Land-Cover Change Analysis and Simulation in Conakry (Guinea), Using Hybrid Cellular-Automata and Markov Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Image Processing
2.4. Image Classification
2.5. Accuracy Assessment of the Land-Cover Classification
2.6. Future Land-Cover Change Based on CA-Markov Chain
3. Results
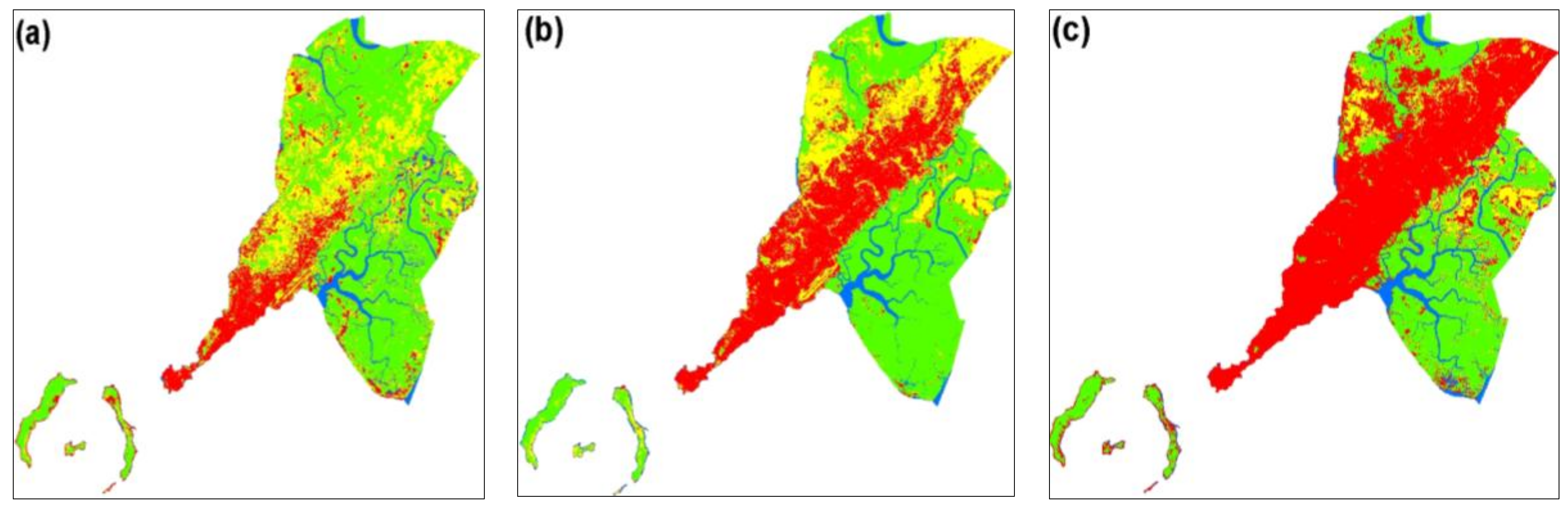
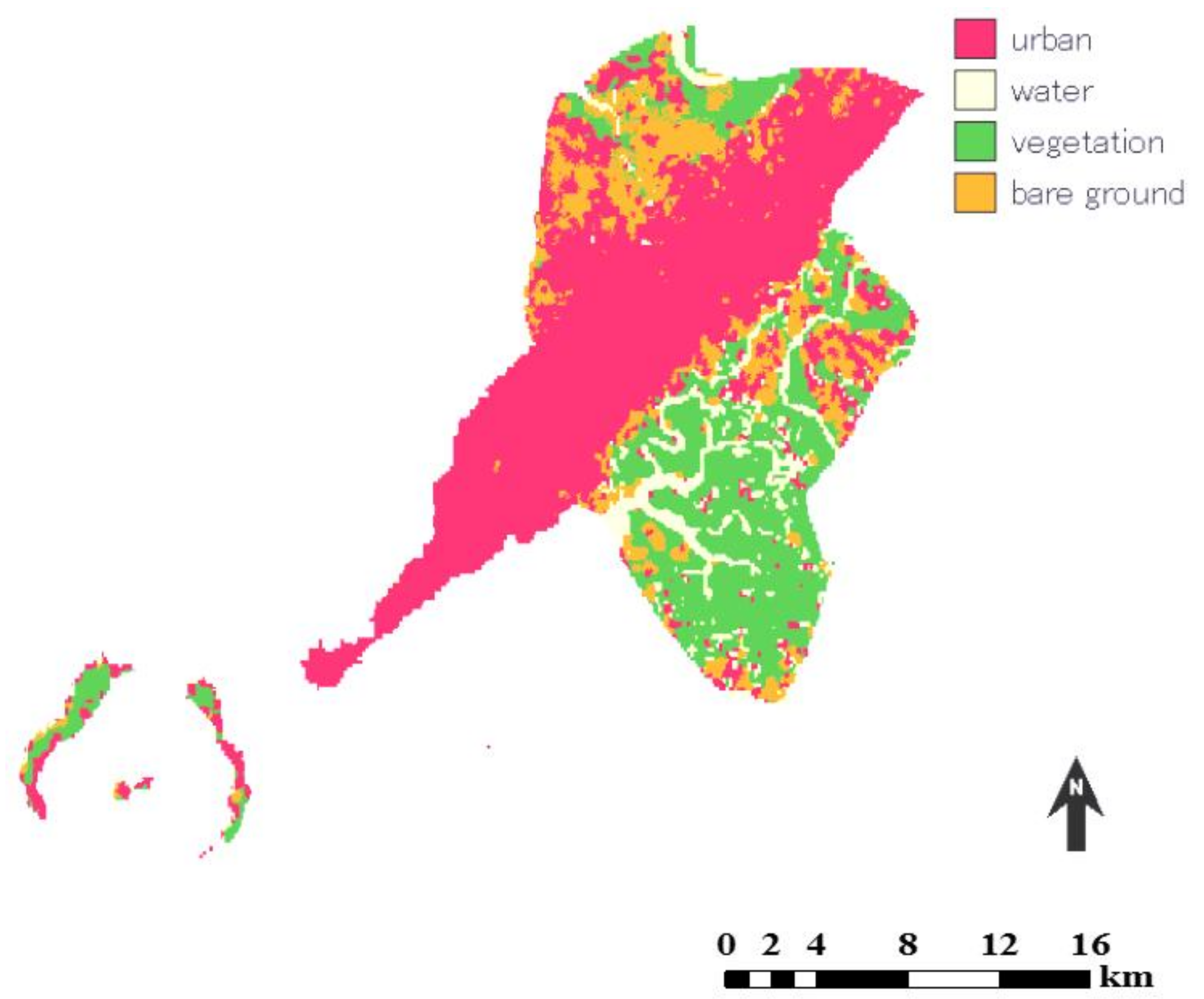
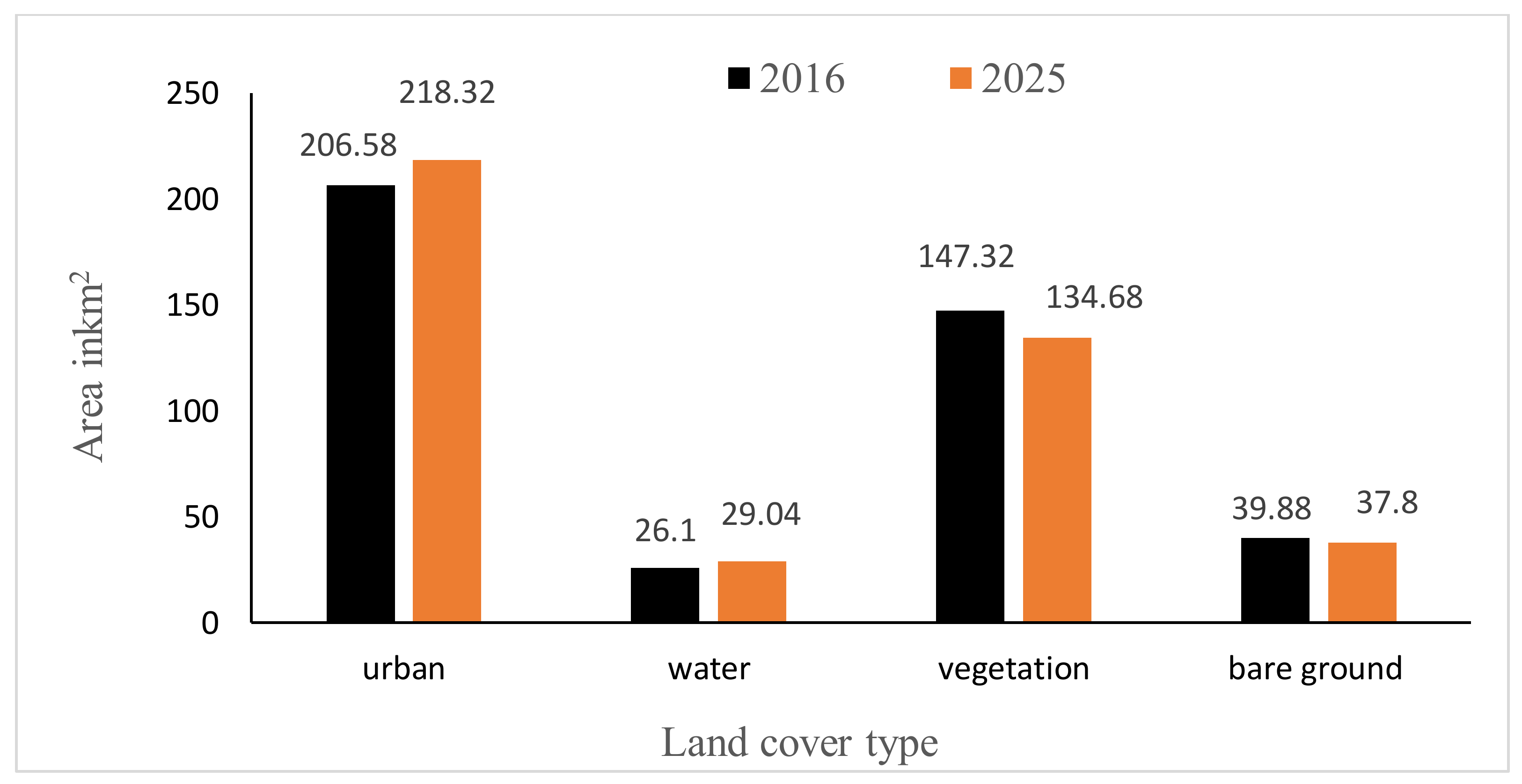
3.1. Land-Cover Classification
3.2. Markov models and the transition probability matrices
