Abstract
The measurement of multiple behavior endpoints in zebrafish can provide informative clues within neurobehavioral field. However, multiple behavior evaluations usually require complicated and costly instrumental settings. Here, we reported a versatile setting that applied ten acrylic tanks arranging into five vertical layers and two horizontal columns to perform multiple behavior assays simultaneously, such as the novel tank diving test, mirror-biting test, social interaction, shoaling, and predator escape assay. In total, ten behavioral performance were collected in a single video, and the XY coordination of fish locomotion can be tracked by using open source software of idTracker and ImageJ. We validated our setting by examining zebrafish behavioral changes after exposure to low dose ethanol (EtOH) for 96 h. Fish were observed staying longer time at bottom of the tank, less mirror biting interest, higher freezing time, less fear in predator test, and tight shoaling behaviors which indicated the anxiogenic effect was induced by low dosage exposure of EtOH in zebrafish. In conclusion, the setting in this study provided a simple, versatile and cost-effective way to assess multiple behavioral endpoints in zebrafish with high reliability and reproducibility for the first time.
1. Introduction
Over the past decades, the application of zebrafish (Danio rerio) as an alternative research animal model for biomedical studies has increased exponentially [1,2,3,4,5]. Being a diploid vertebrate, the genetic constituency of zebrafish resembles to the human genome [6,7,8]. The brain morphology and neurochemistry display also gives an impetus to adopt zebrafish in various mammalian genetic research and pharmacological studies [9]. Furthermore, the use of zebrafish provide a reliable platform for the genotoxicity assessment of chemicals in the field of ecotoxicology [10,11,12]. As they require lower maintenance compared to rodents, zebrafish are considered a useful species that are easy to maintain in large populations to for the study of neurobehavioral and neurodegenerative disorders [13]. Therefore, the zebrafish is an ideal animal model to produce high-throughput screens for behavioral studies in laboratory research.
In addition, the genetic manipulation, pharmacological assessment, and behavioral end-points of zebrafish can be conducted with a simple, cost effective, and robust method [13,14,15]. Based on the phylogenetic approach, the evolutionary pathway of teleost fish suggested that zebrafish and other mammals share a remarkable similarity in their physiological and neuroanatomical aspects. The “ancient design” of the organism soon unfolded the core mechanisms of fundamental features that was not able to access before [16]. As a relatively simple vertebrate species, zebrafish possess all the “classical” vertebrate neurotransmitters, a well-developed neuroendocrine system, and a wide spectrum of behavioral phenotypes that provide robust physiological responses to stress [5,17].
Zebrafish behavior can be defined as the coordination of the internal responses to outside stimulus. According to previous studies on zebrafish behavioral, the responses appeared to be evolutionarily conserved and corresponded to other species [9]. However, conventional data assessment that relied on manual observation was time-consuming, energy-draining, and prone to subjective variation and human errors. Therefore, a set of sophisticated video-tracking tools and data analyzing softwares were developed to incorporate high-throughput screenings of both adult and larval zebrafish locomotions [18,19,20]. For example, observation that an adult zebrafish was capable of exhibiting complex behaviors such as having strong social interaction with others, effective learning abilities, and portraying distinctive reactions to different environmental stimuli [19]. Up to now, the behavioral terminology of zebrafish was still under represented, compared to other animal models that have been comprehensively evaluated and defined in neurophysiological research [13]. A universal and standardized methodology will greatly improve zebrafish behavioral interpretation and reduce inconsistency [14]. Thus, there is a urgent need to implement the current process of zebrafish behavioral assessment, and an appropriate phenotypical method is required to produce large scale behavioral analysis in a short time [20].
There are several simple paradigms that have been developed to assess the zebrafish behaviors. Currently, a novel tank diving test, a social interaction task, a shoaling test, an aggression test, and a predator avoidance test were applied [20]. The novel tank diving test was designed to analyze the instinctual habituation of zebrafish to seek protection in an unfamiliar environment by diving and dwelling at the bottom of the tank [5]. The reaction to sink and remain close to the base of the tank can be referred as thigmotaxis, or in other words, “wall-hugging”, which was similar to the “open-field” test to study the anxiety in rodents [21]. Other behavioral paradigms, including social interaction and shoaling tests, are also well-established fish paradigms, which were conducted to assess zebrafish sociability by observing intraspecific interactions and gender preferences. Shoaling behavior, which represents the complex interaction of animals moving together in coordinated movements, is comparably common in fish models. Generally, zebrafish often swim in shoals under stressful situations, as well as for predator avoidance [22,23]. Interestingly, the shoaling behavior adapted by the zebrafish was not observed in other well-characterized model organisms, such as mice, rats, Drosophila, or even nematodes [24].
By their nature, the encounter of a solitary zebrafish with another individual of the same gender often results in aggressive behavior instead of social cohesion. The mirror-biting test demonstrates the response of a solitary zebrafish to its mirror image. Among the hallmarks of an aggressive display are erected dorsal, caudal, pectoral, and anal fins, and the butting and biting of the mirror [22]. However, the behavior can sometimes be misinterpreted where the subject may attempt to approach and interact with the fish [25]. One of the tests studies the antipredator behavior of the zebrafish in presence of heterospecies [26]. This examination has been rarely studied in zebrafish, thus, little is known of its fear reactions through the experiment [27]. Previous research suggested the potential of the zebrafish as a good model organism to study the correlation between genetic predisposition and antipredator response [2]. Hopefully, our findings will be able to shed light on the relationship between genetic factor and anxiety related abnormalities at the clinical level.
