Abstract
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensors based on transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDC) materials have shown improved performance in terms of sensitivity, detection accuracy (DA), and quality factor (QF) over conventional biosensors. In this paper, we propose a five-layers model containing black phosphorus (BP) and TMDC (Ag/BP/WS2) in Kretschmann configuration. Using TM-polarized light at 633 nm, we numerically demonstrate the highest sensitivity (375°/RIU), DA (0.9210), and QF (65.78 1/RIU) reported so far over similar materials. Refractive index (RI) of the coupling prism has also played an essential role in enhancing the performance of these biosensors. The research on TMDC materials is still new, and these materials bring about opportunities to develop a new class of biosensor.
1. Introduction
Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDC) materials such as MX2 (where M stands for Mo or W and X for S or Se) exhibit unique optical and optoelectronic properties. They are formed by a hexagonal network of transition metal atoms (Mo, W) hosted between two hexagonal lattices of chalcogenide atoms (S, Se). As a result, MX2 materials have been considered excellent candidates for the semiconductor industry such as in high-speed electronics, flexible devices, next-generation solar cells, touch screen display panels, DNA sequencing, and personalized medicine, to name a few [1].
MX2 materials behave like a two-dimensional semiconductor material with direct bandgaps lying in the visible and near-IR range, which is different from other TMDC material such as graphene and hBN whose bandgaps occur at much longer wavelengths. Because of these, recently MX2 has gained considerable interest in biosensing based on surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) [2,3,4,5].
SPPs are collective oscillations of the free-electron gas density at the boundary of the metal sensors (negative permittivity) and dielectric probing media (positive permittivity). The wavevector of these waves depends on the optical property of both the metal layers and surrounding dielectric media involved, the excitation wavelength of the incident light, and excitation conditions [6].
SPR phenomena based on SPP holds the maximum label-free, rapid and real-time sensing capability in the field of biochemical interactions on a surface. Recently, it has been shown that the reproducibility and longevity of the SPR biosensors can be dramatically improved with the help of suitable protective layers such as thin layers of carbohydrate as described in Ref. [7] and a Graphene-covered layer in Ref. [8].
SPR-based biosensors have numerous advantages in applications such as in food safety, biological medicine [9] as well as immune adjustment. When an incident light fulfils the predetermined incident condition, the corresponding surface plasmon waves get excited. As a result, a sharp dip is obtained in reflected light [4,10]. Thus, SPR is mainly a product of electromagnetic energy conversion.
In this work, the materials chosen for the configuration are as follows: 3-d transition metals (Au and Ag), black phosphorus (BP), and MX2. The Au and Ag are widely used for SPR-based biosensor configuration [2]. In these materials, at the IR wavelength region, the reflectance spectrum sharpens significantly, and a narrow SPR curve is produced, meaning high sensing contrast and enhanced sensitivity. Au is also a chemically stable metal. However, the full width at half maximum (FWHM) for Au-based sensors in our case is found to be 10.67° whereas for Ag-based sensors it is 0.71°. This result suggests that Ag provides higher contrast and the sharpest SPR signal over Au meaning that Ag is more capable of enhancing the sensitivity of the biosensor [11,12,13,14,15]. Also, the penetration length of a 50-nm-thick gold film is about 164 nm with a light source of 630 nm, whereas a 50-nm-thick silver film has an enlarged penetration length of 219 nm [15].
The choice of MX2 is due to the higher optical absorption (~5%) over graphene (~2.3%). Likewise, black phosphorus (BP) is chosen due to its direct band gap, higher carrier mobility, and interesting electrical and optical properties [8]. The choice of CaF2 prism glasses is for enhancing sensitivity, quality factor, and detection accuracy [16].
In this paper, we have proposed SPR-based biosensors using Au and Ag metal layers, black phosphorus, four types of TMDC (MoS2, MoSe2, WS2, and WSe2) layers, and a CaF2 prism glass, and theoretically analyzed the sensor performance using the transfer matrix method, MATLAB simulation, and graphical analysis. By taking the refractive index values from 1.33 to 1.35 and using BP and TMDC-coated CaF2 prism glass and a modified Kretschmann arrangement, we have theoretically demonstrated the improved sensitivity of the biosensor for detecting changes in refractive indices of the liquid media.
2. Design Consideration of the Proposed SPR Biosensor
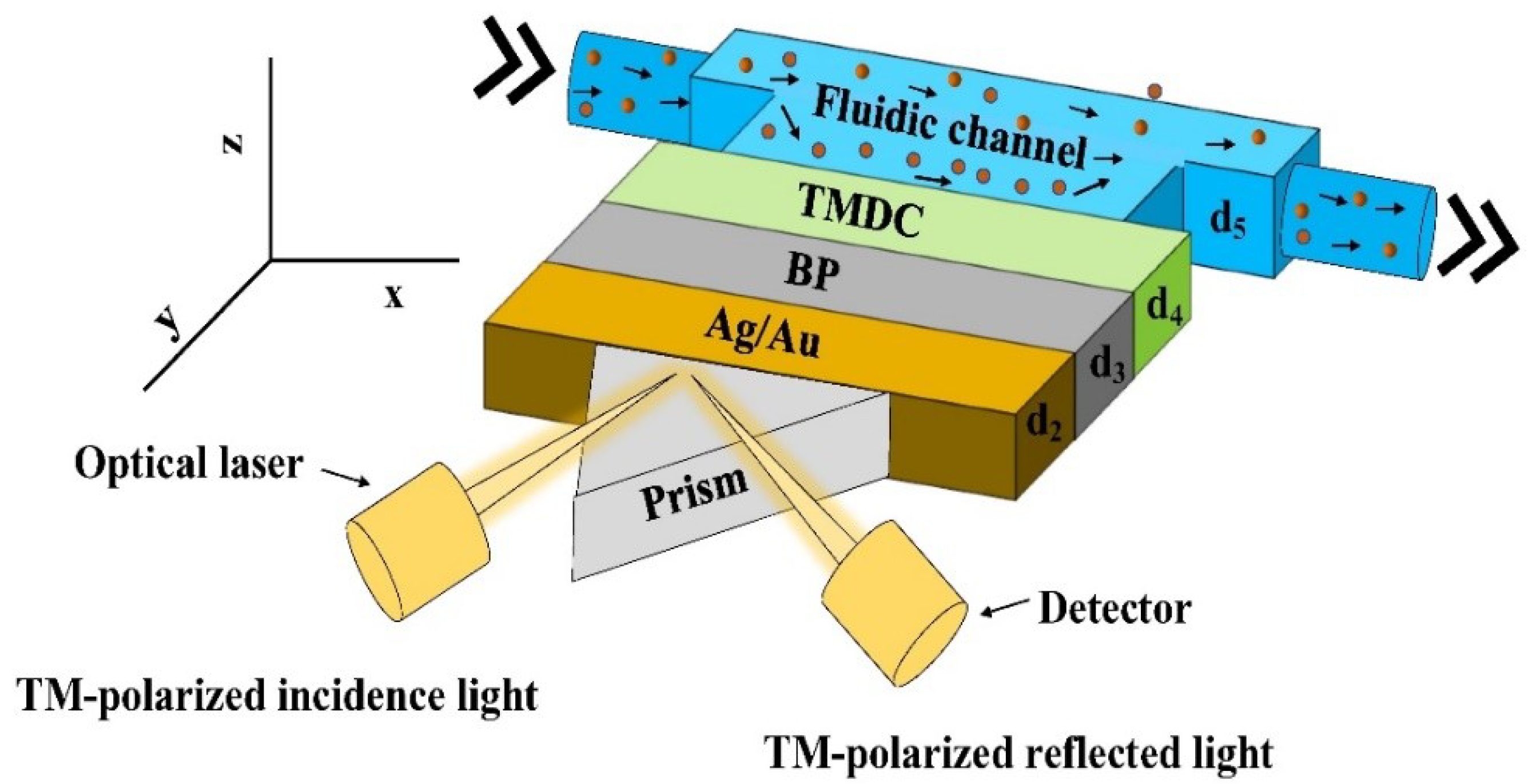
Figure 1 shows a schematic of the proposed five-layer model used for simulation. The first layer is the prism (CaF2, BK7, SF10, 2S2G). The Ag or Au are coupled with the prism and constitute the second layer. In the third layer, black phosphorous (BP) is used for enhancing sensitivity. The fourth layer consists of TMDCs, and the fifth layer is the probing medium as shown by the solid circles in the fluidic channel.
