Abstract
Although the importance of urban infrastructure resilience can be inferred, its terminology remains convoluted within the literature due to a lack of systematic review from a sustainable development planning perspective. This review paper was designed to elucidate connected research themes, scientific popularity, and conceptual boundaries of the term infrastructure resilience in an urban context. Three guiding research questions were asked: What does urban infrastructure resilience really mean? What are the most common research topics connected to urban infrastructure resilience? How can humanity further improve urban infrastructure resilience from a sustainable development planning perspective? To answer these research questions, a two-step literature analysis was adopted consisting of: (i) a scoping review to select relevant publications based on a specific search query; and (ii) a content analysis to reduce and synthesize the scoping review findings further based on the three most applicable publishing outlets. The scoping review reduced articles to 535, while content analysis further condensed it to 84 across three key journals. With North America and Europe leading, the findings corroborated that eight connected subject areas establish the conceptual boundaries of urban infrastructure resilience. The eight related research topics in decreasing abundance were: (1) climate change, (2) floods, (3) disasters, (4) environmental policy, (5) ecosystems, (6) risk assessment, (7) emergency preparedness, and (8) adaptation. In conclusion, these research topics should be pursued when creating urban infrastructure resilience strategies for moving towards sustainability.
1. Introduction
We live in a time of unprecedented global change. As we progress through the early stages of the Anthropocene, not one of the original eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were reached by 2015. The rate of global warming and sea level rise has not lessened [1,2,3], nor has the degradation of our life-supporting biogeophysical systems slowed [4,5,6]. The world’s richest countries have seen improvements in their socioeconomic and material well-being [7]; albeit at the cost of slowly metabolizing natural habitats within their own borders through land cover change, and devastating entire ecosystems across the developing world through globalization [8,9]. Overstepping three of the nine interlinked planetary boundaries—the proposed safe operating space for humanity—has caused Earth’s biogeophysical and thus humanity’s life-supporting systems to become more stressed [10]. At the same time, humanity has witnessed the continuation of the unequal distribution of wealth. As recent as 2011, close to 14.5% of the world’s population was still classified as living in extreme economic poverty (less than US $1.25 a day) and lacked access to natural resources to meet their fundamental needs [11,12]. These global challenges have been propelled mostly by population growth and an increased demand for material well-being [7].
Population growth and rural-to-urban migration continues to fill already swollen cities [13]. In 2008, a major landmark was reached in human evolution with a majority of people classified as living in cities [14,15]; however, the developed world had over 80% urban population by that time and most urban population growth was projected to occur in the developing world [12]. Regarding megacities (populations over 10 million), in 1975 there were three, in 2007 there were 19, and by 2025 projections suggest there will be 27 or more [16]. According to Gerland et al. [17], global population will reach somewhere between 9.6 and 12.3 billion by 2100 and continue growing thereafter with an unknown stabilization date. Humanity has become progressively urban, and the great migration to cities will continue with global population estimated to be 70% urban by 2050 and 100% by 2092 [18]. While urbanization is often positively correlated with socioeconomic development, it has simultaneously been linked to a number of environmental problems [9]. It is now commonly accepted that land cover changes associated with population (e.g., urbanization) disturb and distort ecosystems great distances from source locations [19,20]. Further, the greatest impacts on global change are coming from those direct and indirect causes [13,21]. If humanity is to create sustainable communities across spatial scales, resilience planning will be required.
“Resilience” as a term is now commonplace across many theoretical, applied, and professional fields [22]. “Resilience” characterizes a system’s capacity to absorb shocks and stressors while still maintaining function; furthermore, it is also concerned with a place’s capacity for renewal, reorganization and development after shocks and stressors [23,24]. In resilient coupled human-environmental systems, disturbances have the potential to create opportunities for such things as development and innovation [25]. However, in coupled vulnerable systems, even small disturbances may have catastrophic environmental and social consequences [26]. Within the context of “urban resilience,” previous works have shown that global change has impacted cities, complex human-environmental systems, and the ability for urban populations to recover from climate induced natural hazards and disasters [19,27,28,29,30]. Unlike climate change adaptation, urban resilience involves strengthening a city’s overall ability to systematically anticipate, absorb, and reorganize itself in relation to both known and unknown threats [30,31,32]. This is a timely concern as most cities are poorly equipped to meet this demand because of the combined pressures of population growth, immigration, rural-to-urban migration, and climate change [33].
