Industrial Diffusion Processes in Peri-Urban Environments: A State-of-the-Art Analysis of Current and Future Dimensions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Bibliometric Analysis
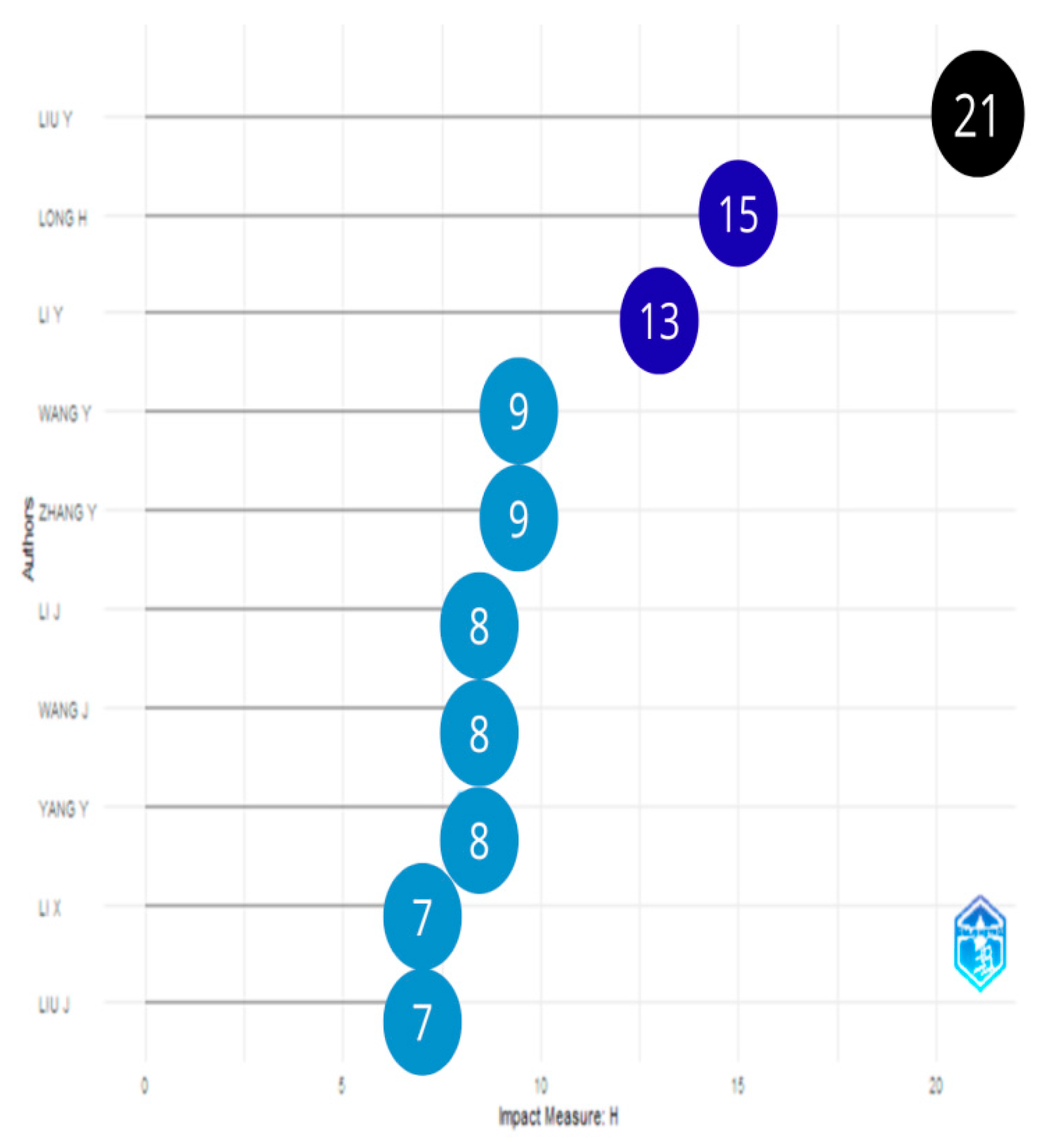
3.1.1. Most Relevant Sources and Authors
- Study of urbanization processes: This line of research includes the work of Wang et al. [27], Poelhekke [50], Yeh et al. [51], Zhou et al. [52], and Li et al. [25]. Within this thematic line, contributions addressing labour mobility between rural and urban areas, such as those by Wu [53], Mohabir et al. [54], and Silveira et al. [55], as well as studies on the consequences of income inequality between these areas, such as Dong and Hao [56], are also relevant.
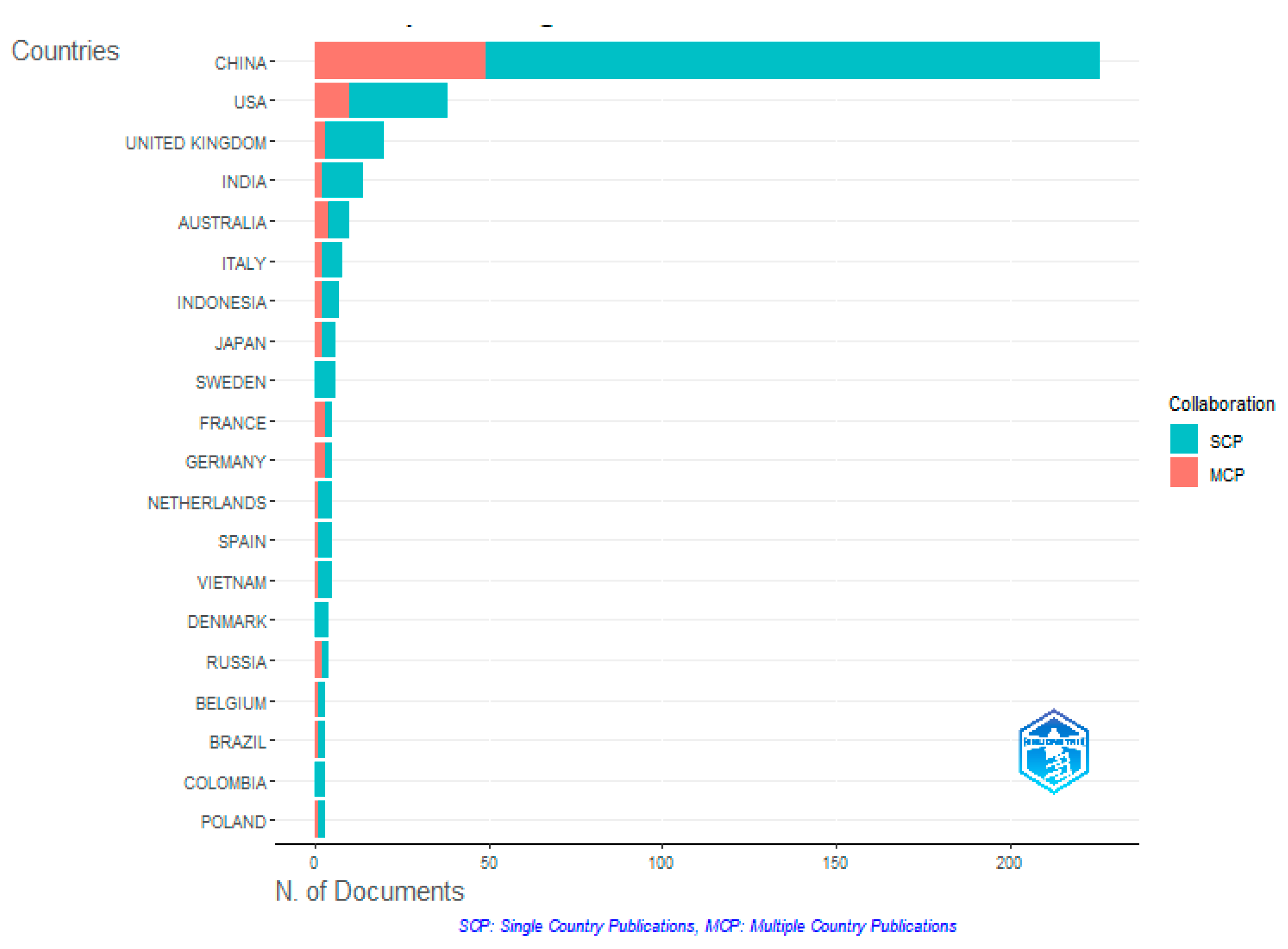
3.1.2. Reference Countries and Co-Citation Network
3.2. Overview of the Social and Intellectual Structure of Research
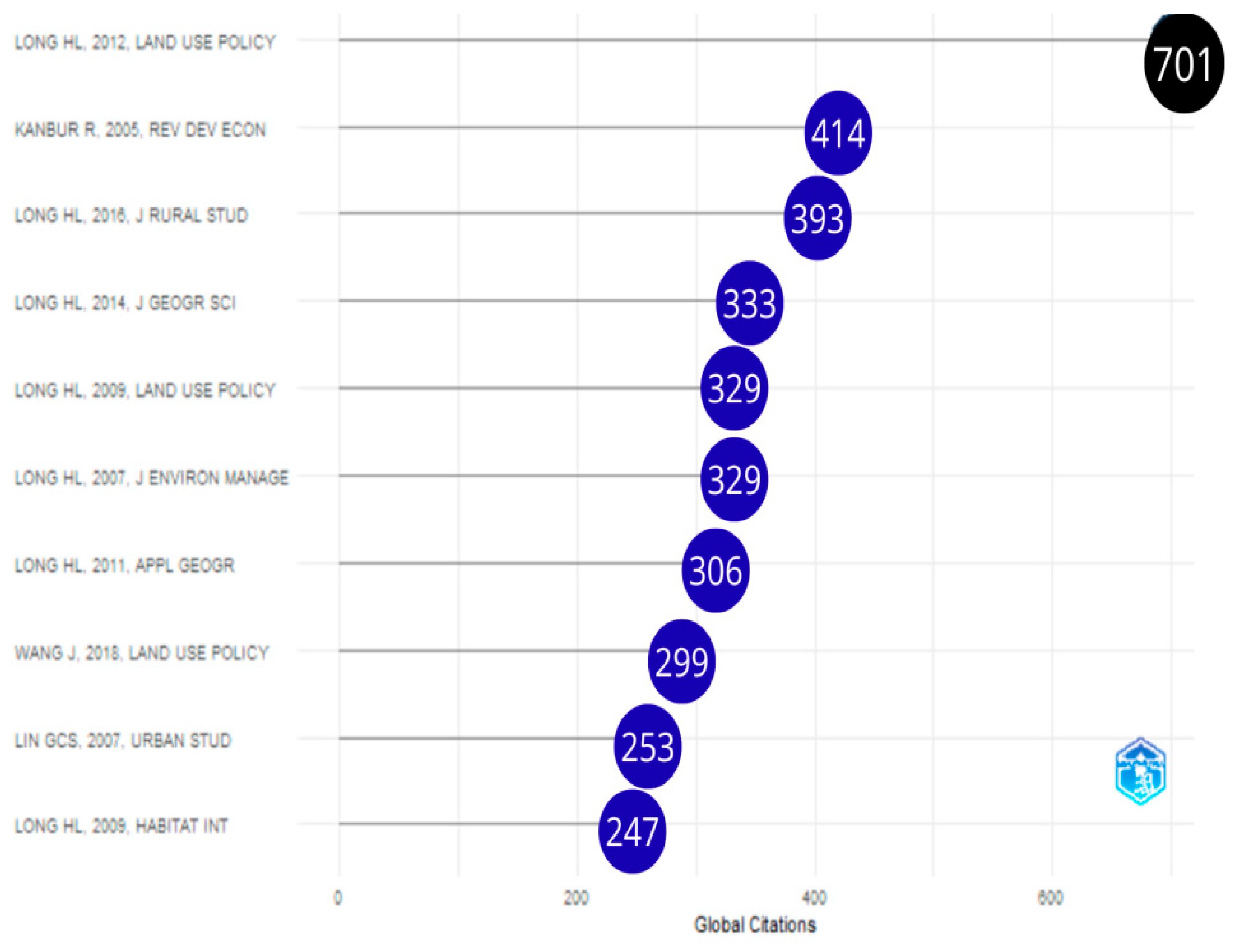
3.2.1. Most Cited Documents
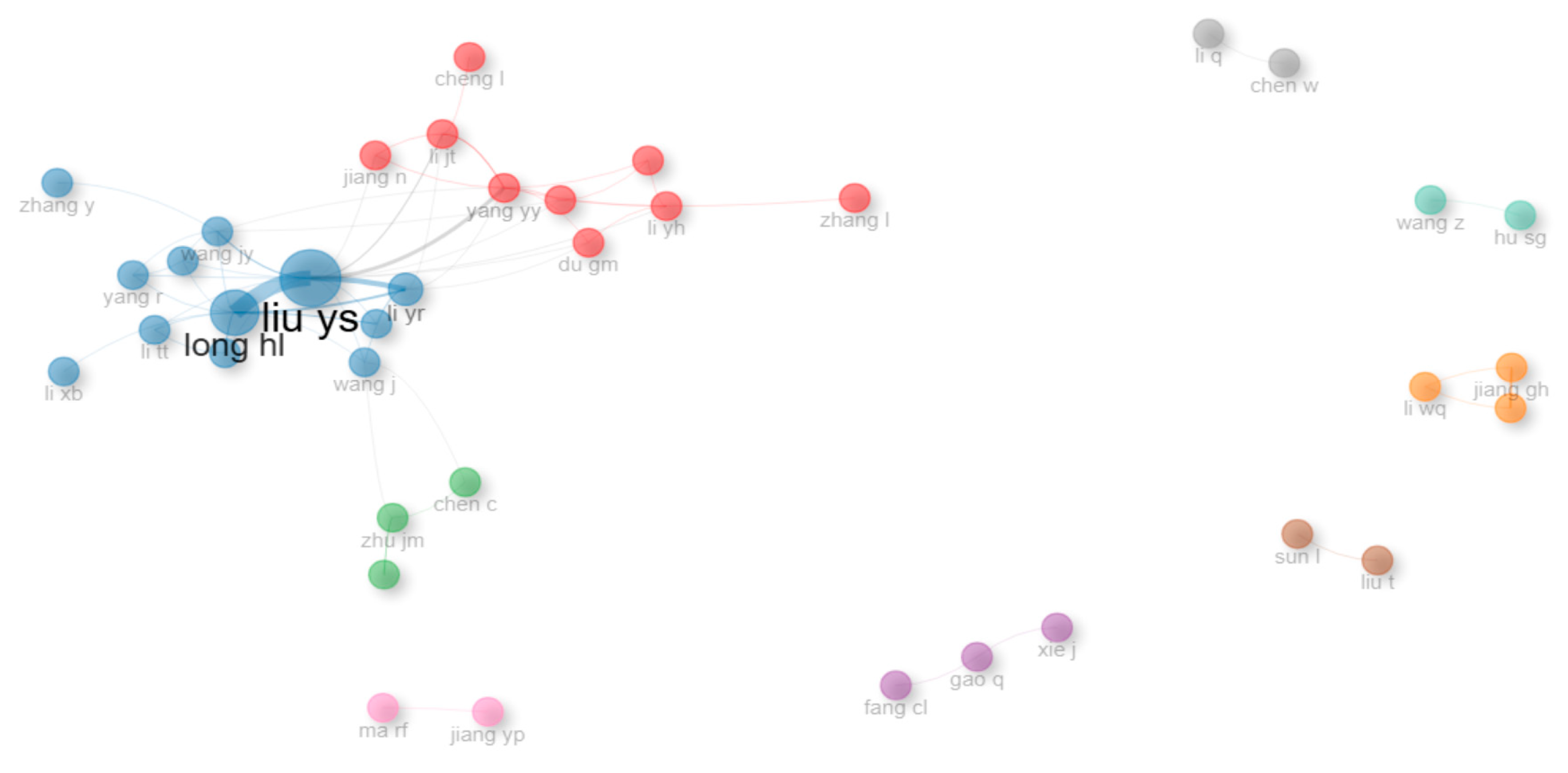
