A Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average with Exogenous Factors (SARIMAX) Forecasting Model-Based Time Series Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Related Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average with Exogenous Factors (ARIMAX)
3.2. Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average with Exogenous Factors Model
3.3. Autocorrelation (ACF) and Partial Autocorrelation (PACF)
3.4. The Augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) Test and the Null Hypothesis
3.5. Study Area and Data Collection
3.6. Error Indices
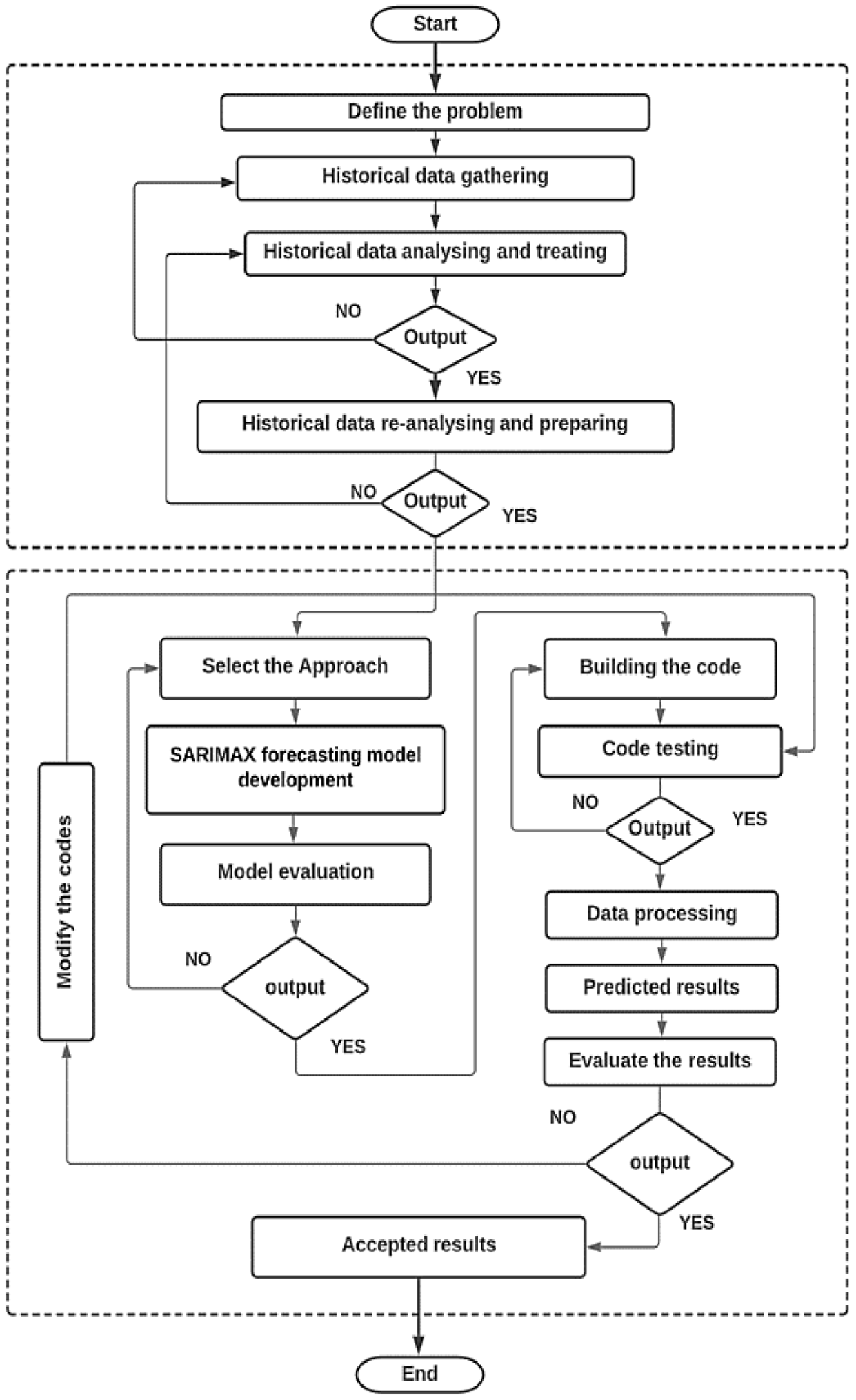
3.7. Model Setup and Configuration
4. Results and Discussion
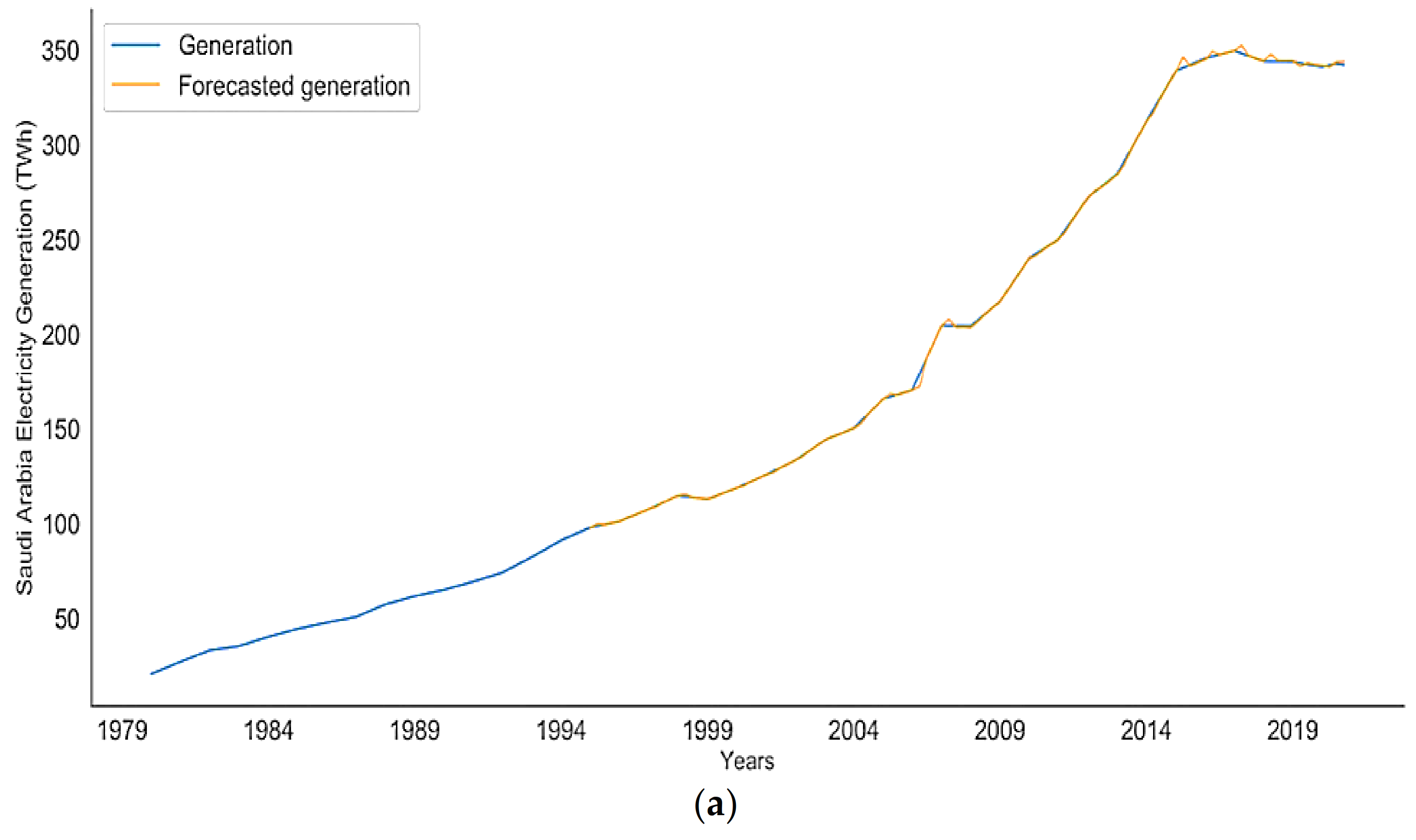
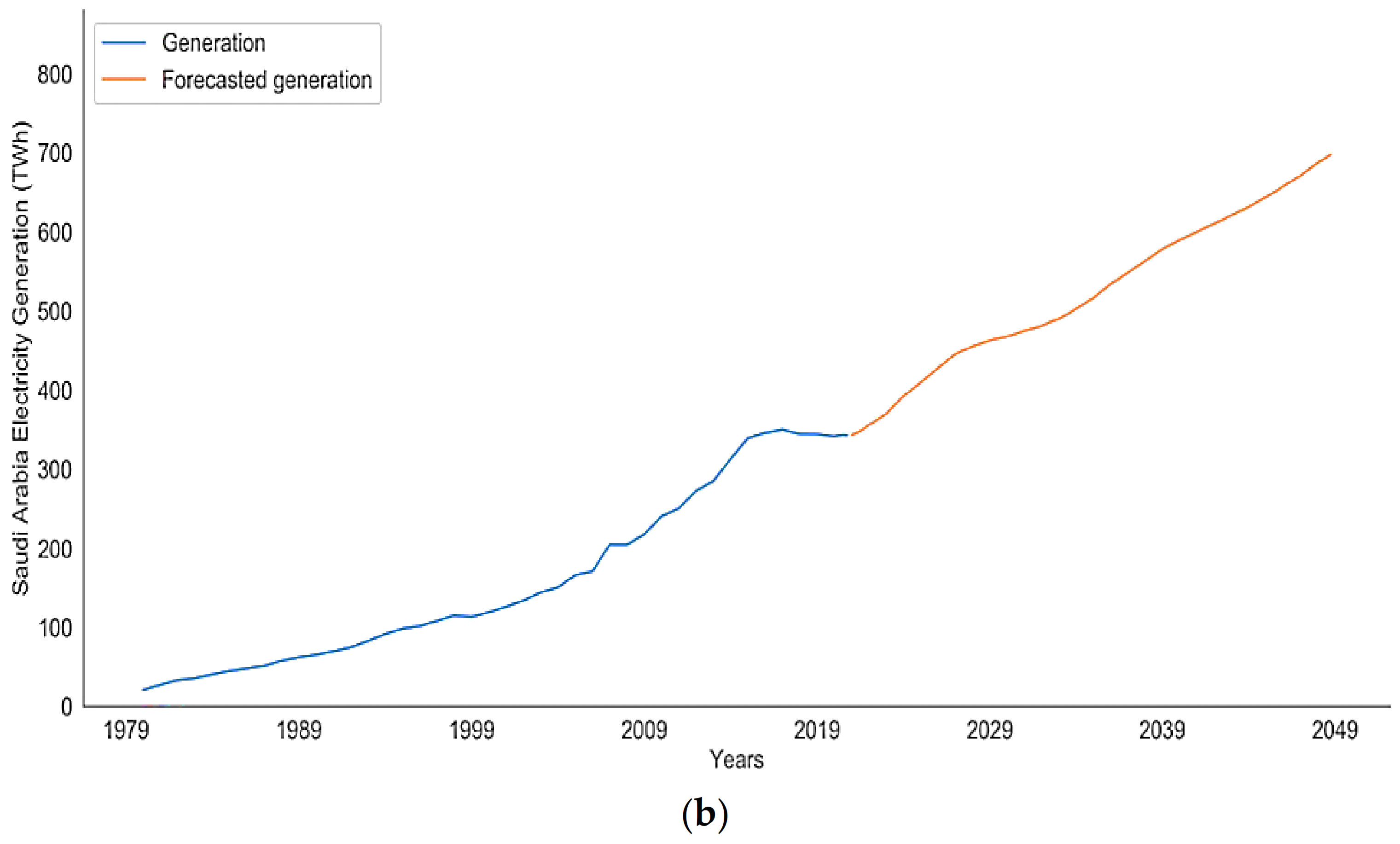
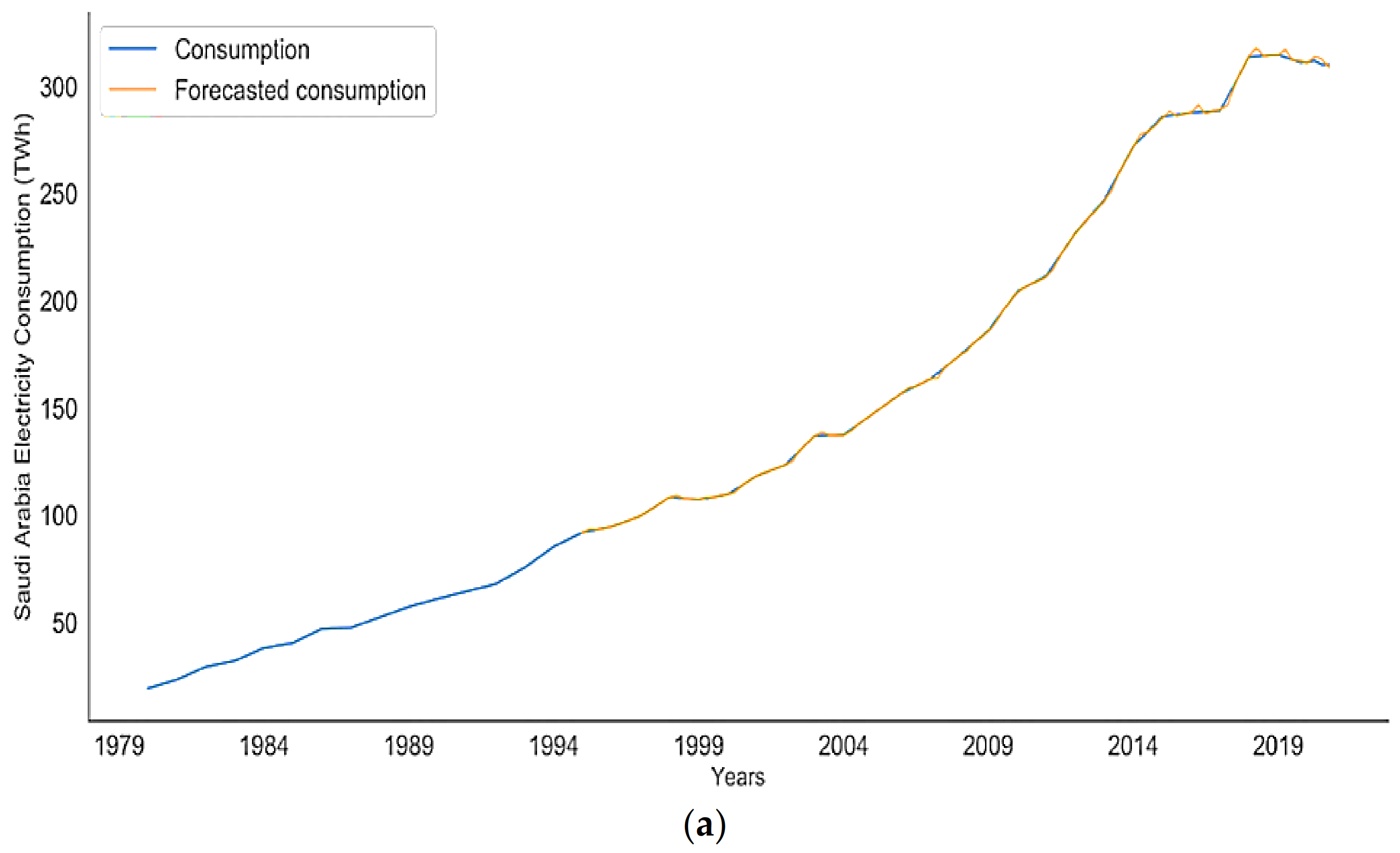
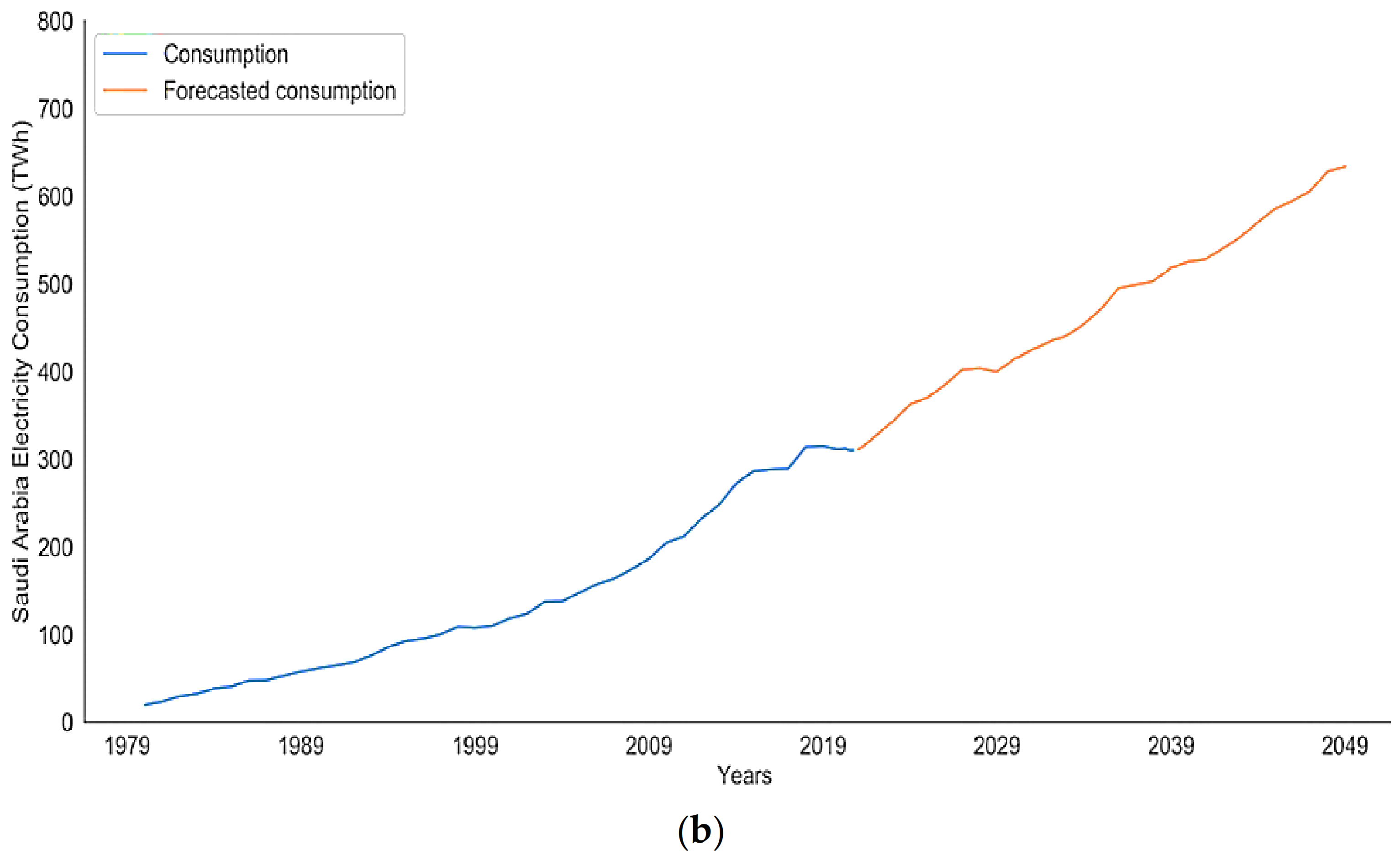
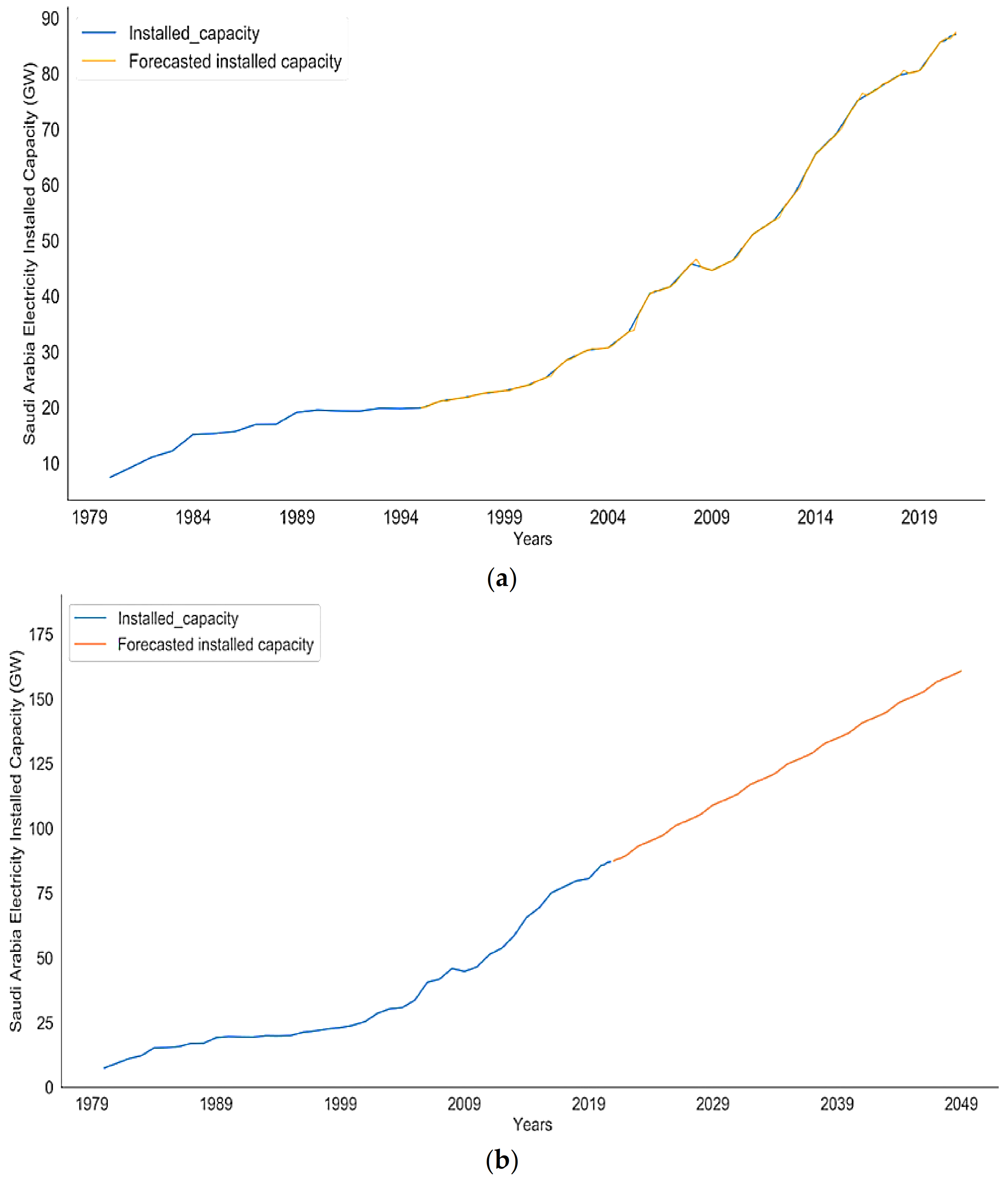
4.1. Future Performance Analysis for Saudi Arabia’s Electricity Sector
4.2. SARIMAX Model Evaluation
5. Conclusions
The Importance of This Work and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsharif, M.H.; Younes, M.K.; Kim, J. Time series ARIMA model for prediction of daily and monthly average global solar radiation: The case study of Seoul, South Korea. Symmetry 2019, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.R.; Csala, D. Short-Term Solar Irradiance Forecasting Model Based on Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Electrical, Communication, and Computer Engineering (ICECCE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–13 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Funahashi, K.-i.; Nakamura, Y. Approximation of dynamical systems by continuous time recurrent neural networks. Neural Netw. 1993, 6, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.R.; Csala, D. Short-Term Wind Speed and Temperature Forecasting Model Based on Gated Recurrent Unit Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd Global Power, Energy and Communication Conference (GPECOM), Antalya, Turkey, 5–8 October 2021; pp. 