Abstract
X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) measurements at the Fe K-edge were performed on aeolian dust in the TALos Dome Ice CorE drilling project (TALDICE) ice core drilled in the peripheral East Antarctic plateau, as well as on Southern Hemisphere potential source area samples. While South American sources show, as expected, a progressive increase in Fe oxidation with decreasing latitude, Antarctic sources show Fe oxidation levels higher than expected in such a cold polar environment, probably because of their very high exposure ages. Results from the TALDICE dust samples are compatible with a South American influence at the site during MIS2 (marine isotopic stage 2, the last and coldest phase of the last glacial period), in particular from Patagonia and Tierra del Fuego. However, a contribution from Australia and/or local Antarctic sources cannot be ruled out. Finally, important changes also occurred during the deglaciation and in the Holocene, when the influence of Antarctic local sources seems to have become progressively more important in recent times. This research is the first successful attempt to extract temporal climatic information from X-ray absorption spectroscopic data of the insoluble mineral dust particles contained in an ice core and shows the high potential of this technique.
1. Introduction
Mineral dust presents important climatic effects, both direct and indirect in relation to the atmospheric radiative budget [1,2,3,4] and with important influences on marine biogeochemical cycles and on the global carbon cycle [5]. During the last climatic cycles, the concentration of dust in the Antarctic ice changed up to 50 times between interglacial-to-glacial periods [6,7] an amount that corresponds to ~25 times in term of depositional flux [8]. The dust concentration dropped to extremely low levels (ppb level) during the Holocene and earlier interglacial thus making dust liquid counting and geochemical analyses extremely challenging [9]. Previous studies based on Sr and Nd radiogenic isotopes on several East Antarctic ice cores from the inner part of the polar plateau concluded that southern South America—in particular Patagonia, including Tierra del Fuego, as well as the southern part of central western Argentina [10,11,12], was the major dust supplier for central East Antarctica during Marine Isotope Stage (MIS) 2 [8,13,14,15] and likely earlier glaciations. These conclusions have been supported by Pb isotope data [13], and major and rare earth elements [10] analyses on the EPICA Dome C ice core. According to these studies, dust source regions for the central part of the EAIS are definitely homogeneous and well-defined during cold glacial periods. Open questions remain for interglacials, when the geochemical signatures are much more difficult to interpret, and a mixture of different remote sources is likely to have occurred [12].
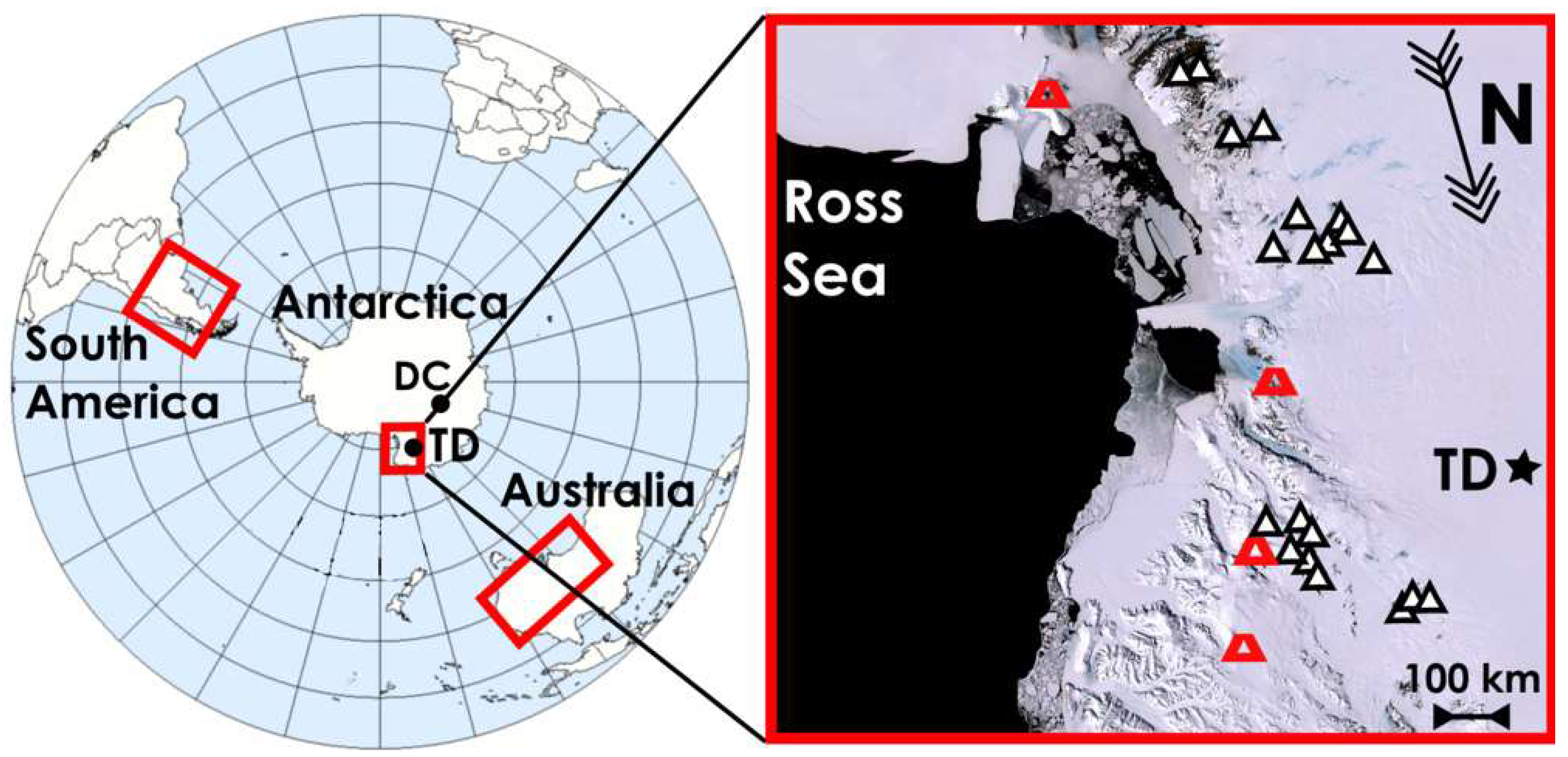
Talos Dome is an area located at the margin of the East Antarctic Plateau (see Figure 1), close to the Ross Ice Sea and to the Southern Pacific Ocean, where the TALDICE (TALos Dome Ice CorE drilling project) ice core was recovered (72°49′ S–159°11′ E, 2,315 m a.s.l). The limited distance from the Southern Ocean and Ross Sea is responsible for the relatively high snow accumulation rate. The modern values of snow accumulation, in the order of 80 mm water equivalent per year (average 2004–1,259 AD, [16]) are relatively high compared to the inner Antarctica and for this reason highly resolved climatic records have been obtained from this core [11]. A peculiar geographical feature of Talos Dome in relation to the atmospheric dust cycle, is the presence of several sizeable ice-free sites in the Northern Victoria Land at only a few hundred km from Talos Dome (exposed moraines, raised beaches, regoliths and glacial deposits) some of which are located at high elevation and could protrude from the ice surface, remaining continuously ice-free since million years [17]. The presence of a coarse dust fraction (particles larger than 10 μm) in the atmospheric dust at Talos Dome [17] that is lacking in the interior of Antarctica, is a strong evidence that local sources play an important role in this marginal region of the ice sheet. The properties of dust in ice cores provide crucial information about the geochemistry and geology of the dust sources, in addition they can also reveal details about their environmental conditions during different climatic periods. However, the very low concentration of mineral particles in Antarctic ice, and their small size represent limitations to the application of well-established geochemical tools typically used in provenance studies.
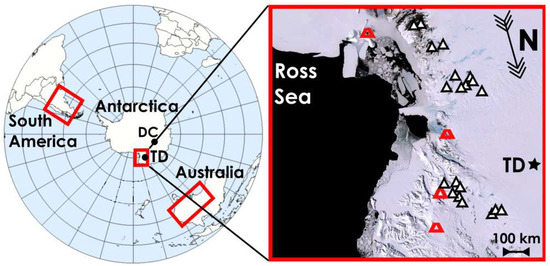
Figure 1.
Map of the possible source areas in South America, Australia and Antarctica, the geographical areas considered in this study. TD stands for Talos Dome and DC for Dome C. On the right a zoom of the Antarctic region surrounding TD with highlighted the positions of the collection sites of the Antarctic potential source areas (PSA) (triangles) and the principal volcanoes (red cones).
