Vergence and Accommodation Cues in Stereo-Localization during the Small-In Large-Out (SILO) Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample and Baseline Examinations
2.2. Assessment of the SILO Effect
2.3. Assessment of AC/A Ratio
2.4. Statistical Analysis
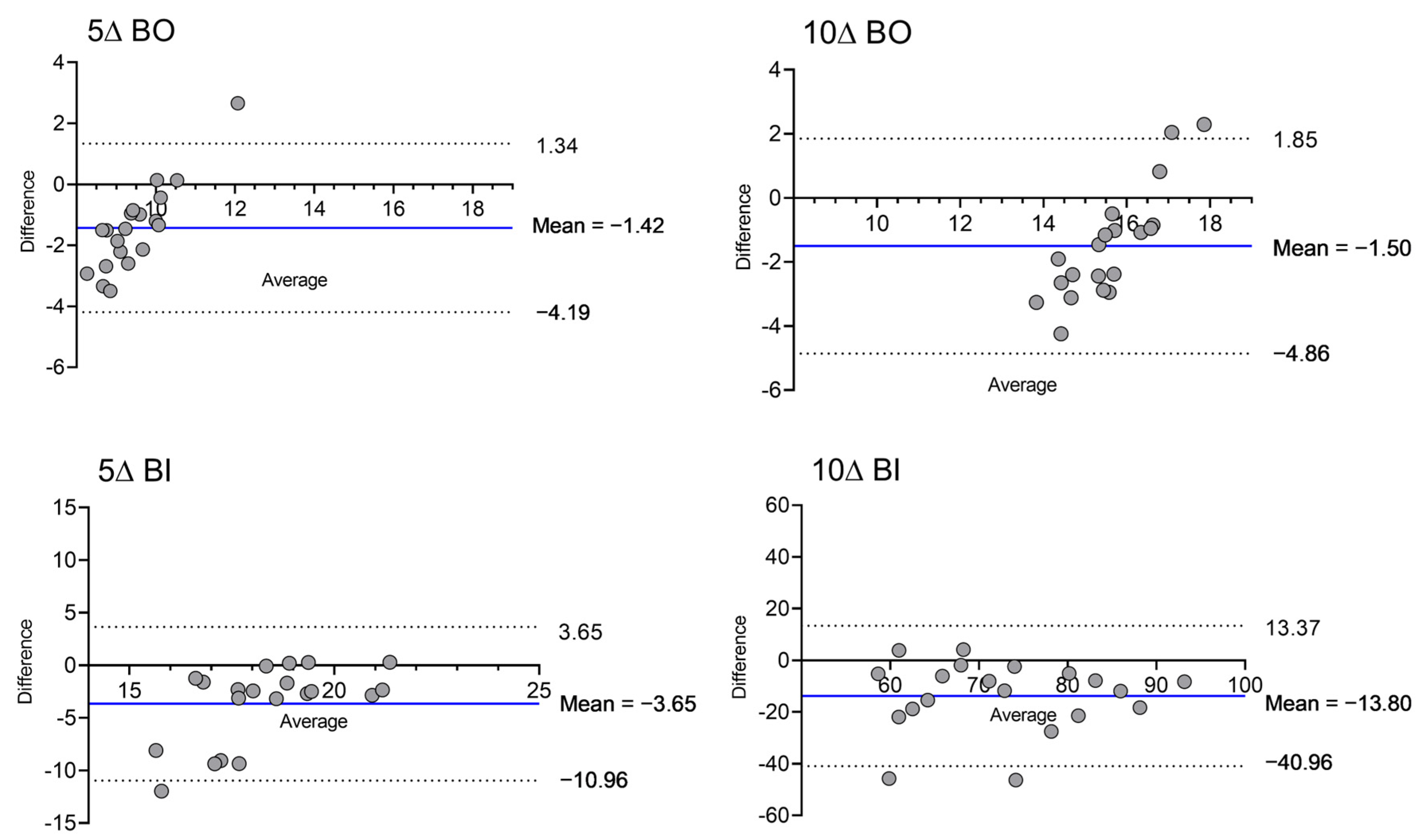
3. Results
3.1. Study Sample Characteristics
3.2. Analysis of the SILO Effect
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Stereo-Localization Accuracy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Convergence Insufficiency Treatment Trial Study Group. Randomized clinical trial of treatments for symptomatic convergence insufficiency in children. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2008, 126, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Convergence Insufficiency Treatment Trial Study Group. Long-term effectiveness of treatments for symptomatic convergence insufficiency in children. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2009, 86, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiman, M.; Kulp, M.T.; Cotter, S.A.; Lawrenson, J.G.; Wang, L.; Li, T. Interventions for convergence insufficiency: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 12, CD006768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Convergence Insufficiency Treatment Trial Study Group. Treatment of symptomatic convergence insufficiency in children enrolled in the Convergence Insufficiency Treatment Trial–Attention & Reading Trial: A randomized clinical trial. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2019, 96, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brautaset, R.; Wahlberg, M.; Abdi, S.; Pansell, T. Accommodation insufficiency in children: Are exercises better than reading glasses? Strabismus 2008, 16, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuffreda, K.J. The scientific basis for and efficacy of optometric vision therapy in nonstrabismic accommodative and vergence disorders. Optometry 2002, 73, 735–762. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scheiman, M.; Wick, B. Clinical Management of Binocular Vision: Heterophoric, Accommodative, and Eye Movement Disorders; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schor, C.; Horner, D. Adaptive disorders of accommodation and vergence in binocular dysfunction. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 1989, 9, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiman, M.; Mitchell, G.L.; Cotter, S.; Cooper, J.; Kulp, M.; Rouse, M.; Borsting, E.; London, R.; Wensveen, J.; Convergence Insufficiency Treatment Trial Study Group. A randomized clinical trial of treatments for convergence insufficiency in children. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2005, 123, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibowitz, H.W.; Shiina, K.; Hennessy, R.T. Oculomotor adjustments and size constancy. Percept. Psychophys. 1972, 12, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Worrell, B.E.; Hirsch, M.J.; Morgan, M.W. An evaluation of prism prescribed by Sheard’s criterion. Am. J. Optom. Arch. Am. Acad. Optom. 