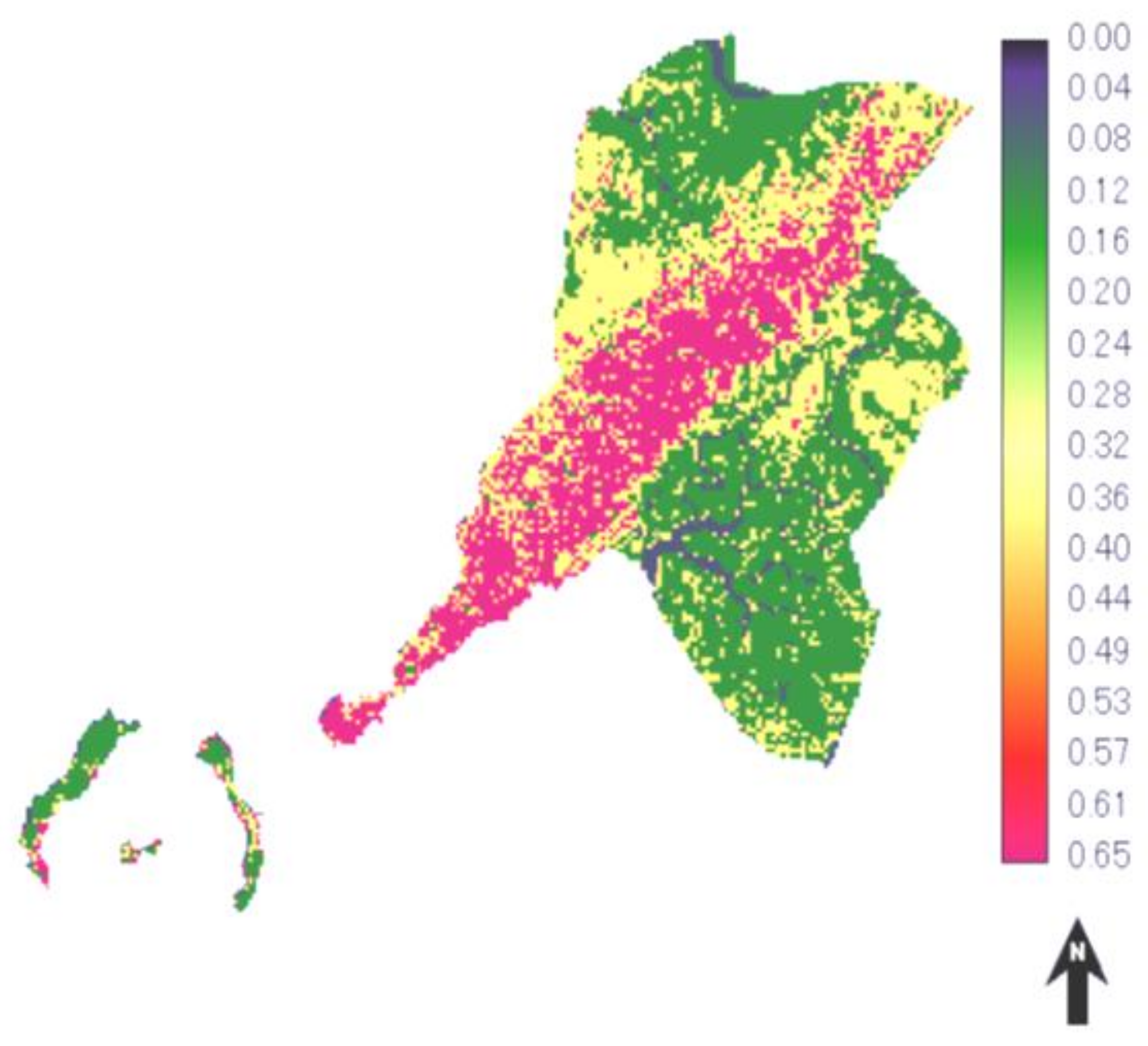
3.3. Accuracy Assessment of the Simulated Markov Model Based on ROC
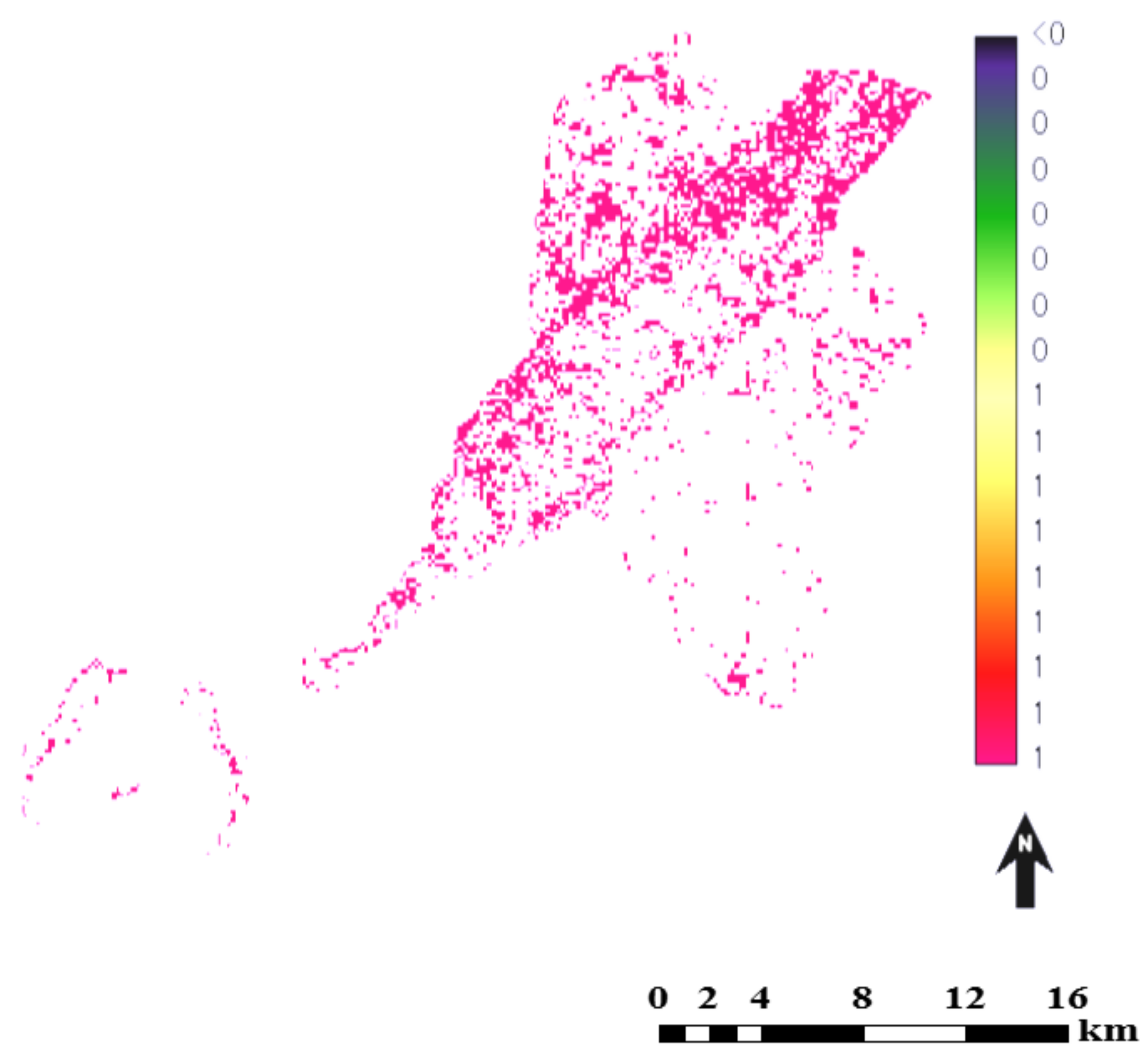
3.4. Simulated Land-Cover Map of Conakry by 2025 Based on CA-Markov Model
4. Discussion
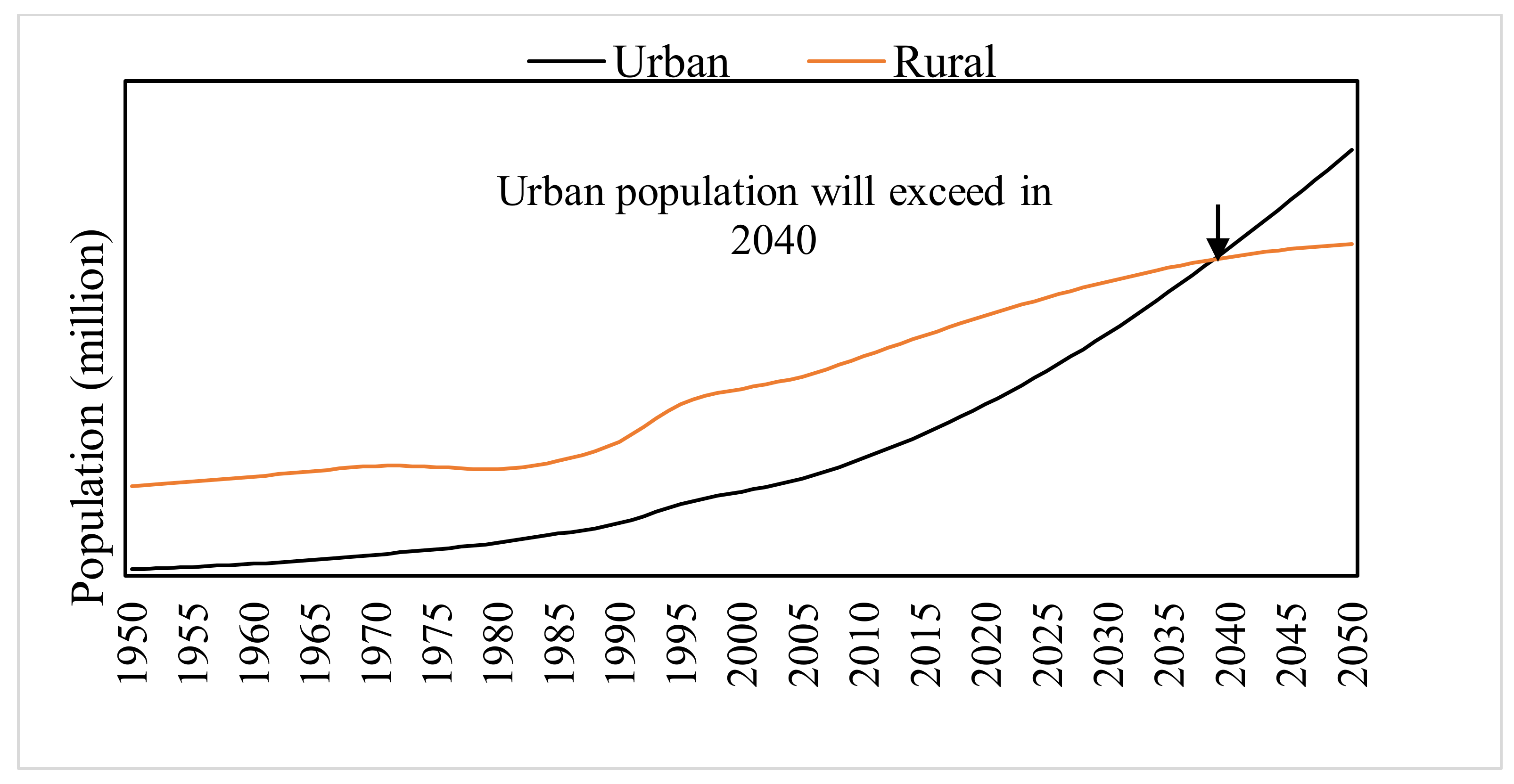
Land-Cover Change and Demographic Dynamics in Conakry
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Reference Image | User’s Accuracy (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classified Image | Urban | Water | Vegetation | Bare Ground | Total Row | |