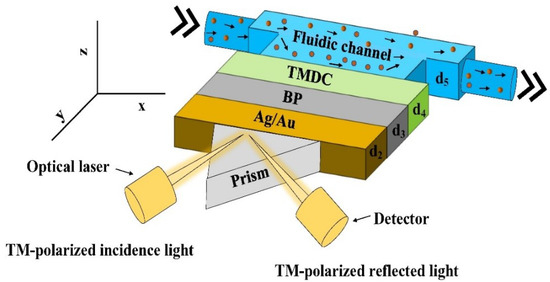
Figure 1.
Schematics of the proposed SPR biosensor.
The proposed SPR technology uses right-angled prism and metal layers for detecting the change in the refractive indices. MATLAB simulation and graphical analysis have been used to study the optical behaviour of the proposed sensor. The angular detection method has been employed for detection using a TM-polarized light having a wavelength of 632 nm. Reflected light intensity does not only vary with the angle of incidence but also with the thickness of TMDC layers. For developing optical nonlinearity for a specific frequency, p-polarized (TM-polarized) optical laser at the wavelength, = 633 nm is used [16] and a detector is used for recording the reflected light from the biosensor.
As shown in Figure 1, the thickness of the metal and MX2 layers are defined by d2, d3, and d4, and the fluidic channel by d5. The thicknesses of metal, BP, and TMDC layers are taken as d2, d3, and d4 with d3 = L × 0.53 nm and d4 = L × 0.65 nm (MoS2), L × 0.7 nm (MoSe2), L × 0.8 nm (WS2) and L × 0.7 nm (WSe2), where L is the number of BP and TMDC layers. The refractive index (n) of the probing medium is 1.33, and the variation of n is considered in the range of 1.33 to 1.35, i.e., ∆n in the range of 0.01 to 0.02. These refractive indices correspond closely to the refractive index of urine (a bio-sample) with various concentrations concerning the specific gravity depending on whether the disease is normal, moderate, acute, or above average [17,18]. Due to the weak van der Waals bonding which exists between successive layers in the multilayers and despite having significant lattice mismatch between the layers, TMDC materials can form complex heterostructures with other layered materials with no misfit dislocations. We plan to grow these layers using molecular beam epitaxy as it has shown to enable high purity heterostructures [19].
3. Numerical and Mathematical Model
Out of three configurations (Otto, Kretschmann, and Grating) of exciting surface plasmons, in this work, Kretschmann configuration is used, as it is more compatible for coupling the prism with the metal film layers. For numerical analysis, we used the transfer matrix method and Fresnel equations performing on the N layer model. Since these methods do not involve approximation, the methods give the most accurate result.
For the calculation, the thicknesses of the layers, dk, are considered in the z-axis, and the refractive index (n) of kth layers and the dielectric constant are considered as ek and nk, respectively. The tangential fields at first boundary z = z1 = 0 are associated with the final boundary tangential field at z = zN−1 [20] as:
Here, P1 and Q1 are the tangential elements of electric and magnetic fields of the first layer boundary, and PN−1 and QN−1 are the boundary fields of the Nth layer where M is represented by the characteristic matrix with Mij [20] and is given as:
The coefficient of reflection and the reflectivity of the reflected light from the sensor are expressed as:
and,
where M11, M22, M12, and M21 represent elements of the transfer matrix, respectively.
3.1. Optical Properties
For optical excitation at an oblique angle, we conceived four prism combinations, CaF2, BK7, SF10, and 2S2G, and their refractive indices are 1.4329, 1.515, 1.723, and 2.358, respectively [21,22]. According to the Drude model, refractive indices of proposed metals can be calculated using Ref. [23] as:
where λc and λP are the collision and plasma wavelengths, respectively. For Ag, P = 1.4541 × 10−7 m and C = 1.7614 × 10−5 m, and for Au, p = 1.6826 × 10−7 m and C = 8.9342 × 10−6 m, respectively. Hence, the refractive index of Ag = 0.8 + 4.236i and Au = 0.1378 + 3.6196i, and of BP = 3.5 + 0.01i. The refractive indices of the TMDCs are MoS2 = 5.0805 + 1.1723i, MoSe2 = 4.6226 + 1.0063i, WS2 = 4.8937 + 0.3124i, and WSe2 = 4.5501 + 0.4332i, respectively [24]. The refractive index of CaF2 was obtained from Ref. [25], and BK7 and SF10 were obtained from Ref. [26]. Various optical parameters are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
The material, dimension, and optical properties of materials at 633 nm.
3.2. Sensitivity and Other Parameters
The sensitivity (S) of an SPR-based biosensor is the most important parameter for evaluating the performance. It is ascertained by the ratio of change in the resonance angle, δθ, and change in refractive index, ∆ns of probing media [27] as:
The resonance condition is evolved as [28]:
where sinθSPR defines the resonance angle, nx is the prism RI, εm is the real part of the metal permittivity, and nd is the RI of dielectrics or probing medium. The ratio of o and C measures the propagation constant of an incident light beam (o = light frequency and C is the speed of the light). The detection accuracy (DA) is calculated by the ratio of change in resonance angle (δθ) and the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the reflectance curve.
