Abstract
Background: Despite the benefits of physical activity (PA), Italy ranks low in leisure-time PA among European countries. Integrating virtual (VR)/enhanced (ER) reality with exercise equipment could boost PA engagement. Limited studies have explored how VR/ER-integrated cycling activity, compared to outdoor settings, influences PA among university students. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the acute effects of a brief cycling session outdoors and indoors on psychological and physiological outcomes, and secondly, investigate the potential of VR/ER-mediated nature experiences as a tool to promote green exercise. Methods: In February 2024, thirty-one subjects (20 M and 11 F; age 24.3 ± 3.2 years; BMI 23.5 ± 3.6 kg/m2) were involved in this randomized crossover-controlled trial, where they were assigned to three different conditions: ER cycling (ERC), VR cycling (VRC), and outdoor cycling (OUTC). Heart rate (HR), Physical Activity Enjoyment (PACE), Intrinsic Motivation Inventory (IMI), and Intention to Perform Green Exercise (INT-GE) were assessed at the end of each condition. Results: The OUTC condition showed significantly greater PACE, IMI, and INT-GE than ERC/VRC (p < 0.001), lower HRmean than ERC/VRC (p < 0.001 and p < 0.05, respectively), and lower HRmax than ERC (p < 0.05). Conclusions: VRC and ERC enhanced engagement and physiological responses during indoor cycling, but outdoor cycling offered superior benefits in motivation, enjoyment, and future engagement intentions. No significant differences were found between VRC and ERC in promoting intentions for outdoor activities, suggesting both technologies could be equally effective.
Keywords:
VR; physical activity; leisure time; sedentary; technology; exercise adherence; physical fitness 1. Introduction
Data from the latest European Health Interview Survey (EHIS) position Italy in 21st place out of 27 countries in the ranking of the percentage of adults engaging in leisure-time physical activity (PA): only 26.7% engage in aerobic physical activity at least once a week, whereas the percentage rises to 44.3% among the adult population of Europe as a whole. In Italy, only one in five people engage in aerobic physical activity for at least 150 min per week, thus adhering to the World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines [1], compared to the European average of one in three. Italians are less active than other Europeans even when it comes to active transportation: only 16% use bicycles compared to a European average of 23.6% [2]. University students are at risk of physical inactivity and early development of non-communicable diseases as this population often makes autonomous lifestyle choices for the first time (e.g., PA-related behaviors, dietary choices, etc.) [3,4,5]. Pleasant and sustainable intervention strategies are therefore needed to promote and increase university students’ participation in PA.
The WHO has set ambitious goals for 2030 aimed at promoting physical activity and sustainability. These include a 15% reduction in physical inactivity among adults and adolescents, and the integration of urban policies that encourage active mobility. These initiatives aim to improve public health and environmental sustainability, reflecting a holistic and cross-sectoral approach [6]. Furthermore, the WHO aims to promote people’s ability to exert greater control over their health by embracing active lifestyles while simultaneously preserving the integrity of the environment [7]. Therefore, it is crucial to foster the capability and motivation of individuals, groups, and communities to embrace active and healthy ways of living.
Replacing car travel with cycling can significantly reduce air pollution and reduce exposure to pollutants [8]. Cycling is increasingly recognized as a crucial element in public health guidelines and active transportation policies. However, uncertainties remain about the effectiveness of various intervention strategies to promote cycling [9]. Reduced mortality risk is linked to frequent cycling activity. When compared to not cycling, there was a 17% decreased risk of death for those who cycled for around 100 min a week. The goal should be to increase involvement among those who do not currently cycle frequently in order to maximize the benefits to public health. Moreover, cycling could potentially produce economic benefits for individuals and communities [8]. Given the potential benefits of increased cycling for public health, well-being, the economy, and the environment, investing in effective measures to enhance cycling behavior is essential [8].
Natural environments offer a significant opportunity for promoting health status and well-being, as time spent in nature benefits physical and psychological health [10]. Studies show positive associations between exposure to the natural environment and indicators of physical health, immune function, obesity, and the incidence of other chronic diseases [11,12,13]. It has been suggested that to maintain higher levels of overall health and well-being, people should spend at least 120 min per week in nature [14]. Green exercise (i.e., PA undertaken in the presence of a natural environment) is particularly beneficial in this regard, as it combines the benefits of physical activity with those provided by exposure to nature [15]. The integration of new technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) and enhanced reality (ER), with traditional exercise equipment (e.g., stationary bikes) could help promote participation in PA, especially among young adults [16,17]. Moreover, a recent study found that brief physical activity breaks performed in outdoor (OUT) settings or throughout exergame modalities can improve selective attention and executive functions [18].
Virtual green exercise, which combines PA with virtual nature representations, is designed to offer the benefits of nature exposure and exercise to those who cannot access to natural environment [19]. This concept has gained interest in the medical community for its potential health benefits [14]. Research by Calogiuri et al. [20] suggests that virtual green exercise can enhance exercise output and improve mood, relieve stress, and aid cognitive restoration. However, the research is still nascent, and a review by Lahart et al. [21] found no consistent psychological or physiological benefits compared to indoor exercise, highlighting the need for more rigorous studies.
VR offers a highly immersive experience, making it a promising tool for simulating natural environments and providing health benefits [22,23]. Immersion may be crucial for these benefits, and VR technology is increasingly used in medical care [24,25]. There are two main types of VR simulations: computer-generated scenarios and 360° videos of real scenes [26]. Interactive designs, such as games and physical activities, can enhance the virtual nature experience, although the effects may vary with different VR simulation types.
