Abstract
The exigency of emotion recognition is pushing the envelope for meticulous strategies of discerning actual emotions through the use of superior multimodal techniques. This work presents a multimodal automatic emotion recognition (AER) framework capable of differentiating between expressed emotions with high accuracy. The contribution involves implementing an ensemble-based approach for the AER through the fusion of visible images and infrared (IR) images with speech. The framework is implemented in two layers, where the first layer detects emotions using single modalities while the second layer combines the modalities and classifies emotions. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) have been used for feature extraction and classification. A hybrid fusion approach comprising early (feature-level) and late (decision-level) fusion, was applied to combine the features and the decisions at different stages. The output of the CNN trained with voice samples of the RAVDESS database was combined with the image classifier’s output using decision-level fusion to obtain the final decision. An accuracy of 86.36% and similar recall (0.86), precision (0.88), and f-measure (0.87) scores were obtained. A comparison with contemporary work endorsed the competitiveness of the framework with the rationale for exclusivity in attaining this accuracy in wild backgrounds and light-invariant conditions.
Keywords:
emotion recognition; multimodal; ensemble; visible images; infrared images; speech; CNN; VIRI; SVM; feature-fusion; decision-fusion; RAVDESS; wild; light-invariant 1. Introduction
An emotional state of a person is the gauge of several manifestations being held in one’s mind. It is an index to perceive the intentions and sentiment of a subject that assists in self-regulating tasks such as monitoring, automatic feedback, therapies, marketing, automotive safety, and assessments. This field of human–computer interaction (HCI), referred to as Affective Computing, assists in shifting the cognitive load from humans to machines. HCI aims to manifest a human–human like interaction between humans and machines. Interaction is more innate when the machine is aware of the user’s emotional state. It becomes imperative when the machine’s decision table looks for responses depending on the user’s mood. For example, an autonomous car might take a quiet, longer path when the user’s emotions dispose of anger, and a congested road is more likely to aggravate that emotion. An impeccable judgment requires a perfect discernment of emotions. Faces, speech, physiological signals, gestures, and even eye gaze carry manifestation of the person’s emotional state. Several works have leveraged these modalities to predict emotions with varied accuracy. A diverse set of mechanisms and techniques have been discovered and applied at junctures to achieve higher accuracy. Paul Ekman, a pioneer in setting the trend of identifying human emotions using Action Units (AU) [1,2,3], identified the six basic emotions that portray the affective states of a person as happiness, anger, surprise, sadness, fear, and disgust [1]. Facial expression was the principal modality for emotion detection, and later a diverse stack of modalities unfolded as corollary modalities.
While uni-modal emotion detection was still blossoming, HCI researchers disembarked on the multimodal territory in the quest for a more accurate and natural way of interaction with machines. The combination of modalities showed a promising perspective and was capable of extracting concealed feelings from perceptible sources. Although assorted combinations of modalities were explored, a survey of various techniques and databases described in the following sections implied the need for a robust AER framework that works under natural conditions. Although the experiments performed in labs boast high accuracy, many have not been proved to work in natural or in-the-wild conditions. A few works conducted the in-the-wild experiments [4,5,6]. However, they were limited by the apprehension of the role of "light" in the detection of emotions. A gloomy environment may affect facial emotion recognition and sometimes even forbid accurate detection. Additionally, facial expressions might not display the correct psychological state of a person if they do not concur with each other. For example, an angry person might not always exhibit facial expressions for the same, and the emotion could be easily confused with neutral or sad. These were some of the issues that still need to be addressed. A framework with the capability of discerning emotions, even in-the-wild conditions, was necessary. The work presented in this paper confronted those limitations with a novel modality—the infrared images.
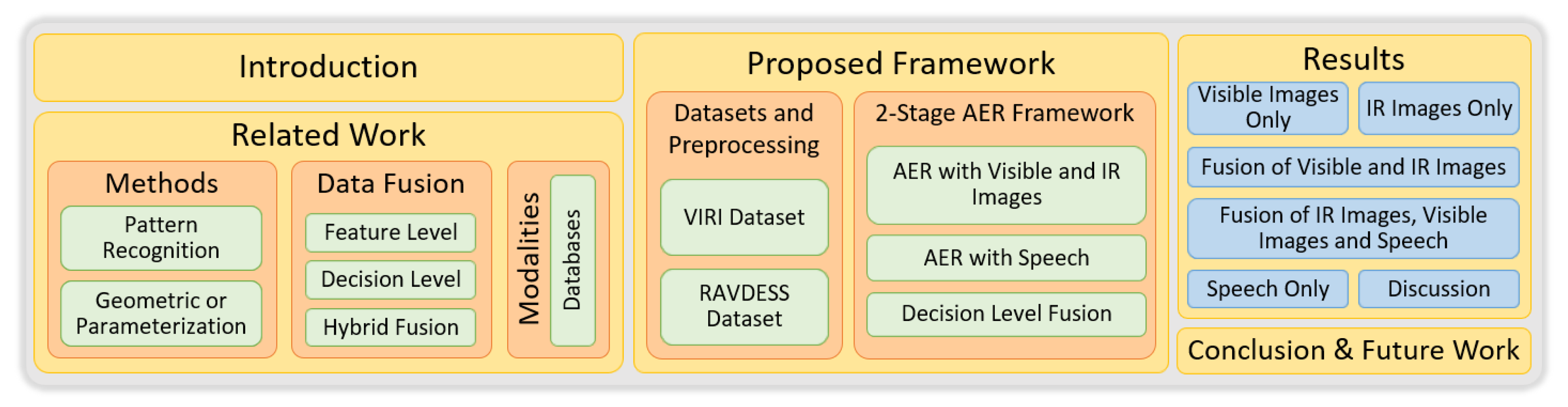
This paper presents an automatic emotion recognition (AER) framework using the fusion of visible images and infrared images with speech. The work follows an ensemble-based approach by exploiting the best services offered by different techniques. We adhered to certain baselines for the development of the framework. A baseline was to avoid the overwhelming use of sensors to eliminate any unwanted stress or anxiety induced due to monitoring. Further, facial expression was used as the principal modality, while infrared images were used to counter the limitations posed in previous approaches. In addition, the speech was used as a supporting modality to refine the classification further. Feature level and decision level fusions were applied at different stages to devise a framework for light-invariant AER in-the-wild conditions. The rest of the paper is organized as shown in Figure 1.
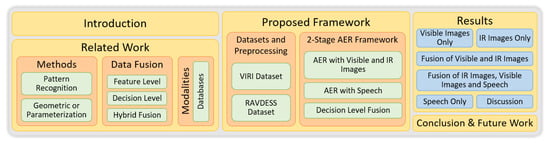
Figure 1.
Research paper outline.
2. Related Work
Affective computing has been improved with time, and the exertion of multitudinous modalities has underpinned the motion. Identification of emotions with multiple modalities has shown a tidy enhancement over the AER systems with unaccompanied modalities. The fusion of different input streams has also been fostered to strengthen the recognition process with the advent of multimodal HCI. This section presents a discussion of related work based on these aspects.
2.1. Use of Speech, Visible, and Infrared Images
Facial expressions were one of the first modalities to indicate the emotional state of a person. Facial Action Coding System (FACS) was first coined by Paul Ekman [1,3]. Facial expressions were followed closely by speech for emotion detection, and several other relevant input types were contrived for a high precision affect recognition. A wonted combination of modalities that forms a very natural blend is the speech and the facial expressions as this is the closest to human–human interaction [4,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. Gestures have been used together with facial and speech data to decipher affective state of a proband [36,37,38,39,40,41,42].
Infrared images have not been used for AER frequently. Wang et al. used IR images for emotion recognition using Deep Boltzmann Machine (DBM) and reported an accuracy of 62.9% with the Natural Visible and Infrared Facial Expression (NVIE) DB [43,44]. The authors reported an accuracy of 68.2% after using additional unlabeled data from other databases to improve feature learning performance. Elbarawy et al. made use of the Imaging, Robotics, and Intelligent Systems (IRIS) DB [45] for AER using the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) with Local Entropy (LE) and Local Standard Deviation (LSD) features [46]. In another work, K-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) and Support Vector Machines (SVM) were combined to generate a recognition model of facial expressions in thermal images. The highest accuracy of 90% was obtained using the LE features with kNN. Another instance of the use of thermal images for AER involved the use of DBM to classify emotions with an accuracy of 51.3% [47]. In addition, Basu et al. used thermal facial images and employed the moment invariant, histogram statistics, and multi-class SVM to achieve an accuracy of 87.50% [48]. A smart thermal system to detect emotions using IR images was also developed with an accuracy of 89.89% [49]. Yoshitomi et al. [50] and Kitazoe et al. [51] performed AER using visible, and thermal facial images; and speech to report an accuracy of 85%. The fusion in this works was elementary and based on the maximum of the output of the three modalities.
Databases form the propellant of the pattern recognition based AER. Any level of sophistication in machine learning (ML) algorithms cannot undermine the merit of a comprehensive database. A diverse set of databases has been developed, ranging from multimodal, bi-modal, and uni-modal databases (used in various combinations with other databases) to assist with multimodal AER. Table 1 summarizes the available databases with their attributes.

Table 1.
Multimodal emotional databases.
2.2. Emotion Identification
Emotion recognition involves finding patterns in the data and classify that data to the emotional states. The methods of emotional identification are predominantly cleaved into two portions, the methods of recognition and the methods of parameterization [85].
Pattern identification in the modalities serves as a primary source of AER by recognition. In [36], authors used Naive Bayes classifier for developing an ensemble-based emotion recognition system and used it to solve the problem of missing data at the fusion stage. Xu et al. used Hidden Markov Models (HMM) and Artificial Neural networks (ANN) for AER utilizing facial expressions and voice [8]. Bahreini et al. used the WEKA tool to apply hybrid fusion methods for voice feature extraction, classification, and collating the result of 79 available classifiers [7]. The Bayesian classifier has also been used for emotion recognition through face, voice, and body gestures [37,39]. Deep Belief Networks (DBN) have been very effective in deciphering the emotions and have been put to use in multiple AER systems. Ranganathan et al. used DBN and Convolutional Deep Belief Networks (CDBN) for unsupervised classification of 23 emotion classes [38]. DBNs and CNNs have also been used with K-Means and Relational auto-encoders for detecting emotions in videos [4]. At the same time, Kim et al. [14] applied four different DBN models using facial and audio data for four emotion classes (angry, happy, neutral, and sad). Nguyen et al. [22] used 3D-CNNs cascaded with DBNs for modeling spatio-temporal information and classifying five emotion categories using facial expressions and speech. Zhang et al. [24] utilized DBNs in a hybrid deep model approach involving CNN and 3D-CNN. CNNs have been pressed to service for work in different forms (3D-CNN, Deep CNNs (DCNN), Multi-function CNN (MCNN)) and combinations to achieve high AER accuracy [11,12,17,22,32,40,82,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93].
