Abstract
In recent decades, manufacturing industries in Europe have undergone a deep transformation due to global market competition, automation, and adaptation to globalized production patterns. The impact of deindustrialization and regional restructuring has been particularly strong on regions outside of metropolitan areas, which may be locked in their specific development path and cannot benefit from agglomeration effects. However, scholars are increasingly shifting their attention to processes of regional renewal, emphasizing the strengths and potentials of such regions. Such potentials holds the concept of Industrial Culture which is defined as a particular cultural setting made up of certain intangible assets, such as skills, attitudes, traditions, tangible monuments, and artefacts. Based on the case study of the district of Zwickau, the authors identify three dimensions of Industrial Culture. These cultural, social, and economic aspects can be underscored by different—albeit often overlapping—actions, opening up new development options for the region if embedded in a broad network of regional actors. Industrial Culture can thus be perceived as a strategic concept to form a coherent approach of regional development by integrating various existing activities in a region.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, manufacturing industries in Europe have undergone a deep transformation due to global market competition, automation, and adaptation to globalized production patterns. This development indicates a deeper shift from industrial societies towards service and knowledge societies where production is no longer the main driver of economic development, but consumption [1,2]. At the same time, the collapse of communism opened state-led economies to competitive markets, resulting in specific challenges and problems of transition in the affected countries. Hence, (old) industrial towns in Central Europe have witnessed the worsening of the already existing trends of job losses in the manufacturing sector, triggering manifold social problems such as unemployment, outmigration, and the loss of social functions which are well documented in the academic literature [3,4].
The impact of deindustrialization on regions outside of metropolitan areas, which cannot benefit from agglomeration effects, has been particularly strong [5,6]. These regions have been in the focus of many studies in economic geography, including an analysis of regional restructuring in the 1980s [4], studies on path dependency and regional lock-in [7,8], and more recently, path interdependence and path creation [9,10]. This latter shift to regional renewal goes hand in hand with an increasing call for place-sensitive regional development emphasizing the strengths and potentials of a region instead of focusing too much on the limitations of path dependency [11,12]. At the same time, regional development is increasingly understood as a holistic concept comprising not only an economic but also social, political, and cultural dimensions [13,14].
Interests in developing place-sensitive development strategies and a more holistic understanding of the evolution of (old) industrial regions suggest that the notion of “Industrial Culture” demands further investigation, as it holds some keys to understanding development processes and unlocking the endogenous potential for the future development of (old) industrial regions. In such places, the long economic predominance of industrial production has brought about a particular cultural setting made up of certain intangible assets, such as skills, attitudes, traditions, tangible monuments, and artefacts [15]. Hence, the concept ties up to a holistic understanding of development, emphasizing in particular the role of a specific regional culture as an “anchor” in both social and economic terms [16].
The concept of Industrial Culture is inseparable from the logic of path renewal or diversification advocated by evolutionary economic geographers. Hence, in this paper we will scrutinize its potential to contribute to this strand in current economic geography. This contribution aims at a more comprehensive theoretical grounding of the term Industrial Culture in current regional development discourses and highlights practical fields of action and their relevance to regional development challenges faced by (old) industrial regions.
To do so, the next section highlights the cultural factors in processes of regional restructuring, specifically in concepts such as path dependency and path renewal. Section 3 focuses on the notion of Industrial Culture and the multiple dimensions it encompasses, while Section 4 presents the case study of the district of Zwickau in Saxony. This study has derived from accompanying research of the Central Europe INTERREG V B project InduCult2.0 (www.inducult.eu) funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF). Both authors worked along with eight participating regions during the project run-time (2016–2019). The findings of this study result from participatory observation during the project lifetime, as well as intense analysis of project and other related documents issued by the District of Zwickau. The example illustrates the theoretical analysis outlined in the previous sections and is followed by a discussion of the case study along the main questions of this paper. The conclusions reflect upon the character of Industrial Culture as tool for regional development and the contribution of the concept to existing development theories.
2. A Cultural Understanding of Regional Restructuring
Since the 1970s, the transformation from an industrial to a service-oriented economy and related regional restructuring processes have been widely researched in economic geography [17]. In these studies, “regional restructuring” has been used as “a label for the complex processes of economic, social, and political transformation in a region, caused by a shift in regimes of capital accumulation and spatial division of labour” [17] (p. 71). Beside these global changes in the economic order leading to deindustrialization, job losses, and decline in old industrial regions, scholars have also emphasized the cultural aspects of restructuring. In his works on industrial districts, Alfred Marshall already emphasized in the early 20th century the importance of industrial atmosphere, acknowledging that industry affects both the physical and the social space, their structure and history [18]. Hudson (1992) then argued that a thick institutional tissue and a specific regional culture of both economic and social dependency has been hindering change and a re-positioning of these regions in a capitalist globalized world [4]. Thus, culture in a broader sociological sense seems to be a decisive, albeit still under-researched, factor when it comes to regional restructuring and development [19].
Recent institutional, relational, and evolutionary approaches have indeed acknowledged that history—and with it, culture—matters for a region’s development [20]. Nevertheless, many influential studies on path dependency and lock-in have painted a diverging picture on the notion of regional culture either as a restraining or as an enabling factor in regional development. For example, in his contribution on the development of the Ruhr area Grabher defined three types of lock-in hindering change in a region [7]: besides the functional and the political lock-in, he also identified a cognitive lock-in resulting from a specific regional culture and industrial atmosphere, which expresses itself in “a common language regarding technical matters, contracting rules, and knowledge [leading to] social processes such as ‘groupthink’” ([7], p. 262). These different forms of lock-in result in a low adaptability of the region as a whole as well as a highly path-dependent development. Yet, the potential that the specific cultural setting of a region may present for regional renewal has not been evaluated in this study.
