Correlation between Official and Common Field-Based Fitness Tests in Elite Soccer Referees
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
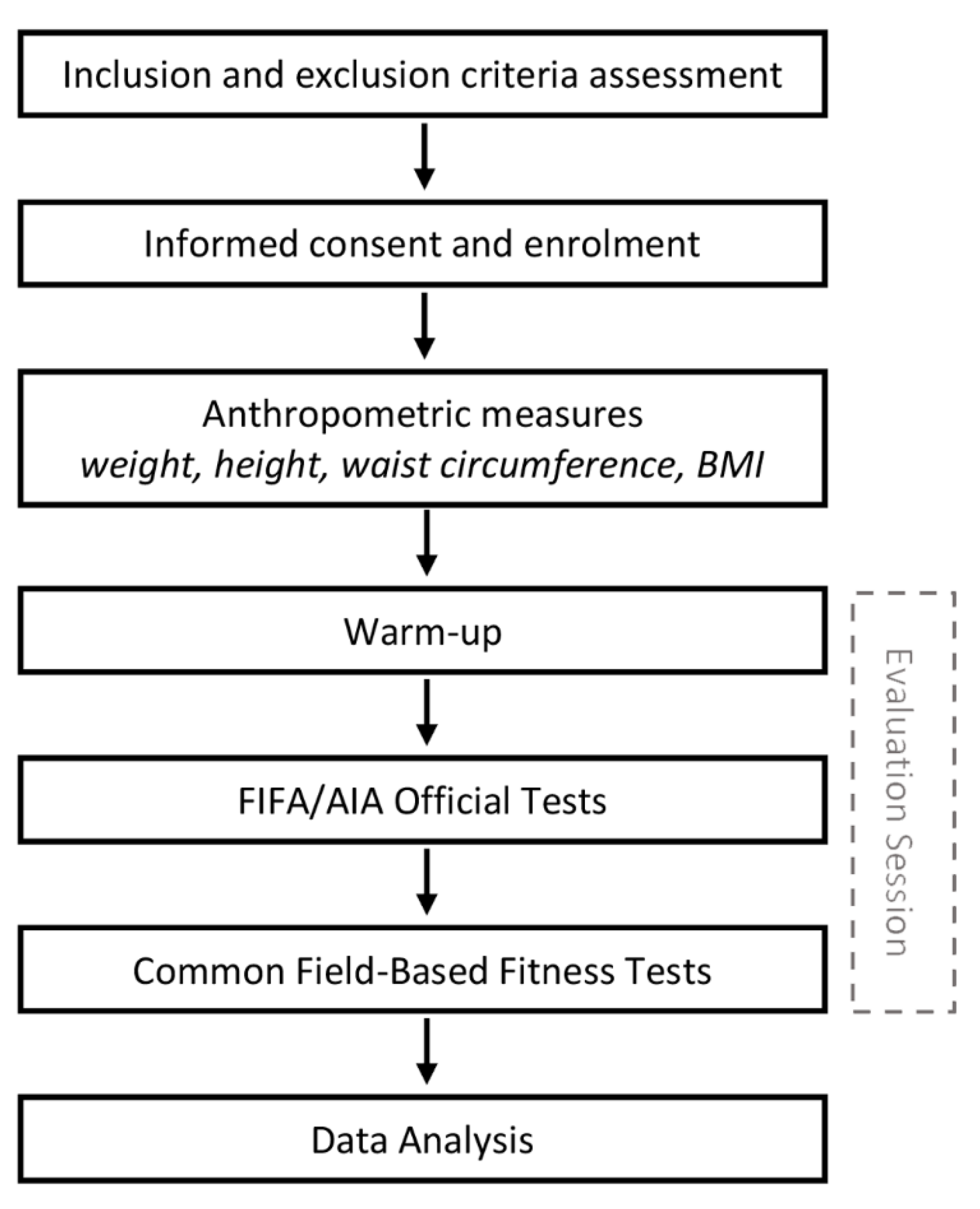
2.2. Study Protocol
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castagna, C.; Abt, G.; D’Ottavio, S. Physiological aspects of soccer refereeing performance and training. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 625–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzini, M.; Junge, A.; Bahr, R.; Helsen, W.; Dvorak, J. Injuries and musculoskeletal complaints in referees and assistant referees selected for the 2006 FIFA World Cup: Retrospective and prospective survey. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ottavio, S.; Castagna, C. Physiological load imposed on elite soccer referees during actual match play. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2001, 41, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Castagna, C.; Abt, G.; D’Ottavio, S. Relationship between fitness tests and match performance in elite soccer referees. J. Strength Cond Res. 2002, 16, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mallo, J.; Navarro, E.; Garcia-Aranda, J.M.; Gilis, B.; Helsen, W. Activity profile of top-class association football referees in relation to performance in selected physical tests. J. Sports Sci. 2007, 25, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2018 Refereeing International Lists Zurich: Fédération Internationale de Football Association. 2018. Available online: https://resources.fifa.com (accessed on 20 February 2019).
