Oculomotor Training Improves Reading and Associated Cognitive Functions in Children with Learning Difficulties: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Testing
2.2.1. Best Corrected Visual Acuity (BCVA)
2.2.2. Amplitude of Accommodation (AA)
2.2.3. Near Point of Convergence (NPC)
2.2.4. MEM Retinoscopy
2.2.5. Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) Test
2.2.6. Reading
2.2.7. Visual Search
2.2.8. Visual Motor Integration Test (VMI)–Visual Perception
2.2.9. Rapid Serial Visual Presentation
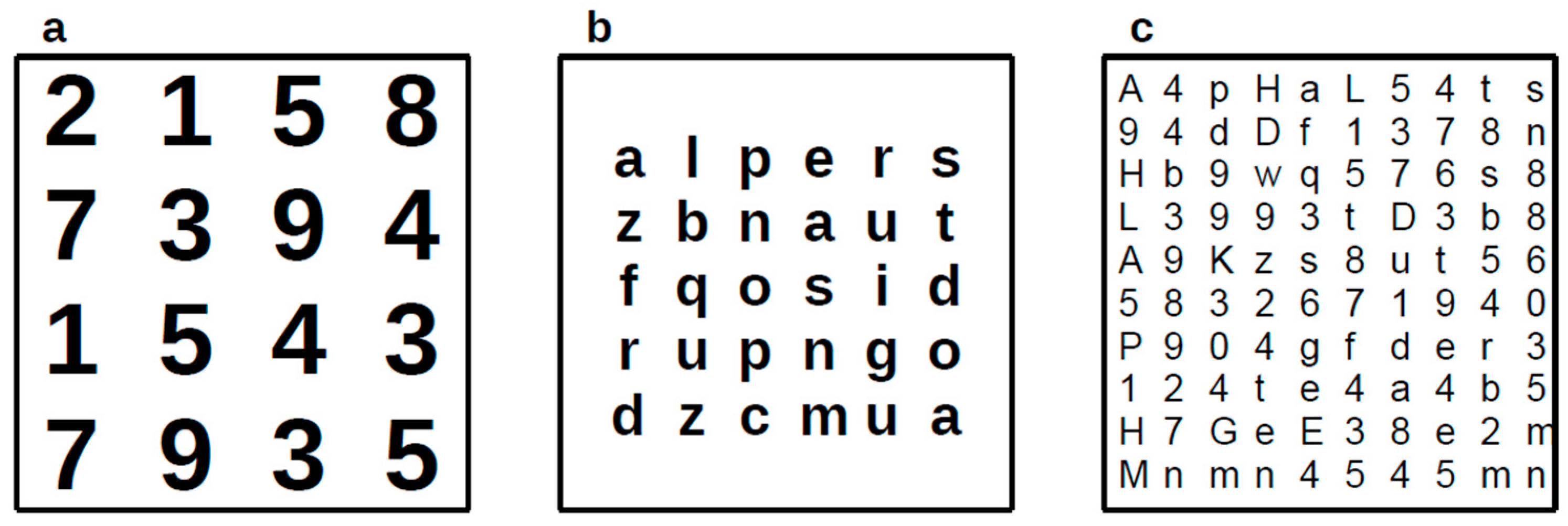
2.2.10. Crowding Test
2.3. Oculomotor Training
- (1)
- Spacing between symbols.
- (2)
- Decreasing the size of the items, changing the font and style of characters.
- (3)
- Changing items from number to letter, symbols, syllables, bisyllabic words, bisyllabic pseudowords and lastly, mixed items.
- (4)
- Time, starting without time restriction, followed with the use of a metronome as soon as possible with an increasing rhythm of about from 50 to 120 bpm.
- (5)
- Varying distance: far, intermediate, and near.
- (6)
- Two or four symbols’ matrices can be used simultaneously, naming each letter on each matrix, and varying the distance between them in horizontal, vertical, and longitudinal directions.
- (7)
- Changing scan strategies, from left-to-right to right-to-left, downward to upward, and external to internal items.
- (8)
- Errors were minimised by emphasising accuracy over speed, and the quality of the performance was the main goal before speed. This represents a form of errorless skill acquisition.
- (9)
- The initial level of training was tailor-made to the level of each child.
- (10)
- Items were changed frequently to avoid boredom.