On the other hand, Hassink [8] and Martin and Sunley [10] emphasize the high relevance of institutional contexts, social capital, and cultural traditions for a region’s path dependence, along other sources of path dependence such as natural resources, sunk costs of local assets and infrastructures, local economic interrelatedness, regional technological “lock-in”, economies of agglomeration, and interregional linkages and interdependencies [10]. For instance, Hassink explicitly highlights culture-based elements such as social capital and trust as important regional assets, while the latter authors go a step further in suggesting the concept of “path interdependence”, emphasizing the “co-evolution of different ‘arenas’—such as the economic, technological, institutional and socio-cultural” [10] (p. 413). With this, they tie up to a holistic, multi-dimensional understanding of regional development acknowledging the interrelations between economic, social, political, and cultural spheres. Thereby, the authors imply a culturally embedded understanding of regional development [21]. To stimulate a new indigenous path of development, the authors acknowledge the importance of learning and education, as well as the “ability of regions to retain skilled and educated labour” [10] (p.420). To maintain this ability, it seems crucial that regions can keep their residents also in times of recession. Soft factors such as culture or a creative scene may be beneficial for this. The latter may also contribute to the “heterogeneity among agents, technologies, institutions and social networks” [10] (p.421) which has been identified as second source of new path creation. The ability of learning (being a cultural competence as such) is also decisive for the “absorptive capacity” of a region for transplanted knowledge from outside (which is the third source of path creation described by Martin and Sunley). In sum, the features they present induce the importance of cultural factors in regional renewal and path creation, without being fully able to address them, among other (obviously much better understood) factors. An interesting contribution from economic geography in this regard is the work by Boschma [22], highlighting different dimensions of proximity for innovation. The named proximities are cognitive, organizational, social, institutional, and geographical, of which at least four are culture-related—if not all, if we see geography as a socio-cultural construct. The contribution further argues for an open understanding of how these different factors might lead to a negative or positive impact on regional development (i.e., lock-in or new path creation). Overall, economic geography should be aware of the potentials which cultural factors may inhere in this regard [9].
This is even more relevant as cultural and creative industries are increasingly considered to be drivers of economic growth [23]. Culture is no longer a separate field, but “folded together with economics” [24] (p. 147). Some scholars like Florida [25] see “the people climate” (i.e., culture) as a panacea for regional restructuring. However, other studies [24] portray industry and culture as competing features of controversial discourses inducing local struggles about a region’s future development paths. Thus, the role of culture and its relation to other aspects of regional development vary depending on the context and should be subject to further research.
Noteworthy for our line of argument is a Special Issue of European Planning Studies published in 2011 that deals with the interdependence of regional and corporate cultures and highlights regional culture as a decisive element of regional development. Clifton, Gärtner, and Rehfeld (2011) argued in their editorial that there is a need for individual paths of regional development, where regional culture has an anchoring role “embedding firms in the regional economy” [16] (p. 1858). In contrast to Grabher (1993), they argued that “specific cultural frames have the potential to give overall orientation and guide regional actions” [16] (p. 1862). Regional culture is thus seen as a resource which could be mobilized for regional renewal instead of constraining it. This assumption is also increasingly forwarded by concepts such as clusters, learning regions, or regional innovation systems [26]. In their understanding of culture, Clifton et al. [16] follow DiMaggio [27] and define it as a collective experience comprising “shared cognitions, values, norms and expressive symbols” [16] (p. 1858), while at the same time integrating tensions and conflict. The interdependence of regional and corporate cultures depends on the degree of firms’ embeddedness in their regional context, also referred to as “productive chorality” [28]. This interdependence and the various forms of interaction between different cultural settings can set in motion a “virtuous circle”, which triggers the co-evolution of regional and corporate change competences, ultimately leading to regional renewal [29]. In these cases, the shared frame of reference fuels trust between the different actors, which is a “precondition for effective knowledge exchange, cooperation and collective learning” [3] (p.1910) and ultimately change.
Thereby, culture is here seen as crucial for the formation and reformation of a region’s identity (see also [19]). It is understood as a dynamic, interactive, multidimensional, and fluid concept which Cooke and Rehfeld [3] grasp by deploying several cultural frames (ethnic, landscape, political, labor and business frames). These frames shape in various ways a region’s self-understanding as well its perception from the outside, and influence regional evolution quite significantly.
With the concept of Industrial Culture, which we see as a specific cultural setting prevalent in (old) industrial regions, we tie up to these studies and add our perspective on the potential of culture for a region’s development.
3. Industrial Culture and Regional Development
3.1. Conceptualizing Industrial Culture
Recent research has introduced the term of Industrial Culture in the context of regional development of industrial regions [15] and additional publications have highlighted the development potentials of the term, especially in the context of smaller industrial towns [19]. Here, Industrial Culture is defined as a transdisciplinary, holistic societal concept, similar to the definition of culture forwarded by Clifton, Gärtner, and Rehfeld [16]. It is seen as a special, place-bound cultural setting based on the concentration of specific expertise, attitudes, values, and traditions. Industrial Culture is grounded in the specific institutionalized routines of industrial structures, their incorporated conventions, beliefs, and production patterns, and the interlinked social factors beyond the factory itself. It builds on tangible and intangible elements originating from the sphere of industrial production in the past, present, and future (Figure 1). In this sense Industrial Culture connects both to an anthropological viewpoint as the culture of distinctive social groups which relate themselves to industry and industrialization (e.g., workers, management, etc.) and to an aesthetic dimension comprising industry-related products and practices of cultural production.
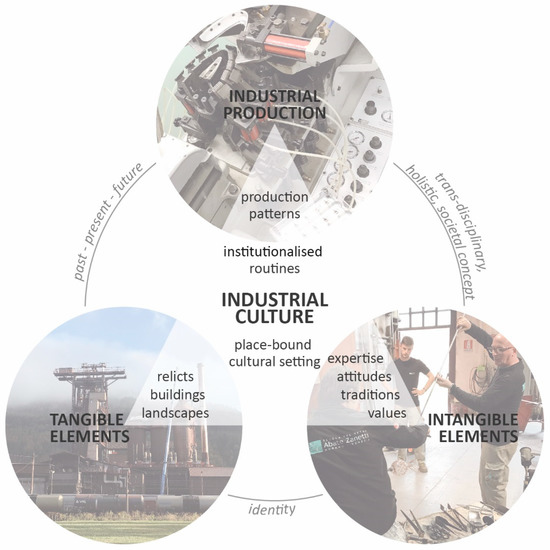
Figure 1.
Concept of Industrial Culture. Source: [19].