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.R.; Csala, D. Wind Speed and Solar Irradiance Prediction Using a Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Model Based on Neural Networks. Energies 2021, 14, 6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ye, L.; Li, Z.; Song, X.; Lang, Y.; Su, J. A novel bidirectional mechanism based on time series model for wind power forecasting. Appl. Energy 2016, 177, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.H.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Agalgaonkar, A.P. Short-term load forecasting using regression based moving windows with adjustable window-sizes. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Industry Application Society Annual Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 5–9 October 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Papalexopoulos, A.D.; Hesterberg, T.C. A regression-based approach to short-term system load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1990, 5, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K.; Smith, K.M.; Culligan, P.J.; Taylor, J.E. Forecasting energy consumption of multi-family residential buildings using support vector regression: Investigating the impact of temporal and spatial monitoring granularity on performance accuracy. Appl. Energy 2014, 123, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Xiao, F.; Wang, S. Development of prediction models for next-day building energy consumption and peak power demand using data mining techniques. Appl. Energy 2014, 127, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-M.; Ko, C.-N. Short-term load forecasting using lifting scheme and ARIMA models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 5902–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, K.; Luck, R.; Mago, P.J.; Cho, H. Building hourly thermal load prediction using an indexed ARX model. Energy Build. 2012, 54, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Babushkin, V.; Afshari, A. Short-term forecasting of temperature driven electricity load using time series and neural network model. J. Clean Energy Technol. 2014, 2, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.-F.; Yu, M.; Dong, S.-Q.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Hong, W.-C. Forecasting short-term electricity load using hybrid support vector regression with grey catastrophe and random forest modeling. Util. Policy 2021, 73, 101294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, S.; Karakatsanis, I. Short-term electricity load forecasting using time series and ensemble learning methods. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Power and Energy Conference at Illinois (PECI), Champaign, IL, USA, 20–21 February 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.; Sandels, C.; Zhu, K.; Nordström, L. A seasonal ARIMA model with exogenous variables for elspot electricity prices in Sweden. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), Stockholm, Sweden, 27–31 May 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Pipattanasomporn, M.; Rahman, S. Day-ahead building-level load forecasts using deep learning vs. traditional time-series techniques. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagropoulos, S.I.; Chouliaras, G.I.; Kardakos, E.G.; Simoglou, C.K.; Bakirtzis, A.G. Comparison of SARIMAX, SARIMA, modified SARIMA and ANN-based models for short-term PV generation forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Energy Conference (ENERGYCON), Leuven, Belgium, 4–8 April 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, F.; Jia, L. Short-term load forecasting based on SARIMAX-LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy (ICPRE), Shanghai, China, 12–14 September 2020; pp. 