Collaborative Changes between Soil Fauna and Urbanization Gradients in Guangzhou’s Remnant Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
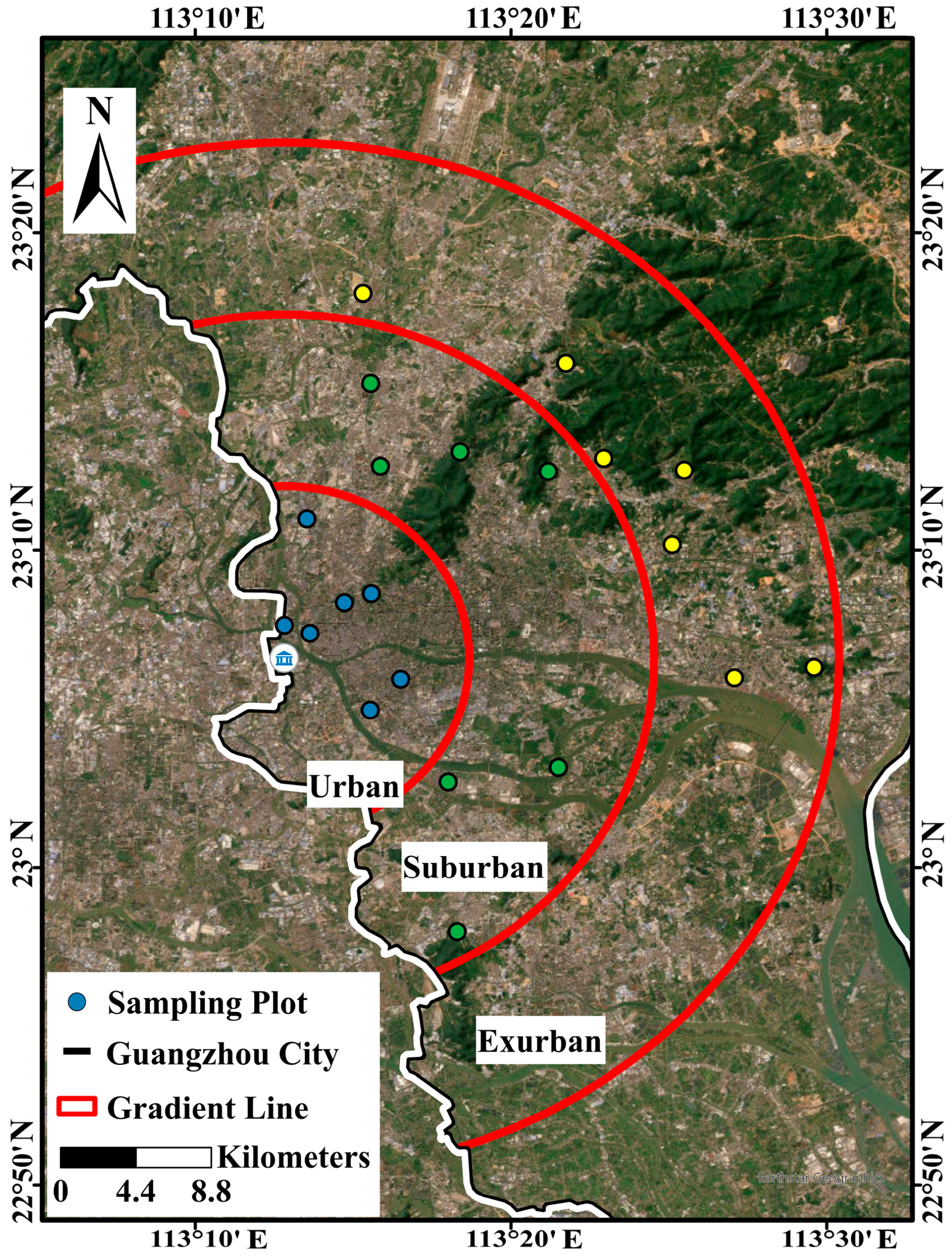
2.1. Study Area and Site Selection
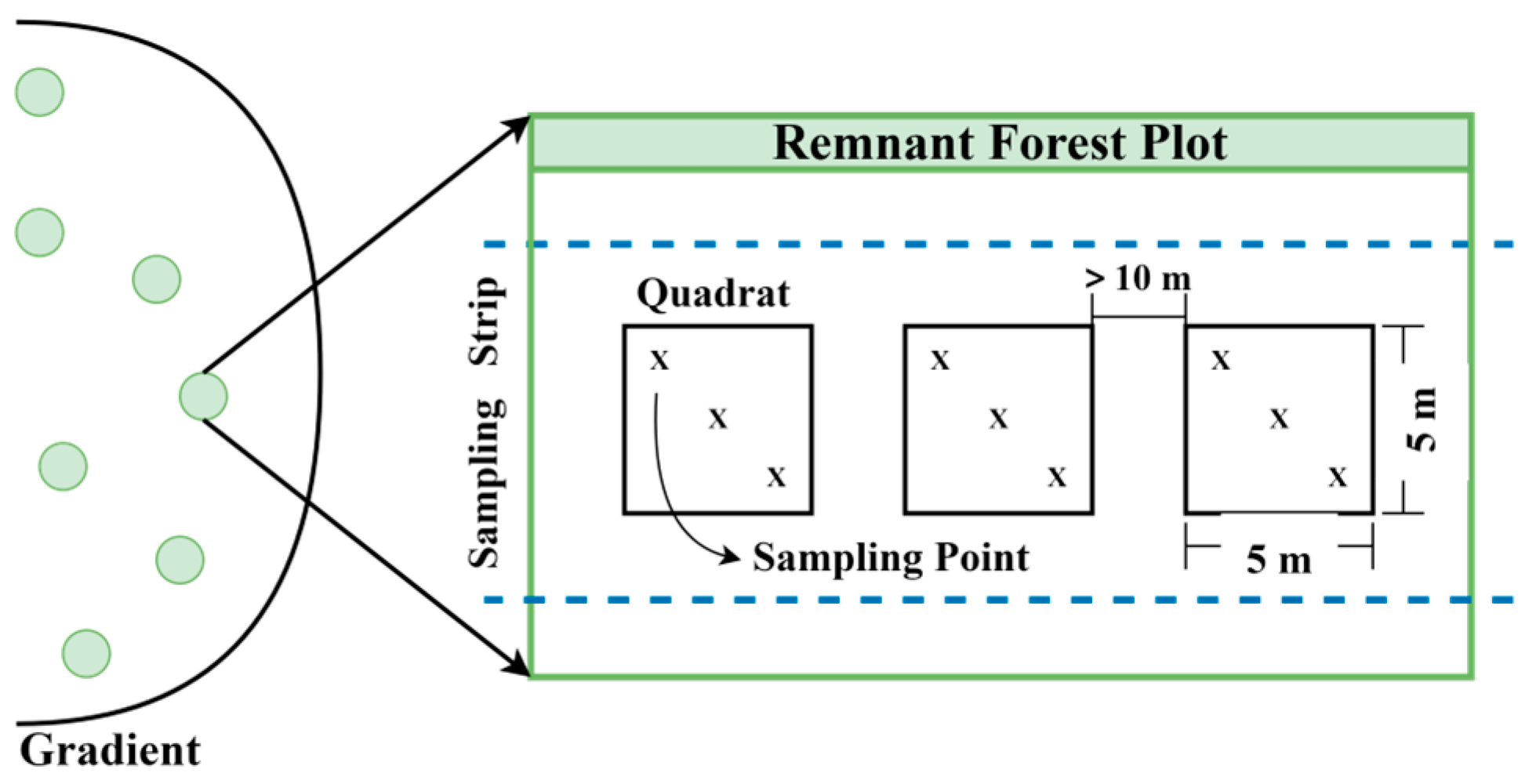
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Indicators and Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Measurement of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3.2. Soil Fauna Sampling and Identification
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
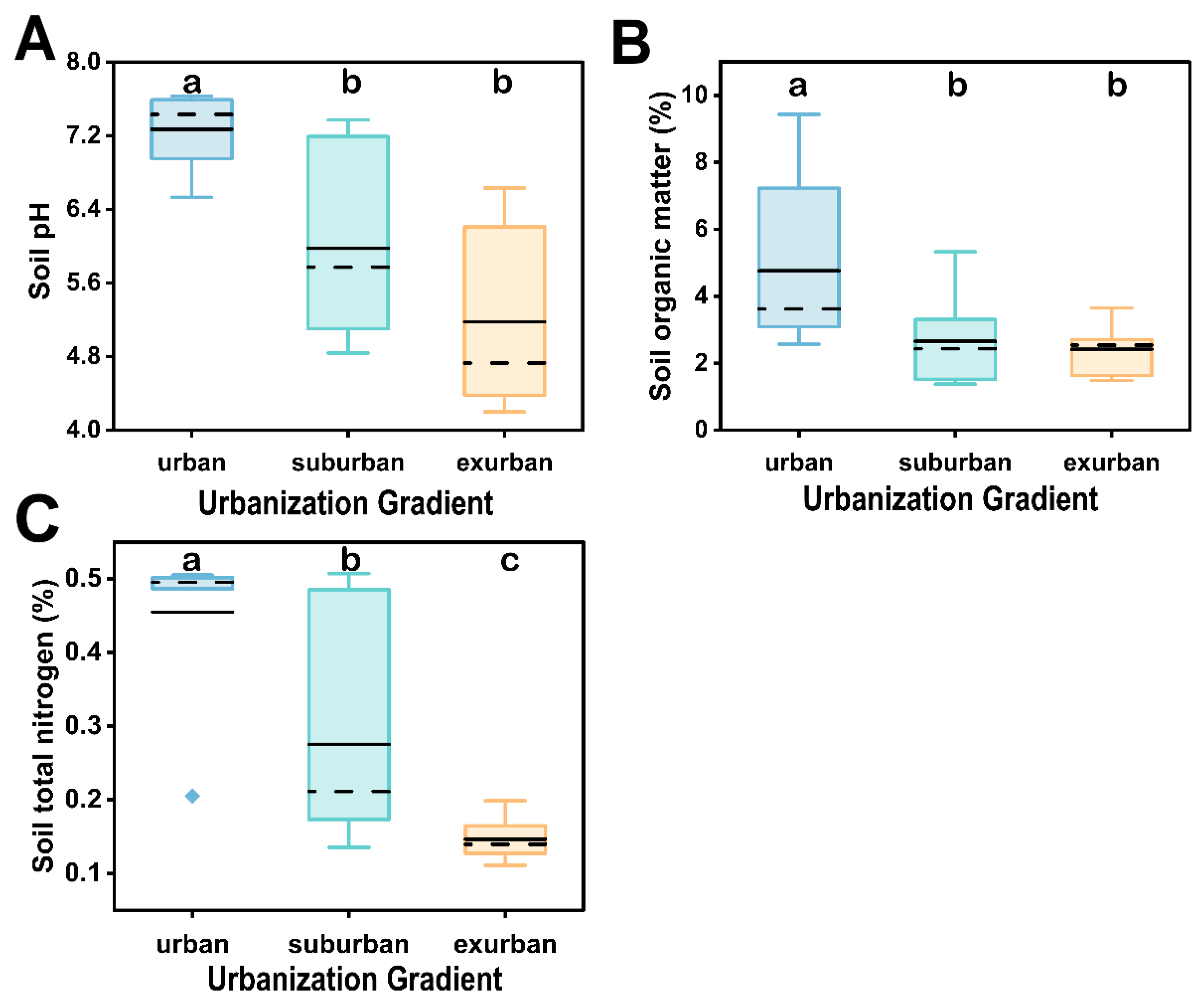
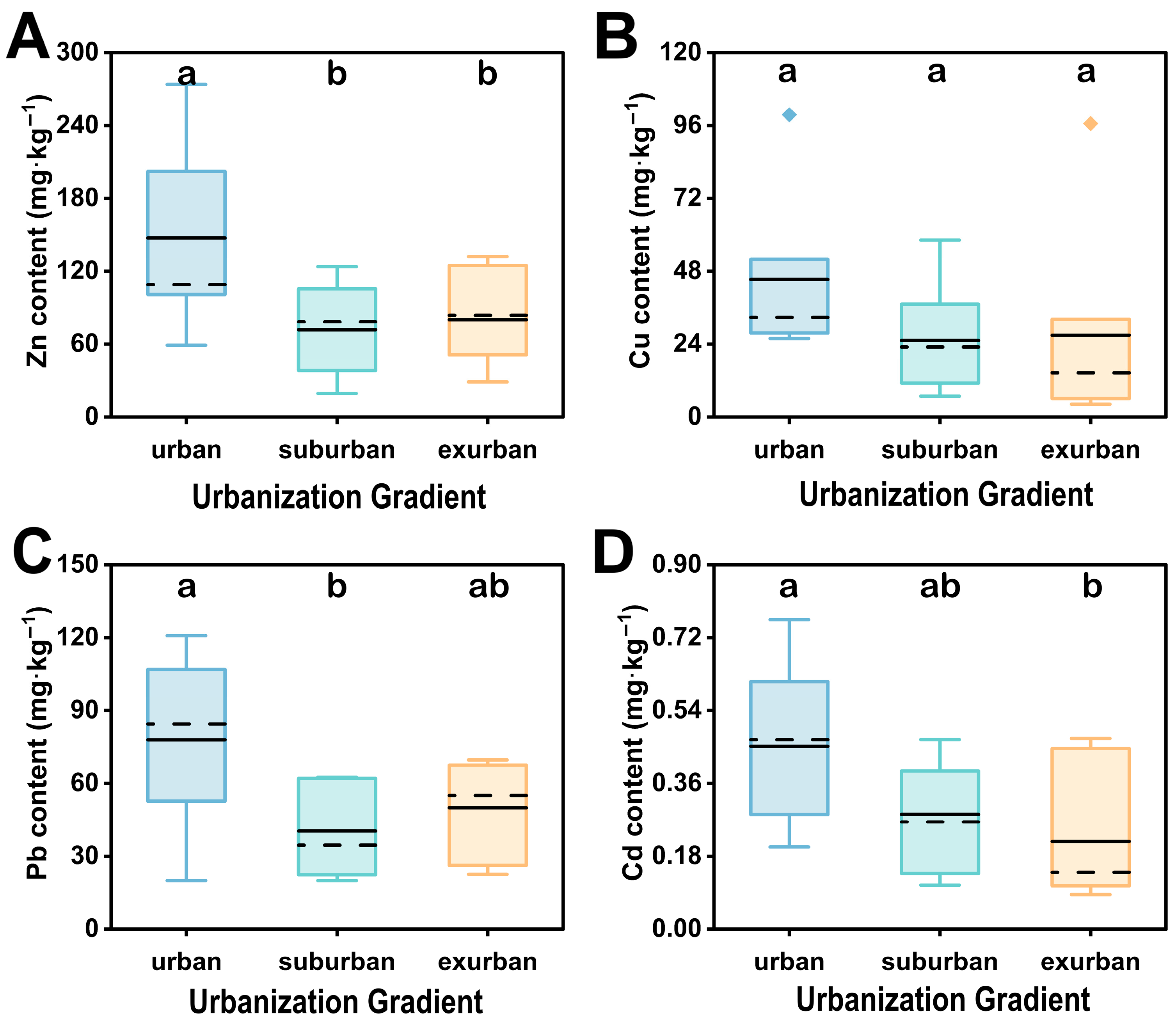
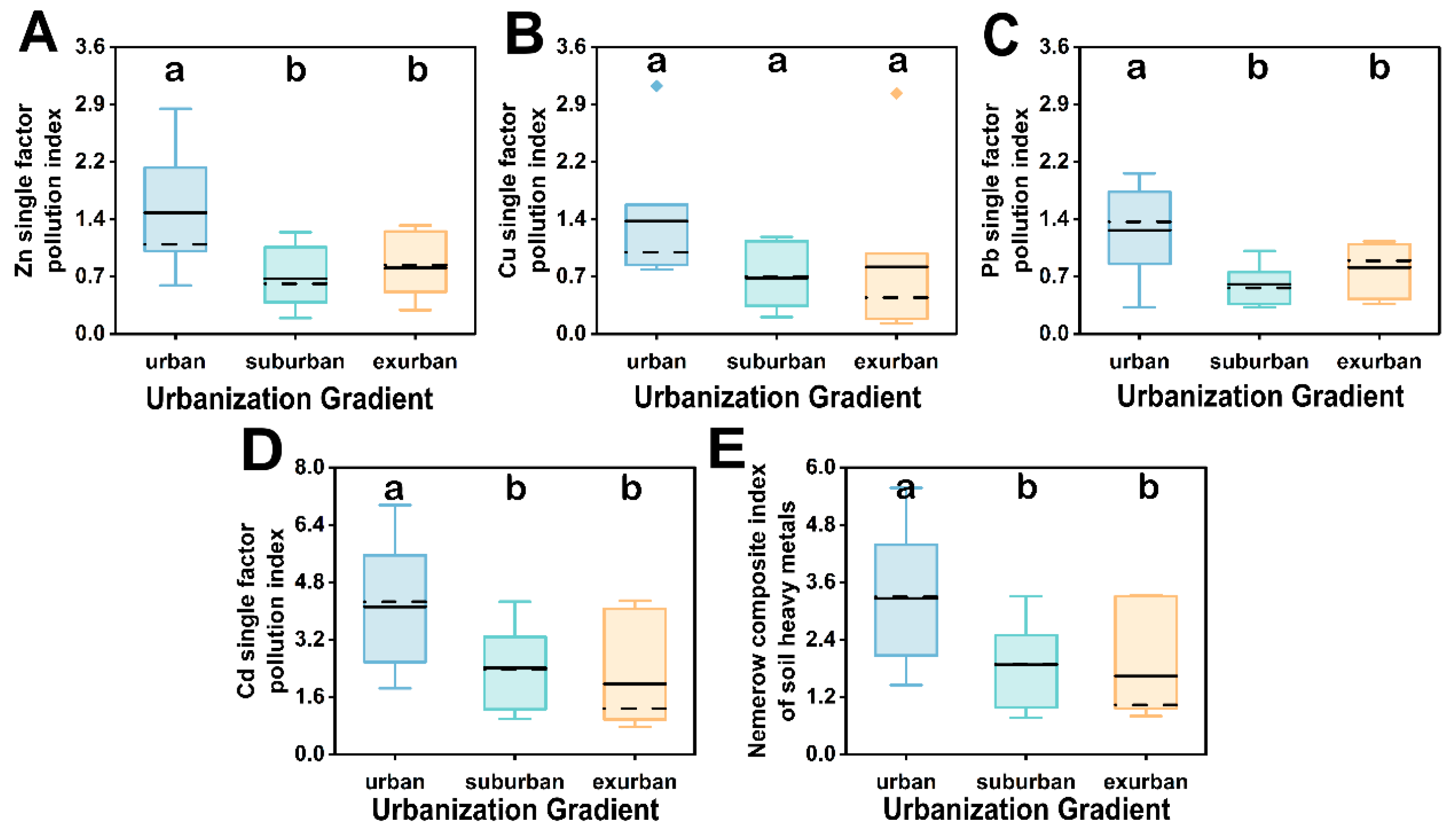
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Characteristics of Remnant Forests along Urbanization Gradient in Guangzhou
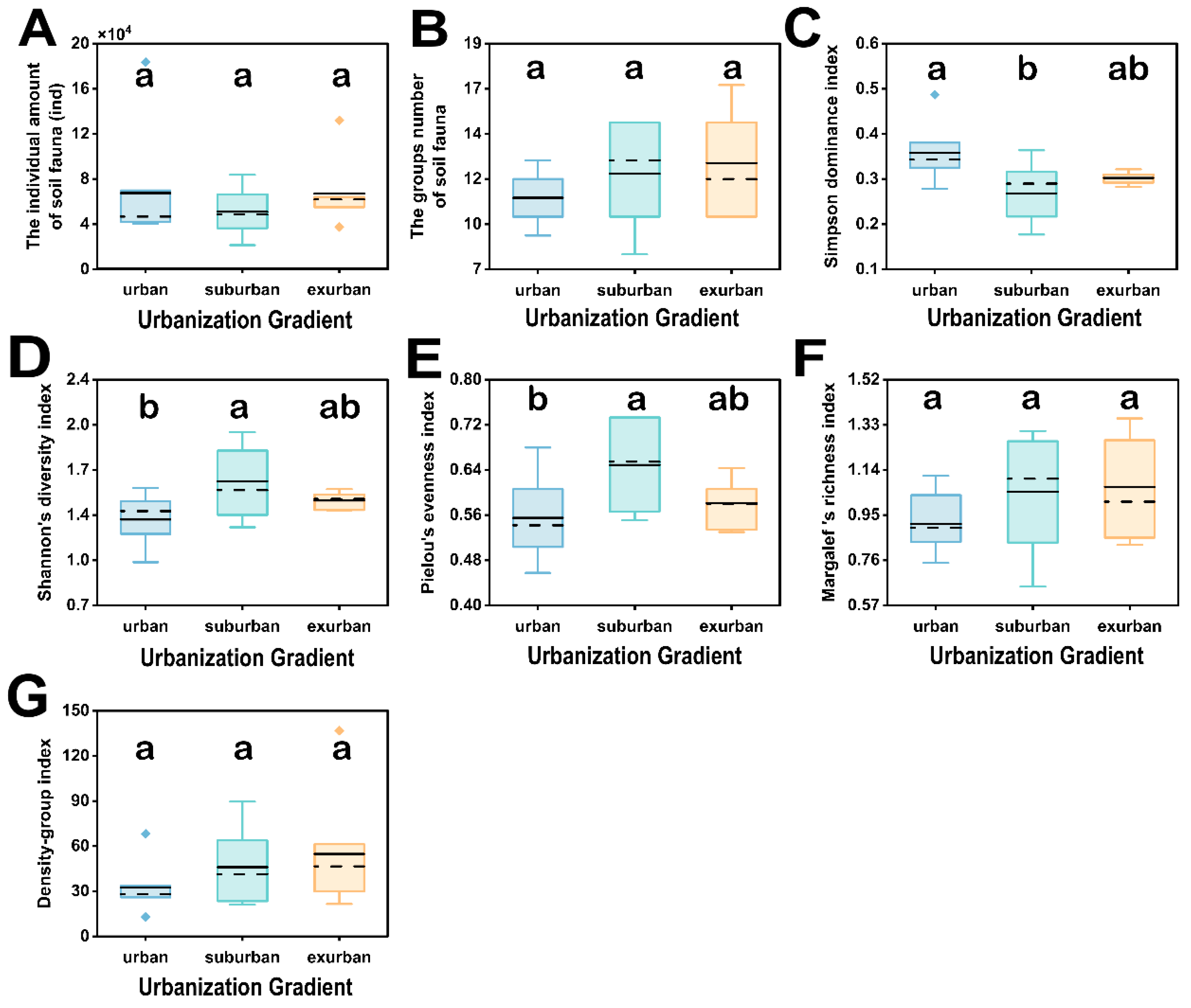
3.2. Soil Fauna Biodiversity of Remnant Forests along Urbanization Gradient in Guangzhou
3.2.1. Composition of Soil Fauna Community
3.2.2. Diversity of Soil Fauna
3.3. The Relationship between Soil Fauna Biodiversity and Environmental Factors in Remnant Forests along Urbanization Gradient in Guangzhou
3.3.1. The Correlation Analysis between Soil Fauna Community Diversity Indices and Various Environmental Factors
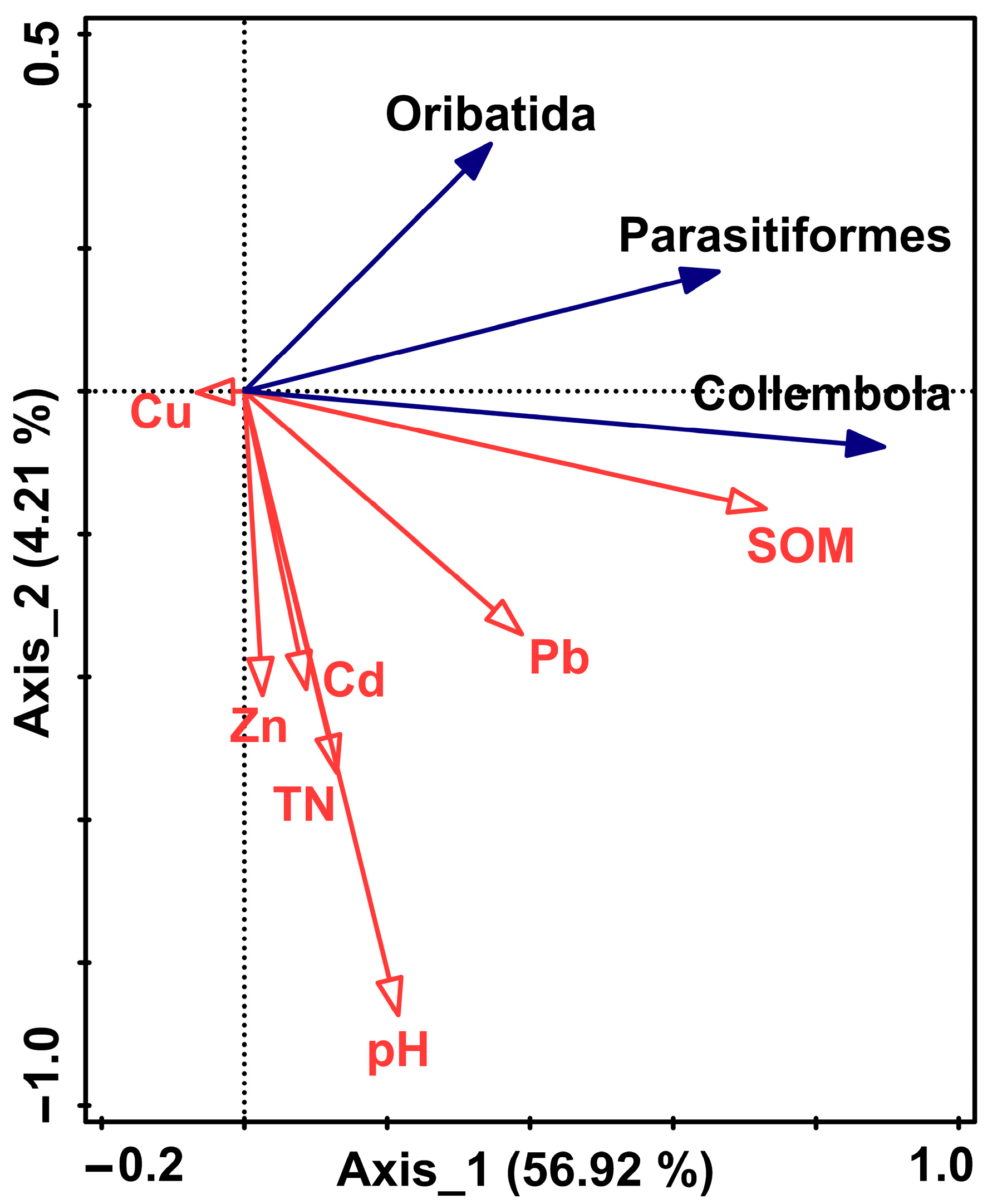
3.3.2. The Redundancy Analysis between the Dominant Soil Fauna Groups in Remnant Forests and Various Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Soil Fauna Community Diversity in Remnant Evergreen Broad-Leaved Forests along Urbanization Gradient
4.2. Analysis of the Mechanism of Soil Fauna Community Changes in Remnant Evergreen Broad-Leaved Forests along Urbanization Gradient
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Gradient | Urban | Suburban | Exurban | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator | ||||
| pH | 7.27 ± 0.14 a | 5.98 ± 0.34 b | 5.18 ± 0.34 b | |
| SOM (%) | 4.76 ± 0.89 a | 2.66 ± 0.47 b | 2.42 ± 0.25 b | |
| TN (%) | 0.45 ± 0.04 a | 0.28 ± 0.05 b | 0.15 ± 0.01 c | |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 147.62 ± 25.00 a | 71.81 ± 13.43 b | 80.26 ± 13.40 b | |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 45.33 ± 9.11 a | 25.24 ± 6.16 a | 26.90 ± 11.29 a | |
