Chromatic Change in Copper Oxide Layers Irradiated with Low Energy Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
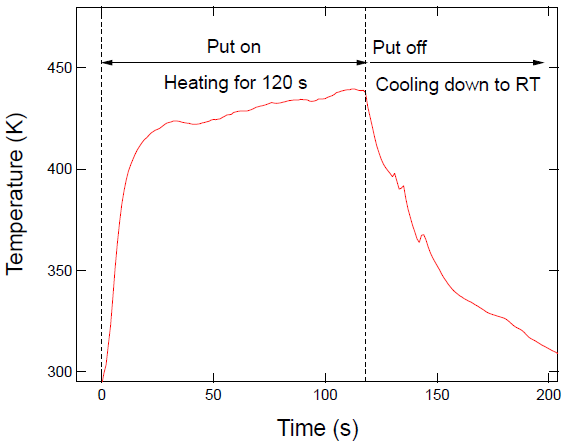
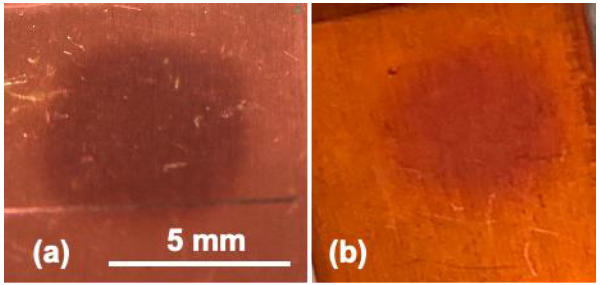
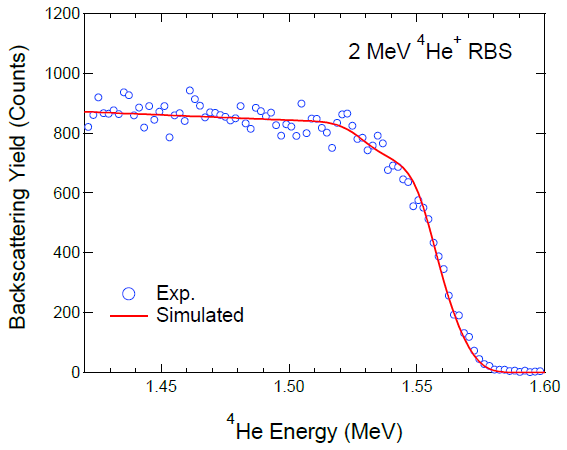
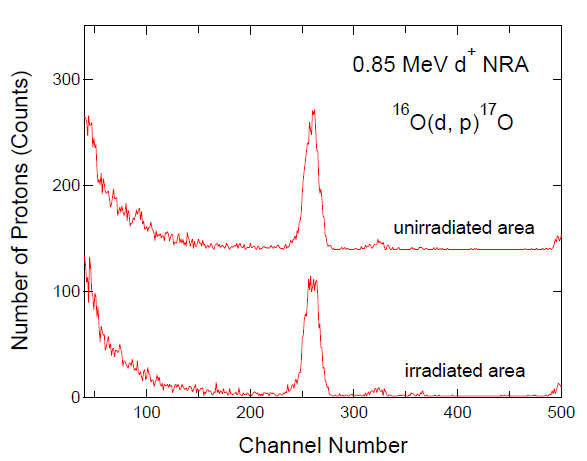
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peña-Rodríguez, O.; Crespillo, M.L.; Díaz-Nuñez, P.; Perlado, J.M.; Rivera, A.; Olivares, J. In situ monitoring the optical properties of dielectric materials during ion irradiation. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.; Olivares, J.; Prada, A.; Crespillo, M.L.; Caturla, M.J.; Bringa, E.M.; Perlado, J.M.; Peña-Rodríguez, O. Permanent modifications in silica produced by ion-induced high electronic excitation: Experiments and atomistic simulations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, B. Origins of a damage-induced green photoluminescence band in fused silica revealed by time-resolved photoluminescence spectroscopy. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 2888–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespillo, M.L.; Graham, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; Weber, W.J. In-situ luminescence monitoring of ion-induced damage evolution in SiO2 and Al2O3. J. Lumin. 2016, 172, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandourko, V.; Umeda, N.; Plaksin, O.; Kishimoto, N. Heavy-ion-induced luminescence of amorphous SiO2 during nanoparticle formation. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2005, 230, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forck, P.; Andre, C.; Becker, F.; Haseitl, R.; Reiter, A.; Walasek-Höhne, B.; Krishnakumar, R.; Ensinger, W. Scintillation Screen Investigations for High Energy Heavy Ion Beams at GSI. In Proceedings of the DIPAC2011, Hamburg, Germany, 16–18 May 2011; pp. 170–172. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.D. The Development and Use of Alumina Ceramic Fluorescent; CERN/PS/90-12(AR); European Laboratory for Particle Physics: Geneva, Switzerland, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Takahiro, K.; Terai, A.; Kawatsura, K.; Naramoto, H.; Yamam, S.; Tsuchiya, B.; Nagata, S.; Nishiyama, F. Rutherford backscattering spectrometry of electrically charged targets: Elegant technique for measuring charge-state distribution of backscattered Ions. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 1823–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, R.K.; Kada, W.; Kawabata, S.; Matsubara, Y.; Sakai, M.; Miura, K.; Satoh, T.; Koka, M.; Yamada, N.; Kamiya, T.; et al. Ion-Beam-Induced Luminescence Analysis of β-SiAlON:Eu Scintillator under Focused Microbeam Irradiation. Sens. Mater. 2016, 28, 837–844. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, A.J.; Thomas, C.B.; Reehal, H.S.; Stevens, P.R.C. A study of the luminescent and electrical characteristics of films of ZnS doped with Mn. J. Lumin. 1983, 28, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calusi, S.; Colombo, E.; Giuntini, L.; Giudice, A.L.; Manfredotti, C.; Massi, M.; Pratesi, G.; Vittone, E. The ionoluminescence apparatus at the LABEC external microbeam facility. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2008, 266, 2306–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, C.; Jüstel, T.; Ronda, C.R.; Schmidt, P.J. Inorganic Luminescent Materials: 100 Years of Research and Application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2003, 13, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiman, J.; Iskanderova, Z.; Best, C.; Dennison, J.R.; Wood, B. Long-term stability of ion-beam treated space polymers in geo-simulated environment. In Proceeding of the 14th ISMSE $ 12th ICPMSE, Biarritz, France, 1–5 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Plis, E.A.; Engelhart, D.P.; Cooper, R.; Johnston, W.R.; Ferguson, D.; Hoffmann, R. Review of Radiation-Induced Effects in Polyimide. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matienzo, L.J.; Emmi, F.; Van Hart, D.C.; Gall, T.P. Interactions of high-energy ion beams with polyimide films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1989, 7, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Computer Simulation of RBS, ERDA, NRA, MEIS and PIGE by Matej Mayer. Available online: https://home.mpcdf.mpg.de/~mam/Version6.html (accessed on 5 December 2020).
- Ziegler, J.F.; Ziegler, M.D.; Biersack, J.P. SRIM—The stopping and range of ions in matter (2010). Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2010, 268, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanuma, S.; Powell, C.J.; Penn, D.R. Calculations of electron inelastic mean free paths. II. Data for 27 elements over the 50–2000 eV range. Surf. Interface Anal. 1991, 17, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, J.; Tsuboyama, S.; Ishizu, K.; Miyamura, K.; Saburi, M. Covalency of copper complex determined by Cu 2p X-ray photoelectron spectrometry. Anal. Sci. 1991, 7, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.M.; Kim, J.; Inamdar, A.I.; Woo, H.; Jo, Y.; Pawar, B.S.; Cho, S.; Kim, H.; Im, H. Multi-functional reactively-sputtered copper oxide electrodes for supercapacitor and electro-catalyst in direct methanol fuel cell applications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Végh, J. The Shirley background revised. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2006, 151, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.R.; Lee, R.N. Comparison of APS and FRESCA core level binding energy measurements. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1982, 20, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seah, M.P.; Gilmore, I.S.; Beamson, G. XPS: Binding energy calibration of electron spectrometers 5—re-evaluation of the reference energies. Surf. Interface Anal. 1998, 26, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R.J.; Swift, P. Energy calibration in electron spectroscopy and the re-determination of some reference electron binding energies. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1980, 21, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, N.S.; Cook, M.G. X-ray photoelectron studies on some oxides and hydroxides of cobalt, nickel, and copper. Anal. Chem. 1975, 47, 2208–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schön, G. ESCA studies of Cu, Cu2O and CuO. Surf. Sci. 1973, 35, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losev, A.; Rostov, K.; Tyuliev, G. Electron beam induced reduction of CuO in the presence of a surface carbonaceous layer: An XPS/HREELS study. Surf. Sci. 1989, 213, 564–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroubaix, G.; Marcus, P. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of copper and zinc oxides and sulphides. Surf. Interface Anal. 1992, 18, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, J.; Machej, T.; Ungier, L.; Ziółkowski, J. ESCA studies of copper oxides and copper molybdates. J. Solid State Chem. 1978, 25, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaarenstroom, S.M.; Winograd, N. ESCA spectra of cadmium and silver oxides. J. Chem. Phys. 1977, 67, 3500–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, J.P.; Hirschwald, W.; Cunningham, J. XPS and XAES studies of transient enhancement of Cu1 at CuO surfaces during vacuum outgassing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1983, 16, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C. Advanced analysis of copper X-ray photoelectron spectra. Surf. Interface Anal. 2017, 49, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzner, G.; Egert, B.; Schmidt, H.P. The stability of CuO and Cu2O surfaces during argon sputtering studied by XPS and AES. Surf. Sci. 1985, 151, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dementyeva, M.M.; Prikhodko, K.E.; Gurovich, B.A.; Bukina, Z.V.; Komarov, D.A.; Kutuzov, L.V. Phase transitions in copper oxide thin films under proton irradiation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Tecnol. 2017, 256, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yang, C.; Gao, Y. Investigations of Cuprous Oxide and Cupric Oxide Thin Films by Controlling the Deposition Atmosphere in the Reactive Sputtering Method. Sens. Mater. 2016, 28, 817–824. [Google Scholar]
- Gevorkyan, V.A.; Reymers, A.E.; Nersesyan, M.N.; Arzakantsyan, A.M. Characterization of Cu2O thin films prepared by evaporation of CuO powder. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 350, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goua, L.; Murphy, C.J. Controlling the size of Cu2O nanocubes from 200 to 25 nm. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butte, S.M.; Waghuley, S.A. Optical properties of Cu2O and CuO. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2220, 020093. [Google Scholar]
- Fredj, N.; Burleigh, T.D. Transpassive Dissolution of Copper and Rapid Formation of Brilliant Colored Copper Oxide Films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, C104–C110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
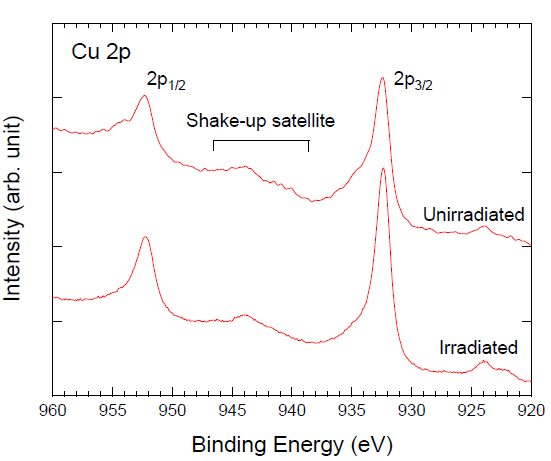
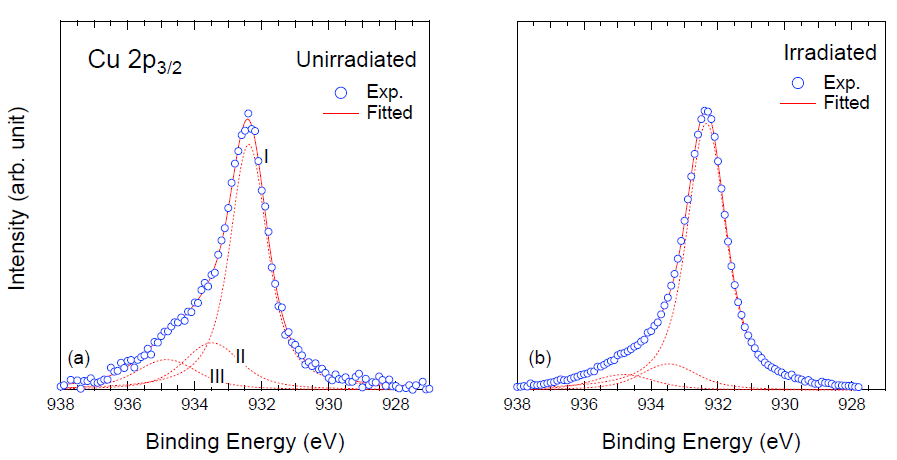
| Samples | Compositions (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Cu2O | CuO | Cu(OH)2 | |
| Unirradiated | 73.8 | 16.5 | 9.7 | |
| (65.7) 1 | (8.1) 1 | |||
| Irradiated | 94.1 | 5.5 | 0.4 | |
| (65.7) 1 | (28.4) 1 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, T.; Nishiyama, F.; Takahiro, K. Chromatic Change in Copper Oxide Layers Irradiated with Low Energy Ions. Quantum Beam Sci. 2021, 5, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs5010007
Kobayashi T, Nishiyama F, Takahiro K. Chromatic Change in Copper Oxide Layers Irradiated with Low Energy Ions. Quantum Beam Science. 2021; 5(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs5010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Takuya, Fumitaka Nishiyama, and Katsumi Takahiro. 2021. "Chromatic Change in Copper Oxide Layers Irradiated with Low Energy Ions" Quantum Beam Science 5, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs5010007
APA StyleKobayashi, T., Nishiyama, F., & Takahiro, K. (2021). Chromatic Change in Copper Oxide Layers Irradiated with Low Energy Ions. Quantum Beam Science, 5(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs5010007