| Urban | 48 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 58 | 83 |
| Water | 2 | 39 | 4 | 3 | 48 | 81 |
| Vegetation | 4 | 3 | 45 | 2 | 54 | 83 |
| Bare ground | 6 | 3 | 1 | 30 | 40 | 75 |
| Total column | 60 | 48 | 53 | 39 | 200 | |
| Producer’s accuracy(%) | 80 | 81 | 85 | 77 | ||
| Overall accuracy: | 0.81 | |||||
| Kappa coefficient | 0.75 | |||||
| Reference Image | User’s Accuracy (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classified Image | Urban | Water | Vegetation | Bare Ground | Total Row | |
| Urban | 46 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 59 | 78 |
| Water | 3 | 38 | 2 | 3 | 46 | 83 |
| Vegetation | 3 | 2 | 39 | 7 | 51 | 76 |
| Bare ground | 1 | 3 | 5 | 35 | 44 | 80 |
| Total column | 53 | 46 | 51 | 50 | 200 | |
| Producer’s accuracy (%) | 87 | 83 | 76 | 70 | ||
| Overall accuracy | 0.79 | |||||
| Kappa coefficient | 0.72 | |||||
| Reference Image | User’s Accuracy (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classified Image | Urban | Water | Vegetation | Bare Ground | Row Total | |
| Urban | 49 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 54 | 91 |
| Water | 2 | 42 | 2 | 1 | 47 | 89 |
| Vegetation | 3 | 2 | 45 | 2 | 52 | 87 |
| Bare ground | 2 | 3 | 2 | 40 | 47 | 85 |
| Total column | 56 | 49 | 50 | 45 | 200 | |
| Producer’s accuracy (%) | 88 | 86 | 90 | 89 | ||
| Overall accuracy | 0.88 | |||||
| Kappa coefficient | 0.83 | |||||
References
- Ouedraogo, I. Land Use Dynamics and Demographic Change in Southern Burkina Faso. Available online: https://pub.epsilon.slu.se/2355/1/Ouedrago_I_100928.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2018).