A city’s progress towards sustainability (human–ecosystem equilibrium [34]) is contingent on its infrastructure resilience. “Infrastructure” is interpreted as the underlying foundation (i.e., basic network) of a human–environmental system. In order to maintain this coupled system, entities such as public works (utilities, structures, equipment, personnel) need to be in place for it to persist indefinitely. Improvement to urban infrastructure is a necessity for fast-growing cities, therefore the planning and engineering communities have focused much of their attention on questions related to minimizing resource consumption and maximizing efficiency through the redesign of infrastructure [35,36,37,38,39,40]. The terminology related to “urban infrastructure resilience” remains convoluted within the literature due to a lack of systematic review from a sustainable development planning perspective. The main goal of this review paper was to elucidate connected research themes, scientific popularity, and conceptual boundaries of the term infrastructure resilience pertaining to urban areas of select Western World countries. These countries were chosen due to their status as either “developed” or “developing” based on the United Nations Human Development Index (http://hdr.undp.org/en). To achieve this goal, the following three guiding research questions were asked: What does urban infrastructure resilience really mean? What are the most common research topics connected to urban infrastructure resilience? How can humanity further improve urban infrastructure resilience from a sustainable development planning perspective? These questions need to be answered for two reasons; (a) the resilience of people is at the core of any form of resilience: without citizen resilience cities cannot withstand major shocks or stresses; (b) planners and stakeholders need to be informed on appropriate interventions to increase urban infrastructure resilience. A well-intended hazard mitigation plan can go a long way in bolstering a city’s resilience. From a broader perspective, the literary synthesis in this research aims to serve as an important step in stimulating interdisciplinary dialog for understanding and creating sustainable cities through urban infrastructure resilience. This is important as the endeavor of urban infrastructure resilience is complemented by those advocating for green infrastructure, as well as those working to increase social justice [41,42].
2. Materials and Methods
In order to uncover connected research themes, scientific popularity, and conceptual boundaries of the investigated topic “urban infrastructure resilience,” and to answer this study’s guiding research questions, a two-step literature analysis was adopted. The two-step method consisted of: (i) a scoping review to select relevant publications based on a specific search query; and (ii) a content analysis to reduce and synthesize the scoping review findings further based on the three most applicable publishing outlets.
Scoping reviews are a relatively new methodology and are considered to be particularly useful when a research topic has not been comprehensively reviewed, or exhibits complexities not answerable in more precise review techniques [43]. Further, they are useful for streamlining information to facilitate improved decision-making [44], which is critical for policy-makers who require knowledge synthesis in a short time. Scoping reviews allow researchers to conduct a top-level search of complex concepts for the purpose of clarifying key subject and research areas. The intent of this scoping review was to investigate the use of concepts connected to urban infrastructure resilience in the literature. Note that scoping reviews seldom evaluate the quality of studies within the review, as the quantity of topics under study is usually only counted in this type of literature analysis [44]. A scoping review was chosen to help examine the literature as many planning and sustainability-related themes are theoretically connected to urban infrastructure resilience but no rigorous and systematic assessment can be found. Following Arksey and O’Malley [44], the scoping review conducted in this study adhered to the three common categories: (1) identification, (2) screening, and (3) inclusion.
Published literature was explored following the PRISMA [45] flowchart displayed in Figure 1, and using the ProQuest Science and Technology search engine. The ProQuest database was selected as the vehicle for this research as it provides a single source for scholarly journals, reports and working papers. The ProQuest tool allows for a range of adaptable filters in order to accurately and easily navigate the database to perform an in-depth scoping review. Specifically, the ProQuest Science and Technology database was selected for this scoping review as it incorporates a wide range of interdisciplinary subject areas needed to adequately capture the multifaceted term of resilience. According to their website, ProQuest offers access to millions of references to research outputs and tens of thousands of full-text documents and publicly available datasets. Although other literature explorations have used more than one search engine, it was believed that using only the ProQuest search engine would reduce double counting and inflated erroneous findings. In order to maximize the scoping review efficiency, entire documents were searched rather than a combination of titles, abstracts, and key words. In detail, ten keywords relating to urban infrastructure resilience were used in conjunction with Boolean operators to form a single comprehensive search query. These keywords were chosen to build from and remain in-line with previous literature and to produce a more focused outcome. For instance, Sharifi et al. [46] used terms such as: “climate,” “planning,” and “urban” in conjunction with “resilient” in their robust literature review of research articles on urban resilience; Meerow et al. [30] detailed the importance of, and complexities, surrounding the notion of “urban” when defining resilience via a literature review. On 10 July 2017, the following ten-word Boolean Logic search query was entered into the ProQuest Science and Technology search engine: “urban” AND “infrastructure” AND “resilience” AND “planning” AND “sustainability” OR “sustainable” OR “vulnerability” OR “adaptation” OR “mitigation” OR “climate change,” resulting in 14,649 publications. Those publications were filtered by full text and peer reviewed articles resulting in 4110, and then screened to remove: (1) papers published before 2007, (2) non-scholarly journal sources, and (3) non-English language publications.
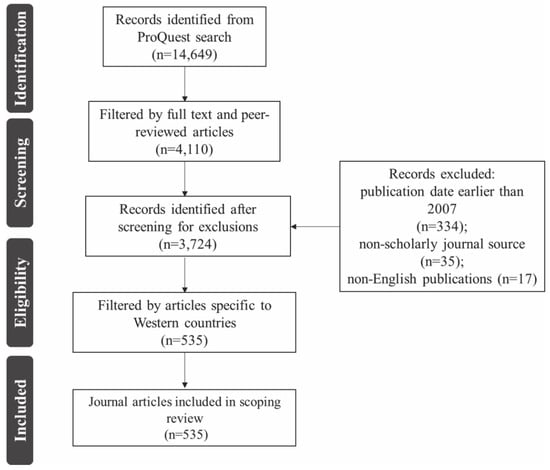
Figure 1.
Literature reducing method used during scoping review to uncover connected research themes, scientific popularity, and conceptual boundaries of “urban infrastructure resilience.” Flowchart adopted from [45].
