Plasma Amino Acid Response to Whey Protein Ingestion Following 28 Days of Probiotic (Bacillus subtilis DE111) Supplementation in Active Men and Women
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Body Composition Analysis
2.3. Blood Collection, Handling, and Storage
2.4. Supplementation Protocol
2.5. Dietary Logs
2.6. Plasma Amino Acid Analysis
2.6.1. Materials
2.6.2. Sample Preparation
2.6.3. LC/MS Data Acquisition and Processing
2.6.4. Quality Control of LC/MS Data
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
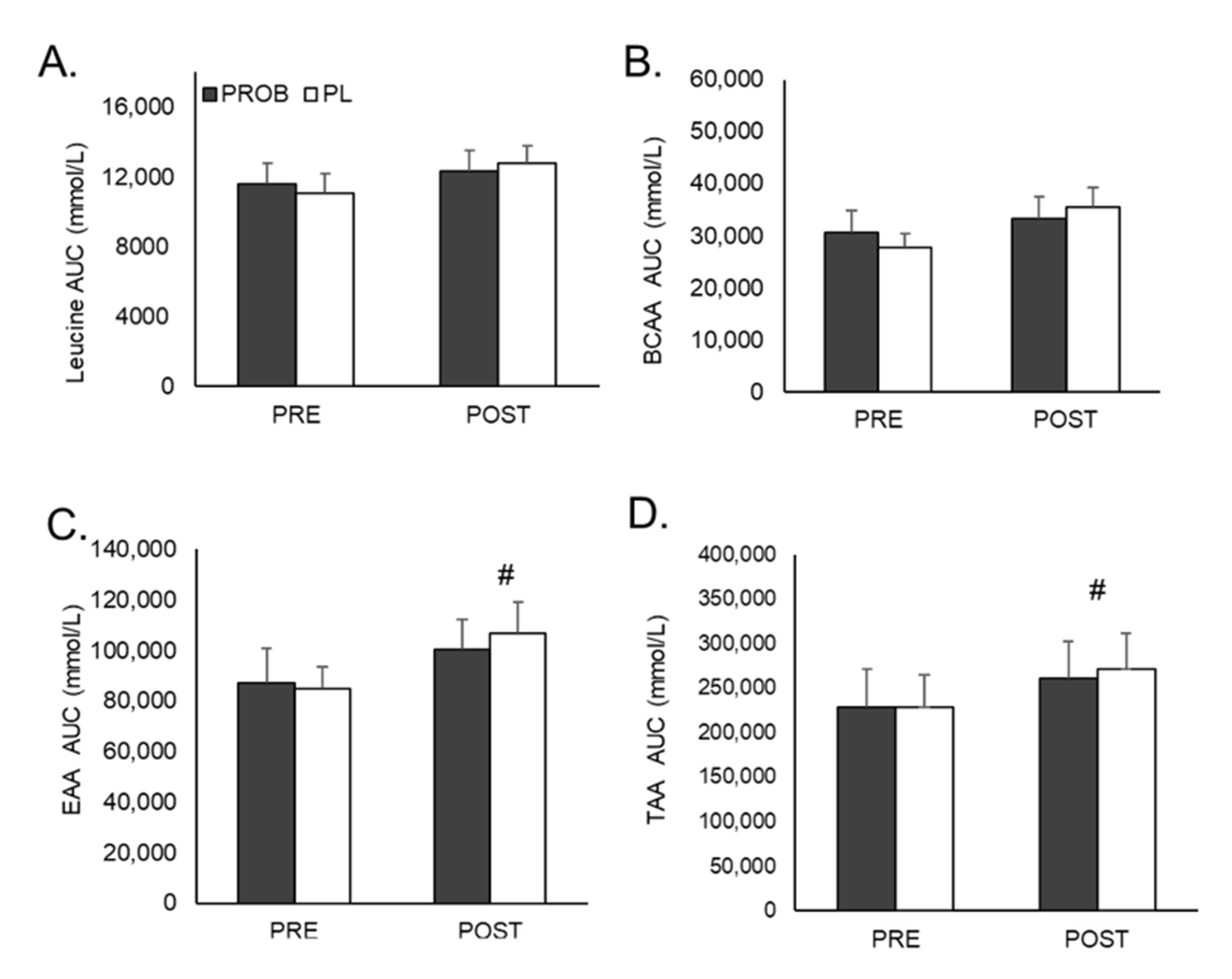
3.2. Plasma Amino Acid Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Möller, G.B.; da Cunha Goulart, M.J.V.; Nicoletto, B.B.; Alves, F.D.; Schneider, C.D. Supplementation of probiotics and its effects on physically active individuals and athletes: Systematic review. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, M.; Bishop, N.C.; Oliveira, M.; Tauler, P. Daily probiotic’s (Lactobacillus casei Shirota) reduction of infection incidence in athletes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, M.; Bishop, N.C.; Oliveira, M.; McCauley, T.; Tauler, P.; Lawrence, C. Effects of a Lactobacillus salivarius probiotic intervention on infection, cold symptom duration and severity, and mucosal immunity in endurance athletes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2012, 22, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, J.N.; Sparks, A.S.; Doran, D.A.; Fleming, S.C.; Langan-Evans, C.; Kirk, B.; Fearn, R.; Morton, J.P.; Close, G.L.J. Four weeks of probiotic supplementation reduces GI symptoms during a marathon race. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, J.N.; Wagenmakers, A.J.; Doran, D.A.; Fleming, S.C.; Fielding, B.A.; Morton, J.P.; Close, G.L. Probiotic supplementation increases carbohydrate metabolism in trained male cyclists: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E504–E513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, R.; Mohr, A.E.; Carpenter, K.C.; Kerksick, C.M.; Purpura, M.; Moussa, A.; Townsend, J.R.; Lamprecht, M.; West, N.P.; Black, K. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Probiotics. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2019, 16, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, R.; Purpura, M.; Stone, J.D.; Turner, S.M.; Anzalone, A.J.; Eimerbrink, M.J.; Pane, M.; Amoruso, A.; Rowlands, D.S.; Oliver, J.M. Probiotic Streptococcus thermophilus FP4 and Bifidobacterium breve BR03 supplementation attenuates performance and range-of-motion decrements following muscle damaging exercise. Nutrients 2016, 8, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzorati, M.; Abbeele, P.V.d.; Bubeck, S.S.; Bayne, T.; Krishnan, K.; Young, A.; Mehta, D.; DeSouza, A.J.M. Bacillus subtilis HU58 and Bacillus coagulans SC208 Probiotics Reduced the Effects of Antibiotic-Induced Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis in an M-SHIME® Model. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhayat, L.; Maresca, M.; Nicoletti, C.; Perrier, J.; Brinch, K.S.; Christian, S.; Devillard, E.; Eckhardt, E. Effect of Bacillus subtilis strains on intestinal barrier function and inflammatory response. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducray, H.A.G.; Globa, L.; Pustovyy, O.; Roberts, M.D.; Rudisill, M.; Vodyanoy, V.; Sorokulova, I. Prevention of excessive exercise-induced adverse effects in rats with Bacillus subtilis BSB3. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labellarte, G.; Maher, M. Tolerance and Effect of a Probiotic Supplement Delivered in Capsule Form. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2019, 10, 626–634. [Google Scholar]