Geochemical techniques such as Thermo-Ionization Mass Spectrometry (TIMS), Proton-Induced X-Ray and Gamma-ray Emission (PIXE-PIGE) techniques and low-background Instrumental Neutron Activation (INAA) were successfully applied to bulk dust from Antarctic ice cores [15,18,19]. Also, single-grain analyses can be applied to ice core samples. Electronic microscope with energy dispersive probe (SEM-EDAX) and Raman spectroscopy provide information about minerals and polymorphs, that are important to infer clues about the environmental conditions under which the sediment transported to the considered site, was produced [20]. Among the major elements, iron is particular important when considering the relationships existing between the biogeochemical cycles, dust, and climate. Indeed, iron associated with mineral dust plays a significant role in controlling the Southern Ocean primary bio-productivity and thus it directly influences the global carbon cycle, with relevant climatic consequences [21,22,23]. Iron concentration in Antarctic ice is normally at the level of 10−12~10−9 gel·g−1ice (grams of element/grams of ice) [24,25], and for this reason its detection is a challenging analytical issue. However, not only concentration matters, there is another essential factor that must be considered when attention is given to the biogeochemical significance of iron: its speciation. The latter, together with the total amount of iron deposited at the ground in association to dust, influences the oceanic bio-productivity. Indeed, the Fe speciation is directly related to its solubility and thus to its bioavailability [26,27]. A major factor capable of influencing such geochemical features is mineralogy, but at present few studies have focused on the construction of ice core records about iron mineralogy and speciation, mostly because of the challenging analytical difficulties.
One of the most important features that influences iron bioavailability is its oxidation state. In minerals and magmas, iron typically occurs as Fe2+ and Fe3+. Considering the superficial crustal environment, the two species are present in different contexts. Fe2+ is indicative of relatively fresh and unaltered rock outcrops, not subjected to intense chemical weathering. The reason is that Fe2+ is not stable in presence of atmospheric oxygen (it is oxidized to Fe3+), therefore rocks exposed for a prolonged time to the atmosphere are generally depleted in Fe2+ and enriched in Fe3+. The latter is dominant where chemical weathering is important and involves the exposition to the atmosphere. For example, in soils or outcrops with a prolonged exposure history [28]. The degree of oxidation of mineral Fe in dust samples could be thus potentially used to evaluate the degree of alteration and iron speciation of dust samples from potential source areas (PSA) and from an Antarctic ice core, to infer novel clues on the dust transport and deposition history in Antarctic during different climatic stages. The primary aim of this work is to demonstrate the feasibility of such an approach. We present here the first characterization concerning the Fe oxidation conditions of insoluble mineral dust particles extracted from ice samples of the Antarctic TALDICE ice core and from PSA samples of the southern hemisphere (Figure 1). After setting up the method [27,28] the goal has been reached through the analysis of the Fe K-edge XANES (X-ray absorption near edge structure) spectra of samples prepared following the procedure described in Section 4.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ice Core Dust Samples
Given the extremely low concentration of dust in Antarctic ice, contamination issues are of primary importance when dealing with such samples. To limit as much as possible the contamination during preparation and measurement, it was necessary to develop a dedicated analytical protocol. Ice cores were cut in a cold room (T < −20 °C) at the Eurocold Laboratory (DISAT, University Milano-Bicocca) and decontaminated with repeated baths in ultra-pure water in an ISO6 class clean room, under an ISO5 laminar flow bench [6]. After melting mineral dust was extracted from meltwater through filtration, using pre-cleaned-acid rinsed [29]) polycarbonate membranes (pore size 0.4 μm). For each membrane, an appropriate amount of meltwater was filtered, to obtain 2–10 μg of dust. After filtration, the membranes were mounted on specifically designed PTFE sample holders and sealed in clean plastic containers until the measurement at the synchrotron facility. For this study, a total of 44 samples were prepared, covering the time period between 2 and 25 kyrs BP, corresponding to the last glacial maximum (LGM, 25–18 kyrs BP), the deglaciation (or termination I, 18–11.7 kyrs BP) and the current interglacial period, the Holocene (11.7 kyrs BP—present).
2.2. PSA Samples
Despite it is relatively recent, elemental speciation with the XANES method is well established in the field of geo- and environmental chemistry [30]. Through this technique it is possible to investigate many elements, but Fe plays a relevant role and many XANES-based studies focused on it [31,32,33,34,35]. Among the geochemical features that is possible to retrieve by XANES, iron oxidation state can be inferred from different spectral features related to the K-edge absorption properties: the pre-edge peak [36] or even from the shift of the energy of the main absorption jump [37]. Since the analysis of the pre-edge strongly depends on the resolution and on the S/N ratio, in this work we focused on the analysis of the edge energy. Its position depends on two main factors: the oxidation state of Fe (i.e., the Fe3+/Fe2+ ratio) and its coordination [37]. However, as discussed in the next paragraphs, dealing with atmospheric dust and PSA, the iron coordination in the inorganic component can be considered only octahedral, thus the position of the K adsorption edge is mostly related to changes in the relative concentration of iron Fe3+ and Fe2+. Indeed, considering upper crustal samples, all the most common iron oxides display a coordination number of six, i.e., it can be assumed that Fe is almost present in its octahedral coordination state [27,35,36].
A total of 74 PSA samples were considered in this work. They were collected from Australia (17), Antarctica (Victoria Land, 20) and South America (34) plus three samples of NIST standard soil. The choice of considering these areas, stems from previous results about the provenance of dust transported to Antarctica in different climatic periods. Several studies suggested South America as the dominant source for the whole East Antarctic Ice Sheet (EAIS) during glacial periods, including the LGM considered in this work [6,8,14]. Australia was suggested as a significant source for the dust deposited in inner EAIS during interglacials [10,19]. Finally, local Antarctic dust sources located in the Victoria Land region were considered since several evidence pointed to a regionalization of the dust cycle in the Ross Sea area during the Holocene [19,21]. For the details about the collection sites and their morphological and environmental features the reader is referred to previous works where they are fully presented and discussed [7,10,17]. Samples considered here are the same considered in [21], where attention was given to other geochemical features (Sr-Nd isotopic composition). The only samples that are here considered for the first time are those from Tierra del Fuego, collected from deflation surfaces and aeolian deposits, from 53° S to 49° S between Chile and Argentina on both sides of the Magellan Strait. PSA samples were prepared to be as similar as possible to ice core dust ones. A gravimetric wet method was used to extract the size fraction below 5 μm, i.e., the one subjected to long range atmospheric transport [6].
2.3. XANES Analysis
In the 70’s the absorption peaks near the X-Ray absorption edges have been shown to arise from shape resonances of the excited photoelectron confined by multiple scattering within a nanoscale cluster centered at the absorbing atomic species in disordered oxides [38] and called with the acronym XANES [39]. Nowadays this spectroscopy is widely used to investigate the site specific electronic and the local geometrical structure (i.e., coordination and bond angles) of nanoscale clusters surrounding the selected absorber atom thanks to the multiple scattering (MS) data analysis in the real space [40]. This technique provides a unique tool to identify the different contributions in the spectra of heterogeneous systems containing several iron oxides [41,42].
XANES experiments were performed at the Diamond Lightsource, on beamline B18, dedicated to X-ray absorption spectroscopy [43]. It was necessary to adopt several expedients to limit sample contamination during the experimental runs. At first a sealed plastic glove box was mounted in direct contact to the experimental chamber of the beamline. Secondarily, clean plastic sheets were applied to the inner walls of the experimental chamber, to limit the inelastic scattering given by the interaction between the incident photons and the metallic walls and reduce the associated background. To further reduce the background signal, measurements were carried out at high-vacuum conditions to exclude the contribution from atmospheric gases. The acquisition of the spectra was done using a Vortex 4-elements silicon-detector. Given its large collection surface, the high resolution (140 eV FWHM at the 5.9 keV Mn Kα line), and the sensitivity for low energy fluorescence and high peak-to-background ratio, it proved to be suited for our low concentration samples. For each sample, the absorption spectrum related to the Fe K-edge transition was acquired three times and averaged. Each acquisition lasted for 0.5–1 h, depending on the sample concentration. The energy interval between 6900 and 7800 eV was considered and the average resolution of the spectra is 0.2 eV (Figure 2). Further details can be found in previous works [44,45].