To date, most of zebrafish behavioral tests were carried out with different settings to obtain several different zebrafish behavioral endpoints. Not only does it require expensive video tapping devices and a licensed software to track the movements, some tests involve complicated programing scripts to function and analyze the data. Despite the advantages of zebrafish being a study model, zebrafish behavioral data are highly variable, even when collected under the same conditions [3]. This limitation can be overcome by producing a high number of samples. Unfortunately, most zebrafish behavior test settings were unable to produce large-scale data [5,18,22,28,29,30]. In this study, an open source software, idTracker, functions to collect motion trajectories by feature matching all crossing frames of objects based on appearance analysis [31]. It can perform 2D [31] or 3D [32] tracking in zebrafish as described before. The goal of our study is to establish a one-step setting to measure multiple zebrafish behavior endpoints simultaneously. In order to evaluate our model, we also treated zebrafish with 0.1% ethanol (EtOH) acutely for 4 days [33] and observed behavior changes using all of the behavior tests. Ethanol was used because it is one of the most prevalent recreational drugs and has been associated with many diseases of the brain and hazardous behavior. At the behavioral level, the presence of ethanol impairs motor coordination, sensory perception, and cognition, as well as being anxiolytic and inducing sedation and hypothermia [34]. Ultimately, we aim to adapt this methodology as the primary approach in large scale drug screening operations in the future.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
Zebrafish of wild type AB strain from Chung Yuan Christian University were applied in this study. All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines issued by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUCs) of Chung Yuan Christian University (application number: CYCU106025, issue date 6 May 2018). Adult zebrafish (~6 months old) with the same batch of fertilization were used in this study. Maintenance and routine culture for the zebrafish were based on the method described before [35].
2.2. Ethanol Treatment
Zebrafish were acutely exposed with 0.1% ethanol for ~96 h and tested the exposed fish in all of the behavior tests to observe their behavioral changes. During acute treatment, the holding tank water was replaced with the appropriate alcohol solution twice a day. No increased mortality or morbidity was observed in our alcohol-exposed fish.
2.3. Video-Tracking and Data Analysis
All video data were processed by computer with Intel i7-5820K core @ 3.3 GHz and 64 GB RAM memory. An open source software, idTracker (http://www.idtracker.es/), was used to collect and convert the fish movement data to trajectories as described [31,32]. Movement tracking were quantified separately for each tank. Based on the trajectories, the data interpretation and definitions that corresponds to the behavioral endpoints were listed in Table 1. All tests were conducted through Mann–Whitney U test, which was pairwise non-parametric analysis that applied as the comparison of fish behaviors and does not require the assumption of normal distribution [36]. Statistical tests were performed using GraphPad Prism (https://www.graphpad.com/), a scientific graphing and statistics software.

Table 1.
Summary of behavior endpoints that can be measured by using zebrafish tower.
3. Results
Behavioral testing was performed between 11:00 and 16:00 at room temperature. The zebrafish tower arrangement was shown in Figure 1A. Each tank was a trapezoid: 22 cm along the bottom, 28 cm at the top, 15.2 cm high, and 15.9 cm along the diagonal side. It was 6.4 cm wide at the top and tapered to 5.1 cm at the bottom. The novel tank diving test, aggression test, predator avoidance test, social interaction test, and shoaling test can be conducted in this tower setting (Figure 1B). All videos for each test were captured by Canon EOS 600D camera with a long-range zoom lens. The zoom lens (EF-S 55–250 mm, Canon, Oita, Japan) was placed at ~5 m in front of the zebrafish tower, following our previous published protocol [32]. The resolution of the video was 1280 × 720 pixels, with a frame rate of 50 fps (frame per second) recorded in black-and-white mode. In order to avoid background light disturbances (e.g., shadow), a LED light plate (60 cm width and 90 cm height, purchased from ZGene Biotech Inc., Taipei, Taiwan) with 265 lux intensity was placed as a background light source to the tower (Figure 1A), to generate a high contrast video and ensure optimal recording.
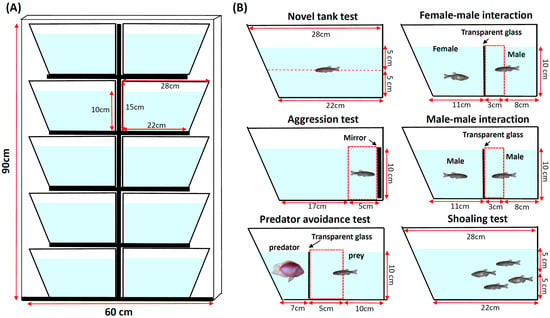
Figure 1.
(A) The schematic picture for zebrafish tower setup. (B) The experimental setting of zebrafish tower for multiple behavior endpoints tests (Upper left corner: novel tank test, center left corner: aggression test, bottom left corner: predator avoidance test, upper right corner: female-male interaction, center right corner: male-male interaction, bottom right corner: shoaling test).
For the novel tank diving test, untreated zebrafish (n = 30) and ethanol treated zebrafish (n = 30) were placed in the tank filled with 1.25 L water. A line was marked at the exterior of the tank, dividing the tank into two equal virtual horizontal portions (Figure 1B). The behavioral responses were recorded for 1 min at each time intervals of 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 min. From the video, the average speed, maximum and minimum speed, distance traveled, freezing, swimming, and rapid time movement percentage, time spent and distance traveled in top/bottom ratio, number of entries to the top, average entry duration, and latency to enter top of zebrafish were analyzed through idTracker and later were calculated by Microsoft Excel 365 software (version 1803 build 9126.2295). In the novel tank test, 5 min of acclimation for untreated wild type fish resulted in a significantly higher time in the top duration (p < 0.001) (Figure 2C), higher number of entries to the top (p < 0.001; p < 0.0001) (Figure 2D), higher total distance traveled in the top (p < 0.001) (Figure 2F) and a lower latency to enter the top portion of the tank (p < 0.01; p < 0.001) (Figure 2E). Furthermore, the freezing time movement ratio started to decrease significantly after 15 min acclimation (p < 0.0001) (Figure 2B). On the other hand, 30 min of acclimation did not make any significant changes in zebrafish average speed (Figure 2A). In contrast with the wild type control, acute 0.1% ethanol treated fish showed different behavior in the novel tank test. Treated fish showed higher activity in the first 1 min of novel tank exposure compared to control fish (p < 0.05) (Figure 2A). After 5 min of novel tank exposure, treated fish exhibited low locomotion activity which was indicated by lower average speed (p < 0.05; p < 0.01) (Figure 2A) and higher freezing time movement ratio (p < 0.05; p < 0.01; p < 0.0001) (Figure 2B). Furthermore, lower time in top duration, number of entries to the top, and total distance traveled in the top portion of the tank (p < 0.05; p < 0.01; p < 0.001; p < 0.0001) (Figure 2C,D,F) also indicated that 0.1% ethanol can affected the exploratory behavior of the zebrafish when they exposed to a new environment. This altered behavior also supported by higher latency of fish to enter the top portion of the tank (p < 0.05; p < 0.01; p < 0.001; p < 0.0001) (Figure 2E). The locomotion trajectories and behavioral changes for novel tank assay can be found in Figure 2M and Video S1.
