Tomietto, M.; Comparcini, D.; Vankova, N.; Marcelli, S.; Cicolini, G. Effectiveness of Virtual Reality in the Management of Paediatric Anxiety during the Peri-operative Period: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2022, 125, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flujas-Contreras, J.M.; Ruiz-Castañeda, D.; Gómez, I. Promoting Emotional Well-Being in Hospitalized Children and Adolescents with Virtual Reality: Usability and Acceptability of a Randomized Controlled Trial. CIN Comput. Inform. Nurs. 2020, 38, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbig, A.; Babu, S.K.; Gatter, S.; Latoschik, M.E.; Brukamp, K.; von Mammen, S. Opportunities and Challenges of Virtual Reality in Healthcare—A Domain Experts Inquiry. Front. Virtual Real. 2022, 3, 837616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraets, C.N.W.; van der Stouwe, E.C.D.; Pot-Kolder, R.; Veling, W. Advances in Immersive Virtual Reality Interventions for Mental Disorders: A New Reality? Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2021, 41, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatoye, F.; Gebrye, T.; Mbada, C.E.; Fatoye, C.T.; Makinde, M.O.; Ayomide, S.; Ige, B. Cost Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Game Compared to Clinic Based McKenzie Extension Therapy for Chronic Non-Specific Low Back Pain. Br. J. Pain 2022, 16, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, T.J.; O’Connell, C.; Qian, J.J.; Kung, T.; Wang, E.; Kinnebrew, S.; Pearson, M.; Kist, M.; Menendez, M.; Rodriguez, S.T. Retrospective Review of the Safety and Efficacy of Virtual Reality in a Pediatric Hospital. Pediatr. Qual. Saf. 2020, 5, e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Vicente, L.; Rodríguez-Cano, S.; Delgado-Benito, V.; Ausín-Villaverde, V.; Cubo Delgado, E. Cybersickness. A Systematic Literature Review of Adverse Effects Related to Virtual Reality. Neurología 2022, 39, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolasinski, E.M. Simulator Sickness in Virtual Environments; Army Research Institute for the Behavioral and Social Sciences: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani, E.; Zucchella, C.; Bottiroli, S.; Federico, A.; Giugno, R.; Sandrini, G.; Chiamulera, C.; Tamburin, S. Telemedicine and Virtual Reality for Cognitive Rehabilitation: A Roadmap for the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabbaa, L.; Ang, C.S.; Siriaraya, P.; She, W.J.; Prigerson, H.G. A Reflection on Virtual Reality Design for Psychological, Cognitive and Behavioral Interventions: Design Needs, Opportunities and Challenges. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2021, 37, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lim, S.H.; Aloweni, F.B.A.B. Virtual Reality Interventions and the Outcome Measures of Adult Patients in Acute Care Settings Undergoing Surgical Procedures: An Integrative Review. J. Adv. Nurs. 2022, 78, 645–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotera, Y.; Richardson, M.; Sheffield, D. Effects of Shinrin-Yoku (Forest Bathing) and Nature Therapy on Mental Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2022, 20, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, M.H.E.M.; Shipley, N.; McAnirlin, O.; Becker, D.; Yu, C.-P.; Hartig, T.; Dzhambov, A.M. An Actual Natural Setting Improves Mood Better Than Its Virtual Counterpart: A Meta-Analysis of Experimental Data. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, G.; Theodorou, A.; Reese, G.; Carrus, G.; Sanesi, G.; Panno, A. Virtual Nature, Psychological and Psychophysiological Outcomes: A Systematic Review. J. Environ. Psychol. 2023, 89, 102044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, A.; Ficarra, S.; Thomas, E.; Bianco, A.; Nordstrom, A. Nature through Virtual Reality as a Stress-Reduction Tool: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Stress Manag. 2023, 30, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, E.; Choe, J.; Choi, S.; Ha, S.; Kim, G. Psychological Effects of Green Experiences in a Virtual Environment: A Systematic Review. Forests 2022, 13, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Baharum, M.R. The Effects of Digital Nature and Actual Nature on Stress Reduction: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Internet Interv. 2024, 38, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, E. Sound and Soundscape in Restorative Natural Environments: A Narrative Literature Review. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 570563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, C.; Sun, M.; Yuan, Y.; Li, P. Effects of Brightness Levels on Stress Recovery When Viewing a Virtual Reality Forest with Simulated Natural Light. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 56, 126865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafti, F.A.; Han, J.; Wekenborg, M.K.; Moere, A.V.; Schierz, J.-H.; Heylighen, A.; Marquardt, G. Beyond Greenery: Exploring Influences of Exposure to Natural Blue Elements on Patients Using Virtual Reality. Build. Environ. 2024, 267, 112227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völker, S.; Kistemann, T. The Impact of Blue Space on Human Health and Well-Being—Salutogenetic Health Effects of Inland Surface Waters: A Review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Bratman, G.N.; Browning, M.H.E.M.; Spengler, J.D.; Olvera-Alvarez, H.A. Stress Recovery from Virtual Exposure to a Brown (Desert) Environment versus a Green Environment. J. Environ. Psychol. 2022, 81, 101775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppakittpaisarn, P.; Wu, C.-C.; Tung, Y.-H.; Yeh, Y.; Wanitchayapaisit, C.; Browning, M.H.E.M.; Chang, C.-Y.; Sullivan, W.C. Durations of Virtual Exposure to Built and Natural Landscapes Impact Self-Reported Stress Recovery: Evidence from Three Countries. Landscape Ecol. Eng. 2023, 19, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Wyles, K.J.; Hernandez, S.M.; Clarke, S.; Schofield, P.; Hughes, S.W. Harnessing the Therapeutic Effects of Nature for Chronic Pain: A Role for Immersive Virtual Reality? A Narrative Review. Eur. J. Pain 2024, 29, e4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nukarinen, T.; Rantala, J.; Korpela, K.; Browning, M.H.E.M.; Istance, H.O.; Surakka, V.; Raisamo, R. Measures and Modalities in Restorative Virtual Natural Environments: An Integrative Narrative Review. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2022, 126, 107008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perciavalle, V.; Blandini, M.; Fecarotta, P.; Buscemi, A.; Di Corrado, D.; Bertolo, L.; Fichera, F.; Coco, M. The Role of Deep Breathing on Stress. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, K.K.-Y.; Loke, A.Y. Effects of Diaphragmatic Deep Breathing Exercises on Prehypertensive or Hypertensive Adults: A Literature Review. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2021, 43, 101315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsea, E.; Drigas, A.; Skianis, C. Breathing, Attention & Consciousness in Sync: The Role of Breathing Training, Metacognition & Virtual Reality. Tech. Soc. Sci. J. 2022, 29, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.E.; Huebschmann, N.A.; Iverson, G.L. Safety and Tolerability of an Innovative Virtual Reality-Based Deep Breathing Exercise in Concussion Rehabilitation: A Pilot Study. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2021, 24, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Vázquez, G.; Adriaanse, M.; Burchell, G.L.; Ostelo, R.; Panayiotou, G.; Vlemincx, E. Virtual Reality Breathing Interventions for Mental Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2024, 49, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girishan Prabhu, V.; Stanley, L.; Morgan, R.; Shirley, B. Designing and Developing a Nature-Based Virtual Reality with Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback for Surgical Anxiety and Pain Management: Evidence from Total Knee Arthroplasty Patients. Aging Ment. Health 2024, 28, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.; Rockstroh, C.; Göritz, A.S. Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Based on Slow-Paced Breathing with Immersive Virtual Reality Nature Scenery. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockstroh, C.; Blum, J.; Göritz, A.S. A Mobile VR-Based Respiratory Biofeedback Game to Foster Diaphragmatic Breathing. Virtual Real. 2021, 25, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, A.; Patron, E.; Gentili, C.; Scilingo, E.P.; Greco, A. Novel VR-Based Biofeedback Systems: A Comparison Between Heart Rate Variability- and Electrodermal Activity-Driven Approaches. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2024, 15, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujato, B. A History of Mindfulness; Bhikkhu Sujato: Wentworth Falls, Australia, 2011; ISBN 978-1-921842-09-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Woolfolk, R.L.; Sime, W.E. Mindfulness Meditation. In Principles and Practice of Stress Management, 3rd ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 393–427. ISBN 978-1-60623-828-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, O.; Shelton, K.H.; Penny, H.; Thompson, A.R. Living with Physical Health Conditions: A Systematic Review of Mindfulness-Based Interventions for Children, Adolescents, and Their Parents. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2023, 48, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, D.R.; Black, N.B. Meditation and Mindfulness in Clinical Practice. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 23, 487–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Kabariti, S.; Likourezos, A.; Drapkin, J.; Hossain, R.; Brazg, J.; Motov, S. Take-Pause: Efficacy of Mindfulness-Based Virtual Reality as an Intervention in the Pediatric Emergency Department. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2022, 29, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, A.A.; Neiman, N.; Caruso, T.J.; Rodriguez, S.; Taylor, K.; Madill, M.; Rives, H.; Nguyen, L. Mindfulness-Based Virtual Reality Intervention for Children and Young Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Pilot Feasibility and Acceptability Study. Children 2021, 8, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaerts, S.; Bonroy, B.; Daems, J.; Sels, R.; Struyf, D.; Gies, I.; van de Veerdonk, W. Virtual Reality for Distraction and Relaxation in a Pediatric Hospital Setting: An Interventional Study with a Mixed-Methods Design. Front. Digit. Health 2022, 4, 866119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, J.K. A History of the Unity Game Engine; Worcester Polytechnic Institute: Worcester, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Birmaher, B.; Brent, D.A.; Chiappetta, L.; Bridge, J.; Monga, S.; Baugher, M. Psychometric Properties of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED): A Replication Study. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 1999, 38, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labaste, F.; Ferré, F.; Combelles, H.; Rey, V.; Foissac, J.; Senechal, A.; Conil, J.; Minville, V. Validation of a Visual Analogue Scale for the Evaluation of the Postoperative Anxiety: A Prospective Observational Study. Nurs. Open 2019, 6, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facco, E.; Stellini, E.; Bacci, C.; Manani, G.; Pavan, C.; Cavallin, F.; Zanette, G. Validation of Visual Analogue Scale for Anxiety (VAS-A) in Preanesthesia Evaluation. Minerva Anestesiol. 2013, 79, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Jyskä, I.; Puura, K.; Turunen, M. Therapeutic Potential of Interactive Audiovisual 360-Degree Virtual Reality Environments for Anxiety Reduction—A Case Study with an Abstract Art Application. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchaine, T.P.; Thayer, J.F. Heart Rate Variability as a Transdiagnostic Biomarker of Psychopathology. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 98, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, A.; Quintana, D. The Relationship Between Mental and Physical Health: Insights from the Study of Heart Rate Variability. Int. J. Psychophysiol. Off. J. Int. Organ. Psychophysiol. 2013, 89, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J.P. An Overview of Heart Rate Variability Metrics and Norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baevsky, R.; Chernikova, A. Heart Rate Variability Analysis: Physiological Foundations and Main Methods. Cardiometry 2017, 10, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Rosenberg, W.; Chanwimalueang, T.; Adjei, T.; Jaffer, U.; Goverdovsky, V.; Mandic, D.P. Resolving Ambiguities in the LF/HF Ratio: LF-HF Scatter Plots for the Categorization of Mental and Physical Stress from HRV. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, J.; Thayer, J.F. Sex Differences in Healthy Human Heart Rate Variability: A Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 64, 288–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, E.O.; Belamkar, V.; Litt, M.D.; Puhl, R.M.; Zempsky, W.T. “There’s Nothing Wrong with You”: Pain-Related Stigma in Adolescents with Chronic Pain. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2022, 47, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strehle, E.-M.; Gray, W.K. Comparison of Skin Conductance Measurements and Subjective Pain Scores in Children with Minor Injuries. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, e502–e506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, E.; Heathcote, L.C.; Eccleston, C.; Simons, L.E.; Palermo, T.M. Assessment of Pain Anxiety, Pain Catastrophizing, and Fear of Pain in Children and Adolescents with Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2018, 43, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karppa, E.; Puura, K.; Jyskä, I.; Turunen, M.; Palmu, S. Case Report: Virtual natural environment solution helped a child cope with a painful procedure. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1355046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, O.; Puhakka, R. Engaging with Nature: Nature Affords Well-Being for Families and Young People in Finland. Child. Geogr. 2020, 18, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolouki, A.; McAnirlin, O.; Browning, M.H.E.M.; Maynard, A. Optimizing Virtual Nature for Psychological and Physiological Well-Being: A Systematic Review of the Moderating Effects of Duration, Nature Type, Sample Characteristics, and Immersiveness and Potential Risks of Bias. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2025, 41, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaş, E.H.; Semerci, R.; Bayram, C. The Effect of a Biofeedback-Based Virtual Reality Game on Pain, Fear and Anxiety Levels during Port Catheter Needle Insertion in Pediatric Oncology Patients: A Randomized Controlled Study. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2024, 70, 102621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydos, İ.A.; Semerci, R.; Savaş, E.H.; Gülersoy, A.; Ürey, H. Golden Breath: Feasibility and Acceptability of a Biofeedback-Based Virtual Reality Game on Reducing Children’s Needle-Related Pain and Fear. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2024, 79, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addab, S.; Hamdy, R.; Le May, S.; Thorstad, K.; Tsimicalis, A. The Use of Virtual Reality during Medical Procedures in a Pediatric Orthopedic Setting: A Mixed-Methods Pilot Feasibility Study. Paediatr. Neonatal Pain 2024, 6, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz-Torres, M.; Soto-Ruiz, N.; Escalada-Hernández, P.; García-Vivar, C.; San Martín-Rodríguez, L. Can Virtual Reality Reduce Pain and Anxiety in Pediatric Emergency Care and Promote Positive Response of Parents of Children? A Quasi-Experimental Study. Int. Emerg. Nurs. 2023, 68, 101268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, J.I.; SooHoo, M.; Laikin, A.M.; Lane, A.S.; Klein, M.J. Effect of an Immersive Virtual Reality Intervention on Pain and Anxiety Associated with Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Placement in the Pediatric Setting: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2122569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitze, A.; Voigt, M.; Klawonn, F.; Dusch, M.; Grigull, L.; Mücke, U. Impact of Virtual Reality on Peri-Interventional Pain, Anxiety and Distress in a Pediatric Oncology Outpatient Clinic: A Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, M.; Youssef, G.J.; McGillivray, J.; Clark, T.-J.; McMillan, L.; McCarthy, M.C. Exploring the Use of Immersive Virtual Reality to Enhance Psychological Well-Being in Pediatric Oncology: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2020, 48, 101804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badke, C.M.; Krogh-Jespersen, S.; Flynn, R.M.; Shukla, A.; Essner, B.S.; Malakooti, M.R. Virtual Reality in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: Patient Emotional and Physiologic Responses. Front. Digit. Health 2022, 4, 867961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felemban, O.M.; Alshamrani, R.M.; Aljeddawi, D.H.; Bagher, S.M. Effect of Virtual Reality Distraction on Pain and Anxiety during Infiltration Anesthesia in Pediatric Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.L.; Choi, K.C. Effects of an Immersive Virtual Reality Intervention on Pain and Anxiety Among Pediatric Patients Undergoing Venipuncture: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e230001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, D.; O’Callaghan, J.; Barrett, M. Virtual Reality Hypnoanxiolysis and Analgesia for Emergency Department Needle-Related Procedures: A Prospective Interventional Cohort Pilot Study Implementation. Mayo Clin. Proc. Digit. Health 2023, 1, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltaci, N.; Bal, S.; Koç, E.; Edis, E.K. Effects of Virtual Reality and Nature Sounds on Pain and Anxiety during Hysterosalpingography: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2024, 70, e20231599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheluzzi, V.; Burrai, F.; Casula, M.; Serra, G.; Al Omary, S.; Merella, P.; Casu, G. Effectiveness of Virtual Reality on Pain and Anxiety in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Procedures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, M.; Maxim, B.; Proctor, J.; Dolins, F. The Effect of Audio Fidelity and Virtual Reality on the Perception of Virtual Greenspace. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 202, 103884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Aijima, R.; Danjo, A. Clinical Effects of Different Virtual Reality Presentation Content on Anxiety and Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, L.; Nguyen, Q.A.; Roettger, C.; Dixon, K.; Offenbächer, M.; Kohls, N.; Hirsch, J.; Sirois, F. Effectiveness of Progressive Muscle Relaxation, Deep Breathing, and Guided Imagery in Promoting Psychological and Physiological States of Relaxation. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5924040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, M.; Rajagopal, T.; Cerecino, F.; O’Neil, M. Mindful Versus Diaphragmatic Breathing: Spirituality Moderates the Impact on Heart Rate Variability. Mindfulness 2021, 12, 2743–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito Sena, M.A.; Damiano, R.F.; Lucchetti, G.; Peres, M.F.P. Defining Spirituality in Healthcare: A Systematic Review and Conceptual Framework. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 756080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, M.D.; Coleman, B.; Wallace, J.M. Spirituality, Religiousness, and Happiness in Children Aged 8–12 Years. J. Happiness Stud. 2010, 11, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittaro, L.; Serafini, M.; Vulcano, Y. Virtual Reality Experiences for Breathing and Relaxation Training: The Effects of Real vs. Placebo Biofeedback. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2024, 188, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, P.; D’Errico, G.; De Paolis, L.T.; Moccaldi, N.; Nuccetelli, F. A Narrative Review of Mindfulness-Based Interventions Using Virtual Reality. Mindfulness 2022, 13, 556–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, D.; Xu, N.; Yang, J. The Effectiveness of Immersive Virtual Reality (VR) Based Mindfulness Training on Improvement Mental-Health in Adults: A Narrative Systematic Review. Explore 2023, 19, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, S.; Mayne, A.; Hood, B. Virtual Reality-Based Mindfulness for Chronic Pain Management: A Scoping Review. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2022, 23, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haisley, K.R.; Straw, O.J.; Müller, D.T.; Antiporda, M.A.; Zihni, A.M.; Reavis, K.M.; Bradley, D.D.; Dunst, C.M. Feasibility of Implementing a Virtual Reality Program as an Adjuvant Tool for Peri-Operative Pain Control; Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial in Minimally Invasive Foregut Surgery. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shires, A.; Sharpe, L.; Davies, J.N.; Newton-John, T.R.O. The Efficacy of Mindfulness-Based Interventions in Acute Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain 2020, 161, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-S.; Beard, K.; Sherbel, M.C.; Nascimento, T.D.; Petty, S.; Pantzlaff, E.; Schwitzer, D.; Kaciroti, N.; Maslowski, E.; Ashman, L.M.; et al. Brain Mechanisms of Virtual Reality Breathing Versus Traditional Mindful Breathing in Pain Modulation: Observational Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, B.; Ma, K.; Hu, L.; Lu, X. The Analgesic Effects and Neural Oscillatory Mechanisms of Virtual Reality Scenes Based on Distraction and Mindfulness Strategies in Human Volunteers. Br. J. Anaesth. 2023, 131, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Data Group | Included (n) 1 | Excluded (n) 1 | Primary Reason for Exclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enrolled participants | 83 | 4 | No IV cannulation |
| SCARED Average | 82 | 1 | Missing data |
| VNE selection | 58 | 4 (+21) | Missing data (+Control) |
| Adapted VAS-A questionnaire: Pain | 81 | 2 | Missing data |
| Adapted VAS-A questionnaire: Anxiety | 80 | 3 | Missing data |
| Customized User Experience questionnaire | 59 | 3 (+21) | Missing data (+Control) |
| VR intervention HRV analysis | 69 | 14 | Insufficient data (in Passive VNE) |
| Periprocedural HRV analysis (S1–S5) | 79 | 4 | Insufficient data quality |
| Periprocedural HRV analysis (S6–S10) | 67 | 16 | First IV cannulation attempt failed |
| Data Group | Deep Breathing 1 | Mindfulness 1 | Passive VNE | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants (n) | 21 | 20 | 21 | 21 |
| Age, mean (SD) | 9.95 (±1.24) years | 10.65 (±1.27) years | 9.95 (±1.32) years | 9.86 (±1.39) years |