By this definition, Industrial Culture goes beyond the classic—mostly aesthetic-oriented—approach, which focuses on industrial heritage and mostly addresses the preservation or reutilization of the tangible remains of industry (i.e., buildings, infrastructures, and landscapes). In this sense, industrial heritage implies a narrower understanding of a specific industry-related culture in its purely material shaping and relates closely to the research linked to “Industrial Archaeology” (for a more detailed discussion of the concept, also related to the term “Industriekultur” used in Germany and to the translations in many other languages in Europe, see [19], p.13). In contrast, Industrial Culture is defined as a set of social characteristics and lifestyles constituted by the link between industrial labor and society, encompassing a range of related academic disciplines [19]. It binds together “influences, contacts and connections which, over time, have settled into each other, moulded each other, produced something new” [30] (p. 183). Thus, it mobilizes specific narratives of the past in order to frame the present and future of (old) industrial towns. Based on this understanding, we consider the intangible, culture-based heritage and presence of industrial production in society being at least equally—maybe even more—important to (old) industrial places than the tangible artefacts.
Industry, culture, and society can be seen as interrelated and coproducing each other. Connecting these three different spheres, the concept of Industrial Culture can serve as a nexus to discuss the economic, social, and cultural effects of the on-going transition towards post-industrial societies [31]. Thereby, it is highly necessary to look deeper into past and current issues of production, work, and related processes, as well as their interconnected context.
Following the evolutionary approaches discussed in Section 2, this paper argues that, on one hand, the industrial past influences the present and future of (old) industrial places and shapes development trajectories. On the other hand, present cultural settings, experiences, and ideas also influence our interpretation of a region’s past. A region’s identity depends upon a specific reading of its history [30]. Thus, Industrial Culture disposes about agentic power which has underlain industrial development, serving as a model for today’s regional actors.
Accordingly, Industrial Culture is understood as a dynamic phenomenon based on social interaction and networking, while being place-bound and locally embedded. It is a concept that emphasizes transformation while connecting to a place’s tradition [30]. As such, the concept has the possibility to serve as a frame for future strategies for (old) industrial regions and especially for small and medium-sized towns, where—on average—the knowledge-intensive service sector is not as developed as in major cities [32]. For these regions, Industrial Culture is a unique opportunity to foster change and connect people to place.
3.2. The Multiple Dimensions of Industrial Culture
Production units and workplaces have strongly influenced (old) industrial communities and have been important (positive) sources of regional identity and major points of reference for their inhabitants—even after they disappeared. As a result of the ongoing structural changes, (old) industrial regions have often faced many challenges, among them a poor outward and inward perception of place, heavily altered and polluted landscapes, social and economic stagnation or decline, loss of general functions, as well as population decline [33,34]. However, these places hold a variety of both tangible and intangible assets that can be utilized to strengthen both their internal and external perception and to break negative stereotypes and latent nostalgic understandings of such places [35].
Culture is considered to be particularly relevant in processes of social change as both an enabling condition and a product of it. Thus, Industrial Culture can be perceived as a reliable and authentic source of identity at the interface of industry, culture and society. It can stimulate the desire to experiment and deal with an (old) industrial region’s specific identity [36,37,38]. The development of this identity is a long-lasting and multilevel process, as Küster [39] describes it for the Ruhr area. Being initially locally bound and based on the working environment of the people, this process was a product of modern location policies and a growing awareness of the historicity of life-worlds. Yet, the mental maps developed became an element of personal identity of the Ruhr area population with strong ties to the local communities and a specific mind-set.
Recent research has discussed Industrial Culture as a valid endogenous potential and a resource (see also the concept of cultural resources of Kebir and Crevoisier 2008 [40]) to tackle at least some development challenges of (old) industrial towns in multiple fields of activity, depending on regional and local framework conditions and opportunities (see the 2018 Special Issue on Industrial Culture in Urban and Regional Development in GeoScape [15]).
Based on the potential of Industrial Culture to address issues of cultural, societal, and economic importance in an integrated way, we highlight here three broad thematic dimensions that could be addressed primarily via regional contexts and echo the concept of cultural frames forwarded by Cooke and Rehfeld [3].
These three dimensions—cultural, social, and economic—are rooted in different understandings of culture and derive from the experiences of the InduCult 2.0 project as briefly outlined by Görmar et al. [31]. The different dimensions interrelate to each other and intersect in concrete activities. Görmar et al. have added to these three elements an environmental dimension. As industry and environment influence and interact with each other, this perspective certainly has some justification. However, we see environment and its interrelation with industry as a cross-cutting theme which could be addressed in the other dimensions either in a creative, artistic way, as a topic for public debate or as part of the regulations for economic activities.
3.2.1. The Cultural Dimension of Industrial Culture
The cultural dimension refers to a narrower aesthetic understanding of culture. In this sense, Industrial Culture comprises both material “artefacts, architecture, performances and artworks with a focus on industrial production [but also] the experience of art, whether in a cultural institution such as a gallery or museum” ([19], p. 15) or in everyday life. Industrial Culture can be addressed by all genres of the high arts and popular culture, as was shown for example in the European City of Culture program in the Ruhr area in 2010 [41].
In this sense, Industrial Culture can be both a means to preserve a distinct cultural heritage and a concept to strengthen the present and future cultural diversity in industrial cities and regions. Thus, Industrial Culture represents the procedural character of culture in a very specific manner: it is rooted in regional history referring to existing industries, local traditions, skills, and monuments, while it can also contain a dynamic and forward-looking character. This enables inclusive cultural progress shaped and created by the people today and in the future.
3.2.2. The Social Dimension of Industrial Culture
The social dimension of Industrial Culture refers to two different perspectives on culture: (1) an anthropological view which defines culture as a means to define and differentiate social communities, their experiences, and their lifestyles, delimiting them from other social groups; and (2) a broader sociological understanding of culture as a process which gives particular meanings and senses to our natural environment and the social realm (see also [19]). In this sense, Industrial Culture can be used as a communication platform to (1) foster local and regional identity (and distinguish a region’s or place’s identity from that of other regions and places) and (2) enable public discourse about industrial transformation and structural change.
