Effects of Different Continuous Aerobic Training Protocols in a Heterozygous Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Type C Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Behavioral Training
2.3. Electrophysiological Recordings in Mouse Hippocampal Slices
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Training Protocols on Physical and Performance Parameters
3.2. Effects of Different Exercise Protocols on Synaptic Plasticity
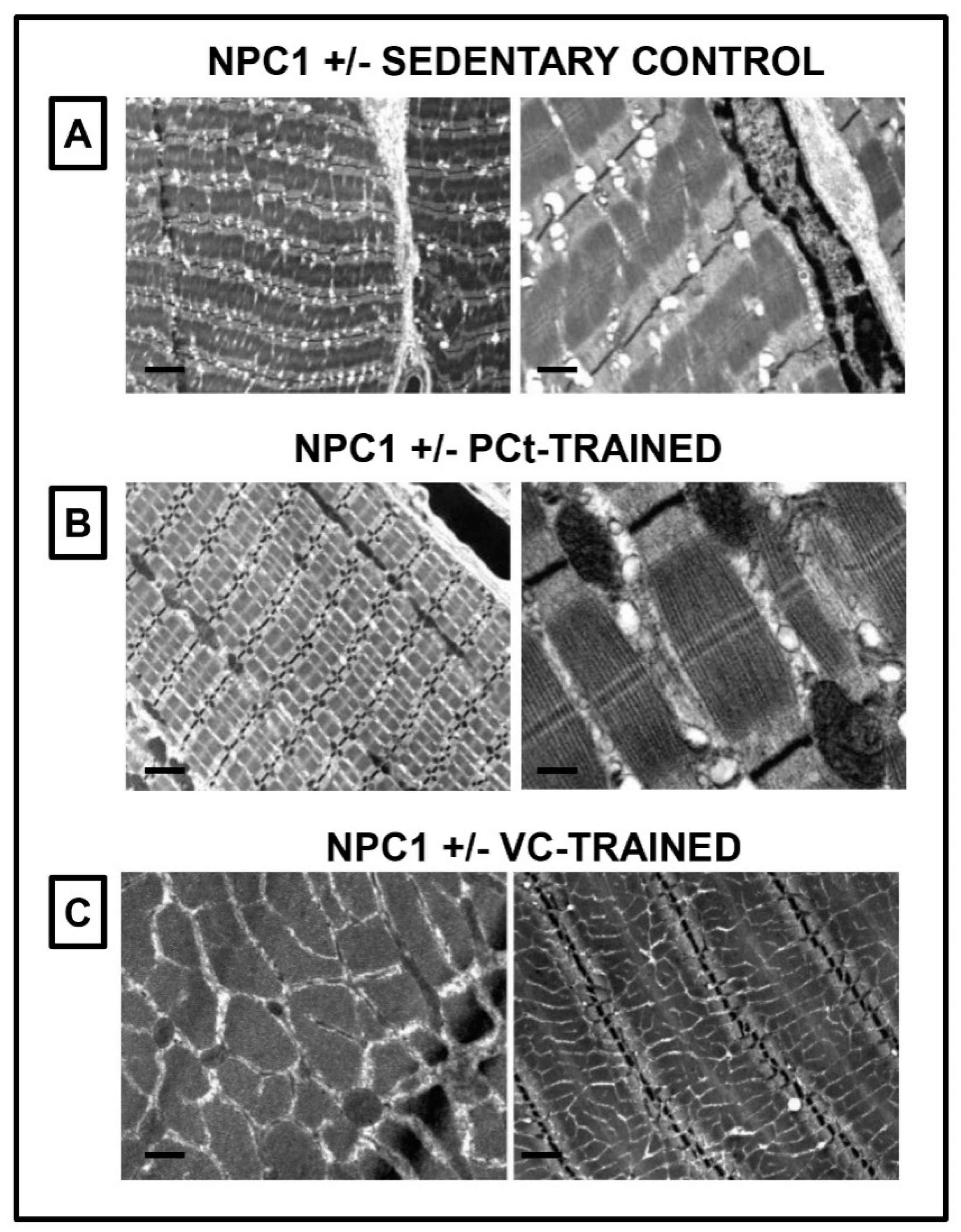
3.3. Ultrastructural Analysis of the Muscle Tissues of NPC1+/− Sedentary Control and NPC1 +/− Trained Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mengel, E.; Klünemann, H.H.; Lourenço, C.M.; Hendriksz, C.J.; Sedel, F.; Walterfang, M.; Kolb, S.A. Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Symptomatology: An Expert-Based Clinical Description. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawamura, N.; Gong, J.S.; Garver, W.S.; Heidenreich, R.A.; Ninomiya, H.; Ohno, K.; Yanagisawa, K.; Michikawa, M. Site-specific Phosphorylation of Tau Accompanied by Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) in Brains of Niemann-Pick Type C Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10314–10319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, B.; Li, J.; Davies, P.; Vincent, I. Deregulation of cdk5, Hyperphosphorylation, and Cytoskeletal Pathology in the Niemann-Pick Type C Murine Model. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6515–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Parker, C.C.; Pentchev, P.G.; Katz, D.; Ghetti, B.; D’Agostino, A.N.; Carstea, E.D. Neurofibrillary Tangles in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Acta Neuropathol. 1995, 89, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, S.; Bridges, L.R.; Case, C.P. Neurofibrillary Tangles in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Brain 1995, 118, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, I.A.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Curry, B.; Suzuki, K.; Shin, R.W.; Pentchev, P.G.; Carstea, E.D.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Paired Helical Filament Tau (PHFtau) in Niemann-Pick Type C Disease Is Similar to PHFtau in Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1992, 90, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluenemann, H.H.; Nutt, J.G.; Davis, M.Y.; Bird, T.D. Parkinsonism Syndrome in Heterozygotes for Niemann-Pick C1. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 335, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassilhas, R.C.; Tufik, S.; de Mello, M.T. Physica Exercise, Neuroplasticity, Spatial Learning and Memory. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotman, C.W.; Berchtold, N.C.; Christie, L.A. Exercise Builds Brain Health: Key Roles of Growth Factor Cascades and Inflammation. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, M.; Cariati, I.; Scimeca, M.; Pallone, G.; Bonanno, E.; Tancredi, V.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Frank, C. Effects of Short-Term Aerobic Exercise in a Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Type C Disease on Synaptic and Muscle Plasticity. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2019, 55, 330–337. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, Y.S.; Patki, G.; Das-Panja, K.; Le, W.D.; Ahmad, S.O. Neuroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Exercise in a Chronic Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease with Moderate Neurodegeneration. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sá, M.J. Exercise Therapy and Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchman, A.S.; Boyle, P.A.; Yu, L.; Shah, R.C.; Wilson, R.S.; Bennett, D.A. Total Daily Physical Activity and the Risk of AD and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults. Neurology 2012, 78, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Fu, Z.; Le, W. Exercise and Parkinson’s Disease. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2019, 147, 45–74. [Google Scholar]
- Loftus, S.F.; Morris, J.A.; Carstea, E.D.; Gu, J.Z.; Cummings, C.; Brown, A.; Ellison, J.; Ohno, K.; Rosenfeld, M.A.; Tagle, D.A.; et al. Murine Model of Niemann-Pick C Disease: Mutation in a Cholesterol Homeostasis Gene. Science 1997, 277, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louhimies, S. Directive 86/609/EEC on the Protection of Animals Used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2002, 30 (Suppl. 2), 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallone, G.; Palmieri, M.; Cariati, I.; Bei, R.; Masuelli, L.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Tancredi, V. Different Continuous Training Modalities Result in Distinctive Effects on Muscle Structure, Plasticity and Function. Biomed. Rep. 2020, 12, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcangelo, G.; Grossi, D.; Racaniello, M.; Cardinale, A.; Zaratti, A.; Rufini, S.; Cutarelli, A.; Tancredi, V.; Merlo, D.; Frank, C. Miglustat Reverts the Impairment of Synaptic Plasticity in a Mouse Model of NPC Disease. Neural. Plast. 