2.4. Procedures
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
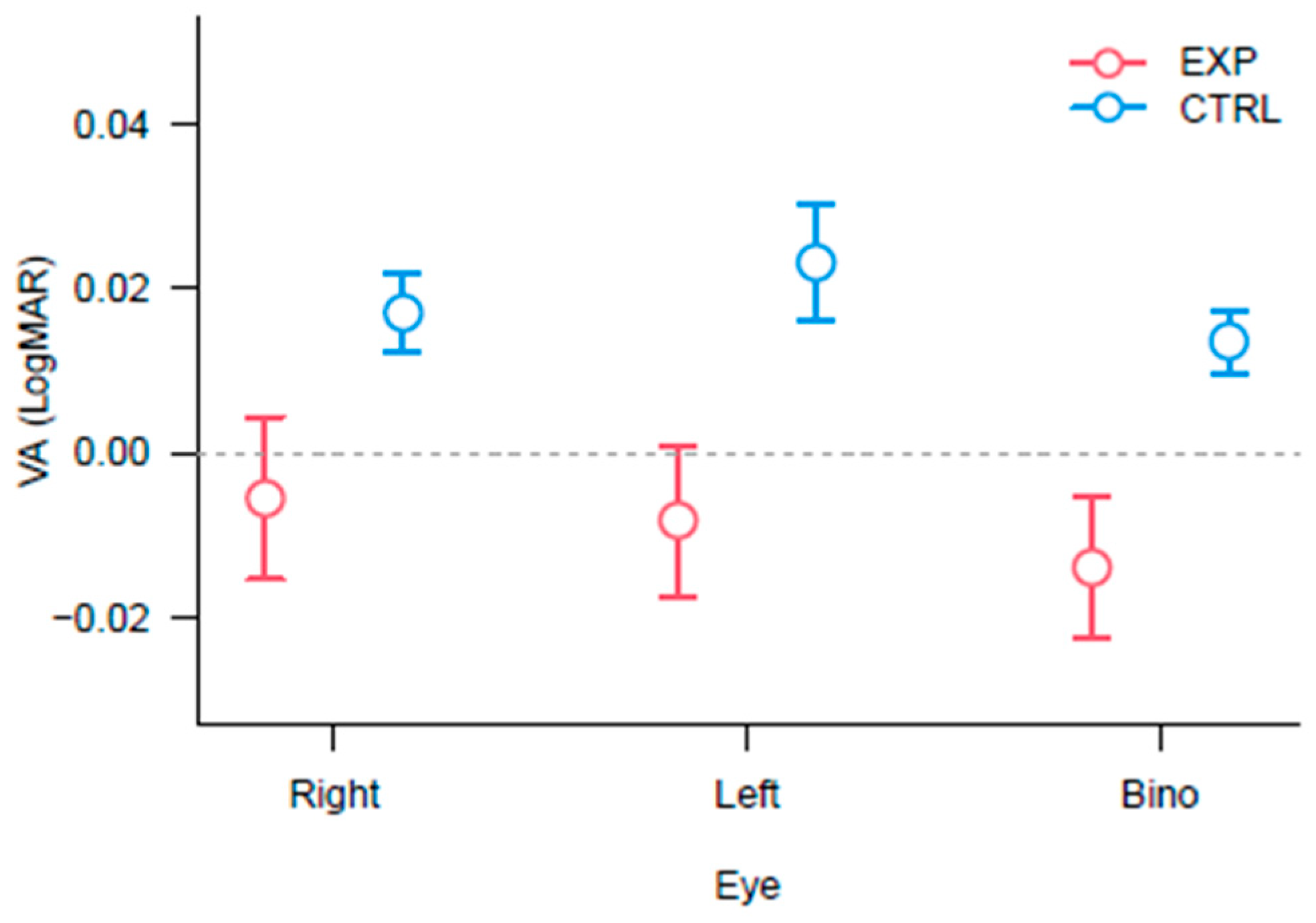
3.1. Best Corrected Visual Acuity
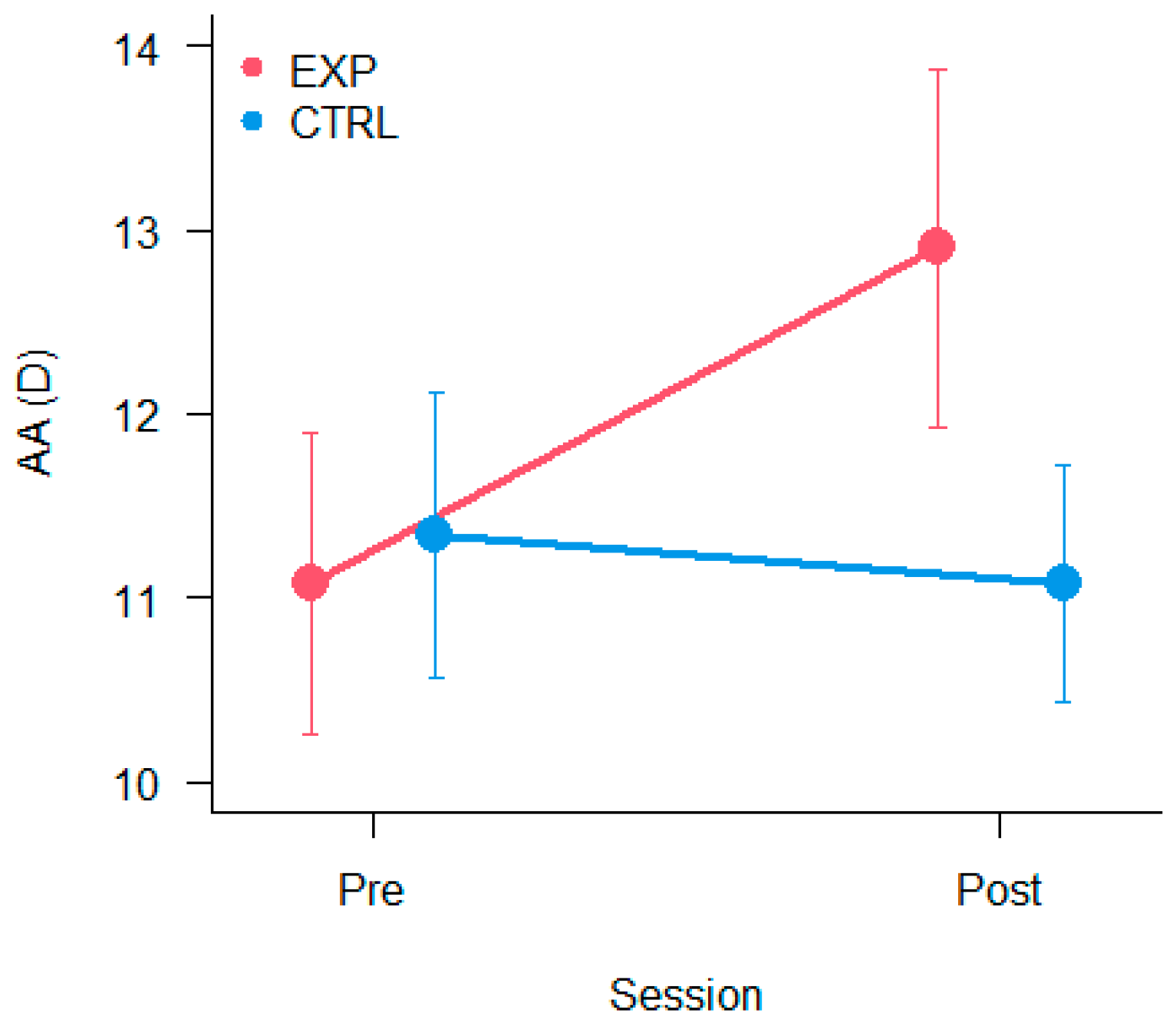
3.2. Amplitude of Accommodation
3.3. Near Point of Convergence (NPC)
3.4. MEM Retinoscopy
3.5. Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) Test
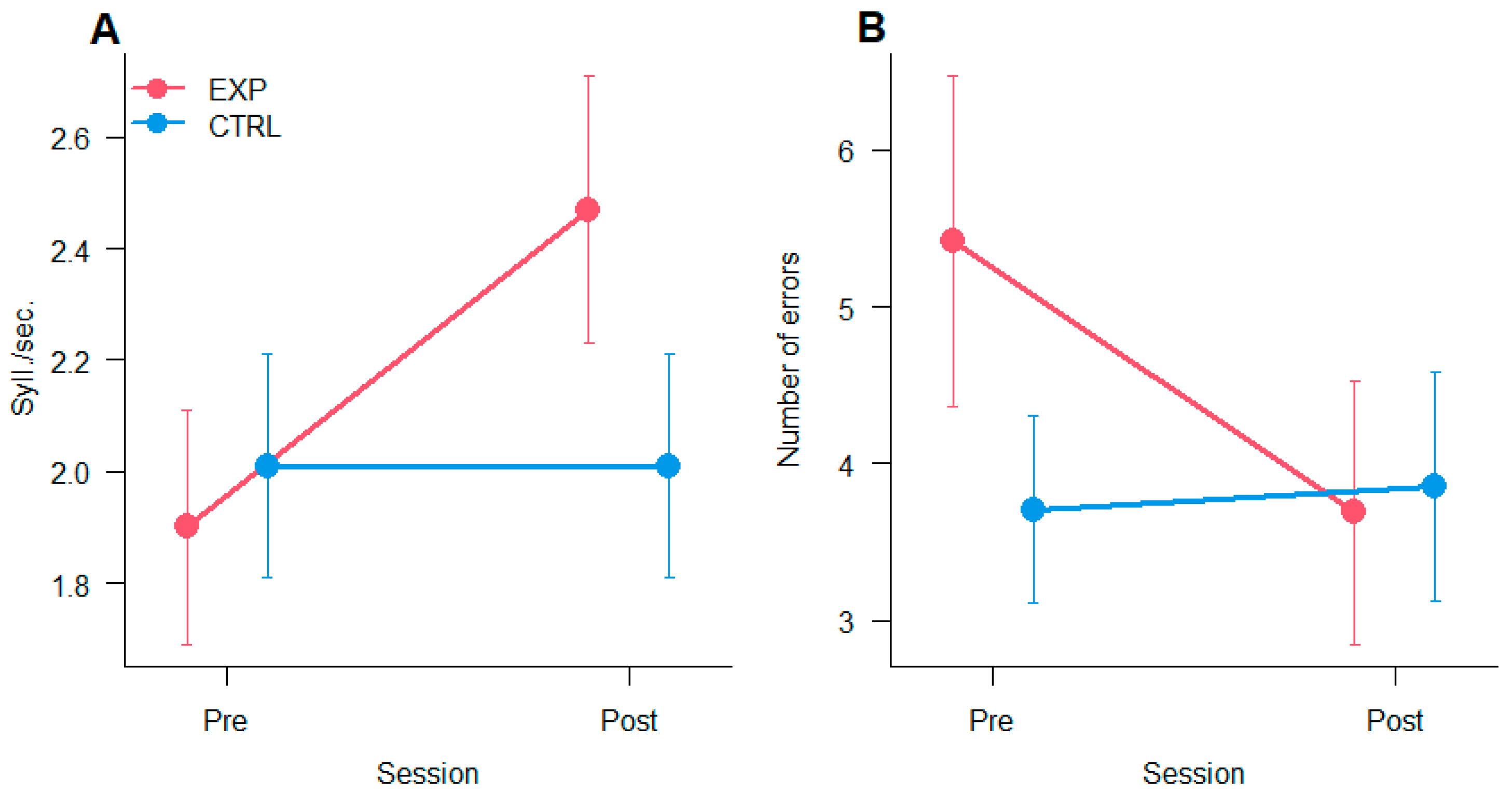
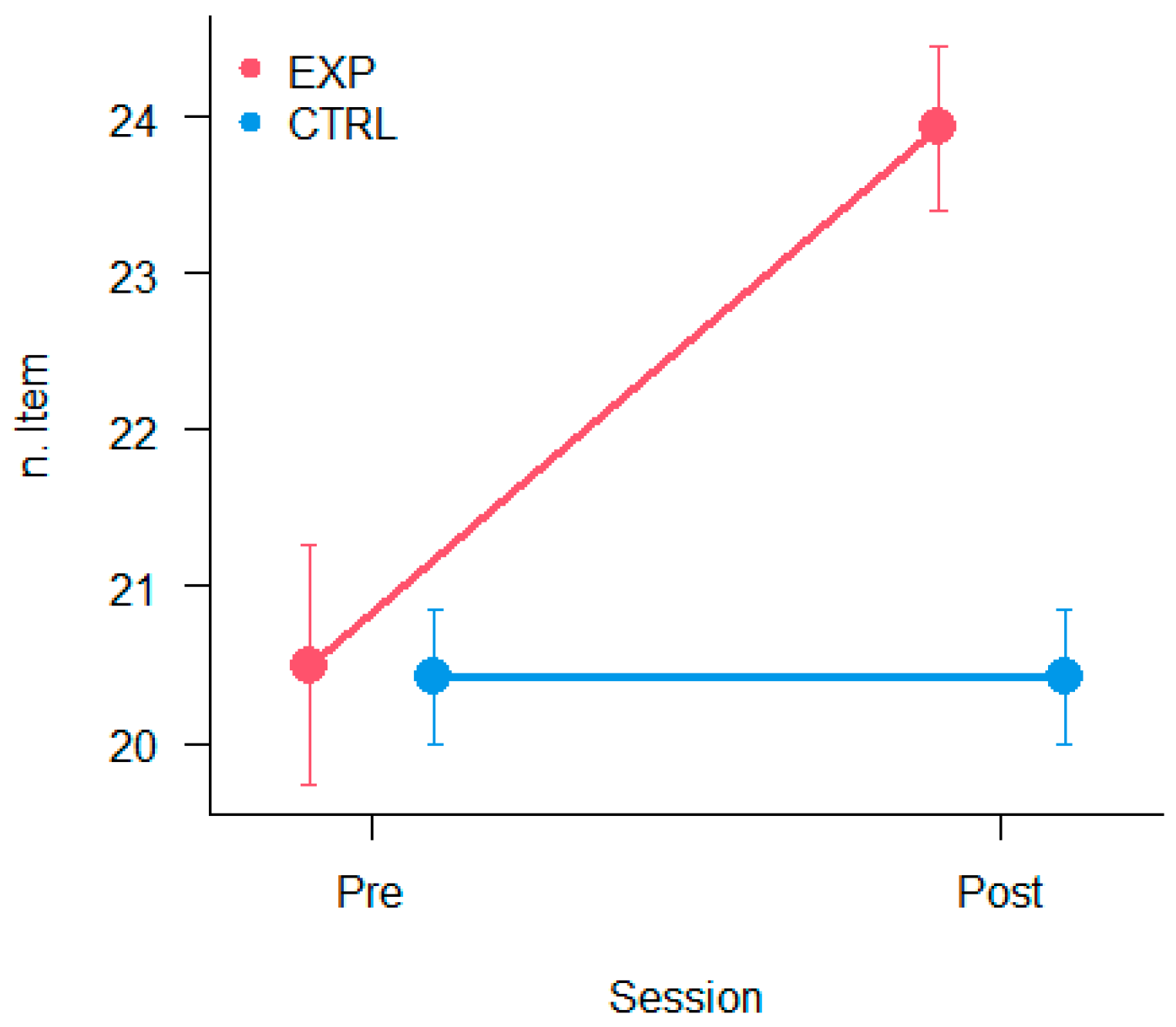
3.6. Reading
3.7. Visual Search
3.8. Visual Motor Integration Test (VMI)–Visual Perception
3.9. Rapid Serial Visual Presentation
3.10. Crowding Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | Amplitude of Accommodation |
| BCVA | Best Corrected Visual Acuity |
| DD | Developmental Dyslexia |
| DEM | Developmental Eye Movement Test |
| NPC | Near Point of Convergence |
| OBOT | Office Based Oculomotor Training |
| RSVP | Rapid Serial Visual Presentation |
| VA | Visual Acuity |
| VMI | test of Visual Motor Integration |
References
- Verhoeven, L.; Reitsma, P.; Siegel, L.S. Cognitive and Linguistic Factors in Reading Acquisition. Read. Writ. 2011, 24, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storch, S.A.; Whitehurst, G.J. Oral Language and Code-Related Precursors to Reading: Evidence from a Longitudinal Structural Model. Dev. Psychol. 2002, 38, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, J.M.; Leonard, L.B. Early Language Milestones and Specific Language Impairment. J. Early Interv. 2016, 38, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.B.; Lonigan, C.J. Identifying Preschool Children at Risk of Later Reading Difficulties: Evaluation of Two Emergent Literacy Screening Tools. J. Learn. Disabil. 2010, 43, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbiero, C.; Montico, M.; Lonciari, I.; Monasta, L.; Penge, R.; Vio, C.; Tressoldi, P.E.; Carrozzi, M.; Petris, A.D.; Cagno, A.G.D.; et al. The Lost Children: The Underdiagnosis of Dyslexia in Italy. A Cross-Sectional National Study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, R.I.; Fawcett, A.J. Procedural Learning Difficulties: Reuniting the Developmental Disorders? Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, M.; Di Filippo, G.; Spinelli, D.; Zoccolotti, P. Crowding, Reading, and Developmental Dyslexia. J. Vis. 2009, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werth, R. Dyslexia Due to Visual Impairments. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchin, A.; Maffioletti, S.; Martelli, M.; Daini, R. Different Trajectories in the Development of Visual Acuity with Different Levels of Crowding: The Milan Eye Chart (MEC). Vis. Res. 2019, 156, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahimi, D.; Aviles, M.; Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J. Oculomotor Patterns in Children with Poor Reading Abilities Measured Using the Development Eye Movement Test. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, I.S.; Ezinne, N.E.; Mohamad Shahimin, M.; Mohd-Ali, B.; Oghre, E.; Zeried, F.M.; Osuagwu, U.L. Age-Matched Comparative Analysis of Binocular Vision Anomalies among Children with Dyslexia in Northern Nigeria. Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghuram, A.; Gowrisankaran, S.; Swanson, E.; Zurakowski, D.; Hunter, D.G.; Waber, D.P. Frequency of Visual Deficits in Children With Developmental Dyslexia. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K. The 35th Sir Frederick Bartlett Lecture: Eye Movements and Attention in Reading, Scene Perception, and Visual Search. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2009, 62, 1457–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, M.P.; Nassibi, N.; Gerard, C.-L.; Bui-Quoc, E.; Seassau, M. Immaturity of the Oculomotor Saccade and Vergence Interaction in Dyslexic Children: Evidence from a Reading and Visual Search Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, M.; Borrelli, M.; Judica, A.; Spinelli, D.; Zoccolotti, P. Reading Words and Pseudowords: An Eye Movement Study of Developmental Dyslexia. Brain Lang. 2002, 80, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccolotti, P.; De Luca, M.; Di Pace, E.; Gasperini, F.; Judica, A.; Spinelli, D. Word Length Effect in Early Reading and in Developmental Dyslexia. Brain Lang. 2005, 93, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portnoy, A.; Gilaie-Dotan, S. Oculomotor-Related Measures Are Predictive of Reading Acquisition in First Grade Early Readers. Vision 2025, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, H.I.; Joseph, H.S.S.L. Children’s