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Alasali, F.; Nusair, K.; Alhmoud, L.; Zarour, E. Impact of the covid-19 pandemic on electricity demand and load forecasting. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutthichaimethee, P.; Ariyasajjakorn, D. Forecasting energy consumption in short-term and long-term period by using arimax model in the construction and materials sector in thailand. J. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 18, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutthichaimethee, P.; Naluang, S. The efficiency of the sustainable development policy for energy consumption under environmental law in Thailand: Adapting the SEM-VARIMAX model. Energies 2019, 12, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, N.; Fukushige, M. Modeling and forecasting hourly electricity demand by SARIMAX with interactions. Energy 2018, 165, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cho, Y. National-scale electricity peak load forecasting: Traditional, machine learning, or hybrid model? Energy 2022, 239, 122366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarsitano, A.; Amerise, I.L. Short-term load forecasting using a two-stage sarimax model. Energy 2017, 133, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.; Stewart, R.A.; Lu, J. Autoregressive with exogenous variables and neural network short-term load forecast models for residential low voltage distribution networks. Energies 2014, 7, 2938–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.J.; Medeiros, M.C. Modeling and forecasting short-term electricity load: A comparison of methods with an application to Brazilian data. Int. J. Forecast. 2008, 24, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.; Ahmad, M.H.; Ismail, Z. Improving Short Term Load Forecasting Using Double Seasonal Arima Model. 2011. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.389.5120 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Kim, M.S. Modeling special-day effects for forecasting intraday electricity demand. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 230, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.; Csala, D. Saudi Arabia’s solar and wind energy penetration: Future performance and requirements. Energies 2020, 13, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Xu, X. A short-term load forecasting model of natural gas based on optimized genetic algorithm and improved BP neural network. Appl. Energy 2014, 134, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponetto, R.; Fortuna, L.; Graziani, S.; Xibilia, M.G. Genetic algorithms and applications in system engineering: A survey. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 1993, 15, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Harbi, F.; Csala, D. Saudi Arabia’s Electricity: Energy Supply and Demand Future Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2019 1st Global Power, Energy and Communication Conference (GPECOM), Nevsehir, Turkey, 12–15 June 2019; pp. 467–472. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, P.; Chu, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Ni, L.; Bao, Y.; Wang, K. Short-term electrical load forecasting using the Support Vector Regression (SVR) model to calculate the demand response baseline for office buildings. Appl. Energy 2017, 195, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.-M.; Li, D.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, J. Short term electricity load forecasting using a hybrid model. Energy 2018, 158, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucolo, M.; Fortuna, L.; Nelke, M.; Rizzo, A.; Sciacca, T. Prediction models for the corrosion phenomena in Pulp & Paper plant. Control. Eng. Pract. 