A relatively low FWHM is preferred when it comes to designing a biosensor that will show the best performance. The sharper the FWHW, the accuracy in determining the angular modulation with high accuracy detection. The magnitude of FWHM is mainly dependent on the excitation configuration, the layers, and the optical properties of the prism used. The detection accuracy can be given as [29]:
The quality factor (QF) is the ratio of the sensitivity of a biosensor and FWHM, and is given as [29]:
4. Results and Analysis
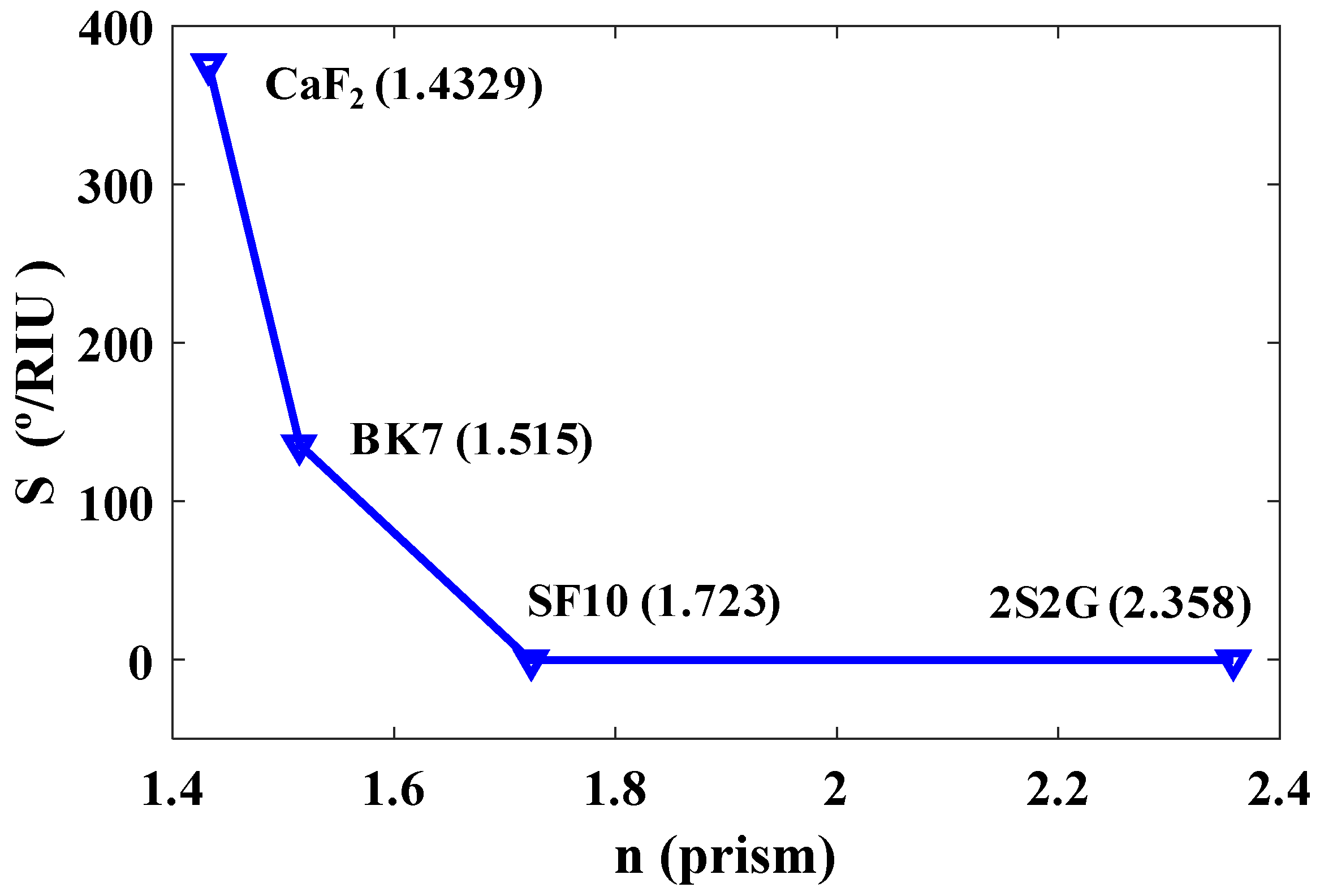
The optical properties of prism materials and their refractive indices have direct effects on the sensitivity of the biosensor. Figure 2 shows the sensitivity of the sensor plotted as a function of the refractive indices of the four types of prism materials at λ = 633 nm for a p-polarized (TM polarized) incident light: CaF2, BK7, SF10, and 2S2G. As shown in Figure 2, the sensitivity decreases with the increasing RI of the prism. The highest sensitivity is achieved for a prism with a smaller refractive index, in this case, CaF2, and it is considered for the final design of the biosensor.
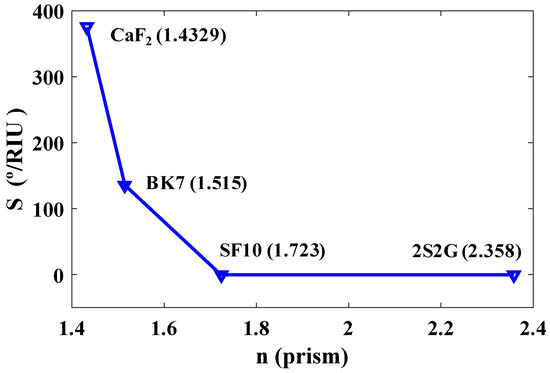
Figure 2.
Sensitivity (%/RIU) versus refractive indices of four types of prisms at = 633 nm.