Eye Movements during Reading. In The Oxford Handbook of Eye Movements; Liversedge, S.P., Gilchrist, I., Everling, S., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-0-19-953978-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rayner, K. Eye Movements in Reading and Information Processing: 20 Years of Research. Psychol. Bull. 1998, 124, 372–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.; Weber, H. Saccadic Reaction Times of Dyslexic and Age-Matched Normal Subjects. Perception 1990, 19, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarlou, F.; Jarollahi, F.; Ahadi, M.; Sadeghi-Firoozabadi, V.; Haghani, H. Oculomotor Rehabilitation in Children with Dyslexia. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran. 2017, 31, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilbao, C.; Carrera, A.; Otin, S.; Piñero, D.P. Eye Tracking-Based Characterization of Fixations during Reading in Children with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifacci, P.; Tobia, V.; Sansavini, A.; Guarini, A. Eye-Movements in a Text Reading Task: A Comparison of Preterm Children, Children with Dyslexia and Typical Readers. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fella, A.; Loizou, M.; Christoforou, C.; Papadopoulos, T.C. Eye Movement Evidence for Simultaneous Cognitive Processing in Reading. Children 2023, 10, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarlou, F.; Ahadi, M.; Jarollahi, F. Eye Movement Patterns in Iranian Dyslexic Children Compared to Non-Dyslexic Children. Auris Nasus Larynx 2021, 48, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.; Slowiaczek, M.L.; Clifton, C.; Bertera, J.H. Latency of Sequential Eye Movements: Implications for Reading. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1983, 9, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, M.; Di Pace, E.; Judica, A.; Spinelli, D.; Zoccolotti, P. Eye Movement Patterns in Linguistic and Non-Linguistic Tasks in Developmental Surface Dyslexia. Neuropsychologia 1999, 37, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seassau, M.; Gérard, C.L.; Bui-Quoc, E.; Bucci, M.P. Binocular Saccade Coordination in Reading and Visual Search: A Developmental Study in Typical Reader and Dyslexic Children. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte-Körne, G. The Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Dyslexia. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2010, 107, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.W.; Slinger-Constant, A.-M. Current Status of Treatments for Dyslexia: Critical Review. J. Child. Neurol. 2004, 19, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, M.T.; Pullman, M.Y. A Compensatory Role for Declarative Memory in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 51, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Viersen, S.; de Bree, E.H.; de Jong, P.F. Protective Factors and Compensation in Resolving Dyslexia. Sci. Stud. Read. 2019, 23, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.P.; Carzola, B.; Fiucci, G.; Potente, C.; Caruso, L. Computer Based Oculomotor Training Improves Reading Abilities in Dyslexic Children: Results from A Pilot Study. Sports Injr. Med. 2018, 2, JSIMD-130. [Google Scholar]
- Jafarlou, F.; Jarollahi, F.; Ahadi, M.; Sadeghi-Firoozabadi, V. Effects of Oculomotor Rehabilitation on the Cognitive Performance of Dyslexic Children with Concurrent Eye Movement Abnormalities. Early Child Dev. Care 2022, 192, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, K.L.; Raymond, J.E. Training of Efficient Oculomotor Strategies Enhances Skill Acquisition. Acta Psychol. 1989, 71, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarlou, F. Oculomotor Rehabilitation Improves Reading Abilities in Dyslexic Children With Concurrent Eye Movement Abnormalities. Clin. Pediatr. 2024, 63, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, J.C.; Court, J.H. Manual for Raven’s Progressive Matrices and Vocabulary Scales 1982. Stand. Progress. Matrices 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Belacchi, C.; Scalisi, T.G.; Cannoni, E.; Cornoldi, C. CPM-Coloured Progressive Matrices. Standardizzazione Italiana; GIUNTI-ORGANIZZAZIONI SPECIALI: Florence, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiman, M.; Wick, B. Clinical Management of Binocular Vision; Wolters Kluwer Health: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-4963-9974-8. [Google Scholar]