2002, 10, 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Ampountolas, A. Modeling and Forecasting Daily Hotel Demand: A Comparison Based on SARIMAX, Neural Networks, and GARCH Models. Forecasting 2021, 3, 580–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, D.; Kourentzes, N. The impact of special days in call arrivals forecasting: A neural network approach to modelling special days. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 264, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice; OTexts: Melbourne, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Papaioannou, G.P.; Dikaiakos, C.; Dramountanis, A.; Papaioannou, P.G. Analysis and modeling for short-to medium-term load forecasting using a hybrid manifold learning principal component model and comparison with classical statistical models (SARIMAX, Exponential Smoothing) and artificial intelligence models (ANN, SVM): The case of Greek electricity market. Energies 2016, 9, 635. [Google Scholar]
- Makridakis, S.; Wheelwright, S.C.; Hyndman, R.J. Forecasting Methods and Applications; John wiley & sons: Paphos, Cyprus, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, K. Hands-On Python for Finance: A Practical Guide to Implementing Financial Analysis Strategies Using Python; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2019; p. 378. [Google Scholar]
- Manigandan, P.; Alam, M.D.; Alharthi, M.; Khan, U.; Alagirisamy, K.; Pachiyappan, D.; Rehman, A. Forecasting Natural Gas Production and Consumption in United States-Evidence from SARIMA and SARIMAX Models. Energies 2021, 14, 6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierens, H.J. ARMAX model specification testing, with an application to unemployment in the Netherlands. J. Econom. 