By linking, for example, the educational system to industry through events such as the “Nights of Industry” or “Open Factory” (e.g., www.langenachtderindustrie.de or www.madeinpadova.it), local pupils and workers can engage with the particularities of their home region and reconnect to its specific place-based identity. Industrial Culture could serve here as a means to restore a certain kind of civic pride and revalue specific industry-related “structures of feeling” [42].
At the same time, Industrial Culture can by an entry point for locals to participate in the development of their hometowns and regions and depict new opportunities to keep up with changing times. A new dialogue can be opened involving population and enterprises, shaping the economic and societal future whilst staying rooted in the region’s history.
3.2.3. The Economic Dimension
The economic dimension of the concept refers on one hand to the increasingly acknowledged importance of social and cultural factors for regional economic development, as spelled out in concepts such as social capital, regional embeddedness, or cognitive proximity (see Section 2). On the other hand, the cultural and creative industries as well as tourism are two branches which can make particular use of a region’s industrial heritage and collaborate with current manufacturing industries to develop innovative solutions for current concerns (e.g., concerning design-oriented products, 3D-printing, new industrial architecture, regional routes on specific industries, etc.,). Thus, Industrial Culture can link creative mind-sets to structures and processes of industrial production.
This cross-over can generate innovation and lead to a diversification of the economic basis. It affects both the corporate and innovation culture of single enterprises and the cultural setting of the whole region [16]. Successful and innovative enterprises cultivate a culture of change [29] and often show a considerable responsibility for their location [43]. Touristic offers complement the economic diversity of a region. In this sense, Industrial Culture contributes to a contemporary re- and post-industrialization as well as a future-oriented place-marketing which attracts enterprises, workers, visitors, and tourists, as shown by the example of the Tabakfabrik Linz (www.tabakfabrik-linz.at).
To sum up, culture, and more specifically Industrial Culture, contributes to a place’s development in multiple dimensions and opens up new spaces of potentiality [44]. Industrial Culture is a time- and place-spanning concept that may shape a region’s identity. The self-awareness of (old) industrial regions is interrelated with industrial traditions and specific industrial “ways of life” [45]. Hence, future prospects of a region may rely not only upon economic and political decisions but also upon the cultural repertoire and social fabric of a region.
4. Case Study—District of Zwickau
4.1. Background
The administrative district (Landkreis) of Zwickau is situated in the state of Saxony in the eastern part of the Federal Republic of Germany. In its current form, the district is an amalgamation of three smaller units brought together in the framework of an administrative reform in 2008. It covers an area of 950 km2 and had 322,000 inhabitants as of 2016. The city of Zwickau is the largest municipality of the district with a population of 90,500 in the same year, being the region’s administrative, industrial, and cultural center. Nevertheless, the district comprises other towns with populations between 19,000 and 23,000 inhabitants (2016). The industrial past and present of the area is mainly based on the textile industry, coal mining, mechanical engineering, and for more than 100 years also the automotive industry [46].
In recent history, the district has been challenged by profound structural transformations. Whereas coal mining ended already in the 1970s, after German unification the region suffered a dramatic shrinkage of the textile industry with mechanical engineering and car production also declining substantially. However, unification opened up new perspectives as well: today Volkswagen Saxony GmbH in Mosel is the biggest enterprise in western Saxony with about 10,000 employees [47]. Automotive and machinery, as well as the textile industry are still the most important branches in the region, where around 2000 industrial enterprises employ 37,000 people [48]. The skills and knowledge of these branches accumulated over time in the region, which was one of the reasons why Volkswagen chose to buy and develop the production plant in Zwickau in the 1990s. On their website they explicitly refer to the 100 years of tradition in the region and emphasize that “Saxony is an automotive region with heart, hospitable, competent and innovative” [47].
With two universities of applied sciences in Zwickau and Glauchau, the district is home to two research institutions supporting the development of the relevant economic branches. While the district currently has the highest tax income and the lowest unemployment rates of Saxony (and it is thus often described as the engine of the Saxon economy) [49], it nevertheless suffers from a distinct population decline, posing a range of serious development issues [50].
4.2. From Industrial Heritage to Industrial Culture
Against the above-described economic and social background, it is apparent that the district has a considerable industrial heritage. The relicts are manifold, including impressive examples of industrial architecture, museums, archives, and mining landscapes with huge waste dumps, subsidence areas, and old shaft frames. An important step towards bringing this heritage onto the political agenda of the region involved the Wirtschaftsregion (Economic Region) Chemnitz-Zwickau GmbH (WiReg), a (now defunct) public management unit founded in 1995. The development concept of the WiReg highlighted the industrial heritage of the region as an integral part of regional development for the first time and served as an underlying reference document for action within the region [51].
Subsequently, several initiatives of the district and City of Zwickau aimed to develop its industrial heritage in the framework of European development programs [52]. Most of these efforts were focused on industrial heritage and only to a smaller degree on Industrial Culture as a wider, overarching concept. This somewhat changed with the latest initiative of the district, the INTERREG V-B project InduCult2.0 (www.InduCult.eu), which aimed less at the implementation of individual projects but rather at generating coherent regional strategies on Industrial Culture in Zwickau and other European regions involved. For this purpose, the project drew on some already successful examples of Industrial Culture in the district of Zwickau, albeit these examples had not been managed or explored in an integrated way [53].
Additional importance has been assigned to these initiatives since the Free State of Saxony has declared 2020 to be the “Year of Industrial Culture”, which is to be the preliminary highlight of the region’s activities in the field of utilizing its Industrial Culture. Zwickau has been assigned as venue for the central event of the year, the state exhibition “Industrial Culture in Saxony”. Two of in total six satellite locations are also located in the district. The setting of the main exhibition site in particular offers the opportunity to pursue a progressive understanding of industrial culture, with a simultaneous view to the past, present, and future. It will put the region and its Industrial Culture in the spotlight on state and national levels in 2020 (www.boom-sachsen.de).
The Year of Industrial Culture forms the culmination point of a process started in 2010, when the scientific advisory board for Industrial Culture in Saxony published ten recommendations for action on how to deal with Industrial Culture—addressing not only political and cultural stakeholders but also the economy, education, and research institutions [54]. Since 2011, Saxony has financed a coordination unit on Industrial Culture whose main task is the promotion of the topic through a wide range of events and lobbying.