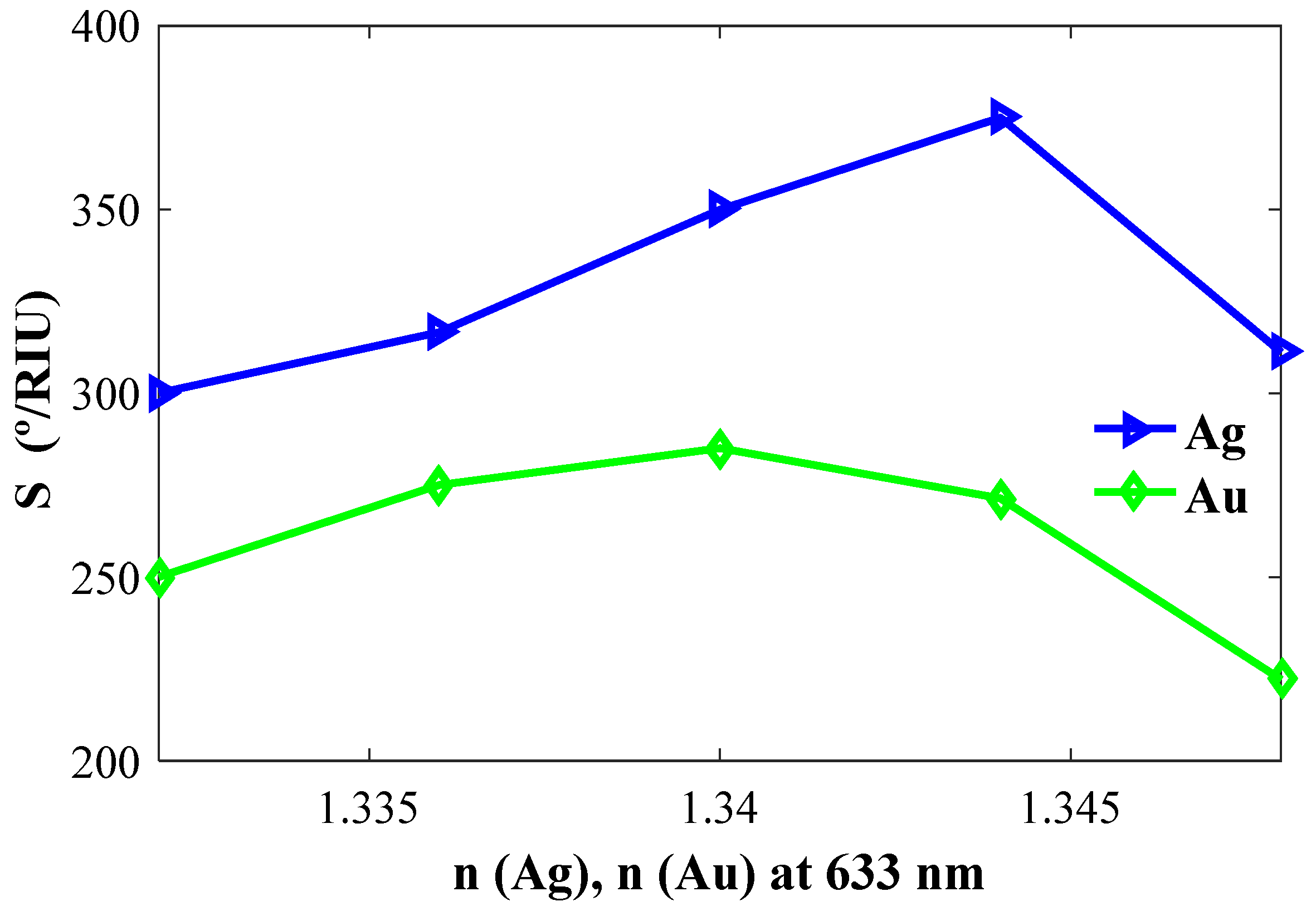
Next, we optimize the Ag and Au layers. Figure 3 describes the calculated performance of Ag- and Au-based sensor configurations with the CaF2 prism. As shown, the sensitivity of the Ag-based configuration shows better coupling with the CaF2 prism over the Au-based configuration. The sensitivity is also increasing with the increase of the refractive index of Ag as well as the overall sensitivity of the model is higher than the sensitivity of the Au-based configuration, and therefore Ag is chosen for the final design.
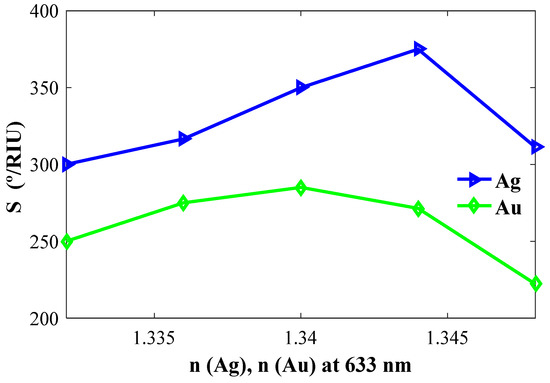
Figure 3.
Sensitivity versus refractive indices of Ag (nAg) and Au (nAu).
4.1. Determination of TMDC Performances
The proposed biosensors were optimized (layer thicknesses, minimum Rp, and δθ) using numerical calculation. The performance results of the biosensors are listed in Table 2. As shown, among all the types, sensors with the WS2 layer exhibit the highest sensitivity, QF, and DA for n = 1.3440. Likewise, TMDCs, MoS2 shows the highest sensitivity for n = 1.3450, and MoSe2 and WSe2 showed the highest sensitivity for n = 1.3460. Between all the four types of TMDCs-based sensors studied here, the sensors with a WS2 layer have much lower energy loss and higher performance (sensitivity of 375°/RIU, QF of 65.78 1/RIU and DA of 0.921).

Table 2.
Comprehensive performance results of a biosensor with different MX2 (M = Mo, W and X = S, Se).
4.2. Determination of Proposed Performance Parameter
Taking out the final model with the optimized layers, we must satisfy three steps: combination parameter, sensitivity, and optimization of layer thickness, which we describe below.
4.2.1. Combination Parameter