3.2.2. Structure of Authors’ Co-Citation Network
3.3. Knowledge Synthesis
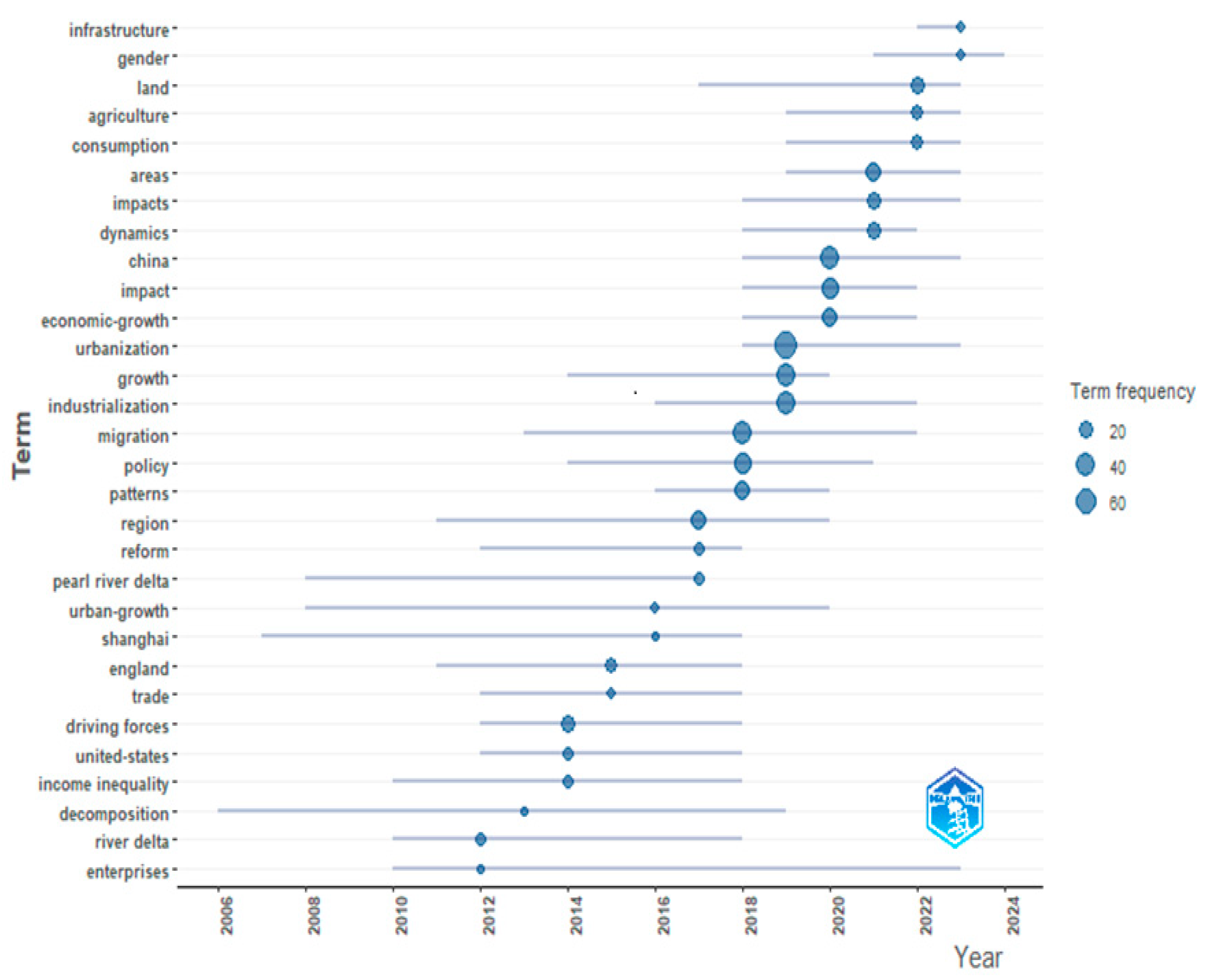
3.3.1. Term Analysis
- ✓
- “Urbanization” (126 (s); 8.07%): This topic is prominently addressed in journals such as Urban Studies, with contributions from Yeh et al. [51], Wu [53], and Lin [58]; Cities, featuring articles by Zhou et al. [52] and Woodworth [59]; and Habitat International, where Long et al. [12], Peng et al. [60], and Li et al. [61] publish their work.
- ✓
- “Industrialization” (125 (s); 8.04%): Journals paying particular attention to this concept include Land Use Policy, with contributions from Tian [62]; Habitat International, featuring works by Long et al. [12] and Peng et al. [60]; and the Journal of Arid Environments, which published an article by Mavrakis et al. [63].
- ✓
- “China” (118 (s); 7.56%): The prominence of this term in Figure 9 reflects the notable contribution of Chinese authors in the field. Many studies are based on case studies across different regions of China, as evidenced in journals such as Land Use Policy (Long et al. [10,11,13,14], Liu et al. [19,20], Wang et al. [26,27], Yangang and Jisheng [64]), Land (Du et al. [65], Wang et al. [66], Miao et al. [67]), or Journal Environmental Management (Long et al. [15], Liu et al. [18]).
- ✓
- “Environmental monitoring” (60 (s); 3.85%): Although less frequent than the previous terms, this concept is important due to its presence in the keyword map, reflecting studies on the environmental impacts of industrialization and urbanization. Journals focusing on environmental issues include Journal of Environmental Management, Environment International, Science of the Total Environment, Environmental Science and Pollution Research, Sustainability, Regional Studies, and Studies in Comparative International Development. Key contributions include works by Long et al. [15], Song et al. [68], Liu et al. [69], Liv et al. [70], Lu [71], Lin [72], and Pierskalla [73].
