Contradiction or Coordination? Spatial Heterogeneity Between Urbanization and Green Development in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Evaluation Index System
2.4. Linear Weighting Method
2.5. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Method
2.6. Coupling Method
3. Results
3.1. Comprehensive Level Analysis
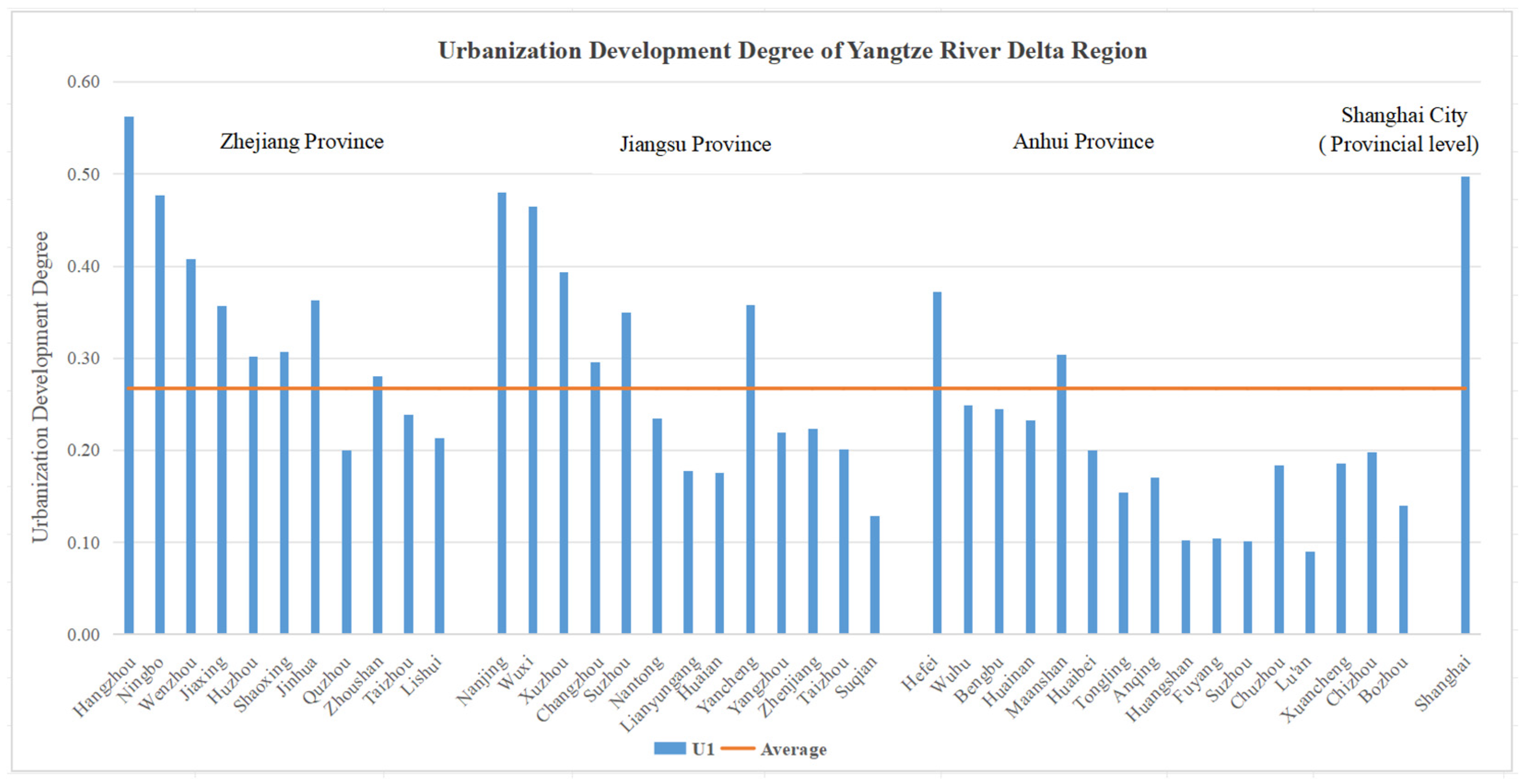
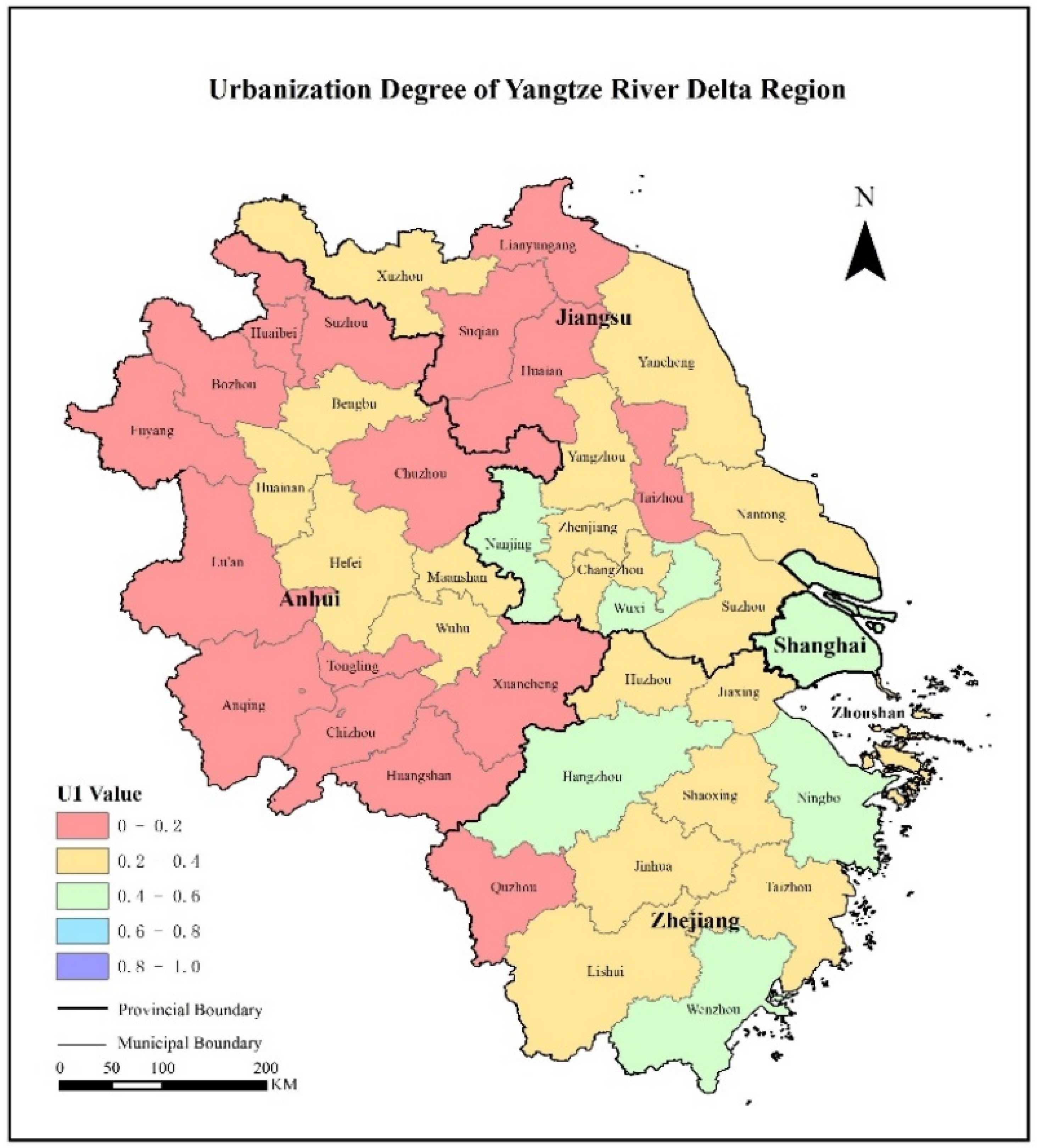
3.2. Analysis of the Urbanization System
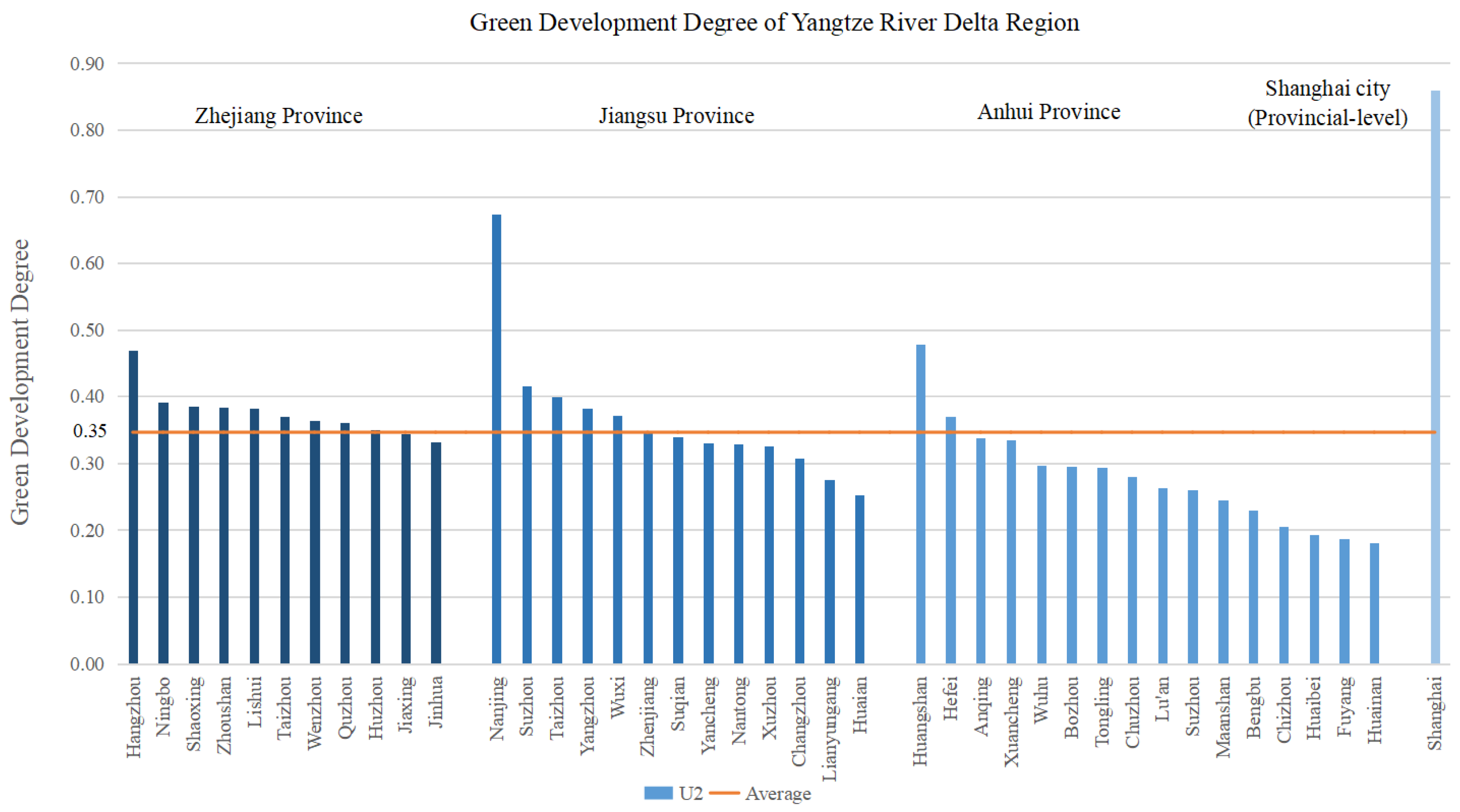
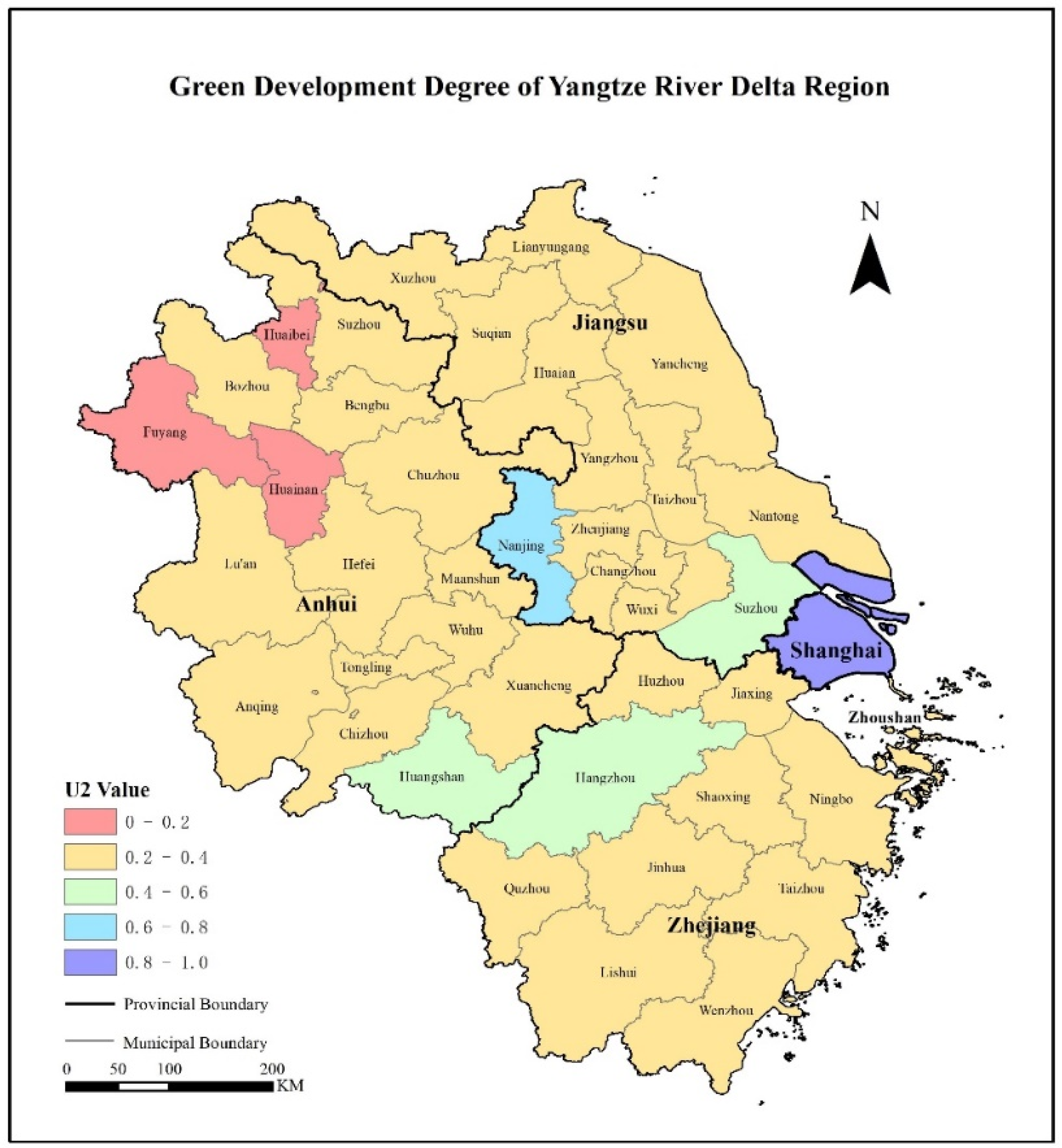
3.3. Analysis of the Green Development System
3.4. Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Degree
3.5. Data Classification and Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Research Findings
4.2. Political Implications
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
4.3.1. Strengths
4.3.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, J. Financial Geographical Structure and the Gap of Green Development: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Geogr. Res. 2022, 2022, 6134985. [Google Scholar]
- Dinda, S.; Chatterjee, N.D.; Ghosh, S. An integrated simulation approach to the assessment of urban growth pattern and loss in urban green space in Kolkata, India: A GIS-based analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107178. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B. Ecological effects of new-type urbanization in China. Renew. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110239. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.; Chen, M.; Lu, D. Revisiting the relationship between urbanization and economic development in China since the reform and opening-up. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.H.; Xu, L.; Qu, G.H.; Yan, Z.J.; Wang, J.X. The impact of energy consumption on environment and public health in China. Nat. Hazards 2017, 87, 675–697. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Xu, L.; Guo, Y.; Wu, H. The inducing factors of environmental emergencies: Do environmental decentralization and regional corruption matter? J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, B. Does high-speed rail improve green development? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 407, 137174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, F. Green Development Evaluation of Tai’an Based on Entropy Method. Geogr. Res. 2022, 2022, 8472758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y.; Ou, J.-J. Green standard and green development: Theory and empirical evidence. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Huang, S. Spatio-temporal patterns and driving factors of green development level in alpine meadow regions: A case study in Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 168, 112751. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, T. Unravelling the impact pathways of green innovation and environmental regulation on China’s green development efficiency goals: Direct and spillover effects. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 168, 112713. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, J.; Peng, J.; Peng, T. Can institutional opening-up promote green development in cities? Evidence from China’s Pilot Free Trade Zones. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 473, 143573. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, S.P.; Hughes, J.E.; Knittel, C.R. Greenhouse gas reductions under low carbon fuel standards? Am. Econ. J. Macroecon. Econ. Policy 2009, 1, 106–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H.; He, G.; Li, B.; Zeng, J.; Cai, Y.; Shen, X. Coupling coordination relationship between urbanization and water environment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 472, 143423. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Zhai, G.; Yu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. Coupling coordination between urbanization and ecosystem services value in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 113, 105715. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Luo, Q.; Cheng, S.; Hu, G.; Wang, X. Coupling coordination analysis of urbanization and ecological environment in Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 161, 111969. [Google Scholar]