Cybersickness is a known issue with VR, but its impact and prevention strategies are under-researched [27,28]. The extent to which adverse symptoms might negate the benefits of virtual nature and how different immersion levels or environments contribute to cybersickness remain unclear, making it difficult to generalize the benefits of virtual nature [28].
ER, also called non-immersive virtual reality, is a two-dimensional scenario delivered through a screen and controlled, in several specific aspects, through a device or components of an instrument that incorporate it [29].
VR and ER technologies have been identified as a novel strategy for encouraging PA and promoting healthier behaviors [30]. Physical exercise can often be influenced by external factors such as weather conditions, lighting, and traffic [31]. However, by incorporating VR and ER into exercise routines, it is possible to mitigate these negative environmental impacts and improve exercise motivation. Consequently, VR and ER technologies have the potential to complement physical interventions and modify human behaviors.
In modern societies, a small percentage of adults report exercising at a level that complies with the majority of public health recommendations [32], indicating that a large number of people lack the motivation necessary to engage in appropriate levels of physical activity. There are two general classes of factors that can account for lack of motivation: low perceived competence or low interest. Some of the qualitative aspects of motivation, such as the degree of perceived autonomy or internal locus of causality, are at least somewhat related to the stability of that motivation [33]. In other words, a significant portion of the population either lacks the motivation or does not have the incentive to engage in PA, or they are motivated by external factors that cannot result in prolonged engagement. This emphasizes how important it is to pay closer attention to the objectives and self-control traits linked to consistent exercise and PA [34].
According to feedback theory, emotions serve the function of providing feedback on which behaviors should be pursued or avoided in the future [35]. In this context, anticipated emotions are considered more important in guiding behavior than emotions actually experienced. This, in the context of exposure to nature through VR/ER, can be facilitated by high levels of presence, i.e., the (psychological) sense of being in the virtual environment. Some studies [19,20] have proposed VR/ER as an effective tool in behavioral change interventions, particularly in promoting outdoor PA.
Currently, few studies have compared the effects of exercise integrated with VR, particularly ER, to those performed in outdoor settings on the promotion of PA in a population of healthy university students. Even fewer have investigated such effects using cycling activities. The primary aim of this study was to investigate the effects of three types of brief physical activity (cycling) on parameters related to intrinsic motivation, enjoyment, and heart rate (HR) variations in young adult Italian university students. Secondly, we aimed to explore the potential of these activities as a tool to promote outdoor physical exercise. We hypothesize that the three conditions (VR, ER, and OUT) will result in similar levels of intrinsic motivation, enjoyment, and HR variation. Regarding the secondary outcome, we hypothesize that, among the technological conditions, the VR condition will induce greater transfer compared to the ER condition in the intention to engage in outdoor physical activities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Participants were recruited from the local fitness center, Polignano a Mare, Bari, Italy (Living S.S.D.), selecting only university students aged between 18 and 30 years. We considered the following exclusion criteria: (1) declining to take part in the study, (2) indications of musculoskeletal disorders or significant lower limb injuries, (3) acute or chronic disease, (4) taking medications that may affect mood and cognitive regulation, (5) habitual performance of physical/sporting activity in an outdoor setting, (6) prior experience in using ER-cycling and/or VR-cycling technologies.
So, thirty-one healthy adults (age, 24.3 ± 3.2 years; body mass, 70.8 ± 14.9 kg; body height, 172.9 ± 9.5 cm; BMI, 23.5 ± 3.6 kg/m2; sex, 11 females and 20 males) were enrolled in this experimental work (between February and March 2024).
A preliminary power analysis [36], was conducted with a Type I error rate α = 0.05 and a Type II error rate β = 0.10 (indicating a statistical power of 90%, i.e., 1 − β). The analysis determined that a total of 27 participants would be adequate to detect medium effect sizes “within factors” (f = 0.30). Informed consent was collected, including comprehensive details about the study’s procedures and tests, along with information about their right to withdraw at any time. This research was carried out in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki and received approval from the Ethics Committee of Bari University (protocol code 0015637|16 February 2023).
2.2. Study Design
A randomized controlled crossover study utilizing within-subjects repeated-measures design was conducted. Each participant experienced all conditions in a random and counterbalanced sequence.
Participants were randomly allocated to one of three cycling conditions: enhanced reality cycling (ERC), virtual reality cycling (VRC), or outdoor cycling (OUTC). The randomization was executed using Research Randomizer, a tool available on an official public website (www.randomizer.org, accessed in February 2024). To reduce potential circadian-related effects, all conditions and assessments took place between 9:30 a.m. and 12:30 p.m., with a one-week washout period between trials. Participants were instructed to abstain from intense physical activity and caffeine for 24 h before each session and throughout the data collection period.
Researcher 1, who was blinded to the treatment assignments, assessed subject characteristics and all outcome measures following each cycling condition. The interventions and evaluation were carried out in the same outdoor setting and indoor fitness center located in Polignano a Mare, Bari (Italy). Researcher 2, responsible for conducting the interventions, did not participate in the assessments and was unaware of the study’s objectives or the treatment allocations.
Figure 1 presents a flow chart illustrating the randomized allocation of participants across the three conditions.
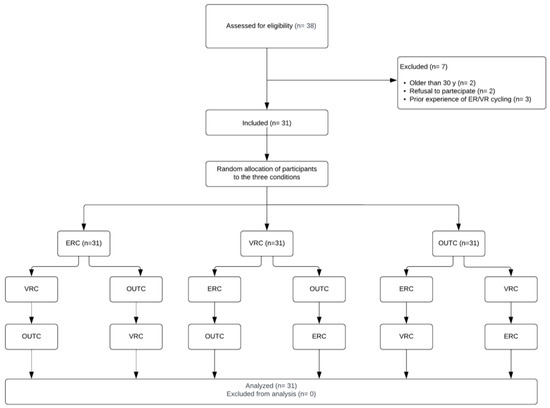
Figure 1.