1971, 48, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedy, J.E.; Saladin, J.J. Association of symptoms with measures of oculomotor deficiencies. Am. J. Optom. Physiol. Opt. 1978, 55, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, R.M.; Cushman, W.B.; Martins, A.J. The precision of gaze. A review. Hum. Neurobiol. 1982, 1, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Charman, W.N. Forming an optical image: The optical elements of the eye. In Optometry: Science, Techniques and Clinical Management, 2nd ed.; Rosenfield, M., Logan, N., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, G.K.; Ciuffreda, K.J.; Rosenfield, M. Proximal contribution to a linear static model of accommodation and vergence. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 1996, 16, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkelens, I.M.; Bobier, W.R. Asymmetries between convergence and divergence reveal tonic vergence is dependent upon phasic vergence function. J. Vis. 2017, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaschinski, W.; Švede, A.; Jainta, S. Relation between fixation disparity and the asymmetry between convergent and divergent disparity step responses. Vis. Res. 2008, 48, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, G.K.; Zhu, H.; Ciuffreda, K.J. Convergence and divergence exhibit different response characteristics to symmetric stimuli. Vis. Res. 1997, 37, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, N.K.; Mani, R.; Hussaindeen, J.R. Changes in stimulus and response AC/A ratio with vision therapy in Convergence Insufficiency. J. Optom. 2017, 10, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brautaset, R.L.; Jennings, A.J. Effects of orthoptic treatment on the CA/C and AC/A ratios in convergence insufficiency. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 2876–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoola, H.; Bruce, A.S.; Atchison, D.A. Validity of clinical measures of the AC/A ratio. Clin. Exp. Optom. 1995, 78, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainey, B.B.; Goss, D.A.; Kidwell, M.; Feng, B. Reliability of the response AC/A ratio determined using nearpoint autorefraction and simultaneous heterophoria measurement. Clin. Exp. Optom. 1998, 81, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripps, H.; Chin, N.B.; Siegel, I.M.; Breinin, G.M. The effect of pupil size on accommodation, convergence, and the AC/A ratio. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1962, 1, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Cornforth, L.L.; Johnson, B.L.; Kohl, P.; Roth, N. Chromatic imbalance due to commonly used red-green filters reduces accuracy of stereoscopic depth perception. Am. J. Optom. Physiol. Opt. 1987, 64, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| AC/A Ratio (Δ/D) | Near Phoria (0.4 m) (Δ) | Distance Phoria (6 m) (Δ) | Stereoacuity (”) | Near Point of Convergence (cm) | Fusional Vergence Ranges (Δ) | Amplitude of Accommodation (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.18 (1.95) | −6.50 (−8.00, 0.25) | 0.00 (−1.00, 1.00) | 25.00 (18.25, 30.25) | 3.00 (3.00, 6.00) | BO = 24.68 (6.63) BI = 16.42 (4.66) | RE = 6.51 (0.99) LE = 6.48 (1.08) |
| AC/A Ratio (Δ/D) | Measured Distance (m or m’) (cm) | Calculated Distance (s or s’) (cm) | Distance Error (s−m) or (s’−m’) (es) (cm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5Δ BO | 10Δ BO | 5Δ BI | 10Δ BI | 5Δ BO | 10Δ BO | 5Δ BI | 10Δ BI | 5Δ BO | 10Δ BO | 5Δ BI | 10Δ BI | |