| Pb (mg/kg) | 78.04 ± 12.51 a | 40.38 ± 6.06 b | 50.01 ± 6.53 ab | |
| Cd (mg/kg) | 0.45 ± 0.07a | 0.28 ± 0.05 ab | 0.22 ± 0.06 b | |
| P(Zn) | 1.52 ± 0.27 a | 0.70 ± 0.14 b | 0.83 ± 0.14 b | |
| P(Cu) | 1.42 ± 0.28 a | 0.70 ± 0.13 a | 0.84 ± 0.35 a | |
| P(Pb) | 1.30 ± 0.21 a | 0.62 ± 0.08 b | 0.83 ± 0.11 b | |
| P(Cd) | 4.11 ± 0.61 a | 2.41 ± 0.39 b | 1.97 ± 0.53 b | |
| Nemerow index | 3.26 ± 0.49 a | 1.88 ± 0.30 b | 1.64 ± 0.40 b | |
| N | 67,617 ± 18,247 a | 51,125 ± 7034 a | 67,107 ± 10,515 a | |
| S | 11.00 ± 0.49 a | 12.29 ± 0.94 a | 12.86 ± 0.91 a | |
| C | 0.36 ± 0.02 a | 0.27 ± 0.02 b | 0.30 ± 0.00 ab | |
| H’ | 1.33 ± 0.06 b | 1.61 ± 0.09 a | 1.47 ± 0.02 ab | |
| J | 0.56 ± 0.03 b | 0.65 ± 0.03 a | 0.58 ± 0.01 ab | |
| D | 0.91 ± 0.04 a | 1.05 ± 0.09 a | 1.07 ± 0.07 a | |
| DG | 32.61 ± 5.97 a | 46.04 ± 8.41 a | 54.80 ± 13.44 a | |
References
- Research Group of the Market Economy Research Institute, Development Research Center of the State Council. New Technological Revolution and China’s Urbanization 2020–2050: Impact, Prospect and Strategy. J. Manag. World 2022, 38, 12–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Lu, D.; Zhang, H. Comprehensive Evaluation and the Driving Factors of China’s Urbanization. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 387–398. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, G. (Eds.) Economic Development Overview. In National Economic and Social Development Statistical Bulletin of the People’s Republic of China 2021; Yearbook Publishing House of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 428–440. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. China’s Urbanization and Carbon Emissions; Social Sciences Academic Press: Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H. The spatial characteristics of beautiful China should be distinctive. China Economic Times, 26 April 2013; p. 005. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, L.; Xu, G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Yu, S.; Chen, X.; Peng, B.; Squartini, A.; Zanella, A. Threshold reaction of soil arthropods to simulative nitrogen deposition in urban green spaces. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 711774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Zanella, A.; Chen, X.; Peng, B.; Lin, J.; Su, J.; Luo, X.; Xu, G.; Squartini, A. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on the bacterial community of urban green spaces. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, R.M.; da Silva, A.L.; Ribeiro, A.I.; Gomes, R.C.; Sperandio, F.C.; Nunes, A.N. Evaluating the Environmental Quality of Forest Remnants Using Landscape Metrics. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fujihara, M.; Li, B.; Yuan, X.; Hara, K.; Da, L.; Tomita, M.; Zhao, Y. Structure and diversity of remnant natural evergreen broad-leaved forests at three sites affected by urbanization in Chongqing metropolis, Southwest China. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 10, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, X.; Feng, S.; Yao, T.; Liang, Q.; Fu, J. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil C, N and P in subtropical forests along an urban to suburban gradient. Chin. J. Ecol. 2016, 35, 591–596. [Google Scholar]
- Magiera, T.; Strzyszcz, Z.; Rachwal, M. Mapping particulate pollution loads using soil magnetometry in urban forests in the Upper Silesia Industrial Region, Poland. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 248, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Gilliam, F.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Mo, J. Changes in soil carbon sequestration in Pinus massoniana forests along an urban-to-rural gradient of southern China recommended citation. Biogeosciences Discuss. 2013, 10, 6609–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Tang, Z.; Tian, D.; Xiang, W.; Sun, W. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of 7 heavy metals in urban forest soils in Changsha City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 7595–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Lu, H. Effects of Urbanization on Soil Community Structure under Subtropical Evergreen Broad-leaved Forests. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 24, 938–946. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Wen, Y.; Cai, S.; Luo, X. Review for the effects of urban topsoil on the ecological health. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 2941–2956. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, D.D.; Magura, T.; Horváth, R.; Debnár, Z.; Tóthmérész, B. Arthropod assemblages and functional responses along an urbanization gradient: A trait-based multi-taxa approach. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 30, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wu, Z.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Lin, M.; Fang, X.; Lin, Y. Inconsistent Patterns of Soil Fauna Biodiversity and Soil Physicochemical Characteristic Along an Urbanization Gradient. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 9, 824004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, Q.; Huang, T.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, S. Distribution Patterns of Soil Fauna in Different Forest Habitat Types of North Hebei Mountains, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Zheng, J.; Wan, J. Spatiotemporal evolution of forest landscape pattern in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area based on “Spatial Morphology-Fragmentation-Aggregation”. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 3032–3044. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y. (Ed.) Economic and Social Statistical Data. In Statistical Bulletin of the National Economic and Social Development of Guangzhou 2021; Guangzhou Yearbook Publishing House: Guangzhou, China, 2022; pp. 512–516. [Google Scholar]
- Guangzhou (Nansha) Vision and Strategy in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Era. Social Sciences in China, 11 June 2018; p. 008.
- Zhang, J.; Jing, S. The Practice and Experience of Constructing Ecological Culture in Guangzhou Since 1978. Urban Insight 2018, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- DB 44/T 1415-2014; Risk Screening Values for Soil Heavy Metal the Pearl River Delta Area. Administration of Quality and Technology Supervision of Guangdong Province: Guangzhou, China, 2014.