Another genre of emotion recognition methods uses facial structure, such as the shape of mouth, eyes, nose, etc. Loomed up by the widespread use of patter-recognition methods, a substantial decline in the application of this genre for AER has been seen in the recent past. Geometric-based methods involve the standardization of the image data followed by the detection of the region containing face and a decision function-based classification of the emotions by investigating and analyzing the facial components. Facial Action Coding System (FACS) was devised to exploit the contraction of facial muscles, which were termed as Action Units (AU) [1,3]. In [94], an AER model was deployed using an extended Kohonen self-organizing map (KSOM). The model utilized a feature vector containing feature points of facial regions such as lip, eyes, etc. Another geometric-based method where candid nodes were placed to track the facial regions of interest was presented in [95]. The work presented an approach using facial AUs and a Candide model. Several other older works have utilized FAUs for AER [96,97,98,99].
2.3. Data Fusion
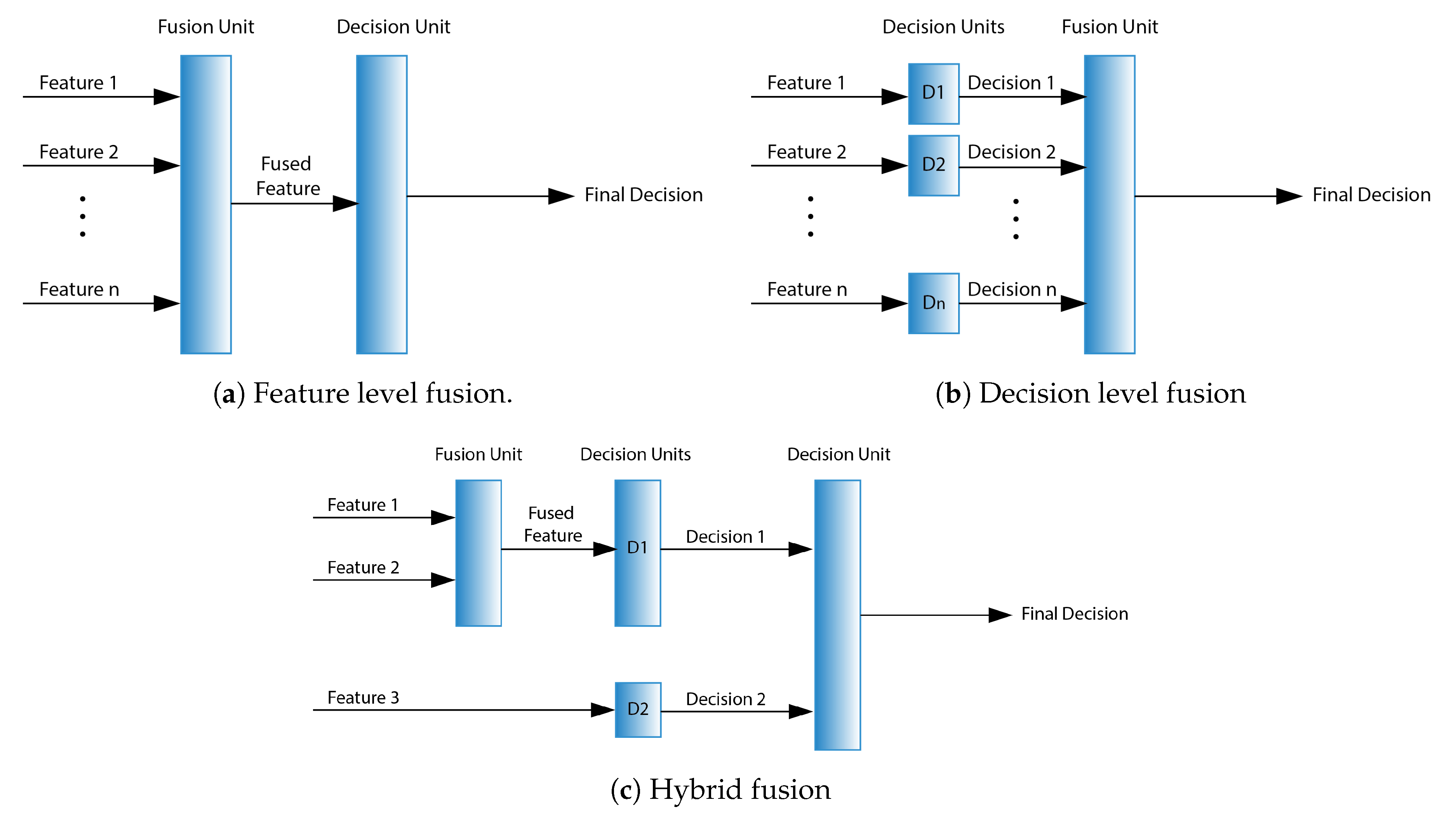
An integration of different modalities to form a coherent combination of input is termed as fusion [100]. Feature level and decision level form the two most widely used forms of fusion [101], while the hybrid approach involves a mix of both. Here we briefly discuss works that used each of these different types of fusion.
2.3.1. Feature Level
Feature level fusion, shown in Figure 2a, is also known as early fusion due to its anterior application to the modalities. Data from facial expressions, voice, and body gestures were combined at the feature level to achieve an accuracy of 78.3% [37,39]. Similarly, multimodal physiological signals were combined to achieve an accuracy of 81.45% for SVM, 74.37% for MLP, 57.75% for kNN, and 75.94% for Meta-multiclass (MMC) classifiers [102]. An ensemble approach was implemented in [11], where a feature output of a CNN was fused with a feature output of a ResNet and fed to a Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) network. In one of the studies, facial features were combined with the EEG features using different feature level techniques such as Multiple feature concatenation (MFC), Canonical Correlational Analysis (CCA), Kernel CCA (KCCA), and MKL [103]. In different studies, modalities were combined using this method, e.g., pulse activity and ECG data [104]; face and speech [18,19,23,26,33,90]; linguistic and acoustic cues [105]; audio and text [93,106,107,108]; audio, video, and text [109,110]; facial texture, facial landmark action, and audio [32]; audio, video, and physiological signals [111]; and speech from two different languages [73].
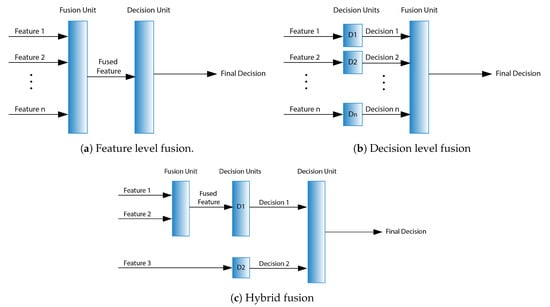
Figure 2.
Feature level fusion.
2.3.2. Decision Level
Decision level fusion or late fusion is usually applied after individual decisions have been taken, as shown in Figure 2b. Such a framework was tested for AER to solve the problem of missing data at the fusion stage [36]. Another work used an ANN for fusion of facial expressions and speech [8]. Using late fusion, Kessous et al. evaluated bi-modal combinations of face, speech, and body gestures [37], while Alonso et al. [9] combined facial data and speech for human–robot interaction. Several other works exploited this fusion method to combine different combinations of input modalities, e.g., face, speech, and body gestures [39,40,41], aligned faces and non-aligned faces [5], face, audio, and physiological signals [88], physiological signals [89], face and speech [13,15,16,17,22,26,27], face and EEG [103], finger pulse activity and ECG data [104], face, speech, and language [112], direct person-independent perspective and relative person-dependent perspectives [113], and facial texture, facial landmark action, and audio [32].
2.3.3. Hybrid Fusion
An integration of feature and decision level fusion in different combinations is termed as a hybrid approach, as shown in Figure 2c. Bahreini et al. used a hybrid fusion approach for a real-time AER using images and voice [7]. In another study, a hierarchical classification fusion framework was developed that utilized a layer of feature level fusion that fed to decision level fusion [6]. Yin et al. proposed a Multiple-fusion-layer based Ensemble classifier of Stacked Autoencoders (MESAE) for AER using physiological signals such as GSR, EMG, EOG, EEG, and Blood Volume Pressure (BVP) [114]. Another 2-stage fusion network where the first stage employed two DCNNs and the second stage integrated the output of these two DCNNs using a fusion network achieved an accuracy of 74.32%, compared to 66.17% (audio) and 60.79% (face) [90]. An ensemble of CNN methods was proposed by [91], where the output of the CNN was fused with a probability based-fusion. Tripathi et al. used various deep-learning-based architectures (LSTM, CNN, fully connected MLP) to first get the best individual detection (Speech: 55.65%, Text: 64.78%, Motion Capture: 51.11%) and then combined the output using an ensemble-based architecture (Speech + Text: 68.40%, Speech + Text + Motion Capture: 71.04%) [115].
3. Proposed Framework
In this section, we discuss the datasets, their pre-processing, and the specifics of the proposed methodology.