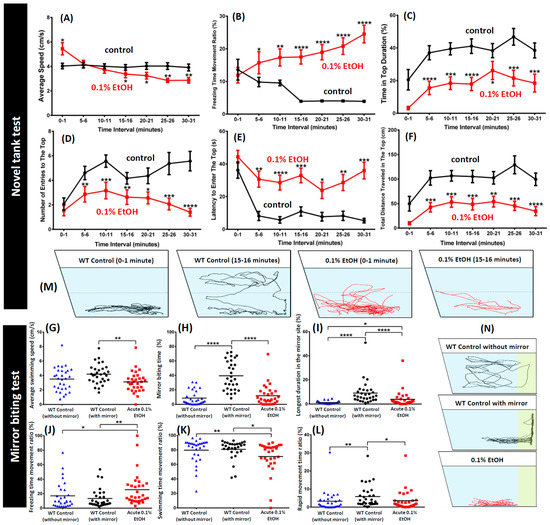
Figure 2.
Comparison of several untreated wild type (WT) and acute 0.1% ethanol treated zebrafish behavior endpoints of 30-min exposure to novel tank or 5-min exposure to the mirror-biting test. For the novel tank test, six endpoints of (A) average speed, (B) freezing time movement ratio, (C) time in bottom duration, (D) number of entries to the top, (E) latency to enter the top, and (F) total distance traveled in the top were analyzed. The data are expressed as the means ± S.E.M. and were analyzed by Mann–Whitney test (n = 30; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001). For mirror-biting tests, six endpoints of (G) average speed, (H) mirror biting time percentage, (I) longest duration in the mirror side, (J) freezing time movement ratio, (K) swimming time movement ratio, and (L) rapid movement time ratio were analyzed. The data are expressed as the means and were analyzed by Mann–Whitney test (n = 30; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001). The locomotion trajectories for novel tank and mirror biting test were summarized in (M,N), respectively.
To assess zebrafish aggressiveness, the mirror-biting test was performed. Untreated zebrafish (n = 30) and ethanol treated zebrafish (n = 30) were introduced to a tank filled with 1.25 L of water with a mirror fixed to the vertical side wall. The fish were left to acclimate to the experimental conditions for 3 min. After acclimation, zebrafish behavior was recorded for 5 min, scoring the average speed, maximum and minimum speed, distance traveled, freezing, swimming, and rapid time movement percentage, mirror biting time percentage, and longest duration in mirror side percentage. The mirror biting zone was designated at the area within 5 cm from mirror (Figure 1B). The mirror-biting test involves a slight modification of the novel tank test, the mirror image stimulation induced aggressive behavioral responses in zebrafish, which significantly affected mirror biting time percentage and longest duration in the mirror side (p < 0.0001) (Figure 2H,I). It was also found increasing rapid movement time ratio (p < 0.01) (Figure 2L), but not for average speed, freezing time movement ratio, and swimming time movement ratio (Figure 2G,J,K). On the other hand, acute 0.1% ethanol treated fish exhibited different behavior in this mirror-biting test. Ethanol, even in low concentration already could reduce fish aggressiveness, which was shown by lower mirror biting time percentage and longest duration in the mirror side percentage (p < 0.0001) (Figure 2H,I). In addition, low locomotion activity affected by ethanol exposure was also shown in this test by lower average speed, swimming movement time ratio, and rapid movement time ratio, and higher freezing time movement ratio (p < 0.05; p < 0.01; p < 0.0001) (Figure 2G,J–L) compared to the wild type control. The locomotion trajectories and behavioral changes for mirror biting assay can be found in Figure 2N and Video S2.
The predator avoidance test was demonstrated in the tank filled with 1.25 L water with a transparent glass separator that was fixed at 15 cm away from the vertical side wall and was left for fish to acclimate to the experimental conditions for 5 min. After untreated fish (n = 30) and ethanol treated zebrafish (n = 30) acclimated, the predator (Convict cichlid Amatitlania nigrofasciata, validated by 16S rRNA barcoding, 5–7 cm body length) was introduced into another side of separator and zebrafish behavior was recorded for 5 min. The predator approaching zone was defined as the area within 5 cm away from separator. The fear response was assessed through the measurement of average speed, maximum and minimum speed, distance traveled, freezing, swimming, and rapid time movement percentage, top/bottom ratio of time spent and traveling distance, predator approaching time percentage, and distance to predator separator in average (Figure 1B). As seen in Figure 3, the fear response behaviors of the zebrafish were exhibited when predator fish was placed into the experiment tank. This finding is further supported by differences seen in some antipredator-related behavioral endpoints. The average speed of untreated wild type zebrafish in the predator condition was significantly lower in the normal condition without predator (p < 0.05) (Figure 3A). Furthermore, predator approaching time and swimming time movement ratio were even lower (p < 0.0001) (Figure 3B,E), while average distance to separator and freezing time movement ratio were significantly higher in the normal condition (p < 0.0001) (Figure 3C,D). On the other hand, there was no significant difference in the rapid movement time ratio for both conditions (Figure 3F). Meanwhile, ethanol treated fish showed less predator avoidance behavior. This phenomenon was indicated by less predator approaching time and the average distance to separator (p < 0.05; p < 0.01) (Figure 3B,C) compared to the wild type when they encountered the same predator. Furthermore, lower locomotion activity compared to the control fish was also exhibited by the ethanol treated fish, which was shown by lower average speed, swimming time movement ratio, and rapid movement ratio even though not all of them were significant (p < 0.05) (Figure 3A,E,F). Low locomotion activity in the treated fish also supported by high freezing time movement ratio (p < 0.05) (Figure 3D). The locomotion trajectories and behavioral changes for predator avoidance can be found in Figure 3K and Video S3.
