Abstract
The historical and cultural significance of artistic works and archaeological artifacts underscores the imperative use of non-destructive testing methods in cultural heritage objects. Analyzing pigments in artwork poses a specific analytical challenge that demands a combination of various techniques to accurately determine chemical compositions. In this context, our work focused on the multi-analytical characterization of samples derived from fragments of a Roman-era Egyptian mummy named Kherima, dating back to around 200 AD. To identify the layers and elemental composition of the pigments used in the decoration, various techniques were employed: X-ray microfluorescence (µXRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), high-resolution optical microscopy (OM), and X-ray computed microtomography (microCT). This multi-analytical approach facilitated the identification of the original pigments in the analyzed mummy fragments, along with insights into the materials used in the ground layer and the techniques applied in artifact manufacturing, indicating their accordance with the historical period and region to which they originally belonged.
1. Introduction
The Napoleonic invasions and European colonial expansion in the 18th and 19th centuries increased Western interest in Egyptian mummies, leading to their commercialization [1]. In 1826, a shipment of Egyptian artifacts, including the mummy Kherima, was controversially auctioned in Rio de Janeiro, where it was acquired by Emperor Dom Pedro I [2,3,4]. Kherima became part of the National Museum’s collection, but much of the museum, including Kherima, was destroyed in a 2018 fire. This study analyzes the remaining samples of Kherima, now the last evidence of the mummy.
Kherima’s embalming technique, involving the individual wrapping of limbs and fingers, is unique compared to the mummification practices in Egypt’s Dakhleh Oasis during the Late Ptolemaic–Roman Period [5] and the composite mummies from Ismant el-Kharab [6]. These distinctions underscore the singularity of Kherima’s method in the context of ancient funerary practices.
To achieve a deeper understanding of unique practices and artifacts, this study emphasizes the importance of non-destructive testing methods. These techniques are essential for the examination of art and archaeological objects, as they enable researchers to analyze the materials, manufacturing technologies, and cultural interactions embodied in these artifacts [7,8]. Additionally, analyzing the composition of these objects is crucial for their conservation and preservation, particularly given the sensitivity of certain materials to environmental factors [9,10]. The accurate identification of pigments and pictorial layers often necessitates the use of multiple analytical techniques, highlighting the need for non-destructive or minimally invasive methods [11]. Non-destructive methods, which do not require the removal of samples from the object and leave it in its original state, allow for the re-analysis of the entire object or its parts with other techniques if further examination is needed [12,13,14]. These approaches prevent damage or alteration, ensuring that artifacts remain intact for future study and public display. Furthermore, they allow researchers to obtain detailed information without compromising the integrity of rare or fragile items.
In cultural heritage research, non-destructive X-ray techniques, such as XRF and XRD, are extensively employed for elemental analysis and crystalline structure characterization, respectively [7,15,16,17,18]. When combined with Raman spectroscopy and FTIR, these methods offer critical insights into the chemical bonds, phases, and both crystalline and molecular structures of archaeological materials [19,20,21,22]. Additionally, X-ray imaging techniques, including radiography and computed tomography (CT), facilitate the non-invasive examination of the internal structures of artifacts [23,24,25,26,27]. The integration of these techniques enables a thorough understanding of both the elemental composition [28] and the structural properties of materials [29,30,31,32,33,34], significantly contributing to the preservation and historical analysis of cultural heritage objects.
Various studies highlighted demonstrate the significant progress made in analyzing and understanding the composition and preservation of Egyptian artifacts through advanced analytical techniques. The authors of [35] emphasized the need for further exploration of rare pigments and the impact of conservation practices, while [36] underscored the importance of a broader, multi-technique approach to fully comprehend preservation processes in ancient mummies. The authors of [37] successfully identified key materials used in ancient Egyptian paintings, though their reliance on X-ray techniques suggests the potential for complementary methods to enhance findings. The authors of [38] provided a detailed analysis of cartonnage layers, identifying various pigments and binders, contributing valuable insights into the materials used. The authors of [22] effectively distinguished between original and restored pigments on a 21st Dynasty coffin, illustrating the importance of non-invasive techniques in restoration studies. Finally, [39] advanced the understanding of cartonnage stratigraphy and pigment composition through multispectral analysis. Additionally, [40] utilized a multi-analytical approach to study pigments from a Late Dynastic Period sarcophagus cover, demonstrating the effectiveness of combining SEM-EDXS, ATR-FTIR, Raman spectroscopy, and VIL to thoroughly understand pigment composition and detect organic binders. Collectively, these studies underscore the need for continued research using a diverse range of analytical methods to further unravel the complexities of ancient Egyptian artifacts and their preservation.
Ref. [4] utilized synchrotron-based X-ray microfluorescence to investigate the pigments on the sarcophagus of the Egyptian mummy Kherima, identifying key pigments such as Egyptian blue, verdigris, and ochre. Hierarchical cluster analysis and principal component analysis were applied to assess whether the sarcophagus samples were contemporaneous with a linen fragment used in the mummy’s wrappings. While the study provides valuable insights through µXRF with synchrotron radiation, it is constrained by the lack of complementary analytical techniques and a broader comparative framework. These limitations highlight the need for more comprehensive research to enhance our understanding of ancient Egyptian pigments and their preservation. In response to these gaps, the present study seeks to characterize the pigments, preparation layers, and linen samples from cartonnage and decorated linen using a suite of techniques, including µXRF, XRD, FTIR, Raman spectroscopy, and microCT. Furthermore, this study aims to correlate the pigments identified in the linen from the mummy’s chest with those found in the cartonnage and to situate these materials and techniques within the broader context of the historical period to which the artifact belongs.
2. Materials and Methods
Two cartonnage samples from the mummy Kherima were examined, each measuring 3 to 4 cm in length. Despite their age, these samples show a yellowish background color with black outlines, with greenish and pink pigments in specific areas. Additionally, exposed ground layers were observed in some parts of the cartonnage. An analysis was conducted on a decorated linen sample that covered the chest of the mummy Kherima. This linen piece is approximately 15 cm long and exhibits degraded pigments (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Table 1 displays the points shown in cartonnage samples (Figure 1) along with their corresponding colors and the layer to which they belong.