- Subasinghe, S.; Estoque, R.; Murayama, Y. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Urban Growth Using GIS and Remote Sensing: A Case Study of the Colombo Metropolitan Area, Sri Lanka. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbanie, S.P.; Griffin, A.L.; Thornton, A. Impacts on the urban environment: Land cover change trajectories and landscape fragmentation in post-war Western Area, Sierra Leone. Remote Sens. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.I.; Duker, A.; Conrad, C.; Thiel, M.; Ahmad, H.S. Analysis of settlement expansion and urban growth modelling using geoinformation for assessing potential impacts of urbanization on climate in Abuja City, Nigeria. Remote Sens. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Guneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Pu, Z. Urbanization and Its Effects on Industrial Pollutant Emissions: An Empirical Study of a Chinese Case with the Spatial Panel Model. Sustainability 2016, 8, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B. Turner II Human Population Growth and Global Land-Use/Cover Change. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1992, 23, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddle, B. Urbanization and Inequality/Poverty. Urban Sci. 2017, 1, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobigny, G.; Gauthier, P.; Houéménou, G.; Choplin, A.; Dossou, H.-J.; Badou, S.; Etougbétché, J.; Bourhy, P.; Koffi, S.; Durski, K.; et al. Leptospirosis and Extensive Urbanization in West Africa: A Neglected and Underestimated Threat? Urban Sci. 2018, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WoldeYohannes, A.; Cotter, M.; Kelboro, G.; Dessalegn, W. Land Use and Land Cover Changes and Their Effects on the Landscape of Abaya-Chamo Basin, Southern Ethiopia. Land 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: Using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traore, A.; Watanabe, T. Modeling Determinants of Urban Growth in Conakry, Guinea: A Spatial Logistic Approach. Urban Sci. 2017, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.W.; Shen, G.Q.; Wang, H.; Hong, J. Simulating land use change in urban renewal areas: A case study in Hong Kong. Habitat Int. 2015, 46, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafizadeh Moghadam, H.; Helbich, M. Spatiotemporal urbanization processes in the megacity of Mumbai, India: A Markov chains-cellular automata urban growth model. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 40, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbick, N.; Chowdhury, D.; Salas, W.; Qi, J. Monitoring Rice Agriculture across Myanmar Using Time Series Sentinel-1 Assisted by Landsat-8 and PALSAR-2. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, F.; Delavar, M.; Pijanowski, B. Urban Growth Modeling Using Cellular Automata with Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Images Calibrated by the Artificial Bee Colony Optimization Algorithm. Sensors 2016, 16, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, L.; Tang, L.; Cui, S.; Yin, K. Simulating urban growth using the SLEUTH model in a coastal peri-urban district in China. Sustainability 2014, 6, 3899–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Poverty and Urban Mobility in Conakry. Available online: http://www.gtkp.com/assets/ uploads/20091127-171237-6675-Conakry_en.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2018).
- African Economic Outlook 2017; African Economic Outlook; OECD Publishing: Ogdensburg, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 9789264274259.
- The World Bank. Guinea—Conakry Urban Development Project; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Sylla, L.; Xiong, D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Bangoura, S.T. A GIS technology and method to assess environmental problems from land use/cover changes: Conakry, Coyah and Dubreka region case study. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2012, 15, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, Y.; Kamusoko, C.; Yamashita, A.; Estoque, R.C. Urban Development in Asia and Africa; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-981-10-3240-0. [Google Scholar]
- Collier, P. African urbanization: An analytic policy guide. Oxf. Rev. Econ. Policy 2017, 33, 405–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmadi, K.; Heppenstall, A.; See, L.; Hogg, J. Modeling Urban Growth Dynamics using Cellular Automata and GIS. In Proceedings of the Third National GIS Symposium, Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia, 7–9 April 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Institut National de la Statistique—Stat-Guinee.org. Available online: http://www.stat-guinee.org/ (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Goerg, O. Couper la Guinée en quatre ou comment la colonisation a imaginé l’Afrique. Vingtième Siècle. Revue d’histoire 2011, 111, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, R.; Odeh, I.O.A.; Ancev, T. Improving the Accuracy of Land Use and Land Cover Classification of Landsat Data Using Post-Classification Enhancement. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.B.; Murayama, Y. Drivers of urban growth in the Kathmandu valley, Nepal: Examining the efficacy of the analytic hierarchy process. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivanit, M.; Hokao, K.; Phonekeo, V. Assessing the Impact of Urbanization on Urban Thermal Environment: A Case Study of Bangkok Metropolitan. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 243–256. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Gong, P. Comparison of classification algorithms and training sample sizes in urban land classification with landsat thematic mapper imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 964–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Quegan, S. Comparative analysis of supervised and unsupervised classification on multispectral data. Appl. Math. Sci. 2013, 7, 3681–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.R. IDRISI Selva Tutorial. In Idrisi Production; Clark Labs-Clark University: Worcester, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 45, pp. 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Rwanga, S.S.; Ndambuki, J.M. Accuracy Assessment of Land Use/Land Cover Classification Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Int. J. Geosci. 2017, 8, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgee, J.; Campbell, J.; Parece, T. Remote Sensing in an ArcMap Environment. Available online: http://virginiaview.cnre.vt.edu/tutorial/RS_in_ArcGIS_AllChapters.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2018).