- Campo Dall’Orto, G.; Facchin, A.; Bellatorre, A.; Maffioletti, S.; Serio, M. Measurement of Visual Acuity with a Digital Eye Chart: Optotypes, Presentation Modalities and Repeatability. J. Optom. 2021, 14, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, A.; Mazzilli, M.; Maffioletti, S. Percentile Distribution of Habitual-Correction Visual Acuity in a Sample of 1500 Children Aged 5 to 15 Years in Italy. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, D.B. Clinical Procedures in Primary Eye Care; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Garzia, R.P.; Richman, J.E.; Nicholson, S.B.; Gaines, C.S. A New Visual-Verbal Saccade Test: The Developmental Eye Movement Test (DEM). J. Am. Optom. Assoc. 1990, 61, 124–135. [Google Scholar]
- Facchin, A. Spotlight on the Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) Test. Clin. Optom. 2021, 13, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornoldi, C.; Colpo, G. Prove Di Lettura MT-2 per La Scuola Primaria: Manuale; Giunti OS: Florence, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Beery, K.E.; Beery, N.A.; Buktenica, N.A. The Beery-Buktenica Developmental Test of Visual-Motor Integration: VMI, with Supplemental Developmental Tests of Visual Perception and Motor Coordination: Administration, Scoring and Teaching Manual; Modern Curriculum Press: Parsippany, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, M.C. Rapid Serial Visual Presentation (RSVP): A Method for Studying Language Processing. In New methods in reading comprehension research; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 91–118. [Google Scholar]
- Pelli, D.G.; Waugh, S.J.; Martelli, M.; Crutch, S.J.; Primativo, S.; Yong, K.X.; Rhodes, M.; Yee, K.; Wu, X.; Famira, H.F.; et al. A Clinical Test for Visual Crowding 2016. F1000Research 2016, 81, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team, R. R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2024. Found. Stat. Comput. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiman, M.; Cotter, S.; Kulp, M.T.; Mitchell, G.L.; Cooper, J.; Gallaway, M.; Hopkins, K.B.; Bartuccio, M.; Chung, I.; Group, the C.I.T.T.S. Treatment of Accommodative Dysfunction in Children: Results from a Randomized Clinical Trial. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wei, S.; Li, S.