Figure 1.
Analyzed samples.
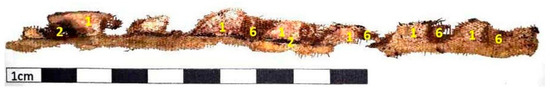
Figure 2.
Highlight of the analyzed linen sample.

Table 1.
Colors found in the cartonnage samples.
Figure 2 illustrates the linen sample, with marked points representing the various shades observed in the decoration. These shades are detailed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Colors found in the linen sample.
µXRF: Pigment and preparation layers in the samples were analyzed using µXRF to investigate elemental composition and spatial distribution. The analyses utilized the M4 Tornado spectrometer (Bruker, Berlin, Germany), featuring computer-controlled operation and a vacuum pump to enhance detection sensitivity for low atomic number elements. Samples were positioned on a triaxial stage driven by stepper motors eliminating the need for sample preparation. The system maintained a fixed geometry between the X-ray tube and detector at a 30° incident angle. The X-ray tube, equipped with a rhodium (Rh) anode operating at 30 W (50 kV and 600 µA), employed capillary collimation to achieve a focal point of approximately 25 µm on the sample. A silicon drift detector (SDD) semiconductor with a 30 mm2 effective area provided high resolution and accommodated up to 250,000 counts per second for the manganese Kα line.
Two experimental configurations were employed to optimize detection: one for elements with atomic numbers below 20 and another for elements above 20. Samples were mounted on a support with a thin film base to minimize interference during measurements. Table 3 presents the experimental configurations for the XRF analyses of the cartonnage samples. The XRF spectra were analyzed using PyMCA version 3.9.4, provided by the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF), which is specifically designed for the processing of X-ray fluorescence data. Two-dimensional maps were generated using the software associated with the M4 Tornado spectrometer.

Table 3.
Experimental setups for µXRF analyses of cartonnage samples.
XRD: The XRD technique was utilized to analyze the preparation layers, with a small amount of material scraped from the cartonnage samples using a steel-blade scalpel, which was then placed in the sample holder. Measurements were conducted with the D2 Phaser (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA), a diffractometer operating in the Bragg–Brentano geometry. This instrument features a LYNXEYE XE-T detector, a copper (Cu) anode X-ray tube emitting a characteristic line at 1.541 Å/8.047 keV (Cu-Kα1), and a maximum power of 300 W (30 kV × 10 mA). Additionally, it includes an integrated flat-panel monitor and DIFFRAC (Eva™ by BRUKER) analysis software v.3.2.
The cartonnage samples were placed in a sample holder with an approximate diameter of 25 mm. The instrument is equipped with automatic goniometric alignment and offers an angular precision of ±0.002° across the range of −2° to 150° in 2θ. Measurements were performed at a voltage of 30 kV and a current of 10 mA, with a scanning range from 20° to 100° and a step size of 0.1°.
Raman spectroscopy: Raman spectroscopy analyses were performed on samples of black pigment (point a), yellow pigment (point b), and the preparation layers (points c and d) from the cartonnage sample. Figure 3 depicts the points analyzed using this technique. Measurements were conducted using a LabRam HR Evolution spectrometer (Horiba Jobin Yvon, Paris, France).
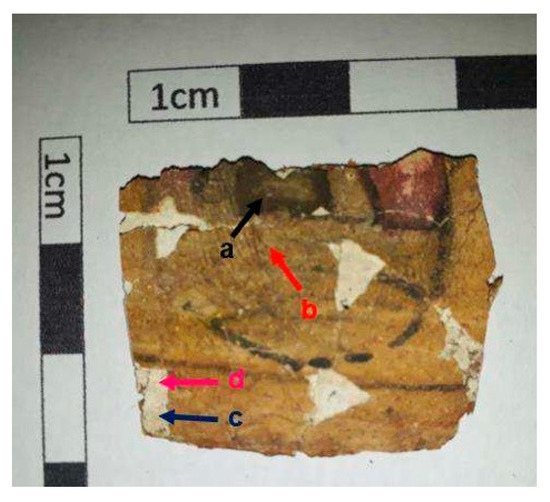

Figure 3.
Points analyzed in the cartonnage sample via Raman spectroscopy.
The samples were excited with laser lines at 488 nm, 514 nm, 633 nm, and 785 nm (selected for optimal quality), and the emitted light was captured using a microscope objective at 100x magnification. Spectra were obtained within the range of 100–2000 cm−1 using a 600 lines/mm grating, with a 2 s acquisition time and 5 accumulations.
FTIR: The FTIR analyses were performed in the mid-infrared region (400–4000 cm−1) using a Vertex 70v FT-IR spectrometer (Bruker, Berlin, Germany), applying the transmission method. This involved preparing tablets by mixing 2 mg of the sample with 100 mg of KBr. Absorbance spectra were collected with a resolution of 2 cm−1 and 32 scans for each sample.
The samples were prepared as pellets consisting of a mixture of 2 mg of pigment extracted from cartonnage and 100 mg of KBr, both ground into a fine powder and subsequently pressed using a hydraulic press. The resulting pellets were placed in the sample holder of the spectrometer. Sampling was conducted for the pink pigment (point 1), the greenish pigment (point 2), and the yellow pigment (point 3). The sampling points are depicted in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
Pigment points analyzed using the FTIR technique.
MicroCT: The cartonnage sample’s structure (Figure 4) was analyzed using microCT. The microCT images were acquired using the Phoenix Vtomex system (General Electric Company, Hürth, Germany), which includes a microfocus X-ray tube with a maximum voltage of 300 kV and a maximum power of 500 W, along with a digital a-Si detector array measuring 410 mm × 410 mm, featuring a pixel size of 200 µm and 14-bit depth. Scanning parameters included a voltage of 60 kV, a current of 310 µA, and a voxel size of 20 µm. The acquisition time was 250 ms per step, with projections obtained over 360° at intervals of 0.20°. Table 4 presents the experimental configurations employed for data acquisition.

