Evolution of the Urban Network in the Yellow River Basin: A Corporate Network Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Relational Urban Systems: Theory and Organization
2.2. China’s Urban Networks: Flows and Institutions
2.3. The YRB as a Research Focus
2.4. Insights and Research Focus
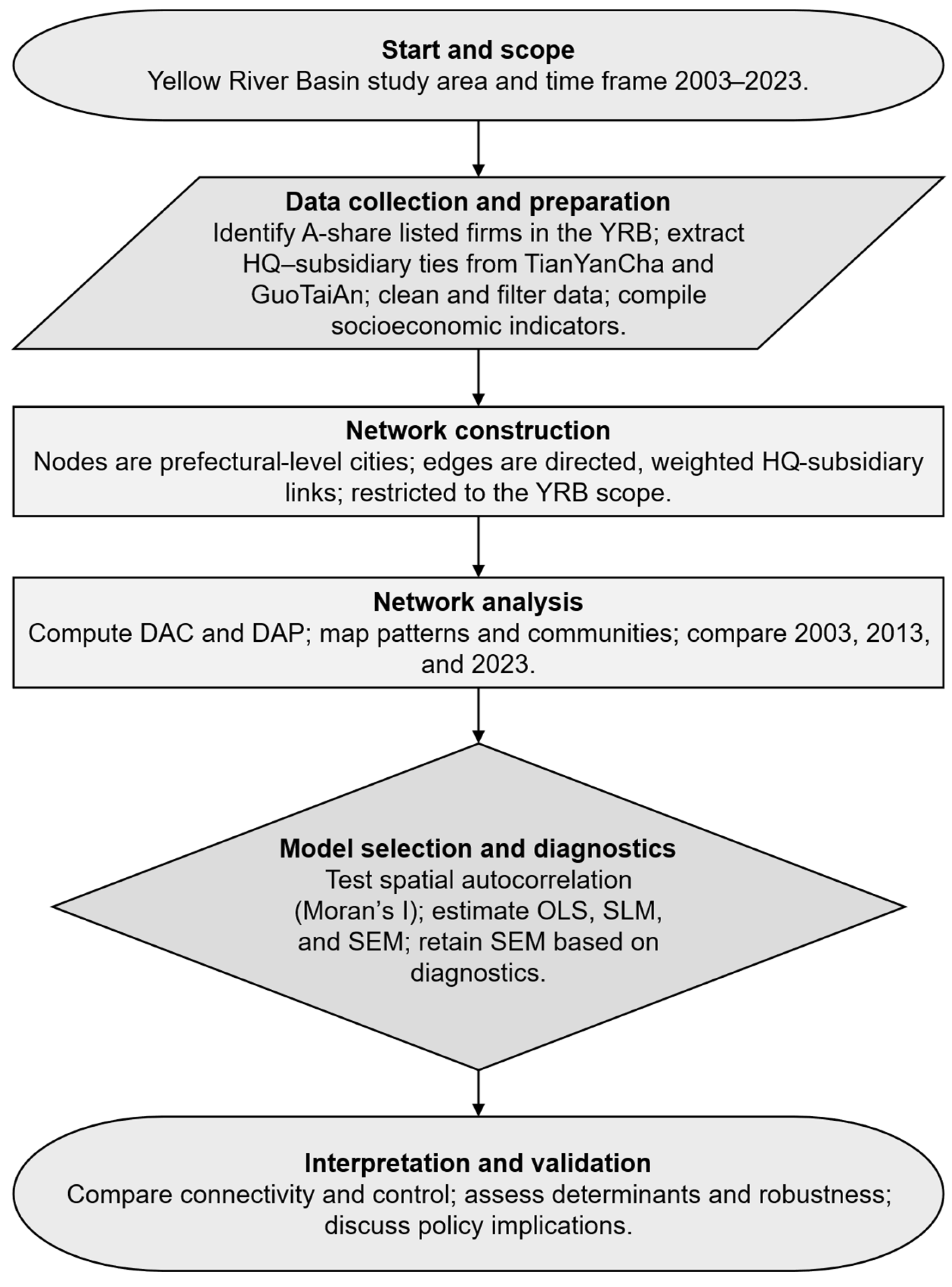
3. Materials and Methods
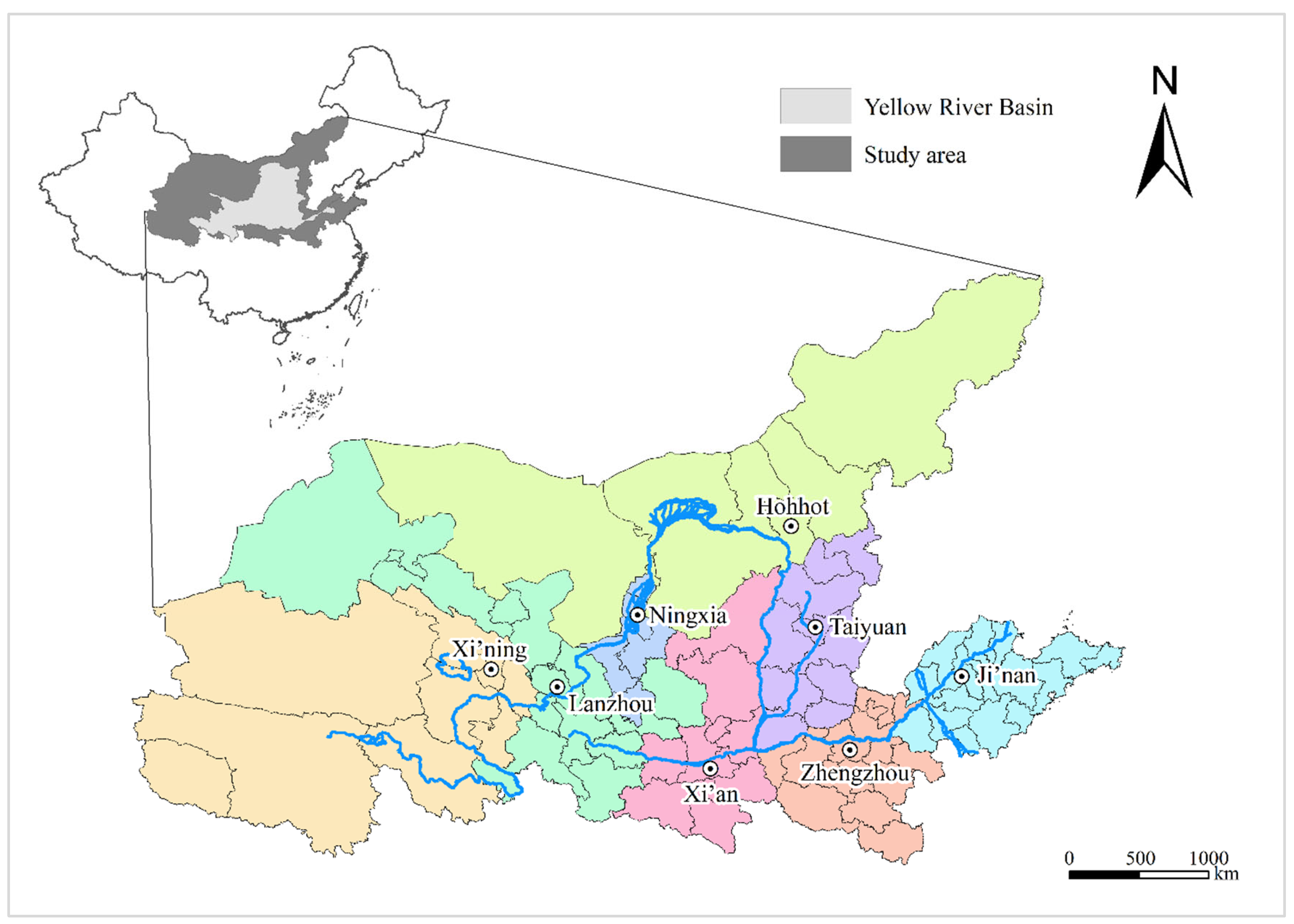
3.1. Study Area and Data Source
3.2. Network Centrality Analysis
3.3. Influencing Factor Analysis of Centrality and Power
4. Results
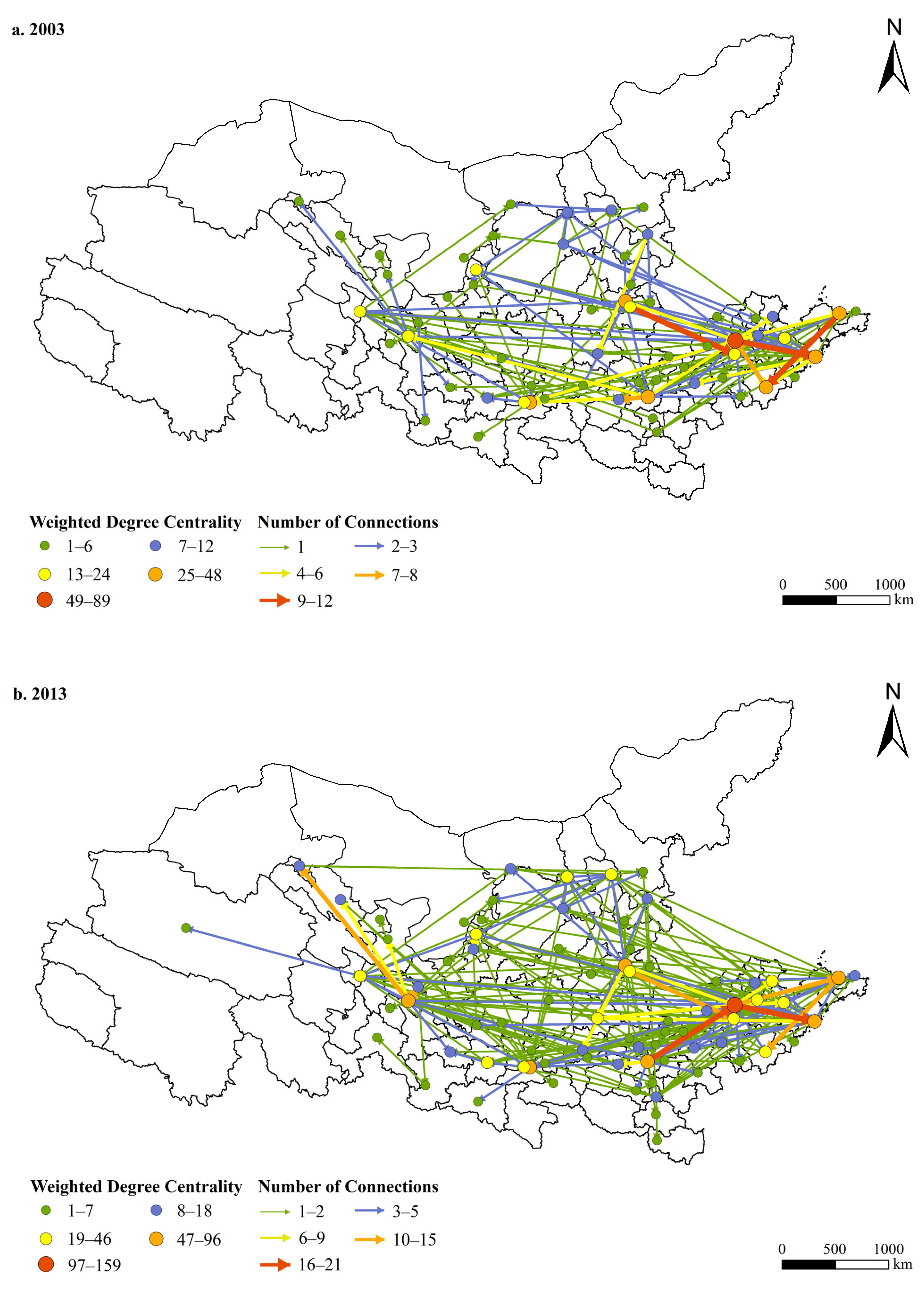
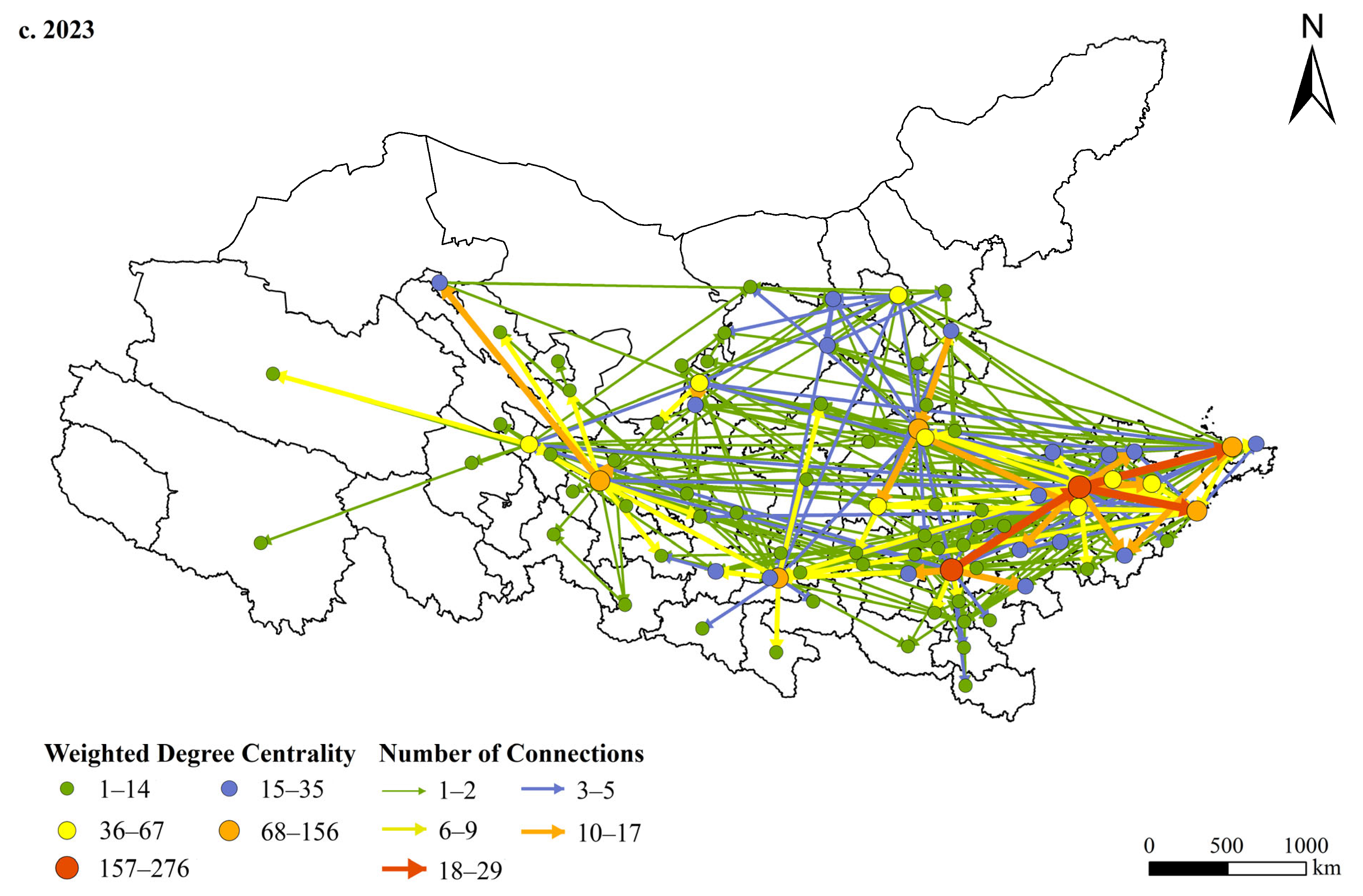
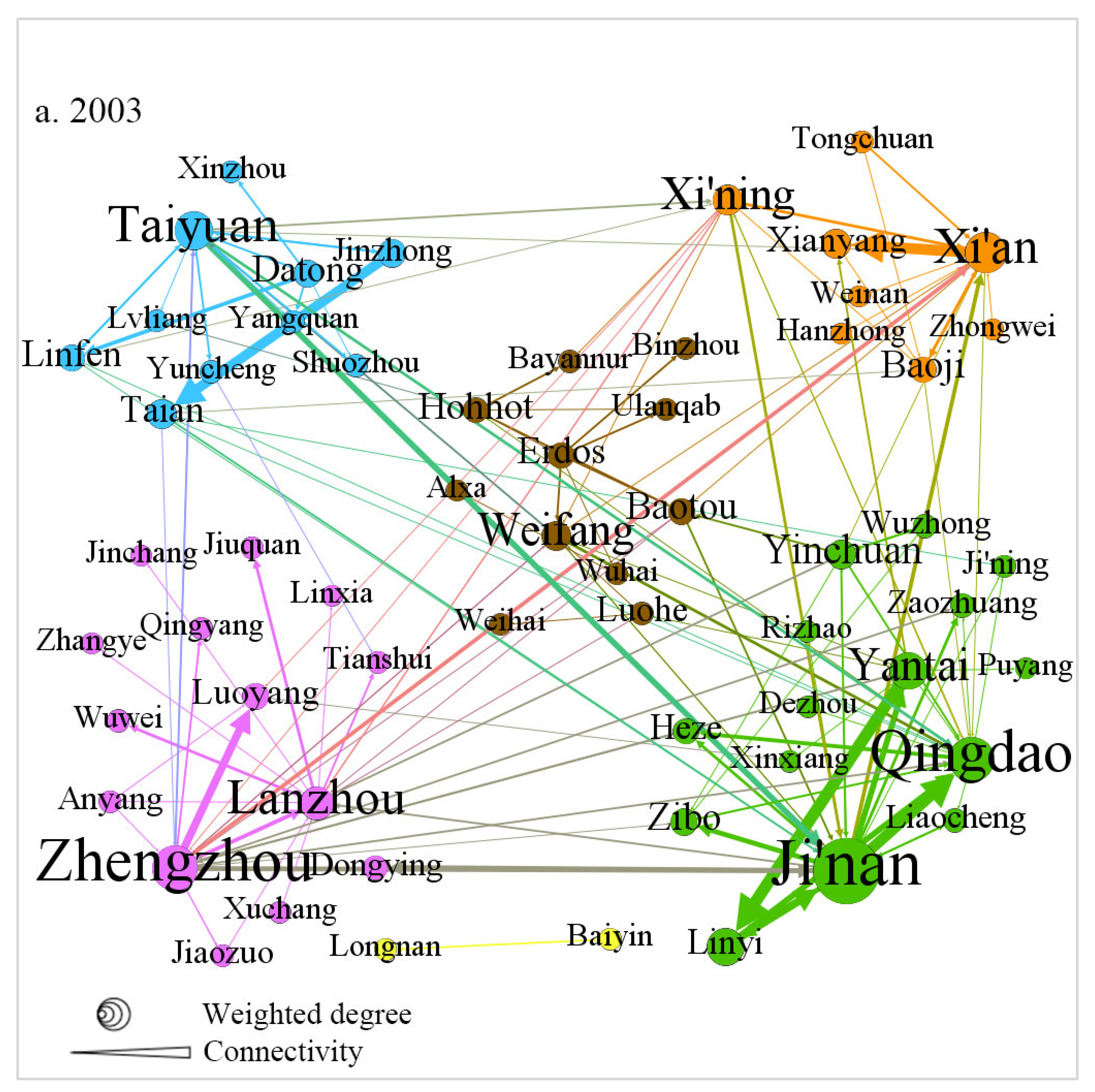
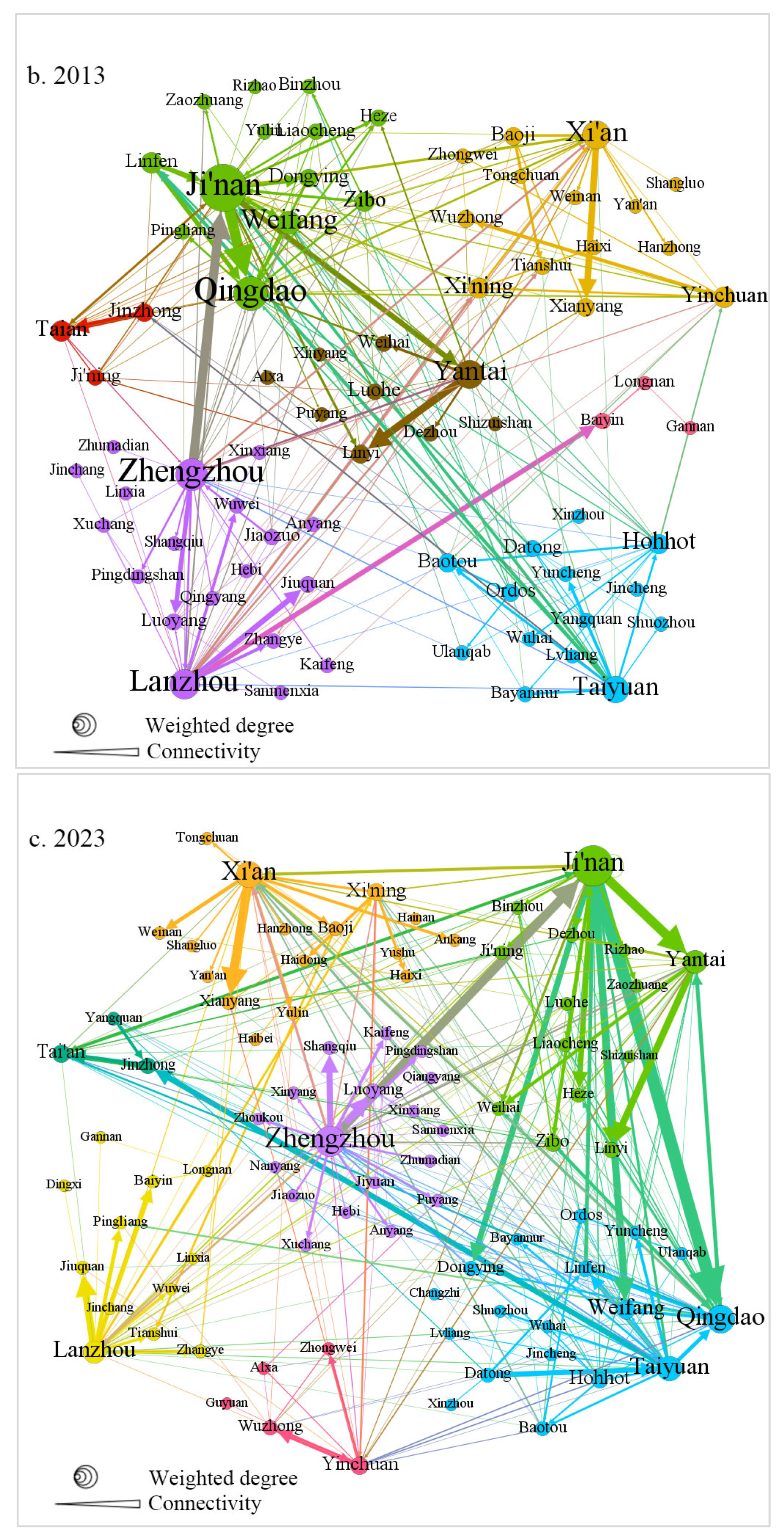
4.1. Evolution of Urban Network Structures in the YRB
4.1.1. Changing Spatial Distribution of Headquarters–Subsidiary Ties (2003–2023)
4.1.2. Community Structures and Cross-Provincial Linkages
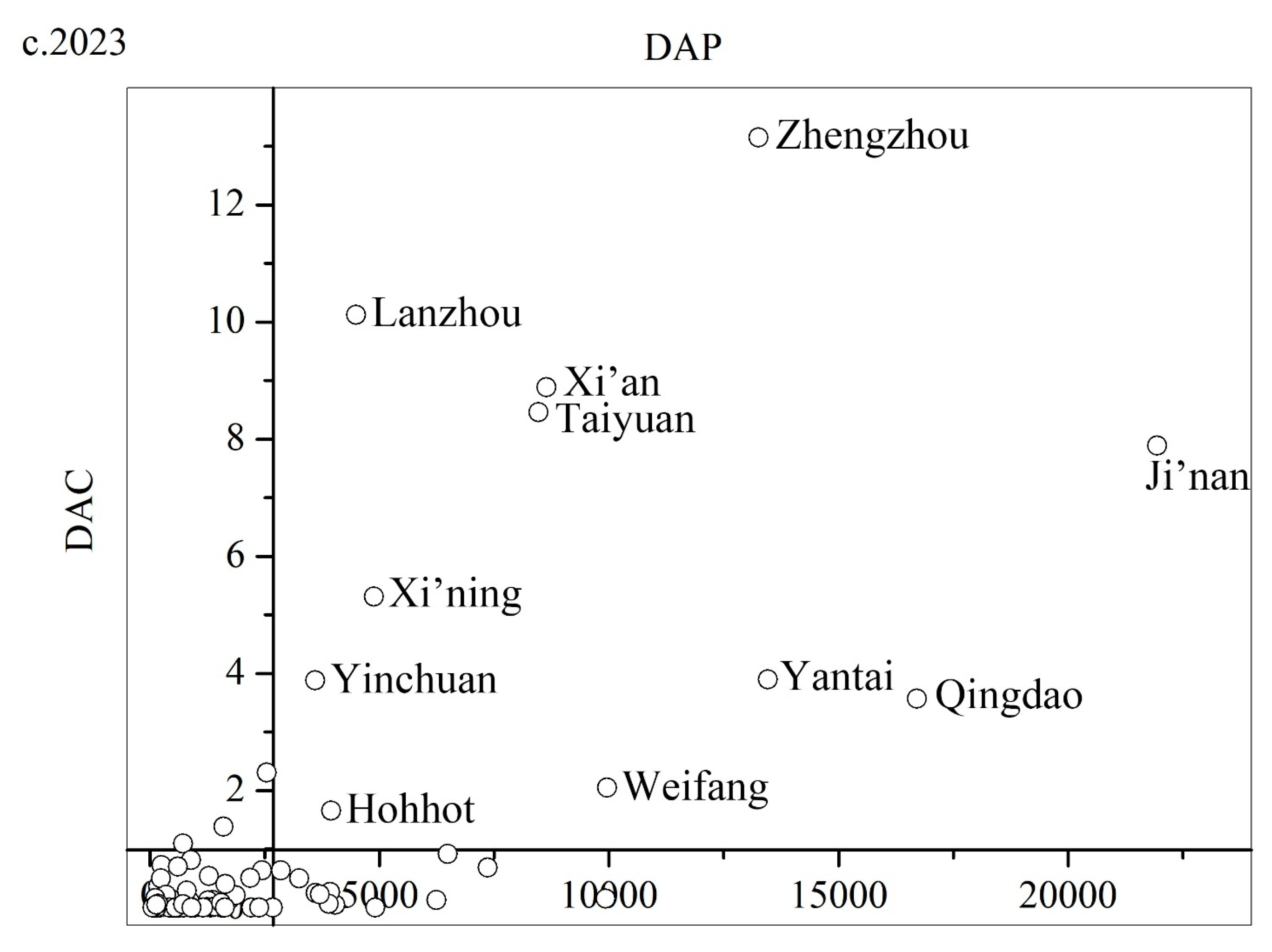
4.2. Power Structure of Cities in the YRB Urban Network
4.3. Influence Factors of Urban Network Structure in the YRB
5. Discussion and Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christaller, W. Central Places in Southern Germany; Carlisle, W.B., Translator; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Castells, M. The Rise of the Network Society; Blackwell Publishers: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sassen, S. The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo, 2nd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Beaverstock, J.V.; Smith, R.G.; Taylor, P.J. World-City Network: A New Metageography? Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2000, 90, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, Z.P. Differentiating Centrality and Power in the World City Network. Urban Stud. 2011, 48, 2733–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Derudder, B. Analyzing Urban Networks through the Lens of Corporate Networks: A Critical Review. Cities 2013, 31, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, J.; Chu, N.; Li, F. The Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Spatial Network of City-Based Innovation Correlation in China: From the Perspective of High Tech Zones. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, Z.P. Does World City Network Research Need Eigenvectors? Urban Stud. 2013, 50, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wei, Y.; Pang, R.; Wang, S.; Feng, Z. Measurement of Directed Alternative Centricity and Power of a Directed Weighted Urban Network: A Case of the Population Flow Network of China during ‘Chunyun’. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 647–660. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, P.J. Specification of the World City Network. Geogr. Anal. 2001, 33, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, E. From Central Place to Network Place: The Shift to Polycentric Development in the Randstad Holland. Environ. Plan. B 2007, 34, 795–810. [Google Scholar]
- Derudder, B.; Taylor, P.; Ni, P.; De Vos, A.; Hoyler, M.; Hanssens, H.; Bassens, D.; Huang, J.; Witlox, F.; Shen, W.; et al. Pathways of Change: Shifting Connectivities in the World City Network, 2000–2008. Urban Stud. 2010, 47, 1861–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J.; Hoyler, M.; Verbruggen, R. External Urban Relational Process: Introducing Central Flow Theory to Complement Central Place Theory. Urban Stud. 2010, 47, 2803–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Goei, B.; Meijers, E.; Kapoen, P.-J.; Priemus, H. The Polycentric Metropolis Unpacked: Concepts, Trends and Policy in the Randstad Holland. Built Environ. 2010, 36, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Alderson, A.S.; Beckfield, J. Power and Position in the World City System. Am. J. Sociol. 2004, 109, 811–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, A.; Meijers, E.; van Ham, M. The Evolution of the Systems of Cities Literature since 1995: Schools of Thought and Their Interaction. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2018, 18, 533–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, A.; Meijers, E.; van Ham, M. Information Diffusion between Dutch Cities: Revisiting Zipf and Pred Using a Computational Social Science Approach. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J.; Derudder, B.; Faulconbridge, J.; Hoyler, M.; Ni, P. Advanced Producer Service Firms as Strategic Networks, Global Cities as Strategic Places. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 90, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, R.C.; Charles-Edwards, E. The evolution of spatial networks of migration in Brazil between 1980 and 2010. Popul. Space Place 2020, 26, e2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derudder, B.; Van Nuffel, N. Connecting the world: Analyzing global city networks through airline flows. In Aeromobilities; Saulo, C., Sven, K., John, U., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2009; pp. 88–107. [Google Scholar]