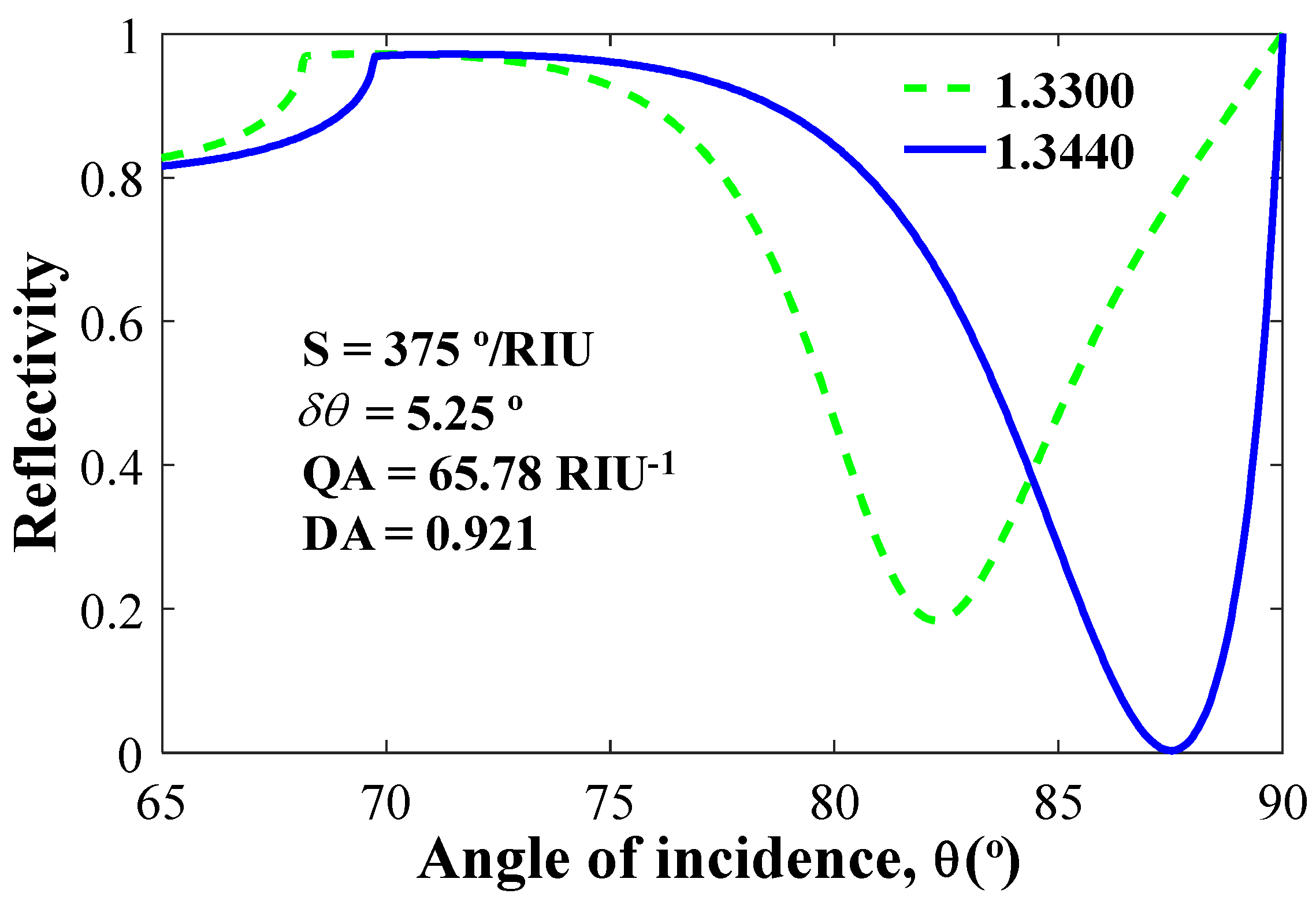
The most fundamental aspect of understanding the performance of an SPR biosensor is the study of spectral and angular studies at variable refractive indices. Figure 4 shows the reflectance versus incident angle, θ. In modelling, we considered four types of structures. Firstly, we took Ag = 35 nm, BP = 0 nm, and WS2 = 0 nm. The obtained sensitivity, QF and DA are 200°/RIU, 43.96 1/RIU and 0.6154, respectively. Secondly, taking Ag = 35 nm, BP = 3 × 0.53 nm, and WS2 = 0 nm, the calculated parameters sensitivity values, QA and DA, are 260.71°/RIU, 47.40 1/RIU and 0.6636, respectively. Thirdly, taking Ag = 35 nm, WS2 = 1 × 0.8 nm, and BP = 0 nm, the calculated parameters include: sensitivity = 239.29°/RIU, QA = 41.98 1/RIU, and DA = 0.5877, respectively. Finally, we take all the values as: Ag = 35 nm, BP = 3 × 0.53 nm, and WS2 = 1 × 0.8 nm. The proposed combination parameters give a sensitivity of 375°/RIU, QF = 65.78 1/RIU, and DA = 0.9210, which is the highest among all the first three combinations.
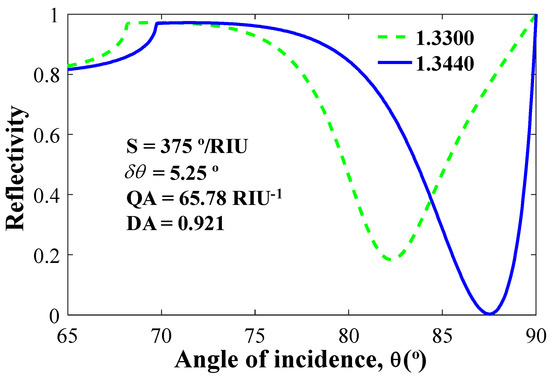
Figure 4.
Normalized reflectivity vs incident angle for n = 1.344 (denoted by blue line) and n = 1.33 (denoted by green line).
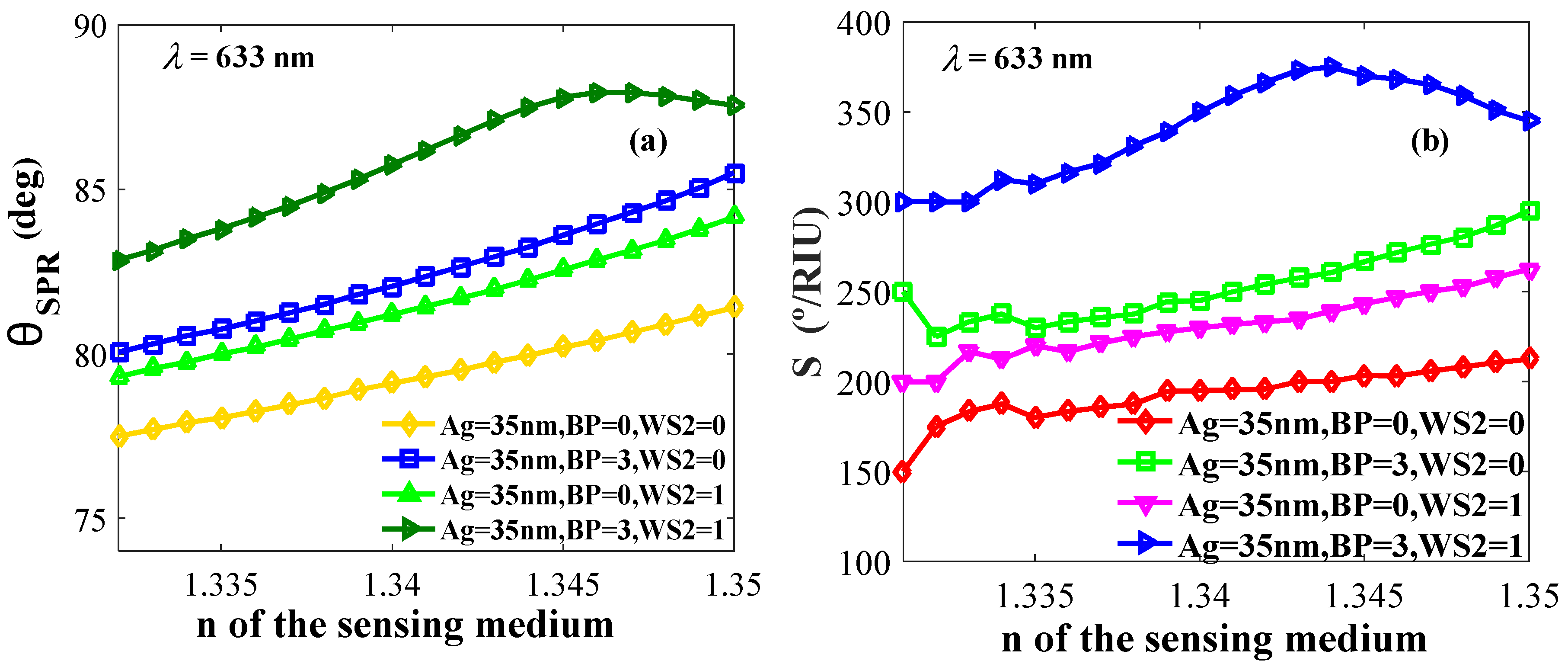
4.2.2. Effect of Refractive Indices on Resonance Angle and Sensitivity
The refractive index plays a vital role in the minimum change for the resonance angle. For obtaining better sensitivity, a high resonance angle is targeted as it shows a better response in the shortest change of n. Figure 5a shows the relation between the resonance angle and variable n, and Figure 5b shows the relation between sensitivity versus n with different layer compositions.