-M.; An, W.; Du, J.; Wang, N. Effect of Reading with a Mobile Phone and Text on Accommodation in Young Adults. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 259, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiman, M.; Kulp, M.T.; Cotter, S.; Mitchell, G.L.; Gallaway, M.; Boas, M.; Coulter, R.; Hopkins, K.; Tamkins, S.; Group, T.C.I.T.T.S. Vision Therapy/Orthoptics for Symptomatic Convergence Insufficiency in Children: Treatment Kinetics. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindmarsh, G.P.; Black, A.A.; White, S.L.; Hopkins, S.; Wood, J.M. Eye Movement Patterns and Reading Ability in Children. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2021, 41, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, A.; Maffioletti, S. The Reliability of the DEM Test in the Clinical Environment. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, N.; Ciuffreda, K.J. Assessment of Neuro-Optometric Rehabilitation Using the Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) Test in Adults with Acquired Brain Injury. J. Optom. 2018, 11, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albonico, A.; Martelli, M.; Bricolo, E.; Frasson, E.; Daini, R. Focusing and Orienting Spatial Attention Differently Modulate Crowding in Central and Peripheral Vision. J. Vis. 2018, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosse, M.-L.; Tainturier, M.J.; Valdois, S. Developmental Dyslexia: The Visual Attention Span Deficit Hypothesis. Cognition 2007, 104, 198–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, M.; Arduino, L.S.; Daini, R. Two Different Mechanisms for Omission and Substitution Errors in Neglect Dyslexia. Neurocase 2011, 17, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daini, R.; Primativo, S.; Albonico, A.; Veronelli, L.; Malaspina, M.; Corbo, M.; Martelli, M.; Arduino, L.S. The Focal Attention Window Size Explains Letter Substitution Errors in Reading. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalvand, H.; Chamani, N.; Rahsepar-Fard, K.; Khorrami-Nejad, M.; Dadgar, H. The Effect of Online Visual Games on Visual Perception, Oculomotor, and Balance Skills of Children with Developmental Dyslexia during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. Ophthalmol. 