- Derudder, B.; Witlox, F. Mapping World City Networks Through Airline Flows: Context, Relevance, and Problems. J. Transp. Geogr. 2008, 16, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessemontet, P.; Kaufmann, V.; Jemelin, C. Switzerland as a single metropolitan area? A study of its commuting network. Urban Stud. 2010, 47, 2785–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krätke, S. Global Media Cities in a Worldwide Urban Network. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2003, 11, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigler, T.J.; Martinus, K. Extending beyond ‘World Cities’ in World City Network (WCN) Research: Urban Positionality and Economic Linkages through the Australia-Based Corporate Network. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2017, 49, 2916–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derudder, B.; Taylor, P. Change in the World City Network, 2000–2012. Reg. Stud. 2016, 50, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derudder, B.; Van Nuffel, N. Analyzing the Changing Connectivity of World Cities. Tijdschr. Voor Econ. En Soc. Geogr. 2009, 100, 437–448. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.; Sun, B. How Has the Inter-City Corporate Network Spatio-Temporally Evolved in China? Evidence from Chinese Investment in Newly Established Enterprises from 1980–2017. Land 2023, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lin, J.; Sun, D. The Role of Institutions and Markets in Shaping Intercity Investment Networks in China. Cities 2024, 153, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, W. Unpacking Urban Network as Formed by Client Service Relationships of Law Firms in China. Cities 2022, 122, 103546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Bi, W.; Lenzer, J.; Zhao, S. Mapping Urban Networks through Interfirm Service Relationships: The Case of China. Urban Stud. 2017, 54, 3639–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Bi, W.; Liu, X.; Sigler, T. Exploring Financial Centre Networks through Inter-Urban Collaboration in High-End Financial Transactions in China. Reg. Stud. 2020, 54, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hou, Q.; Xie, Z.; Mai, X. Urban Network and Regions in China: An Analysis of Daily Migration with Complex Networks Model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, W.; Chu, J. Exploring the Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Resilience Assessment of Urban Networks from the Perspective of Population Flow. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0325908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Mou, N.; Zhang, L.; Yang, T.; Liu, W.; Liu, F. Tourism flow between major cities during China’s National Day holiday: A social network analysis using Weibo check-in data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 225675–225691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Dobruszkes, F.; Wang, J.; Dijst, M.; White, P. Comparing China’s Urban Systems in High-Speed Railway and Airline Networks. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 68, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xue, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R. Analyzing the Topology Characteristics and Effectiveness of the China City Network. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2021, 48, 2554–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, W.; Guo, R.; He, B.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Fan, Y. Urban Network Spatial Connection and Structure in China Based on Railway Passenger Flow Big Data. Land 2022, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Li, L. High-Speed Rail and Aviation in China: Impacts on Intercity Network Connectivity. J. Transp. Geogr. 2021, 92, 103030. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Directional and weighted urban network analysis in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle from the perspective of new media information flow. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, W. Characteristics and Prediction of Urban Interaction Networks from the Perspective of Traffic Flow and Text Information Flow. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2025, 52, 430–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, B.; Guo, Y.; Yi, Z. The impact of intra-city and inter-city innovation networks on city economic growth: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta in China. Land 2023, 12, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zeng, G.; Lin, L.; Zou, L. Hierarchical characteristics and proximity mechanism of intercity innovation networks: A case of 290 cities in China. Complexity 2021, 2021, 5538872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Derudder, B.; Shen, W.; Kong, X. Exploring the Dynamics of the Disaggregated Intercity Corporate Network in the Yangtze River Delta, China: A Relational Event Approach. J. Geogr. Syst. 2022, 24, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, Z. Exploring the Imprint of the