The bundling of activities in the “Year of Industrial Culture” goes well with the attempts of the district to introduce a more coherent and strategic cultural utilization of its industrial past and present. The district has developed a strategic framework on the topic which has highlighted certain values and attitudes and has given a new, contemporary impulse with regard to the region’s “self-confidence (also in the sense of a ‘knowledge of cultural uniqueness’), tolerance, local affinity and openness towards novelty” [53]. The strategic paper on this topic has been elaborated in the frame of a focus group in April 2018 and names five essential fields of action for a living Industrial Culture:
- Industrial Culture as everyday culture;
- Industrial Culture as corporate culture;
- Industrial Culture as a culture of innovation;
- Industrial Culture as a building and urban planning culture;
- Industrial Culture as image of the region.
The established focus group will continue its work as a regional exchange forum on the topic of Industrial Culture beyond the InduCult2.0 project. It comprises 25 public bodies on local and regional levels, museums, small and medium-sized companies, higher education institutes, and creative workshops [53], with a core team of five institutions driving the process. The institutions belonging to the core team are the regional chamber of commerce, the tourism board, the regional agency for economic development, the umbrella organization for creative industries in Saxony (“Kreatives Sachsen”), and the joint district work group on schools and economy. With this instrument, the district intends to connect the past-oriented industrial heritage with the modern economy and attempts to link actors from the diverse fields of activity mentioned above. Yet, it has so far only been able to partially resolve one particular problem of the Zwickau region: the weak involvement of civil society and economic actors in the field of Industrial Culture.
4.3. Living Industrial Culture—Examples from the Field
Backed by the strategic documents of the project, the district of Zwickau implemented several activities, partly been newly developed and partly drawn on already-existing initiatives, which address all three dimensions of Industrial Culture as outlined in Section 3.2. (see Table 1 for an overview of how these dimensions are addressed).

Table 1.
Overview about Industrial-Culture-related activities in the district of Zwickau.
Maybe the most popular and attractive examples addressing mainly the cultural and social dimensions of the concept are the festivals dedicated to Industrial Culture. Festivals are “one of the most important examples of cultural consumption in recent years” and a “characteristic example of immaterial cultural heritage” [55]. As such, festivals have several significant impacts on a region. First, they enable organizers and participants to explore otherwise undiscovered local cultural resources. The long-running, alternative art festival IBUg (www.ibug-art.de) is an excellent example, as each year it invites many artists, activists, and other creative people from the region and beyond to discover industrial brownfields and use them as part of or as a background for their artistic performances.
Another aspect is that festivals can serve as discussion forums (e.g., on the reuse of industrial relicts or the environmental and societal implications of industrial developments). As such, they may encourage the formation of topic-specific groups and networks which may endure beyond the period of the festival and strengthen the participation of citizens and participants in a region’s development. One example here could be the “Days of Industrial Culture” initiated in 2010. Initially the Days of Industrial Culture were organized just in the neighboring district and city of Chemnitz. Gradually, the district of Zwickau was included in the organization, until in 2017 the whole region of Zwickau-Chemnitz took part in the event. This event has two major components: On one hand, museums, historical sites, and contemporary initiatives invite visitors to discover the rich industrial heritage of the region or introduce children to technology and industry (e.g., the educational center “Haus der Entdecker”—House of Discoverers—in Reinsdorf). On the other hand, local companies promote themselves and show their strong commitment to the region, getting into contact with potential employees, customers, and multipliers and highlighting the economic dimension of the event. Another point here is that the consumption related to these festivals often generates considerable monetary benefits for the region. Additionally, these festivals, as well as the 337 technical monuments and industrial museums of the region [56], support the development of a joint tourist destination of the districts of Chemnitz and Zwickau with Industrial Culture as a core theme
In addition, other activities have been implemented to strengthen tourism and shape the image of the region. The interactive installation “Industry Goes Public” displayed industrial companies, their products, innovation, as well as the industrial past of the area by using the innovative technology of Virtual Reality joined with art. Thereby, different actors of the region could be linked and future cooperation fostered. Similarly, new and traditional technologies have been combined in the elaboration of an interactive regional map (www.zeitsprungland.de) including old industrial sites, industrial companies, and related events, thereby offering alternative experiences offside the touristic mainstream. Moreover, the map has also aimed at encouraging the region’s stakeholders to upgrade their offer by including and focusing more on Industrial Culture.
In addition, the district elaborated a brochure under the title “Von Wachstum und Wandel. Unternehmensgeschichten aus dem Landkreis Zwickau” (About Growth and Change. Corporate Stories from the district of Zwickau) [48]. This publication highlights the innovative potential of local companies, but also their history and embeddedness in the region. The brochure contains stories from the textile, machinery and metal industries, from small family businesses as well as big factories with more than 1500 employees, serving primarily as a marketing tool to promote the region as a business location.
Both economic and cultural aspects are present in several initiatives focusing on the versatile re-use of old industrial places, for example, as cultural and creative centers (e.g., Gasometer Zwickau, Kunstplantage Zwickau, Seilfabrik Zwickau, Knopffabrik Zwickau, Tuchfabrik Werdau, Initiative “Raumkomplizen”). The cultural and creative industries have also been the focus of a coaching program in the district. The offer aimed primarily at initiatives in small and medium-sized towns that had the objective of starting a revitalization process of three old industrial areas and consisted of workshops to ultimately develop three roadmaps. During these workshops, tailor-made measures were defined for a low-level development of these areas taking into account the specific needs of cultural initiatives and creative industries [53].
Another cultural highlight has been an artistic intervention at the former mining shaft tower near the city of Zwickau. The installation became a widely recognized landmark in the area, displaying the industrial past of the wider region. The investment was realized after a design competition and with the support of a local company being present on the site of the mural. Due to the success of the funded action, a follow-up installation on the other side of the tower will be implemented at the end of 2019 with a focus on the industrial present and future of the region (see Figure 2).