The remaining 3724 articles were then constrained to Western World countries due to their dominance in the subject matter and “developed” or “developing” status; and in terms of this study, to provide a more detailed analysis of the nature and extent of research evidence in the field of resilience. Narrowing down the scoping review allows this research to more accurately pinpoint key literature and to provide a more in-depth analysis, better suited for policy recommendation. More justification is that policy requires geographic-specific recommendations and global assessments would likely provide too general recommendations or erroneous results altogether. Attempting to preserve geographically-connected relevance, this resulted in 535 documents for the scoping review assessment. The definition of Western World countries remains ambiguous; however, this study included the following countries for analysis: Europe (European Union member states, European Free Trade Association countries, European microstates); the Americas (Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Panama, Mexico, United States of America, Uruguay); Africa (South Africa); and Oceania (Australia and New Zealand). The results from the scoping review were categorized by major subject area as established by the specific classification system within the ProQuest Science and Technology search engine. ProQuest uses a HILCC (Hierarchical Interface of Library of Congress Classification) taxonomy system, which is the standard for academic catalog records, generating structured and topical lists for subject areas on the web [47]. Lastly, the top ten major subject areas were ranked by relative abundance.
The 535 articles chosen for the scoping review were further analyzed using a content analysis. Content analysis of research concepts is widely accepted and has been used across both social and natural sciences [48,49,50]. A content analysis, although it follows similar methodologies, differs from a scoping review. A scoping review in this study is used to synthesize and map out the literature in a particular topic area, meanwhile a content analysis is used to examine patterns and/or subjects in a given subset of literature. The content analysis consists of screening published documents, by one or combination of titles, abstracts, key words, or full documents, which can be grouped according to similarity in meaning. This categorization of subject areas, themes and coding was completed through the ProQuest algorithm and analyzed through the output and individual article screening. Using the aforementioned search query and method from the scoping review, the top three journals (Natural Hazards, Regional Environmental Change, and PLoS ONE) were chosen based on the increased frequency of key terms in their full article publications. In doing so, this common information reducing technique allowed us to focus on those key journals publishing related works on urban infrastructure resilience. Again, following the PRISMA flowchart [45], the 535 scoping review documents were reduced to 84 for the content analysis (Figure 2). The results from the content analysis across the three journals were again categorized by major subject area as established by the specific classification system within the ProQuest Science and Technology search engine. Similarly, the top ten major subject areas were ranked by relative abundance based on their relationship to urban infrastructure resilience. The key areas were identified from ProQuest’s generated subject classification. Finally, the results from the scoping review and content analysis were compared, contrasted, and discussed.
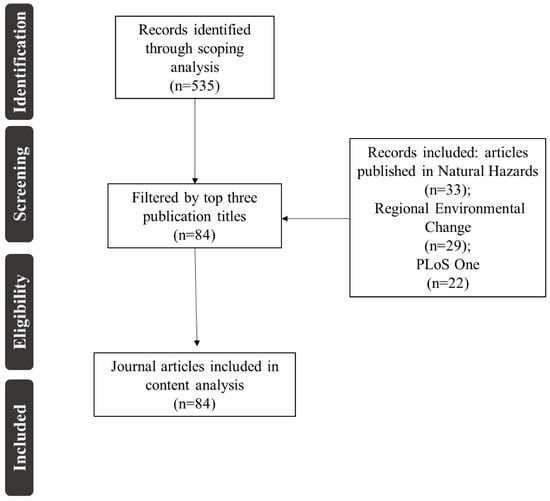
Figure 2.
Flowchart adopted from [45] outlining this study’s content analysis, including selection of the three most relevant journals (Natural Hazards, Regional Environmental Change, and PLoS ONE) publishing topics related to “urban infrastructure resilience”.
3. Results
3.1. Scoping Review
Using the aforementioned search query terms, and filtering refinements, almost half (241) of the 535 documents were from the United States; however, North America and Europe clearly contained the majority of research on urban infrastructure resilience across the countries assessed (Figure 3). As with most research topics, applied sustainability scientists and resilience planners most often work in locations within their own country. Therefore, it is likely that the higher provenance of urban infrastructure resilience related documents from North America and Europe is due to the higher density of research institutes across those continents. Notably, Australia and New Zealand accounted for 102 research documents (19%) in the scoping review, exposing the leadership those nations have taken to address the combat ills associated with climate change and sea level rise. Note that of the 535 sources included in the final scoping review analysis, 68% (n = 364) of the articles were published within the last four years. The number of publications found at this rate signifies the growing importance of urban infrastructure resilience as a research sub-topic for sustainable development and climate change resilience planning.
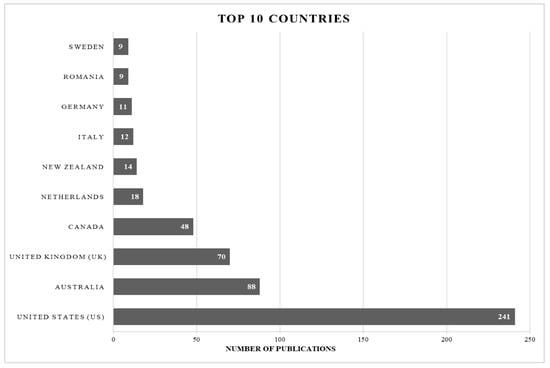
Figure 3.