Randomized allocation to the different conditions.
2.3. Experimental Protocol
Participants were instructed to refrain from engaging in any vigorous activities for a minimum of 30 min before the intervention. Following this, each participant carried out their designated cycling condition based on random assignment.
For the VRC condition, the identical cycling route (Figure 2) used in the OUTC condition was filmed with the Insta360 X3 (Arashi Vision Inc., Shenzhen, China) to produce a 5 K 360-degree video. During the VRC sessions, participants used VR headsets with integrated headphones, along with a Samsung Galaxy S20 FE phone (Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd, Suwon, South Korea) inserted into the headsets, offering an immersive VR simulation of the recorded outdoor cycling route. The 360-degree footage was captured at the same speed (14.5 km/h) as used during indoor sessions. This speed falls into the average speed for recreational cycling activities [37].

Figure 2.
Outdoor cycling route for OUTC/VRC conditions.
In all conditions, the exposure duration was set to 10 min. This time span was selected because it has been previously identified as the minimum necessary to achieve health and well-being benefits from both nature exposure [38] and PA [39]. Additionally, this duration helps prevent or limit the onset of cybersickness [40,41].
The OUTC condition was performed by cycling outside on an outdoor bike pathway (Figure 2). Each participant cycled for 10 min at a predetermined speed of 14.5 km/h. The OUTC condition was performed on a regular muscular city bike, and participants were instructed to maintain the established speed, which was displayed in real time through a cyclo-computer (Garmin®, Edge 540; Garmin Ltd., Olathe, KS, USA) [42]. The ERC condition was performed on a stationary bike (Technogym®, smart bike; Technogym S.p.A, Cesena, Italia) at 14.5 km/h speed, equipped with a monitor (22″ full-HD touchscreen) that reproduces a natural landscape in first person. During the cycling experience, the surrounding landscape adapts to the speed in real time. The same resistance level was set for all three conditions (VRC, OUTC, and ERC) to ensure consistency in the physical effort required across different cycling modalities.
Immediately after the end of each cycling condition, lasting 10 min each, participants were measured for HR (average and maximum) and subjective ratings of intrinsic motivation, physical activity enjoyment, and intention to perform green exercise by answering the Intrinsic Motivation Inventory (IMI), the Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale (PACES), and Intention to Perform Green Exercise (INT-GE) questionnaires, respectively.
2.4. Measures
2.4.1. Heart Rate
Throughout the cycling sessions, the participant’s heart rates were consistently tracked with a wearable device (Polar®, Verity Sense; Polar Electro Oy, Kempele, Finland). Post-test, both the average heart rate (HRmean) and the maximum heart rate (HRmax) were documented. Prior research [43,44] has confirmed the accuracy of such devices for heart rate monitoring in adults. HRmean and HRmax are measurements that are relatively simple to obtain and analyze, and also a useful indicator of cardiovascular load during physical exercise. HRmean provides an idea of the sustained cardiac load throughout the entire exercise session, while HRmax indicates the peak effort reached. These data could help in understanding the physical intensity and the level of cardiac stress imposed by the different cycling conditions (ERC, VRC, OUTC).
2.4.2. Intrinsic Motivation Inventory (IMI)
The Intrinsic Motivation Inventory (IMI) is a multidimensional measurement tool intended to assess participants’ subjective experience related to a target activity. It has been used in several experiments related to intrinsic motivation and self-regulation, originating from original studies [45,46]. The IMI has been widely used in research to assess intrinsic motivation in different scientific fields, such as the academic, and has been gaining acceptance in the sport and exercise domain [47,48]. A smaller number of IMI items can be selected and modified depending on the activity and research question, without adversely affecting the psychometric properties of the measure. Overall, the IMI is a very flexible instrument that offers the opportunity to select/modify relevant items to assess intrinsic motivation in any sport/exercise setting [49]. The used scale consists of 25 items, including the three subscales of value/usefulness (Cronbach α 0.87), interest/enjoyment (Cronbach α 0.94), and perceived choice (Cronbach α 0.89). Following each condition, participants evaluate their level of agreement with each statement using a seven-point scale, from 1 to 7, where 1 means not at all true, 4 is somewhat true, and 7 is very true.
It is designed to be filled out right after engaging in a PA, offering insights into individuals’ intrinsic motivation to perform that specific activity.
2.4.3. Physical Activity of Enjoyment Scale (PACES)
The Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale (PACES) is a survey designed to gauge how much a person enjoys engaging in physical activity [50,51]. The questionnaire includes 16 statements rated on a 5-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). Among these, nine statements reflect positive feelings (e.g., “it energizes me”), while seven express negative sentiments (e.g., “it’s boring”), with Cronbach’s alpha values between 0.78 and 0.89 [52]. The PACES evaluates several aspects of enjoyment, such as positive emotions, psychological involvement, and contentment with the activity [53,54]. It is frequently utilized in studies to understand people’s views and attitudes towards physical exercise, offering insights into the motivational elements that affect exercise behaviors.
2.4.4. Intention to Perform Green Exercise (INT-GE)
Intention to Perform Green Exercise (INT-GE) is part of a group of three questionnaires developed to assess individuals’ beliefs about green (outdoor) exercise [55].
This questionnaire is used to assess the effects of exposure to different conditions on participants’ overall Intention to Perform Green Exercise [56].