- Chengjing, N.; Yixuan, L.; Linsheng, Y.; Li, W.; Fengying, Z. Spatio-temporal characteristics and coupling coordination relationship between urbanization and atmospheric particulate pollutants in the Bohai Rim in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110387. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, M.; Wu, L.; Li, F.; Lin, C. Spatiotemporal dynamics of ecosystem services and the driving factors in urban agglomerations: Evidence from 12 national urban agglomerations in China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 804969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B. Coupling relationship between urbanization and water-related ecosystem services in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt and its socio-ecological driving forces. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109871. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.-G.; Xu, K.; Duan, K. Investigating the intention to participate in environmental governance during urban-rural integrated development process in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 128, 132–141. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Q. Yangtze River Delta in China space-time effect research on influencing factors for ecological civilization construction. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.-H.; Yun, Y.; Sun, J.-N. Entropy method for determination of weight of evaluating indicators in fuzzy synthetic evaluation for water quality assessment. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, N.; Zhang, W.; Ning, X. Can agricultural low-carbon development benefit from urbanization?—Empirical evidence from China’s new-type urbanization pilot policy. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhou, N.; Liu, T.; Siehr, S.A.; Qi, Y. Investigation of a “coupling model” of coordination between low-carbon development and urbanization in China. Energy Policy 2018, 121, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Liu, Y.L. Quantifying the spatiality of urban leisure venues in Wuhan, Central China-GIS-based spatial pattern metrics. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Shu, J.J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. Tempo-spatial variability of urban leisure functional zones: An analysis based on geo-big data. Growth Change A J. Urban Reg. Policy 2021, 52, 1852–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Feng, L.; Yuan, Z.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, X. Dynamic change and evolutionary mechanism of city land leasing network—Taking the Yangtze River Delta region in China as an example. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Gu, J. Coordination evaluation and dynamic adjustment mechanism of China’s green development at inter-provincial level. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariken, M.; Zhang, F.; Chan, N.W.; Kung, H.-T. Coupling coordination analysis and spatio-temporal heterogeneity between urbanization and eco-environment along the Silk Road Economic Belt in China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Feng, K. Coupling analysis of urbanization and energy-environment efficiency: Evidence from Guangdong province. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhong, J.-L.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Xiang, X.; Huang, H. Exploring the coupling coordination and key factors between urbanization and land use efficiency in ecologically sensitive areas: A case study of the Loess Plateau, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 86, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, S. Behavior of Endemic and Non-Endemic Species in Urban Green Infrastructures: Sustainable Strategies in Quito. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.M.; Betts, R.A.; Jones, C.D.; Spall, S.A.; Totterdell, I.J. Acceleration of global warming due to carbon-cycle feedbacks in a coupled climate model. Nature 2000, 408, 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix, K. Comparing the relative mitigation potential of individual proenvironmental behaviors. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suki, N.M.; Sharif, A.; Afshan, S.; Suki, N.M. Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve in Malaysia: The role of globalization in sustainable environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121669. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Cui, Y. Analyzing urban infrastructure economic benefit using an integrated approach. Cities 2018, 79, 124–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Liu, D.F.; Wang, P. Urban simulation incorporating coordination relationships of multiple ecosystem services. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 76, 103432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Tian, K.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, T. Coupling and coordination of socioeconomic and ecological environment in Wenchuan earthquake disaster areas: Case study of severely affected counties in Southwestern China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 71, 102958. [Google Scholar]
- State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Master Plan for Territorial Space of the Yangtze River Delta Ecological and Green Integrated Development Demonstration Zone (2021–2035). 2023, The State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2023/content_5745287.htm (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Deng, Z.; Zong, S.; Su, C.; Chen, Z. Study on the Coupling, Coordinated Development and Driving Factors of Ecological Civilization Construction and New-type Urbanization in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 33, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Yangtze River Delta Multi-Level Rail Transit System Plan. 2021, The State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/ghwb/202107/P020210706504326496368.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Outline for Integrated Regional Development of the Yangtze River Delta. 1 December 2019, The State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2019/content_5462503.htm (accessed on 6 March 2025).