Table 4.
Experimental setups used for the microCT measurements of the car tonnage sample.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cartonnage
A stratigraphic analysis was performed on a cross-sectional fragment of cartonnage, measuring approximately 8 mm thick (Figure 5). µXRF measurements were conducted on the linen of the cartonnage samples to determine the elemental composition of the white linen material, which was free from pigments.
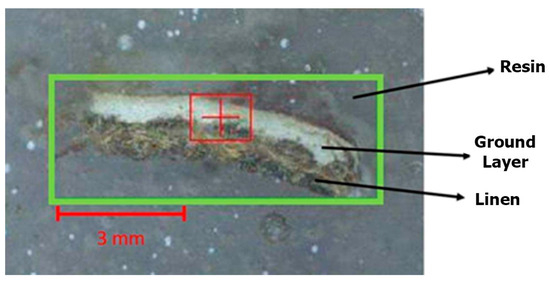
Figure 5.
Cartonnage fragment subjected to cross-sectional analysis.
Subsequently, a µ-XRF elemental distribution map of the cartonnage fragment cross-section was generated to investigate potential multiple ground layers (Figure 6). This mapping revealed two distinct underlying structures. Analysis showed that the lower layer is predominantly composed of calcium, while the upper layer, although thin, contains both calcium and sulfur. Eleven elements were detected using µXRF: magnesium (Mg), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), sulfur (S), chlorine (Cl), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), titanium (Ti), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), and arsenic (As). The µXRF spectra of the preparation layers are shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8. The presence of chlorine in the preparation layers is likely associated with halite salt present in Natron (Na2CO3, NaHCO3, NaCl, and Na2SO4), potentially due to contact with the mummified body [41,42].
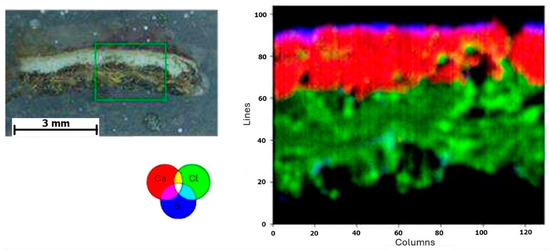
Figure 6.
Elemental mapping of the cross-section of the cartonnage sample fragment.
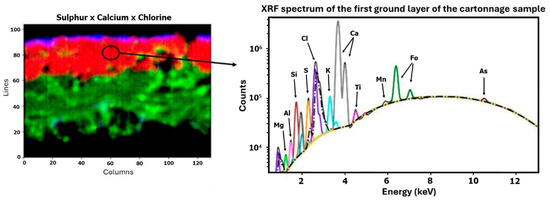
Figure 7.
First ground layer—µXRF results.
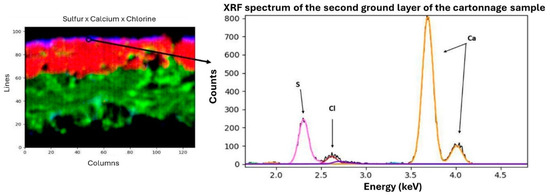
Figure 8.
Second ground layer—µXRF results.
Raman spectroscopy analyses directly examined the ground layers. However, FTIR analyses focused on the pigments. Raman spectroscopy (Figure 9) identified specific bands corresponding to calcite (CaCO3) in the first ground layer (163, 284, and 1085 cm−1) and gypsum (CaSO4 2H2O) in the second layer (1010 and 1120 cm−1) [43,44].
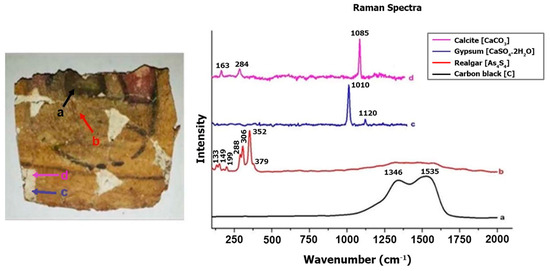
Figure 9.
Raman spectrum of the ground layers and pigments of the cartonnage sample.
Table 5 summarizes the results obtained from µXRF and Raman spectroscopy analyses of the cartonnage sample’s ground layers.

Table 5.
Analysis of ground layers.
The cartonnage sample’s structure was further analyzed using microCT imaging (Figure 10), revealing uniform distributions in both the ground layers (white region) and the linen section (blue region). Figure 10 highlights the high-density material (represented by red points) distributed on the cartonnage surface. This finding supports the results from µXRF, Raman spectroscopy, and FTIR analyses, suggesting that the internal ground layer is composed of less dense calcite, while the external ground layer is likely gypsum (CaSO4·0.5H2O) or anhydrite (CaSO4). The densities of these materials are 2.71 g/cm3 for calcite, 2.98 g/cm3 for anhydrite, and 2.31 g/cm3 for gypsum. Therefore, the microCT data suggest that the red points in the images may be anhydrite crystals.
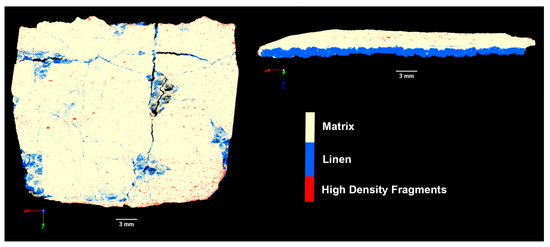
Figure 10.
Analysis of the cartonnage using microCT technique.
These results are consistent with previous studies reporting ground layers composed of gypsum, calcite, and anhydrite, with possible variations in layer order and occasionally other ground layers [35,38,41]. The author of [45] investigated cartonnage fragments from the 1st century A.D. (Roman Period) and found comparable results. His analysis revealed two preparation layers: a lower layer predominantly made of calcite and an upper layer containing gypsum, hemi-hydrated quartz (SiO2), and occasionally anhydrite and halite (NaCl). Scott’s research indicated that two preparation layers were sometimes applied: a coarser lower layer and a finer upper layer, which could include materials such as calcite, magnesite/dolomite (CaMg(CO3)4), and lead white (Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2), among others. This stratigraphy was designed to provide a smoother and purer white base for the subsequent pictorial layer.