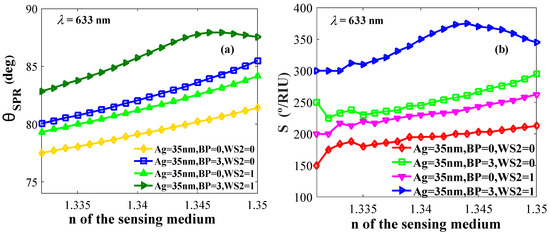
Figure 5.
(a) Resonance angle and (b) sensitivity versus refractive indices of the probing medium.
4.2.3. Optimization of Layer Thicknesses
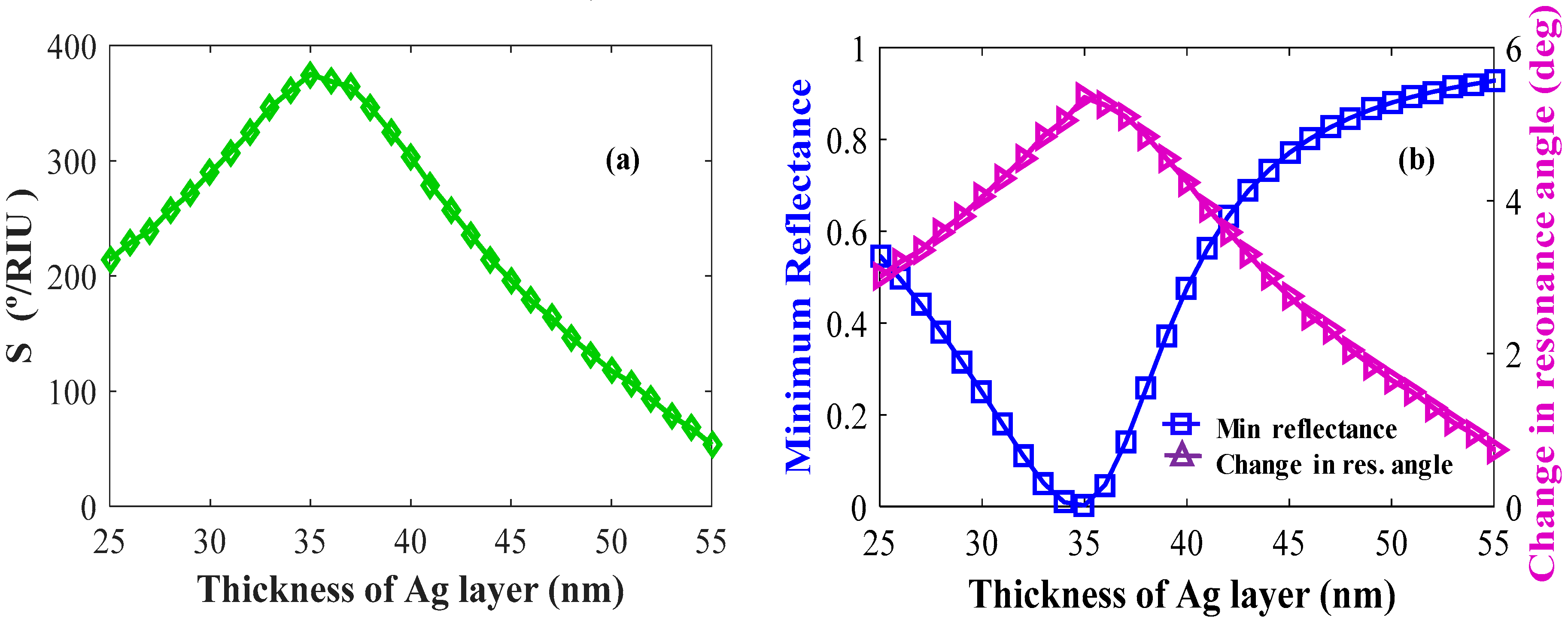
The individual layers and their thicknesses in the Kretschmann configuration have a large effect on sensor performance such as sensitivity, minimum reflectance, and change in resonance angle (δθ). In Figure 6a,b, Ag layers are optimized. As shown in Figure 6a, the maximum sensitivity is obtained for the Ag layer thickness, tAg = 35 nm. The maximum δθ and minimum reflectance shown by these sensors at tAg = 35 nm are shown in Figure 6b.
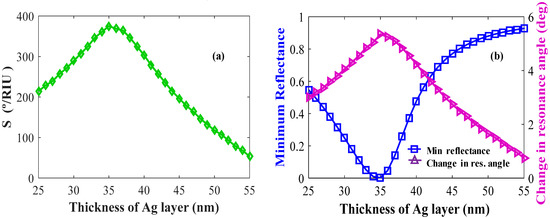
Figure 6.
Layer optimizations: Ag (a) sensitivity versus the number of Ag layers (keeping BP and WS2 constant); (b) change in resonance angle and reflectance versus the number of Ag layers.
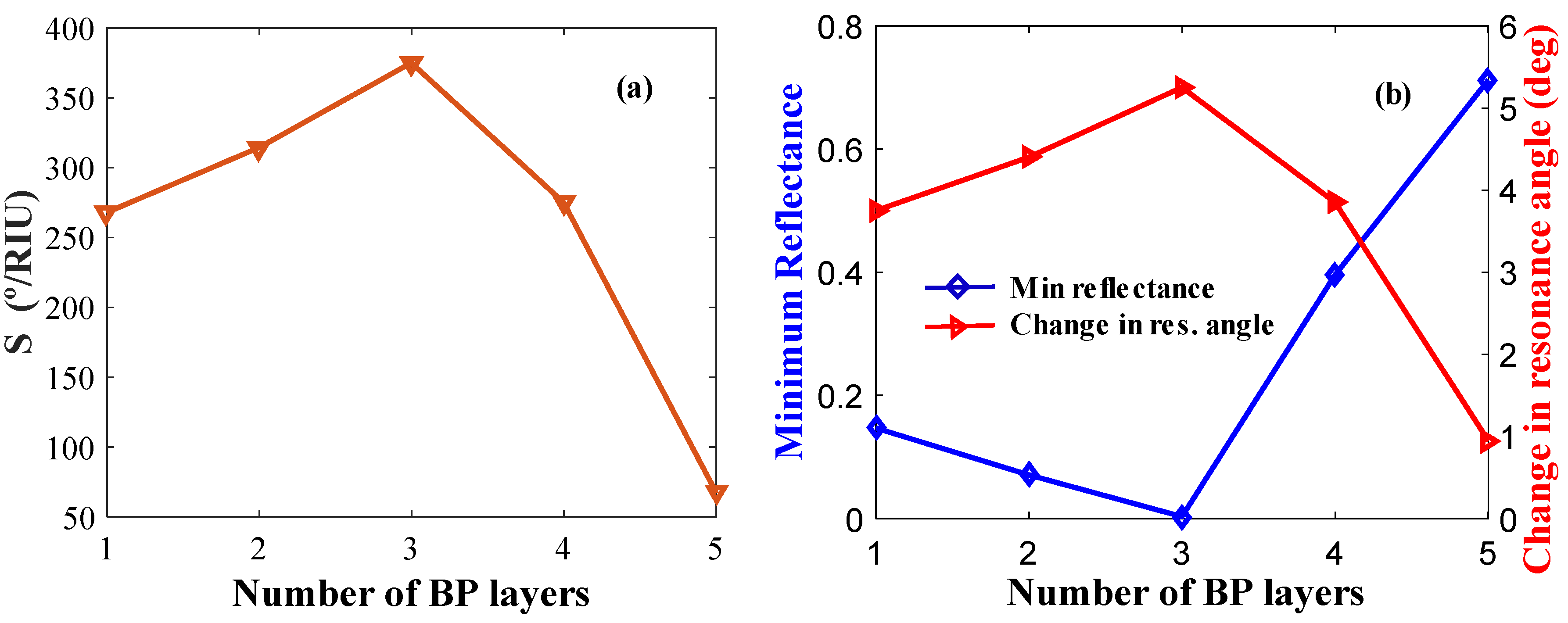
We also optimized the BP layers for the best sensor performance. Figure 7a shows the sensitivity versus number of BP layers. Figure 7b shows δθ and Rp plotted against the number of BP layers. The maximum sensitivity, minimum reflectance, and maximum change in resonance angle are observed for L = 3 layers of BP in the configuration.