| System | Sub-System | Indicators | Unit | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urbanization | Economic Urbanization | Per capita disposable income of urban and rural residents | RMB | + |
| Urban population density | Person per square meter | + | ||
| Gross industrial product as a percentage of GDP | % | + | ||
| Proportion of output value of tertiary industry in GDP | % | + | ||
| Per capita social fixed asset investment | RMB per person | + | ||
| The proportion of the population employed in the tertiary industry | % | + | ||
| Per capita urban road area | Square meter per person | + | ||
| Urban registered unemployment rate at the end of the year | % | - | ||
| Innovation Urbanization | Ten thousand people invent professional authorization quantity | Piece | + | |
| Per capita educational expenditure | RMB 10,000 | + | ||
| Number of research institutes | Institute | + | ||
| Total public library holdings | 10,000 pieces | + | ||
| R&D expenditure | RMB 100 million | + | ||
| R&D personnel number of personnel input | 10,000 people per year | + | ||
| Number of newly registered enterprises per 10,000 people | Institute | + | ||
| Comprehensive energy consumption of RMB 10,000 GDP | Tons of standard coal per RMB 10,000 | - |
| System | Indicators | Unit | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green Development | Urban green coverage | Hectare | + |
| Urban per capita public green space | Square meters per person | + | |
| Sewage treatment rate | % | + | |
| The comprehensive utilization rate of general industrial solid waste | % | + | |
| Average annual concentration of sulfur dioxide | Micrograms per cubic meter | - | |
| PM2.5 | Micrograms per cubic meter | - | |
| Public satisfaction with the environment | % | + | |
| Average number of days with good ambient air quality | % | + |
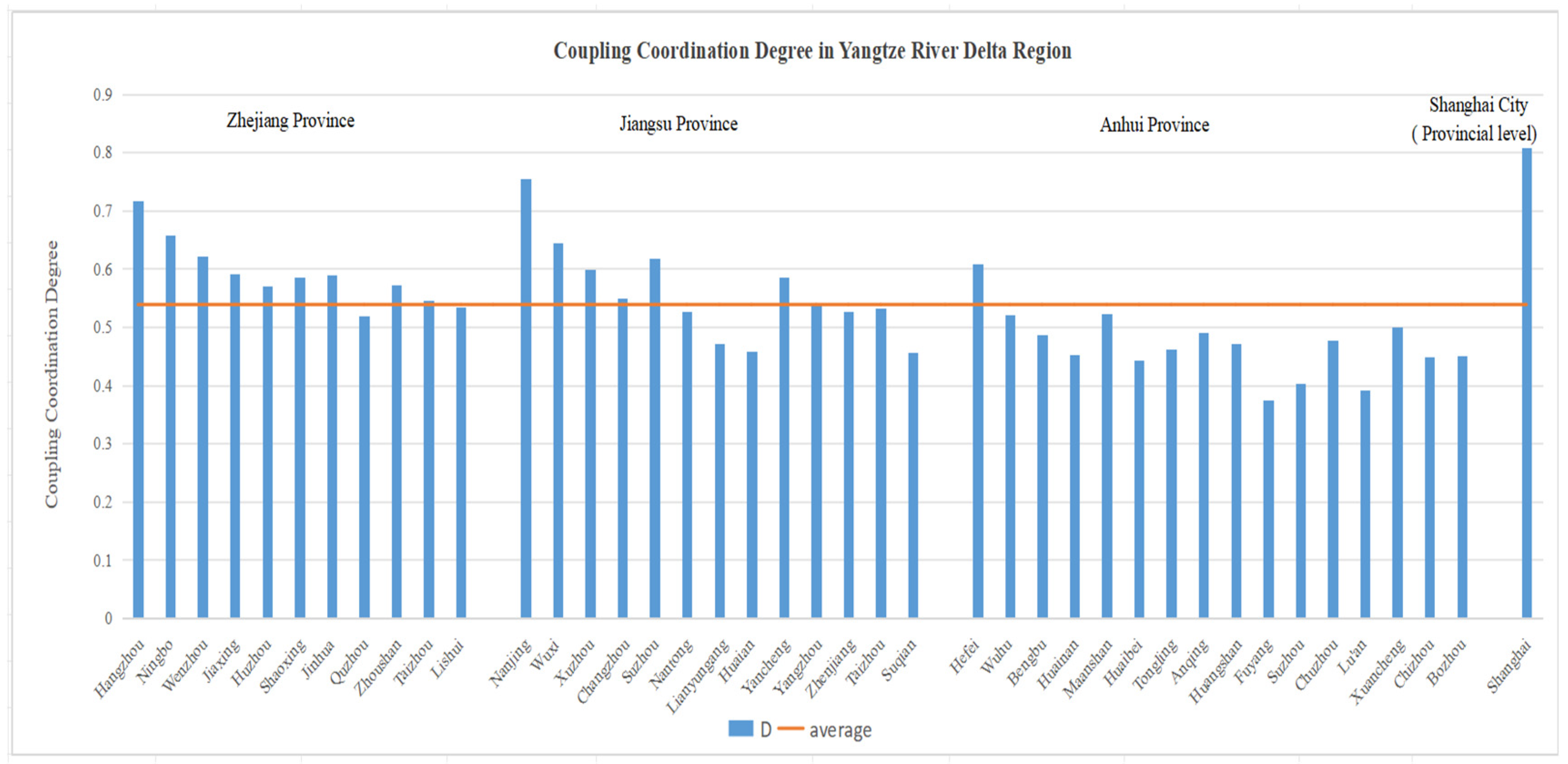
| Provinces | Cities | Composite Index of Urbanization (U1) | Composite Index of Green Development (U2) | Coupling (C12) | Coupling Coordination (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou | 0.56 | 0.47 | 0.996 | 0.717 |
| Ningbo | 0.48 | 0.39 | 0.995 | 0.657 | |
| Wenzhou | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.998 | 0.621 | |
| Jiaxing | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.999 | 0.592 | |
| Huzhou | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.997 | 0.570 | |