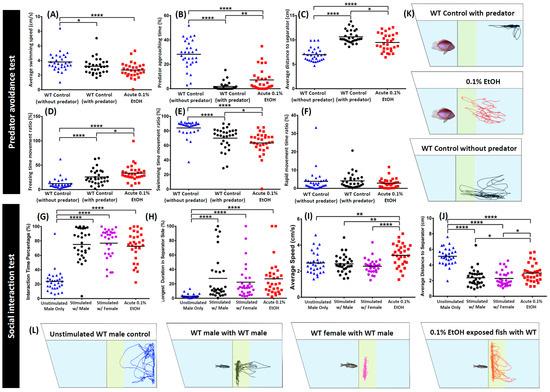
Figure 3.
Comparison of several wild type (WT) zebrafish behavior endpoints before and after predator exposure and after 0.1% ethanol treatment in zebrafish predator test or social interaction test. For predator avoidance test, six endpoints of (A) average speed, (B) predator approaching time percentage, (C) average distance to separator, (D) freezing time movement ratio, (E) swimming time movement ratio, and (F) rapid movement time ratio were analyzed. The data are expressed as the means and were analyzed by Mann–Whitney test (n = 30; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001). For social interaction assay, four endpoints of (G) average speed, (H) interaction time percentage, (I) longest duration in separator side, (J) average distance to separator were analyzed. The data are expressed as the means and were analyzed by Mann–Whitney test (n = 30; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001). The locomotion trajectories for predator avoidance and social interaction were summarized in (K,L), respectively.
For the social interaction test, a solitary untreated male zebrafish (n = 30) and ethanol treated zebrafish (n = 30) were placed in the tank filled with 1.25 L of water with a transparent glass separator fixed at 11 cm away from the vertical side wall and was left for fish to acclimate to the experimental conditions for 5 min. Either male or female zebrafish for male–male or female–male interaction was placed into the other side of the separator, respectively for untreated male zebrafish. Meanwhile, for ethanol treated zebrafish, another male or female wild type zebrafish was placed into the other side of the separator. Zebrafish behavior was recorded for 5 min after acclimation. The zebrafish interaction zone was designated within 3 cm from separator. Average speed, maximum and minimum speed, distance traveled, freezing, swimming, and rapid time movement percentage, interaction time percentage, longest duration in separator side percentage, and average distance to separator were analyzed (Figure 1B). In current social interaction test, we assessed the ability of zebrafish to interact with conspecifics. Conspecifics stimulation in this test affected the preference of the untreated wild type fish. The untreated wild type fish generally preferred to spend more time closer to a conspecific fish: over 70% of the time. It was shown by the increment of interaction time percentage and longest duration in separator (p < 0.0001) (Figure 3H,I) for both male and female. Average distance to separator was also found to be significantly decreased when conspecific fish was placed in the experimental tank (p < 0.0001) (Figure 3J). Meanwhile, there was no significant difference in the average speed endpoint between the unstimulated fish and conspecifics stimulated fish (Figure 3G). While ethanol could affect zebrafish behavior in the other behavior tests which were conducted in this experiment, low concentration of ethanol treated fish appeared to have similar social interaction behavior with the control fish in this test. This was proved by the same level of interaction time percentage and longest duration in the separator side within the control and ethanol treated fish (Figure 3G,H). Surprisingly, higher locomotion activity than the control fish was shown in the ethanol treated fish which was indicated by a higher average speed and average distance to separator (p < 0.05; p < 0.01; p < 0.0001) (Figure 3I,J). The locomotion trajectories and behavioral changes for social interaction can be found in Figure 3L and Video S4.
The shoaling test was conducted in the tank filled with 1.25 L of water. In this experiment, 4 groups of untreated wild type zebrafish, differing in sample size (from 2 to 5 number of fish) were placed for 5 min in the test tank for acclimation. In the meantime, groups of 3 zebrafish were applied for ethanol treated zebrafish. After fish acclimated to the experimental conditions, their behavior was recorded for 5 min. The shoaling behavior was assessed through average speed, maximum and minimum speed, distance traveled, freezing, swimming and rapid movement percentage, time in top percentage, average inter-fish distance, average shoal area, average distance to center of the tank, and average nearest and farthest neighbor distance (Figure 1B). In the shoaling test, the anxiety level was significantly lower compared to only one fish in the control group when zebrafish was placed in groups of 2 to 5 fish. In other words, groups of zebrafish exposure significantly decreased anxiety level in all of shoaling test endpoints (Figure 4). As seen in Figure 4B, zebrafish in groups of 2, 3, and 4 spent longer duration at the top of the tank, which indicated less anxiety (p < 0.05). In fact, zebrafish in groups of five spent the longest time at the top among groups (p < 0.0001). Interestingly, the average swimming speed decreased the more zebrafish there were in a group, suggesting an overall lower anxiety level (p < 0.05) (Figure 4A). There were also significant differences in average inter-fish distance between fish in groups of 2, 3, 4, and 5 (p < 0.01; p < 0.001; p < 0.0001) (Figure 4D); however, fish in groups of 3 and 5 shoal exhibited a lower average distance to center of the tank compared to other groups (p < 0.01) (Figure 4C). The 5-fish shoal displayed farthest neighbor distance (Figure 4E) and large average shoal area (Figure 4F) compared to the other groups (p < 0.0001). On the contrary, when zebrafish were treated with 0.1% ethanol, they formed very tight shoals in groups of 3 fish. This kind of shoal can be indicated by shorter average inter-fish distance, average farthest neighbor distance, and narrower average shoal area (p < 0.01; p < 0.0001) (Figure 4J–L) compared to the control fish. Besides its effect on the shoaling behavior, ethanol also altered the exploratory behavior of the shoal, shown by the low time spent in top duration and average distance to the center of the tank (p < 0.0001) (Figure 4H,I). In addition, the decrement of the average speed in ethanol treated fish also represented less locomotion activity in those fish (p < 0.0001) (Figure 4G). The locomotion trajectories and behavioral changes for shoaling assay can be found in Figure 4M and Video S5.
