Embodied Engagement with Narrative: A Design Framework for Presenting Cultural Heritage Artifacts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Interactive Narrative
2.2. Tangible and Embodied Narrative Systems
2.3. Toward a Narrative Framework
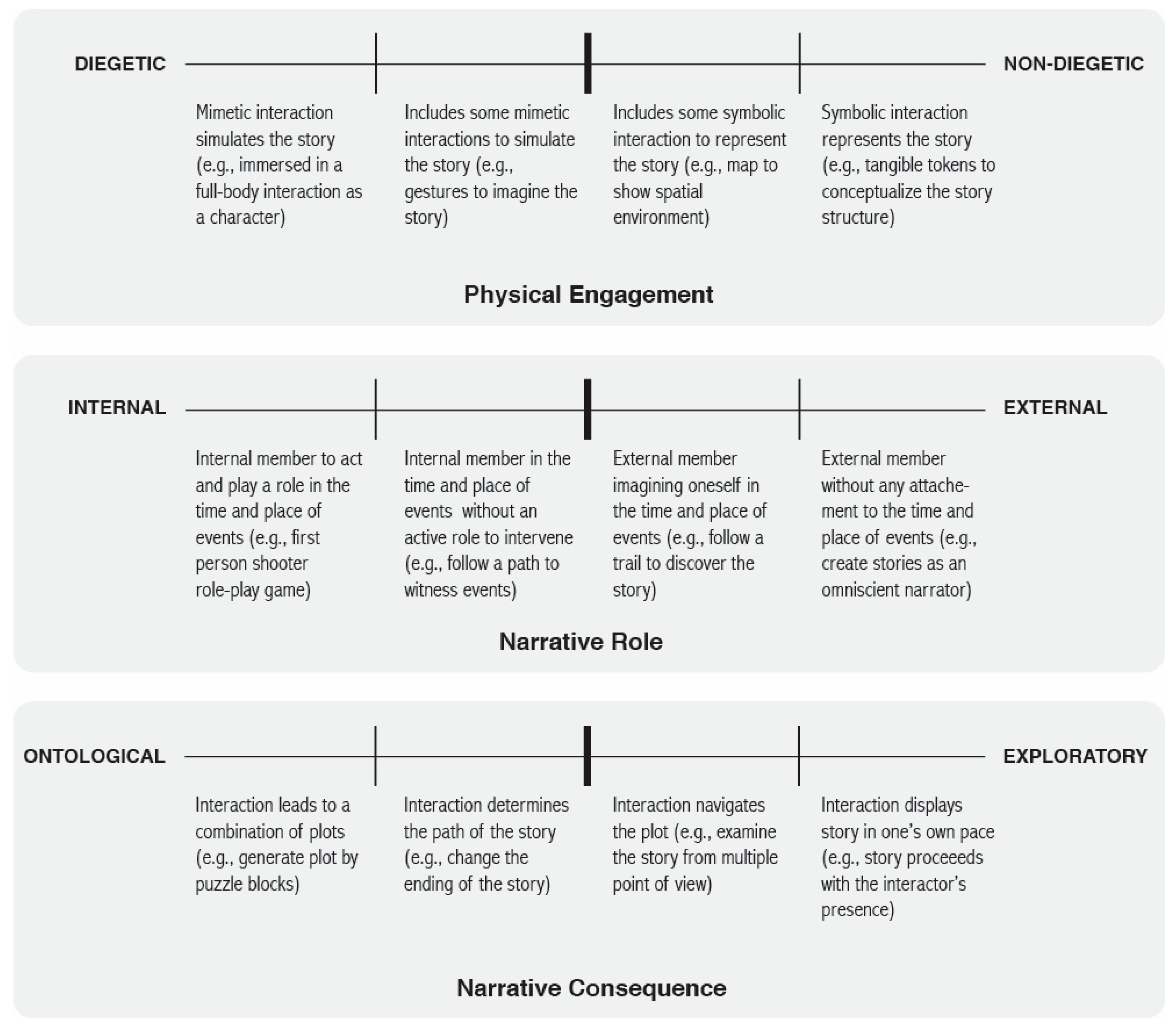
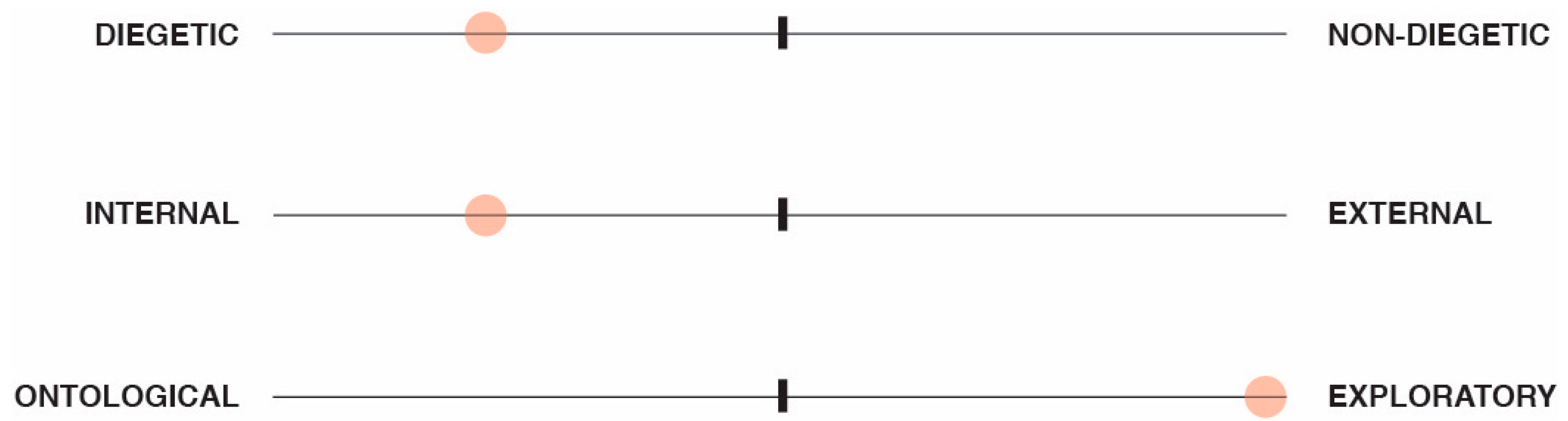
3. Tangible and Embodied Narrative Framework (TENF)
3.1. Diegetic vs. Non-Diegetic
3.2. Internal vs. External
3.3. Ontological vs. Exploratory
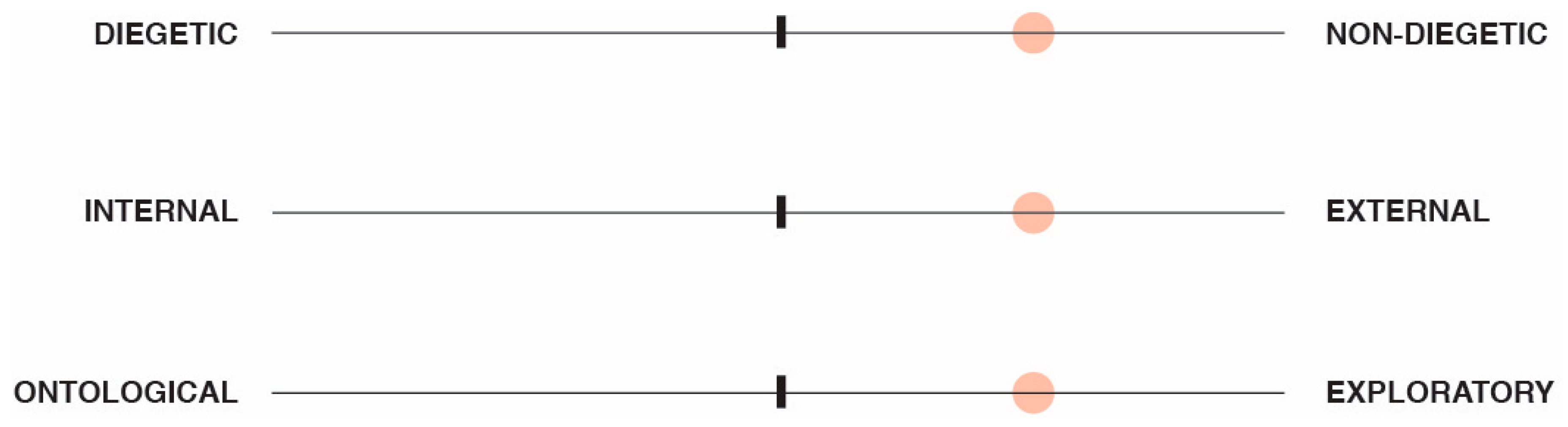
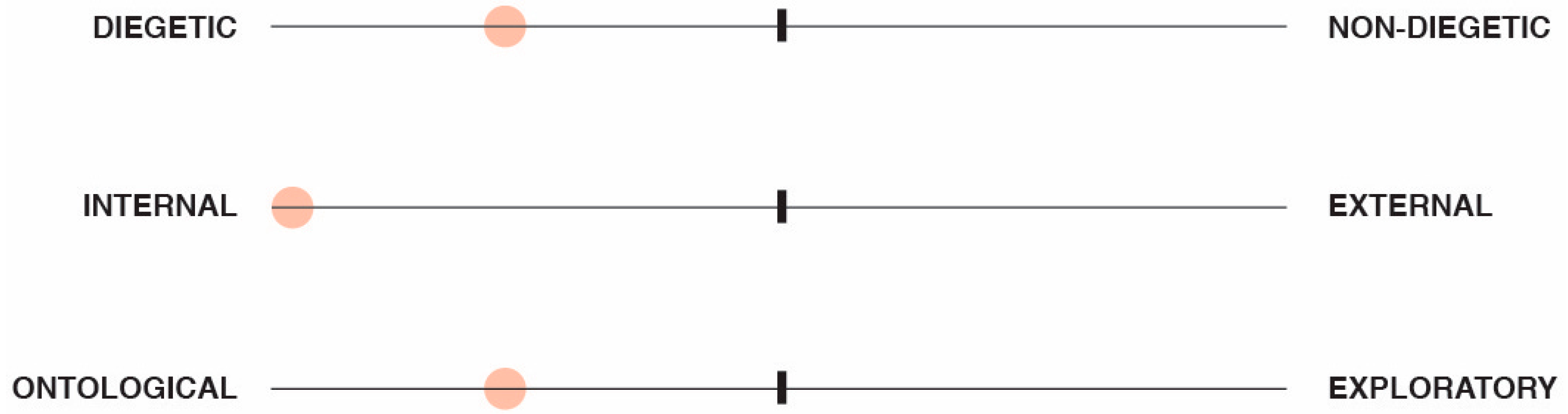
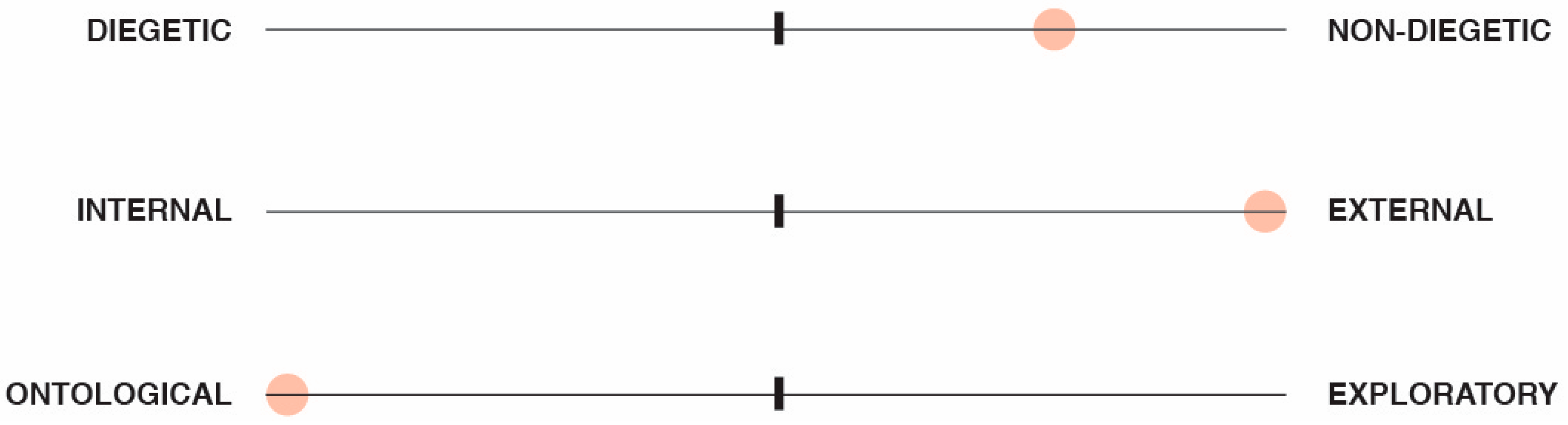
3.4. Structure of the Tangible and Embodied Narrative Framework
4. The Pilot and Case Study Projects
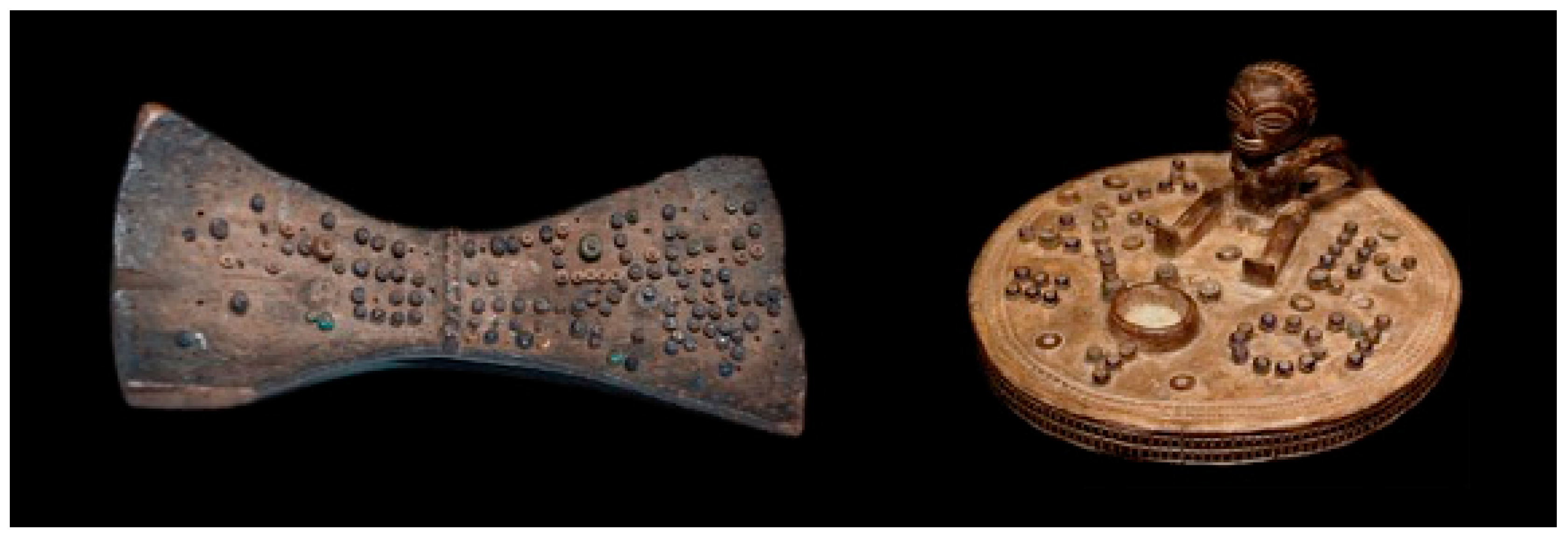
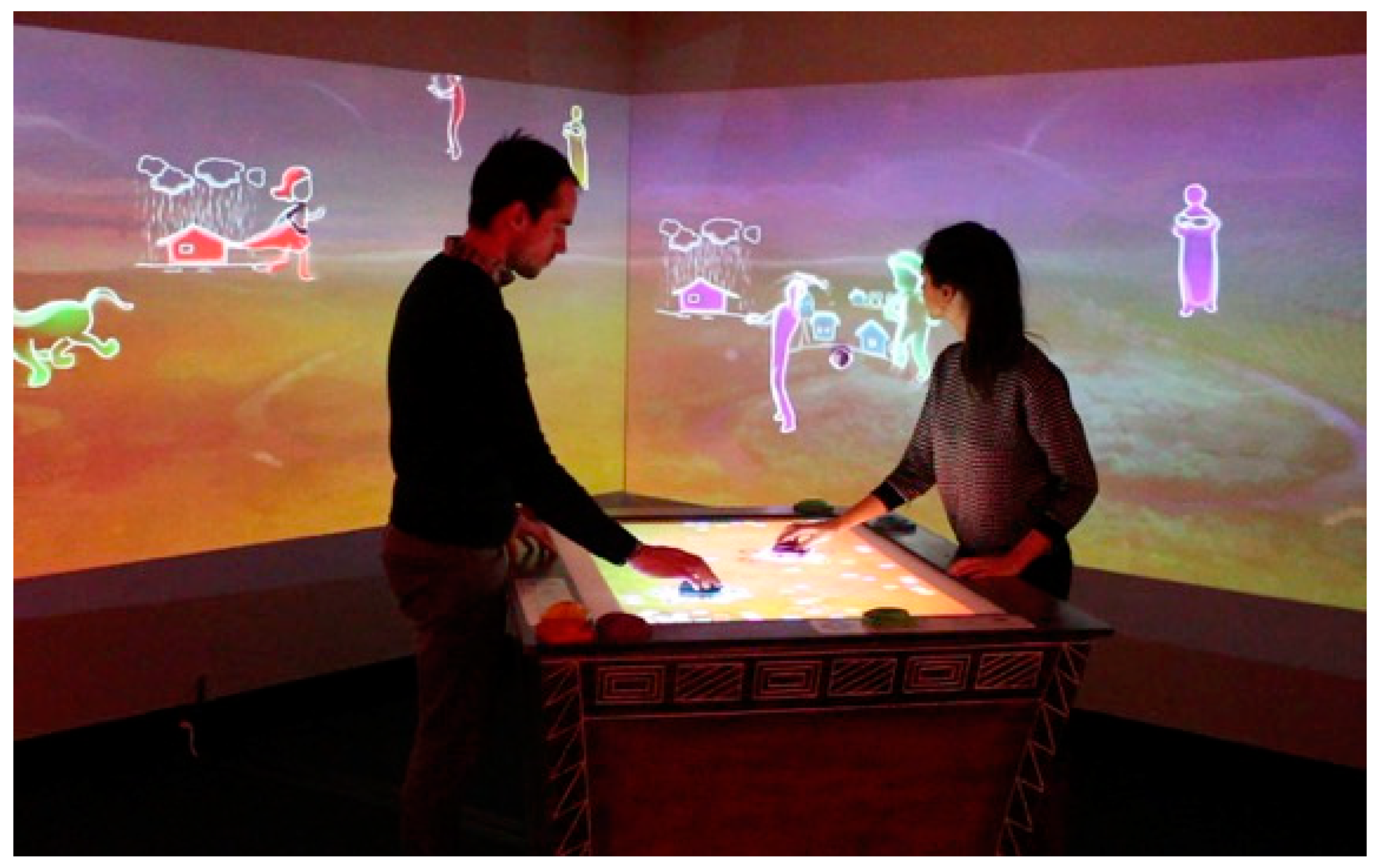
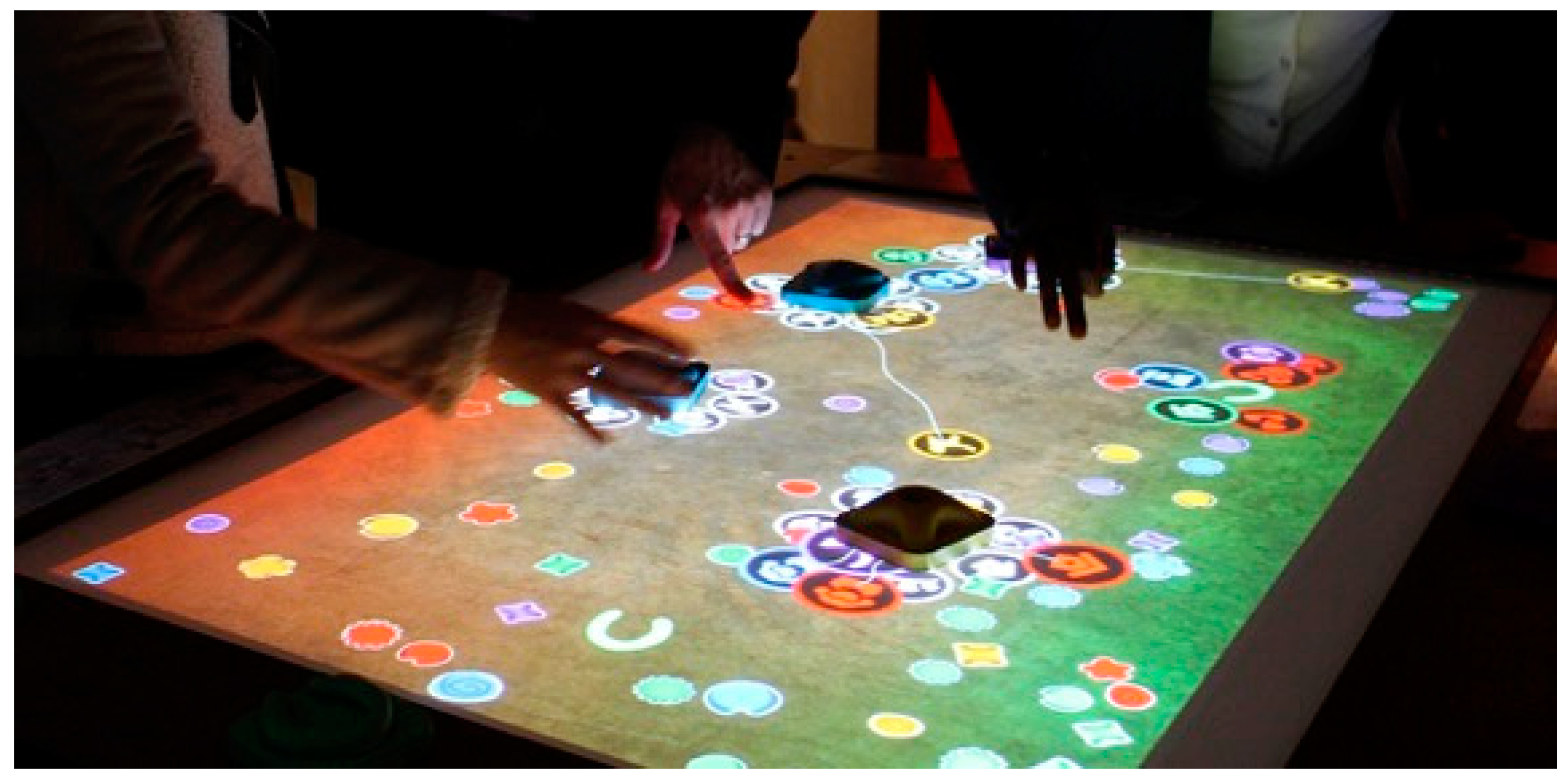
4.1. Pilot Project: Mapping Place (2013–2014)