- Fitness Tests for Match Officials. Zurich: Fédération Internationale de Football Association. 2020. Available online: https://resources.fifa.com (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Weston, M.; Castagna, C.; Helsen, W.; Impellizzeri, F. Relationships among field-test measures and physical match performance in elite-standard soccer referees. J. Sports Sci. 2009, 27, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krustrup, P.; Bangsbo, J. Physiological demands of top-class soccer refereeing in relation to physical capacity: Effect of intense intermittent exercise training. J. Sports Sci. 2001, 19, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangsbo, J.; Iaia, F.M.; Krustrup, P. The Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test: A useful tool for evaluation of physical performance in intermittent sports. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyk, D.; Gorges, W.; Ridder, D.; Wunderlich, M.; Rüther, T.; Sievert, A.; Essfeld, D. Hand-grip strength of young men, women and highly trained. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 99, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, M.; Aşçi, A.; Bayrak, C.; Açikada, C. Relationships among jumping performances and sprint parameters during maximum speed phase in sprinters. J. Strength Cond Res. 2009, 23, 2272–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, K.F.; Dillon, E.K. The Sit and Reach—A Test of Back and Leg Flexibility. Res. Q 1952, 23, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negra, Y.; Chaabene, H.; Amara, S.; Jari, S.; Hammami, M.; Hachana, Y. Evaluation of the Illinois Change of Direction Test in Youth Elite Soccer Players of Different Age. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 58, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hulley, S.B.; Cummings, S.R.; Browner, W.S.; Grady, D.; Newman, T.B. Designing Clinical Research: An Epidemiologic Approach, 4th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; p. 79. [Google Scholar]
- Ingebrigtsen, J.; Bendiksen, M.; Randers, M.B.; Castagna, C.; Krustrup, P.; Holtermann, A. Yo-Yo IR2 testing of elite and sub-elite soccer players: Performance, heart rate response and correlations to other interval tests. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, B.; Klose, A.; Schelleckes, K.; Jekat, C.M.; Krüger, M.; Brand, S.M. Yo-Yo IR1 vs. incremental continuous running test for prediction of 3000-m performance. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzigalli, L.; MichelettiCremasco, M.; La Torre, A.; Rainoldi, A.; Benis, R. Hand grip strength and anthropometric characteristics in Italian female national basketball teams. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen, A.W.; Naver, A.; Bisgaard, K.; Nordgaard-Lassen, I.; Becker, U.; Krag, A.; Slinde, F. Nutrition impact symptoms, handgrip strength and nutritional risk in hospitalized patients with gastroenterological and liver diseases. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R.; Jung, S.M.; Bang, H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.B. Association between muscle strength and type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults in Korea: Data from the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES) VI. Medicine 2018, 97, e10984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, R.M.; Syddall, H.E.; Cooper, R.; Benzeval, M.; Deary, I.J.; Dennison, E.M.; Der, G.; Gale, C.R.; Inskip, H.M.; Jagger, C.; et al. Grip strength across the life course: Normative data from twelve British studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockie, R.G.; Post, B.K.; Dawes, J.J. Physical Qualities Pertaining to Shorter and Longer Change-of-Direction Speed Test Performance in Men and Women. Sports 2019, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, V.Z.; Vidotto, M.C.; Guerra, R.L. Reference equations for the performance of healthy adults on field walking tests. J. Pneumol. 2011, 37, 607–614. [Google Scholar]
- Aragão-Santos, J.C.; De Resende-Neto, A.G.; Nogueira, A.C.; Feitosa-Neta, M.L.; Brandão, L.H.; Chaves, L.M.; Da Silva-Grigoletto, M.E. The effects of functional and traditional strength training on different strength parameters of elderly women: A randomized and controlled trial. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 59, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosselink, R.; Troosters, T.; Decramer, M. Peripheral muscle weakness contributes to exercise limitation in COPD. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaymaz, D.; Candemir, İ.Ç.; Ergün, P.; Demir, N.; Taşdemir, F.; Demir, P. Relation between upper-limb muscle strength with exercise capacity, quality of life and dyspnea in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.J.; Morgan, M.D.; Scott, S.; Walters, D.; Hardman, A.E. Development of a shuttle walking test of disability in patients with chronic airways obstruction. Thorax 1992, 47, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Mean | SD | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Height (cm) | 180.36 | 6.33 | 168–191 |