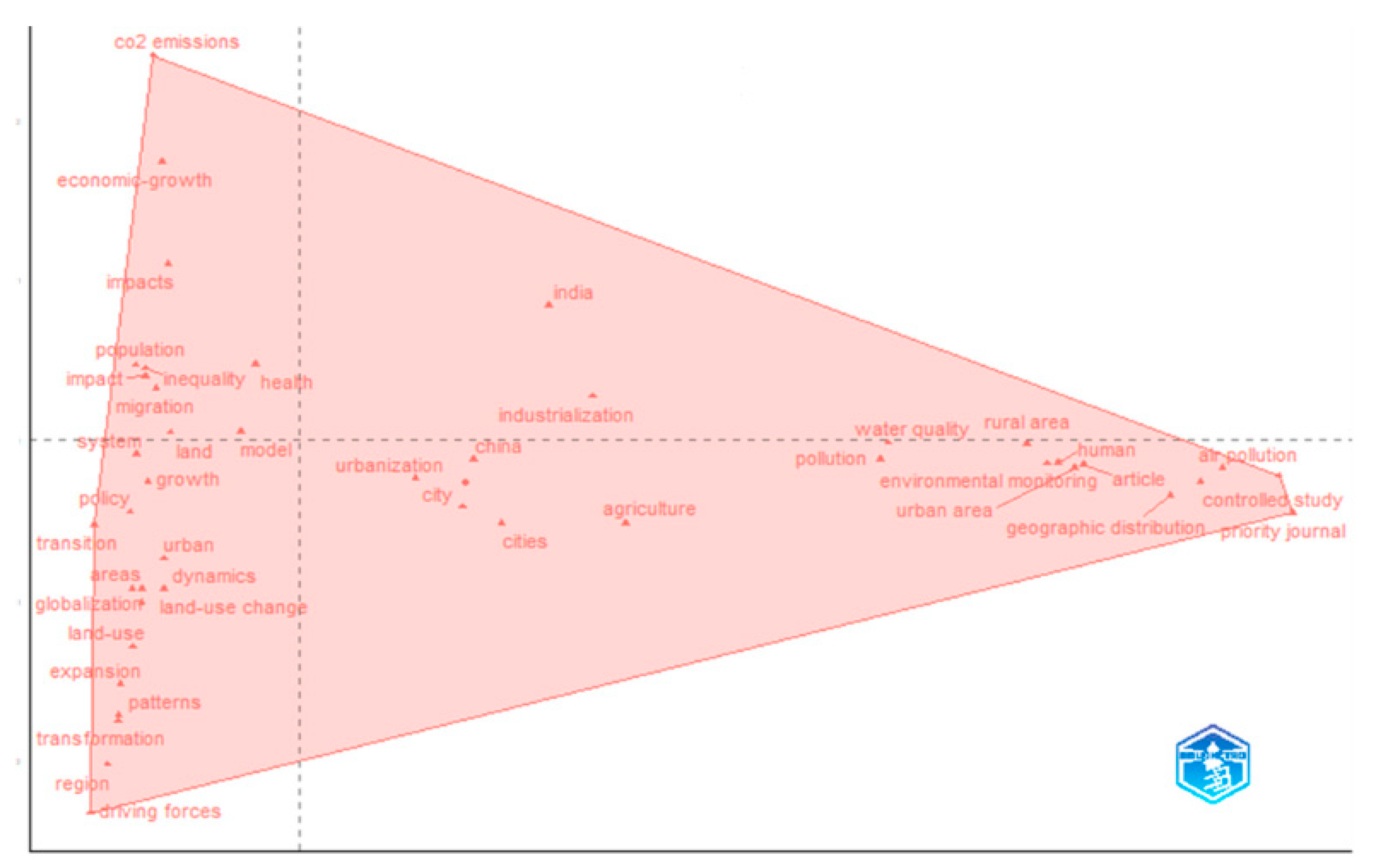
3.3.2. Thematic Map and Factor Analysis of Terms
- ➢
- ➢
- Basic themes quadrant: These issues show a low level of current development but high relevance, including urbanization, China, and cities. The factor analysis in Figure 14 confirms a strong connection between these three terms, and the rightmost portion of the figure links them to environmental monitoring, pollution, and air pollution, indicating a widespread concern among authors regarding the environmental consequences of China’s rapid urbanization processes.
- ➢
- Niche themes quadrant: These issues exhibit a high degree of development but low relevance. As shown in the figure above, the main topics are Growth and Migration. These two issues also appear together in Figure 14, where they interact with other terms such as population and inequality. The connections among these terms highlight specific lines of research and align with some of the clusters identified in Figure 12.
- ➢
- Emerging or declining themes quadrant: These themes show low development and low relevance. The primary topics in this quadrant are economic growth, impact, and model. Figure 14 indicates an increasing relevance of “economic growth”, suggesting that this term may be emerging as a key focus in the field.
3.3.3. Latent Dirichlet Allocation Topic Model (LDA)
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katz, E.; Stark, O. Labor Migration and Risk Aversion in Less Developed Countries. J. Labor Econ. 1986, 4, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinger, D.J. Citizenship issues in China’s internal migration: Comparisons with Germany and Japan. Political Sci. Q. 1999, 114, 455–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F. Urban restructuring in China’s emerging market economy: Towards a framework for analysis. J. Urban Reg. Res. 1997, 21, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C. Land policy reform in China: Assessment and prospects. Land Use Policy 2003, 20, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Huang, Y. Uneven land reform and urban sprawl in China: The case of Beijing. Prog. Plan. 2004, 61, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antrop, M. Changing patterns in the urbanized countryside of Western Europe. Landsc. Ecol. 2000, 15, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamija, P. Economic Development and South Africa: 25 Years Analysis (1994 to 2019). S. Afr. J. Econ. 2020, 88, 298–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Sharma, S.; Batra, I.; Sharma, C.; Kaswan, M.S.; Garza-Reyes, J.A. Industrial revolution and environmental sustainability: An analytical interpretation of research constituents in Industry 4.0. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2024, 15, 22–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkoomar, M.; Marimuthu, F.; Naicker, N.; Mvunabandi, J.D. A meta-analysis of the economic impact of carbon emissions in Africa. Environ. Econ. 2022, 13, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Woods, M.; Zou, J. Accelerated restructuring in rural China fueled by ‘increasing vs. decreasing balance’ land-use policy for dealing with hollowed villages. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Dong, G. Spatio-temporal dynamic patterns of farmland and rural settlements in Su-Xi-Chang region: Implications for building a new countryside in coastal China. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Zou, J.; Liu, Y. Differentiation of rural development driven by industrialization and urbanization in eastern coastal China. Habitat Int. 2009, 33, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Y. Building new countryside in China: A geographical perspective. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Heilig, G.K.; Li, X.; Zhang, M. Socio-economic development and land-use change: Analysis of rural housing land transition in the Transect of the Yangtse River (China). Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Tang, G.; Li, X.; Heilig, G. Socio-economic driving forces of land-use change in Kunshan, the Yangtze River Delta economic area China. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 83, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Tu, S.; Ge, D.; Li, T.; Liu, Y. The allocation and management of critical resources in rural China under restructuring: Problems and prospects. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 47, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H. Land consolidation: An indispensable way of spatial restructuring in rural China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Long, H. Analysis of arable land loss and its impact on rural sustainability in Southern Jiangsu Province of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, R.; Long, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. Implications of land-use change in rural China: A case study of Yucheng, Shandong province. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, Y. Key issues of land use in China and implications for policy making. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Long, H. Spatio-temporal analysis of land-use conversion in the eastern coastal China during 1996–2005. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, Y. Process and cause of urban-rural development transformation in the Bohai Rim Region. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rodríguez, D.; Tang, X. Effects of land lease policy on changes in land use, mechanization and agricultural pollution. Land Use Policy 2017, 64, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rodríguez, D.; Zhang, D.; Ma, K. Crop rotation model for contract farming with constraints on similar profits. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 119, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, N. County-rural revitalization spatial differences and model optimization in Miyun District of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 86, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Shao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y. Land-use changes and policy dimension driving forces in China: Present, trend and future. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Glendinning, A.; Xu, Y. Land-use changes and land policies evolution in China’s urbanization processes. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedwab, R.; Christiaensen, L.; Gindelsky, M. Demography, urbanization and development: Rural push, urban pull and… urban push? J. Urban Econ. 2017, 98, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, T. Urban fortunes and skeleton cityscapes: Real estate and late urbanization in Kigali and Addis Ababa. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2017, 41, 786–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, M. The three phases of land-use change: Implications for biodiversity. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 1864–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, G. Commercial Counter urbanisation: An Emerging Force in Rural Economic Development. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2010, 42, 966–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.; Barreira, A.P.; Guimarães, M.H.; Panagopoulos, T. Historical trajectories of currently shrinking Portuguese cities: A typology of urban shrinkage. Cities 2016, 52, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, C. Development strategies and rural development: Exploring synergies, eradicating poverty. J. Peasant Stud. 2009, 36, 103–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Álvarez, F.J.; Parejo-Moruno, F.M.; Rangel-Preciado, J.F.; Cruz-Hidalgo, E. Regulation of agricultural trade and its implications in the reform of the CAP. The continental products Case Study. Agriculture 2021, 11, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Álvarez, F.J.; Robina Ramírez, R. Relevance of the Uruguay and Doha Rounds in the evolution of international agricultural trade: The Case Study of Latin American countries and continental products. Economies 2023, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Álvarez, F.J.; Durán-Sánchez, A.; Del Rio, M.C.; Álvarez-García, J. Innovation and entrepreneurship as tools for rural development: Case Study Region of La Vera, Extremadura, Spain. In Entrepreneurship and the Community: A Multidisciplinary Perspective on Creative, Social Challenges and Business; Ratten, V., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Álvarez, F.J.; Robina-Ramirez, R. Relevance of territorial identity in the rural development programs: The Case Study of Tajo-Salor (Extremadura, Spain). Economies 2024, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robina-Ramírez, R.; Martín-Lucas, M.; Dias, A.; Castellano-Álvarez, F.J. What role geoparks play improving the health and well-being of senior tourists? Heliyon 2023, 9, e22295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano-Álvarez, F.J.; Robina Ramírez, R.; Nieto Masot, A. Tourism development in the framework of endogenous rural development Programmes: Comparison of the Case Studies of the regions of La Vera and Tajo-Salor. Agriculture 2023, 13, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robina-Ramírez, R.; Castellano-Álvarez, F.J.; Ferreira, P.; Loures, L. Tourism Development in Rural Border Territories: A “Phronetic” Approach to Threats and Opportunities. Agriculture 2025, 15, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Álvarez, F.J.; Robina-Ramírez, R. Long-Term Survival of Investments Implemented under Endogenous Rural Development Programs: The Case Study of La Vera Region (Extremadura, Spain). Agriculture 2023, 13, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Serrano, S.; Pedraza Navarro, I.; Donoso González, M. ¿Cómo hacer una revisión sistemática siguiendo el protocolo PRISMA?: Usos y estrategias fundamentales para su aplicación en el ámbito educativo a través de un caso práctico. Bordón Rev. Pedagog. 2022, 74, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, B.C. Theory of the Bradford Law. J. Doc. 1977, 33, 180–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimkuhler, F.F. The Bradford Distribution. J. Doc. 1967, 23, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Large-scale comparison of bibliographic data sources: Scopus, Web of Science, Dimensions, Crossref, and Microsoft Academic. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2021, 2, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. Science mapping software tools: Review, analysis, and cooperative study among tools. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 62, 1382–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.; Lafferty, J.D. A correlated topic model of Science. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2007, 1, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Gu, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, W. The interval grey QFD method for new product development: Integrate with LDA topic model to analyse online reviews. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 114, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelhekke, S. Urban growth and uninsured rural risk: Booming towns in bust times. J. Dev. Econ. 2011, 96, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.; Chen, Z. From cities to super mega city regions in China in a new wave of urbanisation and economic transition: Issues and challenges. Urban Stud. 2020, 57, 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, W.