Institutional Context on the Urban Network in China: Comparative Analyses Between Corporate-Based Networks with Different Ownership Structures. Glob. Netw. 2024, 24, e12478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Derudder, B.; Huang, J. Examining the Transition Processes in the Pearl River Delta Polycentric Mega-City Region Through the Lens of Corporate Networks. Cities 2017, 60, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiyang, L.; Lucang, W.; Qianguo, L.; Cuixia, Y.A. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of City Connection Networks in the Yellow River Basin Based on Tencent’s Big Data of Population Migration. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 28–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, H. Urban Network Structure and Its Dynamics in the Yellow River Basin. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 202–212. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Han, Z.; Qiao, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.Y.; Duan, Y. The Spatial Connection Pattern and Influencing Factors of Tourism Economy among Cities in the Yellow River Basin. Arid Land Geogr. 2023, 46, 1344–1354. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hang, S.U.; Jiao, G.U.; Jinli, Z.H. Spatial Structure Evolution of Urban Information Network in the Yellow River Basin from Multi Scale Perspective. Arid Land Geogr. 2023, 46, 1206–1216. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X. Evolution and Organization of Urban Tourism Linkages under HSR in the Yellow River Basin. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 211–218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chai, D.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Yang, S. Research on the City Network Structure in the Yellow River Basin in China Based on Two-Way Time Distance Gravity Model and Social Network Analysis Method. Complexity 2020, 2020, 6680954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, S.; Ma, Z.; Tian, M.; Sun, M.; Nie, J. Research on Spatial Structure and Resilience of Complex Urban Network: A Case Study of Jing–Jin–Ji Urban Agglomeration. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 999124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Ren, J.; Chen, X. Spatial Structure and Influencing Factors of Urban Network in the Yellow River Basin from a Multi-Flow Perspective. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 1778–1787. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y. Evolution of an Urban Network in the Yellow River Basin Based on Producer Services. Complexity 2022, 2022, 3667745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wei, Y.D.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W. The Innovation Networks Shaped by Large Innovative Enterprises in Urban China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 599–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D. Regional Development and Its Spatial Structure; Springer: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China City Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China City Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China City Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L.; Bera, A.K. Spatial Dependence in Linear Regression Models with an Introduction to Spatial Econometrics. In Handbook of Applied Economic Statistics; Ullah, A., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 237–289. [Google Scholar]

| Dependent Variables | Explanatory Variables | Description | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAC/ DAP | POL | Administrative hierarchy | 1—provincial capitals and vice-provincial cities 0—other cities |
| GOV | Government intervention | Government expenditure as a percentage of GDP (%) | |
| TRA | Economic openness | FDI utilized ($10,000) | |
| POP | Population density | Permanent population per square kilometer | |
| GDP | Economic development | Per capita GDP (yuan) | |
| IND | Industrial structure | Percent of tertiary sector in GDP (%) | |
| INN | Innovation | Number of patents granted in the year | |
| TRF | Transportation | Road freight volume (10,000 tons) | |
| CAP | Human capital | College students per ten thousand population | |
| PRA | Employment | Employed persons (10,000) | |
| URB | Urbanization level | Percent of urban population | |
| INT | Information technology | Households with internet access (10,000) |
| 2003 | 2013 | 2023 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | DAC | City | DAP | City | DAC | City | DAP | City | DAC | City | DAP |
| Ji’nan | 2337 | Ji’nan | 6.55 | Ji’nan | 8151 | Zhengzhou | 9.80 | Ji’nan | 21,939 | Zhengzhou | 13.15 |
| Linyi | 1823 | Taiyuan | 6.11 | Qingdao | 5999 | Lanzhou | 7.16 | Qingdao | 16,709 | Lanzhou | 10.12 |
| Qingdao | 1702 | Lanzhou | 5.87 | Zhengzhou | 5382 | Ji’nan | 7.14 | Yantai | 13,464 | Xi’an | 8.89 |
| Yantai | 1428 | Zhengzhou | 4.68 | Yantai | 4346 | Taiyuan | 5.88 | Zhengzhou | 13,259 | Taiyuan | 8.46 |