Evaluation of the Mapping Place
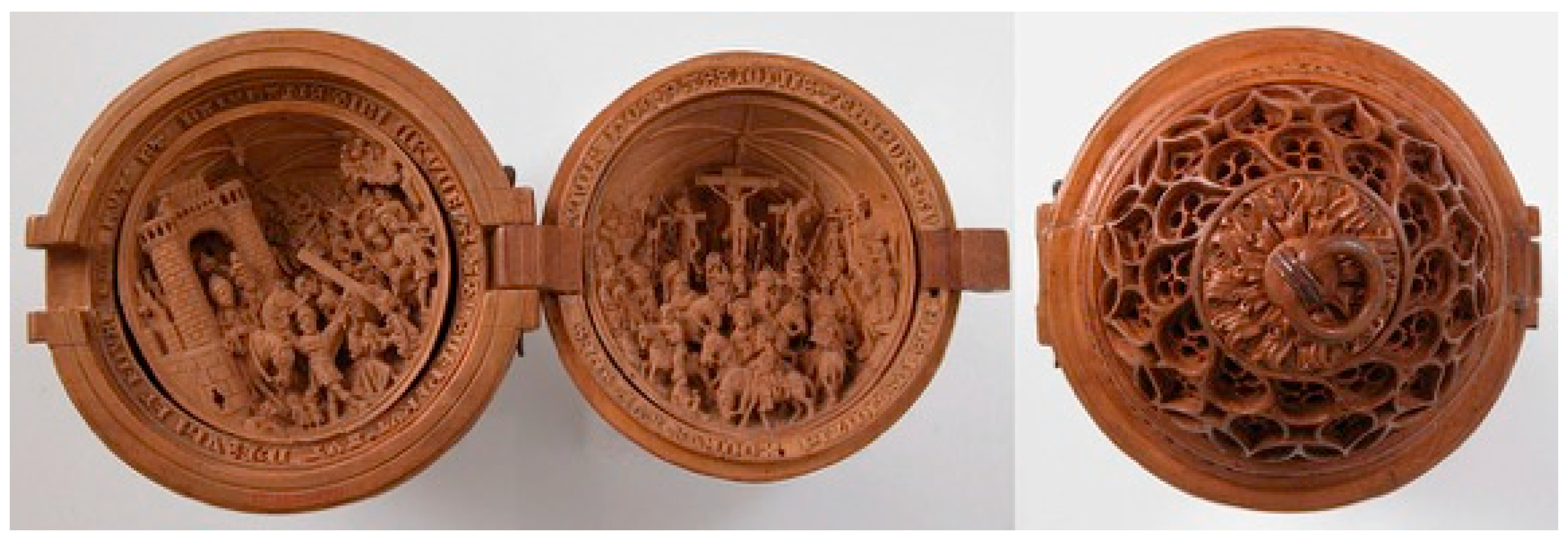
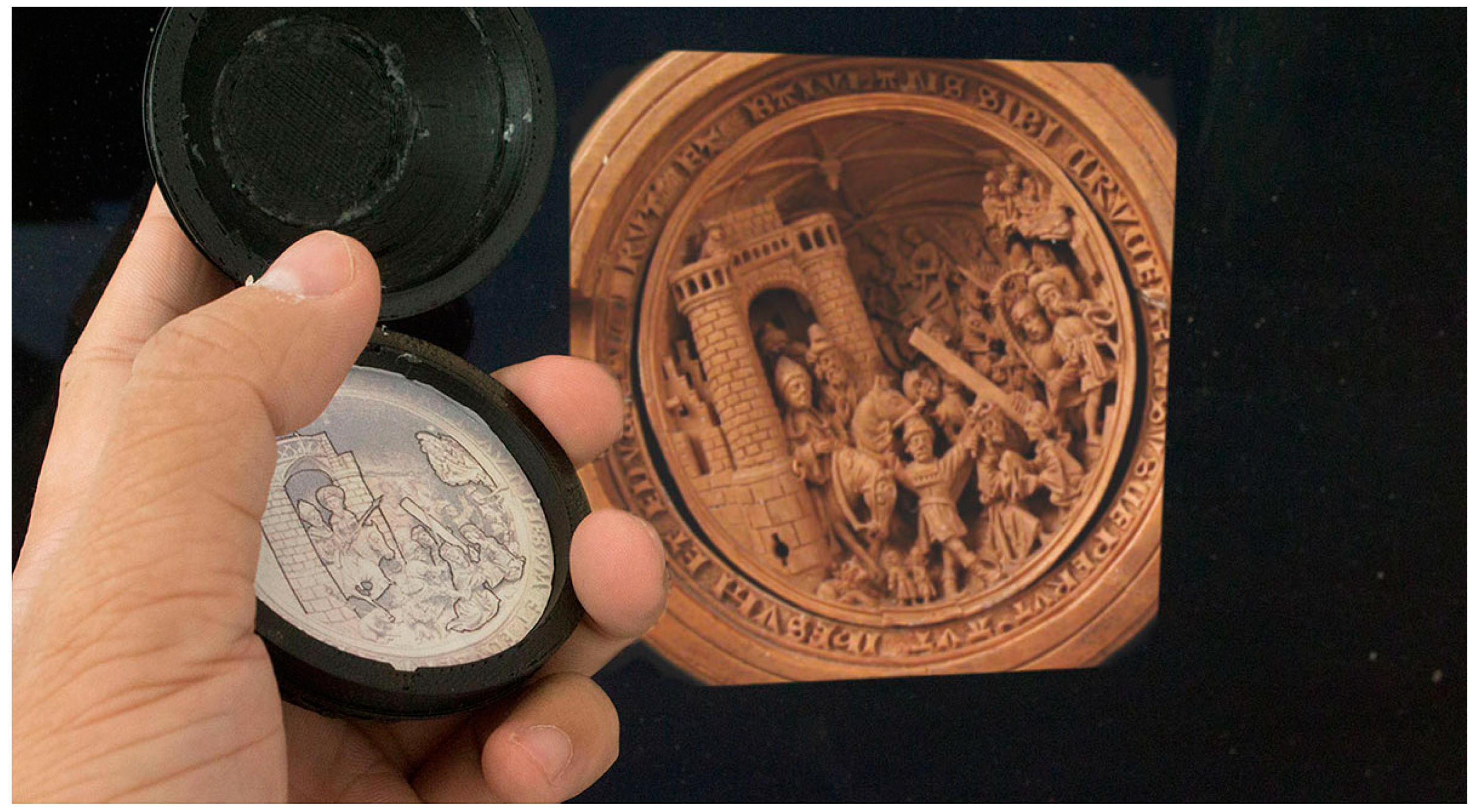
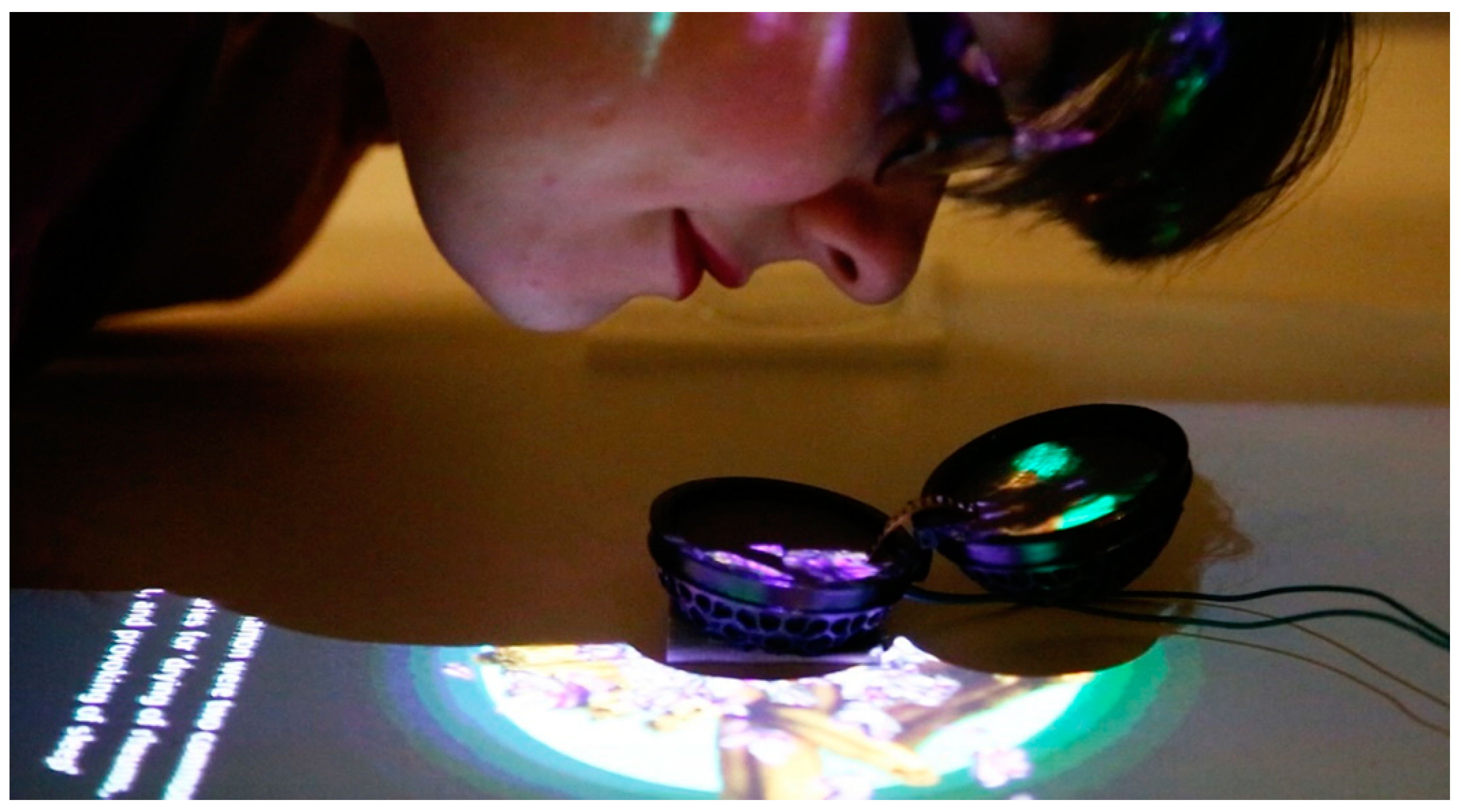
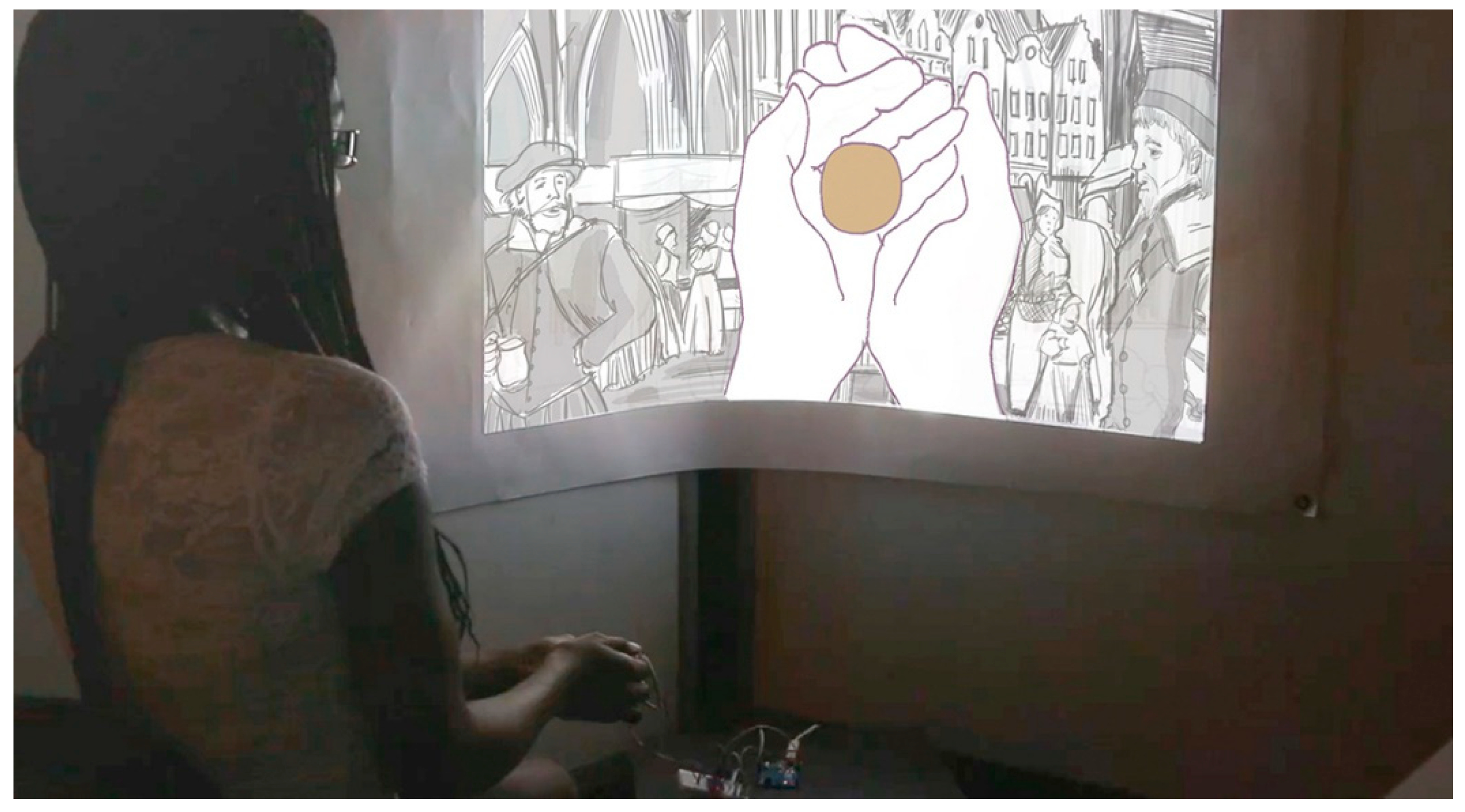
4.2. Case Study: Multi-Sensory Prayer Nuts (2014–2016)
4.2.1. Evaluation of the Multi-Sensory Prayer Nuts
Contextualize Artifacts
Make Personalized Connections
4.3. Conclusion to the Pilot and Case Study Projects
5. Discussion
5.1. Design Recommendations
5.1.1. Simulate Cultural Practices
5.1.2. Associate Visitors with Cultural Perspectives
5.1.3. Provide Simultaneous Digital Feedback
5.2. Limitations and Future Directions
5.3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dourish, P. Where the Action Is: The Foundations of Embodied Interaction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hornecker, E.; Buur, J. Getting a grip on tangible interaction: A framework on physical space and social interaction. In Proceedings of the CHI ’97, Atlanta, GA, USA, 22–27 March 1997; pp. 437–446. [Google Scholar]