Bar chart illustrating proportional abundance of the top ten countries publishing research related to “urban infrastructure resilience” based on the scoping review (n = 535).
Using the major subject areas as established within the ProQuest Science and Technology search engine during the scoping review, 32% of the 535 research products were classified in the climate change category (Figure 4). The subject area floods came in second with 10% of documents categorized. Although the studies included within the final scoping review varied in focus, the top ten subject areas related to urban infrastructure resilience in decreasing abundance were: (1) climate change, (2) floods, (3) disasters, (4) environmental protection, (5) environmental policy, (6) ecosystems, (7) risk assessment, (8) emergency preparedness, (9) adaptation, and (10) infrastructure. In the broadest sense, the ten research subject areas from the scoping review fall into three categories: (i) the natural biogeophysical environment, (ii) environmental planning, management and policy, and (iii) the built environment. These key subject areas highlight important and related topics associated to the newly developing sub-field of urban infrastructure resilience. The results indicate that the topic urban infrastructure resilience has made significant headway in multiple research areas and should be seriously considered by stakeholders, planners, policy-makers, and researchers during future sustainable development and resilience initiatives.
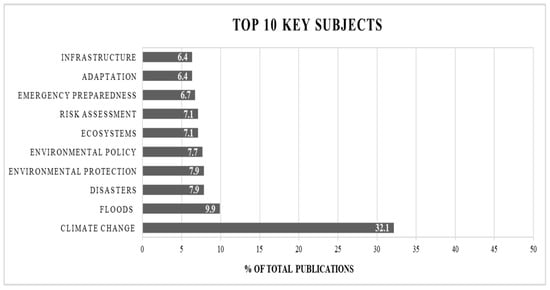
Figure 4.
Bar chart illustrating proportional abundance of the top subject areas related to “urban infrastructure resilience” based on this study’s scoping review (n = 535).
3.2. Content Analysis
Using the major subject areas as established within the ProQuest Science and Technology search engine during content analysis, almost half (46%) of the 84 research articles published in Natural Hazards, Regional Environmental Change, and PLoS One were classified in the category climate change (Figure 5). Again, the connected research area floods came in second with 17 documents. Although theses of the studies varied across the three journal article publishing outlets, the top ten subject areas related to urban infrastructure resilience in decreasing abundance were: (1) climate change, (2) floods, (3) risk assessment, (4) environmental policy, (5) adaptation, (6) disasters, (7) case studies, (8) ecosystems, (9) emergency preparedness, and (10) biological diversity. In the broadest sense, the ten research subject areas from the continent analysis only reiterated two of the three aforementioned scoping review categories: (i) the natural biogeophysical environment, and (ii) environmental planning, management and policy. That said, it should be noted that the built environmental category did have representation within the content analysis but not in the top ten research subject areas. This analysis provides a deeper understanding of the key subject areas relating to resilience and highlights an important comparison between the two results. It not only brings to light the re-occurrence of climate change and flooding in infrastructure resilience, but also pinpoints subject areas that were not present in the scoping review. These can be instrumental in better understanding infrastructure resilience. For example, case studies (ranked 7 on the list) may be a key way that literature is providing vital information on resilience. Future studies should look into the need for more case studies to better understand infrastructure resilience. This study also acknowledges the limitations brought forth by constraining this content analysis to the top three major journals. However, this research has provided the stepping stones for future infrastructure resilience research in conducting and in-depth scoping reviews with subsequent content analysis.
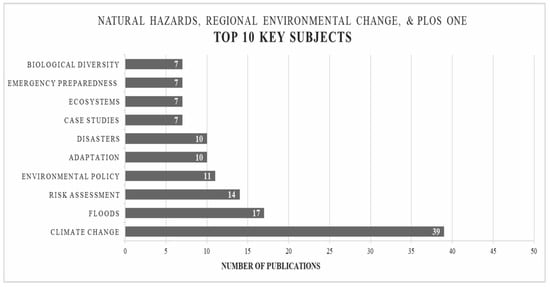
Figure 5.
Bar chart illustrating proportional abundance of top subject areas across the three most relevant journals (Natural Hazards, Regional Environmental Change, and PLoS ONE) used in publishing topics related to “urban infrastructure resilience” based on this study’s content analysis (n = 84).
Many of the findings from the scoping review were mirrored in the content analysis, which was expected due to its nested methodology. Regarding corroboration between the results of the two-step literature review, eight of the top ten subject areas were found in both lists albeit ranked differently. Specifically, climate change, floods, disasters, environmental policy, ecosystems, risk assessment, emergency preparedness, and adaptation were the connected subject areas found in both the scoping review and content analysis. The subject areas infrastructure and environmental protection were found in the scoping review top ten but not in the content analysis. Conversely, the subject areas biological diversity and case studies were present in the content analysis top ten but not in the scoping review. Based on this literature analysis using both a scoping review and content analysis, the term urban infrastructure resilience was found to cross research topics broadly associated with: (i) the natural biogeophysical environment, (ii) environmental planning, management and policy, and (iii) the built environment (Figure 6).
