Structural Deflection Measurement with a Single Smartphone Using a New Scale Factor Calibration Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
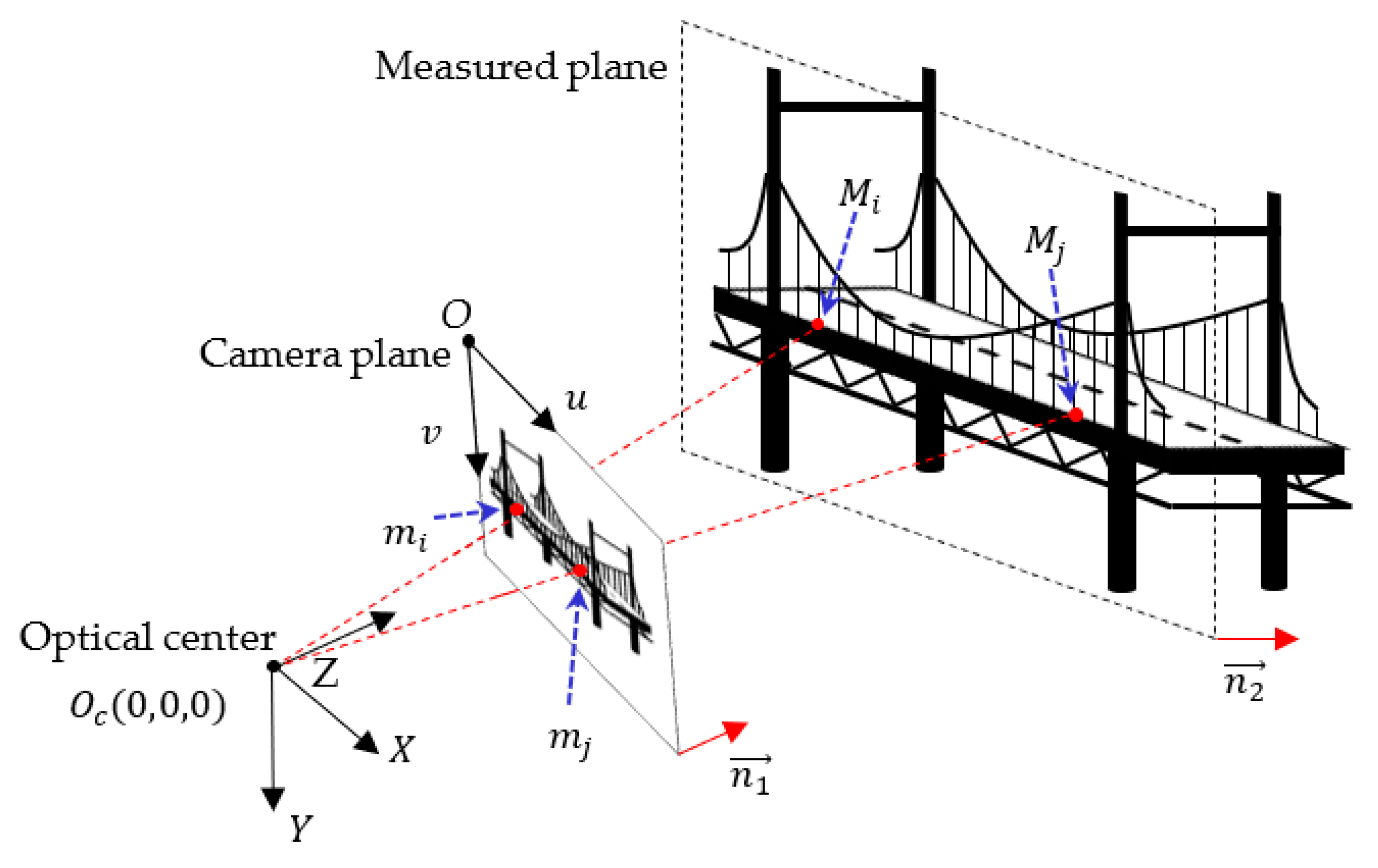
2.1. Principle of Smartphone-Based Structural Deflection Measurement
2.2. Calibration Method of Off-Axis Without Auxiliary Equipment
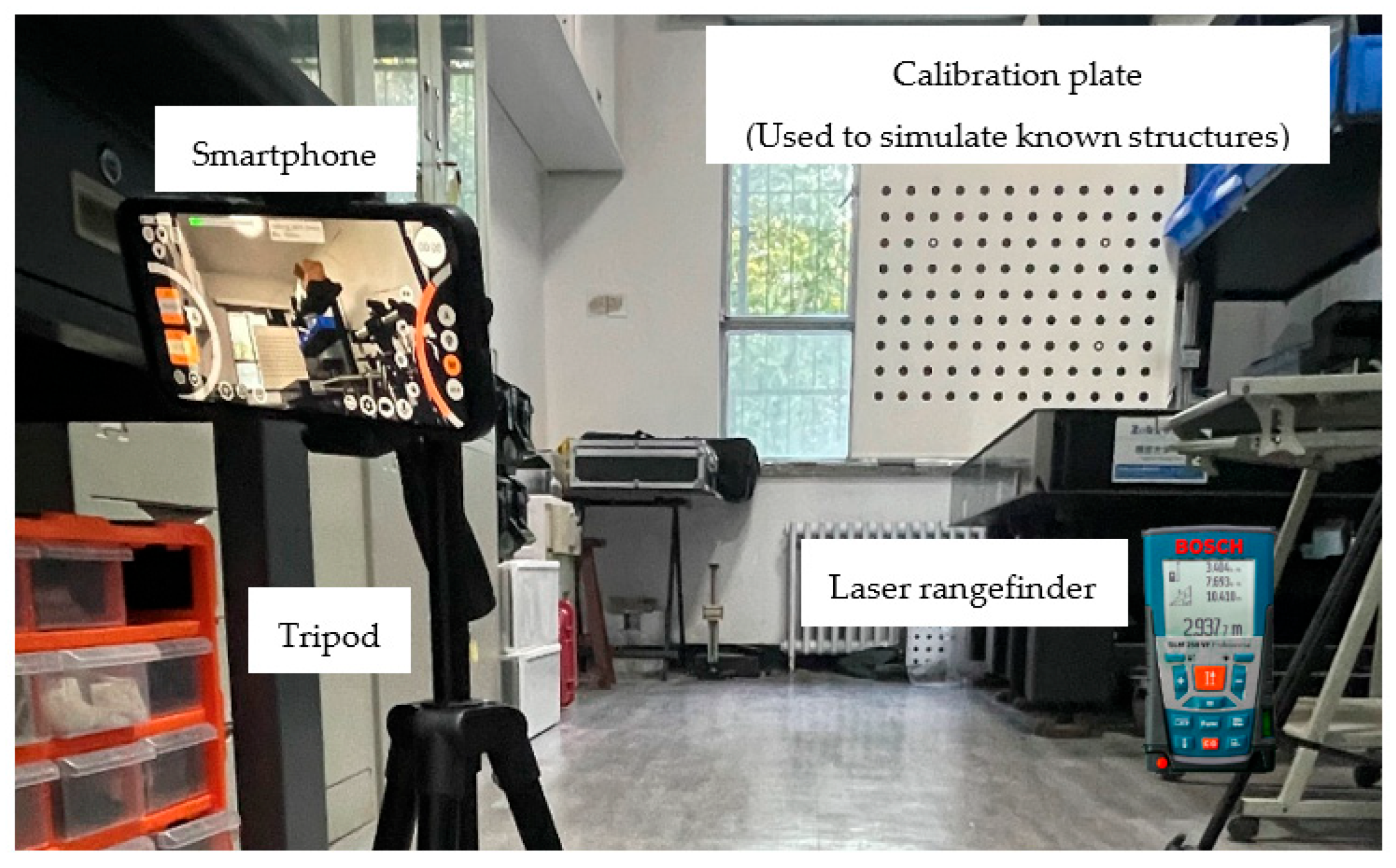
3. Verification Experiments
3.1. Distance Verification Experiments
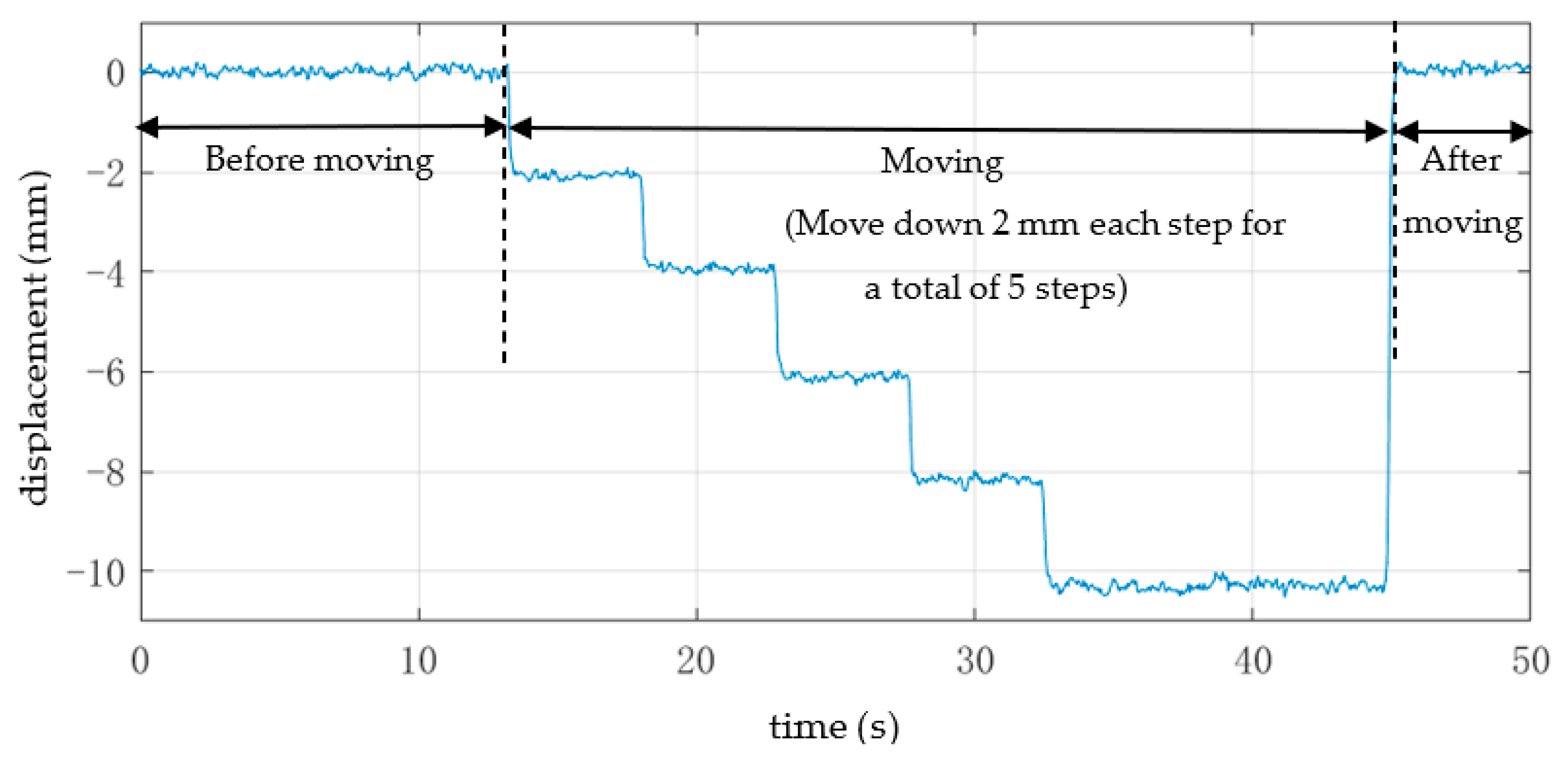
3.2. Deflection Verification Experiment
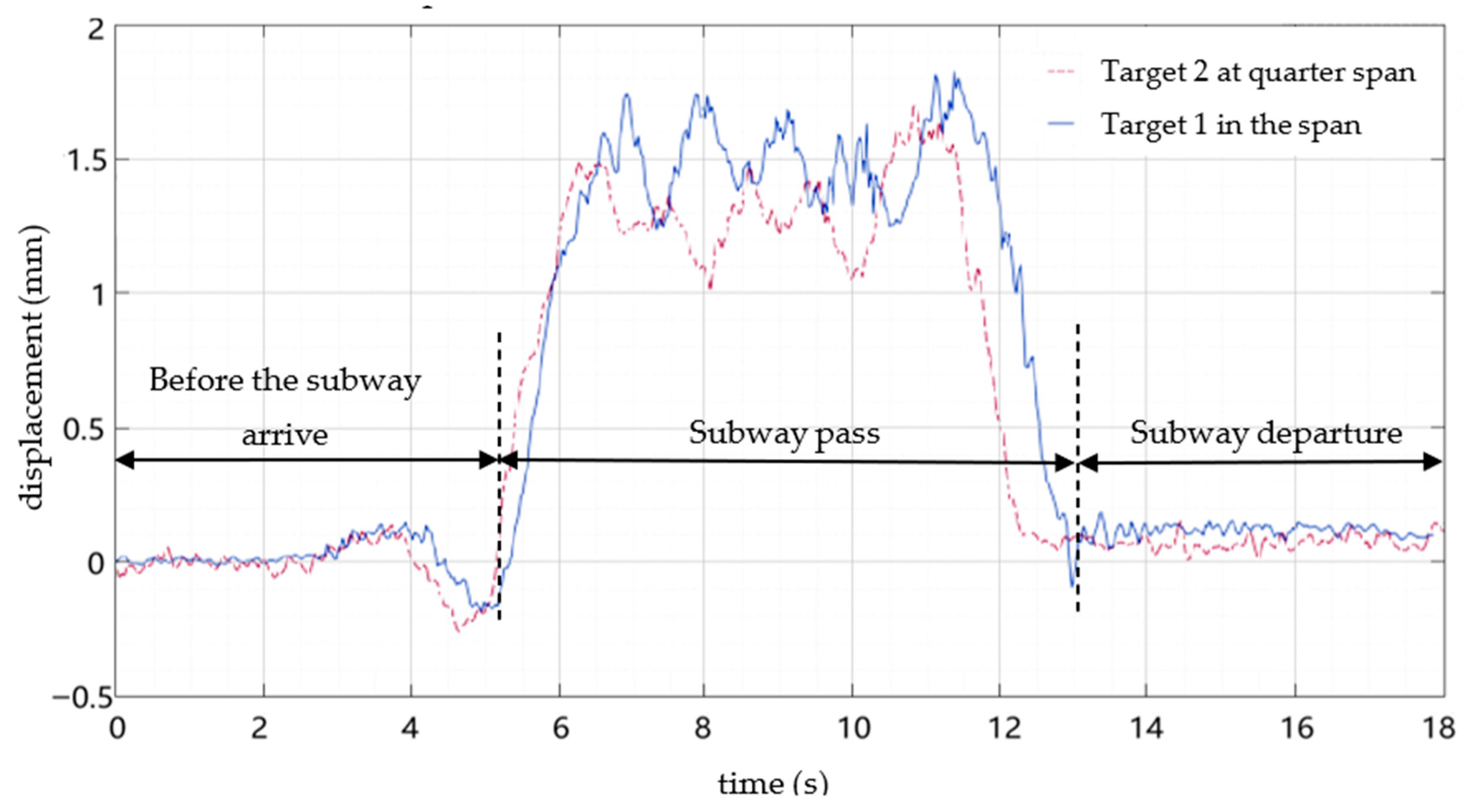
4. Field Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, H.S.; Cheung, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Ahn, J.H. Structural dynamic displacement vision system using digital image processing. NDT E Int. 2011, 44, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.N.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, J.J. A synchronized multipoint vision-based system for displacement measurement of civil infrastructures. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 519146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Ni, Y.; Wai, T.; Wong, K.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Xu, F.J. A vision-based system for dynamic displacement measurement of long-span bridges: Algorithm and verification. Smart Struct. Syst. 2013, 12, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownjohn, J.; Xu, Y.; Hester, D. Vision-Based Bridge Deformation Monitoring. Front. Built Environ. 