| Weight (kg) | 73.67 | 7.38 | 59.2–89 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 78.35 | 5.97 | 67–93 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.65 | 2.07 | 18.58–27.58 |
| Mean | SD | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIFA/AIA official tests: | |||
| 6 × 40-m sprint (s) | 5.63 | 0.18 | 5.34–6.03 |
| YO-YO IR1 (m) | 1678.62 | 292.67 | 1320–2280 |
| Other field-based fitness tests: | |||
| HGS, dominant hand (kg) | 46.14 | 5.55 | 35.65–60 |
| HGS, non-dominant hand (kg) | 42.36 | 5.21 | 33.85–58.5 |
| SLJ (cm) | 225.88 | 17.52 | 201.5–265 |
| SQJ (cm) | 1093.03 | 85.59 | 926–1239 |
| SaR (cm) | 19.69 | 8.93 | 1.5–38 |
| IA (s) | 16.37 | 0.78 | 15.35–18.44 |
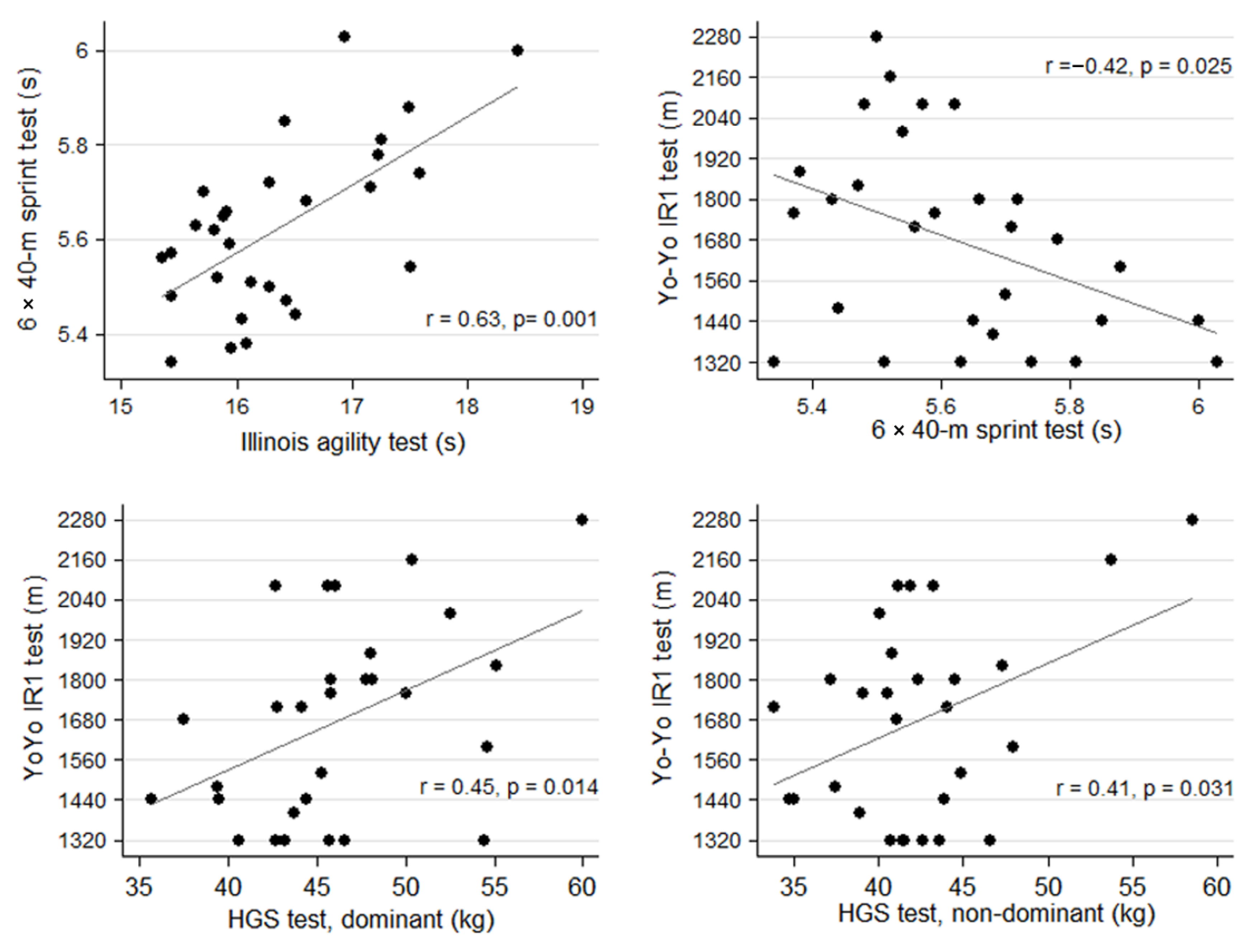
| Test | 6 × 40-m Sprint | YO-YO IR1 |
|---|---|---|
| HGS, dominant | −0.30 (0.112) | 0.45 (0.014) * |
| HGS, non-dominant | −0.18 (0.351) | 0.41 (0.031) * |
| SLJ | 0.04 (0.850) | 0.02 (0.917) |
| SQJ | 0.06 (0.772) | 0.16 (0.401) |
| SaR | −0.01 (0.982) | 0.28 (0.137) |
| IA | 0.63 (0.001) * | −0.29 (0.119) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romano, V.; Tuzi, M.; Di Gregorio, A.; Sacco, A.M.; Belviso, I.; Sirico, F.; Palermi, S.; Nurzynska, D.; Di Meglio, F.; Castaldo, C.; et al. Correlation between Official and Common Field-Based Fitness Tests in Elite Soccer Referees. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2021, 6, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk6030059
Romano V, Tuzi M, Di Gregorio A, Sacco AM, Belviso I, Sirico F, Palermi S, Nurzynska D, Di Meglio F, Castaldo C, et al. Correlation between Official and Common Field-Based Fitness Tests in Elite Soccer Referees. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2021; 6(3):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk6030059
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomano, Veronica, Manuel Tuzi, Ada Di Gregorio, Anna Maria Sacco, Immacolata Belviso, Felice Sirico, Stefano Palermi, Daria Nurzynska, Franca Di Meglio, Clotilde Castaldo, and et al. 2021. "Correlation between Official and Common Field-Based Fitness Tests in Elite Soccer Referees" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 6, no. 3: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk6030059
APA StyleRomano, V., Tuzi, M., Di Gregorio, A., Sacco, A. M., Belviso, I., Sirico, F., Palermi, S., Nurzynska, D., Di Meglio, F., Castaldo, C., Pizzi, A., & Montagnani, S. (2021). Correlation between Official and Common Field-Based Fitness Tests in Elite Soccer Referees. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 6(3), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk6030059