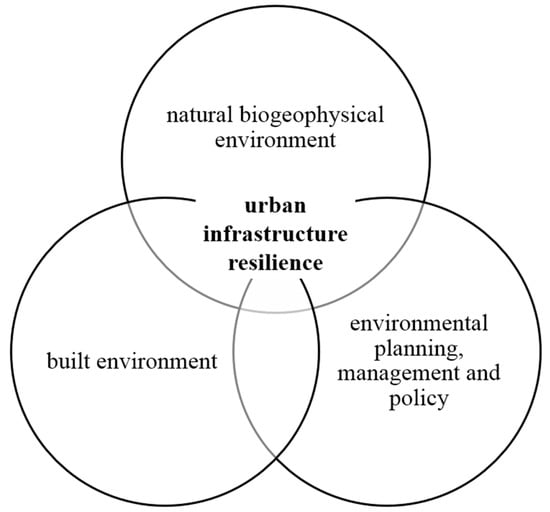
Figure 6.
Venn diagram depicting the scoping and content analysis outputs and themes overlapping with our variable of interest: urban infrastructure resilience.
4. Discussion
4.1. Urban Infrastructure Resilience and Climate Change
Urban infrastructure resilience is a prerequisite for humanity to reach destination sustainability. Akin to the term sustainable development, the concept of urban infrastructure resilience is a necessity but becomes complicated when moving theory into action. The first guiding question in this research article was to define what urban infrastructure resilience is. Answering began by applying a humanistic construct of anatomy function. In doing so, the term urban infrastructure resilience is best compared to the design and function of the human body’s circulatory system. As with the study of blood metrics for providing information on the health and well-being of a person, so should indicators of infrastructure be looked at for providing knowledge about an urban landscape’s function and progress towards sustainability. With this in mind, although there are numerous definitions to draw upon, urban infrastructure resilience can be defined as the ability for the connective network of utilities, structures, equipment, and personnel within a coupled human-environmental ecosystem (e.g., urban landscapes) to be adaptive and operational indefinitely. Similarly, the Climate-Safe Infrastructure Working Group [39] defines climate-safe infrastructure as “infrastructure that is sustainable, adaptive and that meets design criteria that aim for resilience in the face of shocks and stresses caused by the current and future climate.” These definitions address unforeseen but expected shocks and stressors to come from global change; furthermore, they speak to urban infrastructure resilience’s requirement during risk assessments, and makes it prerequisite for successful emergency preparedness and environmental policy-making.
The second guiding research question of this study was to find the most common research topics connected to urban infrastructure resilience. Based on the findings of both the scoping review and content analysis, it was found that urban infrastructure resilience was largely captured by research studies focused on climate change then flooding. It is noteworthy, then, that climate change and flooding are connected to the other research topics; ultimately helping frame urban infrastructure resilience. Further, empirically-based evidence overwhelmingly supports that increases in hurricanes, tropical storms, and flooding are linked to a warming planet. Although commonly accepted as climate change due the ununiformed distribution of climate and weather variables, overall increase in ambient terrestrial and sea temperatures are melting polar ice sheets causing sea levels to rise. With the increase in sea water temperature comes the secondary effect of thermal expansion of liquid, further exacerbating sea-level rise. These increases in sensible and latent heat of course impact the hydrological cycle and thermodynamics, thus causing more erratic and severe weather incidents, producing larger associated natural disasters. Through these highly studied geographical phenomena, Earth’s tropical regions have been expanding poleward taking the intensifying hurricanes, tropical storms, and flooding with them. Paralleling these changes in the biogeophysical system, human population growth and migration to cities in coastal regions has continued across the globe. With these population surges comes the greater need for planning and management of these increasingly complex social-environmental urban systems.
4.2. Planning for Urban Infrastructure Resilience
The third and final guiding research question asked how humanity could further improve urban infrastructure resilience from a sustainable development planning perspective. In order to move theory into practice, sustainable development planning requires applied definitions of “sustainability” and “sustainable development”. Shaker [34] reinterpreted these terms to make them operational by stating: “‘sustainability’ should be viewed as humanity’s target goal of human-ecosystem equilibrium (homeostasis), while ‘sustainable development’ is the holistic approach and temporal processes that lead humanity to its end goal of sustainability” (305). In doing so, resilience (thinking and frameworks) is a stepping-stone for reaching sustainability rather than just in vogue replacement terminology (see [51]). With this in mind, urban infrastructure resilience can be operationalized by attempting to create the inverse of “risk.” Risk is the product of hazard, exposure, and vulnerability, and its evaluation has been driven largely by the insurance industry [52,53]. In recent years there have been a multitude of disruptive events which re-emphasize the need to mitigate risks and to better understand the relationships between infrastructure and climate change in order to strategically cope with these hazards [54]. For specific guidance, the inverse of risk would include reducing or eliminating: inherent dangers associated with climate change and its related and increasing environmental disasters (i.e., heat, landslides, earthquakes, flooding); exposure of the human population, ecological resources, and property to climate change phenomena; and humanity’s susceptibility to harm from exposure to associated environmental and social stresses that come from climate change, population and urban growth synergies. Although urban, regional, and environmental planning have made tremendous progress in establishing resilience against natural disasters in recent decades [55,56], few studies exist that join global change and sustainable development specifically to urban infrastructure resilience. In response, and to supplement this study’s literature review findings, a conceptual diagram was created to illustrate common concepts connecting sustainable development and global change to urban infrastructure resilience (Figure 7).
