Evaluation of Posturographic and Neuromuscular Parameters during Upright Stance and Hand Standing: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Baropodometric Assessment
2.4. sEMG Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gautier, G.; Thouvarecq, R.; Chollet, D. Visual and postural control of an arbitrary posture: The handstand. J. Sports Sci. 2007, 25, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.B. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35, ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.A. Human balance and posture control during standing and walking. Gait Posture 1995, 3, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenkinsop, G.M.; Pain, M.T.; Hiley, M.J. Balance control strategies during perturbed and unperturbed balance in standing and handstand. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 161018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creath, R.; Kiemel, T.; Horak, F.; Peterka, R.; Jeka, J. A unified view of quiet and perturbed stance: Simultaneous co-existing excitable modes. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 377, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuillerme, N.; Danion, F.; Marin, L.; Boyadjian, A.; Prieur, J.M.; Weise, I.; Nougier, V. The effect of expertise in gymnastics on postural control. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 303, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeadon, M.R.; Trewartha, G. Control strategy for a hand balance. Mot. Control 2003, 7, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Readhead, L. Men’s Gymnastics Coaching Manual; Crowood Press: Ramsbury, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Clément, G.; Rezette, D. Motor behavior underlying the control of an upside-down vertical posture. Exp. Brain Res. 1985, 59, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobounov, S.M.; Newell, K.M. Postural dynamics in upright and inverted stances. J. Appl. Biomech. 1996, 12, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanowicz, A.; Niespodziński, B.; Marina, M.; Mieszkowski, J.; Biskup, L.; Kochanowicz, K. Relationship between postural control and muscle activity during a handstand in young and adult gymnasts. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 58, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, D.G.; Trewartha, G. Strategies for maintaining a handstand in the anterior-posterior direction. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2001, 33, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustio, P.; Rainoldi, A.; Petrigna, L.; Rabaglietti, E.; Pizzigalli, L. Postural stability during dual-and triple-task conditions: The effect of different levels of physical fitness in older adults. Sci. Sport. 2021, 36, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croix, G.; Chollet, D.; Thouvarecq, R. Effect of expertise level on the perceptual characteristics of gymnasts. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajano, G.S.; Taylor, J.L.; Orssatto, L.B.; McNulty, C.R.; Blazevich, A.J. Passive muscle stretching reduces estimates of persistent inward current strength in soleus motor units. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb229922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.; Martines, F.; Bianco, A.; Messina, G.; Giustino, V.; Zangla, D.; Iovane, A.; Palma, A. Decreased postural control in people with moderate hearing loss. Medicine 2018, 97, e0244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, M.; Merletti, R.; Rainoldi, A. Atlas of Muscle Innervation Zones: Understanding Surface Electromyography and Its Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, C.O.; Morris, P.E.; Richler, J.J. Effect size estimates: Current use, calculations, and interpretation. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2012, 141, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerby, D.S. The simple difference formula: An approach to teaching nonparametric correlation. Compr. Psychol. 2014, 3, 11.IT.13.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omorczyk, J.; Bujas, P.; Puszczałowska-Lizis, E.; Biskup, L. Balance in handstand and postural stability in standing position in athletes practicing gymnastics. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2018, 20, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Asseman, F.; Caron, O.; Crémieux, J. Is there a transfer of postural ability from specific to unspecific postures in elite gymnasts? Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 358, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, G.; Marin, L.; Leroy, D.; Thouvarecq, R. Dynamics of expertise level: Coordination in handstand. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2009, 28, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenière, Y.; Cuong Do, M.; Bouisset, S. Are dynamic phenomena prior to stepping essential to walking? J. Mot. Behav. 1987, 19, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepers, R.; Breniere, Y. The role of anticipatory postural adjustments and gravity in gait initiation. Exp. Brain Res. 1995, 107, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiou, E.; Caderby, T.; Delafontaine, A.; Fourcade, P.; Honeine, J.-L. Balance control during gait initiation: State-of-the-art and research perspectives. World J. Orthop. 2017, 8, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, S.E.; Winter, D.A.; Frank, J.S.; Patla, A.E.; Prince, F. The initiation of gait in young, elderly, and parkinson’s disease subjects. Gait Posture 1998, 8, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Huffmaster, S.L.A.; Harvey, J.C.; MacKinnon, C.D. Anticipatory postural adjustment patterns during gait initiation across the adult lifespan. Gait Posture 2017, 57, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowiecki, M.; Rum, L.; Laudani, L.; Vannozzi, G. Biomechanical