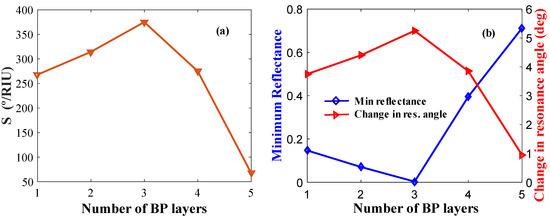
Figure 7.
Layer optimization for BP: (a) Sensitivity versus the number of BP layers (keeping Ag and WS2 layer thickness constant); (b) δθ and minimum reflectance versus the number of BP layers.
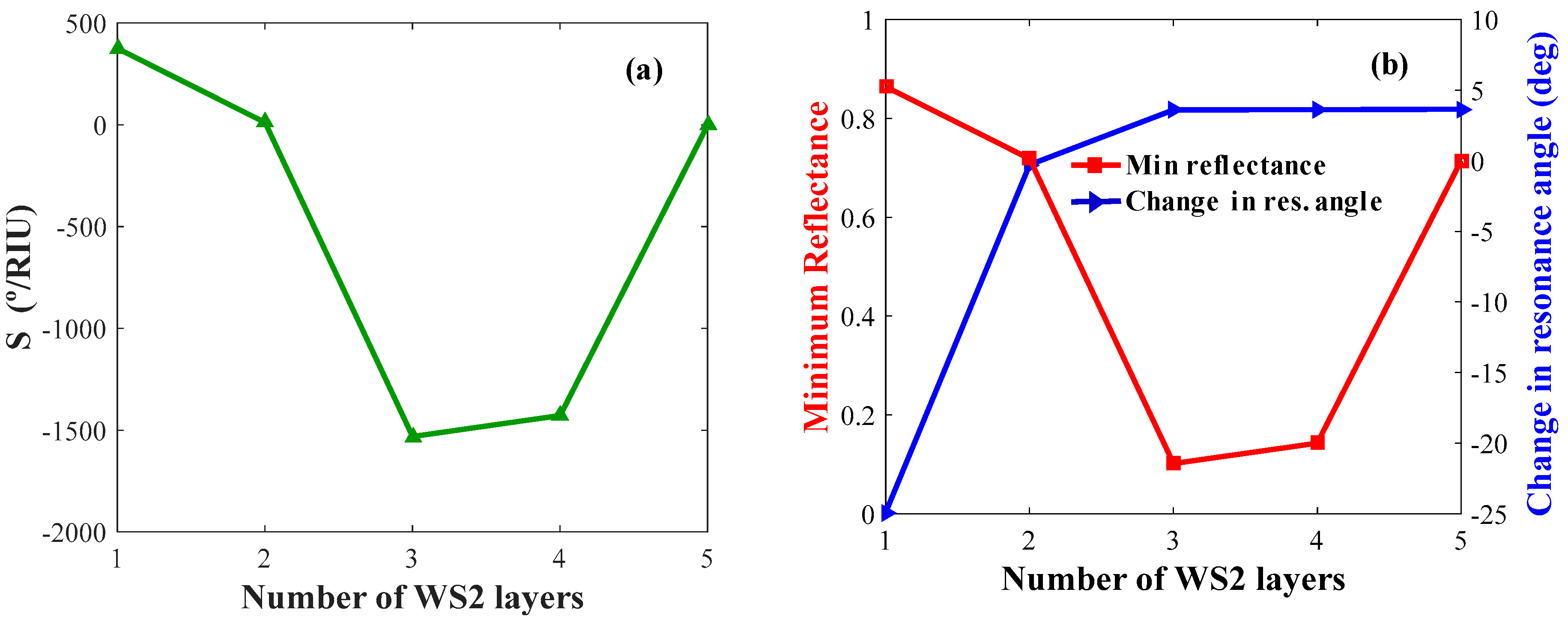
Figure 8a,b shows the sensitivity, δθ, and Rp of the biosensor with optimized WS2 layer thicknesses. By analyzing these figures, the value of maximum sensitivity, δθ, and minimum reflectance are obtained for L = 3, 1, 1, respectively.
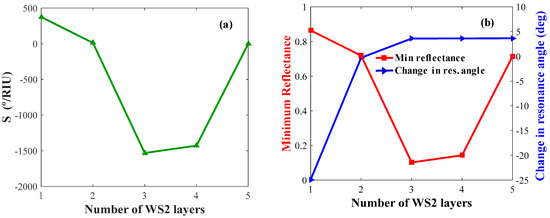
Figure 8.
Layer optimization for WS2: (a) Sensitivity versus the number of WS2 layers (keeping Ag and BP constant); (b) change in resonance angle and minimum reflectance versus the number of WS2 layers.
Ultimately, Table 3 renders all the performance parameters of the biosensors studied in this paper. These include the materials used, the sensitivity, QF, DA, resonance angle, θSPR and change in resonance angle, δθ where the proposed model substantiated the highest sensitivity, QF, and DA.

Table 3.
Performance comparison for different conditional models.