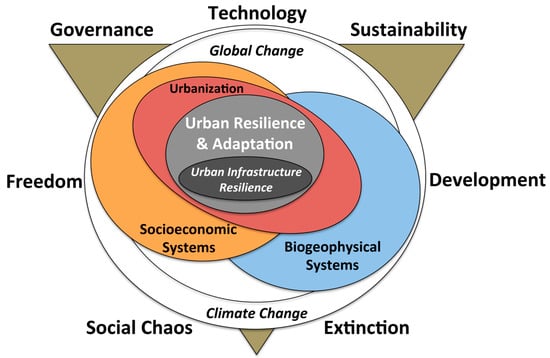
Figure 7.
Diagram of common concepts connecting sustainable development and global change to urban infrastructure resilience.
To be successful at sustainable development at any scale, suitable planning methods, guidelines, and instructions are required. Climate change uncertainties have largely been ignored by planners due to difficulties in integrating adaptive management within the planning process [57]. In order to include urban infrastructure resilience in adaptive planning and governance, some priority areas for sustainable development planners involve understanding how: (i) global change impacts infrastructure function; (ii) urban infrastructure designs and processes impact and/or mitigate climate change; and (iii) policies can improve efficiency through technological advances, and modify human behavior to minimize stress and shock on existing infrastructure. According to Giodarno [57], conducting scenario simulations, quantitative measuring, and evaluating policies will ensure that climate change factors are incorporated into city design. To evaluate progress of planning initiatives towards established goals and benchmarks, and develop sound adaptive management, quantifiable indicators and indices are needed. These tools have been recognized as useful for policy-making [58], yet direct indicators and indices of urban infrastructure resilience remain virtually non-existent. Additionally, indicator-based assessment of landscape function can provide insight on landscape design and function for sustainable development purposes [59]. In such an assessment, Shaker [60] found that increased urban infrastructure density in Moldavian landscapes was a key ingredient for progressing towards sustainability. The future of urban resilience is likely contingent on moving from smart government and smart cities to smarter urbanites, through indicator initiatives and web-based communication tools such as the Notre Dame Global Adaptation Initiative [61]. These new Internet 2.0 tools allow for real time information distribution and data gathering to stakeholders across temporal and spatial scales, while creating a mechanism for real-time adaptive planning and management that has the capacity to modify behaviors towards sustainability [62]. Lastly, information gained from such technology advances must be translated into urban infrastructure resilience strategies if humanity is to ultimately avoid ecosystem extinction and social chaos.
It is increasingly recognized that the resilience of urban infrastructure requires green infrastructure approaches that can reduce the demands and risks on conventional built infrastructure. This approach has been shown to generate a number of co-benefits (e.g., improved air quality) and to be applicable to a number of climate hazards (e.g., flooding) [63,64,65]. There are formal approaches emerging that enable infrastructure designers to formally leverage ecosystem services. For example, the Municipal Natural Assets Initiative in Canada helps municipalities identify, value, and account for natural assets in their financial planning and asset management programs [66]. The resilience of urban infrastructure is increasingly being understood holistically such that grey and green approaches are considered and implemented in concert.
5. Conclusions
“Think globally, act locally.” Climate change impacts will influence cities in ways we are yet to fully understand, thus knowledge creation, education, and preparation are required to build resilience and minimize associated risks. The main goal of this review paper was to elucidate connected research themes, scientific popularity, and conceptual boundaries of the term infrastructure resilience in an urban context within Western World countries. Although urban infrastructure resilience was theoretically apparent, its terminology, connected research themes, and conceptual boundaries remained obscure within the literature due to a lack of systematic review. In response, this paper applied a two-step method consisting of a scoping review and a content analysis to synthesize literature from a sustainable development planning perspective. The scoping review reduced documents to a sample size of 535, while content analysis further condensed it to 84 articles across three journals. Broadly the results of this two-step literature analysis revealed that the term urban infrastructure resilience crosses research topics associated with: (i) the natural biogeophysical environment, (ii) environmental planning, management and policy, and (iii) the built environment. To reiterate, the findings from the two techniques corroborated that eight connected subject areas help to establish the conceptual boundaries of urban infrastructure resilience. Those eight connected research areas were: (1) climate change, (2) floods, (3) disasters, (4) environmental policy, (5) ecosystems, (6) risk assessment, (7) emergency preparedness, and (8) adaptation. The two connected research topics, climate change and floods, captured most of the indirect scientific popularity of urban infrastructure resilience.
While connected concepts of urban infrastructure resilience have been found in the literature, it remains difficult to investigate and apply concepts because resilience practices are specific to individual planning and management agendas [67]. Nevertheless, it is true to state that climate change is posing significant challenges to our aging infrastructure and, in turn, our cities [57]. Note that the results do not uncover the exact research needed for building urban infrastructure resilience, which is seen as a fertile area of resilience research moving forward. Future literature analyses of urban infrastructure resilience could tackle the needed but arduous task of summarizing key issues and priority research topics. Further, although this study focused on developed nations, forthcoming research should undoubtedly consider infrastructure resilience in developing countries as they are often undervalued and underassessed [68]. It was established in this paper that urban infrastructure resilience is an important research topic, and will remain a vital ingredient for creating sustainable communities in our rapidly changing world. Given the importance of infrastructure to the well-being of people living in cities [38,62], direct effort regarding related topics should be continued by others. To conclude, it is hoped that this research will serve as an important step in stimulating interdisciplinary dialog for further understanding the importance of urban infrastructure resilience when creating sustainable cities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R.S. and C.B.; Data curation, V.P. and S.A.; Formal analysis, V.P. and S.A.; Funding acquisition, R.R.S. and C.B.; Investigation, R.R.S. and G.R.; Methodology, V.P. and S.A.; Scoping review screeners, V.P. and S.A.; Project administration, R.R.S.; Visualization, V.P., S.A. and R.R.S.; Writing—original draft, R.R.S., G.R. and V.P.; Writing—review and editing, R.R.S., G.R., C.B., and V.P.