characteristics of handstand walking initiation. Gait Posture 2021, 86, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohleder, J.; Vogt, T. Teaching novices the handstand: A practical approach of different sport-specific feedback concepts on movement learning. Sci. Gymnast. J. 2018, 10, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hedbávný, P.; Sklenaříková, J.; Hupka, D.; Kalichová, M. Balancing in handstand on the floor. Sci. Gymnast. J. 2013, 5, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, E.; Bianco, A.; Bellafiore, M.; Battaglia, G.; Paoli, A.; Palma, A. Determination of a strength index for upper body local endurance strength in sedentary individuals: A cross sectional analysis. Springerplus 2015, 4, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Yazici, A. A dynamic model for handstand in gymnastics. IOSR-JSPE 2016, 3, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Runge, C.; Shupert, C.; Horak, F.; Zajac, F. Ankle and hip postural strategies defined by joint torques. Gait Posture 1999, 10, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Ohkuwa, T.; Itoh, H. Maintenance of upright standing posture during trunk rotation elicited by rapid and asymmetrical movements of the arms. Brain Res. Bull. 2005, 67, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błaszczyszyn, M.; Szczęsna, A.; Piechota, K. Semg activation of the flexor muscles in the foot during balance tasks by young and older women: A pilot study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanowicz, A.; Niespodzinski, B.; Mieszkowski, J.; Marina, M.; Kochanowicz, K.; Zasada, M. Changes in the muscle activity of gymnasts during a handstand on various apparatus. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, H.E.; Vicinanza, D.; Newell, K.M.; Irwin, G.; Williams, G.K. Bidirectional causal control in the dynamics of handstand balance. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, H.; Vicinanza, D.; Newell, K.; Irwin, G.; Williams, G. Dynamics of Handstand Balance. In Proceedings of the 38th International Society of Biomechanics in Sport Conference, Liverpool, UK, 20–24 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Puszczałowska-Lizis, E.; Omorczyk, J. The level of body balance in standing position and handstand in seniors athletes practicing artistic gymnastics. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2019, 21, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

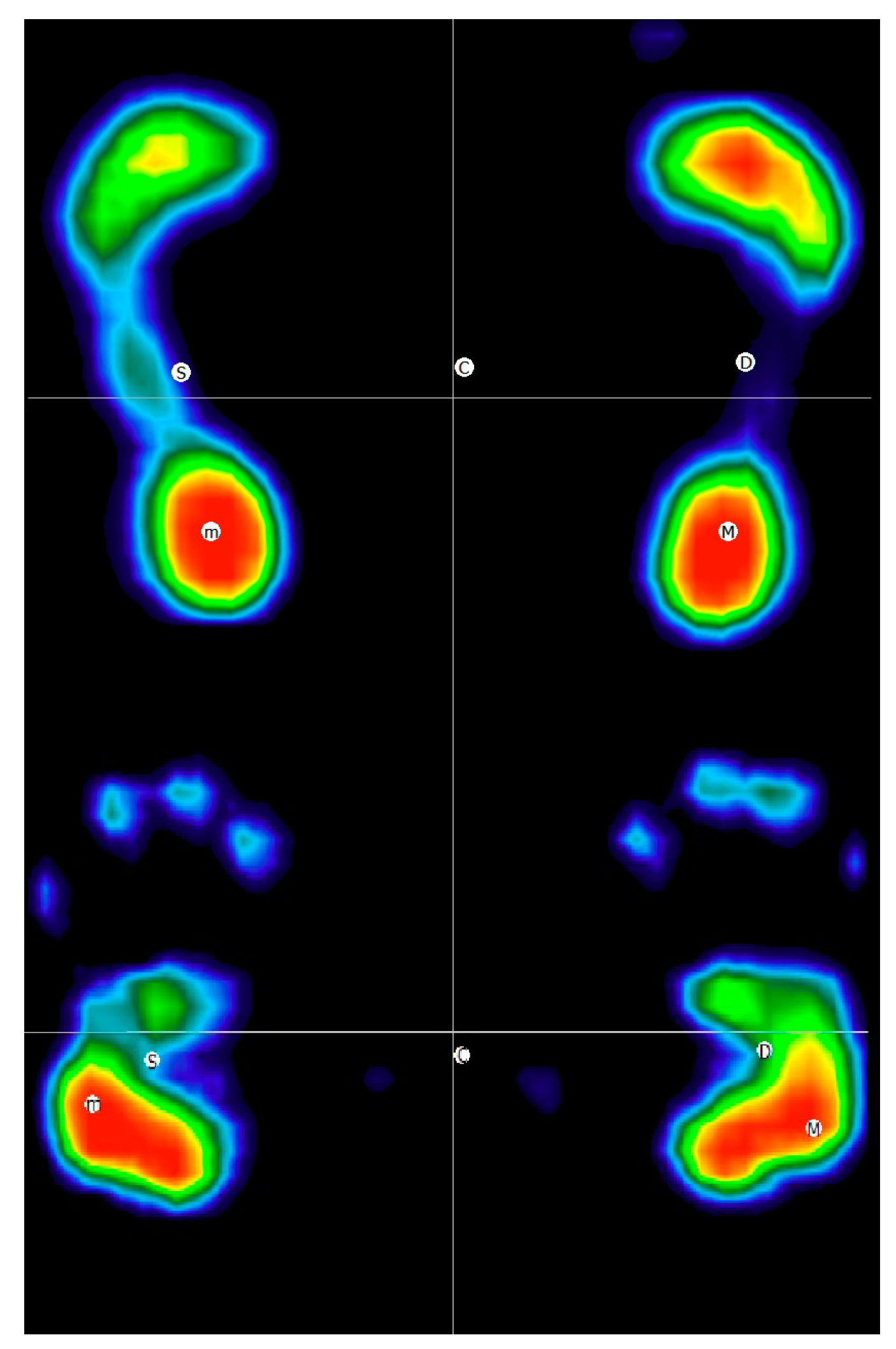

| Standing | Hand Standing | p | ES | CI (95%)-S | CI (95%)-HS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left supporting surface (cm2) | 126.1 ± 22.7 | 86.6 ± 19.2 | <0.01 § | 1.75 | 112.5–139.8 | 75–98.2 |
| Right supporting surface (cm2) | 122.1 ± 21.2 | 90.8 ± 15.2 | <0.01 § | 2.69 | 109.4–135 | 81.6–99.9 |
| Left forefoot/hand (cm2) | 70.4 ± 13.8 | 32.9 ± 7.8 | <0.01 § | 2.70 | 62.1–78.7 | 28.2–37.7 |