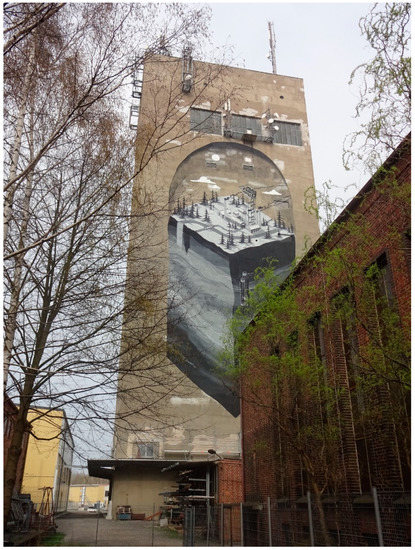

Figure 2.
Tower of Martin-Hoop-Shaft, Zwickau. Photo: Andreas Wust, 2019.
The social dimension of the concept, namely its potential to link industry and education, has been addressed by the Museum of Textiles and Motorsports in Hohenstein-Ernstthal. It initiated an educational program with the topic “Textiles thought differently”. By including lectures, group work, and visits of the related exhibition, the program gained such positive feedback that it will be continued after the project. Additionally, the museum has planned to extend the collaboration to other regional companies that deal with textile industry (textile production, textile machine engineering) and to strengthen the job orientation element, thus fostering the triangle of school–museum–company.
5. Discussion
In the previous sections, we put forward our understanding of Industrial Culture as a potential driver of regional development in (old) industrial regions. The case of Zwickau shows that Industrial Culture can be used in manifold ways to shape a region’s identity and consequently its future development path. The district of Zwickau has long been influenced by its industries, especially the automotive, machinery, and textile sectors, leading to the emergence of a particular “industrial way of life” [45].
As a result of the experiences from the InduCult 2.0 project, we elaborated three dimensions—cultural, social, and economic—which are addressed by the concept of Industrial Culture. Festivals like the Days of Industrial Culture or the IBUg address all three dimensions at the same time. Economic actors like companies (which opened their doors for visitors) and tourism institutions are equally involved in this event as cultural actors (i.e., museums, artists, and historic sites). Pupils and the wider population can explore the artistic interventions in former industrial buildings. With the organization of “morning and night shifts”, the Days of Industrial Culture refer explicitly to industrial modi operandi (www.industriekultur-chemnitz.de). Thus, such festivals continue to tell the industrial narratives by simultaneously using creative approaches for a reinterpretation of the local industrial identity and raising awareness for the specific Industrial Culture of the region [19]. Stakeholders are brought together in a wide network and can be motivated to engage as multipliers and ambassadors for the region´s industrial culture. Residents are invited to explore their relation to their home region, eventually leading to new narratives in civic society and new images.
The example of Zwickau also shows that by the use of new technologies such as Virtual Reality, cultural events can play a significant role in the innovative and inclusive inward and outward presentation of a region. These events not only have the chance to transform the inside perception of an area, but can also positively contribute to a (re-)branding of (old) industrial areas and the tourism sector. The tourism agency of the district of Zwickau recognized this potential, explicitly referring to the multiple temporal dimensions of regional development with their claim of the “Zeitsprungland”.
The active participation of today’s industrial companies in the abovementioned festivals and actions supports the expansion of corporate networks to potential workforces and customers, but also to cultural and educational institutions and the district administration. Another effect of a living Industrial Culture is that companies’ commitment to the region in the sense of a Corporate Regional Responsibility [39] can be enhanced considerably. The same applies for activities like the exhibition of the Museum of Textile and Motorsports in Hohenstein-Ernstthal, which strengthened the collaboration between museum, schools, and companies, and in this way connected both the economic and social dimensions of Industrial Culture. In times of severe lack of qualified workforce in many regions in Europe, such activities may play a crucial role in showing young people their perspectives within the region and consequently binding their workforce here.
In addition, Industrial Culture can also be used to open up new development paths. The reuse of abandoned industrial buildings by the creative industries is now widely promoted, especially in metropolitan areas. However, it is still not common in small and medium-sized towns in the district of Zwickau. As a first visible sign, the tower of a former mining shaft has been transformed into a landmark promoting Industrial Culture. Next steps in this direction are now the coaching sessions for initiatives of the creative industries as well as a study to find out if there is enough potential to establish a creative center in one of the smaller towns in the region combining cultural offers and economic purposes. On that basis, first discussions about potential locations have taken place, focusing on the town of Glauchau. It remains to be seen if the project will be realized in the next few years.
These latter examples show that in the case of the district of Zwickau a certain diversification of the economic base is currently taking place. Automotive, machinery, and textile industries still play an important role in its economic development. However, stakeholders also need to be aware of the restraints that the concentration on just a few industries entails (see Section 2). They need to know about their dependency on big companies such as Volkswagen and aim to avoid negative lock-ins in the region. Currently, signs of cognitive lock-in can be traced in the reluctance of some (mainly economic) actors to network in cross-sectoral settings, potentially leading to difficulties in reaching a critical mass of regional actors for the topic of Industrial Culture over time. Such problems are likely to be faced by other (old) industrial towns and regions as well. The district needs to broaden its network around the implementation of the InduCult 2.0 project, also beyond the state exhibition event in 2020.
The region’s development could be pushed forward by the exploitation of its rich industrial culture in manifold ways. Especially the region’s great technical and industrial heritage in combination with contemporary capabilities und future assets (research, education) can play an important part in the process of cultural and economic renewal. Bringing together people from different branches, from the automotive and textile industries, from the education sector as well as from cultural institutions such as museums and creative industries has the potential to create a unique regional culture leading to “knowledge exchange, cooperation and collective learning” ([3], p. 1910) and ultimately to regional renewal. Culture in this sense can be “an active and lived force” ([44], p. 11) that creates spaces of potentiality and, thereby, shapes the present and future of a region.
Yet, the involvement of some economic key actors and the general public is rather subdued in the region, and despite the important steps taken, the topic of Industrial Culture is still not being utilized to its full potential.
6. Conclusions
This study has contributed to the recent debates on culture as an important aspect of regional development paths. Using the case study of Zwickau, we demonstrated how culture can affect the formation of regional development paths through the formation of specific mind-sets, values and identities.