Funding
This research was funded by the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC) of Canada, grant number 421-2015-1037. Ryerson University provided additional research support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Tignor, M.M.B.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P.M. Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Donat, M.G.; Mueller, B.; Alexander, L.V. No pause in the increase of hot temperature extremes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, A.; Carlson, A.E.; Long, A.J.; Milne, G.A.; Clark, P.U.; DeConto, R.; Horton, B.P.; Rahmstorf, S.; Raymo, M.E. Sea-level rise due to polar ice-sheet mass loss during past warm periods. Science 2015, 349, aaa4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butchart, S.H.M.; Walpole, M.; Collen, B.; van Strien, A.; Scharlemann, J.P.W.; Almond, R.E.A.; Baillie, J.E.M.; Bomhard, B.; Brown, C.; Bruno, J.; et al. Global Biodiversity: Indicators of Recent Declines. Science 2010, 328, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, G.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Barnosky, A.D.; García, A.; Pringle, R.M.; Palmer, T.M. Accelerated modern human–induced species losses: Entering the sixth mass extinction. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceballos, G.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Dirzo, R. Biological annihilation via the ongoing sixth mass extinction signaled by vertebrate population losses and declines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6089–E6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinzettel, J.; Hertwich, E.G.; Peters, G.P.; Steen-Olsen, K.; Galli, A. Affluence drives the global displacement of land use. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rands, M.R.W.; Adams, W.M.; Bennun, L.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Clements, A.; Coomes, D.; Entwistle, A.; Hodge, I.; Kapos, V.; Scharlemann, J.P.W.; et al. Biodiversity conservation: Challenges beyond 2010. Science 2010, 329, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, R.R. The well-being of nations: An empirical assessment of sustainable urbanization for Europe. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2015, 22, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin, F.S., III; Lambin, E.F.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; et al. A safe operating space for humanity. Nature 2009, 461, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Gaffney, O.; Rockström, J.; Öhman, M.C.; Shyamsundar, P.; Steffen, W.; Glaser, G.; Kanie, N.; Noble, I. Sustainable development goals for people and planet. Nature 2013, 495, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Bank. Ending Poverty and Sharing Prosperity; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 1–244. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Urban sustainability: An inevitable goal of landscape research. Landsc. Ecol 2010, 25, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, P.; Kinzig, A. Nature in the Metropolis. Science 2005, 308, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. World Population Prospects: The 2015 Revision; Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations; Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Urbanization Prospects, the 2014 Revision: Highlights; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-92-1-056809-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gerland, P.; Raftery, A.E.; Ševčíková, H.; Li, N.; Gu, D.; Spoorenberg, T.; Alkema, L.; Fosdick, B.K.; Chunn, J.; Lalic, N.; et al. World population stabilization unlikely this century. Science 2014, 346, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batty, M. When all the word’s a city. Environ. Plan. A 2011, 43, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M. Advances in Urban Ecology: Integrating Humans and Ecological Processes in Urban Ecosystems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-387-75509-0. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.G.; Gardner, R.H. Landscape Ecology in Theory and Practice: Pattern and Process, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4939-2793-7. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, R.T.T.; Wu, J. Where to put the next billion people. Nat. News 2016, 537, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, S.; Moench, M. A framework for urban climate resilience. Clim. Dev. 2012, 4, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panarchy: Understanding Transformations in Human and Natural Systems; Gunderson, L.H., Holling, C.S., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-1-55963-856-2. [Google Scholar]
- Navigating Social-Ecological Systems: Building Resilience for Complexity and Change; Berkes, F., Ed.; Digitally print. version.; Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-521-06184-1. [Google Scholar]
- Folke, C. Resilience: The emergence of a perspective for social–ecological systems analyses. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2006, 16, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adger, W.N. Vulnerability. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2006, 16, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dietz, T.; Carpenter, S.R.; Alberti, M.; Folke, C.; Moran, E.; Pell, A.N.; Deadman, P.; Kratz, T.; Lubchenco, J.; et al. Complexity of Coupled Human and Natural Systems. Science 2007, 317, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutter, S.L. The landscape of disaster resilience indicators in the USA. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Shaker, R.R.; Das, R. A review of approaches for monitoring and evaluation of urban climate resilience initiatives. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P.; Stults, M. Defining urban resilience: A review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 147, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Successful Adaptation to Climate Change: Linking Science and Policy in a Rapidly Changing World; Moser, S.C., Boykoff, M.T., Eds.; Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-415-52499-5. [Google Scholar]