The tool comprises five items (i.e., “I want to do green exercise”), each evaluated on a scale from 1 to 7, with 1 meaning “Absolutely disagree” and 7 meaning “Absolutely agree.” Before the items were presented, a definition of green exercise (any type of physical activity or exercise performed outdoors in natural environments like urban parks, beaches, cliffs, countryside, forests, etc.) was provided. Each item specifies a timeframe (“over the next week”) (Cronbach alpha 0.92).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed utilizing JASP software version 0.17.2.1 [57]. Data were reported as mean (M) values with standard deviations (SD) and tested for sphericity using Mauchly’s test. When sphericity was not met, the Greenhouse–Geisser correction was applied.
The Shapiro–Wilk test assessed the normality of all variables. Differences between the three conditions were examined using a one-way repeated measures ANOVA. If significant differences were found, post hoc tests with Bonferroni correction were used to determine specific significant comparisons.
Eta squared (η2) was used to measure the effect size within groups, classified as small (η2 < 0.06), moderate (0.06 ≤ η2 < 0.14), and large (η2 ≥ 0.14) [58]. For post hoc tests, Cohen’s d was calculated, with the effect sizes interpreted as small (0.20 ≤ d < 0.50), moderate (0.50 ≤ d < 0.79), and large (d ≥ 0.80) [59]. Statistical significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
All thirty-one participants involved in the study underwent each of the three cycling conditions without injuries during the research period. The values for the three cycling conditions are detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Changes found between the three cycling conditions.
One-way ANOVA with repeated measures found significant “within-subjects effects” for all the outcomes measures: HRmean (F = 11.701, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.281, large ES), HRmax (F = 3.617, p = 0.033, η2 = 0.108, moderate ES), IMI-Interest/enjoyment (F = 20.179, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.402, large ES), IMI-Value/usefulness (F = 16.669, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.357, large ES), IMI-Perceived choice (F = 7.373, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.197, moderate ES), PACES (F = 12.083, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.287, large ES), and INT-GE (F = 7.613, p = 0.001, η2 = 0.202, large ES).
Bonferroni post hoc test showed that HRmean was significantly higher during the ERC (t = 4.743, p < 0.001, d = 0.627, moderate ES) and VRC (t = 3.196, p = 0.007, d= 0.422, small ES) compared to OUTC sessions.
Greater HRmax was found only in the ERC compared to OUTC sessions (t = 2.575, p = 0.038, d = 0.339, small ES).
Intrinsic motivation level, measured by IMI, was significantly higher in the OUTC condition compared to the others, in the interest/enjoyment (OUTC vs. ERC: t = −5.966, p < 0.001, d = 1.061, large ES; OUTC vs. VRC: t = −4.872, p < 0.001, d = 0.867, large ES) and value/usefulness (OUTC vs. ERC: t = −4.415, p < 0.001, d = 0.715, moderate ES; OUTC vs. VRC: t = −5.430, p < 0.001, d = 0.879, large ES) subscales, while for the perceived choice subscale the values were significantly higher for the OUTC than for the ERC session (OUTC vs. ERC: t = −3.774, p = 0.001, d = 0.464, small ES) and for VRC compared to ERC (t = −2.501, p = 0.045, d = 0.308, small ES).
The level of enjoyment measured by PACES was significantly higher in the OUTC session compared to the others (OUTC vs. ERC: t = −4.081, p < 0.001, d = 0.778, moderate ES; OUTC vs. VRC: t = −4.414, p < 0.001, d = 0.841, large ES).
Finally, the INT-GE score was significantly higher in OUTC compared to the other conditions (OUTC vs. ERC: t = −3.622, p = 0.002, d = 0.580, moderate ES; OUTC vs. VRC: t = −3.068, p = 0.010, d = 0.492, small ES).
4. Discussion
The present study aimed to investigate the effects of three different cycling conditions: ERC, VRC, and OUTC, on intrinsic motivation, enjoyment, and stress among university students. Additionally, it explored the potential of VR/ER-mediated naturalistic experiences in promoting outdoor physical exercise. Our findings showed significant differences across the three conditions, shedding light on the relative effectiveness of each in fostering PA engagement and enjoyment in the university student population.
Firstly, we observed a higher HRmean in the ERC and VRC conditions compared to the OUTC, contrary to what has been observed in previous similar work [60]. This difference could be explained by the different types of PA performed, walking versus cycling, and the different times of the year in which the experimental intervention was set up, summer versus winter; in the previous study, a high outdoor temperature [21] may have affected the increase in the HRmean. Previous studies, albeit with different physical activities and modalities, show either no difference between activities performed outdoors versus indoors [61], or higher heart rate values for activities performed outdoors versus indoors, despite similar perceived exertion [62,63].
However, our results suggest that indoor cycling with enhanced or virtual environments may induce greater physiological responses, and probably greater perceived exertions. The higher HRmax found in the ERC compared to OUTC sessions further supports this notion. This is in line with other work that has observed a reduction in heart rate (mean and max) during PA performed in outdoor settings [21,64]. Moreover, the difference between VRC and OUTC was not significant for the HRmax, suggesting that VR might provide a less strenuous exercise environment than ER. However, it is important to note that several previous studies observe a reduction in heart rate values after exposure to a VR experience in general and not specifically related to exposure to a virtual natural environment [65,66,67,68,69].
Intrinsic motivation, which may be an indicator of future PA behaviors and adherence [70], was significantly higher in the OUTC condition across all subscales (interest/enjoyment, value/usefulness, and perceived choice). This aligns with the broader literature highlighting the benefits of natural environments on psychological well-being and motivation (Twohig-Bennett and Jones, 2018; White et al., 2019) [10,11]. The outdoor setting appears to offer unique motivational benefits that are not entirely replicated by VR or ER, even when these technologies simulate natural environments. The higher perceived choice in the VRC compared to the ERC also suggests that participants felt they had more autonomy and control over their actions, which is an important aspect of intrinsic motivation. When people feel that they are acting out of their own volition and not because of external pressures, their intrinsic motivation is generally higher [47,71].