3.1. Datasets and Pre-Processing
3.1.1. VIRI Dataset
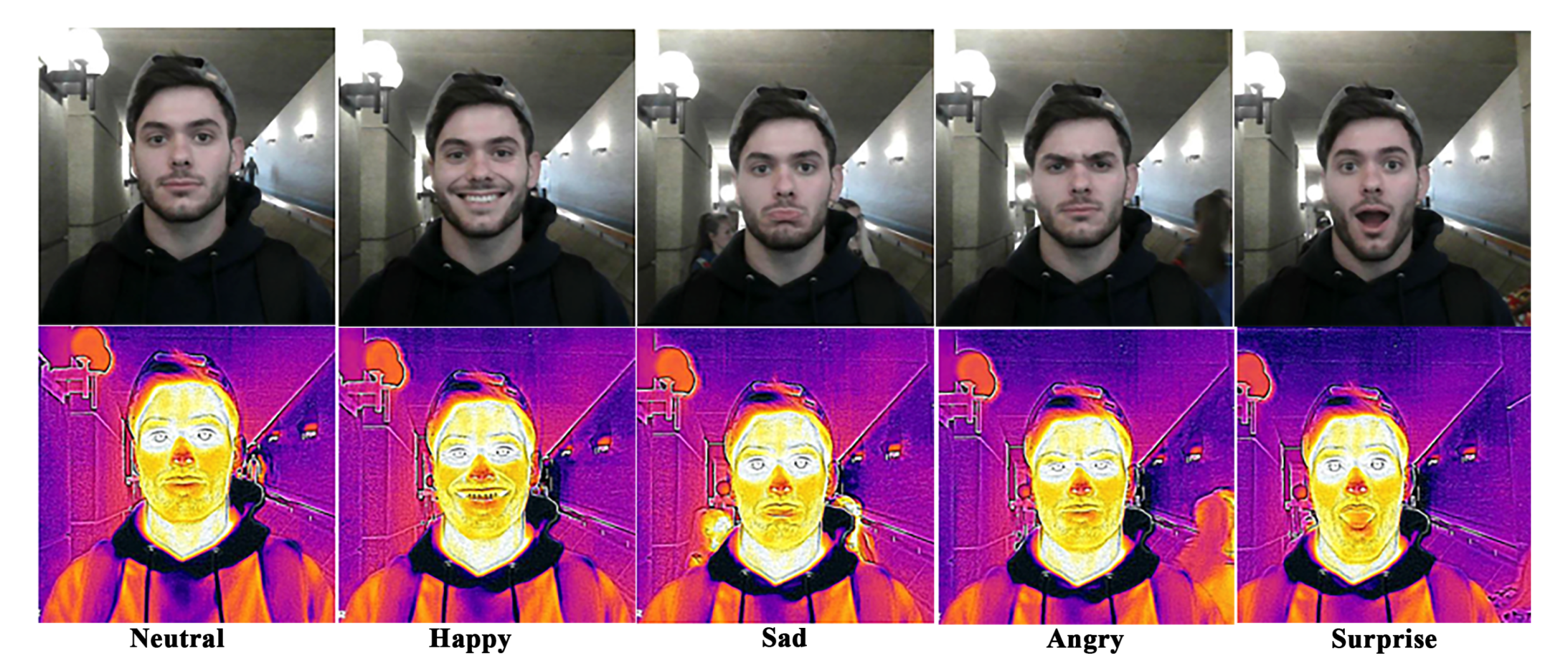
An exiguous number of IR emotional databases are available for use. However, most of them did not serve the requirements of our framework. Consequently, we developed a facial image database of visible and IR images, called VIRI database. This DB confronts the limitations of the existing IR DBs and presents the spontaneous facial expressions in both visible and IR format in uncontrolled wild backgrounds. The DB was created at The University of Toledo and is comprised of the consented pictures from on-campus students. Five expressions have been captured—happy, sad, angry, surprised, and neutral—and comprise 110 subjects (70 males and 40 females), resulting in 550 images in a radiometric JPEG format. This format contains both visible and thermal data captured by the FLIR ONE Pro thermal camera. After extracting visible and Multi-Spectral Dynamic Imaging (MSX) thermal images, a total of 1100 images (550 visible and 550 IR images) were obtained. It is a varied DB in terms of proband’s age (17–35 years) and ethnicity (White, African-American, and Asian). Images were taken in three formats, visible, infrared, and MSX format and VIRI DB contains all the three formats.
Data Pre-processing and Image Augmentation: The resolution of each original extracted image was 1440 × 1080 pixels, and some pre-processing was carried out to remove noise and discrepancies from the images. The subjects were not ideally centered since the images were captured in the wild. A batch process of crop and overexposure was executed on the images to bring the subjects to the center and reduce the darkness in the pictures. Each image’s size was reduced to 227 × 227 pixels to bring it to a size suitable for use in CNN training. Figure 3 shows a sample image set from VIRI DB for all emotion classes. The DB is available for use upon request at the following URL: https://www.yazdan.us/research/repository. For training the CNN for AER by IR images and visible images, the number of images required to achieve a respectable accuracy was not adequate. To proliferate the images and to bring more heterogeneity, a series of image augmentation techniques were applied to each image randomly. Approximately 2000 images of each emotion class were obtained after applying a series of rotation, zoom, skew, distortion, shear, and reflection. The augmented data were then used to train the CNN for AER. Table 2 also presents a brief comparison with related popular datasets showing its superiority due to images captured in-the-wild.
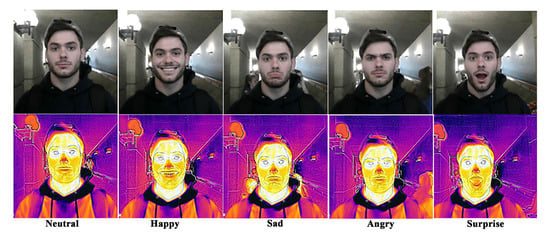
Figure 3.
Sample visible and IR image (VIRI) in Multi-Spectral Dynamic Imaging (MSX) and visible format.

Table 2.
Comparison of the available IR DBs and VIRI. WBK: Wild Background, S/P: Spontaneous/Posed, A: Available.
3.1.2. RAVDESS Dataset
Speech samples were already available in several databases. We selected The Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS), a nascent audio–visual emotional DB in North American English [118]. Developed at the SMART Lab of Ryerson University, Canada, the DB consists of validated emotional speech and songs. A total of 24 professional actors uttered in the North American accent for lexically-matched recitations. The audio portion covers seven emotional states (calm, happy, sad, angry, fearful, surprise, and disgust) and songs comprise of 5 emotions (calm, happy, sad, angry, and fearful). The corpus contains 2452 audio recordings for two emotional levels (normal, strong). Two hundred forty-seven individuals provided the assessment of the DB for the rating, and a set of 72 people provided test-retest data. The DB is available for download under a creative commons license. It should be noted that the images form this dataset were not used owing to the lack of thermal/infrared images and their capturing in controlled environment while we required images captured in-the-wild.
Data Pre-processing: The audio data consists of the recordings with a standard unique filename that identifies the traits of the file. We selected 1886 samples that belonged to the 5 emotion classes our work focused on. However, we faced a few issues during training and found that pre-processing was unavoidable. The length of the files was not uniform and required a batch process of trimming. This was also necessary to eradicate any issues that might arise during the creation of audio spectrograms and the CNN training. Furthermore, during training, some of the files were identified as corrupt and were causing issues in accessing audio vectors. Those files were identified and removed from the training corpus. Finally, the samples for all emotions lied in the range of 370–380, totaling to 1876 (out of 2452). This balance among the samples for each emotion was also a prerequisite to ensure proper training.
3.2. Two-Stage AER Framework
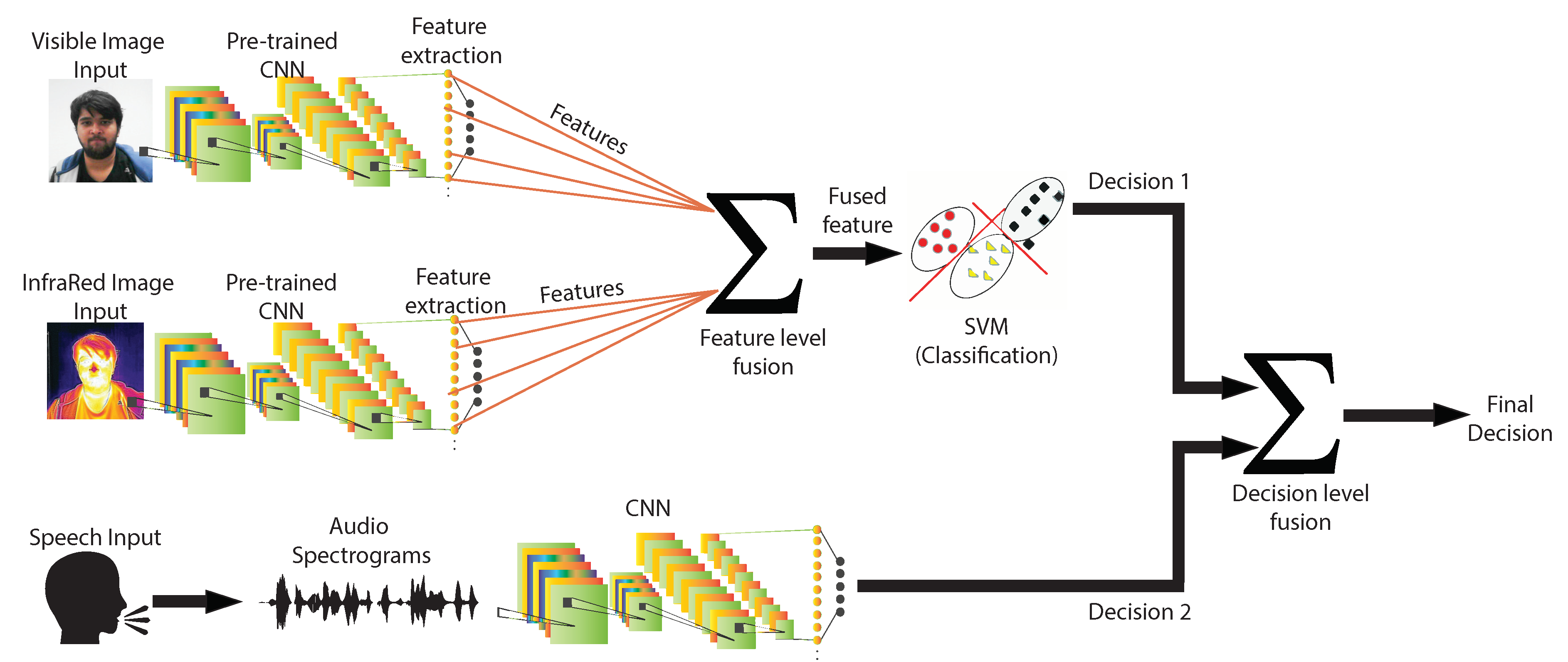
In the proposed method, ANN was employed for deep learning and ensemble-based classification of the emotion. The model consists of two layers of detection. In the first layer, two CNNs were trained using visible and infrared images individually. Transfer learning was incorporated to extract the features of the images. A feature-level fusion at this stage was engaged, and the fused feature was then fed to an SVM for classification. At the same layer, a third CNN was deployed to learn the emotions from the speech by incorporating audio spectrograms for training the ANN. The SVM and the third CNN (for speech) output was fed to a decision-level fusion in the second layer. The final classification was obtained as the output of the second layer. The proposed model is depicted in Figure 4.
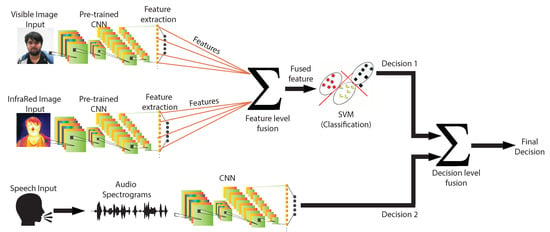
Figure 4.
Proposed model for automatic emotion recognition (AER) using visible images, IR images, and speech.
3.2.1. Stage Ia: AER with Visible and IR Images
Transfer learning is the process of applying a muscle of a pretrained deep learning network by altering some of its layers and fine-tuning it to learn a new function. This process is considerate as it tolerates the absence of a large amount of training data and is capable of training a network with even small datasets. Compared to training from scratch, the process is generally expeditious and superior to networks trained from scratch for the same amount of training data. A typical transfer learning process by CNN for image classification involves the following steps:
- Choose a pre-trained network.