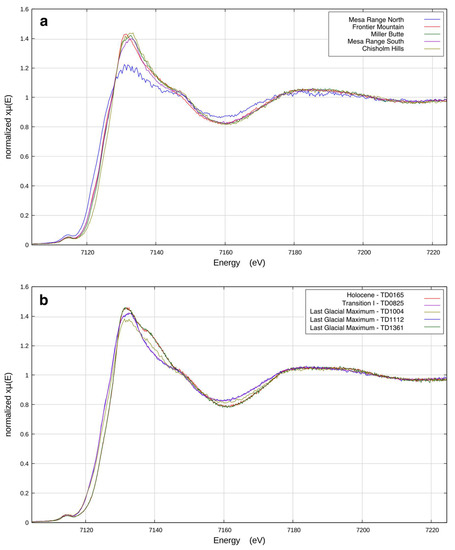
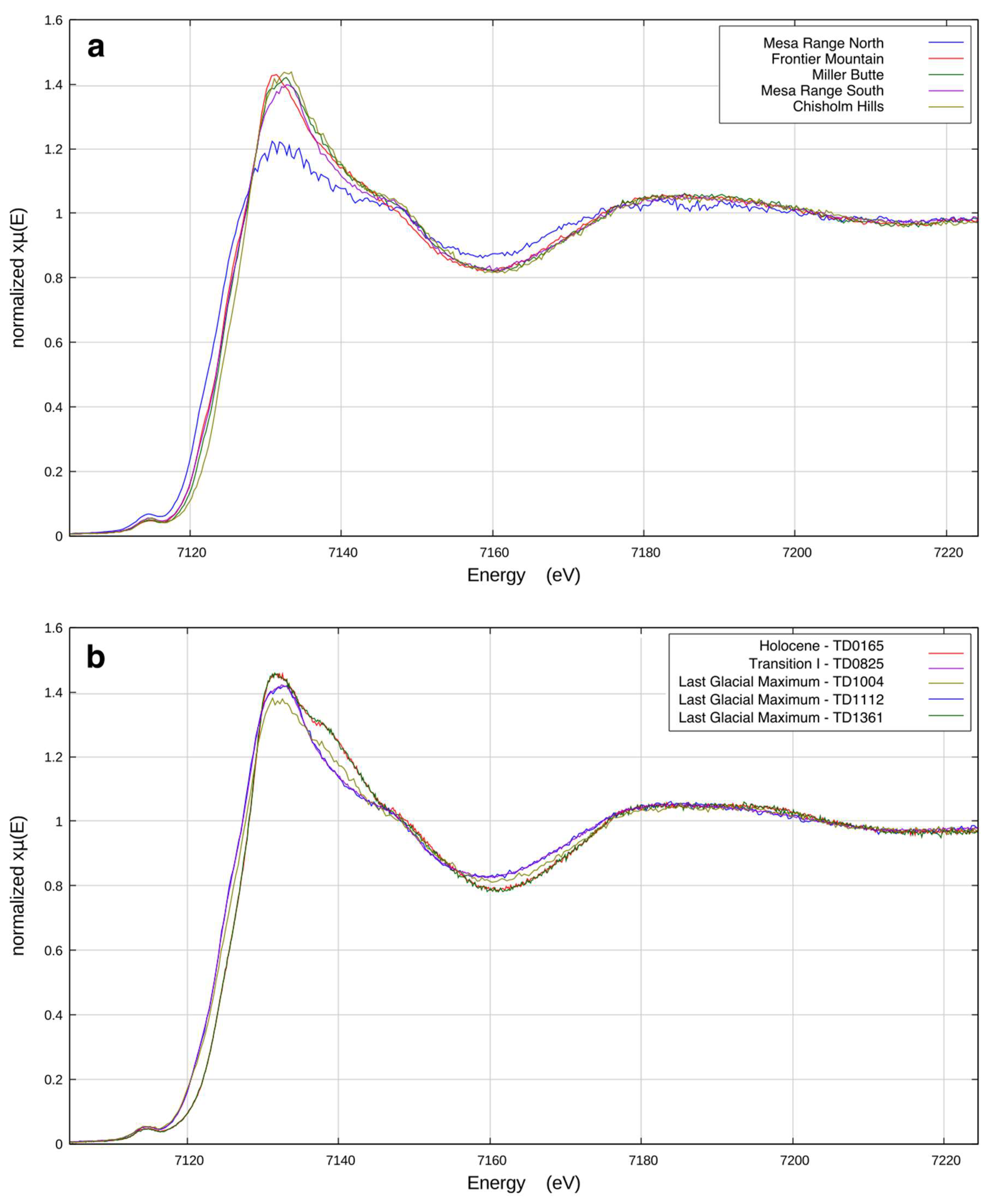
Figure 2.
(a) Comparison of Fe K-edge XANES spectra of soils from different local Antarctic sources; (b) and Fe K-edge spectra from different periods along the TD ice core.
Spectra were normalized using the pre-edge baseline, and the Fe K-edge (E0) was determined to be the inflection point, which is the maximum of the first derivative (see Figure 3 and Figure SM2) or the zero of the second derivative of the XANES spectrum. To compare spectra, they were normalized at the same energy. For the interpretation and analysis of the data we considered the energy corresponding to the normalized signal intensity of 0.8. This choice was made to consider a robust value, minimizing possible electronic contributions at the edge [37]. The accuracy of the method was monitored measuring between one sample and another, the XANES spectrum related to a metallic Fe foil. In this way it was possible to maintain the same energy calibration during the entire run. Conversely, precision was evaluated acquiring the Fe K-edge XANES spectrum of the NIST soil standard reference material (SRM 2709a, San Joaquin soil). It can be seen in Table 1 that the standard deviation of three successive acquisitions is 0.18 eV, a value lower than the detector spectral resolution.
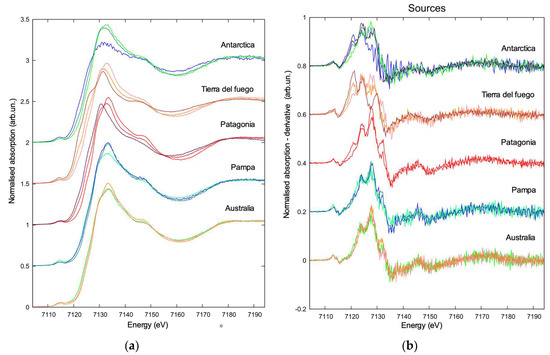
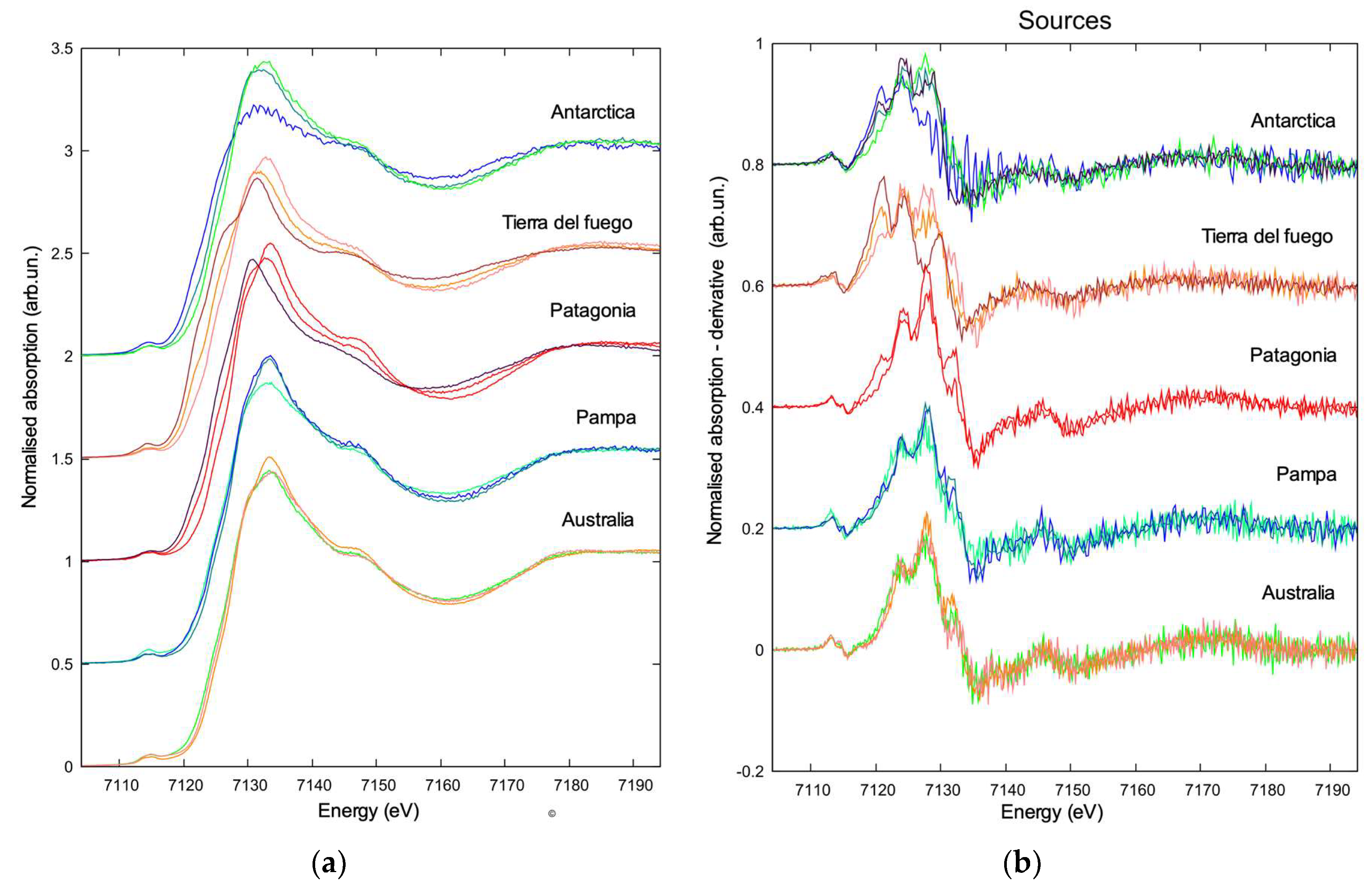
Figure 3.