Enjoyment is a key predictor of exercise adherence [72], and our results show that the PACES scores were significantly higher in the OUTC session, in accordance with previous studies [73,74,75], indicating greater enjoyment of outdoor cycling compared to indoor cycling with VR or ER. This finding underscores the importance of real-world natural environments in enhancing the enjoyment of recreational physical activities, which is crucial for sustaining long-term active behaviors [15].
Over the past three decades, research has consistently shown that interactions with nature offer a wide range of health and well-being benefits [14,76,77]. Various pathways have been identified linking natural contact to physical and psychological health, such as air quality improvement, heat modulation, PA, social cohesion, and stress reduction [78,79].
Green exercise, which includes activities like visiting naturalistic locations, outdoor recreation, and exercising or walking in natural environments, provides synergistic benefits from nature contact and PA. Regular green exercise can lead to long-term benefits such as better self-rated health, higher life satisfaction, and stronger social support. Multiple review studies confirm the additional health and well-being advantages of green exercise compared to indoor or urban PA [80,81].
Our results show that direct exposure to outdoor environments might more effectively promote future engagement in outdoor physical activities; in fact, INT-GE scores were significantly higher following the OUTC sessions compared to both ERC and VRC. While VR and ER can offer immersive and stimulating experiences, they may not sufficiently replicate the motivational impact of actual outdoor exercise, a critical consideration for interventions aimed at promoting sustained PA. Moreover, contrary to our initial hypothesis, we found no significant differences between VRC and ERC conditions in promoting intention to engage in outdoor physical activities, suggesting both technologies could be equally effective.
Our findings have several practical implications. While VR and ER technologies offer innovative ways to engage individuals in PA, especially in settings where access to natural environments is limited, they should complement rather than replace outdoor activities. For college students, experiencing recreational PA could contribute to maintaining an active lifestyle in the long run. Incorporating more outdoor exercise opportunities into their routine could improve their physical and psychological well-being. Universities should consider developing programs that encourage outdoor physical activities, taking advantage of the intrinsic benefits of motivation and enjoyment associated with natural environments. These efforts could contribute to a holistic approach to sustainability, emphasizing both human health and the well-being of the planet.
Strength and Limitations
As far as we know, this is the first study that compares the effects of PA integrated with VR and ER with that performed outdoors on promoting PA in a population of healthy college students. In addition, we examined these effects using cycling activities. Moreover, the outdoor activity was conducted during the winter season, in contrast to many similar studies that typically take place during the spring or summer. This enhances the validity of our findings, as winter conditions often pose challenges to outdoor PA, whereas spring and summer conditions generally promote it.
Highlighting the effects of different cycling modalities, it encourages regular physical activity, which not only enhances individual health but could also reduce healthcare costs over time. Utilizing natural environments for exercise supports the preservation and use of green spaces, benefiting environmental conservation efforts. Additionally, the findings could suggest practical implications for urban planning and university programs and find new ways to motivate young people to participate in physical activity. Moreover, active transportation can contribute to reducing carbon emissions and improving air quality, thus addressing broader environmental sustainability goals. Ultimately, the study shows initial insight into enjoyable and motivating outdoor activities like cycling that can lead to sustained physical activity, supporting both personal health and the well-being of society.
However, there are some limitations to this study. The sample size was relatively small and consisted of students from a specific geographic area, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
We only measured and assessed HR (mean and maximal), without directly assessing perceived exertion (RPE). This may have limited the interpretations of the data, since HR does not always reflect perceived exertion (e.g., HR might be higher but perceived exertion might be low) [82]. Furthermore, HR was not represented as a percentage of everyone’s maximum HR, which reduces its accuracy as an indicator of exercise intensity; this is also because the determination of maximum HR requires a very intense and strenuous effort that could have limited participation in the study. Hypothetical maximal HR related to age was not utilized due to the constraints of these formulas [83].
While the scenario displayed during the VRC session was the same one to which participants were exposed in the OUTC session, the scenario shown during the ERC session, though similar, was different. This could somehow represent a bias of the study, notwithstanding that the results obtained in the two virtual conditions (ERC and VRC) were similar.
The acute intervention study design offers preliminary insights into the specific forms of recreational PA that may enhance intrinsic motivation, potentially leading to sustained engagement in these activities over time. However, to validate and extend these initial findings, longitudinal studies with subsequent follow-up are required.
Additionally, the controlled study environment may not accurately represent participants’ real-world experiences.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, while VR and ER technologies show promise in enhancing engagement and physiological responses during indoor cycling, outdoor cycling offers superior benefits in terms of intrinsic motivation, enjoyment, and intention to engage in future outdoor activities. Promoting outdoor physical activities remains crucial for enhancing the overall health and well-being of university students. Our results show the potential effect of incorporating outdoor physical activity to promote sustained engagement and well-being. However, we cannot provide specific recommendations due to the acute nature of our intervention.