- Song, H.; Wu, K.; Liu, P. Research progress on evaluation methods of soil heavy metal pollution. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2017, 45, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W. Illustrated Handbook of Soil Animals in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Cui, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y. Relationship between Soil Animal Community Structure and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in Lake Taihu Lakeshore, China. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2013, 49, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 623–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of Diversity. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 1997, 11, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Li, J. Re-evaluating the character and application of density-group index (DG). Biodivers. Sci. 2009, 17, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ulanowicz, R.E. Information theory in ecology. Comput. Chem. 2001, 25, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C.J. The Measurement of Diversity in Different Types of Biological Collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovei, G.L.; Horvath, R.; Elek, Z.; Magura, T. Diversity and assemblage filtering in ground-dwelling spiders (Araneae) along an urbanisation gradient in Denmark. Urban Ecosyst. 2019, 22, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, H.; Tuomisto, H. Unearthing the role of biological diversity in soil health. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 85, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y. Distribution Pattern and Influencing Factors of Soil Biodiversity in the Urban-Rural Ecotone of Shanghai. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Gu, W.; Dong, W.; Qiu, L.; Liu, Y.; Tao, L. The community change and diversity of soil fauna after artificial vegetation restoration in highway slope. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 4295–4305. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Wu, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L. Plant’s and soil organism’s diversity across a range of Eucalyptus grandis plantation ages. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 3947–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, H.; Peng, C.