1987, 35, 161–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürre, A.; Fried, R.; Liboschik, T. Robust estimation of (partial) autocorrelation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2015, 7, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, F.L. Characterization of the partial autocorrelation function. Ann. Stat. 1974, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, E.; Påhlman, S. The Effect of Rising Interest Rates on Swedish Condominium Prices. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Independent Statistics & Analysis-U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Available online: https://www.eia.gov/international/data/world#/?pa=0000002&c=4100000002000060000000000000g000200000000000000001&tl_id=2-A&vs=INTL.2-2-AFRC-BKWH.A&vo=0&v=H&end=2016 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- Alharbi, F.R.; Csala, D. GCC countries’ renewable energy penetration and the progress of their energy sector projects. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 211986–212002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
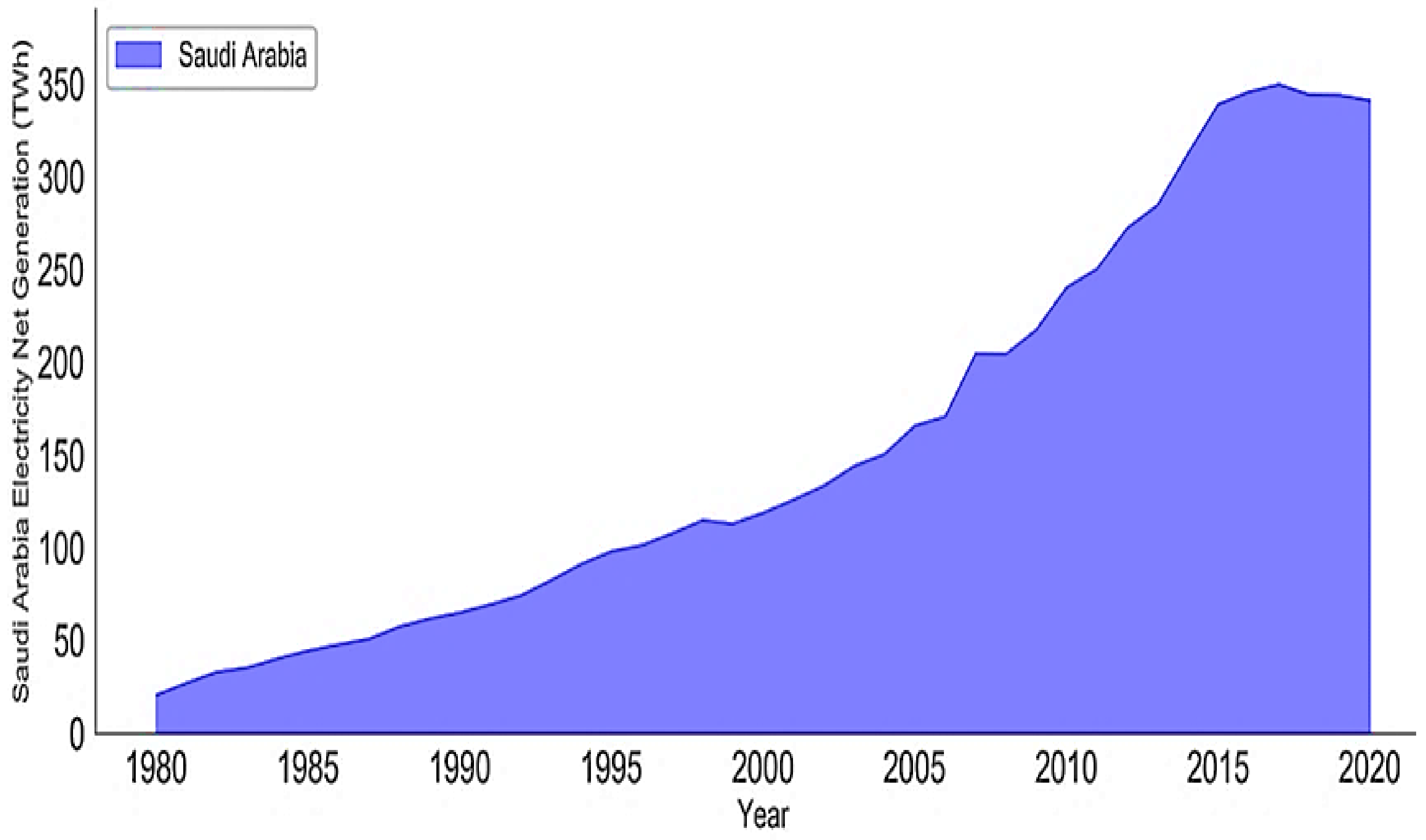

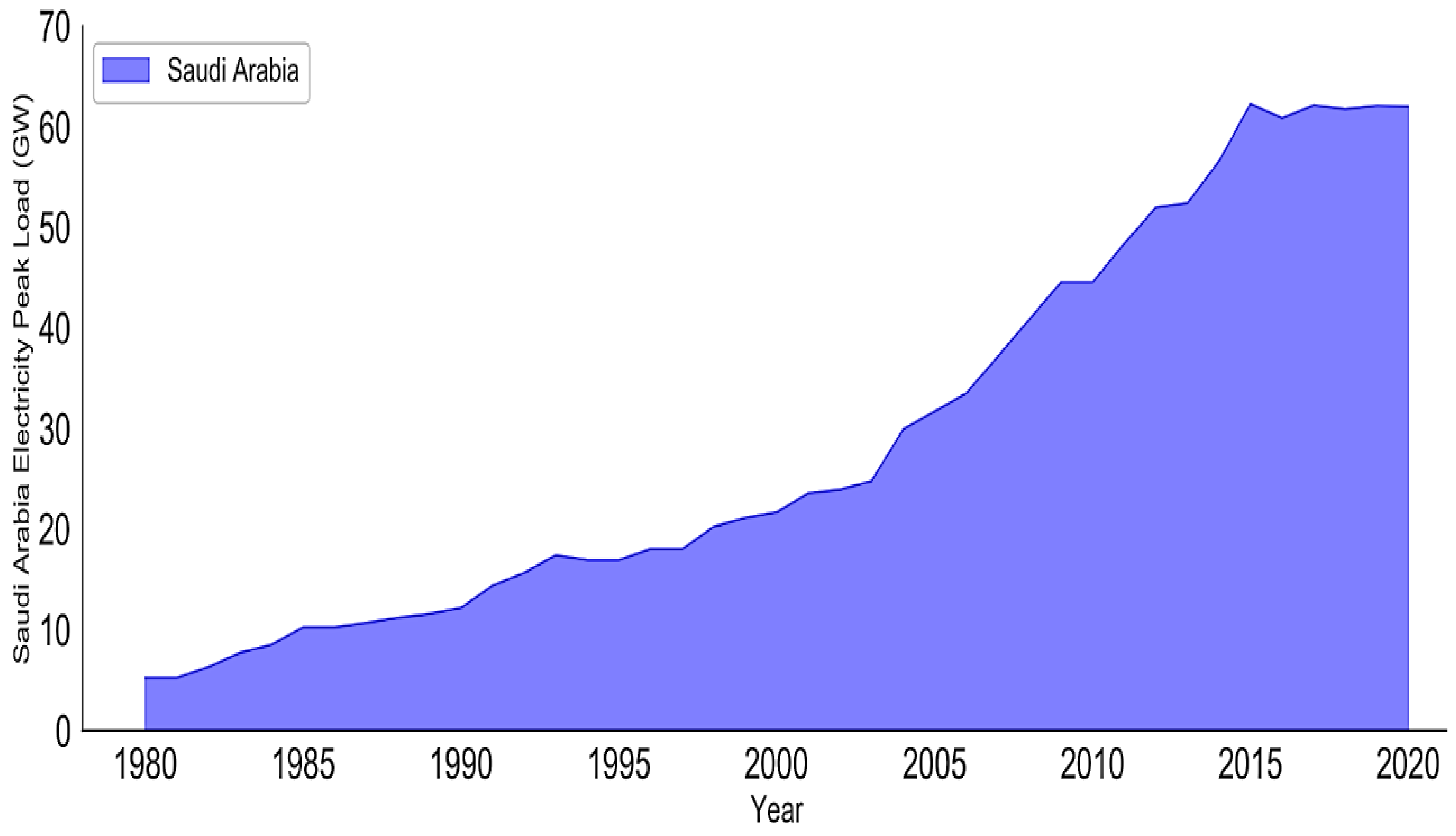
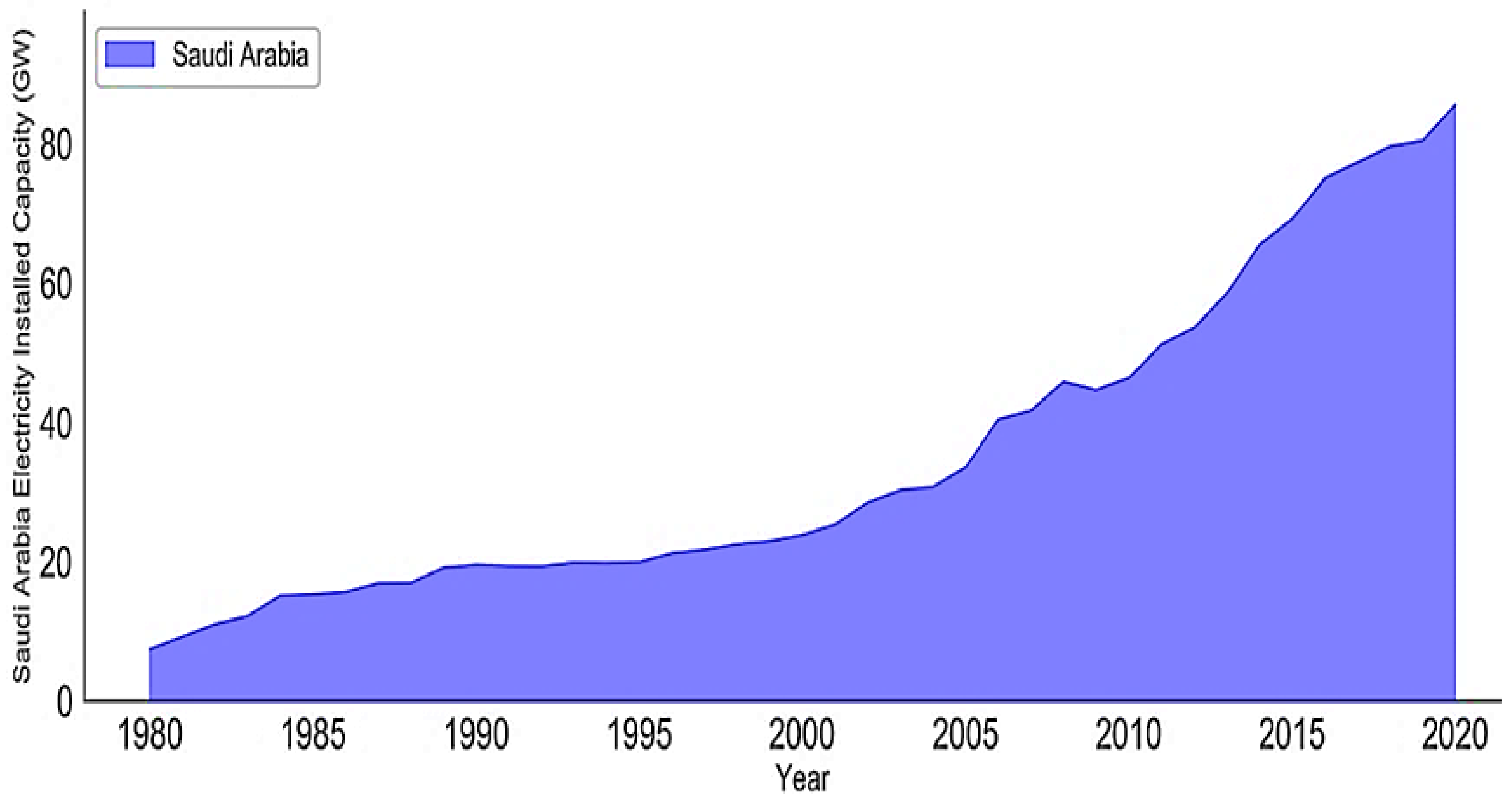

| No. | Metric | Generation (TWh) | Consumption (TWh) | Electric Peak Load (GW) | Installed Capacity (GW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RMSE | 1.2 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| 2 | MAE | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 3 | MSE | 1.5 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.07 |
| 4 | MAPE (%) | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| 5 | p-value (%) | 3 × 10−7 | 2 × 10−8 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | R2 (%) | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| No. | Forecasting Model | MAPE (%) | RMSE (GW) | MAE (GW) | MSE (GW) | R2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SARIMAX [26] | 5.42 | 4298.65 | 3614.03 | 18,478.39 | 79.60 |
