Mechatronic and Robotic Systems Utilizing Pneumatic Artificial Muscles as Actuators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Robotic Systems
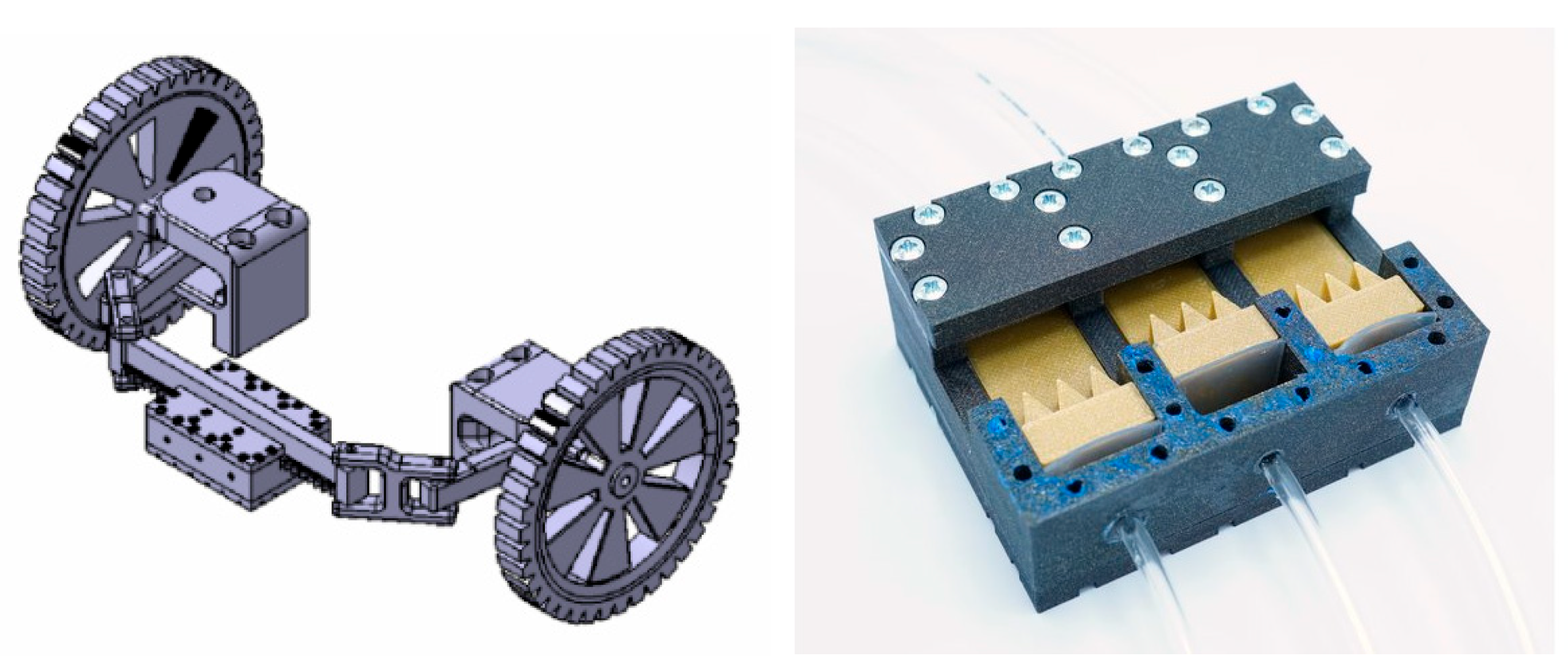
2.1.1. Four-Legged Walking Robot Actuated by PAMs
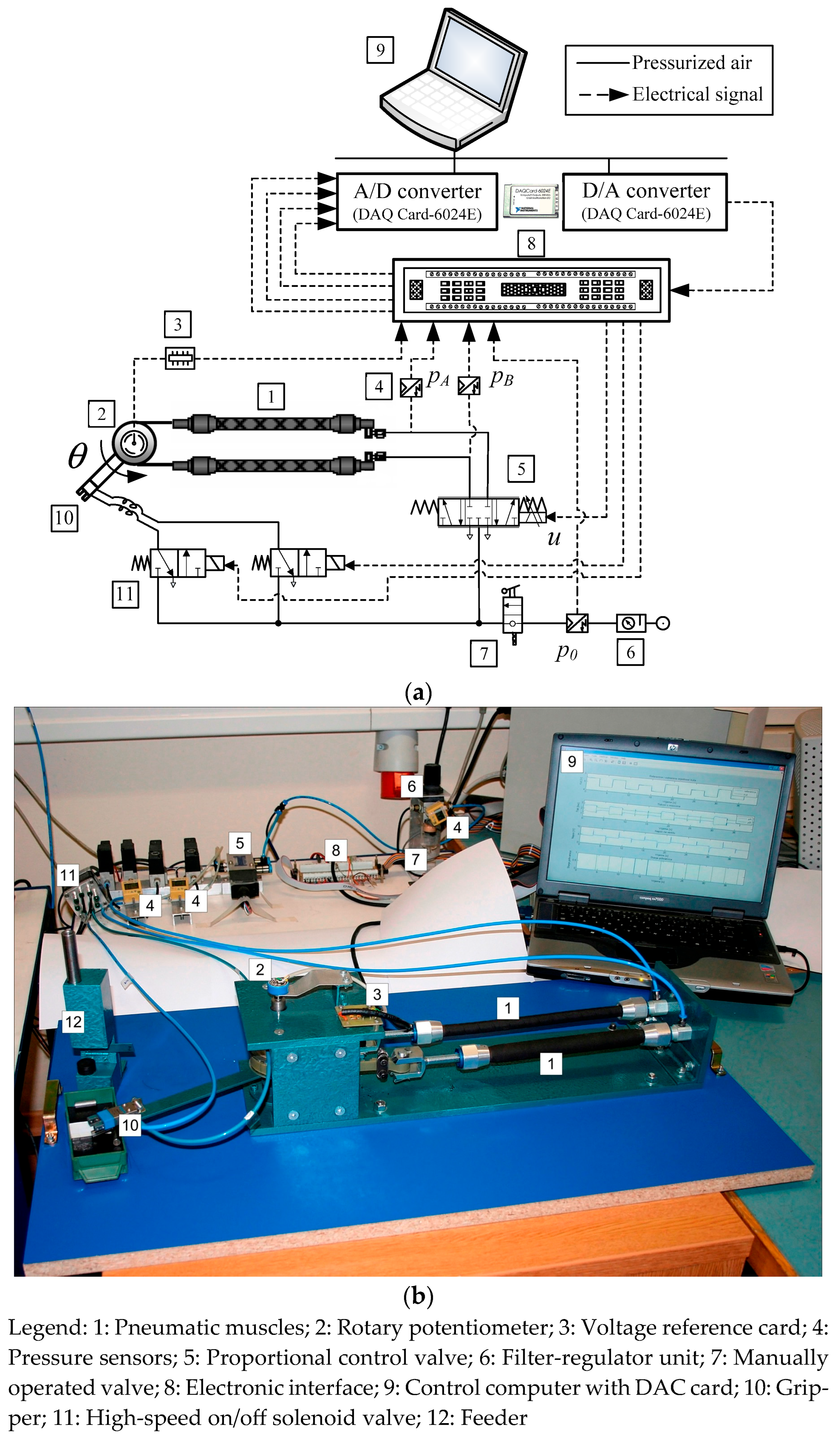
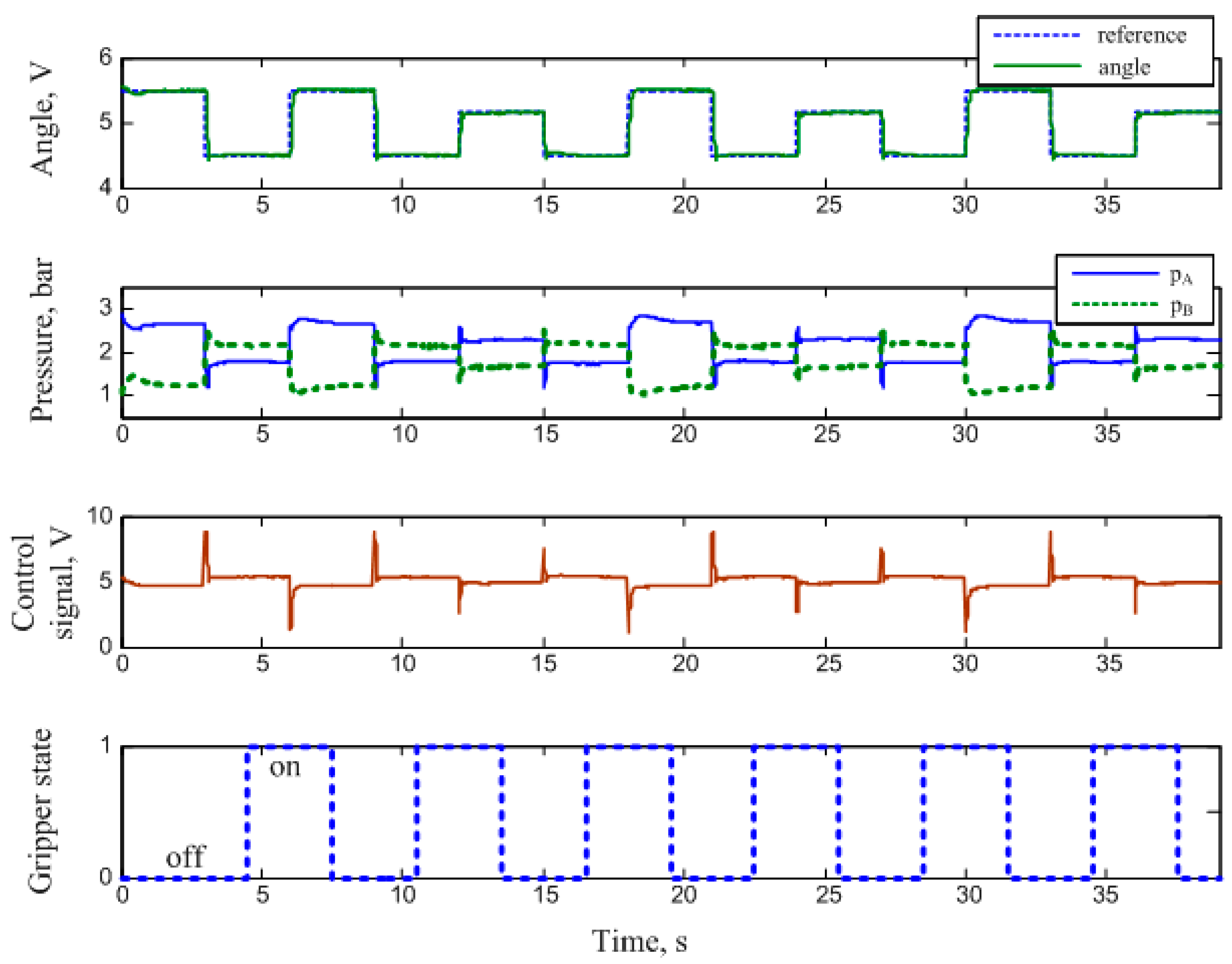
2.1.2. Manipulator Arm Actuated by PAMs
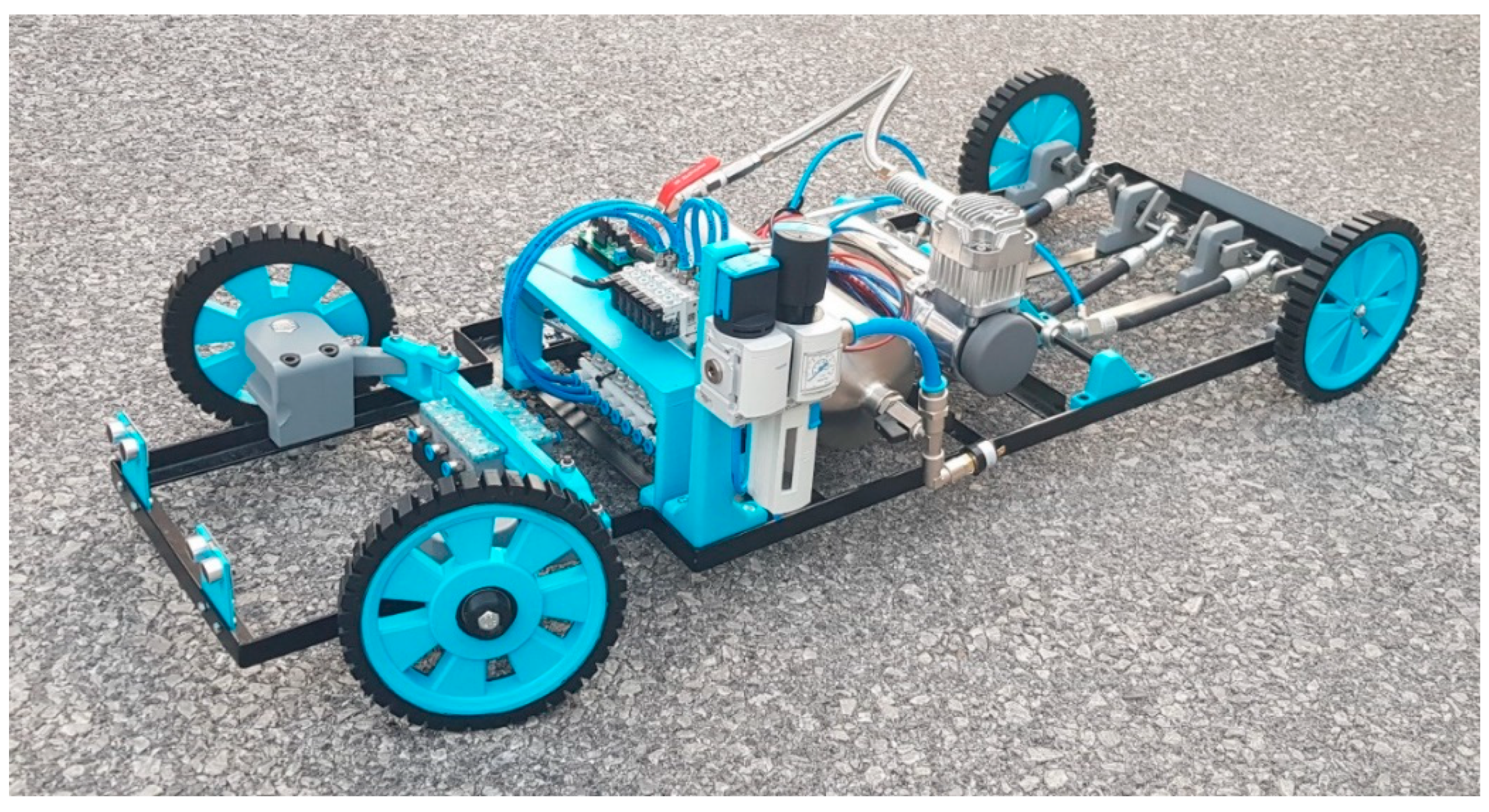
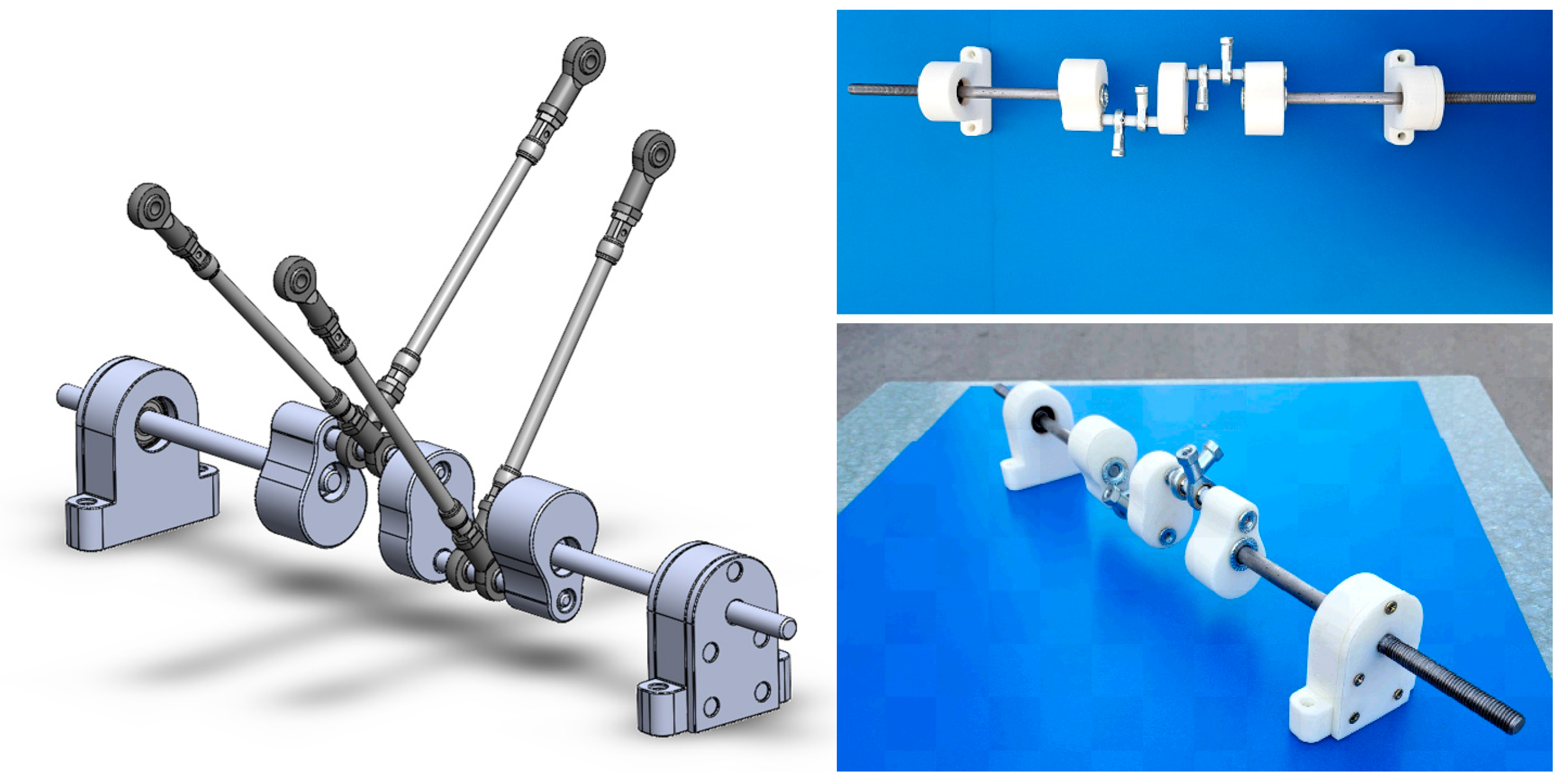
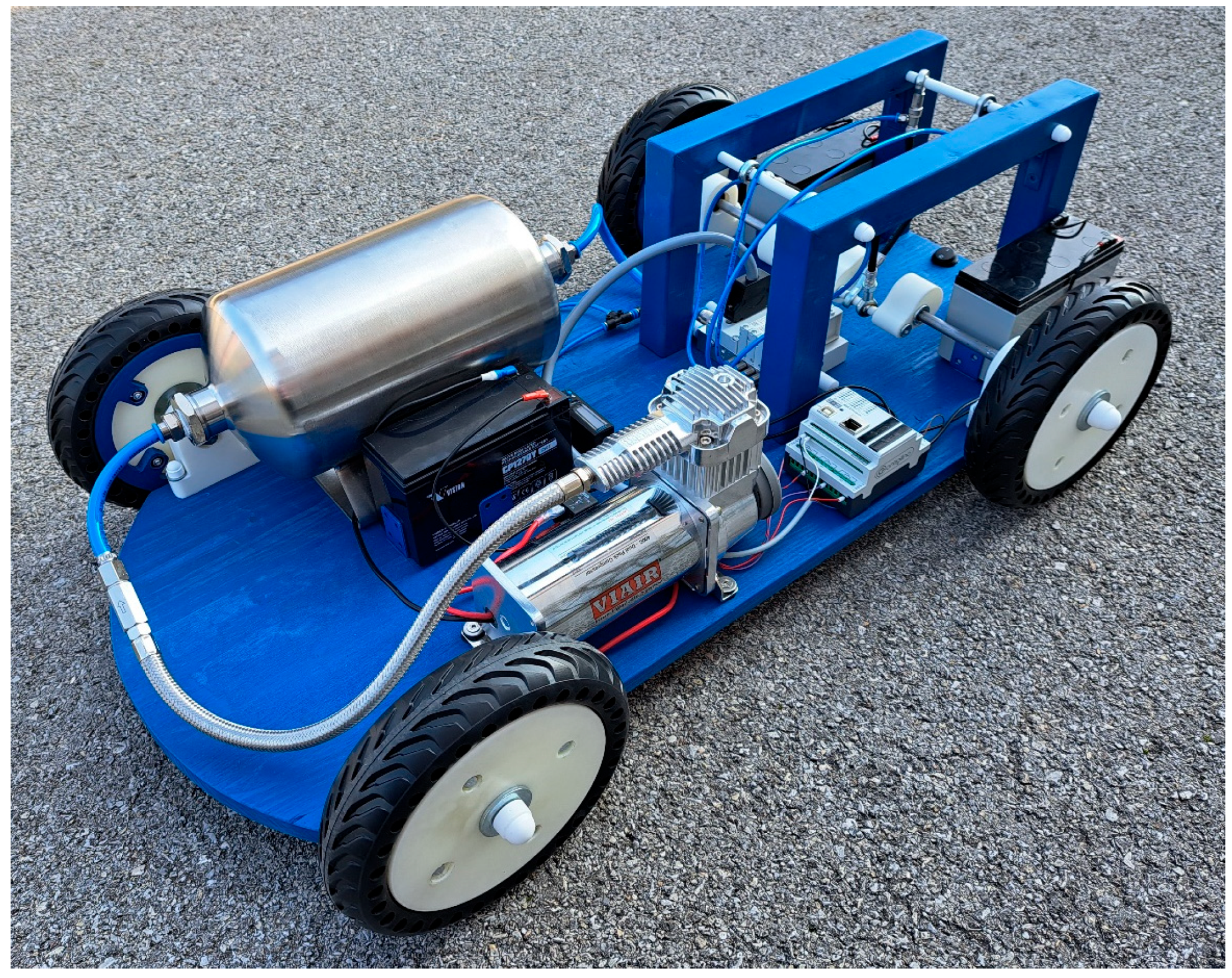
2.2. Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous Vehicles Driven by PAMs
2.3. Mechatronic Systems
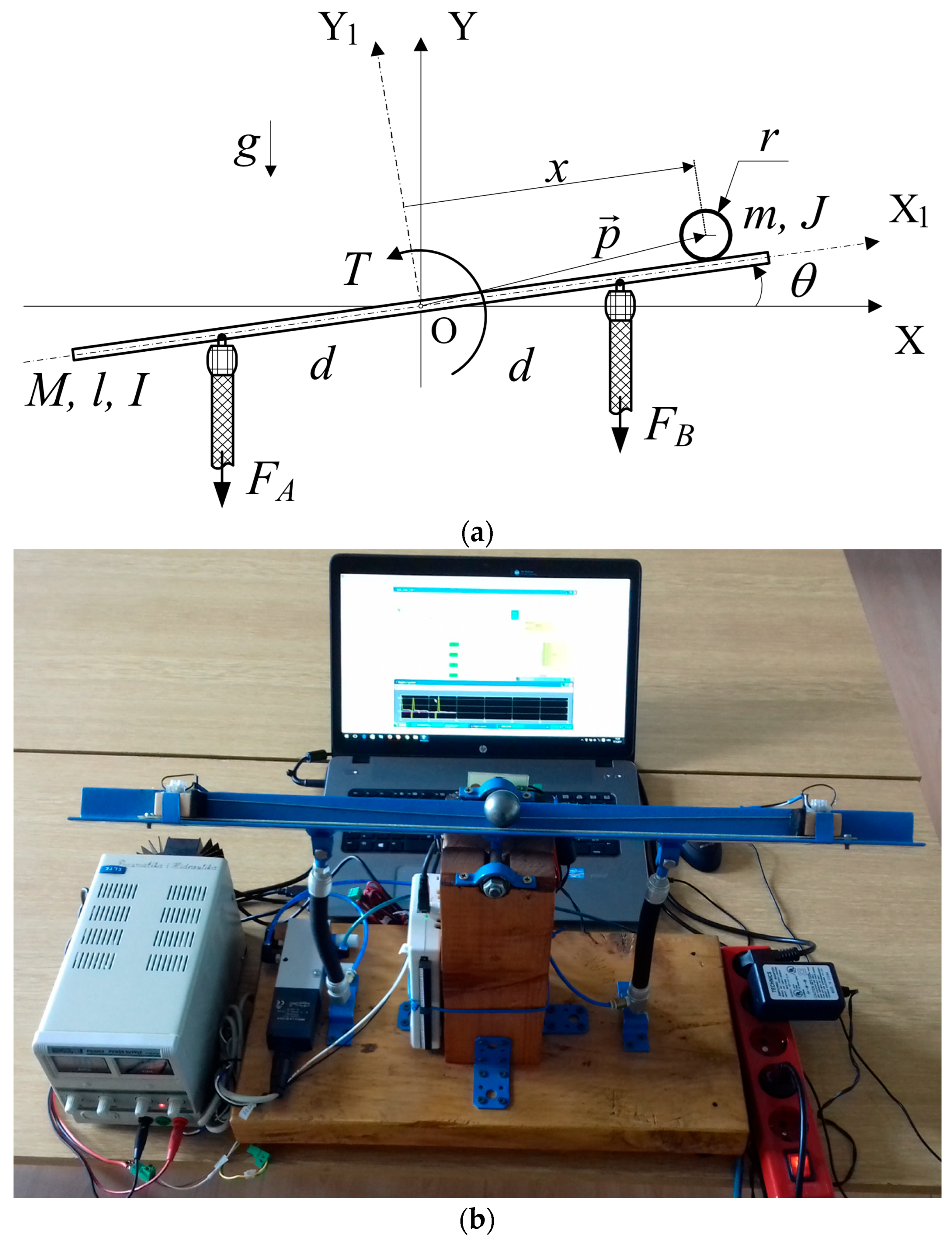
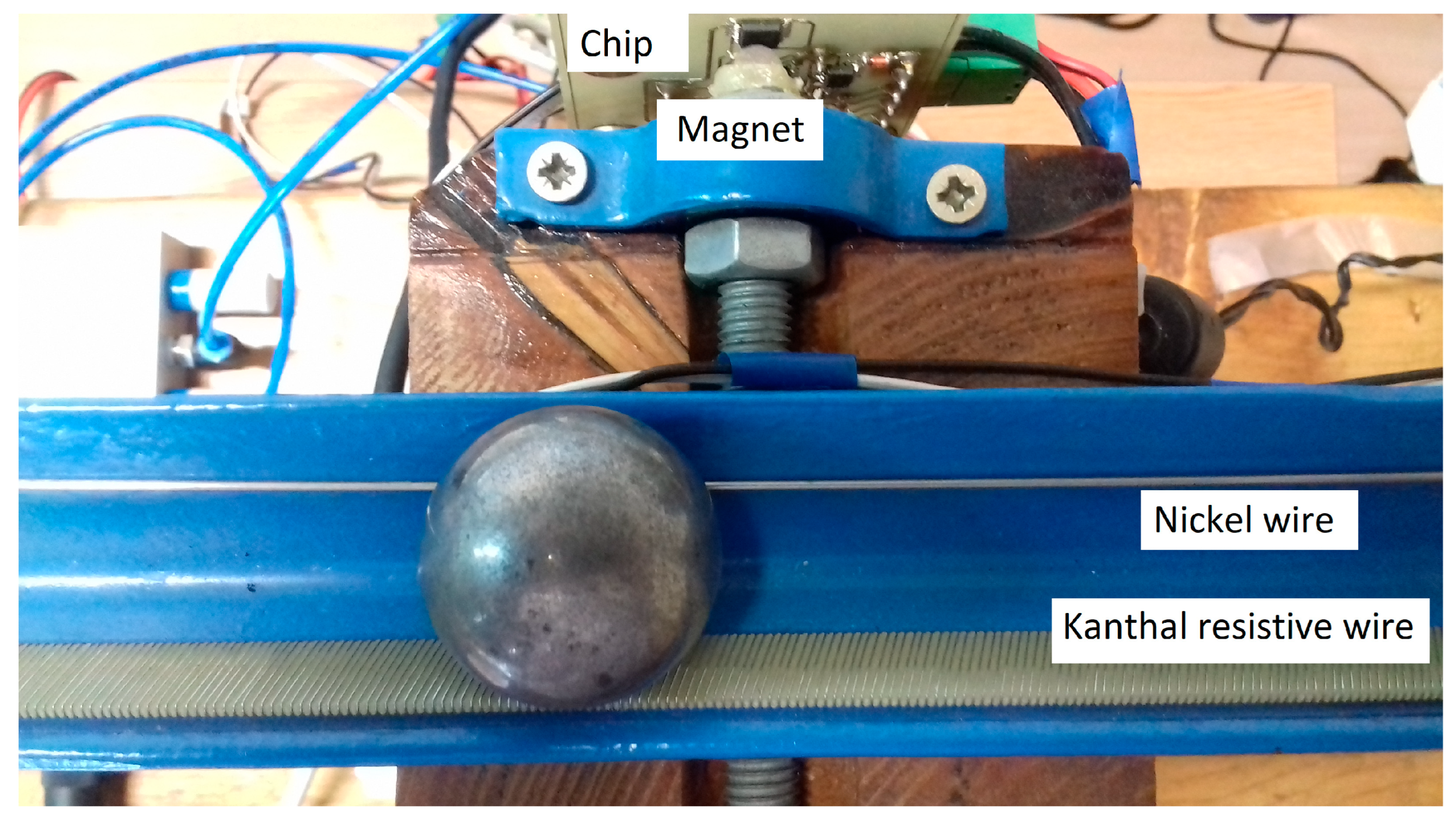
2.3.1. Ball on Beam Balancing Mechanism Actuated by PAMs
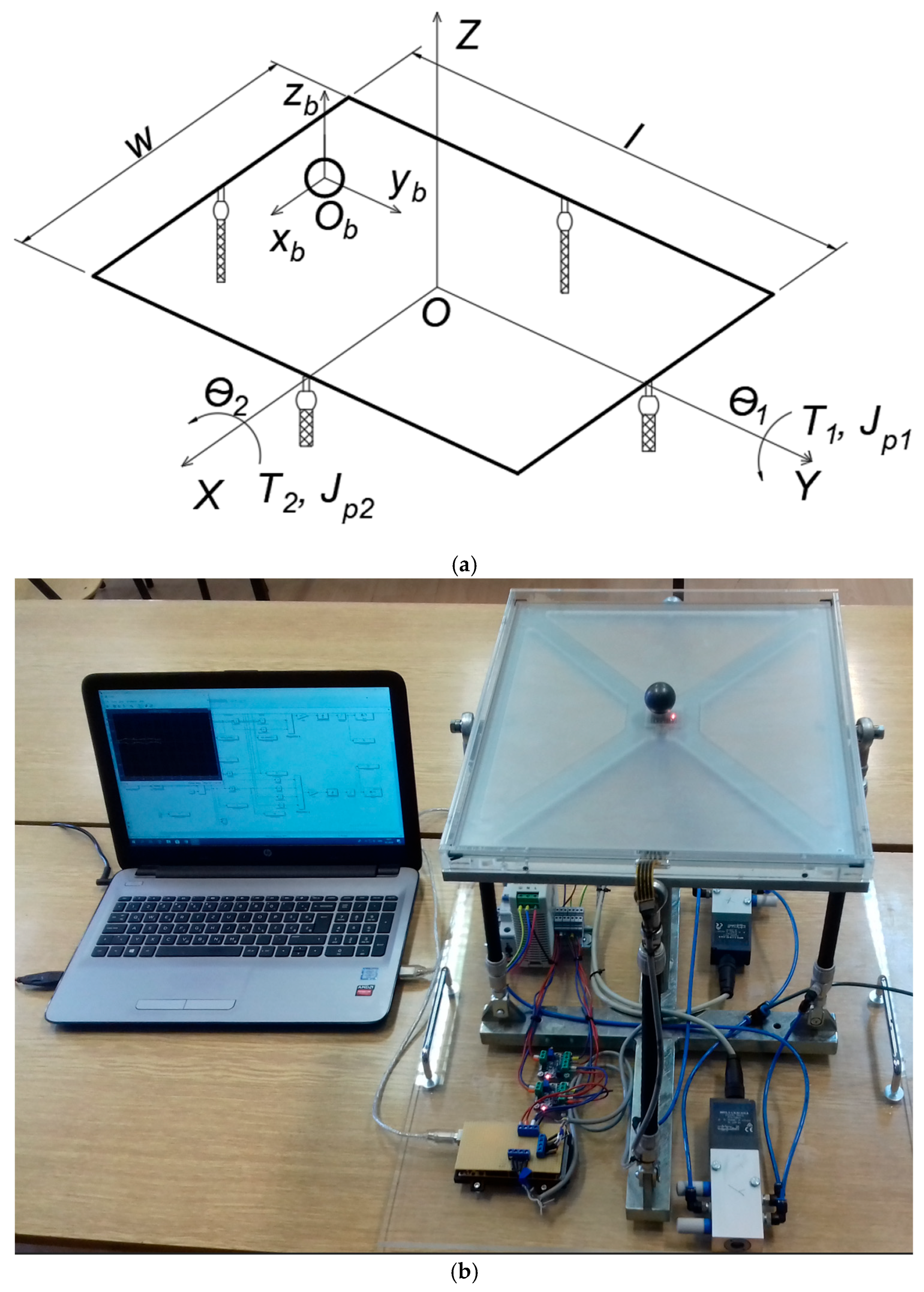
2.3.2. Ball on Plate Balancing Mechanism Actuated by PAMs
2.4. Orthopaedic Devices
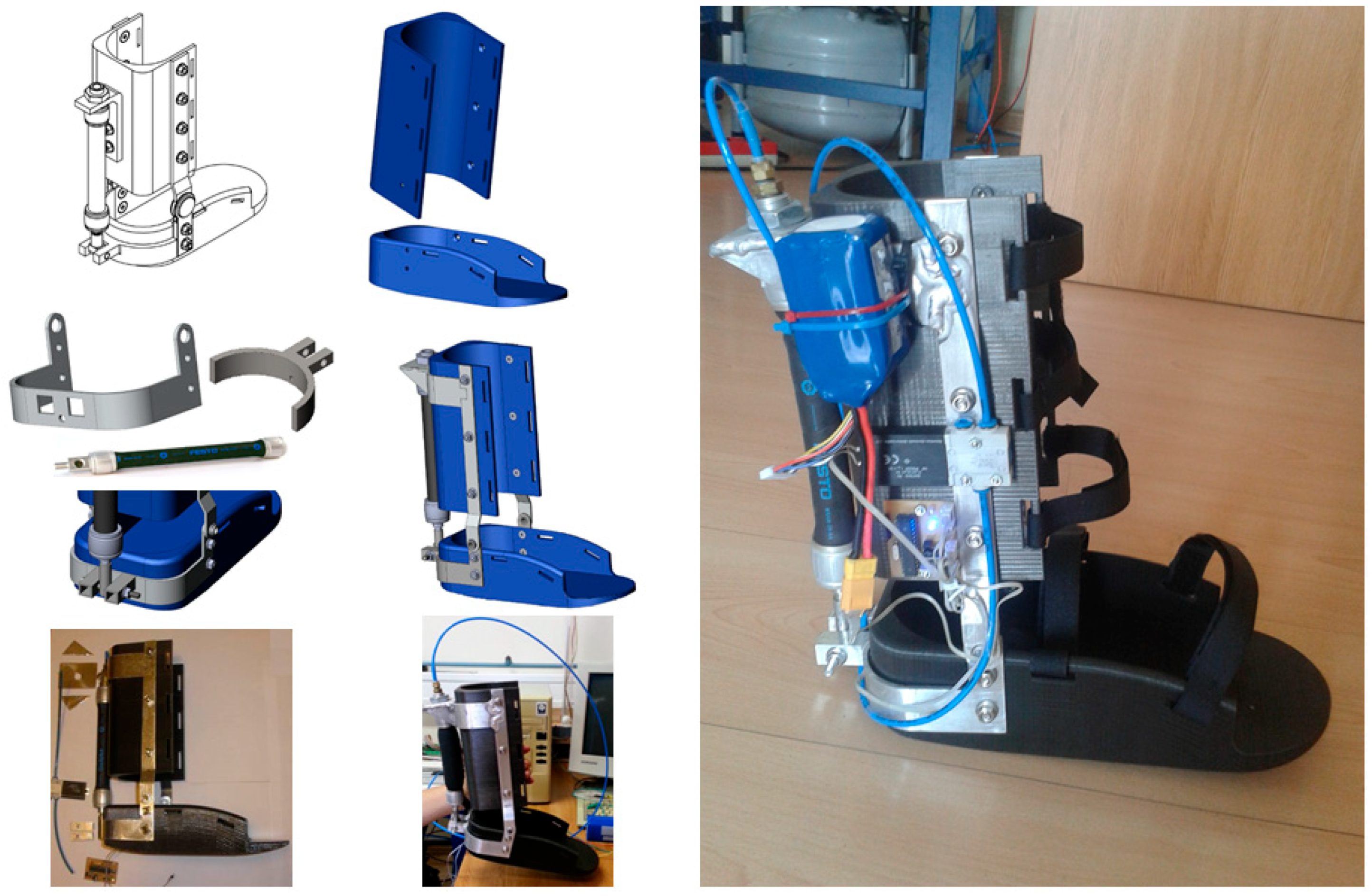
Active Ankle-Foot Orthotic Device Actuated by PAM