Future research should explore the long-term effects of these conditions and include diverse populations. Additionally, investigating other forms of physical activity beyond cycling could provide a broader understanding of how different environments impact various types of exercise.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.P., G.G. and F.F.; methodology, L.P. and G.G.; software, L.P. and I.P.; validation, L.P., G.G. and S.C.; formal analysis, M.G. and C.C.; investigation, L.P. and M.G.; resources, I.P. and C.C.; data curation, L.P. and I.P.; writing—original draft preparation, L.P.; writing—review and editing, G.G. and F.F.; visualization, M.G. and C.C.; supervision, G.G., S.C. and F.F.; project administration, F.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Bari University (protocol code 0015637|16 February 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all parents of the participants involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the first author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
This research project was developed in collaboration with Technogym S.p.A., which provided technical support and materials for the development and execution of the experiments. Their partnership played a significant role in the success of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch-Institut, R. European Health Interview Survey (EHIS) 2—Background and Study Methodology. J. Health Monit. 2019, 4, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravini, E.; Azzolina, D.; Janin, D.; Vercelli, S.; Panella, M.; Rinaldi, C. Health-Related Lifestyles among Italian University Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. Epidemiol. Prev. 2022, 46, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deliens, T.; Deforche, B.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Clarys, P. Determinants of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour in University Students: A Qualitative Study Using Focus Group Discussions. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleman, A.A.; de Waure, C.; Soffiani, V.; Poscia, A.; Di Pietro, M.L. Physical Activity and Health Promotion in Italian University Students. Ann. Dell’istituto Super. Sanita 2015, 51, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröberg, A.; Lundvall, S. The Distinct Role of Physical Education in the Context of Agenda 2030 and Sustainable Development Goals: An Explorative Review and Suggestions for Future Work. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, N.; Calmeiro, L.; Marques, A.; Gomez-Baya, D.; Gaspar De Matos, M. The Role of Blue and Green Exercise in Planetary Health and Well-Being. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, G.; Somers, C.; Baker, G.; Connell, H.; Gray, S.; Kelly, P.; McIntosh, E.; Welsh, P.; Gray, C.M.; Gill, J.M.R. Benefits, Risks, Barriers, and Facilitators to Cycling: A Narrative Review. Front. Sports Act. Living 2023, 5, 1168357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.; Williamson, C.; Baker, G.; Davis, A.; Broadfield, S.; Coles, A.; Connell, H.; Logan, G.; Pell, J.P.; Gray, C.M.; et al. Beyond Cycle Lanes and Large-Scale Infrastructure: A Scoping Review of Initiatives That Groups and Organisations Can Implement to Promote Cycling for the Cycle Nation Project. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoletto, A.; Mauro, M.; Maietta Latessa, P.; Iannuzzi, V.; Gori, D.; Campa, F.; Greco, G.; Toselli, S. Impact of Different Types of Physical Activity in Green Urban Space on Adult Health and Behaviors: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2021, 11, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twohig-Bennett, C.; Jones, A. The Health Benefits of the Great Outdoors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Greenspace Exposure and Health Outcomes. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, L.; Greco, G.; Cataldi, S.; Ciccone, M.M.; De Giosa, A.; Fischetti, F. Multicomponent versus aerobic exercise intervention: Effects on hemodynamic, physical fitness and quality of life in adult and elderly cardiovascular disease patients: A randomized controlled study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, L.; Mazić, S.; Ciccone, M.M.; Cataldi, S.; Fischetti, F.; Greco, G. A 10-Week Multicomponent Outdoor Exercise Program Improves Hemodynamic Parameters and Physical Fitness in Cardiovascular Disease Adult and Elderly Patients. Sport Sci. Health 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.P.; Alcock, I.; Grellier, J.; Wheeler, B.W.; Hartig, T.; Warber, S.L.; Bone, A.; Depledge, M.H.; Fleming, L.E. Spending at Least 120 Minutes a Week in Nature Is Associated with Good Health and Wellbeing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogiuri, G.; Chroni, S. The Impact of the Natural Environment on the Promotion of Active Living: An Integrative Systematic Review. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, G.; Poli, L.; Clemente, F.M.; Francesco, F.; Cataldi, S. The Effectiveness of New Digital Technologies in Increasing Physical Activity Levels and Promoting Active and Healthy Ageing: A Narrative Review. Health Soc. Care Community 2023, 2023, 2803620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, D.J.; Pope, Z.C.; Zeng, N.; Liu, W.; Gao, Z. Comparison of College Students’ Blood Pressure, Perceived Exertion, and Psychosocial Outcomes During Virtual Reality, Exergaming, and Traditional Exercise: An Exploratory Study. Games Health J. 2020, 9, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischetti, F.; Pepe, I.; Greco, G.; Ranieri, M.; Poli, L.; Cataldi, S.; Vimercati, L. Ten-Minute Physical Activity Breaks Improve Attention and Executive Functions in Healthcare Workers. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litleskare, S.; MacIntyre, T.E.; Calogiuri, G. Enable, Reconnect and Augment: A New ERA of Virtual Nature Research and Application. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogiuri, G.; Litleskare, S.; Fröhlich, F. Physical Activity and Virtual Nature: Perspectives on the Health and Behavioral Benefits of Virtual Green Exercise. In Nature and Health; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 127–146. ISBN 978-1-00-315441-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lahart, I.; Darcy, P.; Gidlow, C.; Calogiuri, G. The Effects of Green Exercise on Physical and Mental Wellbeing: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohil, C.J.; Alicea, B.; Biocca, F.A. Virtual Reality in Neuroscience Research and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattila, O.; Korhonen, A.; Pöyry, E.; Hauru, K.; Holopainen, J.; Parvinen, P. Restoration in a Virtual Reality Forest Environment. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 107, 106295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, R.E.J.; Van Dijk, A.; Verhulp, E.E.; De Castro, B.O. Interactive Virtual Reality Assessment of Aggressive Social Information Processing in Boys with Behaviour Problems: A Pilot Study. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 2021, 28, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, A.A.; Neiman, N.; Caruso, T.J.; Rodriguez, S.; Taylor, K.; Madill, M.; Rives, H.; Nguyen, L. Mindfulness-Based Virtual Reality Intervention for Children and Young Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Pilot Feasibility and Acceptability Study. Children 2021, 8, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, N.L.; White, M.P.; Alcock, I.; Garside, R.; Dean, S.G.; Smalley, A.J.; Gatersleben, B. What Is the Best Way of Delivering Virtual Nature for Improving Mood? An Experimental Comparison of High Definition TV, 360° Video, and Computer Generated Virtual Reality. J. Environ. Psychol. 2020, 72, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martirosov, S.; Bureš, M.; Zítka, T. Cyber Sickness in Low-Immersive, Semi-Immersive, and Fully Immersive Virtual Reality. Virtual Real. 2022, 26, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostajeran, F.; Krzikawski, J.; Steinicke, F.; Kühn, S. Effects of Exposure to Immersive Videos and Photo Slideshows of Forest and Urban Environments. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.M.; Read, J.E.; Bennie, C.; Hale, L.A.; Milosavljevic, S. Can Non-Immersive Virtual Reality Improve Physical Outcomes of Rehabilitation? Phys. Ther. Rev. 2012, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.G.; Fox, J. Immersive Virtual Environments, Avatars, and Agents for Health. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-0-19-022861-3. [Google Scholar]
- Salmon, J.; Owen, N.; Crawford, D.; Bauman, A.; Sallis, J.F. Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior: A Population-Based Study of Barriers, Enjoyment, and Preference. Health Psychol. 2003, 22, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisson, S.B.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. International Prevalence of Physical Activity in Youth and Adults. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, P.J.; Carraça, E.V.; Markland, D.; Silva, M.N.; Ryan, R.M. Exercise, Physical Activity, and Self-Determination Theory: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, R.F.; Vohs, K.D.; Nathan DeWall, C.; Zhang, L. How Emotion Shapes Behavior: Feedback, Anticipation, and Reflection, Rather Than Direct Causation. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 2007, 11, 167–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H. Sample Size Determination and Power Analysis Using the G*Power Software. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2021, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, A.; Tayyeb, H.; Al-Falahi, M. Critical Review of Cyclist Speed Measuring Techniques. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 7, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, G.R.; Rakow, D.A.; Eldermire, E.R.B.; Madsen, C.G.; Shelley, S.P.; Sachs, N.A. Minimum Time Dose in Nature to Positively Impact the Mental Health of College-Aged Students, and How to Measure It: A Scoping Review. Front. Psychol. 2020, 10, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.-M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P. Quantity and Quality of Exercise for Developing and Maintaining Cardiorespiratory, Musculoskeletal, and Neuromotor Fitness in Apparently Healthy Adults: Guidance for Prescribing Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dużmańska, N.; Strojny, P.; Strojny, A. Can Simulator Sickness Be Avoided? A Review on Temporal Aspects of Simulator Sickness. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.; Vasconcelos-Raposo, J.; Bessa, M. Presence and Cybersickness in Immersive Content: Effects of Content Type, Exposure Time and Gender. Comput. Graph. 2018, 71, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, S.H.; De Winter, J.; Hagenzieker, M. Support Systems for Cyclists in Automated Traffic: A Review and Future Outlook. Appl. Ergon. 2023, 111, 104043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Belmonte, Ó.; Febles-Castro, A.; Gay, A.; Cuenca-Fernández, F.; Arellano, R.; Ruiz-Navarro, J.J. Validity of the Polar Verity Sense during Swimming at Different Locations and Intensities. Scand. Med. Sci. Sports 2023, 33, 2623–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navalta, J.W.; Davis, D.W.; Malek, E.M.; Carrier, B.; Bodell, N.G.; Manning, J.W.; Cowley, J.; Funk, M.; Lawrence, M.M.; DeBeliso, M. Heart Rate Processing Algorithms and Exercise Duration on Reliability and Validity Decisions in Biceps-Worn Polar Verity Sense and OH1 Wearables. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M. Control and Information in the Intrapersonal Sphere: An Extension of Cognitive Evaluation Theory. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1982, 43, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Connell, J.P.; Plant, R.W. Emotions in Nondirected Text Learning. Learn. Individ. Differ. 1990, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, E.; Duncan, T.; Tammen, V.V. Psychometric Properties of the Intrinsic Motivation Inventory in a Competitive Sport Setting: A Confirmatory Factor Analysis. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1989, 60, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, E.; Wraith, S.; Duncan, T.E. Self-Efficacy, Perceptions of Success, and Intrinsic Motivation for Exercise. J. Appl. Soc. Pyschol. 1991, 21, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, R.B.; Herring, M.P.; Campbell, M.J. Motivation Measures in Sport: A Critical Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, A.; Young, M.C.; Robazza, C. A Contribution to the Validation of the Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale in an Italian Sample. Soc. Behav. Pers. 2008, 36, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendzierski, D.; DeCarlo, K.J. Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale: Two Validation Studies. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 1991, 13, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, A. Valutare Il Piacere Nelle Attività Motorie: Il PACES-It. In Giornale Italiano Della Ricerca Educativa; Pensa MultiMedia Editore srl: Lecce, Italy, 2012; pp. 