| Shaoxing | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.993 | 0.586 | |
| Jinhua | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.999 | 0.589 | |
| Quzhou | 0.20 | 0.36 | 0.958 | 0.518 | |
| Zhoushan | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.988 | 0.572 | |
| Taizhou | 0.24 | 0.37 | 0.977 | 0.545 | |
| Lishui | 0.21 | 0.38 | 0.959 | 0.534 | |
| Jiangsu | Nanjing | 0.48 | 0.67 | 0.986 | 0.754 |
| Wuxi | 0.47 | 0.37 | 0.994 | 0.644 | |
| Xuzhou | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.995 | 0.598 | |
| Changzhou | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.999 | 0.549 | |
| Suzhou | 0.35 | 0.42 | 0.996 | 0.618 | |
| Nantong | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.986 | 0.527 | |
| Lianyungang | 0.18 | 0.28 | 0.977 | 0.471 | |
| Huaian | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.984 | 0.459 | |
| Yancheng | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.999 | 0.586 | |
| Yangzhou | 0.22 | 0.38 | 0.963 | 0.538 | |
| Zhenjiang | 0.22 | 0.35 | 0.976 | 0.528 | |
| Taizhou | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.944 | 0.532 | |
| Suqian | 0.13 | 0.34 | 0.892 | 0.457 | |
| Anhui | Hefei | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.999 | 0.609 |
| Wuhu | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.996 | 0.522 | |
| Bengbu | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.999 | 0.487 | |
| Huainan | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.992 | 0.453 | |
| Maanshan | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.994 | 0.522 | |
| Huaibei | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.999 | 0.443 | |
| Tongling | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.950 | 0.461 | |
| Anqing | 0.17 | 0.34 | 0.944 | 0.490 | |
| Huangshan | 0.10 | 0.48 | 0.762 | 0.470 | |
| Fuyang | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.959 | 0.374 | |
| Suzhou | 0.10 | 0.26 | 0.897 | 0.403 | |
| Chuzhou | 0.18 | 0.28 | 0.978 | 0.477 | |
| Lu’an | 0.09 | 0.26 | 0.872 | 0.392 | |
| Xuancheng | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.958 | 0.499 | |
| Chizhou | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.999 | 0.449 | |
| Bozhou | 0.14 | 0.30 | 0.934 | 0.451 | |
| Shanghai | Shanghai | 0.50 | 0.86 | 0.964 | 0.808 |
| Type | Coupling Coordination Degree Sub-Type | Cities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Coordination | 0.7 ≤ D ≤ 1 | High coordination–urbanization lag | U2 − U1 > 0.1 | Shanghai, Nanjing |