(a) Comparison of Fe K-edge XANES spectra for some representative spectra PSAs discussed in the text; (b) comparison of the first derivative of the XANES spectra at the Fe K-edge for the representative spectra of sources discussed in the text.

Table 1.
The main statistics parameters of PSA from the analysis of the Fe K-edge XANES spectra.
Additional representative XANES spectra of PSA are showed in Figure 3 to demonstrate the variability of these spectra as determined by the mixture of different iron oxides present in the soils from different PSA. Some TD ice core samples are shown, together with their first derivative in Figures SM1 and SM2 in the Supplementary Materials.
3. Results
3.1. The PSA Fe K-Edge Energy Measurements
A summary concerning the data about the Fe K-edge of the PSA samples is reported in Table 1, whereas the Student T-tests applied to data to highlight significant differences between the samples (see Table SM1 of the Supplementary Materials). Australia presents the higher Fe K-edge energy, reflecting a strong oxidation of Fe, an expected scenario due to the climatic and environmental conditions of this continent. Australian PSAs are related to temperate and tropical climatic conditions and highly stable surfaces, characterized by long exposure histories. Such features determine a strong chemical weathering and the occurrence of highly evolved outcrops and soils. Under similar conditions oxidation processes and the in situ formation of iron oxides are both favored [46,47].
Typical soils found in Southern Australia are oxisols, Alfisols podzols, prairie soils and red earth soils [http://www.clw.csiro.au/aclep/soilandlandscapegrid/]; their rusty colors directly reflect the presence of Fe3+, in agreement with XANES spectra that show a high Fe K-edge energy (average value 7126.7 eV), compatible with an almost complete oxidation of the Fe fraction present in these soil samples. In addition to the high oxidation, another feature characterizing the Australian samples is the homogeneity. In these samples the Fe K-edge energy ranges from 7126.39 eV to 7126.93 eV, with a very low standard deviation: 0.14 eV (see also Figure 4).
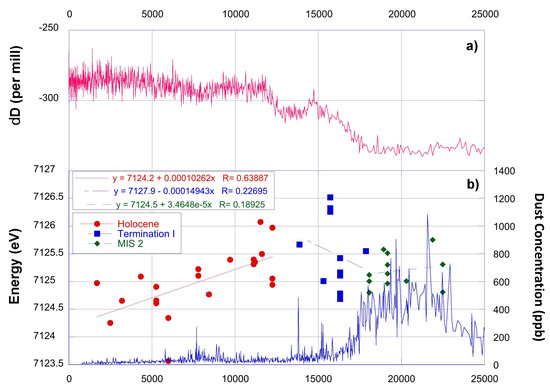
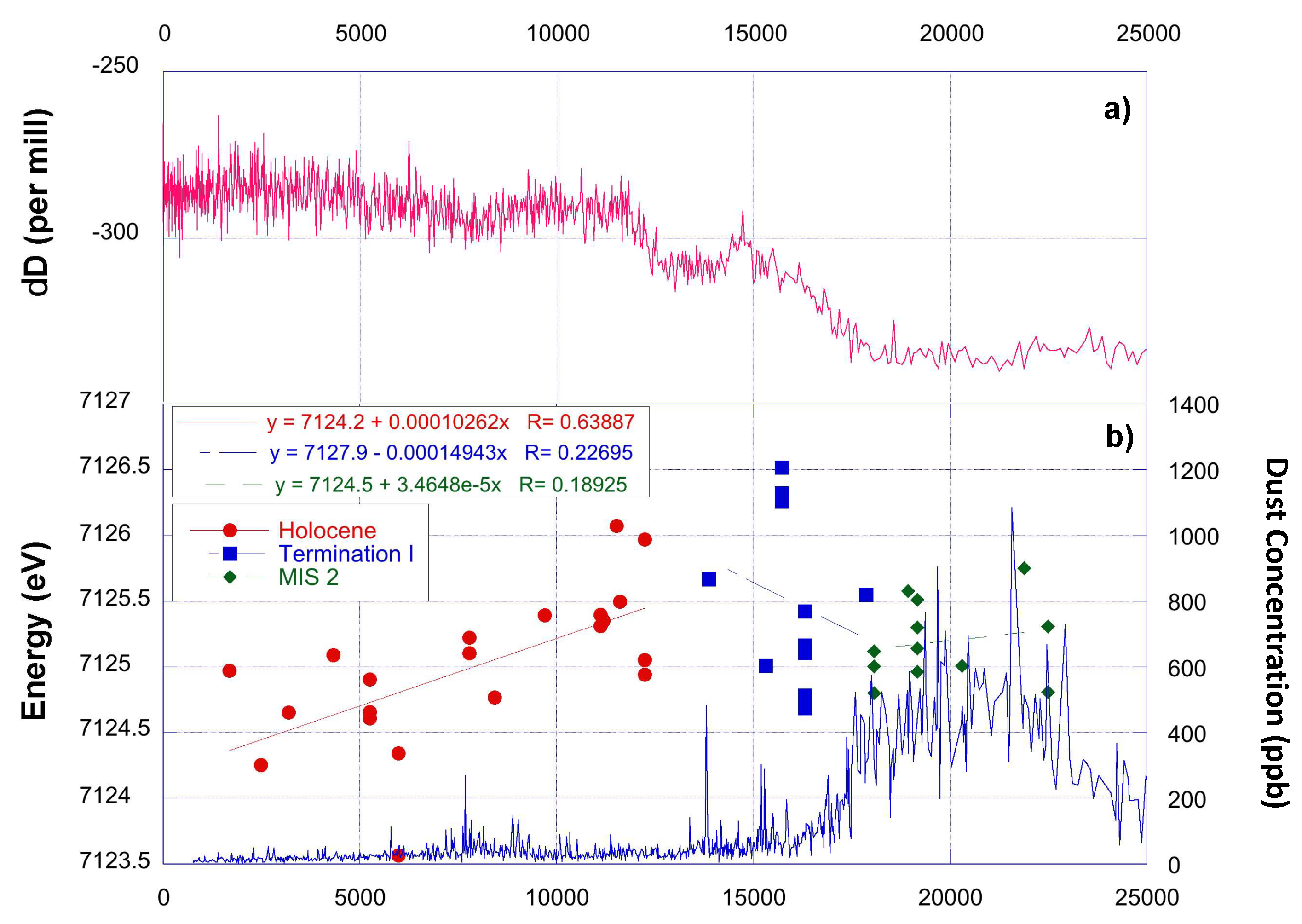
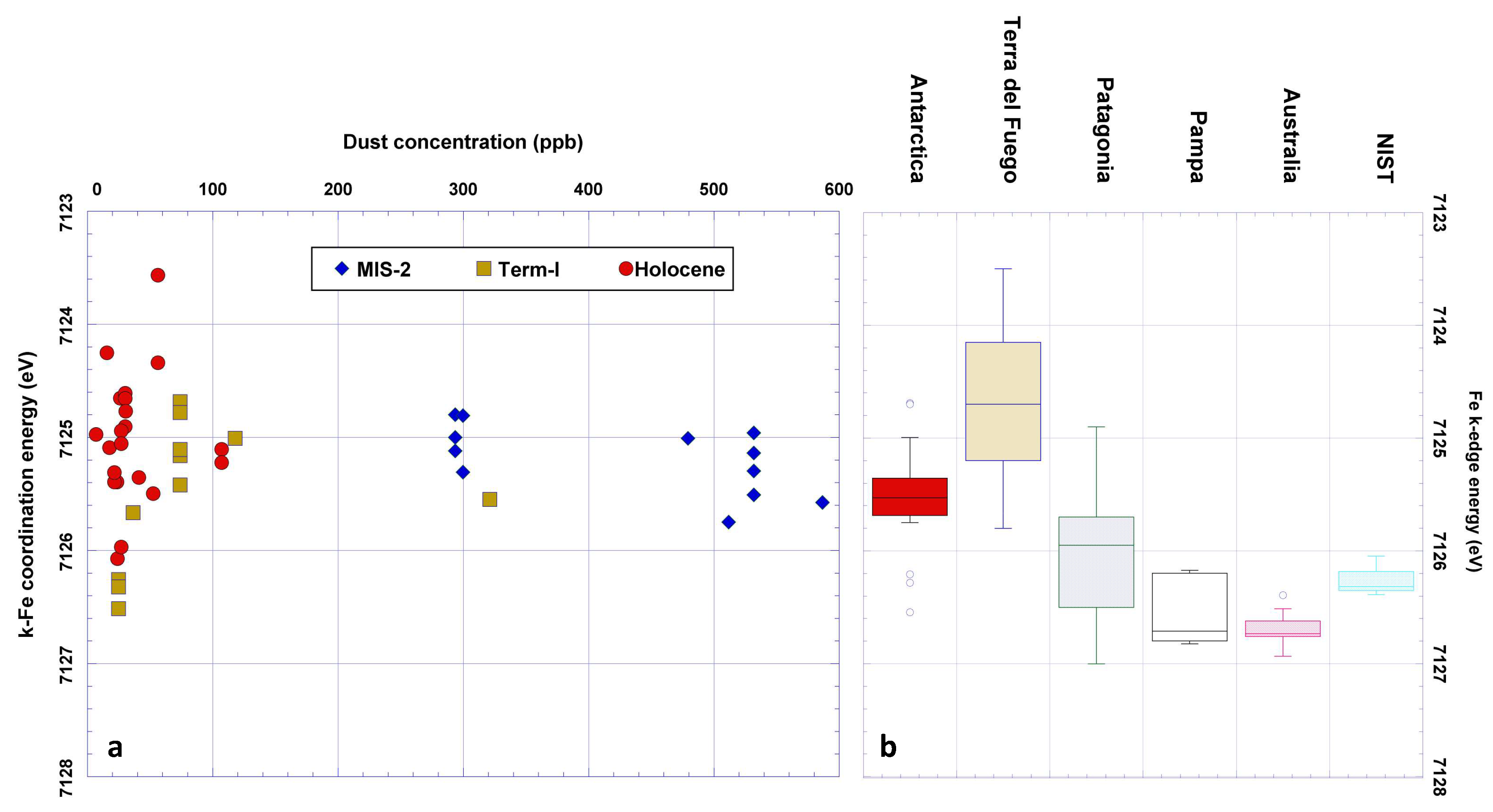
Figure 4.
(a) the TD stable isotope record indicating the climatic changes between MIS2 and Holocene (pink line, [48]). (b) the TD dust mass concentration record (blue line [22,34]) and the Fe K-edge energy positions obtained through from the XANES analysis (circles, square, diamonds for Holocene, Termination I and MIS2 samples, respectively). In the insets, linear regressions are added, together with the equations and the correlation coefficients.
This is a relevant result since Australian PSA samples were collected in different geographic and climatic areas. On the contrary, South America PSA samples [49] are characterized by a wider range of Fe K-edge energy (from 7123.5 eV to 7127.0 eV). This evidence suggests a wide latitudinal extension of the PSA considered in this work (ranging from 30° S to 55° S), implying very different climatic regimes. For this reason, South America samples have been divided into three sub-groups related to their geographical provenance: Pampas—Central Argentina (30°–45° S), Patagonia (45°–52° S) and Tierra del Fuego (south of 52° S). Figure 4 clearly shows an inverse relationship between Fe oxidation and latitude among the South America samples, while those from Pampas-central Argentina regions (30° S to 45° S) display a Fe K-edge energy range from 7126 to 7127 eV. Patagonian samples (45° S to 52° S) falls in a wider energy range from 7124.8 eV to 7127 eV, while those of Tierra del Fuego (south of 52° S) show lower Fe K-edge energies, between 7123.5 eV and 7125.8 eV, suggesting conditions less favorable for oxidative processes. Such results show that the position of the