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y. Addressing the rural in situ urbanization (RISU) in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region: Spatio-temporal pattern and driving mechanism. Cities 2018, 75, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F. The poverty of transition: From industrial district to poor neighbourhood in the city of Nanjing, China. Urban Stud. 2007, 44, 2673–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohabir, N.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, R. Chinese floating migrants: Rural-urban migrant labourers’ intentions to stay or return. Habitat Int. 2017, 60, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.J.; Espíndola, A.L.; Penna, T.J.P. Agent-based model to rural-urban migration analysis. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2006, 364, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Hao, Y. Would income inequality affect electricity consumption? Evidence from China. Energy 2018, 142, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbur, R.; Zhang, X. Fifty years of regional inequality in China: A journey through central planning, reform, and openness. Rev. Dev. Econ. 2005, 9, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.S. Reproducing spaces of Chinese urbanisation: New city-based and land-centred urban transformation. Urban Stud. 2007, 44, 1827–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodworth, M. Ordos Municipality: A market-era resource boomtown. Cities 2015, 43, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Liu, S.; Sun, L. Spatial-temporal changes of rurality driven by urbanization and industrialization: A case study of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area in Chongqing, China. Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Long, H.; Liu, Y.; Tu, S. Multi-scale analysis of rural housing land transition under China’s rapid urbanization: The case of Bohai Rim. Habitat Int. 2015, 48, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L. Land use dynamics driven by rural industrialization and land finance in the peri-urban areas of China: The examples of Jiangyin and Shunde. Land Use Policy 2015, 45, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrakis, A.; Papavasileiou, C.; Salvati, L. Towards (Un) sustainable urban growth? Industrial development, land-use, soil depletion and climate aridity in a Greek agro-forest area. J. Arid Environ. 2015, 121, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangang, F.; Jisheng, L. The modification of North China quadrangles in response to rural social and economic changes in agricultural villages: 1970–2010s. Land Use Policy 2014, 39, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Faye, B. How Different Land Systems Lead to Discrepancy of Rural Population-Land Relationships: Case Study of Heilongjiang Province, China. Land 2023, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cheong, K.C. Urban–rural construction land replacement for more sustainable land use and regional development in China: Policies and practices. Land 2019, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.Y. Occupation of cultivated land for urban–rural expansion in China: Evidence from national land survey 1996–2006. Land 2021, 10, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chen, B.; Ho, H.C.; Kwan, M.P.; Liu, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Cai, J.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; et al. Observed inequality in urban greenspace exposure in China. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Q.E.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Jia, H. Is the impact of atmospheric microplastics on human health underestimated? Uncertainty in risk assessment: A case study of urban atmosphere in Xi’an, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z. Spatiotemporal differentiation and the obstacle factors influencing the coupling coordination between economic development and water pollution control capability in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75681–75698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Guan, X.; He, C.; Zhang, J. Spatio-temporal patterns and policy implications of urban land expansion in metropolitan areas: A case study of Wuhan urban agglomeration, Central China. Sustainability 2014, 6, 4723–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G. Scaling-up regional development in globalizing China: Local capital accumulation, land-centred politics, and reproduction of space. Reg. Stud. 2013, 43, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierskalla, J.H. The politics of urban bias: Rural threats and the dual dilemma of political survival. Stud. Comp. Int. Dev. 2016, 51, 286–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Moreno, J.A.; Palos-Sanchez, P.R.; Pozo-Barajas, R. Sentiment analysis to support business decision-making. A bibliometric study. AIMS Math. 2024, 9, 4337–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://bigml.com/features#interpretable (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Durán-Sánchez, A.; del Río-Rama, M.d.l.C.; Álvarez-García, J.; Castellano-Álvarez, F.J. Scientific Coverage in Water Governance: Systematic Analysis. Water 2019, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Feng, Z.; Wong, K.Y. Dual-track urbanization in a transitional economy: The case of Pearl River Delta in South China. Habitat Int. 2006, 30, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, F.; Ji, X. Research on Township Industry Development under GEP Accounting. A Case Study of Hanwang Town in Xuzhou City. Land 2023, 12, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zheng, X.; Guo, H. The formation of Taobao villages in China. China Econ. Rev. 2019, 53, 106–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, X.; Shen, C.; Chen, Y.; Su, B.; Yin, Q.; Zhou, S. Integration of land ecological consolidation and ecosystem product value realization: A case from the Yangtze riverside industrial park in