| High coordination | 0 ≤ |U1 − U2| ≤ 0.1 | Hangzhou | ||
| High coordination–green lag | U1 − U2 > 0.1 | / | ||
| Moderate Coordination | 0.6 ≤ D < 0.7 | Basic coordination–urbanization lag | U2 − U1 > 0.1 | / |
| Basic coordination | 0 ≤ |U1 − U2| ≤ 0.1 | Ningbo, Wenzhou, Wuxi, Suzhou, Hefei | ||
| Basic coordination– green lag | U1 − U2 > 0.1 | / | ||
| Low Coordination | 0.5 ≤ D < 0.6 | Basic imbalance–urbanization lag | U2 − U1 > 0.1 | Quzhou, Zhoushan, Taizhou, Lishui, Yangzhou, Zhenjiang, Taizhou |
| Basic imbalance | 0 ≤ |U1 − U2| ≤ 0.1 | Jiaxing, Huzhou, Shaoxing, Jinhua, Xuzhou, Changzhou, Nantong, Yancheng, Wuhu, Maanshan | ||
| Basic imbalance–green blocked | U1 − U2 > 0.1 | / | ||
| Mild Imbalance | 0.4 ≤ D < 0.5 | Severe imbalance–urbanization lag | U2 − U1 > 0.1 | Suqian, Tongling, Anqing, Huangshan, Suzhou, Xuancheng, Bozhou |
| Severe imbalance | 0 ≤ |U1 − U2| ≤ 0.1 | Lianyungang, Huaian, Bengbu, Huainan, Huaibei, Chuzhou, Chizhou | ||
| Sever imbalance–green blocked | U1 − U2 > 0.1 | / | ||
| Moderate Imbalance | 0 < D < 0.4 | High imbalance–urbanization | U2 − U1 > 0.1 | Lu’an |
| High imbalance | 0 ≤ |U1 − U2| ≤ 0.1 | Fuyang | ||
| High imbalance–green lag | U1 − U2 > 0.1 | / | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jing, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lang, Y.; Miao, Q. Contradiction or Coordination? Spatial Heterogeneity Between Urbanization and Green Development in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9040089
Jing Y, Yang Y, Lang Y, Miao Q. Contradiction or Coordination? Spatial Heterogeneity Between Urbanization and Green Development in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Urban Science. 2025; 9(4):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9040089
Chicago/Turabian StyleJing, Ying, Yuxuan Yang, Yue Lang, and Qing Miao. 2025. "Contradiction or Coordination? Spatial Heterogeneity Between Urbanization and Green Development in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China" Urban Science 9, no. 4: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9040089
APA StyleJing, Y., Yang, Y., Lang, Y., & Miao, Q. (2025). Contradiction or Coordination? Spatial Heterogeneity Between Urbanization and Green Development in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Urban Science, 9(4), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9040089