| 2.80 | 9.10 | 15.20 | −18.00 | −72.80 | 10.09 | 16.22 | −19.69 | −75.18 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 1.69 | 2.38 |
| 4.50 | 6.80 | 13.10 | −18.30 | −70.30 | 9.73 | 15.75 | −18.38 | −66.16 | 2.93 | 2.65 | 0.08 | −4.14 |
| 7.60 | 8.90 | 13.50 | −16.50 | −62.80 | 9.85 | 15.90 | −18.80 | −68.92 | 0.95 | 2.40 | 2.30 | 6.12 |
| 6.70 | 8.00 | 12.20 | −16.00 | −56.00 | 9.51 | 15.46 | −17.60 | −61.26 | 1.51 | 3.26 | 1.60 | 5.26 |
| 2.90 | 8.00 | 17.20 | −17.00 | −67.00 | 10.21 | 16.38 | −20.17 | −78.76 | 2.21 | −0.82 | 3.17 | 11.76 |
| 3.80 | 7.40 | 13.10 | −11.60 | −67.10 | 10.09 | 16.22 | −19.69 | −75.18 | 2.69 | 3.12 | 8.09 | 8.08 |
| 9.00 | 8.00 | 14.50 | −12.70 | −64.40 | 10.60 | 16.88 | −21.76 | −91.89 | 2.60 | 2.38 | 9.06 | 27.49 |
| 3.40 | 9.40 | 15.80 | −12.40 | −70.50 | 10.60 | 16.88 | −21.76 | −91.89 | 1.20 | 1.08 | 9.36 | 21.39 |
| 2.90 | 13.40 | 16.20 | −13.00 | −51.00 | 10.74 | 17.05 | −22.35 | −97.29 | −2.66 | 0.85 | 9.35 | 46.29 |
| 1.60 | 9.00 | 15.40 | −19.00 | −67.00 | 9.85 | 15.90 | −18.80 | −68.92 | 0.85 | 0.50 | −0.20 | 1.92 |
| 4.80 | 7.90 | 13.40 | −16.00 | −62.90 | 9.40 | 15.31 | −17.23 | −59.07 | 1.50 | 1.91 | 1.23 | −3.83 |
| 1.90 | 10.10 | 14.60 | −19.50 | −56.50 | 9.96 | 16.06 | −19.23 | −71.91 | −0.14 | 1.46 | −0.27 | 15.41 |
| 2.40 | 7.00 | 14.10 | −18.00 | −77.60 | 10.34 | 16.54 | −20.68 | −82.70 | 3.34 | 2.44 | 2.68 | 5.10 |
| 3.10 | 10.60 | 19.00 | −21.50 | −79.20 | 10.47 | 16.71 | −21.21 | −87.05 | −0.13 | −2.29 | −0.29 | 7.85 |
| 4.30 | 8.10 | 14.90 | −16.10 | −50.00 | 9.96 | 16.06 | −19.23 | −71.91 | 1.86 | 1.16 | 3.13 | 21.91 |
| 3.30 | 8.60 | 14.10 | −19.50 | −79.00 | 10.74 | 17.05 | −22.35 | −97.29 | 2.14 | 2.95 | 2.85 | 18.29 |
| 6.40 | 9.90 | 12.30 | −18.20 | −37.00 | 10.34 | 16.54 | −20.68 | −82.70 | 0.44 | 4.24 | 2.48 | 45.70 |
| 5.50 | 8.50 | 18.10 | −16.80 | −53.10 | 9.96 | 16.06 | −19.23 | −71.91 | 1.46 | −2.04 | 2.43 | 18.81 |
| 3.40 | 7.10 | 14.00 | −9.80 | −80.00 | 10.60 | 16.88 | −21.76 | −91.89 | 3.50 | 2.88 | 11.96 | 11.89 |
| 3.30 | 9.40 | 16.10 | −20.00 | −89.00 | 10.74 | 17.05 | −22.35 | −97.29 | 1.34 | 0.95 | 2.35 | 8.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Argilés, M.; Cardona, G.; Hosa-Vila, S.; Sunyer-Grau, B. Vergence and Accommodation Cues in Stereo-Localization during the Small-In Large-Out (SILO) Effect. Vision 2022, 6, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040063
Argilés M, Cardona G, Hosa-Vila S, Sunyer-Grau B. Vergence and Accommodation Cues in Stereo-Localization during the Small-In Large-Out (SILO) Effect. Vision. 2022; 6(4):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040063
Chicago/Turabian StyleArgilés, Marc, Genis Cardona, Sandra Hosa-Vila, and Bernat Sunyer-Grau. 2022. "Vergence and Accommodation Cues in Stereo-Localization during the Small-In Large-Out (SILO) Effect" Vision 6, no. 4: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040063
APA StyleArgilés, M., Cardona, G., Hosa-Vila, S., & Sunyer-Grau, B. (2022). Vergence and Accommodation Cues in Stereo-Localization during the Small-In Large-Out (SILO) Effect. Vision, 6(4), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040063