- Ullmer, B.; Ishii, H. Emerging frameworks for tangible user interfaces. IBM Syst. J. 2000, 39, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, E. The Power of Touch: Handling Objects in Museum and Heritage Context; Routledge: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dudley, S. Museum Materialities: Objects, Engagements, Interpretations; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Latham, K.F. Numinous experiences with museum objects. Visit. Stud. 2013, 16, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, D.; Ciolfi, L.; van Dijk, D.; Hornecker, E.; Not, E.; Schmidt, A. Integrating material and digital: A new way for cultural heritage, interactions. ACM Interact. Mag. 2013, 20, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannon, L.; Benford, S.; Bowers, J.; Heath, C. Hybrid design creates innovative museum experiences. Commun. ACM 2005, 48, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, M.S.; Solovey, E.T.; Jacob, R.J. Tangible programming and informal science learning: Making TUIs work for museums. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Interaction Design and Children, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–13 June 2008; pp. 194–201. [Google Scholar]
- Antle, A.N.; Wise, A.F.; Hall, A.; Nowroozi, S.; Tan, P.; Warren, J.; Eckersley, R.; Fan, M. Youtopia: A collaborative, tangible, multi-touch, sustainability learning activity. In Proceedings of the Interaction Design for Children Conference, New York, NY, USA, 24–27 June 2013; pp. 565–568. [Google Scholar]