- Replace the final layers to adapt to the new dataset.
- Tweak the values of hyperparameters to achieve higher accuracy and train.
For this work, a pre-trained CNN, the AlexNet, was used to perform transfer learning over the VIRI DB. AlexNet has been trained for more than a million images (called the ImageNet database [119]) and can classify them into 1000 categories. It is a 25-layer deep CNN that comprises of a diverse set of layers for specific operations. For image classification, a mandatory image input layer provides an input image to CNN after data normalization. The original 1440 × 1080 pixel images in the database were down-sampled to 227 × 227 to feed to the input layer due to the image size accepted by AlexNet. There is a convolutional layer that smears sliding convolutional filters to the input from the image input layer and produces a feature map as the output. There are multiple Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) layers in the CNN. AlexNet was modified for the classification of emotions by replacing the last three layers with new layers that were appointed to learn from the new database. Five new layers (2 fully connected, one activation, one softmax, and one classification layer) were added as the final layers of the network, which resulted in a 27-layer CNN. The features generated at the last fully connected layer (3rd last layer of the CNN) were extracted and used for the feature level fusion.
We also employed pooling layers whose primary function is to down-sample the input to reduce the size that helps decrease the computations performed in subsequent layers and reduce over-fitting. Several dropouts, fully connected, and channel normalization layers were also used. The final layers include a softmax (that applies the softmax function) and a classification layer that gives the class probability of the input. It is the output unit activation function after the last fully connected layer.
A feature level fusion technique, based on Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) [120,121], has been applied to combine the features extracted from the two CNNs in the first layer of the framework. The CCA is a multivariate statistical analysis method for the mutual association between two arbitrary vectors. The fused feature vector is more discriminative than any of the individual input vectors. We used the summation method to combine the transformed feature vectors. The fused features from the two CNNs were fed to an SVM classifier for intermediate classification of AER. Fundamentally, it maps the data as points in space in a manner that the categories they belong to reside as far away from each other as possible. Hence, when it encounters a new data, it maps the data in the same space and gives predictions of the category it belongs to by finding which side of the boundary it was mapped. The SVM classified the fused vector for producing image classification (visible and IR images) for AER.
3.2.2. Stage Ib: AER with Speech
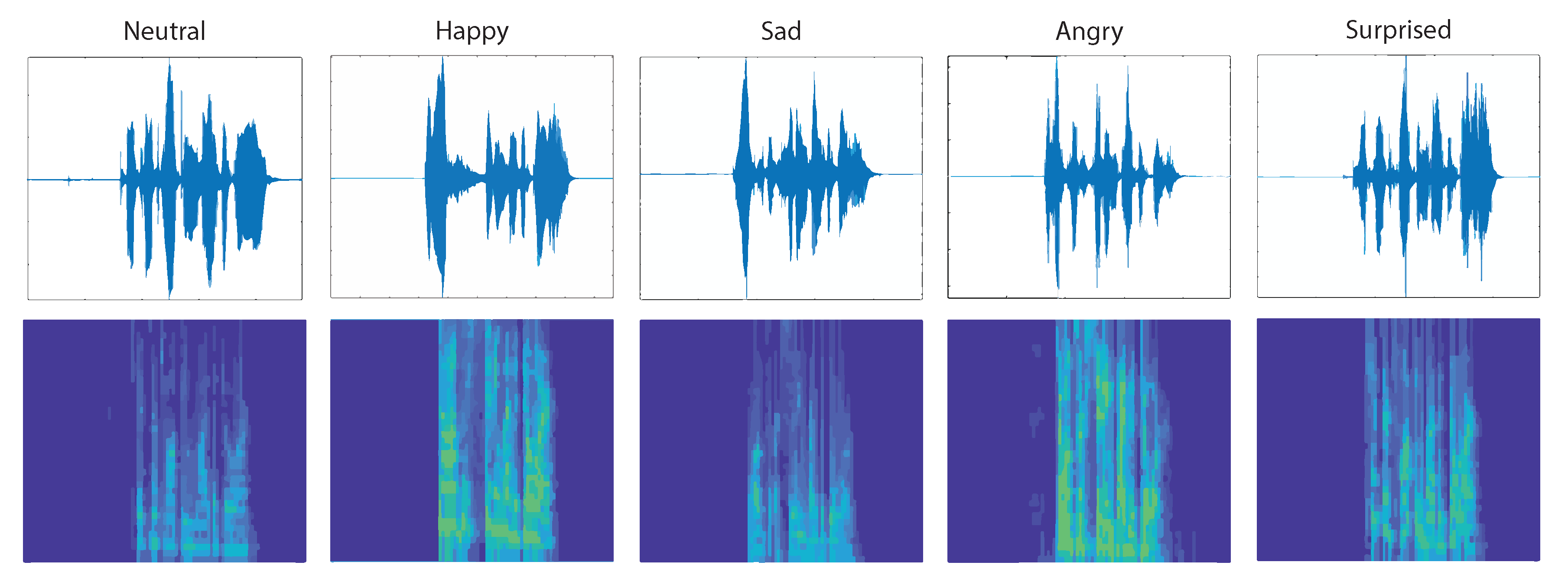
Speech-based emotion recognition was the second major component of the AER framework developed in this work. As shown in Figure 4, emotion recognition through speech was carried out by training a CNN with the spectrograms of the speech data. A spectrogram may be defined as a plot of the spectrum of frequencies of a signal with time. Usually represented as a heat map, spectrograms are a visual representation of the speech signal, while the variation in brightness or colors depicts the intensities. Representation of speech waveforms with their spectrograms is shown in Figure 5. A separate 24-layer CNN was put to service for training the speech emotion recognition portion. The speech and songs from RAVDESS DB were used to train this CNN for detecting the emotional content with background noise and silences for effectively incorporating their inevitable presence during the testing and validation. CNN performed the classification for the speech signals, and this formed the decision to be fed in the final decision level fusion besides the image classification decision.
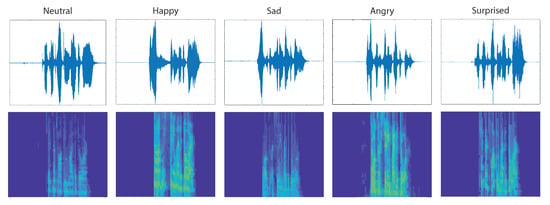
Figure 5.
Audio waveforms and their spectrograms for the five basic emotions.
3.2.3. Stage II: Decision Level Fusion
As a culmination of this work, the classifications from speech and images were combined using a decision level fusion at the second stage of the framework. A late fusion technique termed as weighted decision templates (WDT) [122] was applied to integrate the decisions emanating from SVM (for images) and the CNN (for speech) as shown in Figure 4. The decision template (DT) fusion algorithm computes the DTs per category by taking an average of the decisions for the training samples belonging to each class by every classifier. The WDT is an improvement over the conventional DT as it assigns weights to each classifier based on its performance and output. A more reliable classifier (higher accuracy) is weighted more and contributes significantly to making a decision. We used the fusion rule of the weighted sum to evaluate the final probability of a result after fusion belonging to a specific emotion.
4. Results
The framework was trained over the VIRI and RAVDESS datasets. The results were combined using a feature level fusion and a decision level fusion at different stages to achieve adequate accuracy. This section provides an overview of the results at every stage of the framework and compares individual and fused input modalities’ accuracy. The framework accuracy augmented with each layer of an integrated modality, and the trend is illustrated in the results obtained. The results are presented in the form of confusion matrices and the well-known measures derived from the matrices, i.e., accuracy, precision, recall, and -measure.