2017, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuc, T.; Catbas, F.N. Computer vision-based displacement and vibration monitoring without using physical target on structures. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 13, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q. Experimental validation of cost-effective vision based structural health monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 88, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromanis, R.; Xu, Y.; Lydon, D.; Martinez del Rincon, J.; Al-Habaibeh, A. Measuring Structural Deformations in the Laboratory Environment Using Smartphones. Front. Built Environ. 2019, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Lei, D.; Zhu, F.; Bai, P.; Zhang, J. A non-contact displacement measurement system based on a portable smartphone with digital image methods. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2022, 20, 1322–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, H. Computer vision-based displacement identification and its application to bridge condition assessment under operational conditions. Smart Constr. 2024, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, H.; Zhong, Y. Smart structural health monitoring using computer vision and edge computing. Eng. Struct. 2024, 319, 118809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Tian, L.; Song, X. Real-time, non-contact and targetless measurement of vertical deflection of bridges using off-axis digital image correlation. NDT E Int. 2016, 79, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Pan, B. Remote Bridge Deflection Measurement Using an Advanced Video Deflectometer and Actively Illuminated LED Targets. Sensors 2016, 16, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, X.; Pan, B. Cost-Effective and Ultraportable Smartphone-Based Vision System for Structural Deflection Monitoring. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 8843857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mourikis, A.I. Online temporal calibration for camera-IMU systems: Theory and algorithms. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 947–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mourikis, A.I. 3-D Motion Estimation and Online Temporal Calibration for Camera-IMU Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 5709–5716. [Google Scholar]
- Rehder, J.; Nikolic, J.; Schneider, T.; Siegwart, R. A General Approach to Spatiotemporal Calibration in Multi-sensor Systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehder, J.; Nikolic, J.; Schneider, T.; Hinzmann, T.; Siegwart, R. Extending kalibr: Calibrating the extrinsics of multiple IMUs and of individual axes. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 4304–4311. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Shen, S. Autocalibration of low-cost IMU and camera for navigation in cluttered environments. IEEE Sen. J. 2021, 21, 15625–15636. [Google Scholar]