Fe K-edge in South American PSA samples is strongly controlled by latitude and thus by the climatic conditions characterizing the different areas where samples were collected. The relatively high oxidation of the PSA samples from the Pampas—Central Argentina samples, comparable to the Australian ones, reflects the climatic and pedogenetic processes occurring in this region. The Pampa area is originating from soils produced by the strong alteration of acid parent materials (Andean rocks and volcanic products) and Mollisols and Alfisols. The latter are from the humid Pampa area where the pedogenetic processes are responsible for the processing formation of aluminum and iron oxides. Considering the arid mid-latitude area of the Central Argentinean plateau, Entisols and Aridisols are common, pointing to a slower, but active, oxides formation [50]. Despite the presence of soils that are very similar to the ones found on the central Argentina plateau, Patagonian samples present lower energies for the Fe K-edge, in accordance to less oxidized conditions. This could be related to the temperate-to-cold climatic conditions found in Patagonia. Here, the degree of chemical weathering is weakened by the low temperatures and reduces the oxidation processes [50]. Finally, the semi-arctic climate of Tierra del Fuego easily explains the occurrence of very low Fe K-edge energies that confirms poor chemical weathering and a larger amount of Fe2+. It should be also considered that during the LGM, this region was extensively covered by a continental ice cap whose presence was responsible for the massive production and deposition of glacial and volcanic sediments. Given the cold climate and the recent deposition of such sediments, it is reasonable to associate these samples to a less weathered geochemical signature.
Focusing on the Antarctic PSA samples, it would have been expected to find very low values for the energy of the Fe K-edge, owing to the cold and dry climate of Victoria Land, not favorable to chemical weathering and to the development of soils conditions [17]. Cryoturbation and permafrost processes represent the only active mechanism [51]. XANES results partly support these considerations. Despite the average Fe K-edge energy of Antarctic PSA is actually the lower one among the considered regions (7125.5 eV, see also Figure 4 and Table 1), its variability is high, and some samples shows a moderately high energy, reflecting a relevant Fe oxidation. Only South America PSA showed a larger variability, but in this case a wide geographical area was considered, at variance of the Antarctic samples. All the Antarctic PSA were indeed collected in Victoria Land, representing the major area with free-ice of this Antarctic sector, within a few hundred km. To explain the high variability, it is necessary to consider additional factors. At first Antarctic PSA considered in this work are both ‘primary’ dust sources, for example regoliths, i.e., the primary product deriving from the alteration (chemical and mostly physical) of the many ice-free rocky outcrops characterizing Victoria Land, and ‘secondary’ sources. The latter consist in PSA samples obtained from reworked and mixed deposits, composed by sediments that were already subjected to transport, for example glacial drifts, and aeolian deposits, as it was extensively described in earlier studies [17]. In addition, we must underline that Victoria Land presents a complex geological history, resulting in the outcropping of many different lithologies within a few km. A final, but important feature, is the long exposure history of many ice-free sites of Victoria Land, that in some cases remained deglaciated for several million years. Such long exposure ages and the occasional occurrence of favorable conditions for chemical weathering [17,52] could explain the high Fe K-edge energy displayed by some of these Antarctic samples.