4.1. Visible Images Only
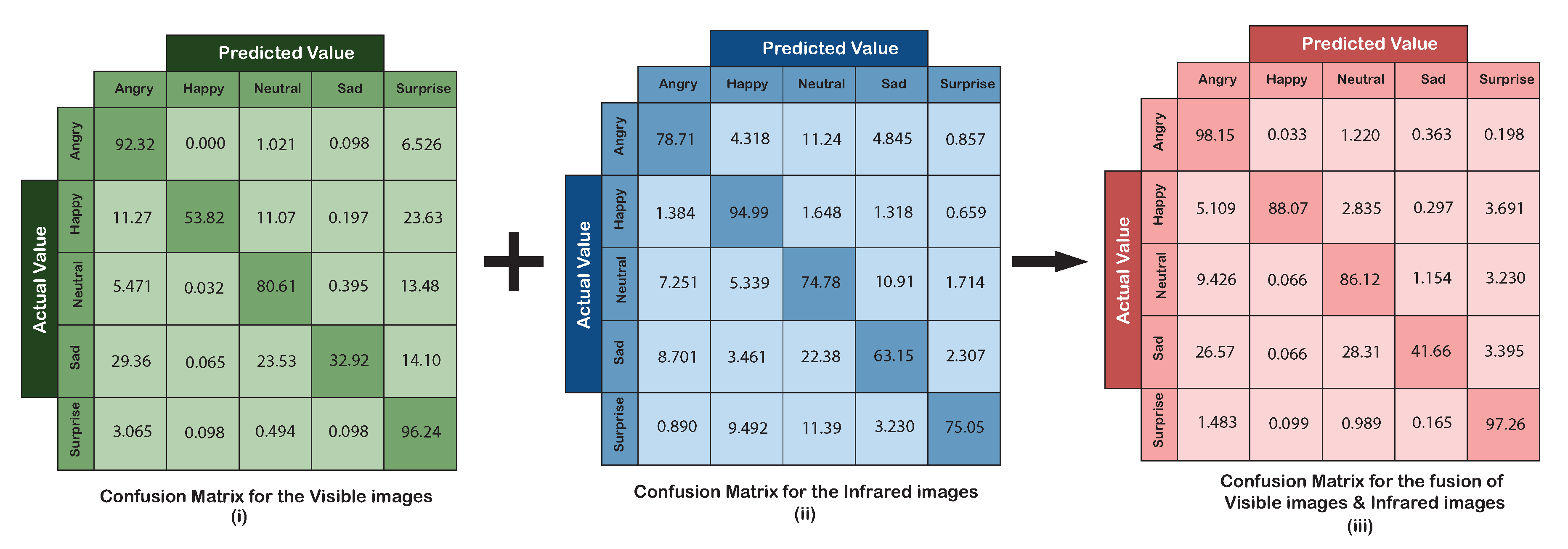
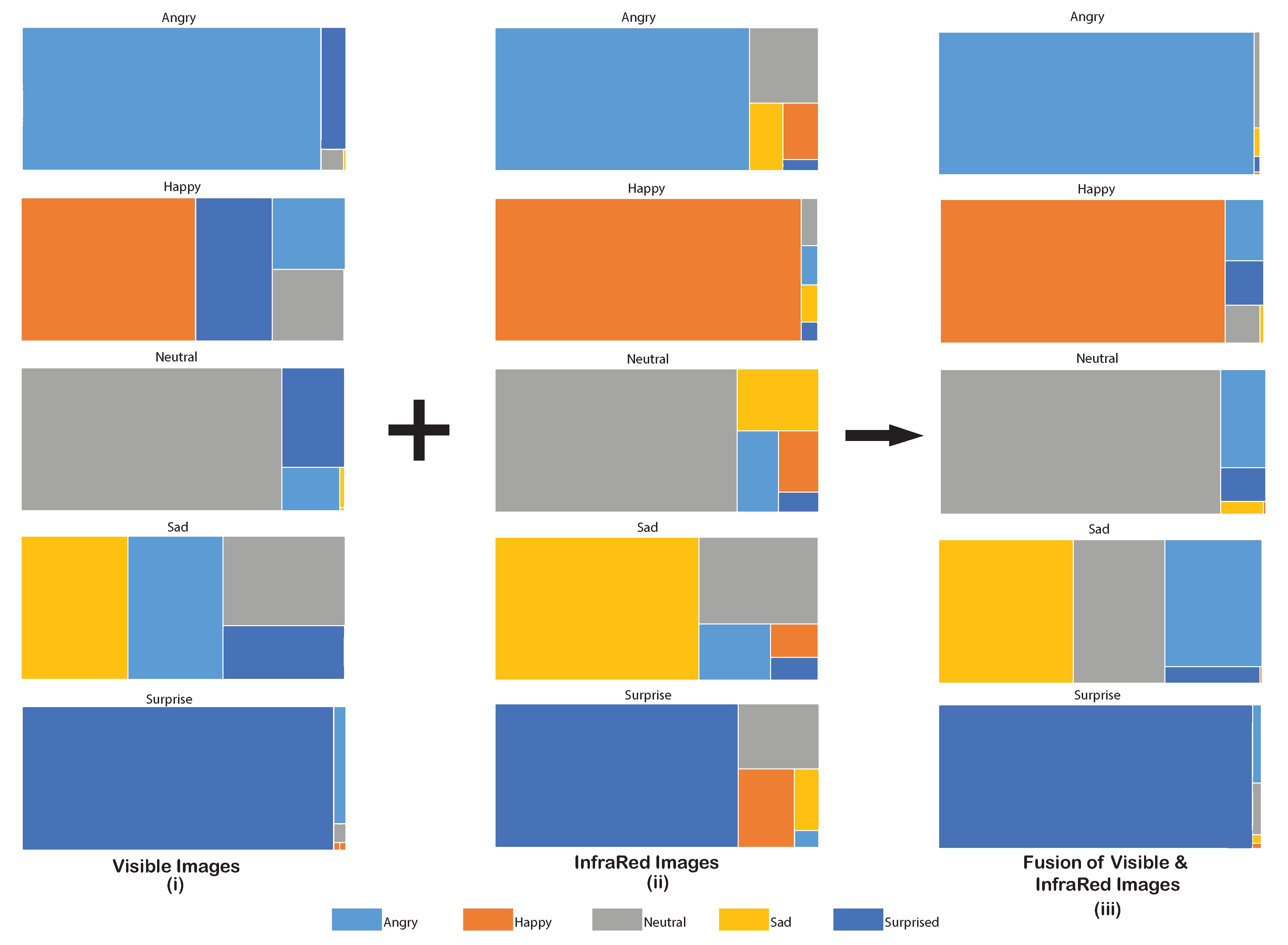
The first layer of the framework was meant for solitary identification of emotions. The CNN for visible images was able to identify emotions with an overall accuracy of 71.19%. The confusion matrix for the AER with visible images, as shown in Figure 6i, indicates that the accuracy of individual emotions ranges between 32.92% (sad)–92.32% (angry). The treemap for the detected emotional category’s proportional distribution is presented in Figure 7i. The emotions were correctly classified with low confusion with other emotions if the area of the detected emotion is more compared to the other emotional categories in a treemap. It can be observed that the pronounced emotions such as angry and surprise were detected without much uncertainty. Emotions that were more likely to be confused with other emotions showed a lower proportion in terms of area in the treemap, e.g., sad emotion was heavily confused with angry, neutral, and surprise emotions when only visible images were used. The recall for the AER by visible images was 0.71, with the precision and f-measure being 0.78 and 0.75, respectively.
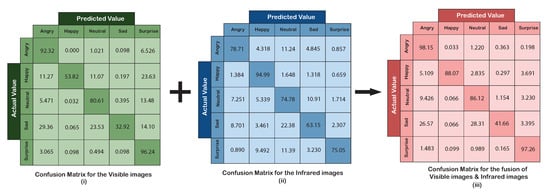
Figure 6.
Confusion matrix for the visible images, infrared images, and fusion of images.
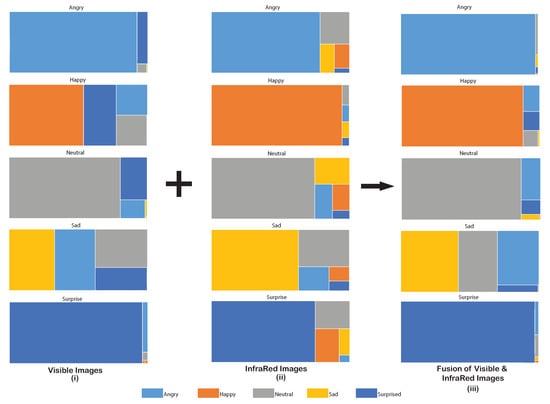
Figure 7.
Treemap displaying the proportional accuracy for every detected emotion in the visible images, infrared images, and the fusion of the images.
4.2. IR Images Only
The overall accuracy achieved from the second CNN using IR images was 77.34%. The confusion matrix for the AER with infrared images is shown in Figure 6ii, which shows that the accuracy for individual emotions varied between 63.15–94.99%. Clearly, this range is better than what was achieved with visible images; however, the worst performed for this type of data was still the sad expression. Although sad emotion was mostly confused with neutral emotion, it was expected due to similarities in the facial expressions of these emotions. The proportional distribution of the detected emotions is depicted in the treemaps shown in Figure 7ii. The IR images were able to identify happy emotion with the least confusion. The recall for the AER using the IR images was 0.77, while the precision and f-measures were both 0.78.
4.3. Fusion of IR and Visible Images
A feature level fusion of the visible and infrared images produced an improvement over the individual image types. This was observed in the accuracy of the SVM classifier, which was recorded to be 82.26%. The confusion matrix for the fused images is depicted in Figure 6iii. Proportional distribution of the detected emotions after fusion is shown in Figure 7iii. Except for the surprise emotion, all other emotions exhibit improved accuracy compared to the use of the individual type of images. The improved recall, precision, and f-measures for the fused images were obtained as 0.82, 0.85, and 0.83, respectively.
4.4. Speech Only
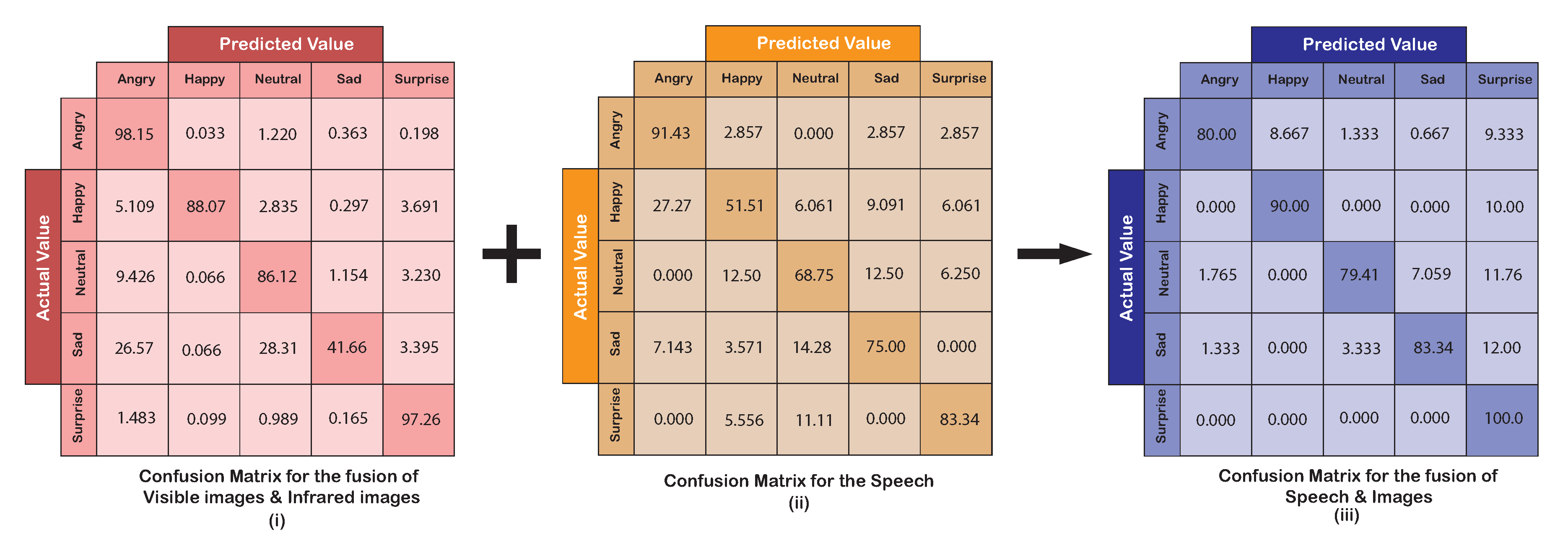
Speech recognition was the final unit of the first layer of the framework. It was a supporting modality for the facial expressions, but a solitary mention of the metrics for the AER by speech alone is also presented. CNN for speech signals was able to classify emotions in speech with an accuracy of 73.28%. The confusion matrix for the speech is shown in Figure 8ii. A proportional distribution treemap for the AER by speech for all emotional classes has been shown in Figure 9ii. The area distribution in the treemap for the speech signals indicate a clear detection of angry and surprise emotions while the remaining three-faced confusion during classification. The recall was found to be 0.73, while both precision and f-measures were found to be 0.72.
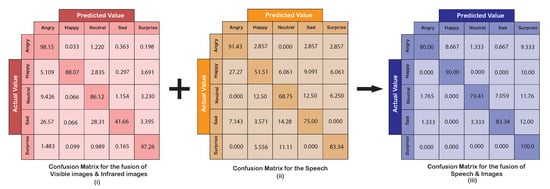
Figure 8.