The four pigments in the paint layer of the cartonnage were analyzed using µXRF (Figure 11) and FTIR techniques (Figure 12). Additionally, Raman spectroscopy was employed specifically to examine the yellow and black pigments (as shown in Figure 9).
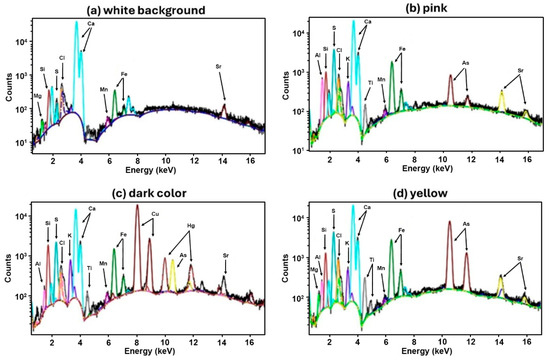
Figure 11.
Cartonnage XRF spectra.
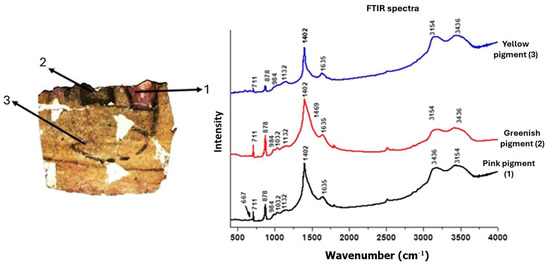
Figure 12.
Infrared spectra (FTIR) of the pigments analyzed in the cartonnage sample.
White Background. The white background spectrum (Figure 11) shows a predominance of calcium, which is a common component of the base layer and is consistent across all analyzed points. Silicon, strontium, and iron are also present, but their roles or origins are not definitively established [46]. The presence of the calcium mineral is confirmed by the FTIR spectra (Figure 12), where it is possible to visualize the bands 711, 878, and 1402 cm−1, which can be attributed to calcite (CaCO3). Bands at around 1032 and 1132 cm−1 were also visualized in the spectra, which can be related to the Si-O bond indicating the presence of quartz (SiO4). Even the band at 984 cm−1 can be associated with the vibration of the Al(OH) structure, present in the mineral kaolinite [Al2Si2O5(OH)4]. All these bands were detected in all FTIR spectra recorded, justifying the detection of calcium and silicon at all points where elemental analysis was performed. [44,47]
Red/Pink pigment. Analysis of the red/pink pigment using µXRF and FTIR revealed a significant presence of aluminum. Raman spectroscopy was not feasible due to induced fluorescence interference with Raman bands. The FTIR band at 667 cm−1, associated with Al-O vibrations, suggests the presence of hydrated alumina (Al2O3 3H2O). µXRF images indicate a high intensity of aluminum in the pink pigment area (Figure 13). This suggests the use of a pigment like Madder Lake, derived from red dyes extracted from Rubia species roots and dissolved in alumina, tin chloride, and other substances. This dyeing method was likely introduced to Egypt during the Eighteenth Dynasty (1550–1292 BCE). The rarity of Madder Lake implies the artifact’s uniqueness [48,49,50].
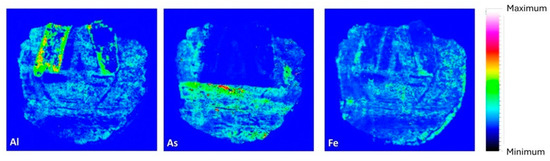
Figure 13.
Elemental distribution map of aluminum, arsenic, and iron elements in the cartonnage sample.
Yellow pigment. The yellow paint layer was analyzed using µXRF and Raman spectroscopy. µXRF revealed high concentrations of arsenic and iron (Figure 13). The presence of arsenic suggests pigments such as Realgar (As4S4) or Orpiment (As2S3), with Raman spectroscopy confirming Realgar through bands at 133, 149, 199, 288, 306, 352, and 379 cm−1 [22,51,52]. Realgar was likely imported from regions like Kurdistan or Cyprus and was used extensively in Egyptian art from the Middle Kingdom to the end of the Third Intermediate Period [53]. The detection of arsenic and iron elements in pigment-containing areas supports the presence of a Realgar and Goethite mixture in the analyzed cartonnage sample, consistent with earlier studies on artifacts from the early Roman Period [35]. Figure 14 presents a 100× magnified image of the yellow pigment showing an arsenic grain and a white grain identified as anhydrite due to its high sulfur content. This supports the hypothesis of gypsum in the outer ground layer.
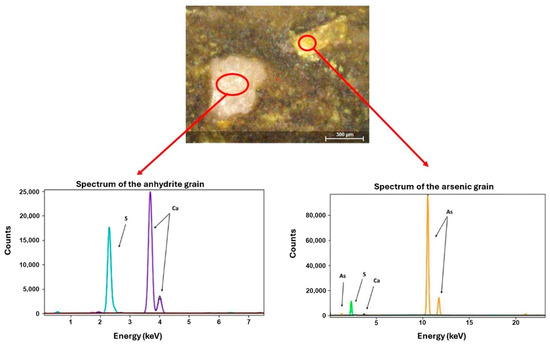
Figure 14.
Image of the yellow pigment displaying both an arsenic grain and an anhydrite grain.
Greenish Pigment. The greenish pigment analysis identified the presence of mercury, suggesting the use of Vermilion (HgS). Over time, Vermilion can darken due to environmental factors such as humidity and light [8]. This phenomenon occurs due to the transformation of the trigonal structure α-HgS (cinnabar), which has a red hue, into the cubic structure β-HgS (metacinnabar) with a black hue. The distribution of mercury elemental mapping (Figure 15) corroborates this identification, where the Hg mapping is associated with regions where in the visible image it has a black hue [54,55]. Vermilion’s presence indicates that the mummy Kherima held a high social status, as it was a rare and valuable pigment [45,53].