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- Mullen, S.P.; Olson, E.A.; Phillips, S.M.; Szabo, A.N.; Wójcicki, T.R.; Mailey, E.L.; Gothe, N.P.; Fanning, J.T.; Kramer, A.F.; McAuley, E. Measuring Enjoyment of Physical Activity in Older Adults: Invariance of the Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale (Paces) across Groups and Time. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teques, P.; Calmeiro, L.; Silva, C.; Borrego, C. Validation and Adaptation of the Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale (PACES) in Fitness Group Exercisers. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowers, E.; Freeman, P.; Gladwell, V. The Development of Three Questionnaires to Assess Beliefs about Green Exercise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogiuri, G.; Keegan, B.J.; Birkheim, S.L.; Rydgren, T.L.; Flaten, O.E.; Fröhlich, F.; Litleskare, S. A Mixed-Methods Exploration of Virtual Reality as a Tool to Promote Green Exercise. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JASP Team. JASP, Version 0.17.3; JASP: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and Reporting Effect Sizes to Facilitate Cumulative Science: A Practical Primer for t-Tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A Power Primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, G.; Centrone, C.; Poli, L.; Silva, A.F.; Russo, L.; Cataldi, S.; Giustino, V.; Fischetti, F. Impact of Coastal Walking Outdoors and Virtual Reality Indoor Walking on Heart Rate, Enjoyment Levels and Mindfulness Experiences in Healthy Adults. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahnesjö, J.; Karlsson, P.S.; Bergman, P. The Effect of Exercising in Different Environments on Heart Rate and Power Output among Older Adults—A Randomized Crossover Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouere, B.M.; Baileys, B.; Reneau, P. The Physiological Differences in Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and RPE During Outdoor Running Versus Indoor Treadmill Running: 1640 Board #187 May 28 3:30 PM–5:00 PM. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuegen, K.; Breitenbecher, K.H. Walking Outdoors Increases Heart Rate but Not Perceived Exertion. Ecopsychology 2022, 14, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson Coon, J.; Boddy, K.; Stein, K.; Whear, R.; Barton, J.; Depledge, M.H. Does Participating in Physical Activity in Outdoor Natural Environments Have a Greater Effect on Physical and Mental Wellbeing than Physical Activity Indoors? A Systematic Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, G.; Theodorou, A.; Reese, G.; Carrus, G.; Sanesi, G.; Panno, A. Virtual Nature, Psychological and Psychophysiological Outcomes: A Systematic Review. J. Environ. Psychol. 2023, 89, 102044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.H.M.; Qiu, L.; Esposito, G.; Mai, K.P.; Tam, K.-P.; Cui, J. Nature in Virtual Reality Improves Mood and Reduces Stress: Evidence from Young Adults and Senior Citizens. Virtual Real. 2023, 27, 3285–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.P.; Mayer, M.D.; Fellows, A.M.; Cowan, D.R.; Hegel, M.T.; Buckey, J.C. Relaxation with Immersive Natural Scenes Presented Using Virtual Reality. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2017, 88, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaust, T.; Felnhofer, A.; Kothgassner, O.D.; Höllmer, H.; Gorzka, R.-J.; Schulz, H. Exposure to Virtual Nature: The Impact of Different Immersion Levels on Skin Conductance Level, Heart Rate, and Perceived Relaxation. Virtual Real. 2022, 26, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhai, Y. Impacts of Landscape Type, Viewing Distance, and Permeability on Anxiety, Depression, and Stress. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oman, R.; McAuley, E. Intrinsic Motivation and Exercise Behavior. J. Health Educ. 1993, 24, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standage, M.; Duda, J.L.; Ntoumanis, N. A Model of Contextual Motivation in Physical Education: Using Constructs from Self-Determination and Achievement Goal Theories to Predict Physical Activity Intentions. J. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 95, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, D.S.; Rodrigues, F.; Cid, L.; Monteiro, D. Enjoyment as a Predictor of Exercise Habit, Intention to Continue Exercising, and Exercise Frequency: The Intensity Traits Discrepancy Moderation Role. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 780059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M.; Munoz, S.-A.; MacRury, S. What Motivates Participants to Adhere to Green Exercise? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladwell, V.F.; Brown, D.K.; Wood, C.; Sandercock, G.R.; Barton, J.L. The Great Outdoors: How a Green Exercise Environment Can Benefit All. Extrem Physiol. Med. 2013, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerson, M.; Gladwell, V.; Gallagher, D.; Barton, J. Influences of Green Outdoors versus Indoors Environmental Settings on Psychological and Social Outcomes of Controlled Exercise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, M.P.; DeVille, N.V.; Elliott, E.G.; Schiff, J.E.; Wilt, G.E.; Hart, J.E.; James, P. Associations between Nature Exposure and Health: A Review of the Evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stott, D.; Forde, D.; Sharma, C.; Deutsch, J.M.; Bruneau, M.; Nasser, J.A.; Vitolins, M.Z.; Milliron, B.-J. Interactions with Nature, Good for the Mind and Body: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, L.S.; Shanahan, D.F.; Fuller, R.A. A Review of the Benefits of Nature Experiences: More Than Meets the Eye. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuben, A.; Manczak, E.M.; Cabrera, L.Y.; Alegria, M.; Bucher, M.L.; Freeman, E.C.; Miller, G.W.; Solomon, G.M.; Perry, M.J. The Interplay of Environmental Exposures and Mental Health: Setting an Agenda. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, T.; Mitchell, R.; De Vries, S.; Frumkin, H. Nature and Health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2014, 35, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Bosch, M.; Ode Sang, Å. Urban Natural Environments as Nature-Based Solutions for Improved Public Health—A Systematic Review of Reviews. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoubi, B.; Zbidi, S.; Vandewalle, H.; Chamari, K.; Driss, T. Relationships between Rating of Perceived Exertion, Heart Rate and Blood Lactate during Continuous and Alternated-Intensity Cycling Exercises. Biol. Sport 2017, 35, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shookster, D.; Lindsey, B.; Cortes, N.; Martin, J.R. Accuracy of Commonly Used Age-Predicted Maximal Heart Rate Equations. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2020, 13, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).