- Vázquez-Quintero, G.; Solís-Moreno, R.; Pompa-García, M.; Villarreal-Guerrero, F.; Pinedo-Alvarez, C.; Pinedo-Alvarez, A. Detection and Projection of Forest Changes by Using the Markov Chain Model and Cellular Automata. Sustainability 2016, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, O.; Zhao, S.; Osman, T.; Salheen, M.; Eid, Y. Applying a Hybrid Model of Markov Chain and Logistic Regression to Identify Future Urban Sprawl in Abouelreesh, Aswan: A Case Study. Geosciences 2016, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braimoh, A.K.; Vlek, P.L.G. Land-Cover Dynamics in an Urban Area of Ghana. Earth Interact. 2004, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsanjani, J.J.; Helbich, M.; Kainz, W.; Boloorani, A.D. Integration of logistic regression, Markov chain and cellular automata models to simulate urban expansion. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 21, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Phinn, S. Developing a cellular automaton model of urban growth incorporating fuzzy set approaches. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on GeoComputation, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 24–26 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, G.; Moura, A.C.M. Land Cover projection based on Chain Markov and Cellular Automata: Case study of Pampulha Land Cover projection based on Chain Markov and Cellular. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Changing Cities II: Spatial, Design, Landscape & Socio-Economic Dimensions, Porto Heli, Greece, 22–26 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hensher, D.A.; Johnson, L.W. Applied Discrete Choice Modelling. 1981. Available online: https://trid.trb.org/view.aspx?id=1206392 (accessed on 23 March 2018).
- Pontius, R.G.; Schneider, L.C. Land-cover change model validation by an ROC method for the Ipswich watershed, Massachusetts, USA. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddighi Balde, B.; Kobayashi, H.; Matsumura, I.; Esham, M.; Alam, A.; Tolno, E. Land Use Change and their Determinants in the Coastal Area of Guinea: A Study based on Spatial Analysis and Field Survey. J. Jpn. Agric. Syst. Soc. 2014, 30, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Archondo-callao, R.; Region, A.; Bank, T.W. Sub-Saharan Africa Transport Policy Program; Annual Report; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, S.; Fik, T.; Dwivedi, P. Proximate Causes of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change in Bannerghatta National Park: A Spatial Statistical Model. Forests 2017, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, S.; Saklani, A. Urban sprawl modeling using cellular automata. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2014, 17, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimal, B.; Zhang, L.; Keshtkar, H.; Wang, N.; Lin, Y. Monitoring and Modeling of Spatiotemporal Urban Expansion and Land-Use/Land-Cover Change Using Integrated Markov Chain Cellular Automata Model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Jin, B.X.; Wei, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.L. Using Ca-Markov Model to Model the Spatiotemporal Change of Land Use/Cover in Fuxian Lake for Decision Support. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Majedi, H.; Monavari, S.; Alesheikh, A.; Kheirkhah Zarkesh, M. Dynamic Simulation of Urban Expansion Based on Cellular Automata and Logistic Regression Model: Case Study of the Hyrcanian Region of Iran. Sustainability 2016, 8, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koranteng, A.; Zawila-Niedzwiecki, T. Modelling forest loss and other land use change dynamics in Ashanti Region of Ghana. Folia For. Pol. 2015, 57, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manuschevich, D.; Beier, C.M. Simulating land use changes under alternative policy scenarios for conservation of native forests in south-central Chile. Land Use Policy 2016, 51, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dams, J.; Woldeamlak, S.T.; Batelaan, O. Predicting land-use change and its impact on the groundwater system of the Kleine Nete catchment, Belgium. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 1369–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrosa, J.J.; Zipperer, W.C.; Andreu, M.G. Projecting Land-Use and Land Cover Change in a Subtropical Urban Watershed. Urban Sci. 2018, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.-F.; Tsou, K.-W. Modeling and simulation of the future impacts of urban land use change on the natural environment by SLEUTH and cluster analysis. Sustainability 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

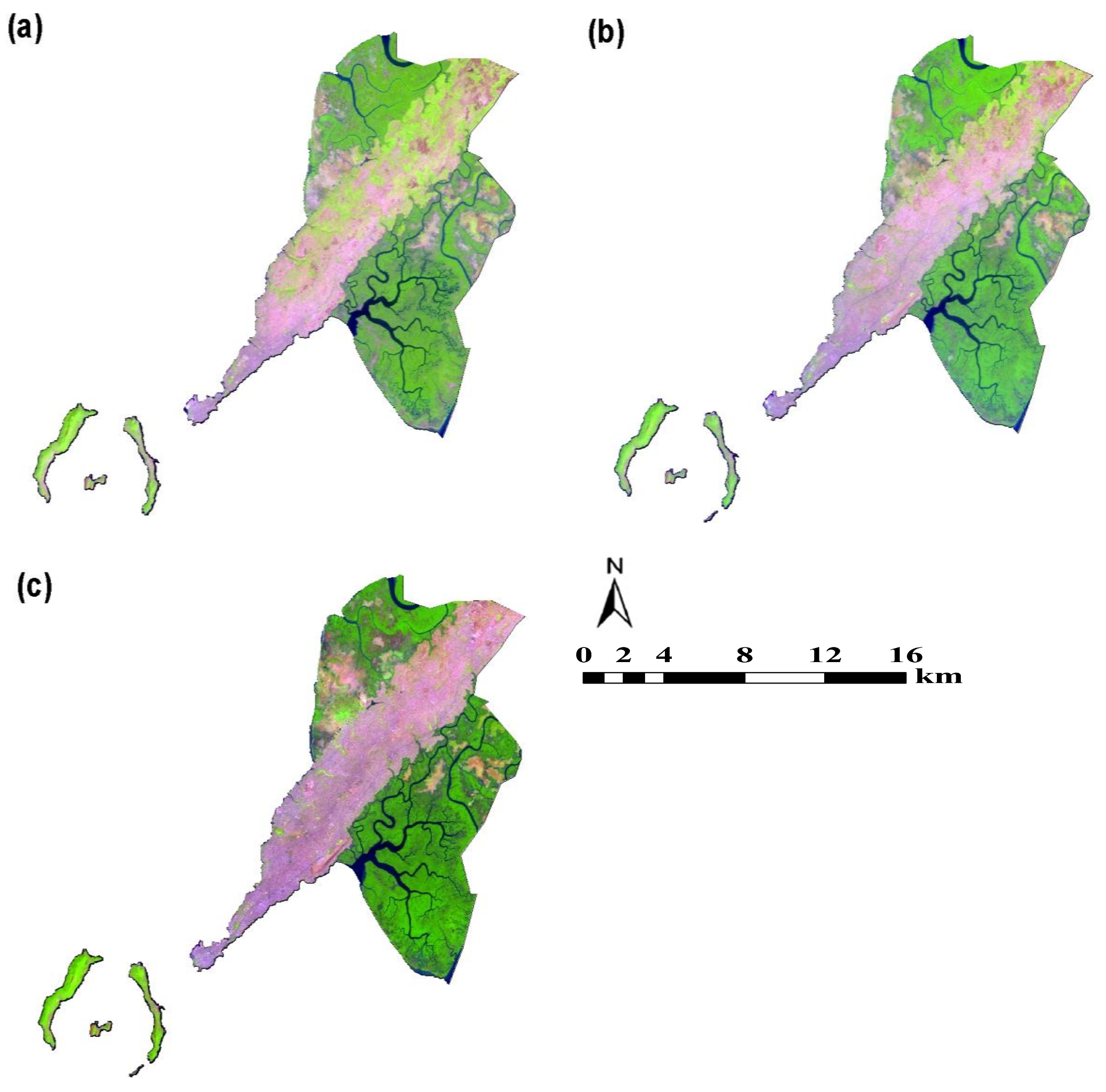


| Satellite | Sensor | Path/Row | Spatial Resolution | Date of Acquisition | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 5 | TM | 202/53 | 30 m | 01/03/1986 | USGS |
| Landsat 7 | ETM+ | 202/53 | 30 m | 12/19/2000 | USGS |
| Landsat 8 | OLI | 202/53 | 30 m | 01/20/2016 | USGS |
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Urban | Residential, commercial, industrial, transportation, utilities, communication etc. |
| Water | Rivers, lakes, ponds, reservoirs, and other water bodies |
| Vegetation | Mangrove forests, high vegetation, reserved forest, non-reserved forest |
| Bare ground | Fallow land, bare exposed, parks, shrubs, area and transition |
| Probability of Transition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From/To | Urban | Water | Vegetation | Bare Ground | Total |
| urban | 0.936 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.063 | 1.000 |
| water | 0.016 | 0.862 | 0.108 | 0.011 | 1.000 |
| vegetation | 0.326 | 0.096 | 0.459 | 0.117 | 1.000 |
| bare ground | 0.127 | 0.051 | 0.000 | 0.821 | 1.000 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Traore, A.; Mawenda, J.; Komba, A.W. Land-Cover Change Analysis and Simulation in Conakry (Guinea), Using Hybrid Cellular-Automata and Markov Model. Urban Sci. 2018, 2, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci2020039
Traore A, Mawenda J, Komba AW. Land-Cover Change Analysis and Simulation in Conakry (Guinea), Using Hybrid Cellular-Automata and Markov Model. Urban Science. 2018; 2(2):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci2020039
Chicago/Turabian StyleTraore, Arafan, John Mawenda, and Atupelye Weston Komba. 2018. "Land-Cover Change Analysis and Simulation in Conakry (Guinea), Using Hybrid Cellular-Automata and Markov Model" Urban Science 2, no. 2: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci2020039
APA StyleTraore, A., Mawenda, J., & Komba, A. W. (2018). Land-Cover Change Analysis and Simulation in Conakry (Guinea), Using Hybrid Cellular-Automata and Markov Model. Urban Science, 2(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci2020039