2016, 2016, 3830424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenka, R.C.; Nicoll, R.A. Long-term Potentiation—A Decade of Progress? Science 1999, 285, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcangelo, G.; Triossi, T.; Buglione, A.; Melchiorri, G.; Tancredi, V. Modulation of Synaptic Plasticity by Short-Term Aerobic Exercise in Adult Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 332, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scimeca, M.; Orlandi, A.; Terrenato, I.; Bischetti, S.; Bonanno, E. Assessment of Metal Contaminants in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by EDX Microanalysis. Eur. J. Histochem. 2014, 58, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scimeca, M.; Piccirilli, E.; Mastrangeli, F.; Rao, C.; Feola, M.; Orlandi, A.; Gasbarra, E.; Bonanno, E.; Tarantino, U. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and Myostatin Pathways: Key Mediator of Human Sarcopenia. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancredi, V.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Grassi, F.; Tarroni, P.; Palmieri, G.; Santoni, A.; Eusebi, F. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alters Synaptic Transmission in Rat Hippocampal Slices. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 146, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancredi, V.; D’Antuono, M.; Cafè, C.; Giovedì, S.; Buè, M.C.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Onofri, F.; Benfenati, F. The Inhibitory Effects of interleukin-6 on Synaptic Plasticity in the Rat Hippocampus Are Associated With an Inhibition of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase ERK. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazakoff, B.N.; Howland, J.G. Acute Stress Disrupts Paired Pulse Facilitation and Long-Term Potentiation in Rat Dorsal Hippocampus Through Activation of Glucocorticoid Receptors. Hippocampus 2010, 20, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, R.S.; Voss, M.W.; Erickson, K.I.; Kramer, A.F. Physical Activity and Cognitive Vitality. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2015, 66, 769–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, M.W.; Vivar, C.; Kramer, A.F.; van Praag, H. Bridging Animal and Human Models of Exercise-Induced Brain Plasticity. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassilhas, R.C.; Lee, K.S.; Fernandes, J.; Oliveira, M.G.M.; Tufik, S.; Meeusen, R.; de Mello, M.T. Spatial memory Is Improved by Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Through Divergent Molecular Mechanisms. Neuroscience 2012, 202, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