- Geneva, P.; Eckenhoff, K.; Lee, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, G. OpenVINS: A Research Platform for Visual-Inertial Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 4666–4672. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Nobuhara, S.; Nakamura, R.; Sakurada, K. SOIC: Semantic Online Initialization and Calibration for LiDAR and Camera. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. One-shot calibration of low-cost inertial sensors using a smartphone. Sensors 2023, 23, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, B.; Li, K.; Tong, W. Fast, robust and accurate digital image correlation calculation without redundant computations. Exp. Mech. 2013, 53, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sina.com. Beijing Subway Line 13 Records Daily Passenger Volume Exceeding 300,000 for the First Time. Available online: https://news.sina.com.cn/c/2007-10-04/015414020510.shtml (accessed on 10 January 2025).





Method | Reference Value (Laser Rangefinder) | Solution Without Optimization | Local Parameter Optimization | Global Parameter Optimization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Point | Measured Value | Error | Measured Value | Error | Measured Value | Error | ||
| 4.348 | 3.998 | −0.350 | 4.435 | 0.087 | 4.333 | −0.015 | ||
| 4.435 | 3.768 | −0.667 | 4.179 | −0.256 | 4.393 | −0.042 | ||
| 4.393 | 3.854 | −0.539 | 4.274 | −0.119 | 4.384 | −0.009 | ||