Changzhou, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wang, P.; Yao, G. Exploring the dynamic mechanisms of farmland abandonment based on a spatially explicit economic model for environmental sustainability: A case study in Jiangxi Province, China. Sustainability 2014, 6, 1260–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Ma, R.; Liang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, L.; Luo, M.; Mao, Y. Perception analysis of the transformation from a fishery-led to industry-led island with its human settlement changes: A Case Study of Liuheng Island, Zhoushan City, China. Land 2023, 12, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lei, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, J. Differentiation of rural development driven by natural environment and urbanization: A Case Study of Kashgar Region, Northwest China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kuang, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H. Industrial land expansion in rural China threatens environmental securities. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhang, W.; Gong, M. Differentiation and correlation of spatial pattern and multifunction in rural settlements considering topographic gradients: Evidence from Loess Hilly Region, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, F.; Liu, J.; Zheng, L. The effects of public environmental concern on urban-rural environmental inequality: Evidence from Chinese industrial enterprises. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Mao, M.; Shi, J.; Hua, W. The spatio-temporal analysis of urban-rural coordinated development and its driving forces in Yangtze River Delta. Land 2021, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Long, H.; Ma, L.; Tu, S.; Liao, L.; Chen, K.; Xu, Z. How does the community resilience of urban village response to the government-led redevelopment? A case study of Tangjialing village in Beijing. Cities 2019, 95, 102396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ge, X.; Liu, G.J.; Chen, F. Spatial differentiation of non-grain production on cultivated land and its driving factors in coastal China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Chen, X. Tilling another’s land: Migrant farming under rural industrialization and urbanization in China. J. Agrar. Change 2022, 22, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.; Dewancker, B.; Ardhyanto, A. Urban-Rural revitalization space for sustainable social value: An evaluation in redesigning-built environment in Taiwan. Land 2023, 12, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Y.R.; Wang, H.K. Dilemmas of local governance under the development zone fever in China: A case study of the Suzhou region. Urban Stud. 2008, 45, 1037–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.J.; Sun, P.; Zhu, T. Direct and indirect effect of urbanization on energy intensity: A province-level study for China. Energy 2017, 123, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Land use conflict identification and sustainable development scenario simulation China’s southeast coast. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Su, C. Urbanization and carbon emissions: A panel threshold analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 26073–26081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacherzak, A.; Hełdak, M. Borough development dependent on agricultural, tourism, and economy levels. Sustainability 2019, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zeeshan, M.; Ullah, I.; Rehman, A.; Afridi, F. Trade openness and urbanization impact on renewable and non-renewable energy consumption in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 41653–41668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xia, X.H.; Chen, B.; Sun, L. Public participation in achieving sustainable development goals in China: Evidence from the practice of air pollution control. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragayah, H.M.Z. Income inequality in Malaysia. Asian Econ. Policy Rev. 2008, 3, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisdorf, J.L. From domestic manufacture to industrial revolution: Long-run growth and agricultural development. Oxf. Econ. Pap. 2006, 58, 264–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Song, G.; Liu, S. Factors influencing farmers’ willingness and behavior choices to withdraw from rural homesteads in China. Growth Change 2022, 53, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
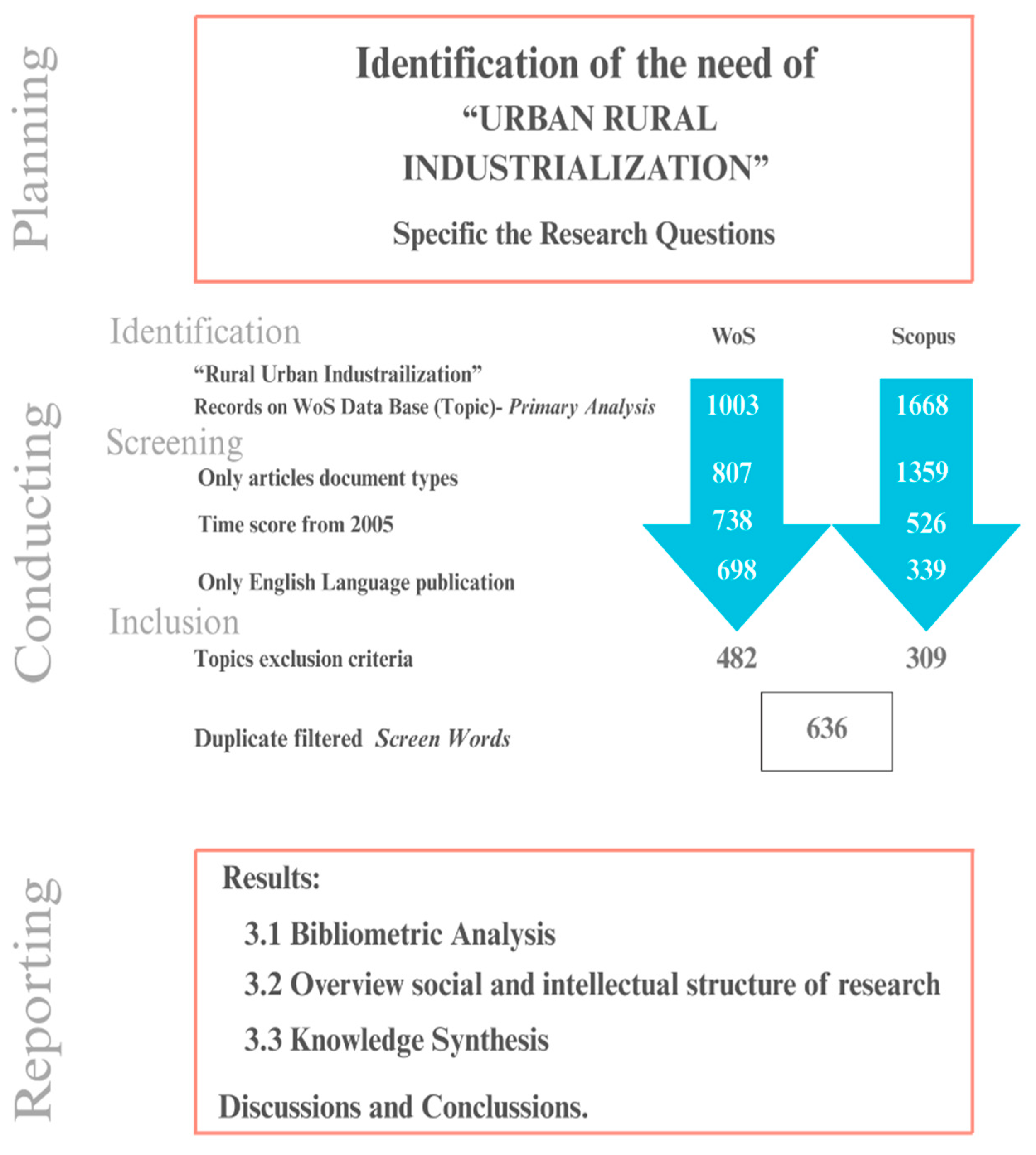
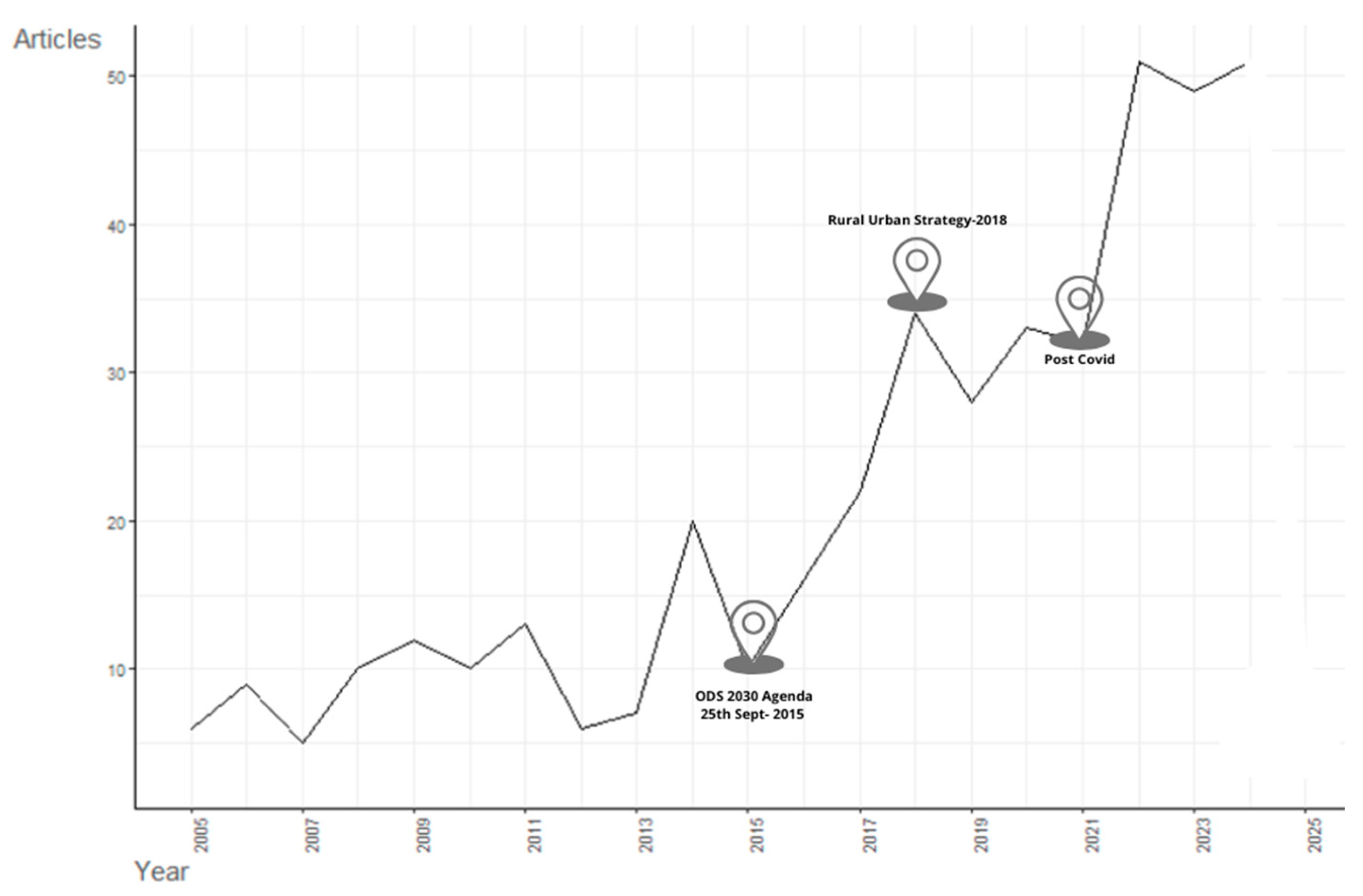
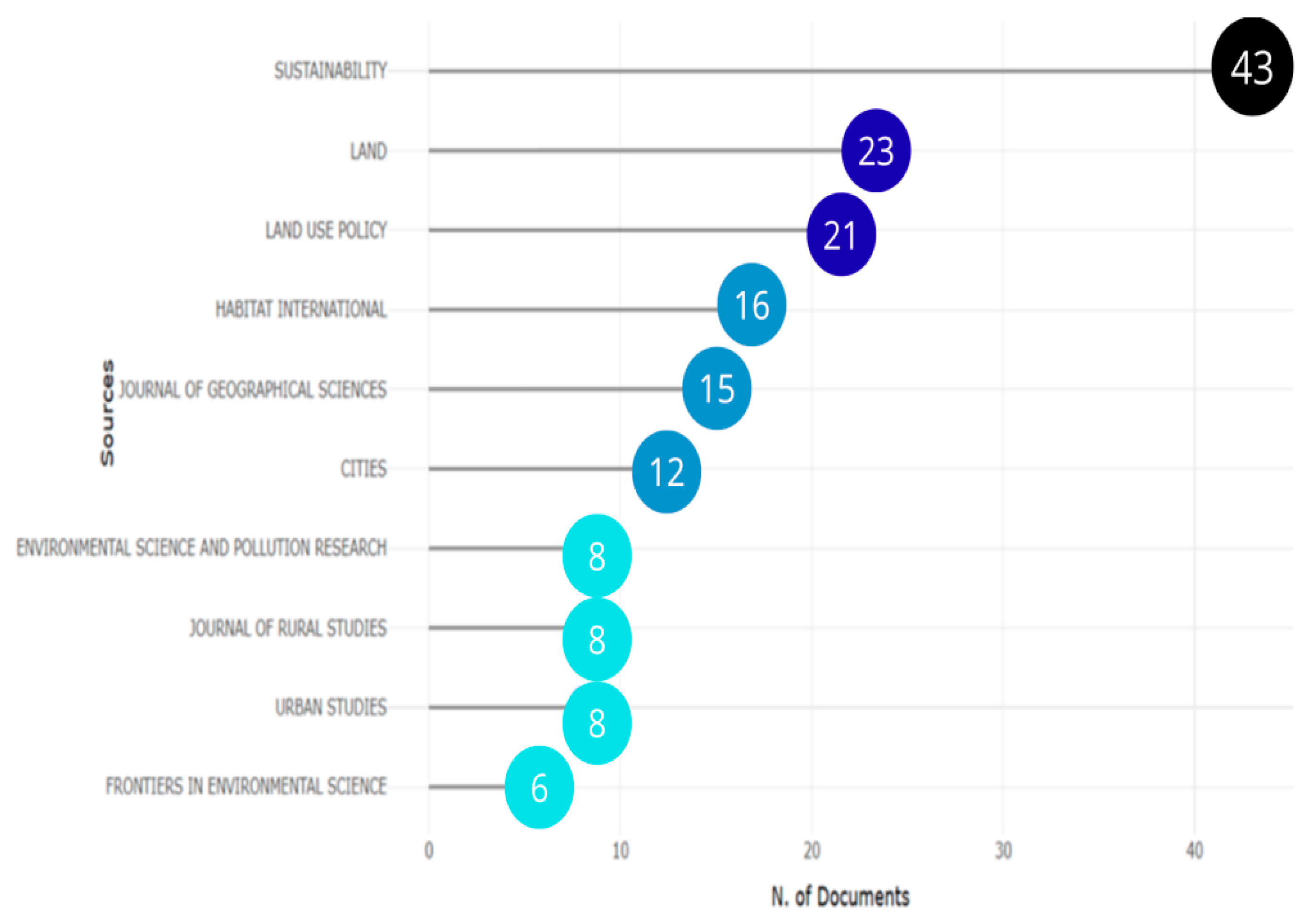
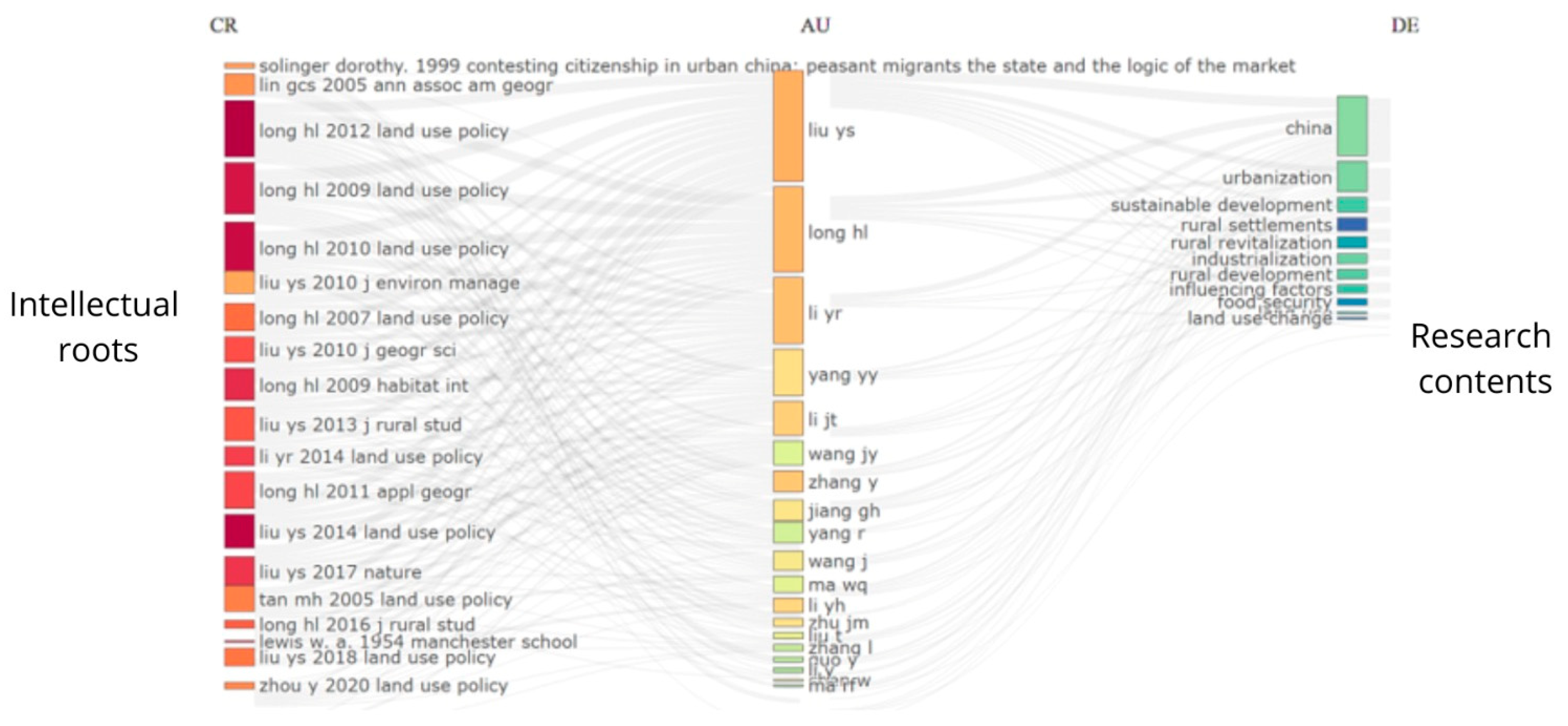




| Database | Search Criteria | Total |
|---|---|---|
| WoS | (TS = (URBAN RURAL INDUSTRIALIZATION)) NOT (DT = (“PROCEEDINGS PAPER” OR “REVIEW” OR “EARLY ACCESS” OR “EDITORIAL MATERIAL” OR “RETRACTED PUBLICATION” OR “BOOK REVIEW” OR “MEETING ABSTRACT”) OR PY = (“1999” OR “1998” OR “1997” OR “1996” OR “1995” OR “1994” OR “1992” OR “1991” OR “1990” OR “1989” OR “1985” OR “1978” OR “1977” OR “1975” OR “1967” OR “2004” OR “2003” OR “2002” OR “2001” OR “2000”) OR LA = (“SPANISH” OR “TURKISH” OR “FRENCH” OR “PORTUGUESE” OR “RUSSIAN” OR “CHINESE” OR “GERMAN” OR “ITALIAN” OR “SLOVENIAN” OR “AFRIKAANS” OR “CROATIAN” OR “DUTCH” OR “LITHUANIAN” OR “NORWEGIAN” OR “POLISH” OR “SLOVAK”) OR TMSO = (“6.178 Gender & Sexuality Studies” OR “1.120 Inflammatory Bowel Diseases & Infections” OR “1.156 Healthcare Policy” OR “6.73 Social Psychology” OR “1.137 Sleep Science & Circadian Systems” OR “1.44 Nutrition & Dietetics” OR “1.65 Allergy” OR “3.83 Bioengineering” OR “1.112 Palliative Care” OR “1.21 Psychiatry” OR “1.26 Diabetes” OR “1.36 Ophthalmology” OR “1.55 Urology & Nephrology-General” OR “6.24 Psychiatry & Psychology” OR “1.127 Molecular & Cell Biology-Pharmacology” OR “1.150 Hearing Loss” OR “1.163 