3. Discussion and Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalita, B.; Leonessa, A.; Dwivedy, S.K. A Review on the Development of Pneumatic Artificial Muscle Actuators: Force Model and Application. Actuators 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daerden, F.; Lefeber, D. Pneumatic Artificial Muscles: Actuators for robotics and automation. Eur. J. Mech. Environ. Eng. 2002, 47, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jamil, B.; Oh, N.; Lee, J.-G.; Lee, H. A Review and Comparison of Linear Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2024, 11, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palko, A.; Smrček, J. The use of pneumatic artificial muscles in robot construction. Ind. Robot 2011, 38, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, D.G.; Tsagarakis, N.; Medrano-Cerda, G.A. Bio-mimetic actuators: Polymeric pseudo muscular actuators and pneumatic muscle actuators for biological emulation. Mechatronics 2000, 10, 499–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kato, Y.; Ohnishi, K. Position Control of a Double Air Chamber PAM Actuator Using a Sliding Mode Control with a Disturbance Observer. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2025, 37, 114–123. Available online: https://www.fujipress.jp/jrm/rb/robot003700010114/ (accessed on 15 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, J. Adaptive Control of Dual PAM Soft Actuators with Hysteresis Compensation Using Neural Networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, F.L.; Shepherd, R.F.; Majidi, C. Trends in Bioinspired Soft Robotics: Advances in Actuation, Modeling, and Control. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.12312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.K.; Nguyen, H.T.C. Intelligent switching control of a pneumatic muscle robot arm using learning vector quantization neural network. Mechatronics 2007, 17, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-K.; Yen, P.-L.; Yuan, T.-H. Angle Control of a one-Dimension Pneumatic Muscle Arm using Self-Organizing Fuzzy Control. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Taipei, Taiwan, 8–11 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Mei, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Hysteresis modeling and trajectory tracking control of the pneumatic muscle actuator using modified Prandtl–Ishlinskii model. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 120, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhd Yusoff, M.A.; Mohd Faudzi, A.A.; Hassan Basri, M.S.; Rahmat, M.F.; Shapiai, M.I.; Mohamaddan, S. Switching Model Predictive Control for Thin McKibben Muscle Servo Actuator. Actuators 2022, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, K.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Takayama, H.; Takuma, T. Pneumatic-driven jumping robot with anthropomorphic muscular skeleton structure. Auton. Robot. 2010, 28, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrelst, B.; Vermeulen, J.; van Ham, R.; Lefeber, D. Control Architecture for the Pneumatically Actuated Dynamic Walking Biped ‘Lucy’. Mechatronics 2005, 15, 703–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbeck, K.S.; Kern, N.I.; Bachmann, R.J.; Quinn, R.D. Design of a Quadruped Robot Driven by Air Muscles. In Proceedings of the First IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Pisa, Italy, 20–22 February 2006; pp. 875–880. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Cicirelli, F.; Vinci, A.; Guerrieri, A.; Qi, W.; Fortino, G. Quadruped Robots: Bridging Mechanical Design, Control, and Applications. Robotics 2025, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, L.Q.; Ye, X.F.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.L. Prototype development and gait planning of biologically inspired multi-legged crablike robot. Mechatronics 2013, 23, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Dong, X.; Lin, Z.; Tang, C.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.-J. Untethered Robotic Millipede Driven by Low-Pressure Microfluidic Actuators for Multi-Terrain Exploration. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 12142–12149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šitum, Ž.; Herceg, S.; Bolf, N.; Ujević Andrijić, Ž. Design, Construction and Control of a Manipulator Driven by Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. Sensors 2023, 23, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šitum, Ž.; Benić, J.; Grbić, Š.; Vlahović, F.; Jelenić, D.; Kosor, T. Mechatronic systems with pneumatic drive. In Proceedings of the