| Zhengzhou | 1418 | Xi’an | 3.30 | Weifang | 3617 | Xi’an | 5.83 | Weifang | 9962 | Ji’nan | 7.89 |
| Taiyuan | 1080 | Qingdao | 3.14 | Linfen | 3138 | Yantai | 4.76 | Linyi | 9931 | Xining | 5.31 |
| Xi’an | 1013 | Ordos | 3.08 | Xi’an | 2903 | Weifang | 3.60 | Xi’an | 8640 | Yantai | 3.90 |
| Zibo | 783 | Datong | 2.87 | Taiyuan | 2894 | Qingdao | 3.22 | Taiyuan | 8463 | Yinchuan | 3.88 |
| Xining | 698 | Yantai | 2.86 | Zibo | 2483 | Datong | 2.37 | Zibo | 7359 | Qingdao | 3.57 |
| Weifang | 644 | Yinchuan | 1.76 | Dongying | 2427 | Yinchuan | 2.33 | Tai’an | 6488 | Datong | 2.31 |
| Xianyang | 596 | Hohhot | 1.33 | Tai’an | 2238 | Luohe | 1.96 | Dongying | 6237 | Weifang | 2.05 |
| Dongying | 582 | Luohe | 1.33 | Lanzhou | 2211 | Xining | 1.91 | Heze | 4909 | Hohhot | 1.65 |
| Yinchuan | 554 | Jinzhong | 1.11 | Xining | 1953 | Hohhot | 1.88 | Xining | 4881 | Wuzhong | 1.39 |
| Heze | 535 | Xining | 1.11 | Linyi | 1879 | Ordos | 1.32 | Lanzhou | 4489 | Ordos | 1.10 |
| Lanzhou | 453 | Baiyin | 1.00 | Yinchuan | 1626 | Baiyin | 1.05 | Dezhou | 4036 | Tai’an | 0.91 |
| Tai’an | 428 | Wuzhong | 0.78 | Heze | 1488 | Wuzhong | 1.03 | Hohhot | 3949 | Luohe | 0.81 |
| Zaozhuang | 410 | Tai’an | 0.61 | Hohhot | 1401 | Longnan | 1.00 | Liaocheng | 3928 | Jiyuan | 0.72 |
| Luoyang | 407 | Alxa | 0.50 | Weihai | 1398 | Tai’an | 0.87 | Weihai | 3893 | Yuncheng | 0.70 |
| Liaocheng | 403 | Luoyang | 0.50 | Liaocheng | 1320 | Baotou | 0.82 | Xianyang | 3705 | Zibo | 0.69 |
| Linfen | 338 | Linfen | 0.46 | Xianyang | 1278 | Zibo | 0.77 | Luoyang | 3608 | Baotou | 0.64 |
| Variables | DAC | DAP | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 2013 | 2023 | 2003 | 2013 | 2023 | |||||||||||||
| Coef. | Std. Err. | p > |t| | Coef. | Std. Err. | p > |t| | Coef. | Std. Err. | p > |t| | Coef. | Std. Err. | p > |t| | Coef. | Std. Err. | p > |t| | Coef. | Std. Err. | p > |t| | |
| POL | 2.690 *** | 0.178 | 0.000 | 1.204 *** | 0.257 | 0.000 | 0.479 ** | 0.196 | 0.015 | 0.335 | 0.000 | 1.783 *** | 0.500 | 0.000 | 3.084 *** | 0.403 | 0.000 | 2.690 *** |
| GOV | −6.292 *** | 1.171 | 0.000 | −3.089 *** | 0.837 | 0.000 | −1.149 ** | 0.567 | 0.043 | 2.226 | 0.046 | −3.828 ** | 1.605 | 0.017 | −4.473 *** | 1.112 | 0.000 | −6.292 *** |
| lnTRA | 0.016 | 0.037 | 0.670 | 0.087 ** | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.060 * | 0.035 | 0.087 | 0.073 | 0.361 | 0.065 | 0.075 | 0.381 | 0.072 *** | 0.071 | 0.008 | 0.016 |
| POP | −2.695 | 2.509 | 0.283 | −6.177 ** | 2.481 | 0.013 | −0.439 | 2.038 | 0.830 | 4.934 | 0.451 | −2.905 | 4.686 | 0.535 | −2.713 | 3.973 | 0.495 | −2.695 |