A comparison of the sensitivity values shown by some of the prism-based SPR biosensors reported elsewhere and in this paper is shown in Table 4. As shown, the table corroborates that the proposed model ensured the highest sensitivity among all the reported results. The improvement of the sensitivity of our configuration is also due to the addition and optimization of a black phosphorus (BP) layer as it is found to significantly improve the electric field at the interface of the metal sensor and probing medium. For example, at room temperature, BP is thermodynamically stable, and it has a puckered lattice configuration that gives the benefit of a higher surface to volume ratio. Since. Van der Waals forces—the attraction of intermolecular forces between molecules is higher for BP; these forces tightly hold multiple layers of BP and consequently offer a higher molar response factor. The chosen WSe2 is also an excellent candidate for the SPR study as it offers a direct bandgap, higher absorption rate, and less energy loss of electrons. The refractive index difference between the metal sensor and probing medium (Δn) was kept constant at 0.014 to investigate the performance of the proposed biosensor. With the addition of a new magnetic layer in the proposed configuration and magnetic activity, our proposed structure is expected to exhibit an excellent magneto-optic effect and enhanced sensitivity, detection level and quality factors over the SPR biosensors as well.

Table 4.
Sensitivity comparison of prism-based SPR biosensor with the present work (λ = 600 & 633 nm).
The refractive index values of the probing samples used in our calculation closely correspond to the refractive index of a bio-sample such as urine, as the biological properties are dependent on the variation of the refractive index of the dielectric medium. The proposed biosensor, if manufactured, is suitable for practical applications, for example, they can be used in public washrooms or private toilets in homes where people can test the samples. The measured results can act as a primary indicator for possible health issues in humans, thus preventing frequent visits to the doctor or hospital.
5. Conclusions
We numerically investigated biosensors based on transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDC) and black phosphorous layers and accomplished an excellent sensitivity, detection accuracy and quality factor. Among all the TMDCs, WS2 ascertained the highest sensitivity of 375°/RIU, a quality factor of 65.78 1/RIU, and a detection accuracy of 0.9210. We also explored the ability of Ag and Au layers to tune on the sensitivity, optimized prism material, and chose CaF2 as the coupling prism. A long range of refractive indices is used for ensuring the maximum sensitivity of the proposed SPR biosensor. Although the research on TMDC-based biosensors is still very young, it offers many exciting promises and opportunities in biomedical industries.
Author Contributions
Writing an original draft paper, formatting, and simulating by M.H.H.H. and J.N.N.; Necessary theoretical materials providing, and formal analysis by K.N.S.; Writing—review and editing, and approval by C.R.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Manzeli, S.; Ovchinnikov, D.; Pasquier, D.; Yazyev, O.V.; Kis, A. 2d transition metal dichalcogenides. Nature Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizal, C.; Pisana, S.; Hrvoic, I. Improved magneto-optic surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Photonics 2018, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatyeva, D.O.; Knyazev, G.A.; Kapralov, P.O.; Dietler, G.; Sekatskii, S.K.; Belotelov, V.I. Magneto-optical plasmonic heterostructure with ultranarrow resonance for sensing applications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piliarik, M.; Homola, J. Surface plasmon resonance (spr) sensors: Approaching their limits? Opt. Exp. 2009, 17, 16505–16517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, J.N.; Shushama, K.N.; Asrafy, F.; Hasib, M.H.H.; Khan, M.A.G. Sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance biosensor using black phosphorus and WSe2. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques (ICREST), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 10–12 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Regatos, D.; Sepúlveda, B.; Fariña, D.; Carrascosa, L.G.; Lechuga, L.M. Suitable combination of noble/ferromagnetic metal multilayers for enhanced magneto-plasmonic biosensing. Opt. Exp. 2011, 19, 8336–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizal, C. Magneto-optic surface plasmon resonance ti/au/co/au/pc configuration and sensitivity. Magnetochemistry 2018, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wu, L.; Guo, J.; Dai, X.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, D. Tuning and sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance biosensor with graphene covered au-mos 2-au films. IEEE Photon. J. 2016, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsaiah, K.; Jha, S.N.; Bhardwaj, R.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, R. Optical biosensors for food quality and safety assurance—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavík, R.; Homola, J. Ultrahigh resolution long range surface plasmon-based sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Neal, A.T.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Tománek, D.; Ye, P.D. Phosphorene: An unexplored 2d semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS NANO 2014, 8, 4033–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, S.; Johnston, K.S.; Yee, S.S. High sensitivity surface plasmon resonace sensor based on phase detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 35, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sa, B.; Li, Y.-L.; Qi, J.; Ahuja, R.; Sun, Z. Strain engineering for phosphorene: The potential application as a photocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 26560–26568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulenburger, L.; Baczewski, A.D.; Zhu, Z.; Guan, J.; Tomanek, D. The nature of the interlayer interaction in bulk and few-layer phosphorus. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 8170–8175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Hasan, M.R.; Rikta, K.A.; Anower, M. A novel graphene coated surface plasmon resonance biosensor with tungsten disulfide (ws2) for sensing DNA hybridization. Opt. Mater. 2018, 75, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahed, H.; Nadri, C. Sensitivity enhancement of spr optical biosensor based on graphene–MOS2 structure with nanocomposite layer. Opt. Mater. 2019, 88, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim, N.; Uddin, M.N. Surface plasmon resonance biosensor in healthcare application. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), Cochin, India, 14–16 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, L.A.; Addou, R.; Wallace, R.M.; Hinkle, C.L. Molecular beam epitaxy of transition metal dichalcogenides. In Molecular Beam Epitaxy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 515–531. [Google Scholar]
- Shushama, K.N.; Rana, M.M.; Inum, R.; Hossain, M.B. Sensitivity enhancement of graphene coated surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2017, 49, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, P.; Neumann, D.; Zabel, H. X-ray refractive index: A tool to determine the average composition in multilayer structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1986, 48, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.; Christy, R. Optical constants of transition metals: Ti, v, cr, mn, fe, co, ni, and pd. Phys. Rev. B 1974, 9, 5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.B.; Zuo, Y.L.; Cui, B.S.; Li, D.; Yun, J.J.; Wu, K.; Wang, T.; Xi, L. Post annealing induced magnetic anisotropy in cofesi thin films on mgo(0 0 1). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 085006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; Dai, X.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, D. Sensitivity enhancement by using few-layer black phosphorus-graphene/tmdcs heterostructure in surface plasmon resonance biochemical sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitson, I.H. A redetermination of some optical properties of calcium fluoride. Appl. Opt. 1963, 2, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott Zemax Catalog 2017-01-20b [http://www.Schott.Com]. Available online: https://refractiveindex.info/download/data/2017/schott_2017-01-20b.agf (accessed on 22 May 2019).
- Sharma, A.K.; Pandey, A.K. Blue phosphorene/mos 2 heterostructure based spr sensor with enhanced sensitivity. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2018, 30, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraha, K.; Bambang Setio Utomo, A. Computational study of sensitivity enhancement in surface plasmon resonance (spr) biosensors by using the inclusion of the core-shell for biomaterial sample detection. Biosensors 2018, 8, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.; Verma, A.; Prajapati, Y.; Saini, J. Influence of black phosphorous on performance of surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2017, 49, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Zeng, S.; Jiang, L.; Hong, L.; Xu, G.; Dinh, X.-Q.; Qian, J.; He, S.; Qu, J.; Coquet, P. Sensitivity enhancement of transition metal dichalcogenides/silicon nanostructure-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).