| Sex division | 13 females, 8 males | 12 females, 8 males | 12 females, 9 males | 7 females, 14 males |
| SCARED Average, median (IQR) | 15.00 (10.75) | 11.00 (10.25) | 11.00 (9.75) 2 | 15.50 (14.75) |
| Prior IV cannulations (0–3/4+) | 11/10 | 14/6 | 16/5 | 15/6 |
| Fear of needles (no/mild/clear) | 7/7/7 | 8/6/6 | 3/9/9 | 7/5/9 |
| Prior virtual reality experience (yes/no) | 12/9 | 17/3 | 11/10 | - |
| Motion sickness sensitivity (low/medium/high) | 11/6/4 (participants) | 15/4/0 (participants) | 16/5/0 (participants) | - |
| Data Group | Deep Breathing 1 | Mindfulness 1 | Passive VNE | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants (n) | 21 | 20 | 21 | 21 |
| General treatment experience (positive/neutral/negative) | 16/2/3 | 16/3/1 | 17/3/1 | 3/14/4 |
| Data Group | Deep Breathing 1 | Mindfulness 2 | Passive VNE | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants (n) | 21 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| VAS-A Pain expectation, mean (SD) | 2.52 (±1.75) | 2.63 (±1.80) | 2.30 (±1.45) | 2.90 (±1.37) |
| VAS-A Pain experience, mean (SD) | 2.29 (±1.68) | 1.42 (±1.39) | 1.50 (±1.57) | 2.00 (±1.70) |
| VAS-A Anxiety expectation, mean (SD) | 1.52 (±1.66) | 1.68 (±1.95) | 1.65 (±1.42) | 2.85 (±1.73) |
| VAS-A Anxiety experience, mean (SD) | 1.57 (±1.86) | 1.11 (±1.63) | 1.00 (±1.41) | 1.65 (±1.84) |
| Data Group | Deep Breathing 1 | Mindfulness 2 | Passive VNE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participants (n) | 20 | 19 | 20 |
| Q1: It was easy for me to adjust to being in VR, mean (SD) | 4.70 (±1.89) | 5.21 (±1.13) | 5.00 (±1.56) |
| Q2: It was easy for me to focus on the exercise, mean (SD) | 4.15 (±1.84) | 4.68 (±1.16) | 5.00 (±1.21) |
| Q3: The application was helpful/useful to me, mean (SD) | 3.50 (±2.14) | 4.68 (±1.45) | 5.40 (±1.05) |
| Q4: The application was boring for me, mean (SD) | 1.25 (±1.80) | 1.00 (±1.70) | 0.30 (±.73) |
| Data Group | Deep Breathing 1 | Mindfulness 2 | Passive VNE | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants (n) | 20 | 18 | 11 | 20 |
| HR S1 (120 s) median (IQR) (bpm) | 87.50 (18.75) | 92.50 (19.50) | 87.00 (16.00) | 82.50 (18.75) |
| HR S2 (120 s) median (IQR) (bpm) | 85.00 (22.25) | 91.50 (24.50) | 91.00 (26.00) | 87.50 (17.00) |
| SDNN S1 (120 s) median (IQR) (ms) | 36.25 (22.10) | 42.30 (34.28) | 37.00 (21.90) | 58.60 (25.85) |
| SDNN S2 (120 s) median (IQR) (ms) | 62.70 (31.78) | 59.10 (53.35) | 34.80 (28.50) | 51.75 (41.38) |
| RMSSD S1 (120 s) median (IQR) (ms) | 32.15 (29.63) | 32.00 (38.40) | 28.80 (32.30) | 53.55 (45.95) |
| RMSSD S2 (120 s) median (IQR) (ms) | 53.50 (44.33) | 49.35 (56.65) | 27.90 (26.50) | 49.55 (49.65) |
| LF/HF ratio S1 (120 s) median (IQR) | 1.554 (1.962) | 1.021 (1.487) | 1.250 (2.125) | 0.955 (1.290) |
| LF/HF ratio S2 (120 s) median (IQR) | 0.456 (0.532) | 1.055 (1.377) | 1.467 (1.910) | 1.506 (1.661) |
| SI S1 (120 s) median (IQR) | 14.00 (6.08) | 12.80 (10.07) | 13.70 (5.70) | 9.15 (4.27) |
| SI S2 (120 s) median (IQR) | 8.40 (5.30) | 9.05 (11.80) | 14.00 (9.80) | 9.70 (6.40) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jyskä, I.; Turunen, M.; Puura, K.; Karppa, E.; Palmu, S.; Viik, J. Reducing Periprocedural Pain and Anxiety of Child Patients with Guided Relaxation Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment: A Clinical Research Study. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9120115
Jyskä I, Turunen M, Puura K, Karppa E, Palmu S, Viik J. Reducing Periprocedural Pain and Anxiety of Child Patients with Guided Relaxation Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment: A Clinical Research Study. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction. 2025; 9(12):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9120115
Chicago/Turabian StyleJyskä, Ilmari, Markku Turunen, Kaija Puura, Elina Karppa, Sauli Palmu, and Jari Viik. 2025. "Reducing Periprocedural Pain and Anxiety of Child Patients with Guided Relaxation Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment: A Clinical Research Study" Multimodal Technologies and Interaction 9, no. 12: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9120115
APA StyleJyskä, I., Turunen, M., Puura, K., Karppa, E., Palmu, S., & Viik, J. (2025). Reducing Periprocedural Pain and Anxiety of Child Patients with Guided Relaxation Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment: A Clinical Research Study. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 9(12), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9120115