- Ciolfi, L.; McLoughlin, M. Designing for meaningful visitor engagement at a living history museum. In Proceedings of the 7th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction: Making Sense through Design, Copenhagen, Denmark, 14–17 October 2012; pp. 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hornecker, E. “I don’t understand it either, but it is cool”—Visitor interactions with a multi-touch table in a museum. In Proceedings of the 2008 3rd IEEE International Workshop on Horizontal Interactive Human Computer Systems, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1–3 October 2008; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, L. The Art of Museum Exhibitions: How Story and Imagination Create Aesthetic Experiences; Left Coast Press: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, D.L. What Makes Learning Fun?: Principles for the Design of Intrinsically Motivating Museum Exhibits; Rowman Altamira: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Riedl, M.O.; Bulitko, V. Interactive narrative: An intelligent systems approach. Ai Mag. 2012, 34, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.-L. Avatars of Story: Narrative Modes in Old and New Media; University of Minnesota Press: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, M.-L. Narrative as Virtual Reality 2: Revisiting Immersion and Interactivity in Literature and Electronic Media; JHU Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2015; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, J.H. Hamlet on the Holodeck: The Future of Narrative in Cyberspace; Mit Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, J.H.; Clifton, P.; Blumenthal, H.; Nandakumar, A.; Ganapathi, B.; Murray, J.; Mazalek, A. Universal Threshold Object: Designing Haptic Interaction for Televised Interactive Narratives. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction, Stanford, CA, USA, 15–19 January 2015; pp. 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Bordwell, D.; Thompson, K.; Smith, J. Film Art: An Introduction; McGraw-Hill Education: Berkshire, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mazalek, A.; Davenport, G.; Ishii, H. Tangible viewpoints: A physical approach to multimedia stories. In Proceedings of the Tenth ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MULTIMEDIA’02, Juan les Pins, France, 1–6 December 2002; pp. 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheiner, M.; Troxler, F.; Tobler, T.; Erdin, T. Birdly. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH, Vancouver, Canada, 10–14 August 2014; Available online: http://s2014.siggraph.org/attendees/emerging-technologies/events/birdly.html (accessed on 21 December 2018).