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, F. Effect of Long-Term Cultivation and Fertilization on Community Diversity of Cropland Soil Animals. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2010, 43, 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Braaker, S.; Ghazoul, J.; Obrist, M.K.; Moretti, M. Habitat connectivity shapes urban arthropod communities: The key role of green roofs. Ecology 2014, 95, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ke, X. Analysis of the ecological function of forest greening transformation in Yuexiu Park. Guangdong Landsc. Archit. 2003, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B. Development and Countermeasures of Vegetation Landscape in Baiyun Mountain Scenic Spot, Guangzhou. Mod. Landsc. Archit. 2008, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X. Plant community investigation and landscape optimization research in Yuexiu Park, Guangzhou. Rural Sci. Technol. 2019, 76–77. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Deng, C.X.; Luo, C.L.; Luo, Z.W.; Shen, J.L.; Xie, W.F. Characteristics of soil animal community with different garden plants and various planting periods in Wenjiang District, Chengdu, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 3859–3868. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes-Oliveira, V.B.; Bianchi, M.O.; Espíndola, E.L.G. Changes in soil mesofauna structure due to different land use systems in south Minas Gerais, Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Wei, L.; Yin, X. Soil animals and their response to soil pollution in Kaifeng City. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2007, 44, 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, T. Study on the Structural Characteristics of Soil Fauna Community and Its Correlation with Heavy Metal Pollution in Heavy Metal Polluted Areas: A Case Study of Shanxi Linfen Iron and Steel Co., Ltd. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi Normal University, Xi’an, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Angon, P.B.; Islam, M.S.; Kc, S.; Das, A.; Anjum, N.; Poudel, A.; Suchi, S.A. Sources, effects and present perspectives of heavy metals contamination: Soil, plants and human food chain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crommentuijn, T.; Doodeman, C.; Vanderpol, J.; Doornekamp, A.; Rademaker, M.; Vangestel, C. Sublethal Sensitivity Index as an Ecotoxicity Parameter Measuring Energy Allocation under Toxicant Stress: Application to Cadmium in Soil Arthropods. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1995, 31, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xiang, C.; Liu, Z. Effect of Heavy Metal Pollution on Soil Animals. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2008, 24, 454–457. [Google Scholar]
- Austruy, A.; Laplanche, C.; Mombo, S.; Dumat, C.; Deola, F.; Gers, C. Ecological changes in historically polluted soils: Metal (loid) bioaccumulation in microarthropods and their impact on community structure. Geoderma 2016, 271, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, L. Interrelationships between soil fauna and soil environmental factors in China: Research advance. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 21, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar]

| Grade | Pi | Pollution Assessment | Ni | Pollution Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pi ≤ 1.0 | No pollution | Ni ≤ 0.7 | No pollution |
| 2 | 1.0 < Pi ≤ 2.0 | Slightly pollution | 0.7 < Ni ≤ 1.0 | Slightly pollution |
| 3 | 2.0 < Pi ≤ 3.0 | Lightly pollution | 1.0 < Ni ≤ 2.0 | Lightly pollution |
| 4 | 3.0 < Pi ≤ 5.0 | Moderately pollution | 2.0 < Ni ≤ 3.0 | Moderately pollution |
| 5 | Pi > 5.0 | Seriously pollution | Ni > 3.0 | Seriously pollution |
| Soil Fauna Group | Urban | Suburban | Exurban | Sum by Group | Proportion (%) | Abundance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collembola | 236,824 | 121,978 | 167,727 | 526,529 | 40.47 | +++ |
| Oribatida | 121,212 | 103,388 | 160,937 | 385,537 | 29.64 | +++ |
| Parasiformes | 69,265 | 68,246 | 86,920 | 224,431 | 17.25 | +++ |
| Diptera larvae | 12,563 | 7046 | 10,865 | 30,474 | 2.34 | ++ |
| Diplopoda | 11,544 | 12,987 | 8997 | 33,528 | 2.58 | ++ |
| Microdrile oligochaetes | 8828 | 13,242 | 4245 | 26,315 | 2.02 | ++ |
| Symphyla | 1699 | 8489 | 6282 | 16,470 | 1.27 | ++ |
| Isopoda | 2718 | 6366 | 2208 | 11,292 | 0.87 | + |