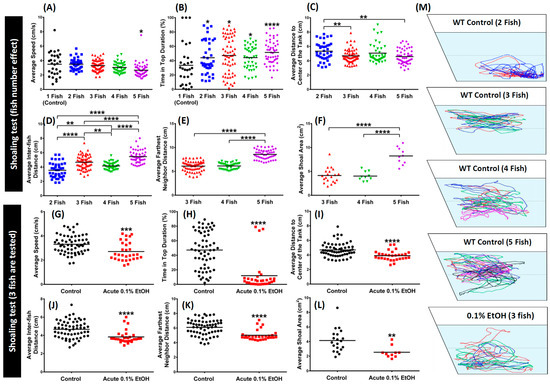
Figure 4.
Comparison of zebrafish shoaling behavior affected by different shoal sizes or 0.1% ethanol exposure. For shoal size comparison, six endpoints of (A) average speed, (B) time in top duration, (C) average distance to center of the tank, (D) average inter-fish distance, (E) average farthest neighbor distance, (F) average shoal area were analyzed. The data are expressed as the means and were analyzed by Mann-Whitney test (n 1 Fish = 30; n 2 Fish = 40; n 3 Fish = 60; n 3 Fish = 40; n 5 Fish = 50; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01****, p < 0.0001). For 0.1% ethanol exposure (shoaling size = 3), six endpoints of (G) average speed, (H) time in top duration, (I) average distance to center of the tank, (J) average inter-fish distance, (K) average farthest neighbor distance, (L) average shoal area were analyzed. The data are expressed as the means and were analyzed by Mann-Whitney test (n = 30; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001). The locomotion trajectories for shoaling were summarized in (M).
4. Discussion
In this study, we established a novel and versatile setup to assess multiple behavior endpoints simultaneously in zebrafish by using five different behavior tests: the novel tank diving test, mirror-biting test, predator test, social interaction, and shoaling test. The zebrafish exhibited different behavioral responses to the five tests conditions and their trajectory changes can be tracked by using an open source video-tracking software, idTracker. All of the behavior endpoints can be measured by using this novel zebrafish tower are listed in Table 1.
The novel tank test is based on natural instinct within animal seeking protection in a new environment by freezing, diving, and reducing exploration. As the fish gradually acclimates to the novel environment, an increase in exploration mostly occurs [18]. In the novel tank test presented in this study, response was observed and quantified through recording camera, and the phenotypic measurements were done by computerized video tracking. Significant changes, such as increased time spent at the top, increased number of entries to the top, increased total distance traveled to the top, and decreased latency to enter the top, were already displayed within the first 5 min of acclimation. Interestingly, longer acclimation time (~15 min) was required to restore freezing time movement ratio. Despite a small decrease of freezing time movement ratio within the first 5 min, it showed that zebrafish locomotor was strongly affected by an exposure to a new environment. On the other hand, the average speed for zebrafish showed no significant change within 30 min which represents undistributed zebrafish movement types (freezing movement, swimming movement, and rapid movement) before 15 min acclimation. Generally, these results were consistent with previous findings, in which the fish responded to anxiety by diving deeper into the tank in a novel environment. Therefore, the reactions demonstrated the natural instinct of a fish to seek protection in an unfamiliar habitat by lingering close to the base/wall, freezing, and reduced exploration. After 15 min acclimation, the fish increased its exploration behavior and became familiarized with the surroundings. On the contrary to the untreated wild type zebrafish behaviors, acute exposure of 0.1% ethanol was found to give significant anxiogenic-like effects to zebrafish behavior when they were exposed to new environment. As has been widely reported, ethanol induced significant dose-dependent locomotor hypoactivity or hyperactivity in zebrafish [37]. In another behavior study done by Lockwood et al. (2004) [36], they showed that larval zebrafish exhibited chronic sensitivity to ethanol in a dose- and time-dependent manner. They initially become hyperactive, and as ethanol accumulates, they become hypoactive and sedated, which is similar to what has been observed in humans and other animal models [38]. In this study, the lack of overt behavioral responses caused by ethanol accumulation were shown by significantly low locomotion activity and reduced exploratory behavior, suggesting higher level of stress and anxiety in ethanol treated fish. In agreement with earlier reports on the behavioral effects of ethanol withdrawal, our results demonstrate the ability of psychoactive drug to elicit withdrawal-related phenotypes in zebrafish [39]. When compared to the open-field test in rodent, the novel tank test in zebrafish proved that it can also be considered as an animal model to study anxiety [5,18].
Aggression has been studied in other fish species including Siamese fighting fish (Betta splendens) and family Cichlidae, yet, these species do not have the effective genetic development that is in zebrafish. Hence, characterization of the zebrafish and development of appropriate quantification techniques to measure its behavior associated to aggression are very important [40]. In the mirror-biting test, most of the zebrafish showed aggressive behavior during the first ten minutes. An increase in mirror biting time percentage as well as longer duration spent near mirror was observed. This suggested that the zebrafish may perceived their own mirror image as themselves, and fish that displayed reduced aggression phenomenon was considered having lack of social behavior and may have neurological disorder [41]. However, the zebrafish locomotor activity was not affected by the mirror stimulation. No significant difference was observed for the average speed, freezing time movement ratio, and swimming movement time ratio. Nevertheless, there was a slight increase in rapid movement time ratio of zebrafish in tanks with mirror, which suggested that zebrafish that failed to obtain any physical contact may trigger aggressiveness through the rapid movement towards the mirror image (Figure 3F). In zebrafish, agonistic behavior can be modified by exposure to pharmacological compounds including ethanol. In this study, exposure of low concentration of EtOH decreased aggression of the fish. Reduced mirror biting time and longest duration in the mirror side indicated that the EtOH treated fish loss their aggression. This result is in line with previous report on the aggressive behavioral effects of ethanol by Norton et al. (2010) and Pham et al. (2012). After ethanol exposure, the fish aggression will be inhibited at a chronic exposure or high sedative dose [22,42].