2023, 43, 5011–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CITT Study group Effect of Vergence/Accommodative Therapy on Reading in Children with Convergence Insufficiency: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2019, 96, 836. [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Fawcett, A.J. Cognitive-Motor Training Improves Reading-Related Executive Functions: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study in Dyslexia. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Dhia, A.; Bucci, M.-P.; Naffeti, C.; Ben Saad, H.; Hammouda, O.; Driss, T. Combined Cognitive and Motor Training Improves Reading, Writing and Motor Coordination in Dyslexic Children. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, A.; Simioni, M.; Maffioletti, S.; Daini, R. Broken Ring enVision Search (BReViS): A New Clinical Test of Attention to Assess the Effect of Layout and Crowding on Visual Search. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Facchin, A.; Maffioletti, S.; Maffioletti, M.; Esposito, G.; Bonetti, M.; Girelli, L.; Daini, R. Oculomotor Training Improves Reading and Associated Cognitive Functions in Children with Learning Difficulties: A Pilot Study. Vision 2025, 9, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9040083
Facchin A, Maffioletti S, Maffioletti M, Esposito G, Bonetti M, Girelli L, Daini R. Oculomotor Training Improves Reading and Associated Cognitive Functions in Children with Learning Difficulties: A Pilot Study. Vision. 2025; 9(4):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9040083
Chicago/Turabian StyleFacchin, Alessio, Silvio Maffioletti, Marta Maffioletti, Gabriele Esposito, Marta Bonetti, Luisa Girelli, and Roberta Daini. 2025. "Oculomotor Training Improves Reading and Associated Cognitive Functions in Children with Learning Difficulties: A Pilot Study" Vision 9, no. 4: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9040083
APA StyleFacchin, A., Maffioletti, S., Maffioletti, M., Esposito, G., Bonetti, M., Girelli, L., & Daini, R. (2025). Oculomotor Training Improves Reading and Associated Cognitive Functions in Children with Learning Difficulties: A Pilot Study. Vision, 9(4), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9040083