This is especially valid for (old) industrial towns with a long and enduring prominence of the manufacturing sector, shaping the daily cultural habits, trades, ways of thinking and communication. Industrial Culture is conceptualized as a dynamic phenomenon, based on social interaction and networking, while being place-bound and locally embedded, bringing about a special set of elements linked to the predominance of industrial production. While we have also referred to limiting aspects of Industrial Culture, especially in form of cognitive “lock-ins”, we have laid out its potential to tackle some of the complex development challenges faced by small and medium-sized (old) industrial towns across Europe. Highlighting the intangible endogenous resources of such towns and regions helps to widen the focus of the renewal of (old) industrial regions beyond the (now well-explored) material legacies of industry, such as disused buildings and infrastructures. Thus, it also holds the key for a more inclusive discourse on regional change, potentially involving broader sections of the population.
In this way, Industrial Culture comprises three interrelated dimensions (i.e., cultural, social, and economic) which can be underscored by different, albeit often overlapping, actions, opening up new development options for the regions. Which of the dimensions are pursued by the towns and regions depends mainly on their actual development needs and already existing activities in the regions. In this regard, it is important to understand the notion of Industrial Culture in a regional development context as a strategic option that integrates various existing activities in the regions, in order to form a coherent approach towards the topic. Thereby, the concept itself is clearly based on a broad regional actors’ network, joining stakeholders from different fields and sections of society. It is especially here where the practical reflections in this article point to the ambivalent nature of the concept: it could either be restraining and leading to a cognitive lock-in of the multiple actors engaged in the region (i.e., by not activating relevant actors from all sectors) or open up new perspectives and enable alternative development paths.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: F.G., J.H.; methodology: F.G., J.H.; writing—original draft preparation: F.G., J.H.; writing—review and editing: F.G., J.H.; visualization: J.H.; project administration: J.H., F.G.
Funding
The research leading to this article was funded in the frame of the projects InduCult 2.0, which was co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund via the INTERREG CENTRAL EUROPE program (2016-2019), and “Agents of change in old-industrial regions in Europe” funded by Volkswagen Foundation (2019-2021).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank their project colleagues Wolfgang Fischer, Thilo Lang, Robert Nadler, Danko Simic, and Andreas Wust for the joint work in the InduCult 2.0 project and Carsten Debes and Nadir Kinossian for comments on earlier versions of this paper. Also we would like to thank both anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bell, D. Welcome to the post-industrial society. Phys. Today 1976, 2, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, M. The Rise of the Network Society, The Information Age: Economy, Society and Culture; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, P.; Rehfeld, D. Path Dependence and New Paths in Regional Evolution: In Search of the Role of Culture. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2011, 19, 1909–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, R. Institutional Change, Cultural Transformation and Economic Regeneration: Myths and Realities from Europe’s Old Industrial Areas; University of Durham, Department of Geography: Durham, UK, 1992; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Simmie, J. Innovation and Urban Regions as National and International Nodes for the Transfer and Sharing of Knowledge. Reg. Stud. 2003, 37, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickcek, G.A.; McKinney, H. Small Cities Blues: Looking for Growth Factors in Small- and Medium-Sized Cities. Econ. Dev. Q. 2006, 20, 232–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabher, G. The weakness of strong ties. The lock-in of regional development in the Ruhr area. In The Embedded Firm: On the Socioeconomic of Industrial Networks; Grabher, G., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1993; pp. 255–277. [Google Scholar]
- Hassink, R. Locked in decline? On the role of regional lock-ins in old industrial areas. In Handbook of Evolutionary Economic Geography; Boschma, R., Martin, R., Eds.; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 2010; pp. 450–468. [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon, D.; Dawley, S.; Pike, A.; Cumbers, A. Rethinking Path Creation: A Geographical Political Economy Approach. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 95, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Sunley, P. Path dependence and regional economic evolution. J. Econ. Geogr. 2006, 6, 395–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iammarino, S.; Rodríguez-Pose, A.; Storper, M. Why Regional Development Matters for Europe’s Economic Future; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Agtmael, A.V.; Bakker, F. The Smartest Places on Earth. Why Rustbelts are the Emerging Hotspots of Global Innovation, 1st ed.; Public Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Pose, A. The revenge of the places that don’t matter (and what to do about it). Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2018, 11, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, A.; Rodríguez-Pose, A.; Tomaney, J. What Kind of Local and Regional Development and for Whom? Reg. Stud. 2010, 41, 1253–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harfst, J.; Wust, A.; Nadler, R. Conceptualizing industrial culture. GeoScape 2018, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, N.; Gärtner, S.; Rehfeld, D. Companies, Cultures, and the Region: Interactions and Outcomes. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2011, 19, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, A.; Dale, B. From regional restructuring to regional renewal: Cases from Norway. Nor. Geogr. Tidsskr. Nor. J. Geogr. 2014, 68, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A. Industries and Trade: A Study of Industrial Technique and Business Organization; Macmillan: London, UK, 1919. [Google Scholar]
- Görmar, F.; Harfst, J.; Simic, D.; Wust, A. The Transformative Power of Industrial Culture—From Concepts to Actions; Universität Graz: Graz, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Isaksen, A.; Jakobsen, S.-E.; Njøs, R.; Normann, R. Regional industrial restructuring resulting from individual and system agency. Innov. Eur. J. Soc. Sci. Res. 2018, 32, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garud, R.; Kumaraswamy, A.; Karnøe, P. Path Dependence or Path Creation? J. Manag. Stud. 2010, 47, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschma, R. Proximity and Innovation: A critical assessment. Reg. Stud. 2005, 39, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.J. Cultural-Products Industries and Urban Economic Development: Prospects for Growth and Market Contestation in Global Context. Urban Aff. Rev. 2004, 39, 461–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruickshank, J.; Ellingsen, W.; Hidle, K. A crisis of definition: Culture versus industry in Odda, Norway. Geogr. Ann. Ser. B Hum. Geogr. 2013, 95B, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florida, R. The Rise of the Creative Class—Revisited, 10th ed.; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moulaert, F.; Sekia, F. Territorial Innovation Models: A Critical Survey. Reg. Stud. 2003, 37, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maggio, P. Culture and economy. In The Handbook of Economic Sociology; Smelser, N., Swedberg, R., Eds.; Princeton University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 27–58. [Google Scholar]
- Becattini, G. Beyond geo-sectoriality: The productive chirality of places. Investig. Reg. J. Reg. Res. 2015, 32, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Van Prud’homme Reine, P.; Dankbaar, B. A Virtuous Circle? Co-evolution of Regional and Corporate Cultures. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2011, 19, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, D. Places and their Past. Hist. Workshop J. 1995, 39, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görmar, F.; Wust, A.; Metalidis, I.; Debes, C.; Harfst, J. The Transformative Power of Industrial Culture. Transnational Argumentation Brochure. 2018. Available online: http://interreg-central.eu/Content.Node/InduCult2.0/Transnational.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- Harfst, J.; Wirth, P. Zur Bedeutung endogener Potenziale in klein- und mittelstädtisch geprägten Regionen–Überlegungen vor dem Hintergrund der Territorialen Agenda 2020. Raumforsch. Und Raumordn. 1995, 72, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, P.; Cernic-Mali, B.; Fischer, W. (Eds.) Post-Mining Regions in Central Europe; OEKOM: München, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, M. (Ed.) Bright Future for Black Towns—Economic Performance and Place-Based Characteristics of Industrial Regions in Europe-Comparative Cross-National Report. 2017. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325195233_Economic_performance_and_place-based_characteristics_of_industrial_regions_in_Europe (accessed on 18 September 2019).