Laboratory studies have shown that zebrafish exhibits fright reactions in response to both visual and olfactory cues when facing predators [43]. Zebrafish may respond to predator in a variety of ways that may be categorized as either active avoidance (panic, escape/fleeing, and erratic movements) or passive avoidance (remaining still, or moving more slowly) [44]. In this test, zebrafish were observed to move away from the living predator of convict cichlid. This phenomenon was supported with a lower predator approaching time percentage and a higher average distance from separator, which were consistent with previous findings [4]. As expected, the predator model paradigm induced fear responses when a predator was near. The fear response indeed resulted in higher average distance to separator when the predator was present. Furthermore, the presence of the predator caused a slight decrease in average speed, increased freezing time movement ratio, and decreased swimming time movement ratio. Our results were supported by previous studies that suggest zebrafish freezing or crowding reaction in response to a fear stimulus [2]. In addition, alcohol may modify this behavioral response either by altering levels of anxiety, perceptual, or motor mechanisms. In our experiment, acute 0.1% ethanol treatment caused the fish to lose their anti-predatory behavior, showed by increment of predator approaching time and decrement of average distance to separator between the predator and tested fish. In consistent with previous findings, accumulation of alcohol can impair zebrafish anti-predatory behavior, including lower jumping frequency, which is possibly as a result of the anxiolytic effect of alcohol [42,45,46,47].
Zebrafish are a highly social species and it is known to be inclined to staying near to its conspecifics both in the laboratory and by nature. A solitary zebrafish in a tank is expected to approach and stay in the proximity of a group of conspecifics upon presentation to the group [48]. In this social interaction test, different genders were introduced to determine the social preference of male zebrafish subjects. Overall, fish preferred to spend longer time with a conspecific fish regardless of its gender. A significant increase of interaction time percentage, increased time spent in separator side, and decreased average distance to separator were observed, which is consistent with previous reports stating fish tends to spend longer time with its conspecific [20,41]. This further validates that zebrafish are a highly social species that often form shoals and swim in groups. Nonetheless, the social preference of male zebrafish was not affected by different genders of the same species.
Furthermore, in both humans and in comparative animal models, exposure to moderate levels of alcohol during early brain development leads to numerous behavioral problems such as abnormal social behavior [47]. However, here, we acutely exposed adult zebrafish to a low level of ethanol, and observed no significant differences between the ethanol treated fish and control fish in their social interaction behavior. The current ethanol exposure only slightly reduced individual social behavior in this species, showed by higher average distance of the treated fish to the separator [49]. This phenomenon possibly due to low concentration of ethanol used in this experiment.
Shoaling is the formation of a relatively non-polarized groups of adult zebrafish, held together by social pressures. Like other teleost, zebrafish form shoals when placed in a novel tank, and this strategy allows fast adaptation to the new environment and represents a functional unity that ensures protection and safety [50]. The shoaling test is used to assess overall social behaviors in a group of zebrafish and reflect stress or anxiety in zebrafish. For example, a high level of anxiety/fear can cause the shoal to “tighten” (the fish swim closer together) with a smaller inter-fish distance and potentially forming a school [22]. In this test, zebrafish spent most of their time swimming in dynamic groups. One of the shoaling behaviors this experiment showed was the decreased average speed of movement in zebrafish when put in groups; this corresponds to the experiment conducted by Miller et al. [51]. Furthermore, zebrafish in groups of 3, 4, and 5 were less stressed compared to fish in groups of 2. Based on their swimming behavior, zebrafish with lower anxiety tended to swim looser in shoals with an increased inter-fish distance. This was also demonstrated by reduced average distance to center of the tank with fish in groups of 3, 4, and 5. The shoaling test is also expected to reveal potential thigmotactic behavior in zebrafish to account for their reaction to fear [52]. Another anxiety parameter is the exploratory behavior of the fish, which can be accessed by the time spent at the top of the tank. The results were consistent with previous research done by Pagnussat et al. [3] when groups of zebrafish were placed in a novel tank, the new environment become the main stress factor, however their cohesion and cooperative function as a group was preserved. Therefore, zebrafish in groups will spend longer duration at the top portion of the tank. In addition, when exposed to a new tank, single fish were more stressed than groups of fish [3]. Also, the exploratory behavior increased in both shoal area and average farthest neighbor distance. The shoaling zebrafish were more dispersed in the split depth tank and they were able to explore both shallow and deep areas [50]. On the other hand, when fish were exposed acutely with a low concentration of ethanol, they exhibited different shoaling behavior. Confirming previous results, our results showed that low dose of ethanol caused the fish to form tighten shoal [37]. This shoaling pattern was indicated by reduced nearest neighbor distance and this abnormality most likely due to the disinhibitory effect of ethanol, allowing conspecifics to approach closer than controls [22].
In the future, we believe this method also can be used to understand the modeling of zebrafish biological behavior that can be later used for simulation purposes. Based on the recorded motion data, motions of animal is possible to be accurately synthesized by involving various combinations of recorded sequences [53]. Social interaction of zebrafish studies also can contribute in the field of human behavior study since they are highly social species with a complex structure like human beings. For an example, the interaction of zebrafish becomes different when they form a shoal. This is also the case in grouped of humans when interaction becomes an essential part of the overall group behavior [54]. Furthermore, several models have been studied over the past twenty years to simulate individuals, groups, and crowds of character of human for different purposes even though little effort has been made to really understand how humans avoid colliding with each other in real-life and navigate interactions [55,56].