Parasitology-General” OR “1.194 Tuberculosis & Leprosy” OR “1.228 Virology-Tropical Diseases” OR “1.23 Antibiotics & Antimicrobials” OR “1.252 Smoking Cessation” OR “1.261 Parasitology-Trypanosoma & Leishmania” OR “1.264 Longevity” OR “1.324 Bacterial Toxins & Diseases” OR “1.80 Bone Diseases” OR “1.81 Reproductive Biology” OR “2.59 Pigments, Sensors & Probes” OR “3.171 Photo productivity” OR “3.97 Plant Pathology” OR “8.124 Environmental Sciences” OR “3.60 Herbicides, Pesticides & Ground Poisoning” OR “3.91 Contamination & Phytoremediation” OR “8.19 Oceanography, Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences” OR “6.153 Climate Change” OR “3.2 Marine Biology” OR “3.45 Soil Science” OR “4.169 Remote Sensing” OR “3.16 Phytochemicals” OR “7.133 Geotechnical Engineering” OR “7.177 Combustion” OR “8.205 Ocean Dynamics” OR “8.312 Gas Hydrates” OR “6.146 Anthropology” OR “8.93 Archaeology” OR “10.290 Art” OR “6.11 Education & Educational Research” OR “6.269 Political Philosophy” OR “4.48 Knowledge Engineering & Representation” OR “10.240 Music” OR “10.268 History & Philosophy of Science” OR “6.256 Religion” OR “6.288 Information & Library Science”)) | 482 |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY (urban AND rural AND industrialization) AND PUBYEAR > 2004 AND PUBYEAR < 2026 AND (EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “MEDI”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “EART”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “ARTS”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “ENGI”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “AGRI”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “BUSI”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “ENER”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “COMP”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “BIOC”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “MULT”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “PHAR”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “CHEM”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “MATH”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “MATE”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “IMMU”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “PHYS”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “PSYC”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “CENG”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “DECI”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “NURS”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “NEUR”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “Undefined”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “VETE”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “HEAL”) OR EXCLUDE (SUBJAREA, “DENT”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “ar”)) AND (LIMIT-TO ( LANGUAGE, “English”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (SRCTYPE, “j”)) | 309 |
| RQ | Research Problems | Analysis | Software |
|---|---|---|---|
| RQ 1 | Current state of research | Citation analysis | Biblioshiny 4.1 |
| RQ 2 | Social and intellectual structure of research | Countries and co-citation network | Biblioshiny 4.1 VOSviewer 1.6.20 |
| RQ 3 | Trending topics and themes | Network visualization of keywords Factorial Analysis LDA Topics Model | Biblioshiny 4.1 VOSviewer 1.6.20 Big-ML (C) 2025 |
| Description | Results |
|---|---|
| Timespan | 2005:2025 |
| Sources (journals, book chapters) | 325 |
| Documents | 636 |
| Annual growth rate % | 3.23 |
| Document average age | 7.08 |
| Average citations per doc | 28.95 |
| DOCUMENT CONTENTS | |
| Keywords Plus (ID) | 2675 |
| Author’s Keywords (DE) | 2275 |
| Authors | 1484 |
| Authors of single-authored docs | 143 |
| AUTHORS COLLABORATION | |
| Single-authored docs | 149 |
| Co-authors per doc | 3.13 |
| International co-authorships % | 17.61 |
| DOCUMENT TYPES | |
| Article | 621 |
| Book chapter | 15 |
| Title Topic | Co-Occurrence | Cluster (Figure 11) | Thematic Group (Figure 12 and Figure 13) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Migration and socio-environmental dynamics in rural areas | 14.38% | 3, 4 | Niche |
| 2. Urbanization and environmental impact | 22.53% | 2 | Basic |
| 3. Policies, planning, and local dynamics | 24.23% | 1 | Basic |
| 4. Spatial change and evolution of human settlements | 22.56% | 3 | Basic |
| 5. Urbanization, industrialization, and rural areas | 29.77% | 1 | Motor |
| 6. Land use: ecological and spatial patterns | 34.27% | 5 | Emerging |
| 7. Sustainable assessment of urbanization | 35.22% | 1 | Basic |
| 8. Urbanization: employment, housing, challenges rural areas | 14.51% | 1, 3 | Motor |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez, F.T.; Castellano-Álvarez, F.J.; Robina-Ramírez, R. Industrial Diffusion Processes in Peri-Urban Environments: A State-of-the-Art Analysis of Current and Future Dimensions. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9090378
Sánchez FT, Castellano-Álvarez FJ, Robina-Ramírez R. Industrial Diffusion Processes in Peri-Urban Environments: A State-of-the-Art Analysis of Current and Future Dimensions. Urban Science. 2025; 9(9):378. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9090378
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez, Fernando Toro, Francisco Javier Castellano-Álvarez, and Rafael Robina-Ramírez. 2025. "Industrial Diffusion Processes in Peri-Urban Environments: A State-of-the-Art Analysis of Current and Future Dimensions" Urban Science 9, no. 9: 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9090378
APA StyleSánchez, F. T., Castellano-Álvarez, F. J., & Robina-Ramírez, R. (2025). Industrial Diffusion Processes in Peri-Urban Environments: A State-of-the-Art Analysis of Current and Future Dimensions. Urban Science, 9(9), 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9090378