| Right forefoot/hand (cm2) | 67.8 ± 13.9 | 34.3 ± 8.1 | <0.01 § | 2.30 | 59.5–76.2 | 29.4–39.2 |
| Left backfoot/hand (cm2) | 55.7 ± 10.1 | 53.7 ± 12.9 | 0.60 § | 0.14 | 49.6–61.8 | 45.9–61.5 |
| Right backfoot/hand (cm2) | 54.4 ± 9.3 | 56.4 ± 8.3 | 0.45 § | 0.21 | 48.8–60 | 51.4–61.4 |
| Left supporting surface (%) | 50.3 ± 1.8 | 45.1 ± 4.9 | <0.01 # | 0.91 | 49.2–51.4 | 42.2–48.1 |
| Right supporting surface (%) | 49.7 ± 1.8 | 54.9 ± 4.9 | <0.01 # | 0.91 | 48.6–50.8 | 51.9–57.8 |
| Left forefoot/hand (%) | 49.1 ± 7.3 | 27.6 ± 6.1 | <0.01 § | 2.17 | 44.8–53.5 | 24.3–30.9 |
| Right forefoot/hand (%) | 47.8 ± 6.6 | 25.1 ± 5.4 | <0.01 § | 2.30 | 43.8–51.7 | 21.5–28.8 |
| Left backfoot/hand (%) | 50.8 ± 7.3 | 72.4 ± 6.1 | <0.01 § | 2.17 | 46.5–55.2 | 69.1–75.7 |
| Right backfoot/hand (%) | 52.2 ± 6.6 | 74.9 ± 5.4 | <0.01 § | 2.30 | 48.3–56.2 | 71.2–78.5 |
| Standing | Hand Standing | p | ES | CI (95%)-S | CI (95%)-HS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVC (μV) | 194.6 ± 147.9 | 405.6 ± 200.6 | 0.01 # | 0.78 | 105–284 | 284–527 |
| Mean Amplitude (μV) | 11.5 ± 12.6 | 326.1 ± 145.3 | <0.01 # | 1.00 | 3.9–19.2 | 238–414 |
| MDF (Hz) | 164.4 ± 30.0 | 99.3 ± 28.3 | <0.01 § | 1.54 | 146–183 | 82.2–116 |
| Mean Frequency (Hz) | 114.4 ± 23.2 | 69.1 ± 15.1 | <0.01 § | 2.13 | 100.3–128.4 | 60–78 |
| Normalized Amplitude (%RMS) | 5.2 ± 2.6 | 92.9 ± 45.8 | <0.01 § | 1.90 | 3.6–6.8 | 65.2–120.6 |
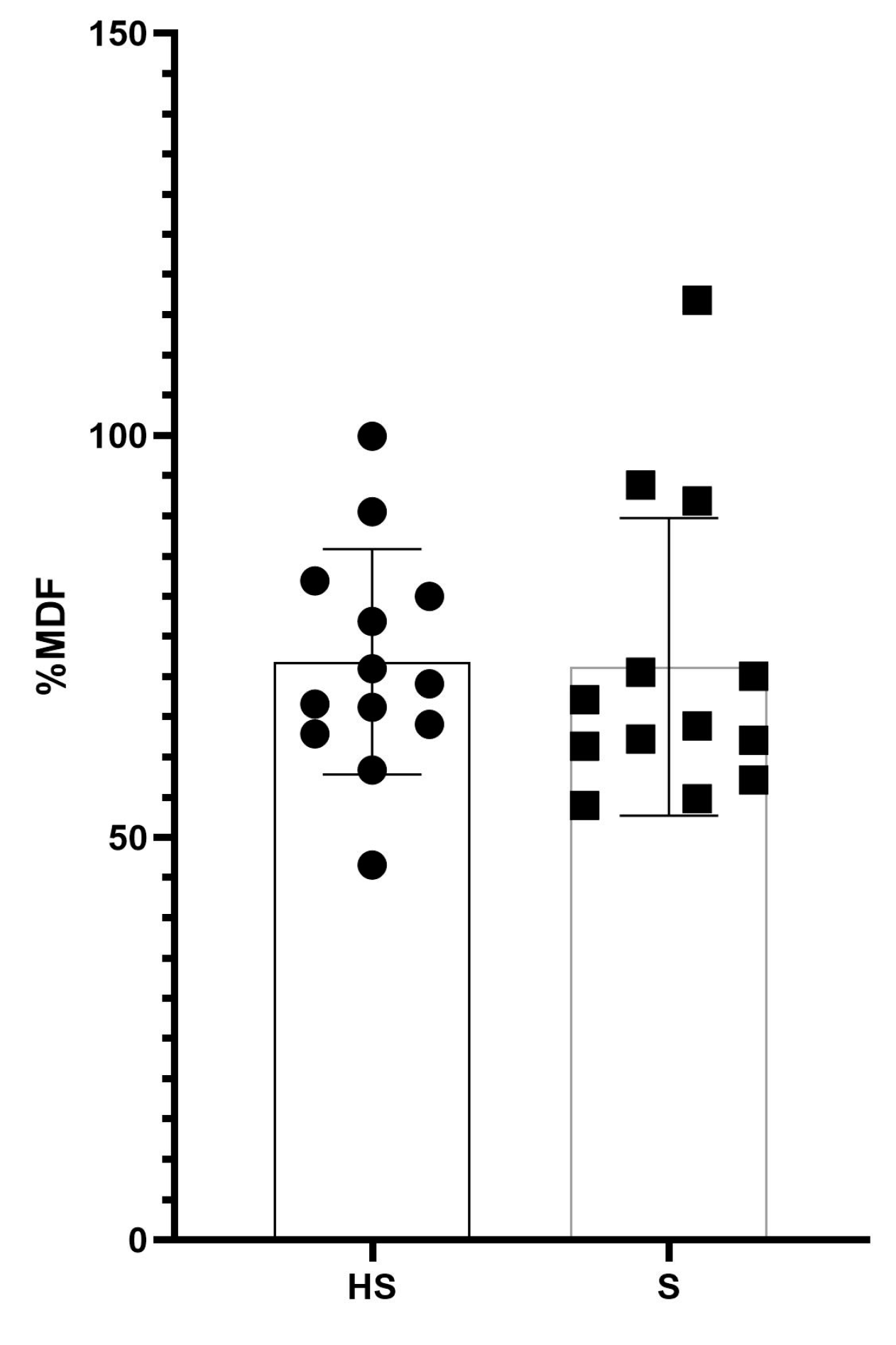
| Normalized Frequency (%MDF) | 71.2 ± 18.5 | 71.9 ± 14.0 | 0.54 # | 0.21 | 60–82.4 | 63.4–80.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomas, E.; Rossi, C.; Petrigna, L.; Messina, G.; Bellafiore, M.; Şahin, F.N.; Proia, P.; Palma, A.; Bianco, A. Evaluation of Posturographic and Neuromuscular Parameters during Upright Stance and Hand Standing: A Pilot Study. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8020040
Thomas E, Rossi C, Petrigna L, Messina G, Bellafiore M, Şahin FN, Proia P, Palma A, Bianco A. Evaluation of Posturographic and Neuromuscular Parameters during Upright Stance and Hand Standing: A Pilot Study. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2023; 8(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomas, Ewan, Carlo Rossi, Luca Petrigna, Giuseppe Messina, Marianna Bellafiore, Fatma Neşe Şahin, Patrizia Proia, Antonio Palma, and Antonino Bianco. 2023. "Evaluation of Posturographic and Neuromuscular Parameters during Upright Stance and Hand Standing: A Pilot Study" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 8, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8020040
APA StyleThomas, E., Rossi, C., Petrigna, L., Messina, G., Bellafiore, M., Şahin, F. N., Proia, P., Palma, A., & Bianco, A. (2023). Evaluation of Posturographic and Neuromuscular Parameters during Upright Stance and Hand Standing: A Pilot Study. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 8(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8020040