Figure 15.
Elemental distribution of copper and mercury in cartonnage sample.
The µXRF spectrum showed a significant silicon peak, suggesting Egyptian blue or green pigment (CaO.CuO.4SiO2) may also be present. Egyptian blue, like Vermilion, can darken over time due to varnish application [10]. The Malachite pigment is typically identified by FTIR through the vibrational modes of CO3 at 878 and 1402 cm−1, which are also characteristic of calcite. However, in the spectrum of the greenish pigment (Figure 12), a broadening of the band around 1402 cm−1 is observed. This broadening may be attributed to the presence of a reinforcing band near 1469 cm−1, also associated with Malachite, which exhibits two distinctive bands within the 1300–1500 cm−1 region [56,57,58,59].
Black Pigment. Raman spectroscopy of the black pigment revealed characteristic bands around 1346 and 1535 cm−1, indicating Carbon Black pigment (Ca5(OH)(PO4)3) [40,60,61]. This aligns with ancient Egyptian practices of using carbon-based compounds such as soot, charcoal, or burned animal bones for black pigments [62].
In all pigments. The FTIR peak observed at 1635 cm−1 may indicate the presence of proteins, suggesting the use of a binder in the painting, likely pointing to the application of tempera [63,64]. Additionally, the peaks at 3154 and 3436 cm−1, also present in all analyzed pigments, are indicative of the stretching vibrations of water, suggesting moisture in the analyzed samples [59,64,65].
Microscopy and Additional Analysis. High-resolution optical microscopy (OM) provided insights into the degradation characteristics of pigments and materials in the cartonnage. Figure 16a,b show dark areas and changes in texture indicative of degradation over time [66]. Microscopic analysis also revealed green crystals likely corresponding to Malachite pigment (Cu2(CO3)2(OH)2). µXRF and FTIR analyses further support the presence of Egyptian blue or green pigment (CaO·CuO·4SiO2).
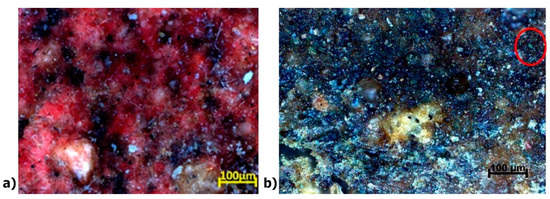
Figure 16.
(a) High-resolution optical microscopy (OM) images of the reddish area with darker spots, and (b) an optical microscopy image of the green-colored area.
Figure 17a,b show µXRF elemental distribution maps of sulfur (S) and copper (Cu). The spatial correlation of these elements suggests a potential link to the dark pigmentation observed in this cartonnage region. This dark coloration may be due to compounds such as iron (II) sulfide (FeS), iron (III) sulfide (Fe2S3), or iron and copper sulfide (FeCuS2). Mercury (Hg) highlighted in purple in Figure 17b, detected in the red-colored region, supports the use of Vermilion (HgS). Cinnabar can degrade into metacinnabar (HgSx), which appears darker, consistent with the images in Figure 3 and Figure 16a [67,68].

Figure 17.
XRF elemental distribution: (a) presence of Ca, As, and S; (b) presence of Cu, Hg, and Fe.
The results obtained are summarized and presented in Table 6, and XRF spectra are shown in Figure 11.

Table 6.
Analysis of pigments.
3.2. Linen
Figure 18 presents the analyzed linen sample, while Figure 19 illustrates the XRD spectrum obtained from the analysis of the fiber of the linen.

Figure 18.
Analyzed sample of decorated linen, highlighting the fiber.
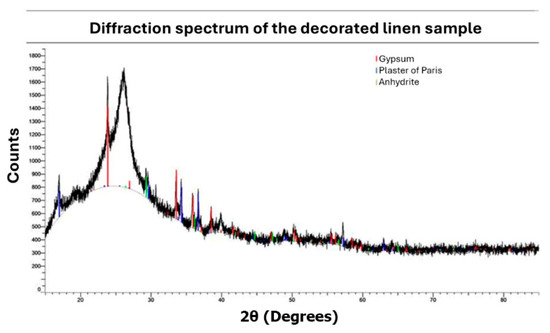
Figure 19.
XRD analysis of linen.
XRD analysis of the linen provided insights into the composition of both the fabric and the black pigment, while µXRF identified the elements present in the fabric, suggesting potential pigments used in its dyeing. The results and spectra are presented in Table 7 and Figure 20.

Table 7.
Analysis of linen.
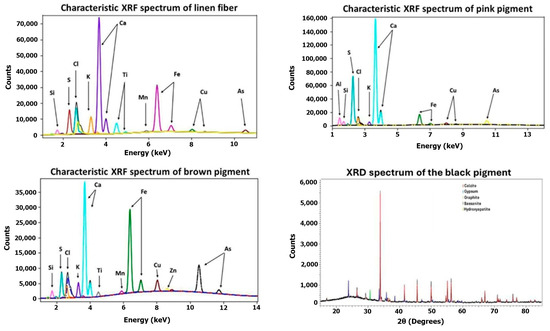
Figure 20.
Linen XRF and XRD spectra.
Linen Fiber. Using the XRD technique, it was possible to detect the compounds: gypsum, bassanite, and anhydrite, commonly employed for shaping linen and as a ground layer [35,38,41]. The chlorine detected via µXRF likely originates from halite salts found in the Natron used during embalming.
Pink Pigment. The pink pigment analyzed by µXRF was found to contain aluminum, sulfur, and calcium as its primary elements. The presence of aluminum likely indicates the use of hydrated alumina, suggesting that a red pigment such as Madder Lake was employed [48,49], thereby contributing to the pink pigment observed in the cartonnage sample. Additionally, the presence of arsenic implies that pigments such as Realgar or Orpiment, which are often blended to produce brighter hues [38], were also used. XRD analysis did not provide conclusive information regarding the composition of the red/pink pigment. Consequently, while the µXRF analysis is qualitative, the detected elements suggest that the red pigment is probably a mixture of Madder Lake with Realgar (As4S4) or Orpiment (As2S3) [69].