3.2. Talos Dome Mineral Dust
The dust record of the Talos Dome ice core over the last 25 ky reflect the effects related to the climatic transition from the last glacial period to the current interglacial one, the Holocene. The effects on the dust cycle are well known: a drastic decrease of the atmospheric dust burden. It was related to environmental and atmospheric changes that affected the southern hemisphere during this period [20]. At Talos Dome the dust depositional flux during the LGM was 6–7 times higher than in the Holocene [19]. As for the EPICA Dome C ice core, typical Holocene dust concentrations in ice at Talos Dome were reached around 14.6 ky BP, just before the Antarctic Cold Reversal, about 3000 years before the effective onset of the Holocene, likely because of changes in the hydrologic cycle [6]. Interestingly, the position of the Fe K-edge energy of Talos Dome ice core dust samples does not follow the dust concentration during the last 25 ky (Figure 4a), but is more likely correlated with the assemblage of Fe-bearing minerals that determining the final shape of the XANES spectra also tune the energy at the Fe K-edge. Data are summarized in Table 2, whereas the Student T-tests are reported in the Table SM2 in the Supplementary Materials.

Table 2.
The statistical parameters related to the energy position of the Fe K-edge in the Talos Dome ice core mineral dust samples for the different climatic periods considered in this work.
MIS2 presents a low variability of the Fe K-edge (mean energy 7125.19 ± 0.09 eV), despite dust mass concentration changes measured in this period (between 300 and 800 ng g−1). This evidence points to a homogeneous dust composition in term of Fe content minerals and supports the hypothesis that during glacial periods dust transported to Antarctica is uniform at the continental scale [20].
The end of MIS2 occurred at around 18 ky BP, corresponding to the onset of the last deglaciation, also known as Termination I (Figure 4a). This is an intermediate climatic period when changes from full glacial to interglacial conditions occurred. The relevant climatic and environmental changes that characterized this period are also confirmed by the dust concentration record of the Talos Dome ice core, which shows a significant decrease of the concentration (Figure 4b). Also, the Fe K-edge energy was affected by the climatic transition. In this period, it shows a high variability and slightly higher average values with respect to MIS2 (mean: 7125.50 ± 0.63 eV).
During the Holocene, i.e., the current interglacial, the transition edge decreases quite uniformly during the entire climatic period. From early to late Holocene a linear decreasing trend is recognized (Figure 4b). The variance (0.32) and standard error (0.12) of the iron K-edge energy position remain high also during the Holocene (Table 2). It must be noted that this could be related to the extremely low dust concentration during this period. However, it is evident that a change from more to less oxidized iron-bearing mineral phases occurred during the Holocene and the last part of Termination I (the last 13,500 years).
4. Discussion
The energy of the Fe K-edge of PSA samples shows a clear difference between the less weathered areas of Antarctica and the more oxidized Australian samples, reflecting the strong climatic differences of these southern hemisphere regions (Figure 5b). Not only PSA, but also Talos Dome mineral dust samples present a relevant variability with respect to the Fe mineral composition, in particular when considering the three climatic periods that define the last 25 kyrs (Figure 5a and Student T-tests in Table SM3 in the Supplementary Materials). In the last glacial period the Fe oxidation of TALDICE dust is compatible with a South American provenance from Patagonia and Tierra del Fuego (the average iron K-edge energy for the Talos Dome MIS2 dust is 7125.2 eV, while the average for the PSA America origins from Patagonia and Tierra del Fuego is 7124.7 and 7125.6 eV respectively) although we cannot rule out also the Antarctic sources, owing to a mean K-edge transition that is very close to the one of southern South America samples (average value 7125.5 eV). When complementary data are considered, it is very likely that the Antarctic local contribution was actually present during MIS2, also considering that many Antarctic PSAs were ice-free also during this period [17,52], being probably negligible considering the intense contribution from South America. During Termination I the transport of dust from South America to Antarctica decreased, mainly because of changes in the hydrological cycle. The iron K-edge energy in this period shows evident changes. The beginning of Termination I is characterized by an increase of Fe oxidation (increase of the Fe K-edge energy), decreasing in the next period, and this trend is maintained during the entire Holocene.
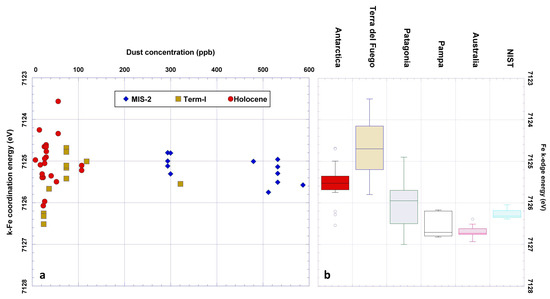
Figure 5.
(a) The mineral dust concentration vs. Fe K-edge energy for different climatic periods of TD samples, and (b) the box-plot of the Fe K-edge energy of the different PSA samples compared to the NIST standard.
The position of the Fe K-edge shift obtained considering the linear fit shown in Figure 4b changes from 7125.5 eV at the beginning of the Holocene (12 Kyr BP), to less oxidized values during late Holocene (7124.4 eV at 2.5 Kyr BP) when the local dust contribution became more relevant. It suggests that the shift to interglacial conditions determined a first increase of the Fe oxidation, probably related to a first mobilization of the glacial deposits accumulated during MIS2 and heavily reworked. Successively the position of the edge starts decreasing, and the trend persists across the entire Holocene. It is responsible for the decrease of the Fe K-edge from the maximum value of 7126.1 eV at 12 ky BP to the minimum value of 7124.2 at 2.5 ky BP. The lower value (7123.55 eV) is from one sample at 6 ky BP, with a possible volcanic contamination. Two hypotheses can interpret these findings:
- the geochemical properties of the dust deposited at TD change in relation to environmental and climatic modifications of the PSA [44];
- the shift from glacial to interglacial conditions impacted the dust cycle and the atmospheric circulation at TD, with changes in terms of dust provenance and of the relative contribute from different PSA.
The climatic shift from cold and dry conditions of MIS2 to the interglacial period, characterized by a wetter and warmer climate, affected the production and emission of dust over the continents, with further consequences concerning the pedogenetic processes. Interglacial conditions, thanks to the reinforcement of the hydrological cycle and to an increase of temperatures, favor chemical alterations and oxidative processes with an expected increase of the Fe K-edge energy. If the first hypothesis was correct, we would have appreciated an increase of the Fe K-edge as a consequence of the last climatic transition, with a strong increasing oxidation (higher transition energies), characterizing the Talos Dome Holocene dust. This is exactly the opposite of what has been actually observed (Figure 4b). Consequently, the second hypothesis based on the change in the relative weight of the different sources, appears the best scenario to explain the Holocene presented in Figure 4b. In agreement with earlier studies [19,21] we suggest that during the deglaciation and Early Holocene a progressive change in terms of active dust sources with respect to TD occurred. While the transport of dust from South America progressively decreased, local Antarctic sources gained importance and became dominant, with possible but minor contributions also from Australia, in agreement with climate models [45]. This second scenario can thus explain the less oxidized Fe signature observed during the Holocene with lower Fe K-edge energies, as expected for dust emitted by high altitude glacial deposits and regoliths from Northern Victoria Land, such as those present in the Mesas outcropping area [21]. The role played by local Antarctic sources is also supported by the dust grain size distributions observed in Talos Dome ice core samples (Figure 4b and Figure 5a). They are containing local coarse particles (5–10 µm diameter). Although present both during MIS2 and Holocene, these coarse particles became more abundant in relative terms during the Holocene and especially during late Holocene, when they account for 50–70% of total dust mass [17].
The possible role played by in situ oxidation of Fe minerals within ice is not discussed here, despite preliminary results showed its relevance only in very deep ice, in agreement with what already observed in the EPICA Dome C ice core [53] and, in the case of TALDICE below 1400 m [54].