In this pioneer study, a robust and reliable system was established to validate the correlation of zebrafish behavioral endpoints with anxiety and fear-related phenotypes following the exposure of low concentration ethanol treated fish to a novel tank, a predator, conspecific social interactions, shoaling behavior and self-mirror image. We proposed that these behavioral endpoints can be used in future investigation for screening potential novel neurotoxic compounds. Most importantly, this setup is able to accommodate a large number of samples in a single attempt (n = 10 in each test), which make the scale-up process and high-throughput screening feasible. Although rodents have been the primary animal model to study neurobehavioral disorder, the utilization of zebrafish to analyze their social interactive behavior will be able to encourage more research in current mental issues [57,58,59].
Despite zebrafish being an ideal animal model for neuroscience research, there are still a few minor drawbacks in this study. While the experiment was performed simultaneously, the operator was required to transfer all experimental subjects into the tanks as faster as possible to standardize the acclimation period of each experiment. This may cause unpredicted disturbance to the zebrafish and provoke bias behavioral responses to anxiety. Furthermore, to process large scale data samples, a high-speed processor computer with the aid of Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) operation are recommended to boost the overall calculation speed of fish trajectories. As the operation of idTracker was conducted manually, it was time-consuming and tedious to perform on large data. Therefore, a simpler and subtle program is needed to develop in order to speed up the process in the future.
To sum up, a versatile facility was designed and reported in this study that can be used to measure multiple major behavior endpoints in adult zebrafish for the first time. Our results supported the use of zebrafish as the next leading model of research in neurological disorders and degeneration. With the aid of this new tools, we believe it will have great breakthrough for researches like phenotypic screen of genetic mutants, pharmaceutical and toxicological evaluation of interesting chemical compounds in the coming future.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2411-5134/3/4/75/s1.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Ministry of Science and Technology (grant no. MOST105-2313-B-033-001-MY3 and MOST107-2622-B-033-001-CC2) to CDH.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dooley, K.; Zon, L.I. Zebrafish: A model system for the study of human disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2000, 10, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speedie, N.; Gerlai, R. Alarm substance induced behavioral responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 188, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnussat, N.; Piato, A.L.; Schaefer, I.C.; Blank, M.; Tamborski, A.R.; Guerim, L.D.; Bonan, C.D.; Vianna, M.R.; Lara, D.R. One for all and all for one: The importance of shoaling on behavioral and stress responses in zebrafish. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R.; Lee, V.; Blaser, R. Effects of acute and chronic ethanol exposure on the behavior of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 85, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H. Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbazuk, W.B.; Korf, I.; Kadavi, C.; Heyen, J.; Tate, S.; Wun, E.; Bedell, J.A.; McPherson, J.D.; Johnson, S.L. The syntenic relationship of the zebrafish and human genomes. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Currie, P.D. Animal models of human disease: Zebrafish swim into view. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Gerlai, R. Zebrafish as an emerging model for studying complex brain disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bambino, K.; Chu, J. Zebrafish in toxicology and environmental health. Curr. Top Dev. Biol. 2017, 124, 331–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.J.; Jia, Y.F.; Chen, N.; Bian, W.P.; Li, Q.K.; Ma, Y.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Pei, D.S. Zebrafish as a model system to study toxicology. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teraoka, H.; Dong, W.; Hiraga, T. Zebrafish as a novel experimental model for developmental toxicology. Congenit. Anomal. 2003, 43, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Gebhardt, M.; Stewart, A.M.; Cachat, J.M.; Brimmer, M.; Chawla, J.S.; Craddock, C.; Kyzar, E.J.; Roth, A.; Landsman, S. Towards a comprehensive catalog of zebrafish behavior 1.0 and beyond. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, R.; Chadwick, L.; McGinnis, G. Behavioral measures of anxiety in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, R.T.; MacRae, C.A. Systematic approaches to toxicology in the zebrafish. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R. Social behavior of zebrafish: From synthetic images to biological mechanisms of shoaling. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 234, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strungaru, S.-A.; Robea, M.A.; Plavan, G.; Todirascu-Ciornea, E.; Ciobica, A.; Nicoara, M. Acute exposure to methylmercury chloride induces fast changes in swimming performance, cognitive processes and oxidative stress of zebrafish (Danio rerio) as reference model for fish community. J. Trace Element. Med. Biol. 2018, 47, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachat, J.; Stewart, A.; Grossman, L.; Gaikwad, S.; Kadri, F.; Chung, K.M.; Wu, N.; Wong, K.; Roy, S.; Suciu, C. Measuring behavioral and endocrine responses to novelty stress in adult zebrafish. Nature Protoc. 2010, 5, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachat, J.; Stewart, A.; Utterback, E.; Hart, P.; Gaikwad, S.; Wong, K.; Kyzar, E.; Wu, N.; Kalueff, A.V. Three-dimensional neurophenotyping of adult zebrafish behavior. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, R.; Gerlai, R. Behavioral phenotyping in zebrafish: Comparison of three behavioral quantification methods. Behav. Res. Methods 2006, 38, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bencan, Z.; Sledge, D.; Levin, E.D. Buspirone, chlordiazepoxide and diazepam effects in a zebrafish model of anxiety. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 94, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, M.; Raymond, J.; Hester, J.; Kyzar, E.; Gaikwad, S.; Bruce, I.; Fryar, C.; Chanin, S.; Enriquez, J.; Bagawandoss, S. Assessing social behavior phenotypes in adult zebrafish: Shoaling, social preference, and mirror biting tests. In Zebrafish Protocols for Neurobehavioral Research; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 231–246. [Google Scholar]