Brown Pigment. The µXRF technique enabled the detection of 11 elements: silicon, sulfur, chlorine, potassium, calcium, titanium, manganese, iron, copper, zinc, and arsenic. The analysis of the brown pigment detected a significantly higher count of copper compared to the linen fiber without pigment. This suggests the pigment may be green, resembling Malachite (Cu2(CO3)2(OH)2), rather than brown.
Black Pigment. µXRF analysis was inconclusive in characterizing the black pigment, but XRD analysis identified graphite (C) and hydroxyapatite (Ca5(OH)(PO4)3), suggesting that it might be Carbon Black [53,70]. This information indicates that the black pigment used in the decorated linen is the same pigment used in its cartonnage.
The analyses conducted on the cartonnages, and decorated linen samples enabled the characterization of the preparation layers and pigments utilized. Table 8 summarizes the results obtained for the characterization of the ground layers and pigments in the cartonnages and decorated linen samples.

Table 8.
Proposed characterization of the ground layers and pigments in the cartonnages and decorated linen samples.
4. Conclusions
This study offers a comprehensive multi-analytical characterization of the pigments and materials used in the decorative paintings of the cartonnage and linen covering the mummy Kherima. Through the integration of techniques such as µXRF, XRD, FTIR, Raman spectroscopy, and microCT, the research successfully revealed new details about the artifact’s chemical composition, identified the pigments and ground layers utilized by ancient Egyptian artists, and provided fresh insights into their artistic practices.
The analysis revealed that the cartonnage was constructed with a linen base, overlaid with a calcite-rich layer. The instrumental investigation identified the use of both traditional and complex pigments from the Egyptian color palette in the cartonnage’s decoration, including Orpiment, Vermilion, Malachite, Egyptian blue, Realgar, and Carbon Black. The white pigment in the linen sample was determined to be a combination of calcite and quartz, while the red pigments were confirmed as Orpiment and Madder Lake. Although the precise composition of the green pigment remains unresolved, it is hypothesized to be a mixture of Vermilion and either Egyptian blue or Malachite.
Despite these significant findings, further investigations are necessary to identify the organic compounds that constitute the paintings, particularly the binders used. Understanding these organic components is crucial for a more complete picture of the materials and techniques employed by ancient Egyptian artists.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.S., M.A. and D.O.; methodology, F.S., R.B. and M.A.; validation, F.S., R.N., R.S., H.G.F. and M.A.; formal analysis, F.S., R.N., R.S., H.G.F. and A.M.; investigation, F.S., R.N., R.S., H.G.F. and A.M.; data curation, F.S., R.F., M.A. and D.O.; writing—original draft, F.S., R.N., I.F., J.C., M.A. and D.O.; writing—review and editing, I.F., J.C., R.B., A.d.P. and D.O.; visualization, F.S., R.B. and A.M.; supervision, J.A., M.A., R.L. and D.O.; project administration, M.A. and D.O.; funding acquisition, R.F., J.A., M.A., R.L. and D.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Brazilian Council of Science and Technological Development—CNPq, INCT INAIS (grant 406303/2022-3), and partially financed by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior, Brazil (CAPES) financial code 001. The authors also acknowledge the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ) for their financial support.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be available from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Baber, T.T. Ancient corpses as curiosities: Mummymania in the age of early travel. J. Anc. Egypt. Interconnect. 2016, 8, 60–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakos, M. Egiptomania-o Egito no Brasil; Paris Editorial: São Paulo, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Brancaglion, A., Jr.; Lima, T.A.; de Souza, S.M.M. The Egyptian collection of Museu Nacional, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and the conservation of mummies in a tropical environment. J. Biol. Res. Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. 2005, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calza, C.; Anjos, M.; de Souza, S.M.; Brancaglion, A., Jr.; Lopes, R.T. X-ray microfluorescence with synchrotron radiation applied in the analysis of pigments from ancient Egypt. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 90, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufderheide, A.C.; Cartmell, L.; Zlonis, M.; Sheldrick, P. Mummification practices at Kellis site in Egypt’s Dakhleh Oasis. J. Soc. Study Egypt. Antiq. 2004, 31, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Aufderheide, C.; Zlonis, M.; Cartmell, L.M.; Zimmerman, M.R.; Sheldrick, P.; Cook, M.; Molto, J.E. Human mummification practices at Ismant el-Kharab. J. Egypt. Archaeol. 1999, 85, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaens, A. Non-destructive analysis and testing of museum objects: An overview of 5 years of research. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2005, 60, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liritzis, I.; Laskaris, N.; Vafiadou, A.; Karapanagiotis, I.; Volonakis, P.; Bratitsi, M. Archaeometry: An overview. Sci. Cult. 2020, 6, 49–98. [Google Scholar]
- Spring, M.; Grout, R. The blackening of vermilion: An analytical study of the process in paintings. Natl. Gallery Tech. Bull. 2002, 23, 50–61. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, V.; Stacey, R.; Middleton, A. The blackening of paint containing Egyptian blue. Stud. Conserv. 2004, 49, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Mansour, M.; Badr, N.; Salem, M. A study of biodeterioration and chromatic alterations of painted and gilded mummy cartonnage at the Saqqara Museum storeroom, Egypt. Archaeometry 2018, 60, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, I.A.; Busani, T.; de Sá, M.H. The surface behavior of gilding layer imitations on polychrome artefacts of cultural heritage. Surf. Interface Anal. 2011, 43, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.; Edwards, H.G.; Vandenabeele, P. Analytical Archaeometry: Selected Topics; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, E. Spectrometry as a non-destructive technique in identifying cultural archaeological heritage. In Spectroscopic Techniques for Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Research; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Čechák, T.; Musílek, L.; Trojek, T.; Kopecká, I. Application of X-ray fluorescence analysis in investigations of historical monuments. Acta Polytech. 