In summary, the XANES-based Fe speciation analysis permits to evaluate the different contributions of mineral dust from the possible source areas that supply dust to the East Antarctic plateau. Some difficulties remain to distinguish unambiguously the contribution of some geographically different sources with similar Fe oxidation conditions, and only a comprehensive mineralogical study may help to clarify the role of different sources. However, as already demonstrated by many researches on mineral samples containing iron atoms in both tetrahedral and octahedral sites a clear energy shifts by 2–3 eV to high energy is observed increasing the Fe3+ occupancy. Moreover, as shows in Ref. [48] the iron T-O distances are typically much lower than 2 Å (1.65–1.66 Å) while octahedral distances are greater than 2 Å (2.06–2.11 Å). In addition, to the different potentials due to the symmetry, a tetrahedral iron coordination should give a strong pre-edge feature while the difference in distance of 20–25% should also imply a clear shift of the XANES features. Consequently, in our samples the fractional presence of tetrahedral coordinated iron would give rise to a significant shift in the edge position and of the XANES features. The joint analysis of pre-edge and XANES features indicates that tetrahedral/non-centro-symmetrical components, if present, are small or negligible. A discussion on the analysis of the pre-edge of iron in octahedral site in minerals has been recently published [55].
Despite the limitations, spectroscopic data presented in this contribution support earlier evidence of a South American provenance for the dust deposited in peripheral East Antarctica during MIS2 and highlights a progressive enhancement in the relative proportion of local dust sources during the Holocene. Although preliminary, this research is the first attempt to extract climatic information from XANES spectroscopic data obtained from the analysis of insoluble mineral dust particles contained in an ice core. Although other methods such as the analysis of the pre-edge: centroid and/or fit, represent powerful approach that can be used for the Fe speciation, at present we cannot obtain a reliable Fe K-edge dataset to compare with the high concentrated PSA samples because of the very low concentration and the complex composition of the mineral dust trapped in the Antarctic ice. For the same reason, the possibility to extract the Fetot/Fe3+ ratio is not yet possible at this stage.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2410-3896/3/4/45/s1.
Author Contributions
V.M., G.B., B.D. performed the TALDICE paleoclimatic interpretation and sources/ice core relationships; C.M., G.C., D.H. performed the experiments at Diamond, and data analysis of XAFS spectra. All authors wrote the manuscript and contributed to the discussion/interpretation of the results.
Funding
Part of this research has been also founded by Italian National Antarctic Program project n° PNRA 2013/B2.10, PI S. Rocchi (UNIPI). The support of DARA Department of the Italian Presidenza del Consiglio dei Ministri is gratefully acknowledged.
Acknowledgments
This research is a collaboration made among Milano-Bicocca University, INFN-Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, and the Diamond Light Source facility. Part of the sample preparation was performed at the EuroCold Lab at University of Milano-Bicocca, founded by Italian National Science Foundation Next Data Project. XANES spectra were collected in the framework of Proposals 90U5 and 3082M at SSRL, a national user facility operated by Stanford University on behalf of the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic E he iron T-O distances are typically mnergy Sciences. XANES measurements were also performed at Diamond, the UK national synchrotron radiation facility in the framework of the proposal NT1984 and at ESRF within the experiment 08-01-1031 on Beamline BM08. We strongly acknowledge the staff of the Italian CRG LISA for support of XANES measurements at the beamline BM08 at ESRF within the experiment 08-01-1031 and for many fruitful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Maher, B.A.; Prospero, J.M.; Mackie, D.; Gaiero, D.; Hesse, P.P.; Balkanski, Y. Global connections between aeolian dust, climate and ocean biogeochemistry at the present day and at the last glacial maximum. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 61–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, V. Mineralogy of atmospheric microparticles deposited along the Greenland ice core project ice core. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1997, 102, 26725–26734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, V.; Petit, J.R. Atmospheric dust concentration record from the Hercules neve firn core, northern Victoria land, Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 1998, 27, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, V.; Villa, S.; Finizio, A.; Delmonte, B.; Casati, P.; Marino, F. Variability of anthropogenic and natural compounds in high altitude-high accumulation alpine glaciers. Hydrobiologia 2006, 562, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickells, T.; Boyd, P.; Hunter, K.A. Biogeochemical impacts of dust on the global carbon cycle. In Mineral Dust; Knippertz, B., Stuut, J.B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 359–384. [Google Scholar]
- Delmonte, B.; Basile-Doelsch, I.; Petit, J.; Maggi, V.; Revel-Rolland, M.; Michard, A.; Jagoutz, E.; Grousset, F. Comparing the epica and vostok dust records during the last 220,000 years: Stratigraphical correlation and provenance in glacial periods. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2004, 66, 63–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmonte, B.; Andersson, P.; Hansson, M.; Schoberg, H.; Petit, J.; Basile-Doelsch, I.; Maggi, V. Aeolian dust in east Antarctica (epica-dome c and vostok): Provenance during glacial ages over the last 800 kyr. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, F.; Delmonte, B.; Petit, J.R.; Bigler, M.; Kaufmann, P.R.; Hutterli, M.A.; Stocker, T.F.; Ruth, U.; Steffensen, J.P.; Maggi, V. Dust—Climate couplings over the past 800,000 years from the Epica dome c ice core. Nature 2008, 452, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmonte, B.; Petit, J.R.; Krinner, G.; Maggi, V.; Jouzel, J.; Udisti, R. Ice core evidence for secular variability and 200-year dipolar oscillations in atmospheric circulation over east Antarctica during the Holocene. Clim. Dyn. 2005, 24, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel-Rolland, M.; De Deckker, P.; Delmonte, B.; Hesse, P.; Magee, J.; Basile-Doelsch, I.; Grousset, F.; Bosch, D. Eastern Australia: A possible source of dust in east Antarctica interglacial ice. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 249, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezzotti, M.; Pourchet, M.; Flora, O.; Gandolfi, S.; Gay, M.; Urbini, S.; Vincent, C.; Becagli, S.; Gragnani, R.; Proposito, M.; et al. Spatial and temporal variability of snow accumulation in east Antarctica from traverse data. J. Glaciol. 2005, 51, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarchilli, C.; Frezzotti, M.; Ruti, P. Snow precipitation at four ice core sites in east Antarctica: Provenance, seasonality and blocking factors. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 2107–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallelonga, P.; Gabrielli, P.; Balliana, E.; Wegner, A.; Delmonte, B.; Turetta, C.; Burton, G.; Vanhaecke, F.; Rosman, K.; Hong, S.; et al. Lead isotopic compositions in the epica dome c ice core and southern hemisphere potential source areas. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, I.; Grousset, F.; Revel, M.; Petit, J.; Biscaye, P.; Barkov, N. Patagonian origin of glacial dust deposited in east Antarctica (Vostok and Dome c) during glacial stages 2, 4 and 6. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1997, 146, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grousset, F.; Biscaye, P.; Revel, M.; Petit, J.; Pye, K.; Joussaume, S.; Jouzel, J. Antarctic (dome c) ice-core dust at 18 ky bp—Isotopic constraints on origins. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1992, 111, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezzotti, M.; Bitelli, G.; De Michelis, P.; Deponti, A.; Forieri, A.; Gandolfi, S.; Maggi, V.; Mancini, F.; Remy, F.; Tabacco, I.; et al. Geophysical survey at talos dome, east antarctica: The search for a new deep-drilling site. Ann. Glaciol. 2004, 39, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmonte, B.; Baroni, C.; Andersson, P.; Schoberg, H.; Hansson, M.; Aciego, S.; Petit, J.; Albani, S.; Mazzola, C.; Maggi, V.; et al. Aeolian dust in the talos dome ice core (east Antarctica, pacific/ross sea sector): Victoria land versus remote sources over the last two climate cycles. J. Quat. Sci. 2010, 25, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccolo, G.; Clemenza, M.; Delmonte, B.; Maffezzoli, N.; Nastasi, M.; Previtali, E.; Prata, M.; Salvini, A.; Maggi, V. A new method based on low background instrumental neutron activation analysis for major, trace and ultra-trace element determination in atmospheric mineral dust from polar ice cores. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 922, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, F.; Calzolai, G.; Caporali, S.; Castellano, E.; Chiari, M.; Lucarelli, F.; Maggi, V.; Nava, S.; Sala, M.; Udisti, R. Pixe and pige techniques for the analysis of antarctic ice dust and continental sediments. Nuclear Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B-Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2008, 266, 2396–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmonte, B.; Paleari, C.; Ando, S.; Garzanti, E.; Andersson, P.; Petit, J.; Crosta, X.; Narcisi, B.; Baroni, C.; Salvatore, M.; et al. Causes of dust size variability in central east Antarctica (dome b): Atmospheric transport from expanded south American sources during marine isotope stage 2. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 168, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickells, T.; An, Z.; Andersen, K.; Baker, A.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Cao, J.; Boyd, P.; Duce, R.; Hunter, K.; et al. Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate. Science 2005, 308, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.; Baker, A.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Duce, R.; Jickells, T.; Kubilay, N.; Prospero, J.; Tegen, I. Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, S.; Queguiner, B.; Armand, L.; Belviso, S.; Bombled, B.; Bopp, L.; Bowie, A.; Brunet, C.; Brussaard, C.; Carlotti, F.; et al. Effect of natural iron fertilization on carbon sequestration in the southern ocean. Nature 2007, 446, 1070–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspari, V.; Barbante, C.; Cozzi, G.; Cescon, P.; Boutron, C.; Gabrielli, P.; Capodaglio, G.; Ferrari, C.; Petit, J.; Delmonte, B. Atmospheric iron fluxes over the last deglaciation: Climatic implications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.; Sedwick, P.; Morgan, V.; Boutron, C. Iron in ice cores from law dome: A record of atmospheric iron deposition for maritime east antarctica during the holocene and last glacial maximum. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolaor, A.; Vallelonga, P.; Cozzi, G.; Gabrieli, J.; Varin, C.; Kehrwald, N.; Zennaro, P.; Boutron, C.; Barbante, C. Iron speciation in aerosol dust influences iron bioavailability over glacial-interglacial timescales. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1618–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroth, A.; Crusius, J.; Sholkovitz, E.; Bostick, B. Iron solubility driven by speciation in dust sources to the ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K. The composition of the continental-crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccolo, G.; Maffezzoli, N.; Clemenza, M.; Delmonte, B.; Prata, M.; Salvini, A.; Maggi, V.; Previtali, E. Low-background neutron activation analysis: A powerful tool for atmospheric mineral dust analysis in ice cores. J. Radioanal. Nuclear Chem. 2015, 306, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.; Jamieson, H.; Lanzirotti, A.; Andrade, C.; Hall, G. The speciation of arsenic in iron oxides in mine wastes from the giant gold mine, nwt: Application of synchrotron micro-xrd and micro-xanes at the grain scale. Can. Mineral. 2005, 43, 1205–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajt, S.; Sutton, S.; Delaney, J. X-ray microprobe analysis of iron oxidation-states in silicates and oxides using X-ray-absorption near-edge structure (xanes). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 5209–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galoisy, L.; Calas, G.; Arrio, M. High-resolution xanes spectra of iron in minerals and glasses: Structural information from the pre-edge region. Chem. Geol. 2001, 174, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawn, D.; Doner, H.; Zavarin, M.; McHugo, S. Microscale investigation into the geochemistry of arsenic, selenium, and iron in soil developed in pyritic shale materials. Geoderma 2002, 108, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prietzel, J.; Thieme, J.; Eusterhues, K.; Eichert, D. Iron speciation in soils and soil aggregates by synchrotron-based X-ray microspectroscopy (xanes, mu-xanes). Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, P.; Caquineau, S.; Chevaillier, S.; Klaver, A.; Desboeufs, K.; Rajot, J.; Belin, S.; Briois, V. Dominance of goethite over hematite in iron oxides of mineral dust from western Africa: Quantitative partitioning by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 12740–12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, M.; Farges, F.; Petit, P.; Brown, G.; Martin, F. Oxidation state and coordination of Fe in minerals: An fek-xanes spectroscopic study. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 714–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, A.; O’Neill, H.; Jayasuriya, K.; Campbell, S.; Foran, G. Xanes calibrations for the oxidation state of iron in a silicate glass. Am. Mineral. 2003, 88, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzarotti, A.; Bianconi, A.; Burattini, E.; Grandolfo, M.; Habel, R.; Piacentini, M. Core transitions from the al 2p level in amorphous and crystalline Al2O3. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 1974, 63, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, M.; Scafati, A.; Bianconi, A.; Mobilio, S.; Palladino, L.; Reale, A.; Burattini, E. X-ray absorption near edge structures (XANES) in simple and complex Mn compounds. Solid State Commun. 1980, 35, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfatto, M.; Natoli, C.R.; Bianconi, A.; Garcia, J.; Marcelli, A.; Fanfoni, M.; Davoli, I. Multiple-scattering regime and higher-order correlations in X-ray-absorption spectra of liquid solutions. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 34, 5774–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koningsberger, D.C.; Prins, R. (Eds.) X-ray Absorption: Principles, Applications, Techniques of EXAFS, SEXAFS, and XANES Chemical Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 2, pp. 1–673. [Google Scholar]
- Bianconi, A.; Fritsch, E.; Calas, G.; Petiau, J. X-ray-absorption near-edge structure of 3d transition elements in tetrahedral coordination: The effect of bond-length variation. Phys. Rev. B Condense. Matter 1985, 32, 4292–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, A.J.; Cibin, G.; Ramos, S.; Smith, A.D.; Scott, S.M.; Varandas, L.; Pearson, M.R.; Krumpa, N.A.; Jones, C.P.; Robbins, P.E. B18: A Core XAS Spectroscopy Beamline for Diamond. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 190, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelli, A.; Hampai, D.; Giannone, F.; Sala, M.; Maggi, V.; Marino, F.; Pignotti, S.; Cibin, G. Xrf-xanes characterization of deep ice core insoluble dust. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibin, G.; Marcelli, A.; Maggi, V.; Sala, M.; Marino, F.; Delmonte, B.; Albani, S.; Pignotti, S. First combined total reflection X-ray fluorescence and grazing incidence X-ray absorption spectroscopy characterization of aeolian dust archived in Antarctica and alpine deep ice cores. Spectrochim. Acta Part B-At. Spectrosc. 2008, 63, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, B.; Russell, J.; Wilson, M. Iron-oxide and clay-minerals and their relation to colors of red and yellow podzolic soils near Sydney, Australia. Geoderma 1975, 14, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Gilkes, R. Properties and distribution of iron-oxides and their association with minor elements in the soils of south-western Australia. J. Soil Sci. 1992, 43, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombolini, F.; Brigatti, M.F.; Marcelli, A.; Cibin, G.; Mottana, A.; Giuli, G. Local and average Fe distribution in trioctahedral micas: Analysis of Fe K-edge XANES spectra in the phlogopite–annite and phlogopite tetraferriphlogopite joins on the basis of single-crystal XRD refinements. Eur. J. Mineral. 2002, 14, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmonte, B.; Petit, J.; Basile-Doelsch, I.; Lipenkov, V.; Maggi, V. First characterization and dating of east Antarctic bedrock inclusions from Subglacial lake vostok accreted ice. Environ. Chem. 2004, 1, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoenfelt, E.; Sun, J.; Winckler, G.; Kaplan, M.; Borunda, A.; Farrell, K.; Moreno, P.; Gaiero, D.; Recasens, C.; Sambrotto, R.; et al. High particulate iron(ii) content in glacially sourced dusts enhances productivity of a model diatom. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmonte, B.; Andersson, P.; Schoberg, H.; Hansson, M.; Petit, J.; Delmas, R.; Gaiero, D.; Maggi, V.; Frezzotti, M. Geographic provenance of aeolian dust in east Antarctica during Pleistocene glaciations: Preliminary results from talos dome and comparison with east Antarctic and new Andean ice core data. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccolo, G.; Delmonte, B.; Albani, S.; Baroni, C.; Cibin, G.; Frezzotti, M.; Hampai, D.; Marcelli, A.; Revel, M.; Salvatore, M.C.; et al. Regionalization of the atmospheric dust cycle on the periphery of the East Antarctic ice sheet since the last glacial maximum. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Tison, J.L.; Morel-Fourcade, M.C.; Susini, J. Micro-investigation of EPICA Dome C bottom ice: Evidence of long term in situ processes involving acid-salt interactions, mineral dust, and organic matter. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 78, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccolo, G.; Cibin, G.; Delmonte, B.; Hampai, D.; Marcelli, A.; Di Stefano, E.; Macis, S.; Maggi, V. The Contribution of Synchrotron Light for the Characterization of Atmospheric Mineral Dust in Deep Ice Cores: Preliminary Results from the Talos Dome Ice Core (East Antarctica). Condens. Matter 2018, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdenzi, F.; Della Ventura, G.; Cibin, G.; Macis, S.; Marcelli, A. Accurate Fe3+/Fetot ratio from XAS spectra at the Fe K-edge. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).