Confusion matrix for the images, the speech, and the fusion of images and speech.
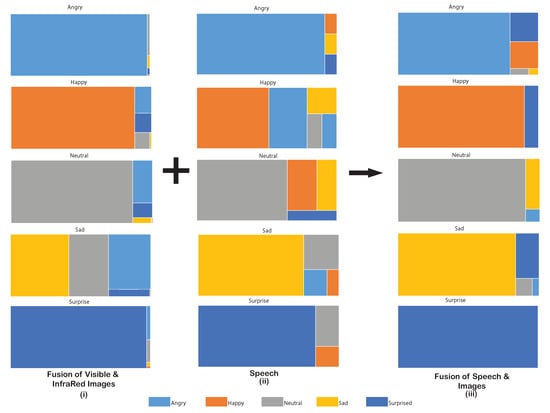
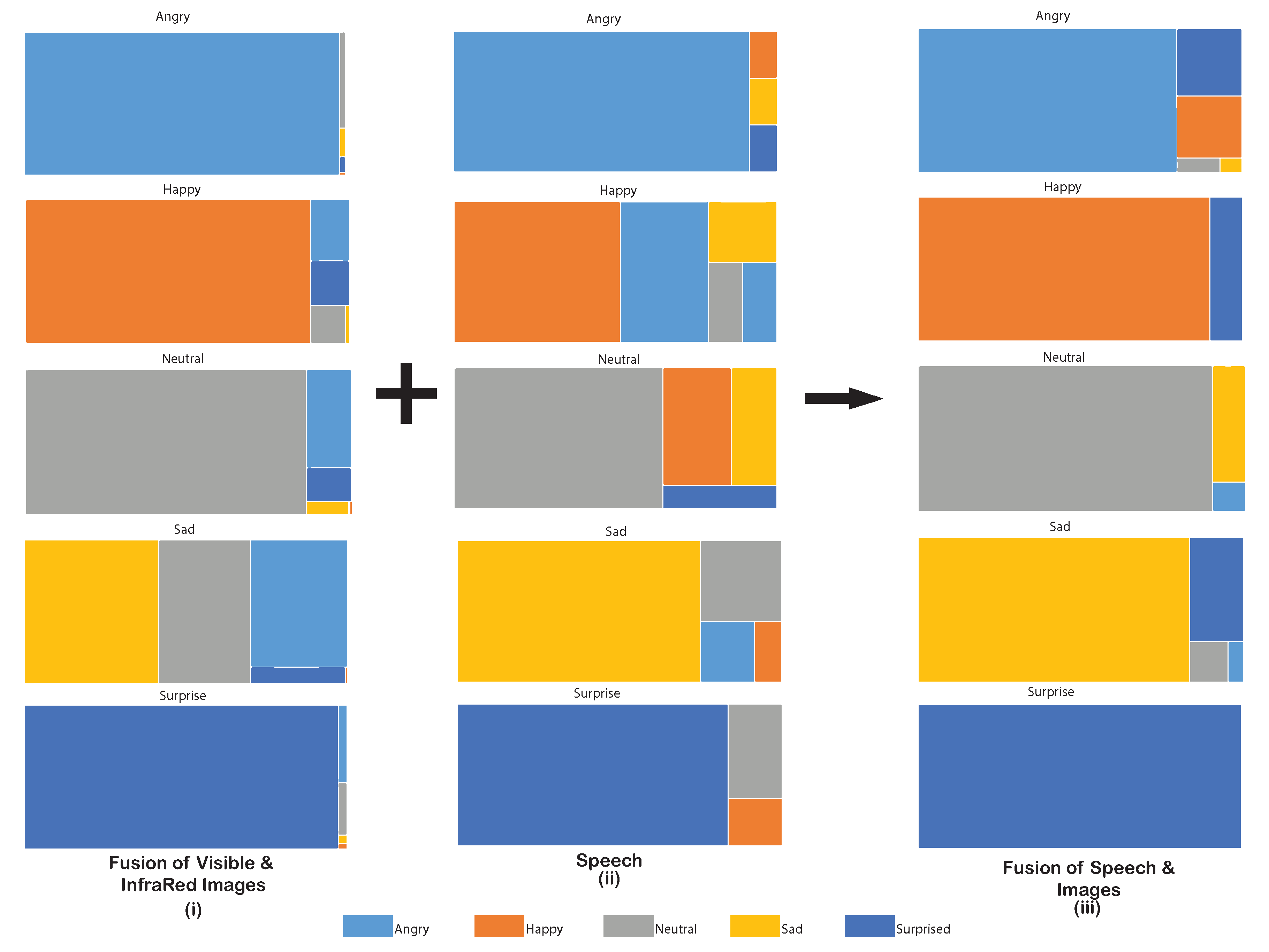
Figure 9.
Treemap displaying the proportional accuracy for every detected emotion in the images, the speech, and the fusion of the images and speech.
4.5. Fusion of IR Images, Visible Images, and Speech
The second layer of the AER framework, which fused the results obtained with images and speech, was able to achieve a noteworthy improvement over the individual or fused (visible and IR) results. The confusion matrix of the emotional classification for the proposed AER framework is shown in Figure 8iii. The treemap in Figure 9iii depicts the accuracy of the AER framework while displaying the ambiguity the framework faces while classifying the emotions. The largest area for the correctly classified emotion conveys the superiority of the ensemble-based framework over the individual modalities. An accuracy of 86.36% was achieved for this step. A recall of 0.86, a precision of 0.88, and the F-measure of 0.87 was achieved. It is noteworthy that the accuracy achieved lied between 79.41–100.0%.
4.6. Discussion
The metrics for the individual modalities and subsequent fusion of those modalities are presented in Table 3. Certain emotions are harder to comprehend and pose difficulty in recognition, e.g., differentiating between emotions such as sad and neutral is challenging, attributing to similarities in their facial expressions. Minute changes in the facial regions when exhibiting these emotions can also be a rationale for such ambiguity. This is evident from the low classification accuracy with both image type, i.e., visible and infrared. The sad emotion was muddled with angry and neutral emotions because the facial regions such as the shape of mouth do not alter significantly. Overall, the low proportion of the detected emotion in the treemap (Figure 7i,ii) for these emotions show a lesser area as compared to other emotions. However, they still outperform individual modalities or fused results of both types of images.

Table 3.
Comparison of the AER metrics by different modalities (Visible: V, Infrared: IR, Speech: S).
Contrarily, loud emotions such as surprise, angry, and happy posed less ambiguity in their detection. This is again evident from the treemaps of visible and IR images in Figure 7i,ii. A contrasting observation of this fact is the lower area of facial region engaged by the emotion happy for detection in the visible images. A wide-eyed expression generally accounts for the angry and surprised emotions. This is evident from the treemap of visible images (Figure 7i) where, to some extent, both of these expressions were confused with each other. Another trait for a loud emotional expression is the opening of the mouth in amazement or for laughing in joy. This can be seen as a source of confusion while detecting emotion happy with surprise.
The temperature of facial regions turned out to be a rescuer, as expected. The intricacies of the emotional detection for subtle emotions were handled well by IR images. The fusion of the visible and IR images provided better detection accuracy for these emotions. The increase in the area of anticipated emotion for all the emotional categories in the treemap (Figure 7iii) elucidates this information. All five expressions, happy, angry, sad, neutral, and surprise were detected with justifiable accuracy by the mere fusion of IR and visible images. However, a clashing observation for this trend is observed in case of sad emotion where it was confused with the affective state of neutral and angry due to the reasons mentioned above.
The speech was harnessed to further tackle this ambiguity by clarifying the confusion between facially similar expressions. The tone and pitch of the speech govern the shape of the audio spectrograms, and these spectrograms were able to identify emotions based on their trend in a CNN. The speech was also used alone for AER and did a decent job of classification with an accuracy of 73.28%. This was quite similar to the ones achieved by visible or IR images alone but less than their fusion. In the speech, when expressing an angry or surprised emotion, the pitch is generally high, and these emotions are less ambiguous to identify. This is evident from treemap in Figure 9ii where emotions surprise and angry do cover majority of the area for their perceived emotions. The affective states of sad and neutral were not very sharp in classification because of their similarity with other emotional classes while exhibiting them. Emotion happy also showed a slight confusion with angry because of the evident similarity of being loud while exhibiting these emotions.
Finally, the fusion of speech with the images provided a high accuracy framework that distinguished emotions with higher credibility. The fusion of images with speech removed the ambiguity where the other modality suitably removed a confusion in two emotions. The treemap in the Figure 9iii shows a clear classification for all the emotions with the surprise emotion being classified with surety and sad emotion being the least accurate emotion to be classified. The fusion of images and speech was able to achieve an accuracy of 86.36%. The Table 4 presents a comparison of the presented method with the recent multimodal emotional detection works.

Table 4.