| Value | Reference Value (Precision Control Displacement Platform) | Mean | Variance | Error | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step | |||||
| 1 | 0.000 | 0.012 | 0.007 | 0.012 | |
| 2 | −2.000 | −2.072 | 0.004 | −0.072 | |
| 3 | −4.000 | −3.940 | 0.004 | 0.060 | |
| 4 | −6.000 | −6.105 | 0.004 | −0.105 | |
| 5 | −8.000 | −8.166 | 0.006 | −0.166 | |
| 6 | −10.000 | −10.296 | 0.008 | −0.296 | |
| 7 | 0.000 | 0.056 | 0.006 | 0.056 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, L.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, X. Structural Deflection Measurement with a Single Smartphone Using a New Scale Factor Calibration Method. Infrastructures 2025, 10, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10090238
Tian L, Yuan Y, Yu L, Zhang X. Structural Deflection Measurement with a Single Smartphone Using a New Scale Factor Calibration Method. Infrastructures. 2025; 10(9):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10090238
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Long, Yangxiang Yuan, Liping Yu, and Xinyue Zhang. 2025. "Structural Deflection Measurement with a Single Smartphone Using a New Scale Factor Calibration Method" Infrastructures 10, no. 9: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10090238
APA StyleTian, L., Yuan, Y., Yu, L., & Zhang, X. (2025). Structural Deflection Measurement with a Single Smartphone Using a New Scale Factor Calibration Method. Infrastructures, 10(9), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10090238