- Gorbet, M.G.; Orth, M.; Ishii, H. Triangles: Tangible interface for manipulation and exploration of digital information topography. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 18–23 April 1998; pp. 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Sindorf, L.; Liao, I.; Frazier, J. Using a tangible versus a multi-touch graphical user interface to support data exploration at a museum exhibit. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction, Stanford, CA, USA, 15–19 January 2015; pp. 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Klemmer, S.R.; Hartmann, B.; Takayama, L. How bodies matter: Five themes for interaction design. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Designing Interactive Systems, University Park, PA, USA, 26–28 June 2006; pp. 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Fernaeus, Y.; Tholander, J.; Jonsson, M. Beyond representations: Towards an action-centric perspective on tangible interaction. Int. J. Arts Technol. 2008, 1, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djajadiningrat, T.; Wensveen, S.; Frens, J.; Overbeeke, K. Tangible products: Redressing the balance between appearance and action. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2004, 8, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wii Remote. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wii_Remote (accessed on 30 October 2018).
- Center for Civil and Human Rights. Lunch Counter Simulation. Available online: https://www.civilandhumanrights.org/lessons-lunch-counter/ (accessed on 30 October 2018).
- Van Dijk, J.; van der Lugt, R.; Hummels, C. Beyond distributed representation: Embodied cognition design supporting socio-sensorimotor couplings. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Tangible, Embedded and Embodied Interaction, Munich, Germany, 6–19 February 2014; pp. 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, M.T.; Dulake, N.; Ciolfi, L.; Duranti, D.; Kockelkorn, H.; Petrelli, D. Using tangible smart replicas as controls for an interactive museum exhibition. In Proceedings of the TEI’16: Tenth International Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction, Munich, Germany, 16–19 February 2014; pp. 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Harley, D.; Chu, J.H.; Kwan, J.; Mazalek, A. Towards a framework for tangible narratives. In Proceedings of the TEI’16: Tenth International Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 14–17 February 2016; pp. 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Memory: Luba Art and the Making of History; Museum for African Art: New York, NY, USA, 1996.
- Chu, J.H.; Clifton, P.; Harley, D.; Pavao, J.; Mazalek, A. Mapping Place: Supporting Cultural Learning through a Lukasa-inspired Tangible Tabletop Museum Exhibit. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction, Stanford, CA, USA, 15–19 January 2015; pp. 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Charmaz, K. Constructing Grounded Theory: A Practical Guide through Qualitative Analysis; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, J.H.; Harley, D.; Kwan, J.; McBride, M.; Mazalek, A. Sensing History: Contextualizing Artifacts with Sensory Interactions and Narrative Design. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM Conference on Designing Interactive Systems, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 4–8 June 2016; pp. 1294–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, J.; Chu, J.H.; Harley, D.; McBride, M.; Mazalek, A. Grasping Cultural Context through Multisensory Interactions. In Proceedings of the TEI’16: Tenth International Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 14–17 February 2016; pp. 482–487. [Google Scholar]
- Falkenburg, R.L. Toys for the Soul: Prayer-Nuts and Pomanders in Late Medieval Devotion. In A Sense of Heaven. 16th-Century Boxwood Carvings for Private Devotion; The Henry Moore Institute: Leeds, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Scholten, F. Prayer-nut for Francois Du Puy. Burlingt. Mag. 2011, 153, 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Scholten, F. Prayer-Nuts and Other Boxwood Micro-Carvings. In A Sense of Heaven: 16th Century Boxwood Carvings for Private Devotion; The Henry Moore Institute: Leeds, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Soden-Smith, R.H. Notes on Pomanders. Archaeol. J. 1874, 31, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, C.; Howes, D. The museum as sensescape: Western sensibilities and indigenous artifacts. In Sensible Objects: Colonialism, Museums and Material Culture; Berg: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 199–222. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, J.P. An Introduction to Discourse Analysis: Theory and Method; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, S.; Antle, A.N.; Van Den Hoven, E. Embodied metaphors in tangible interaction design. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2012, 16, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, D.; Dulake, N.; Marshall, M.; Kockelkorn, H.; Pisetti, A. Do it together: The effect of curators, designers, and technologists sharing the making of new interactive visitors’ experiences. In Proceedings of the Museums and the Web, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–9 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Katyal, S.K. Technoheritage. Cal. L. Rev. 2017, 105, 1111. [Google Scholar]






| Type | Project Title | Physical Engagement | Narrative Role | Narrative Consequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-museum Projects | Triangles | Triangle pieces represent characters, events, and setting | Interactor is a narrator overseeing the story | Story unfolds as the interactor stitches together the triangles |
| Nintendo Wiimote | Interface enables gesturing as if one were immersed in the game world | Interactor is an actor in the game world | Appropriate game play can lead to winning or losing | |
| Tangible Spatial Narratives | Tangible pawns represent characters in the story | Interactor is a focalizer to examine the story | Moving around the pawns shows different parts of the story | |
| NOOT | Physical tags record different parts of a conversation | Interactor is a creator to record the story | The playback device plays the audio recordings when triggered | |
| Museum Projects | Interaction to view Plankton Populations | Physical ring on an interactive tabletop functions as a magnifying glass | Interactor is an external focalizer | Moving around the physical ring shows the plankton populations |
| Lunch Counter Simulation | Physical bar table and stools reenact a historic event for interactors to be immersed in | Interactor is a focalizer in the actual scene | Audio from the sit-in event is played without any interactivity | |
| Youtopia | Tangible objects on an interactive tabletop enable manipulation of the story | Interactor is a creator of a virtual city | Interactors develop a city in diverse ways that are sustainable | |
| The Hague and the Atlantic Wall exhibit | Tangible objects represent different perspectives to engage in the historic event | Interactor is a focalizer to examine the story | Moving around the objects shows different parts of the story |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, J.H.; Mazalek, A. Embodied Engagement with Narrative: A Design Framework for Presenting Cultural Heritage Artifacts. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2019, 3, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3010001
Chu JH, Mazalek A. Embodied Engagement with Narrative: A Design Framework for Presenting Cultural Heritage Artifacts. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction. 2019; 3(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Jean Ho, and Ali Mazalek. 2019. "Embodied Engagement with Narrative: A Design Framework for Presenting Cultural Heritage Artifacts" Multimodal Technologies and Interaction 3, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3010001
APA StyleChu, J. H., & Mazalek, A. (2019). Embodied Engagement with Narrative: A Design Framework for Presenting Cultural Heritage Artifacts. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 3(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3010001