Comparison of state-of-the-art in multimodal AER with the proposed work.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
This work presents a novel multimodal approach for facial emotion detection by the fusion of visible and IR images with speech. A framework based on the ensemble approach of emotion detection using pattern detection methods is presented. A novel database comprising of visible and corresponding IR images was created to tackle the inevitable light invariant conditions. The fusion of visible and infrared images classified emotions depicted with an accuracy of 82.26%. Speech samples from the RAVDESS multimodal dataset resulted in detection accuracy of 73.28%. The decisions from the images and speech were fused using decision templates (a decision level fusion technique) to achieve an overall accuracy of 86.36%. A comparison of the accuracy with the recent work in multimodal emotion detection proves the framework’s superiority. The framework is able to detect emotions with a comparable accuracy with most of the contemporary work. The rationale for its exclusivity is its attainment of this accuracy in the wild background and light invariant conditions. The framework could be further perfected in various ways. For example, using the images and voice samples from the same subjects and using other modalities such as physiological signals might further enhance the framework for detecting the emotional intensity and subtle expressions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.Y.J.; data curation, M.F.H.S.; formal analysis, M.F.H.S.; investigation, M.F.H.S.; methodology, A.Y.J.; project administration, A.Y.J.; resources, A.Y.J.; software, A.Y.J.; supervision, A.Y.J.; validation, M.F.H.S. and A.Y.J.; writing—original draft, M.F.H.S.; writing—review and editing, A.Y.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References and Notes
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Facial Action Coding System; Consulting Psychologists Press, Stanford University: Palo Alto, Santa Clara County, CA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.; Hager, J. Facial Action Coding System: The Manual on CD ROM. In A Human Face; Network Information Research Co.: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V.; Hager, J.C. FACS investigator’s guide. In A Human Face; Network Information Research Co.: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2002; p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Kahou, S.E.; Bouthillier, X.; Lamblin, P.; Gulcehre, C.; Michalski, V.; Konda, K.; Jean, S.; Froumenty, P.; Dauphin, Y.; Boulanger-Lewandowski, N.; et al. Emonets: Multimodal deep learning approaches for emotion recognition in video. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 2016, 10, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Dong, S.Y.; Roh, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, S.Y. Fusing Aligned and Non-Aligned Face Information for Automatic Affect Recognition in the Wild: A Deep Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Li, L.; Wu, X.; Zuo, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G.; He, J.; Zhu, X. Combining feature-level and decision-level fusion in a hierarchical classifier for emotion recognition in the wild. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 2016, 10, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreini, K.; Nadolski, R.; Westera, W. Data Fusion for Real-time Multimodal Emotion Recognition through Webcams and Microphones in E-Learning. Int. J.-Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2016, 32, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cao, T.; Feng, Z.; Dong, C. Multi-Modal Fusion Emotion Recognition Based on HMM and ANN. In Proceedings of the Contemporary Research on E-business Technology and Strategy, Tianjin, China, 29–31 August 2012; pp. 541–550. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Martín, F.; Malfaz, M.; Sequeira, J.; Gorostiza, J.F.; Salichs, M.A. A multimodal emotion detection system during human–robot interaction. Sensors 2013, 13, 15549–15581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Chi, Z.; Fu, H. Emotion recognition in the wild with feature fusion and multiple kernel learning. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–16 November 2014; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 508–513. [Google Scholar]
- Tzirakis, P.; Trigeorgis, G.; Nicolaou, M.A.; Schuller, B.; Zafeiriou, S. End-to-End Multimodal Emotion Recognition using Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.08619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.M.M.; Stepanov, E.A. Enhanced face/audio emotion recognition: Video and instance level classification using ConvNets and restricted Boltzmann Machines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Intelligence, Leipzig, Germany, 23–27 August 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 939–946. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrišek, S.; Gajšek, R.; Mihelič, F.; Pavešić, N.; Štruc, V. Towards efficient multi-modal emotion recognition. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, H.; Provost, E.M. Deep learning for robust feature generation in audiovisual emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 3687–3691. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Muhammad, G.; Alhamid, M.F.; Song, B.; Al-Mutib, K. Audio-visual emotion recognition using big data towards 5G. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2016, 21, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Muhammad, G. Audio-visual emotion recognition using multi-directional regression and Ridgelet transform. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 2016, 10, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, F.; Marjanovic, M.; Njegus, A.; Escalera, S.; Anbarjafari, G. Fusion of classifier predictions for audio-visual emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Chi, Z.; Fu, H. Facial expression recognition in video with multiple feature fusion. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2016, 9, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zheng, W.; Xu, Q.; Lu, G.; Li, H.; Wang, B. Sparse Kernel Reduced-Rank Regression for Bimodal Emotion Recognition From Facial Expression and Speech. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2016, 18, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. Exploring sources of variation in human behavioral data: Towards automatic audio-visual emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII), Xi’an, China, 21–24 September 2015; pp. 748–753. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, E.; Yang, L.; Jiang, D.; Sahli, H. Multimodal dimensional affect recognition using deep bidirectional long short-term memory recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII), Xi’an, China, 21–24 September 2015; pp. 208–214. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.; Nguyen, K.; Sridharan, S.; Ghasemi, A.; Dean, D.; Fookes, C. Deep spatio-temporal features for multimodal emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 24–31 March 2017; pp. 1215–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Mao, Q.; Tu, J.; Zhan, Y. Multimodal shared features learning for emotion recognition by enhanced sparse local discriminative canonical correlation analysis. Multimed. Syst. 2019, 25, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Huang, T.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Learning Affective Features with a Hybrid Deep Model for Audio-Visual Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2017, 28, 3030–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid, F.; Manso, L.J.; Núnez, P. A Novel Multimodal Emotion Recognition Approach for Affective Human Robot Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Haq, S.; Jan, T.; Jehangir, A.; Asif, M.; Ali, A.; Ahmad, N. Bimodal Human Emotion Classification in the Speaker-Dependent Scenario; Pakistan Academy of Sciences: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2015; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Gideon, J.; Zhang, B.; Aldeneh, Z.; Kim, Y.; Khorram, S.; Le, D.; Provost, E.M. Wild wild emotion: A multimodal ensemble approach. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Tokyo, Japan, 12–16 November 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 501–505. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Guan, L.; Venetsanopoulos, A.N. Kernel cross-modal factor analysis for information fusion with application to bimodal emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2012, 14, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, F.; Marjanovic, M.; Njegus, A.; Escalera, S.; Anbarjafari, G. Audio-visual emotion recognition in video clips. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 10, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afouras, T.; Chung, J.S.; Senior, A.; Vinyals, O.; Zisserman, A. Deep audio-visual speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanie, S.; Nagrani, A.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Emotion recognition in speech using cross-modal transfer in the wild. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.05561. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Zheng, W.; Cui, Z.; Tang, C.; Zhang, T.; Zong, Y. Multi-cue fusion for emotion recognition in the wild. Neurocomputing 2018, 309, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, K.P.; Ang, L.M.; Ooi, C.S. A Combined Rule-Based & Machine Learning Audio-Visual Emotion Recognition Approach. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 9, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall, A.; Kaur, A.; Goecke, R.; Gedeon, T. Emotiw 2018: Audio-video, student engagement and group-level affect prediction. In Proceedings of the 2018 on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Boulder, CO, USA, 16–20 October 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 653–656. [Google Scholar]
- Avots, E.; Sapiński, T.; Bachmann, M.; Kamińska, D. Audiovisual emotion recognition in wild. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2018, 30, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Andre, E.; Lingenfelser, F.; Kim, J. Exploring fusion methods for multimodal emotion recognition with missing data. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2011, 2, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessous, L.; Castellano, G.; Caridakis, G. Multimodal emotion recognition in speech-based interaction using facial expression, body gesture and acoustic analysis. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 2010, 3, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, H.; Chakraborty, S.; Panchanathan, S. Multimodal emotion recognition using deep learning architectures. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Caridakis, G.; Castellano, G.; Kessous, L.; Raouzaiou, A.; Malatesta, L.; Asteriadis, S.; Karpouzis, K. Multimodal emotion recognition from expressive faces, body gestures and speech. In Artificial Intelligence and Innovations 2007: From Theory to Applications; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; Volume 247, pp. 375–388. [Google Scholar]
- Ghayoumi, M.; Bansal, A.K. Multimodal architecture for emotion in robots using deep learning. In Proceedings of the Future Technologies Conference (FTC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–7 December 2016; pp. 901–907. [Google Scholar]
- Ghayoumi, M.; Thafar, M.; Bansal, A.K. Towards Formal Multimodal Analysis of Emotions for Affective Computing. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Distributed Multimedia Systems, Salerno, Italy, 25–26 November 2016; pp. 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Filntisis, P.P.; Efthymiou, N.; Koutras, P.; Potamianos, G.; Maragos, P. Fusing Body Posture with Facial Expressions for Joint Recognition of Affect in Child-Robot Interaction. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.01805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; He, M.; Gao, Z.; He, S.; Ji, Q. Emotion recognition from thermal infrared images using deep Boltzmann machine. Front. Comput. Sci. 2014, 8, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Lv, S.; Lv, Y.; Wu, G.; Peng, P.; Chen, F.; Wang, X. A natural visible and infrared facial expression database for expression recognition and emotion inference. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2010, 12, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, B. Dataset 02: IRIS Thermal/Visible Face Database. DOE University Research Program in Robotics under grant DOE-DE-FG02-86NE37968. Available online: http://vcipl-okstate.org/pbvs/bench/ (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Elbarawy, Y.M.; El-Sayed, R.S.; Ghali, N.I. Local Entropy and Standard Deviation for Facial Expressions Recognition in Thermal Imaging. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2018, 7, 580–586. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Wang, S.; Lan, W.; Fu, H.; Ji, Q. Facial expression recognition using deep Boltzmann machine from thermal infrared images. In Proceedings of the 2013 Humaine Association Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII), Geneva, Switzerland, 2–5 September 2013; pp. 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, A.; Routray, A.; Shit, S.; Deb, A.K. Human emotion recognition from facial thermal image based on fused statistical feature and multi-class SVM. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), New Delhi, India, 17–20 December 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Albarran, I.A.; Benitez-Rangel, J.P.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Morales-Hernandez, L.A. Human emotions detection based on a smart-thermal system of thermographic images. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 81, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitomi, Y.; Kim, S.I.; Kawano, T.; Kilazoe, T. Effect of sensor fusion for recognition of emotional states using voice, face image and thermal image of face. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, RO-MAN 2000, Osaka, Japan, 27–29 September 2000; pp. 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Kitazoe, T.; Kim, S.I.; Yoshitomi, Y.; Ikeda, T. Recognition of emotional states using voice, face image and thermal image of face. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, Beijing, China, 16–20 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Soleymani, M.; Lichtenauer, J.; Pun, T.; Pantic, M. A multimodal database for affect recognition and implicit tagging. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caridakis, G.; Wagner, J.; Raouzaiou, A.; Curto, Z.; Andre, E.; Karpouzis, K. A multimodal corpus for gesture expressivity analysis. In Multimodal Corpora: Advances in Capturing, Coding and Analyzing Multimodality; LREC: Valletta, Malta, 17–23 May 2010; pp. 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Caridakis, G.; Wagner, J.; Raouzaiou, A.; Lingenfelser, F.; Karpouzis, K.; Andre, E. A cross-cultural, multimodal, affective corpus for gesture expressivity analysis. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 2013, 7, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. Deap: A database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringeval, F.; Sonderegger, A.; Sauer, J.; Lalanne, D. Introducing the RECOLA multimodal corpus of remote collaborative and affective interactions. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Shanghai, China, 22–26 April 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, H.; Pigat, D.; Fridenson, S.; Berggren, S.; Tal, S.; Golan, O.; Bölte, S.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Lundqvist, D. The EU-emotion stimulus set: A validation study. Behav. Res. Methods 2016, 48, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, O.; Kotsia, I.; Macq, B.; Pitas, I. The eNTERFACE’05 audio-visual emotion database. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops, Atlanta, GA, USA, 3–7 April 2006; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Guan, L. Recognizing human emotional state from audiovisual signals. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2008, 10, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valstar, M.F.; Jiang, B.; Mehu, M.; Pantic, M.; Scherer, K. The first facial expression recognition and analysis challenge. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition and Workshops (FG 2011), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; pp. 921–926. [Google Scholar]