| 2 | LSTM [26] | 2.98 | 3106.64 | 2027.57 | 9651.24 | 86.10 |
| 3 | ANN [26] | 4.97 | 4109.63 | 3562.24 | 16,889.12 | 81.80 |
| 4 | SVR [26] | 4.16 | 3615.72 | 3004.19 | 13,073.43 | 82.20 |
| 5 | MLR model [24] | 20.06 | 22.91 | - | - | - |
| 6 | BP model [24] | 13.50 | 16.87 | - | - | - |
| 7 | Grey model [24] | 12.11 | 14.48 | - | - | - |
| 8 | ANN model [24] | 8.65 | 10.15 | - | - | - |
| 9 | ANFIS model [24] | 6.42 | 6.89 | - | - | - |
| 10 | ARIMA model [24] | 6.29 | 3.41 | - | - | - |
| 11 | SEM-VARIMAX model [24] | 1.06 | 1.19 | - | - | - |
| 12 | SARIMAX proposed model | 0.30 | 1 | 0.60 | 1 | 99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, F.R.; Csala, D. A Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average with Exogenous Factors (SARIMAX) Forecasting Model-Based Time Series Approach. Inventions 2022, 7, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions7040094
Alharbi FR, Csala D. A Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average with Exogenous Factors (SARIMAX) Forecasting Model-Based Time Series Approach. Inventions. 2022; 7(4):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions7040094
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Fahad Radhi, and Denes Csala. 2022. "A Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average with Exogenous Factors (SARIMAX) Forecasting Model-Based Time Series Approach" Inventions 7, no. 4: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions7040094
APA StyleAlharbi, F. R., & Csala, D. (2022). A Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average with Exogenous Factors (SARIMAX) Forecasting Model-Based Time Series Approach. Inventions, 7(4), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions7040094