- Cuentas, A.; Deaton, J.; Davidson, J.; Ardita, C. The Effect of Bacillus subtilis DE111 on the Daily Bowel Movement Profile for People with Occasional Gastrointestinal Irregularity. J. Probiotics Health 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, J.R.; Bender, D.; Vantrease, W.C.; Sapp, P.A.; Toy, A.M.; Woods, C.A.; Johnson, K.D. Effects of probiotic (Bacillus subtilis DE111) supplementation on immune function, hormonal status, and physical performance in division I baseball players. Sports 2018, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toohey, J.C.; Townsend, J.R.; Johnson, S.B.; Toy, A.M.; Vantrease, W.C.; Bender, D.; Crimi, C.C.; Stowers, K.L.; Ruiz, M.D.; van Dusseldorp, T.A.; et al. Effects of Probiotic (Bacillus subtilis) Supplementation During Offseason Resistance Training in Female Division I Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 34, 3173–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, W.K.; Phillips, B.E.; Williams, J.P.; Rankin, D.; Lund, J.N.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J. A Dose-rather than delivery profile–dependent mechanism regulates the “muscle-full” effect in response to oral essential amino acid intake in young men. J. Nutr. 2014, 145, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Areta, J.L.; Burke, L.M.; Ross, M.L.; Camera, D.M.; West, D.W.; Broad, E.M.; Jeacocke, N.A.; Moore, D.R.; Stellingwerff, T.; Phillips, S.M.; et al. Timing and distribution of protein ingestion during prolonged recovery from resistance exercise alters myofibrillar protein synthesis. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.; Snipe, R.; Kitic, C.; Gibson, P.R. Systematic review: Exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome—Implications for health and intestinal disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijck, K.; Pennings, B.; van Bijnen, A.A.; Senden, J.M.; Buurman, W.A.; Dejong, C.H.; Van Loon, L.J.; Lenaerts, K. Dietary protein digestion and absorption are impaired during acute postexercise recovery in young men. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R356–R361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.A.; Gisolfi, C.V.; Lambert, G.P. Effect of exercise intensity on active and passive glucose absorption. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2006, 16, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, R.; Zaragoza, J.; Purpura, M.; Iametti, S.; Marengo, M.; Tinsley, G.M.; Anzalone, A.J.; Oliver, J.M.; Fiore, W.; Biffi, A. Probiotic Administration Increases Amino Acid Absorption from Plant Protein: A Placebo-Controlled, Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter, Crossover Study. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, R.A.; Moon, J.M.; Russo, T.J.; Ratliff, K.M.; Mumford, P.W.; Jäger, R.; Purpura, M.; Kerksick, C.M. Bacillus coagulans GBI-30, 6086 improves amino acid absorption from milk protein. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshaghabee, F.M.; Rokana, N.; Gulhane, R.D.; Sharma, C.; Panwar, H. Bacillus as Potential Probiotics: Status, Concerns, and Future Perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.E.; Moore, D.R.; Kujbida, G.W.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Ingestion of whey hydrolysate, casein, or soy protein isolate: Effects on mixed muscle protein synthesis at rest and following resistance exercise in young men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.M. The impact of protein quality on the promotion of resistance exercise-induced changes in muscle mass. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinsen, H.C.; Schiebergen-Bronkhorst, B.; Roeleveld, M.; Jans, J.; de Sain-van der Velden, M.; Visser, G.; van Hasselt, P.; Verhoeven-Duif, N. Rapid quantification of underivatized amino acids in plasma by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) coupled with tandem mass-spectrometry. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, B.; Tomazela, D.M.; Shulman, N.; Chambers, M.; Finney, G.L.; Frewen, B.; Kern, R.; Tabb, D.L.; Liebler, D.C.; MacCoss, M.J. Skyline: An open source document editor for creating and analyzing targeted proteomics experiments. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2010, 26, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Aubry, A.-F.O.; Arnold, M.E. Selecting the correct weighting factors for linear and quadratic calibration curves with least-squares regression algorithm in bioanalytical LC-MS/MS assays and impacts of using incorrect weighting factors on curve stability, data quality, and assay performance. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8959–8966. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, J.R.; Morimune, J.E.; Jones, M.D.; Beuning, C.N.; Haase, A.A.; Boot, C.M.; Heffington, S.H.; Littlefield, L.A.; Henry, R.N.; Marshall, A.C. The Effect of ProHydrolase® on the Amino Acid and Intramuscular Anabolic Signaling Response to Resistance Exercise in Trained Males. Sports 2020, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, C.; Bansal, S.; Booth, B.; DeStefano, A.J.; Rose, M.J.; Sailstad, J.; Shah, V.P.; Skelly, J.P.; Swann, P.G.; Weiner, R. Quantitative bioanalytical methods validation and implementation: Best practices for chromatographic and ligand binding assays. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1962–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, R.; Crombach, N.; Gijsen, A.P.; Walrand, S.; Fauquant, J.; Kies, A.K.; Lemosquet, S.; Saris, W.H.; Boirie, Y.; van Loon, L.J. Ingestion of a protein hydrolysate is accompanied by an accelerated in vivo digestion and absorption rate when compared with its intact protein. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farup, J.; Rahbek, S.K.; Storm, A.C.; Klitgaard, S.; Jorgensen, H.; Bibby, B.M.; Serena, A.; Vissing, K. Effect of degree of hydrolysis of whey protein on in vivo plasma amino acid appearance in humans. Springerplus 2016, 5, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnfield, M.M.; Trenerry, C.; Carey, K.A.; Cameron-Smith, D. Plasma amino acid response after ingestion of different whey protein fractions. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wijck, K.; Lenaerts, K.; Van Loon, L.J.; Peters, W.H.; Buurman, W.A.; Dejong, C.H. Exercise-induced splanchnic hypoperfusion results in gut dysfunction in healthy men. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio, J.; Leaf, A.; Carson, C.; Ellerbroek, A.; Axelrod, C.; Silver, T.; Burgess, V.; Peacock, C. The effects of probiotic supplementation in active men and women. J. Exerc. Nutr. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Osterberg, K.L.; Boutagy, N.E.; McMillan, R.P.; Stevens, J.R.; Frisard, M.I.; Kavanaugh, J.W.; Davy, B.M.; Davy, K.P.; Hulver, M.W. Probiotic supplementation attenuates increases in body mass and fat mass during high-fat diet in healthy young adults. J. Obes. 2015, 23, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Amino Acid | g/100 g |
|---|---|
| Alanine | 3.5 |
| Arginine | 2.3 |
| Aspartic Acid | 8.4 |
| Cystine | 1.7 |
| Glutamic Acid | 13.3 |
| Glycine | 1.4 |
| Histidine | 1.6 |
| Isoleucine | 4.6 |
| Leucine | 8.8 |
| Lysine | 7.5 |
| Methionine | 1.6 |
| Phenylalanine | 2.6 |
| Proline | 6.6 |
| Serine | 4.6 |
| Threonine | 4.5 |
| Tryptophan | 1.3 |
| Tyrosine | 2.3 |
| Valine | 4.4 |
| Variable | Group | Pre | Post | Group × Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Mass (kg) | PROB | 83.1 ± 17.7 | 83.7 ± 18.1 | p = 0.346 |
| PL | 74.6 ± 12.2 | 74.8 ± 12.0 | ||
| Lean Body Mass (kg) | PROB | 65.5 ± 17.0 | 65.6 ± 17.0 | p = 0.785 |
| PL | 60.7 ± 11.2 | 60.9 ± 11.0 | ||
| Fat Mass (kg) | PROB | 17.6 ± 6.9 | 18.1 ± 7.5 | p = 0.168 |
| PL | 13.9 ± 4.7 | 13.9 ± 4.9 | ||
| Body Fat (%) | PROB | 21.6 ± 8.3 | 21.9 ± 8.9 | p = 0.243 |
| PL | 18.8 ± 5.9 | 18.6 ± 6.1 | ||
| Total Body Water (kg) | PROB | 47.7 ± 12.4 | 47.8 ± 12.5 | p = 0.883 |
| PL | 44.3 ± 8.2 | 44.5 ± 8.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Townsend, J.R.; Vantrease, W.C.; Jones, M.D.; Sapp, P.A.; Johnson, K.D.; Beuning, C.N.; Haase, A.A.; Boot, C.M. Plasma Amino Acid Response to Whey Protein Ingestion Following 28 Days of Probiotic (Bacillus subtilis DE111) Supplementation in Active Men and Women. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2021, 6, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk6010001
Townsend JR, Vantrease WC, Jones MD, Sapp PA, Johnson KD, Beuning CN, Haase AA, Boot CM. Plasma Amino Acid Response to Whey Protein Ingestion Following 28 Days of Probiotic (Bacillus subtilis DE111) Supplementation in Active Men and Women. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2021; 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk6010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleTownsend, Jeremy R., William C. Vantrease, Megan D. Jones, Philip A. Sapp, Kent D. Johnson, Cheryle N. Beuning, Allison A. Haase, and Claudia M. Boot. 2021. "Plasma Amino Acid Response to Whey Protein Ingestion Following 28 Days of Probiotic (Bacillus subtilis DE111) Supplementation in Active Men and Women" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 6, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk6010001
APA StyleTownsend, J. R., Vantrease, W. C., Jones, M. D., Sapp, P. A., Johnson, K. D., Beuning, C. N., Haase, A. A., & Boot, C. M. (2021). Plasma Amino Acid Response to Whey Protein Ingestion Following 28 Days of Probiotic (Bacillus subtilis DE111) Supplementation in Active Men and Women. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 6(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk6010001