- Bänziger, T.; Scherer, K.R. Introducing the geneva multimodal emotion portrayal (gemep) corpus. In Blueprint for Affective Computing: A sourcebook; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 271–294. [Google Scholar]
- Haq, S.; Jackson, P.J. Multimodal emotion recognition. In Machine Audition: Principles, Algorithms and Systems; University of Surrey: Guildford, UK, 2010; pp. 398–423. [Google Scholar]
- Valstar, M.; Schuller, B.; Smith, K.; Eyben, F.; Jiang, B.; Bilakhia, S.; Schnieder, S.; Cowie, R.; Pantic, M. AVEC 2013: The continuous audio/visual emotion and depression recognition challenge. In Proceedings of the 3rd ACM International Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge, Barcelona, Spain, 21 October 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Valstar, M.; Schuller, B.; Smith, K.; Almaev, T.; Eyben, F.; Krajewski, J.; Cowie, R.; Pantic, M. Avec 2014: 3d dimensional affect and depression recognition challenge. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhalehpour, S.; Onder, O.; Akhtar, Z.; Erdem, C.E. BAUM-1: A Spontaneous Audio-Visual Face Database of Affective and Mental States. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 8, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, C.E.; Turan, C.; Aydin, Z. BAUM-2: A multilingual audio-visual affective face database. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2015, 74, 7429–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas-Cowie, E.; Cowie, R.; Sneddon, I.; Cox, C.; Lowry, O.; Mcrorie, M.; Martin, J.C.; Devillers, L.; Abrilian, S.; Batliner, A.; et al. The HUMAINE database: Addressing the collection and annotation of naturalistic and induced emotional data. In Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 488–500. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, M.; Kroschel, K.; Narayanan, S. The Vera am Mittag German audio-visual emotional speech database. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Hannover, Germany, 23 June–26 April 2008; pp. 865–868. [Google Scholar]
- McKeown, G.; Valstar, M.; Cowie, R.; Pantic, M.; Schroder, M. The semaine database: Annotated multimodal records of emotionally colored conversations between a person and a limited agent. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, G.; Valstar, M.F.; Cowie, R.; Pantic, M. The SEMAINE corpus of emotionally coloured character interactions. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Suntec City, Singapore, 19–23 July 2010; pp. 1079–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Gunes, H.; Pantic, M. Dimensional emotion prediction from spontaneous head gestures for interaction with sensitive artificial listeners. In Intelligent Virtual Agents; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Metallinou, A.; Yang, Z.; Lee, C.c.; Busso, C.; Carnicke, S.; Narayanan, S. The USC CreativeIT database of multimodal dyadic interactions: From speech and full body motion capture to continuous emotional annotations. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2016, 50, 497–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.M.; Lee, C.C. Fusion of multiple emotion perspectives: Improving affect recognition through integrating cross-lingual emotion information. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 5820–5824. [Google Scholar]
- Dailey, M.N.; Joyce, C.; Lyons, M.J.; Kamachi, M.; Ishi, H.; Gyoba, J.; Cottrell, G.W. Evidence and a computational explanation of cultural differences in facial expression recognition. Emotion 2010, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.; Akamatsu, S.; Kamachi, M.; Gyoba, J. Coding facial expressions with gabor wavelets. In Proceedings of the Third IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, 14–16 April 1998; pp. 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, M.J.; Budynek, J.; Akamatsu, S. Automatic classification of single facial images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1999, 21, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanade, T.; Cohn, J.F.; Tian, Y. Comprehensive database for facial expression analysis. In Proceedings of the Fourth IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Grenoble, France, 28–30 March 2000; pp. 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.; Cohn, J.F.; Kanade, T.; Saragih, J.; Ambadar, Z.; Matthews, I. The extended cohn-kanade dataset (ck+): A complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt, F.; Paeschke, A.; Rolfes, M.; Sendlmeier, W.F.; Weiss, B. A database of german emotional speech. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Lisbon, Portugal, 4–8 September 2005; Volume 5, pp. 1517–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall, A.; Goecke, R.; Lucey, S.; Gedeon, T. Collecting large, richly annotated facial-expression databases from movies. IEEE Multimed. 2012, 1, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Erhan, D.; Carrier, P.L.; Courville, A.; Mirza, M.; Hamner, B.; Cukierski, W.; Tang, Y.; Thaler, D.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Challenges in representation learning: A report on three machine learning contests. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Daegu, Korea, 3–7 November 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, H.W.; Nguyen, V.D.; Vonikakis, V.; Winkler, S. Deep learning for emotion recognition on small datasets using transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–13 November 2015; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall, A.; Goecke, R.; Sebe, N.; Gedeon, T. Emotion recognition in the wild. In Journal on Multimodal User Interfaces; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 10, pp. 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, C.; Bulut, M.; Lee, C.C.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Mower, E.; Kim, S.; Chang, J.N.; Lee, S.; Narayanan, S.S. IEMOCAP: Interactive emotional dyadic motion capture database. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2008, 42, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Siddiqui, M.F.H.; Javaid, A.Y. Facial Emotion Recognition: A Survey and Real-World User Experiences in Mixed Reality. Sensors 2018, 18, 416. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Hendricks, L.A.; Kuchenbecker, K.J.; Darrell, T. Deep learning for tactile understanding from visual and haptic data. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Pramerdorfer, C.; Kampel, M. Facial Expression Recognition using Convolutional Neural Networks: State of the Art. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.02903. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Cao, S.; Li, L.; He, J.; Yu, L. Exploring multimodal visual features for continuous affect recognition. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 12–16 October 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Keren, G.; Kirschstein, T.; Marchi, E.; Ringeval, F.; Schuller, B. End-to-end learning for dimensional emotion recognition from physiological signals. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Hong Kong, China, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Huang, T.; Gao, W. Multimodal Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Audio-Visual Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, New York, NY, USA, 6–9 June 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, G.; Hou, Z.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Jiang, L.; Xun, E. Ensemble of Deep Neural Networks with Probability-Based Fusion for Facial Expression Recognition. Cogn. Comput. 2017, 9, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Pappagari, R.; Kulkarni, P.; Villalba, J.; Carmiel, Y.; Dehak, N. Deep neural networks for emotion recognition combining audio and transcripts. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, S.; Marsic, I. Deep Multimodal Learning for Emotion Recognition in Spoken Language. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.08332. [Google Scholar]
- Majumder, A.; Behera, L.; Subramanian, V.K. Emotion recognition from geometric facial features using self-organizing map. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsia, I.; Pitas, I. Facial expression recognition in image sequences using geometric deformation features and support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.I.; Kanade, T.; Cohn, J.F. Recognizing action units for facial expression analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, J.J.; Kanade, T.; Cohn, J.F.; Li, C.C. Automated facial expression recognition based on FACS action units. In Proceedings of the Third IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Nara, Japan, 14–16 April 1998; pp. 390–395. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.l.; Kanade, T.; Cohn, J.F. Evaluation of Gabor-wavelet-based facial action unit recognition in image sequences of increasing complexity. In Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face Gesture Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 21 May 2002; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Lien, J.J.J.; Kanade, T.; Cohn, J.F.; Li, C.C. Detection, tracking, and classification of action units in facial expression. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2000, 31, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.F.H.; Javaid, A.Y.; Carvalho, J.D. A Genetic Algorithm Based Approach for Data Fusion at Grammar Level. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 14–16 December 2017; pp. 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Atrey, P.K.; Hossain, M.A.; El Saddik, A.; Kankanhalli, M.S. Multimodal fusion for multimedia analysis: A survey. Multimed. Syst. 2010, 16, 345–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.K.; Tiwary, U.S. Multimodal fusion framework: A multiresolution approach for emotion classification and recognition from physiological signals. NeuroImage 2014, 102, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kortelainen, J.; Zhao, G.; Li, X.; Moilanen, A.; Seppänen, T.; Pietikäinen, M. Multi-modal emotion analysis from facial expressions and electroencephalogram. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 147, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshvarpour, A.; Abbasi, A.; Goshvarpour, A. Fusion of heart rate variability and pulse rate variability for emotion recognition using lagged poincare plots. Australas Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2017, 40, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gievska, S.; Koroveshovski, K.; Tagasovska, N. Bimodal feature-based fusion for real-time emotion recognition in a mobile context. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII), Xi’an, China, 21–24 September 2015; pp. 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Byun, S.; Jung, K. Multimodal Speech Emotion Recognition Using Audio and Text. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04635. [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, D.; Gorantla, S.; Poria, S.; Zimmermann, R. Self-attentive feature-level fusion for multimodal emotion detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR), Miami, FL, USA, 10–12 April 2018; pp. 196–201. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.W.; Song, K.Y.; Jeong, J.; Choi, W.Y. Convolutional Attention Networks for Multimodal Emotion Recognition from Speech and Text Data. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.06606. [Google Scholar]
- Majumder, N.; Hazarika, D.; Gelbukh, A.; Cambria, E.; Poria, S. Multimodal sentiment analysis using hierarchical fusion with context modeling. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2018, 161, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, D.; Poria, S.; Zadeh, A.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.P.; Zimmermann, R. Conversational Memory Network for Emotion Recognition in Dyadic Dialogue Videos. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; (Long Papers). Volume 1, pp. 2122–2132. [Google Scholar]
- Mencattini, A.; Ringeval, F.; Schuller, B.; Martinelli, E.; Di Natale, C. Continuous monitoring of emotions by a multimodal cooperative sensor system. Procedia Eng. 2015, 120, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shah, M.; Chakrabarti, C.; Spanias, A. A multi-modal approach to emotion recognition using undirected topic models. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Melbourne, Australia, 1–5 June 2014; pp. 754–757. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, P.P.; Zadeh, A.; Morency, L.P. Multimodal local-global ranking fusion for emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Boulder, CO, USA, 16–20 October 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Recognition of emotions using multimodal physiological signals and an ensemble deep learning model. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 2017, 140, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Beigi, H. Multi-Modal Emotion recognition on IEMOCAP Dataset using Deep Learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.05788. [Google Scholar]
- Dataset 01: NIST Thermal/Visible Face Database 2012.
- Nguyen, H.; Kotani, K.; Chen, F.; Le, B. A thermal facial emotion database and its analysis. In Proceedings of the Pacific-Rim Symposium on Image and Video Technology, Guanajuato, Mexico, 28 October–1 November 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 397–408. [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone, S.R.; Russo, F.A. The Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS): A dynamic, multimodal set of facial and vocal expressions in North American English. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A Large-Scale Hierarchical Image Database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, FL, USA, 22–24 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.S.; Zeng, S.G.; Liu, Y.; Heng, P.A.; Xia, D.S. A new method of feature fusion and its application in image recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, M.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.; Alhalabi, W. Fully automatic face normalization and single sample face recognition in unconstrained environments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 47, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, A.; Wang, L.; Qi, J. A Multiple Classifier Fusion Algorithm Using Weighted Decision Templates. Sci. Prog. 2016, 2016, 3943859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).