- Benneworth, P.; Clifton, N.; Doucet, B.; Goebel, C.; Hamm, R.; Schmitz, Y. The regeneration of image in old industrial regions: Agents of change and changing agents. In Mönchengladbacher Schriften zur Wirtschaftswissenschaftlichen Praxis; Culliver: Goettingen, Germany, 2009; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Häyrynen, S.; Nyman, J. Introduction: Changing Single-Industry Communities as Examples of Identity Formation. In Locality, Memory, Reconstruction: The Cultural Challenges and Possibilities of Former Single-Industry Communities; Häyrynen, S., Turunen, R., Nyman, J., Eds.; Cambridge Scholars: Newcastle, UK, 2012; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Strangleman, T.; Rhodes, J.; Linkon, S. Introduction to crumbling cultures: Deindustrialisation, class and memory. Int. Labor Work. Cl. Hist. 2013, 84, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, N.G. Manufactured Sites: Re-Thinking the Post-Industrial Landscape: Rethinking the Post-Industrial Landscape in the Urban Environment; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Küster, T. Ruhrgebietspolitik und Ruhrgebietsidentität 1870–1930. In Industriekultur und Regionale Identität; Stadler, A., Streitt, U., Eds.; Oberoesterreichisches Landesmuseum Linz: Linz, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kebir, L.; Crevoisier, O. Cultural resources and regional development: The case of the cultural legacy of watchmaking. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2008, 16, 1189–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhr.2010. Cultural Capital of Europe. Programme-Overview. Available online: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/RUHR.2010_%E2%80%93_Kulturhauptstadt_Europas (accessed on 18 September 2019).
- Williams, R. Culture. In The Cultural Geography Reader; Oakes, T., Price, P., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Vonnahme, L.; Graffenberger, M.; Görmar, F.; Lang, T. Kaum beachtet, gemeinsam stark. Informationen zur Raumentwicklung 2018, 6, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, J.; Lang, T. Peripheralisation: A Politics of Place, Affect, Perception and Representation. Sociol. Rural. 2018, 58, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, D. Industrial Culture in a post-industrial world: The case of the North of England. City 2002, 6, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsch, R.; Schäfer, M. Wirtschaftsgeschichte Sachsens im Industriezeitalter; Edition Leipzig: Leipzig, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Volkswagen Sachsen Zahlen und Fakten [Facts and Figures]. 2019. Available online: https://www.volkswagen-sachsen.de/de/unternehmen/zahlen-und-fakten.html (accessed on 27 September 2019).
- Landkreis Zwickau. Unternehmensgeschichten aus dem Landkreis Zwickau.Von Wachstum und Wandel. 2019. Available online: https://www.landkreis-zwickau.de/download/InduCult2.0/Broschuere_Von-Wandel-und-Wachstum_dt.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- MDR—Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk. Available online: https://www.mdr.de/sachsen/chemnitz/zwickau/kommunalwahl-sachsen-landkreisportrait-landkreis-zwickau-100.html (accessed on 27 September 2019).
- Landkreis Zwickau. Integriertes Regionales Entwicklungskonzept—Irek Landkreis Zwickau 2030. 2018. Available online: https://www.landkreis-zwickau.de/download/wirtschaft/IREK_ZWICKAU_2030_Ergebnisbericht.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- Wireg. Informationen zum Projektmanagement Floez. 2008. Available online: http://floez-sachsen.de/dokument/Abschlu%C3%9Fbericht_Informationen_zum_Projektmanagement_Floez_2007-2008_1355476372_775.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2019).
- Harfst, J.; Wirth, P.; Simic, D. Utilising Endogenous Potentials via Regional Policy-Led Development Initiatives in (Post-) Industrial Regions of Central Europe. In The Role of Public Sector in Local Economic and Territorial Development. Innovation in Central, Eastern and South Eastern Europe; Finka, M., Jasso, M., Husar, M., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Debes, C.; Zimmermann, G. Regional Strategy on ‘New Industrial Culture’; Landkreis Zwickau: Zwickau, Germany, 2019; Available online: http://interreg-central.eu/Content.Node/InduCult2.0.html#Documents_&_Publications (accessed on 27 September 2019).
- Wissenschaftlicher Beirat für Industriekultur in Sachsen (Scientific Advisory Board for Industrial Culture in Saxony). Industriekultur in Sachsen. Handlungsempfehlungen des Wissenschaftlichen Beirates für Industriekultur in Sachsen. 2010. Available online: http://www.kdfs.de/do/314.0.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2019).
- McKercher, B.; Wei, W.; Tse, T. Are short duration festival tourist attractions? J. Sustain. Tour. 2006, 14, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landkreis Zwickau. Argumente für Eine Lebendige Industriekultur im Landkreis Zwickau (Arguments for a Living Industrial Culture in the District of Zwickau); Landkreis Zwickau: Zwickau, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).