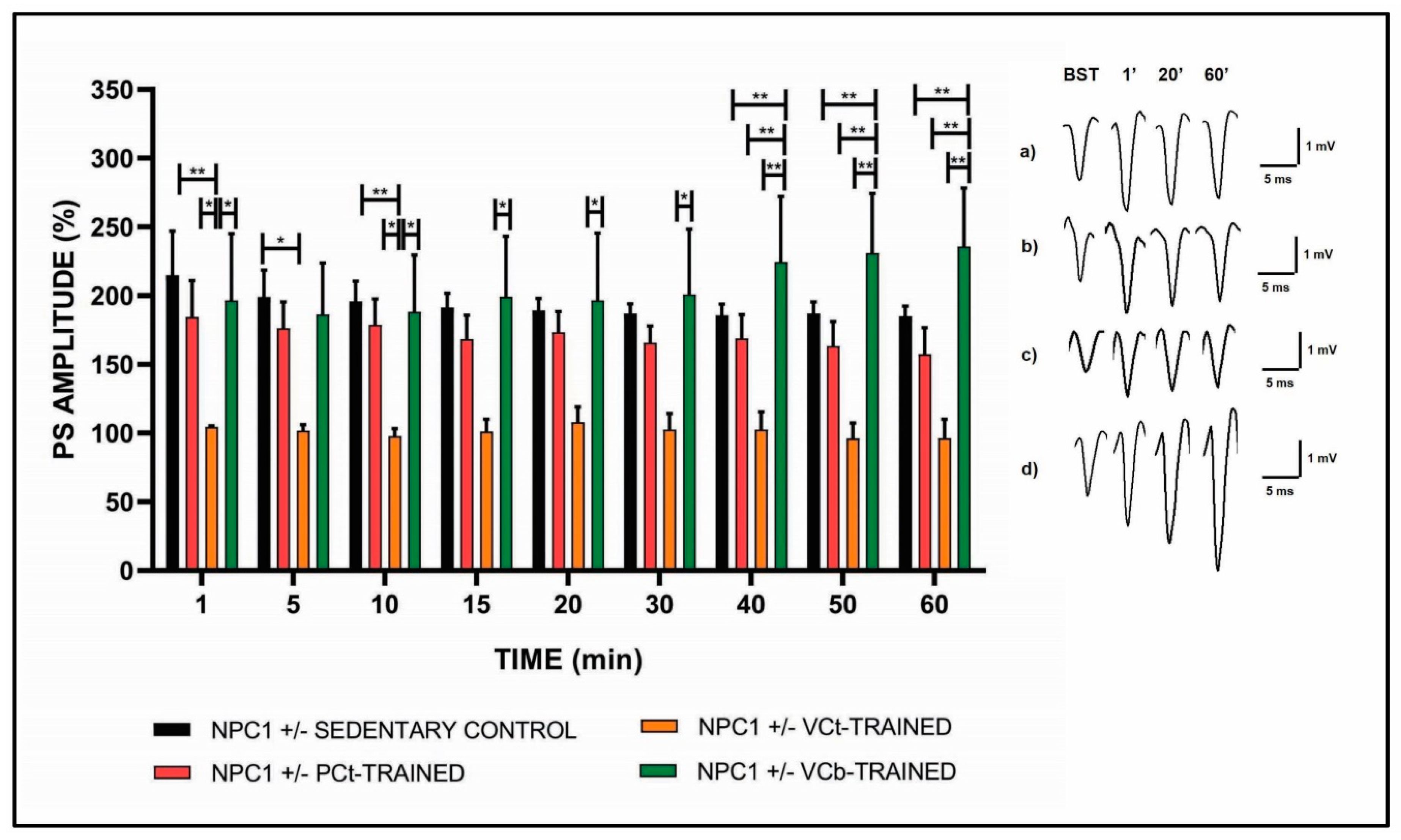
| TIME (Min) | NPC1 +/- SEDENTARY CONTROL (% PS Amplitude) | NPC1 +/− CPt- TRAINED (% PS Amplitude) | NPC1 +/− CVt- TRAINED (% PS Amplitude) | NPC1 +/− CVb- TRAINED (% PS Amplitude) | SIGNIFICANCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 214.9 ± 32.0 | 184.5 ± 26.4 | 104.5 ± 0.9 | 196.6 ± 58.6 | < 0.01 |
| 5 | 199.1 ± 19.5 | 176.4 ± 19.1 | 101.8 ± 4.3 | 186.4 ± 47.5 | < 0.05 |
| 10 | 195.9 ± 14.6 | 178.8 ± 18.7 | 97.7 ± 5.5 | 188.2 ± 41.2 | < 0.05 |
| 15 | 191.4 ± 10.3 | 168.5 ± 17.2 | 101.1 ± 8.9 | 199.2 ± 51.1 | < 0.05 |
| 20 | 189.3 ± 8.8 | 173.5 ± 14.8 | 107.9 ± 14.1 | 196.6 ± 48.8 | < 0.05 |
| 30 | 187.0 ± 7.0 | 165.7 ± 12.4 | 102.6 ± 11.5 | 200.9 ± 47.5 | < 0.05 |
| 40 | 185.7 ± 8.2 | 168.9 ± 17.2 | 102.6 ± 12.9 | 224.5 ± 67.6 | < 0.01 |
| 50 | 186.9 ± 8.5 | 163.4 ± 17.6 | 96.0 ± 11.4 | 231.0 ± 73.2 | < 0.01 |
| 60 | 185.2 ±17.2 | 157.3 ± 19.5 | 96.3 ± 13.7 | 235.8 ± 77.4 | < 0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cariati, I.; Scimeca, M.; Tancredi, V.; D’Amico, A.G.; Pallone, G.; Palmieri, M.; Frank, C.; D’Arcangelo, G. Effects of Different Continuous Aerobic Training Protocols in a Heterozygous Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Type C Disease. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk5030053
Cariati I, Scimeca M, Tancredi V, D’Amico AG, Pallone G, Palmieri M, Frank C, D’Arcangelo G. Effects of Different Continuous Aerobic Training Protocols in a Heterozygous Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Type C Disease. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2020; 5(3):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk5030053
Chicago/Turabian StyleCariati, Ida, Manuel Scimeca, Virginia Tancredi, Agata Grazia D’Amico, Gabriele Pallone, Mattia Palmieri, Claudio Frank, and Giovanna D’Arcangelo. 2020. "Effects of Different Continuous Aerobic Training Protocols in a Heterozygous Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Type C Disease" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 5, no. 3: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk5030053
APA StyleCariati, I., Scimeca, M., Tancredi, V., D’Amico, A. G., Pallone, G., Palmieri, M., Frank, C., & D’Arcangelo, G. (2020). Effects of Different Continuous Aerobic Training Protocols in a Heterozygous Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Type C Disease. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 5(3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk5030053