International Conference Fluid Power 2019, Maribor, Slovenia, 19–20 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Almutairi, N.B.; Zribi, M. On the sliding mode control of a ball on a beam system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2010, 59, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshmiri, M.; Jahromi, A.F.; Mohebbi, A.; Amoozgar, M.H.; Xie, W.F. Modeling and control of ball and beam system using model based and non-model based control approaches. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 2012, 5, 14–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Chan, W.S.; Chang, C.W. TS fuzzy model-based adaptive dynamic surface control for ball and beam system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 2251–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šitum, Ž.; Trslić, P. Ball and Beam Balancing Mechanism Actuated With Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. ASME J. Mech. Robot. 2018, 10, 055001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Choudhury, I.A.; Mamat, A.B. Mechanism and Design Analysis of Articulated Ankle Foot Orthoses for Drop-Foot. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 867869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.E.; Sawicki, G.S.; Ferris, D.P. Mechanical performance of artificial pneumatic muscles to power an ankle–foot orthosis. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1832–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorter, K.A.; Xia, J.; Hsiao-Wecksler, E.T.; Durfee, W.K.; Kogler, G.F. Technologies for Powered Ankle-Foot Orthotic Systems: Possibilities and Challenges. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidl, R.; Linjama, M.; Schmidt, S. Discussion: Is the future of fluid power digital? Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control. Eng. 2012, 226, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, R.; Malzahn, J.; Murrenhoff, H.; Schmitz, K. A Survey of Industrial Internet of Things in the Field of Fluid Power: Basic Concept and Requirements for Plug-and-Produce. Fluid Power Syst. Technol. 2018, 51968, V001T01A015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.J. Hands-on experiments in dynamic systems and control for applied education in robotics and automation. In Proceedings of the World Automation Congress, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 12–16 May 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šitum, Ž.; Benić, J.; Cipek, M. Mechatronic and Robotic Systems Utilizing Pneumatic Artificial Muscles as Actuators. Inventions 2025, 10, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10040044
Šitum Ž, Benić J, Cipek M. Mechatronic and Robotic Systems Utilizing Pneumatic Artificial Muscles as Actuators. Inventions. 2025; 10(4):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10040044
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠitum, Željko, Juraj Benić, and Mihael Cipek. 2025. "Mechatronic and Robotic Systems Utilizing Pneumatic Artificial Muscles as Actuators" Inventions 10, no. 4: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10040044
APA StyleŠitum, Ž., Benić, J., & Cipek, M. (2025). Mechatronic and Robotic Systems Utilizing Pneumatic Artificial Muscles as Actuators. Inventions, 10(4), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions10040044