- Engeszer, R.E.; da Barbiano, L.A.; Ryan, M.J.; Parichy, D.M. Timing and plasticity of shoaling behaviour in the zebrafish, danio rerio. Anim. Behav. 2007, 74, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saverino, C.; Gerlai, R. The social zebrafish: Behavioral responses to conspecific, heterospecific, and computer animated fish. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 191, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretz, J.A.; Martins, E.P.; Robison, B.D. The effects of early and adult social environment on zebrafish (Danio rerio) behavior. Environ.Biol. Fishes 2007, 80, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R.; Fernandes, Y.; Pereira, T. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) responds to the animated image of a predator: Towards the development of an automated aversive task. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 201, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, S.L.; Gerlai, R. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) responds differentially to stimulus fish: The effects of sympatric and allopatric predators and harmless fish. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 186, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachat, J.; Kyzar, E.J.; Collins, C.; Gaikwad, S.; Green, J.; Roth, A.; El-Ounsi, M.; Davis, A.; Pham, M.; Landsman, S. Unique and potent effects of acute ibogaine on zebrafish: The developing utility of novel aquatic models for hallucinogenic drug research. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 236, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toms, C.N.; Echevarria, D.J. Back to basics: Searching for a comprehensive framework for exploring individual differences in zebrafish (Danio rerio) behavior. Zebrafish 2014, 11, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puttonen, H.A.; Sundvik, M.; Rozov, S.; Chen, Y.-C.; Panula, P. Acute ethanol treatment upregulates th1, th2, and hdc in larval zebrafish in stable networks. Front. Neural Circ. 2013, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Escudero, A.; Vicente-Page, J.; Hinz, R.C.; Arganda, S.; De Polavieja, G.G. Idtracker: Tracking individuals in a group by automatic identification of unmarked animals. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audira, G.; Sampurna, B.P.; Juniardi, S.; Liang, S.-T.; Lai, Y.-H.; Hsiao, C.-D. A simple setup to perform 3D locomotion tracking in zebrafish by using a single camera. Inventions 2018, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Champagne, D.L.; Alia, A.; Richardson, M.K. Large-scale analysis of acute ethanol exposure in zebrafish development: A critical time window and resilience. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlugos, C.A.; Rabin, R.A. Ethanol effects on three strains of zebrafish: Model system for genetic investigations. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 74, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdesh, A.; Chen, M.; Martin-Iverson, M.T.; Mondal, A.; Ong, D.; Rainey-Smith, S.; Taddei, K.; Lardelli, M.; Groth, D.M.; Verdile, G. Regular care and maintenance of a zebrafish (Danio rerio) laboratory: An introduction. J. Visual. Exp. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.C.; Anthony, C.D. Using randomization techniques to analyse behavioural data. Anim. Behav. 1996, 51, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, R.; Penalosa, Y. Stimuli affecting zebrafish (Danio rerio) behavior in the light/dark preference test. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockwood, B.; Bjerke, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Guo, S. Acute effects of alcohol on larval zebrafish: A genetic system for large-scale screening. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 77, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachat, J.; Canavello, P.; Elegante, M.; Bartels, B.; Hart, P.; Bergner, C.; Egan, R.; Duncan, A.; Tien, D.; Chung, A. Modeling withdrawal syndrome in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R. Zebra fish: An uncharted behavior genetic model. Behav. Genet. 2003, 33, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.M.; Nguyen, M.; Wong, K.; Poudel, M.K.; Kalueff, A.V. Developing zebrafish models of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Progr. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 50, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, W.; Bally-Cuif, L. Adult zebrafish as a model organism for behavioural genetics. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, R.; Gerlach, G.; Lawrence, C.; Smith, C. The behaviour and ecology of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Biol. Rev. 2008, 83, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seguin, D.; Shams, S.; Gerlai, R. Behavioral responses to novelty or to a predator stimulus are not altered in adult zebrafish by early embryonic alcohol exposure. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 2667–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R.; Lahav, M.; Guo, S.; Rosenthal, A. Drinks like a fish: Zebra fish (Danio rerio) as a behavior genetic model to study alcohol effects. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 67, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S. Linking genes to brain, behavior and neurological diseases: What can we learn from zebrafish? Genes, Brain Behav. 2004, 3, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, Y.; Gerlai, R. Long-term behavioral changes in response to early developmental exposure to ethanol in zebrafish. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pather, S.; Gerlai, R. Shuttle box learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 196, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, M.O.; Annan, L.V.; Kanellopoulos, A.H.; Brock, A.J.; Combe, F.J.; Baiamonte, M.; Teh, M.-T.; Brennan, C.H. The utility of zebrafish to study the mechanisms by which ethanol affects social behavior and anxiety during early brain development. Progr. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidel, A.J.; Assmann, K.L.; Werlang, C.C.; Bertoncello, K.T.; Francescon, F.; Rambo, C.L.; Beltrame, G.M.; Calegari, D.; Batista, C.B.; Blaser, R.E. Subchronic atrazine exposure changes defensive behaviour profile and disrupts brain acetylcholinesterase activity of zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2014, 44, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, N.; Gerlai, R. Quantification of shoaling behaviour in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 184, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buske, C.; Gerlai, R. Early embryonic ethanol exposure impairs shoaling and the dopaminergic and serotoninergic systems in adult zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousas, C.; Newbury, P.; Anagnostopoulos, C.-N. Measuring the Steps: Generating Action Transitions between Locomotion Behaviours. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Computer Games: AI, Animation, Mobile, Interactive Multimedia, Educational & Serious Games (CGAMES), Louisville, KT, USA, 30 July–1 August 2013; pp. 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Durupınar, F. From Audiences to Mobs: Crowd Simulation with Psychological Factors. Ph.D. Thesis, Bilkent University, Çankaya, Üniversiteler, Turkey, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Van Basten, B.J.; Jansen, S.E.; Karamouzas, I. Exploiting motion capture to enhance avoidance behaviour in games. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Motion in Games, Zeist, The Netherlands, 21–24 November 2009; pp. 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, A.; Musse, S.R.; de Oliveira, L.P.L.; Bodmann, B.E. Modeling individual behaviors in crowd simulation. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computer Animation and Social Agents, New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 7–9 May 2003; pp. 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, S.P.; Dunnett, S.B. Tests to assess motor phenotype in mice: A user’s guide. Nat. Rev. Neuroscience 2009, 10, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabeshima, T.; Kim, H.-C. Involvement of genetic and environmental factors in the onset of depression. Experim. Neurobiol. 2013, 22, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigman, J.L.; Graybeal, C.; Holmes, A. Predictably irrational: Assaying cognitive inflexibility in mouse models of schizophrenia. Front. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).