| Diplura | 1869 | 4159 | 5264 | 11,292 | 0.87 | + |
| Scolopendromorpha | 1699 | 1529 | 510 | 3738 | 0.29 | + |
| Pauropoda | 1020 | 2209 | 3057 | 6286 | 0.48 | + |
| Araneae | 1019 | 850 | 1190 | 3059 | 0.24 | + |
| Protura | 850 | 2463 | 5942 | 9255 | 0.71 | + |
| Acariformes | 340 | 340 | 1020 | 1700 | 0.13 | + |
| Uropygi | 170 | 679 | 510 | 1359 | 0.10 | + |
| Thysanoptera | 0 | 2546 | 340 | 2886 | 0.22 | + |
| Coleoptera larvae | 0 | 340 | 1528 | 1868 | 0.14 | + |
| Coleoptera adult | 1699 | 1019 | 2208 | 4926 | 0.38 | + |
| Sum by gradient | 473,319 | 357,876 | 469,750 |
| N | S | C | H’ | J | D | DG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | −0.12 | −0.22 | 0.32 | −0.19 | −0.14 | −0.16 | −0.42 |
| SOM | 0.57 ** | −0.00 | 0.27 | −0.25 | −0.31 | −0.08 | 0.09 |
| TN | 0.07 | −0.38 | 0.34 | −0.31 | −0.12 | −0.40 | −0.29 |
| Zn | −0.12 | −0.25 | 0.38 | −0.38 | −0.33 | −0.22 | −0.39 |
| Cu | −0.03 | −0.06 | 0.24 | −0.25 | −0.24 | −0.06 | −0.15 |
| Pb | 0.17 | −0.27 | 0.51 * | −0.54 * | −0.50 * | −0.29 | −0.31 |
| Cd | −0.08 | −0.17 | 0.33 | −0.28 | −0.25 | −0.14 | −0.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Yu, S.; Xu, G.; Ling, Y.; Mo, L.; Chen, Y.; Wan, H. Collaborative Changes between Soil Fauna and Urbanization Gradients in Guangzhou’s Remnant Forests. Urban Sci. 2024, 8, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8030122
Wu Z, Yu S, Xu G, Ling Y, Mo L, Chen Y, Wan H. Collaborative Changes between Soil Fauna and Urbanization Gradients in Guangzhou’s Remnant Forests. Urban Science. 2024; 8(3):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8030122
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhijian, Shiqin Yu, Guoliang Xu, Yunan Ling, Lingzi Mo, Yuying Chen, and Hongfu Wan. 2024. "Collaborative Changes between Soil Fauna and Urbanization Gradients in Guangzhou’s Remnant Forests" Urban Science 8, no. 3: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8030122
APA StyleWu, Z., Yu, S., Xu, G., Ling, Y., Mo, L., Chen, Y., & Wan, H. (2024). Collaborative Changes between Soil Fauna and Urbanization Gradients in Guangzhou’s Remnant Forests. Urban Science, 8(3), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8030122