- Maru, Y.T.; Stafford Smith, M.; Sparrow, A.; Pinho, P.F.; Dube, O.P. A linked vulnerability and resilience framework for adaptation pathways in remote disadvantaged communities. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 28, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, S. The End of Population Growth—Project Syndicate. Available online: https://www.project-syndicate.org/commentary/the-end-of-population-growth?barrier=accesspaylog (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Shaker, R.R. The spatial distribution of development in Europe and its underlying sustainability correlations. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, M.; Marvin, S. Can cities shape socio-technical transitions and how would we know if they were? Res. Policy 2010, 39, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, H.; Steinberger, J.K. Reducing energy and material flows in cities. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2010, 2, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäffler, A.; Swilling, M. Valuing green infrastructure in an urban environment under pressure—The Johannesburg case. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 86, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, M.; Bolbocean, O.; McNally, M.; Conroy, M.; Bednarczuk, D.; Hyland, F.; Coyne, E.; Marie, C. “Howya gettin’ on?” Investigating Public Transport Satisfaction Levels in Galway, Ireland. Urban Sci. 2018, 2, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate-Safe Infrastructure Working. Paying It Forward: The Path Toward Climate-Safe Infrastructure In California; Strategic Growth Council: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–257. [Google Scholar]
- Amec Foster Wheeler Environment & Infrastructure; Credit Valley Conservation. Infrastructure and Buildings Working Group—Adaptation State of Play Report; Canada’s Climate Change Adaptation Platform, Infrastructure and Buildings Working Group: Ottawa, ON, Cannada, 2017; pp. 1–178. [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm, G. The Implementation of Green Infrastructure: Relating a General Concept to Context and Site. Sustainability 2017, 9, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorn, N. How can resilient infrastructures contribute to social justice? Preface to the special issue of sustainable and resilient infrastructure on resilience infrastructures and social justice. Sustain. Resilient Infrastruct. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H.; McInerney, P.; Parker, D.; Soares, C.B. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Yamagata, Y. Resilient Urban Planning: Major Principles and Criteria. Energy Procedia 2014, 61, 1491–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.P. Hilcc. J. Internet Cat. 2002, 5, 19–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.P. Basic Content Analysis, 2nd ed.; Sage University Papers Series; Sage Publications: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1990; ISBN 978-0-8039-3863-2. [Google Scholar]
- Antrop, M. The language of landscape ecologists and planners: A comparative content analysis of concepts used in landscape ecology. Land Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 55, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krippendorff, K. Content Analysis: An Introduction to its Methodology; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-5063-9566-1. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, M.H.; Craig, R.K. The End of Sustainability. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2014, 27, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, D. Role of Insurance in Reducing Flood Risk. Geneva Pap. Risk Insur. 2008, 33, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, D. The risk triangle. In Natural Disaster Management; Tudor Rose Holdings: Leicester, UK, 1999; pp. 102–103. [Google Scholar]
- Achour, N.; Miyajima, M.; Pascale, F.; DFPrice, A. Hospital resilience to natural hazards: Classification and performance of utilities. Disaster Prev. Manag. 2014, 23, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, J. From fail-safe to safe-to-fail: Sustainability and resilience in the new urban world. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.E.; McDaniels, T.; Fox, J.; Dhariwal, R.; Longstaff, H. Toward Disaster-Resilient Cities: Characterizing Resilience of Infrastructure Systems with Expert Judgments. Risk Anal. 2014, 34, 416–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, T. Adaptive planning for climate resilient long-lived infrastructures. Util. Policy 2012, 23, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.L. Strengths and weaknesses of common sustainability indices for multidimensional systems. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mander, Ü.; Uuemaa, E. Landscape assessment for sustainable planning. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, R.R. Examining sustainable landscape function across the Republic of Moldova. Habitat Int. 2018, 72, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ND-GAIN Country Index // Notre Dame Global Adaptation Initiative // University of Notre Dame. Available online: https://gain.nd.edu/our-work/country-index/ (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Rybarczyk, G.; Banerjee, S.; Starking-Szymanski, M.D.; Shaker, R.R. Travel and us: The impact of mode share on sentiment using geo-social media and GIS. J. Locat. Based Serv. 2018, 12, 40–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, A.; Castillo-Salgado, C. Health Co-Benefits of Green Building Design Strategies and Community Resilience to Urban Flooding: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šakić Trogrlić, R.; Rijke, J.; Dolman, N.; Zevenbergen, C. Rebuild by Design in Hoboken: A Design Competition as a Means for Achieving Flood Resilience of Urban Areas through the Implementation of Green Infrastructure. Water 2018, 10, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, G.D.; Parker, J. Data for an Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA) of a Public Green Infrastructure and Urban Nature Space in Perth, Western Australia. Data 2018, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, S.J.; Cairns, S. Defining and Scoping Municipal Natural Assets; Making Nature Count: Report; Municipal Natural Assets Initiative, 2017; pp. 1–14. Available online: https://www.assetmanagementbc.ca/wp-content/uploads/definingscopingmunicipalnaturalcapital-final-15mar2017.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Opdyke, A.; Javernick-Will, A.; Koschmann, M. Infrastructure hazard resilience trends: An analysis of 25 years of research. Nat. Hazards 2017, 87, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, J.; Bonzanigo, L.; Nicolas, C. Improving Infrastructure Resilience in Developing Countries. Oxf. Handb. Plan. Clim. Chang. Hazards 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).