Effects of Stochastic Resonance on Sensorimotor Performance during Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
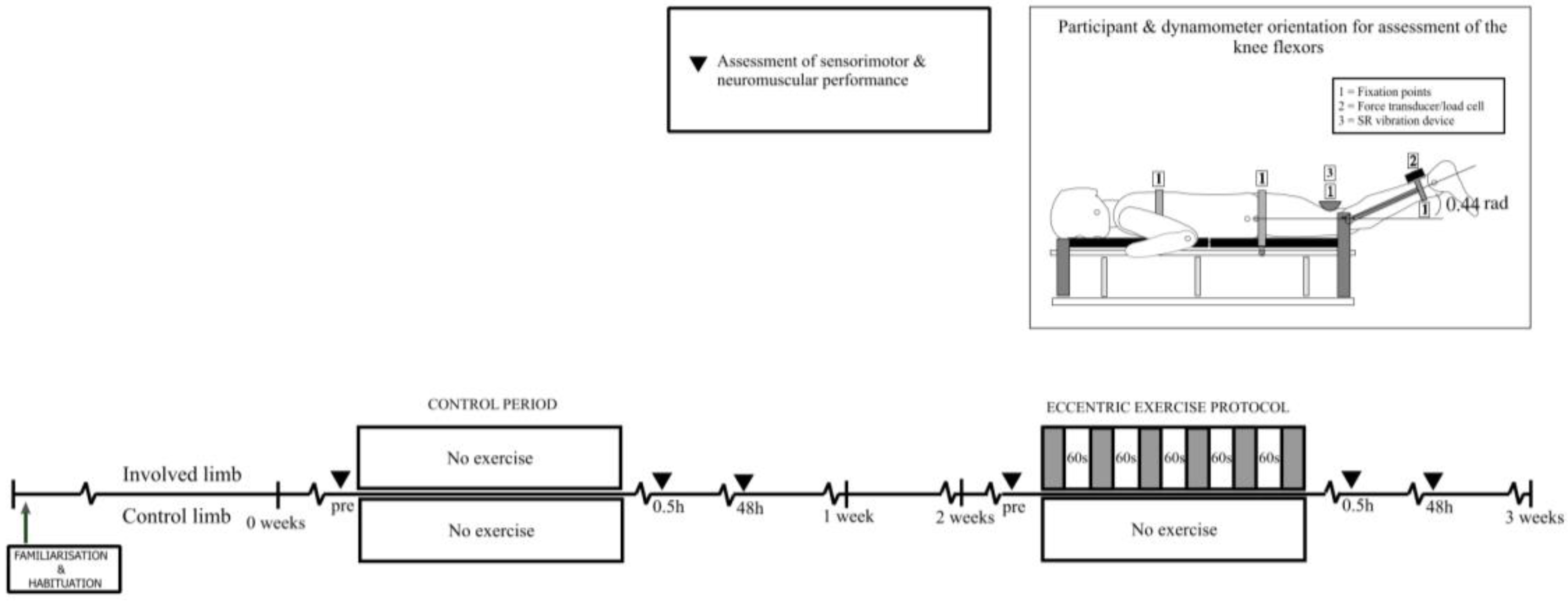
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.2.1. Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage (EIMD) Protocol
2.2.2. Stochastic Resonance Protocol
2.2.3. Assessment of Peak Force
2.2.4. Assessment of Sensorimotor Performance
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Verified EIMD
3.2. Effects of Stochastic Resonance (SR) Stimulation on Force Error (FE)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Proske, U.; Morgan, D.L. Muscle damage from eccentric exercise: Mechanism, mechanical signs adaptation and clinical applications. J. Physiol. 2001, 537, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupka, N.; Tarnopolsky, M.; Yardley, N.; Phillips, S. Cellular adaptation to repeated eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 91, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, N.; Eston, R.G.; Minshull, C.; Rees, D. Effects of antecedent flexibility conditioning on neuromuscular and sensorimotor performance during exercise-induced muscle damage. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2013, 11, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, J.M.; Clarkson, P.M.; James, R.; Miles, M.; Westerfer, M.; Clark, S.; Donelly, A.E. Neuromuscular dysfunction following eccentric exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1995, 27, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockett, C.; Warren, N.; Gregory, J.E.; Morgan, D.L.; Proske, U. A comparison of the effects of concentric versus eccentric exercise on force and position sense at the human elbow joint. Brain Res. 1997, 771, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.; Twist, C.; Eston, R. Neuromuscular Function after exercise induced muscle damage. Sports Med. 2004, 34, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colby, S.; Francisco, A.; Bing, Y.; Kirkendall, D.; Finch, M.; Garret, W. Electromyographic and Kinematic Analysis of Cutting Maneuvers Implications for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Am. J. Sports Med. 2000, 28, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lephart, S.M.; Fu, F.H. Proprioception and Neuromuscular Control in Joint Stability; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Beynnon, B.D.; Renstrom, P.A.; Konradsen, L.; Elmqvist, L.G.; Gottleib, D.; Dirks, M. Validation of Techniques to Measure Knee Proprioception. In Proprioception Neuromuscular Control Joint Stability; Lephart, S.M., Fu, F., Eds.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2000; pp. 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Paschalis, V.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Giakas, G.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Pappas, A.; Koutedakis, Y.; Theodorou, A. Eccentric exercise affects the upper limbs more than the lower limbs in position sense and reaction angle. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proske, U.; Gregory, J.E.; Morgan, D.L.; Percival, P.; Weerakkody, N.S.; Canny, B.J. Force matching errors following eccentric exercise. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2004, 23, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, J.E.; Morgan, D.L.; Proske, U. Responses of muscle spindles following a series of eccentric contractions. Exp. Brain Res. 2004, 157, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammaitoni, L.; Hanggi, P.; Jung, P.; Marchesoni, F. Stochastic resonance. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1998, 70, 223–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.J.; Imhoff, T.T.; Grigg, P. Noise-enhanced tactile sensation. Nature 1996, 383, 770. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Montero-Odasso, M.; Bean, J.; Kerrigan, D.C.; Collins, J.J. Noise-enhanced vibrotactile sensitivity in older adults, patients with stroke, and patients with diabetic neuropathy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo, E.; Doti, R.; Faubert, J. Ubiquitous Crossmodal Stochastic Resonance in Humans: Auditory Noise Facilitates Tactile, Visual and Proprioceptive Sensations. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.; Arnold, B.; Blackburn, J.; Brown, C.; Guskiewicz, K. Enhanced balance associated with coordination training with Stochastic Resonance Stimulation in subjects with functional ankle stability. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2007, 4, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Gravelle, D.; Laughton, C.; Katdare, K.; Niemi, J.; Lipsitz, L.; Collins, J. Noise Enhanced balance in older Adults. NeuroReport 2002, 13, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priplata, A.A.; Niemi, J.B.; Harry, J.D.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Collins, J.J. Vibrating insoles and balance control in elderly people. Lancet 2003, 362, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.; Blackburn, J.; Olcott, C.; Dirshl, D.; Weinhold, P. The Effect of Stochastic Resonance Electrical Stimulation and neoprene sleeve on knee proprioception. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2009, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twist, C.; Gleeson, N.; Eston, R. The effects of plyometric exercise on unilateral balance performance. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marginson, V.; Rowlands, A.V.; Gleeson, N.P.; Eston, R.G. Comparison of the Symptoms of Exercise Induced Muscle Damage after an Initial and Repeated bout of Plyometric Exercise in Men and Boys. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highton, J.M.; Twist, C.; Eston, R. The Effects of Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage on Agility and Sprint Running Performance. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2009, 7, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minshull, C.; Gleeson, N.P.; Eston, R.G.; Bailey, A.; Rees, D. Single measurement reliability and reproducibility of volitional and magnetically-evoked indices of neuromuscular performance in adults. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2009, 19, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beynnon, B.D.; Johnson, R.J. Anterior cruciate ligament injury rehabilitation in athletes: Biomechanical considerations. Sports Med. 1996, 22, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, J.; Carr, R.; Morgan, D. Stochastic Resonance in Muscle Receptors. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 9, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallerud, H.; Gleeson, N. Effects of stretching on performances involving stretch-shortening cycles. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.J.; Proske, U. Effect of muscle fatigue on the sense of limb position and movement. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 170, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marqueste, T.; Decherchi, P.; Messan, F.; Kipson, N.; Gre´lot, L.; Jammes, Y. Eccentric exercise alters muscle sensory motor control through the release of inflammatory mediators. Brain Res. 2004, 1023, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewett, T.E.; Myer, G.D.; Ford, K.R. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries in Female Athletes: Part 1, Mechanisms and Risk Factors. Am. J. Sports Med. 2006, 34, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strojnik, V.; Komi, P.V. Neuromuscular fatigue after maximal stretch-shortening cycle exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 84, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
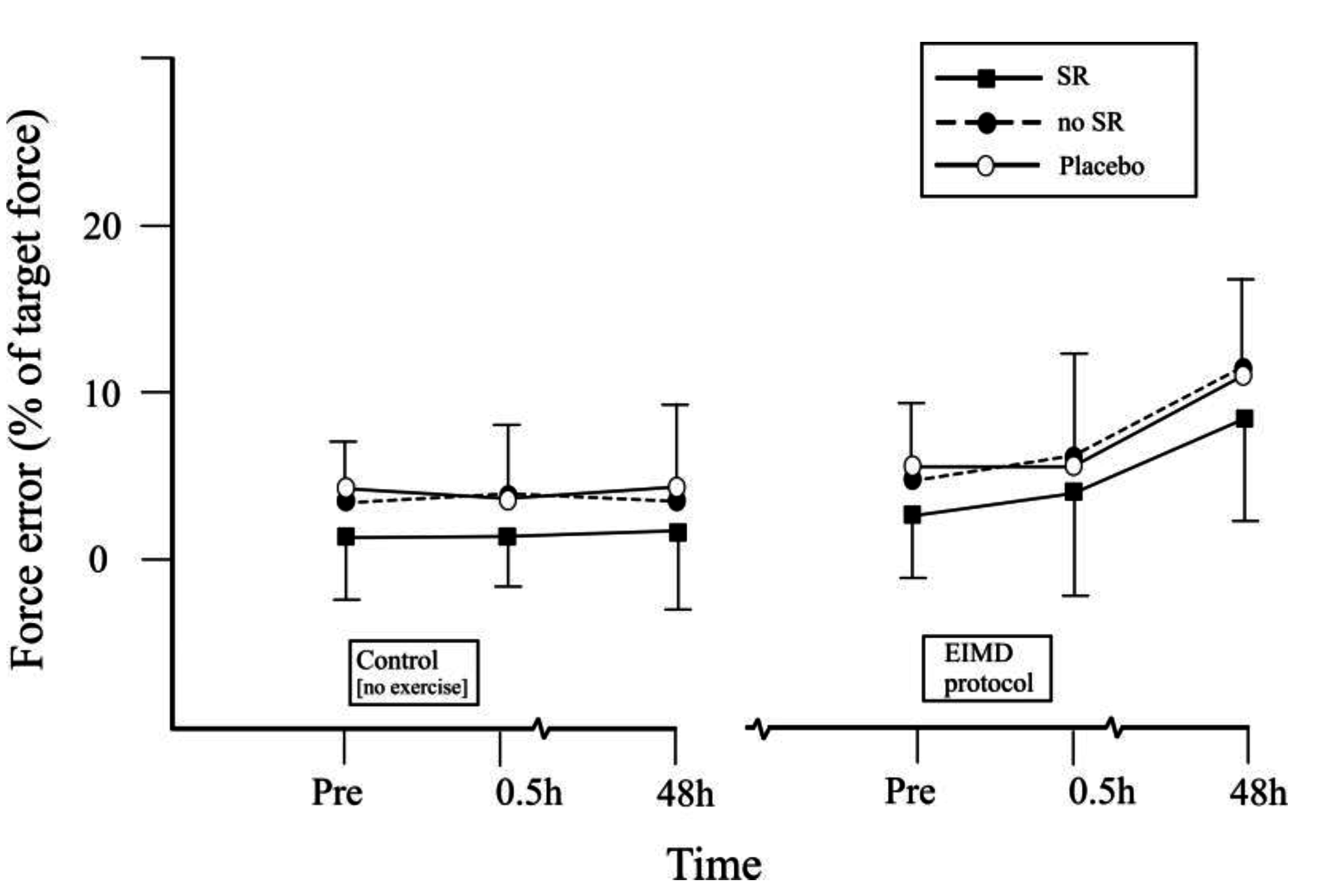
| Force Error (%) | Condition | Experimental Period | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | EIMD | ||||||
| Pre | 0.5 h | 48 h | Pre | 0.5 h | 48 h | ||
| Non-preferred leg ‡ | SR | 3.2 ± 3.2 | 2.9 ± 2.9 | 3.5 ± 3.4 | 3.7 ± 2.3 | 3.9 ± 3.7 | 8.1 ± 5.1 |
| no SR | 5.7 ± 3.7 | 5.8 ± 3.2 | 4.9 ± 3.8 | 5.6 ± 3.1 | 6.3 ± 3.1 | 10.7 ± 4.0 | |
| placebo | 5.2 ± 3.9 | 5.6 ± 3.7 | 5.1 ± 4.1 | 5.7 ± 3.3 | 6.0 ± 3.7 | 10.8 ± 4.4 | |
| Control leg † | SR | 3.7 ± 3.0 | 3.2 ± 2.9 | 3.3 ± 3.7 | 3.9 ± 3.4 | 3.6 ± 2.7 | 3.8 ± 3.8 |
| no SR | 5.9 ± 3.9 | 5.5 ± 3.4 | 5.0 ± 4.2 | 6.0 ± 4.1 | 6.5 ± 3.6 | 5.2 ± 3.6 | |
| placebo | 5.7 ± 3.3 | 5.8 ± 3.6 | 5.0 ± 4.7 | 5.6 ± 3.5 | 5.9 ± 3.8 | 5.5 ± 4.3 | |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gleeson, N. Effects of Stochastic Resonance on Sensorimotor Performance during Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2017, 2, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk2020016
Gleeson N. Effects of Stochastic Resonance on Sensorimotor Performance during Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2017; 2(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk2020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleGleeson, Nigel. 2017. "Effects of Stochastic Resonance on Sensorimotor Performance during Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 2, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk2020016
APA StyleGleeson, N. (2017). Effects of Stochastic Resonance on Sensorimotor Performance during Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 2(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk2020016