| lnGDP | −0.111 ** | 0.056 | 0.049 | 0.152 ** | 0.071 | 0.032 | 0.089 ** | 0.074 | 0.029 | 0.110 | 0.000 | 0.851 *** | 0.137 | 0.000 | 0.987 *** | 0.153 | 0.000 | −0.111 ** |
| IND | 3.621 *** | 0.872 | 0.000 | 0.753 * | 0.697 | 0.080 | 0.144 ** | 0.107 | 0.016 | 1.661 | 0.056 | 0.817 ** | 1.293 | 0.028 | 0.443 ** | 0.217 | 0.041 | 3.621 *** |
| lnINN | −0.167 *** | 0.034 | 0.000 | 0.376 *** | 0.064 | 0.000 | 0.311 *** | 0.060 | 0.000 | 0.067 | 0.000 | 0.311 ** | 0.123 | 0.011 | 0.271 ** | 0.120 | 0.024 | −0.167 *** |
| lnTRF | 0.190 *** | 0.057 | 0.001 | 0.355 *** | 0.088 | 0.000 | 0.418 *** | 0.077 | 0.000 | 0.110 | 0.000 | 0.002 * | 0.167 | 0.088 | 0.846 *** | 0.157 | 0.000 | 0.190 *** |
| lnCAP | 0.156 *** | 0.048 | 0.001 | 0.372 *** | 0.071 | 0.000 | 0.339 *** | 0.081 | 0.000 | 0.093 | 0.017 | 0.046 ** | 0.137 | 0.040 | 0.548 *** | 0.164 | 0.001 | 0.156 *** |
| lnPRA | −0.059 | 0.065 | 0.362 | −0.285 *** | 0.066 | 0.000 | −0.116 * | 0.068 | 0.085 | 0.126 | 0.124 | −0.290 ** | 0.123 | 0.018 | −0.292 ** | 0.130 | 0.024 | −0.059 |
| URB | −0.001 | 0.003 | 0.761 | −0.013 *** | 0.005 | 0.010 | −0.003 ** | 0.005 | 0.039 | 0.005 | 0.029 | 0.065 *** | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.018 ** | 0.009 | 0.048 | −0.001 |
| lnINT | 0.009 | 0.053 | 0.867 | 0.120 | 0.131 | 0.361 | 0.092 | 0.075 | 0.223 | 0.101 | 0.077 | 0.700 *** | 0.252 | 0.005 | 0.497 *** | 0.149 | 0.001 | 0.009 |
| R2 | 0.746 | 0.975 | 0.986 | 0.694 | 0.646 | 0.714 | ||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Wang, E.; Gao, X.; Hu, Y. Evolution of the Urban Network in the Yellow River Basin: A Corporate Network Perspective. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9110465
Chen X, Wang E, Gao X, Hu Y. Evolution of the Urban Network in the Yellow River Basin: A Corporate Network Perspective. Urban Science. 2025; 9(11):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9110465
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaofei, Enru Wang, Xiaoling Gao, and Yonggui Hu. 2025. "Evolution of the Urban Network in the Yellow River Basin: A Corporate Network Perspective" Urban Science 9, no. 11: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9110465
APA StyleChen, X., Wang, E., Gao, X., & Hu, Y. (2025). Evolution of the Urban Network in the Yellow River Basin: A Corporate Network Perspective. Urban Science, 9(11), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9110465