2005, 45, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesareo, R.; Bustamante, A.; Fabian, J.; Calza, C.; Anjos, M.D.; Lopes, R.T.; Alva, W.; Chero, L.; Gutierrez, F.; Espinoza, M.D.C.; et al. Pre-Columbian alloys from the royal tombs of Sipán and from the Museum of Sicán. Non-destructive XRF analysis with a portable equipment. ArcheoSciences Rev. D’archeom. 2009, 33, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artioli, G. Science for the cultural heritage: The contribution of X-ray diffraction. Rend. Lincei 2013, 24, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, V.; Cotte, M.; Vanmeert, F.; de Nolf, W.; Janssens, K. X-ray diffraction mapping for cultural heritage science: A review of experimental configurations and applications. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.P.; Ribeiro, I.M.; Calza, C.; Oliveira, A.L.; Felix, V.S.; Ferreira, D.S.; Pimenta, A.R.; Pereira, R.V.; Pereira, M.O.; Lopes, R.T. Analysis of a Brazilian baroque sculpture using Raman spectroscopy and FT-IR. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 154, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropret, P.; Madariaga, J.M. Applications of Raman spectroscopy in art and archaeology. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2014, 50, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, S.; Sciutto, G.; Bonacini, I.; Mazzeo, R. New Frontiers in Application of FTIR Microscopy for Characterization of Cultural Heritage Materials. In Analytical Chemistry for Cultural Heritage; Mazzeo, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 129–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonizzoni, L.; Bruni, S.; Gargano, M.; Guglielmi, V.; Zaffino, C.; Pezzotta, A.; Pilato, A.; Auricchio, T.; Delvaux, L.; Ludwig, N. Use of integrated non-invasive analyses for pigment characterization and indirect dating of old restorations on one Egyptian coffin of the XXI dynasty. Microchem. J. 2018, 138, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witte, Y.; Cnudde, V.; Pieters, K.; Dierick, M.; Vlassenbroeck, J.; Van Hoorebeke, L.; Jacobs, P. X-ray microCT applied to natural building materials and art objects. X-Ray Spectrom. Int. J. 2008, 37, 383–387. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, A.; Oliveira, D.; Filho, H.G.; Latini, R.; Bellido, A.; Assis, J.; Anjos, M.; Lopes, R. Archeological ceramic artifacts characterization through computed microtomography and x-ray fluorescence. X-Ray Spectrom. 2017, 46, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; de Paula, A.; Goncalves, F.; Sanches, F.; Nardes, R.; Santos, R.; Azeredo, S.; Araújo, O.; Machado, A.; Anjos, M.; et al. Analysis of a wooden statue by non-destructive x-ray techniques. X-Ray Spectrom. 2023, 52, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, M. X-ray techniques dedicated to materials characterization in cultural heritage. Chem. Sel. 2023, 8, e202301306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentelman, K. Analyzing the heterogeneous hierarchy of cultural heritage materials: Analytical imaging. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 10, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marguí, E.; Queralt, I.; de Almeida, E. X-ray fluorescence spectrometry for environmental analysis: Basic principles, instrumentation, applications and recent trends. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutterotti, L.; Dell’Amore, F.; Angelucci, D.E.; Carrer, F.; Gialanella, S. Combined x-ray diffraction and fluorescence analysis in the cultural heritage field. Microchem. J. 2016, 126, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C. New advances in using Raman spectroscopy for the characterization of catalysts and catalytic reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 3519–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, V.; Allodi, V.; Bottari, C.; D’Amico, F.; Galli, G.; Gessini, A.; La Russa, M.F.; Longo, F.; Majolino, D.; Mariotto, G.; et al. Spectroscopic investigation of roman decorated plasters by combining FT-IR, micro-Raman and UV-Raman analyses. Vib. Spectrosc. 2016, 83, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid, H.; Carrasco-Nuñez, G.; Manea, V. Improved method for effective rock microporosity estimation using x-ray microtomography. Micron 2017, 97, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigorelli, L.; Re, A.; Guidorzi, L.; Cavaleri, T.; Buscaglia, P.; Nervo, M.; Facchetti, F.; Borla, M.; Grassini, S.; Giudice, A.L. X-ray imaging investigation on the gilding technique of an ancient Egyptian taweret wooden statuette. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, V.; Canevali, C.; Corti, C.; De Kock, T.; Rampazzi, L.; Recchia, S.; Sansonetti, A.; Tedeschi, C.; Cnudde, V. Understanding the microstructure of mortars for cultural heritage using x-ray CT and MIP. Materials 2021, 14, 5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.A.; Dennis, M.; Khandekar, N.; Keeney, J.; Carson, D.; Dodd, L.S. An Egyptian cartonnage of the Graeco-Roman period. Stud. Conserv. 2003, 48, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, S.; Nielsen, O.F.; Christensen, D.H.; Edwards, H.G.; Farwell, D.W.; David, R.; Lambert, P.; Gniadecka, M.; Wulf, H.C. Near-infrared Fourier transform Raman spectroscopy of skin samples from the ‘tomb of the two brothers’, Khnum-Nakht and Nekht-Ankh, XIIth dynasty Egyptian mummies (ca 2000 BC). J. Raman Spectrosc. 2003, 34, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uda, M. Characterization of pigments used in ancient Egypt. In X-rays for Archaeology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aal, S.A. Characterization and examination of pigments, grounds and media from ancient Egyptian cartonnage. Egypt. J. Archaeol. Restor. Stud. 2014, 4, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.F.; Darwish, S.S.; El Sheikha, A.M. Multispectral analysis and investigation of overlapping layer cartonnage fragments from Egyptian Museum, Cairo. Sci. Cult. 2020, 6, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, C.A.; Comite, V.; Fermo, P.; Bergomi, A.; Trombino, L.; Guglielmi, V. A multi-analytical approach for the characterisation of pigments from an Egyptian sarcophagus cover of the late dynastic period: A case study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tawab, N.A.; Badr, I.; Mahran, A. Analytical investigation of cartonnage fragment from late period. Egypt. J. Archaeol. Restor. Stud. 2012, 2, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Magdy, M.; Ismail, M.; Issa, Y.; Abdel-Maksoud, G.; Ibrahim, M. An analytical study for understanding the degradation process of a late period mummy. Adv. Res. Conserv. Sci. 2020, 1, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiani, M.C.; Cosentino, A.; Mangone, A. Pigments checker version 3.0, a handy set for conservation scientists: A free online Raman spectra database. Microchem. J. 2016, 129, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.P.; Coelho, F.A.; Felix, V.S.; Pereira, M.O.; de Souza, M.A.T.; Anjos, M.J. Analysis of 19th century ceramic fragments excavated from Pirenópolis (Goiás, Brazil) using FT-IR, Raman, XRF and SEM. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 193, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.A.; Warmlander, S.; Mazurek, J.; Quirke, S. Examination of some pigments, grounds, and media from Egyptian cartonnage fragments in the Petrie Museum, University College London. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlir, K.; Griesser, M.; Buzanich, G.; Wobrauschek, P.; Streli, C.; Wegrzynek, D.; Markowicz, A.; Chinea-Cano, E. Applications of a new portable (micro) XRF instrument having low-z elements determination capability in the field of works of art. X-Ray Spectrom. Int. J. 2008, 37, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klisińska-Kopacz, A.; Fraczek, P.; Obarzanowski, M.; Czop, J. Non-invasive study of pigment palette used by Olga Boznańska investigated with analytical imaging, XRF, and FTIR spectroscopy. Heritage 2023, 6, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, J.; Sotiropoulou, S. A technical step forward in the integration of visible induced luminescence imaging methods for the study of ancient polychromy. Herit. Sci. 2017, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, C.; Doherty, B.; Gentili, P.L.; Miliani, C.; Romani, A.; Brunetti, B.G.; Sgamellotti, A. Vibrational and electronic properties of painting lakes. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 92, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, V.; Deviese, T.; Hacke, M.; Higgitt, C. Technological insights into madder pigment production in antiquity. Br. Mus. Tech. Res. Bull. 2014, 8, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, R.; Martens, W.; Kloprogge, J. Raman spectroscopic study of cinnabar (HgS), realgar (As4S4) and orpiment (As2S3) at 298 and 77k. Neues Jahrb. Mineral. Monatshefte 2002, 10, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Frost, R.L. Structure comparison of orpiment and realgar by raman spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Lett. 2017, 50, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, L.M.; Fuchs, R. Characterization of the pigments in a Ptolemaic Egyptian book of the dead papyrus. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2011, 3, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calza, C.; Anjos, M.J.; de Souza, S.M.M.; Brancaglion, A., Jr.; Lopes, R.T. Pigments analysis in cartonnages of an Egyptian mummy of the roman period using x-ray fluorescence spectrometry. J. Biol. Res.-Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. 2005, 80, 136–138. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Warren, W.S.; Fischer, M.C. Visualization of vermilion degradation using pump-probe microscopy. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buti, D.; Rosi, F.; Brunetti, B.G.; Miliani, C. In-situ identification of copper-based green pigments on paintings and manuscripts by reflection ftir. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 2699–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.E.; Silva, L.P.; Edwards, H.G.; de Oliveira, L.F.C. Diffuse reflection FTIR spectral database of dyes and pigments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrick, M.R.; Stulik, D.; Landry, J.M. Infrared Spectroscopy in Conservation Science; Getty Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Valadas, S.; Candeias, A.; Dias, C.; Schiavon, N.; Cotovio, M.; Pestana, J.; Gil, M.; Mirão, J. A multi-analytical study of the fifteenth century mural paintings of the Batalha Monastery (Portugal) in view of their conservation. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 113, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluveras-Tenorio, A.; Spepi, A.; Pieraccioni, M.; Legnaioli, S.; Lorenzetti, G.; Palleschi, V.; Vendrell, M.; Colombini, M.P.; Tinè, M.R.; Duce, C.; et al. A multi-analytical characterization of artists’ carbon-based black pigments. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 3287–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccato, A.; Jehlicka, J.; Moens, L.; Vandenabeele, P. Raman spectroscopy for the investigation of carbon-based black pigments. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, G.G. Color in ancient Egypt. Erişim Tarihi 2016, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Creagh, D.; Lee, A.; Otieno-Alego, V.; Kubik, M. Recent and future developments in the use of radiation for the study of objects of cultural heritage significance. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2009, 78, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Taleb, T.; Orabi, E. Degradation of vermilion red color in oil and mural paintings: A comparative applied study. Egypt. J. Archaeol. Restor. Stud. 2019, 9, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, S.; Lampakis, D.; Karapanagiotis, I.; Panayiotou, C.; Afifi, H.A.; Hady, M.A.-E. Investigation of painted stucco in historic buildings of delta, Egypt. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2017, 9, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masic, A.; Nicola, M. Nir luminescence and composition of Egyptian blue as markers in archaeometric evaluations. Microsc. Microanal. 2021, 27, 3004–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardes, R.C. Analysis of the pigments in two modern Egyptian papyri using XRF technique. Braz. J. Radiat. Sci. 2021, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franquelo, M.; Duran, A.; Castaing, J.; Arquillo, D.; Rodriguez, J.P. XRF, µ-XRD and µ-spectroscopic techniques for revealing the composition and structure of paint layers on polychrome sculptures after multiple restorations. Talanta 2012, 89, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pages-Camagna, S.; Laval, E.; Vigears, D.; Duran, A. non-destructive and in situ analysis of Egyptian wall paintings by x-ray diffraction and x-ray fluorescence portable systems. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 100, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daveri, A.; Malagodi, M.; Vagnini, M. The bone black pigment identification by non-invasive, in situ infrared reflection spectroscopy. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 6595643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).