Natural Bacterial Co-Infection in Farmed European Sea Bass Intended for Experimental Research in Sicily, Southern Italy: Pathological Findings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Clinical Signs
2.2. Postmortem Investigation
2.3. Pathological Examination
2.4. Microbiology
2.5. Molecular Analysis
3. Results
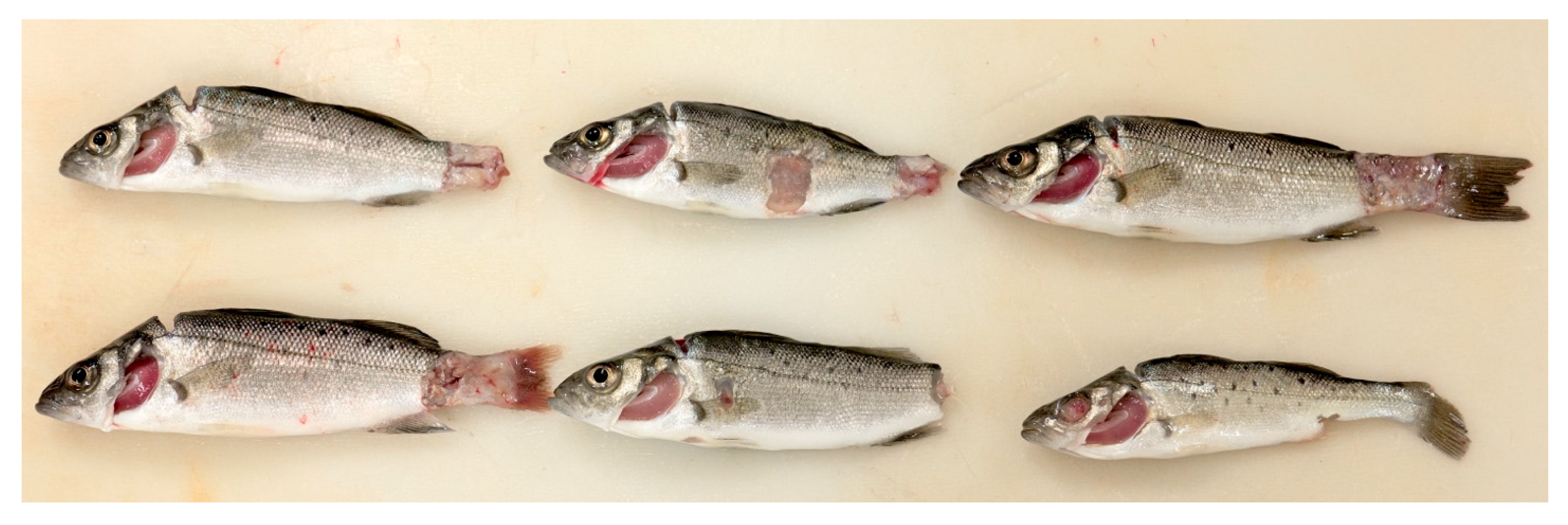
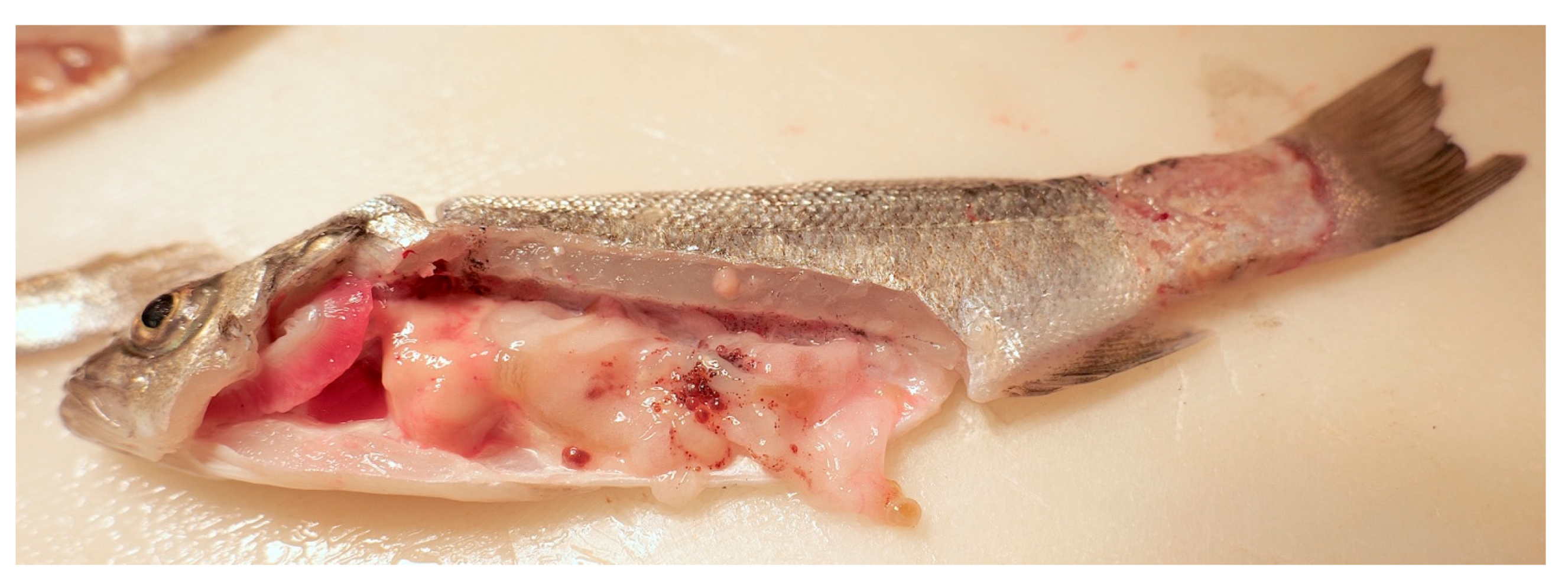
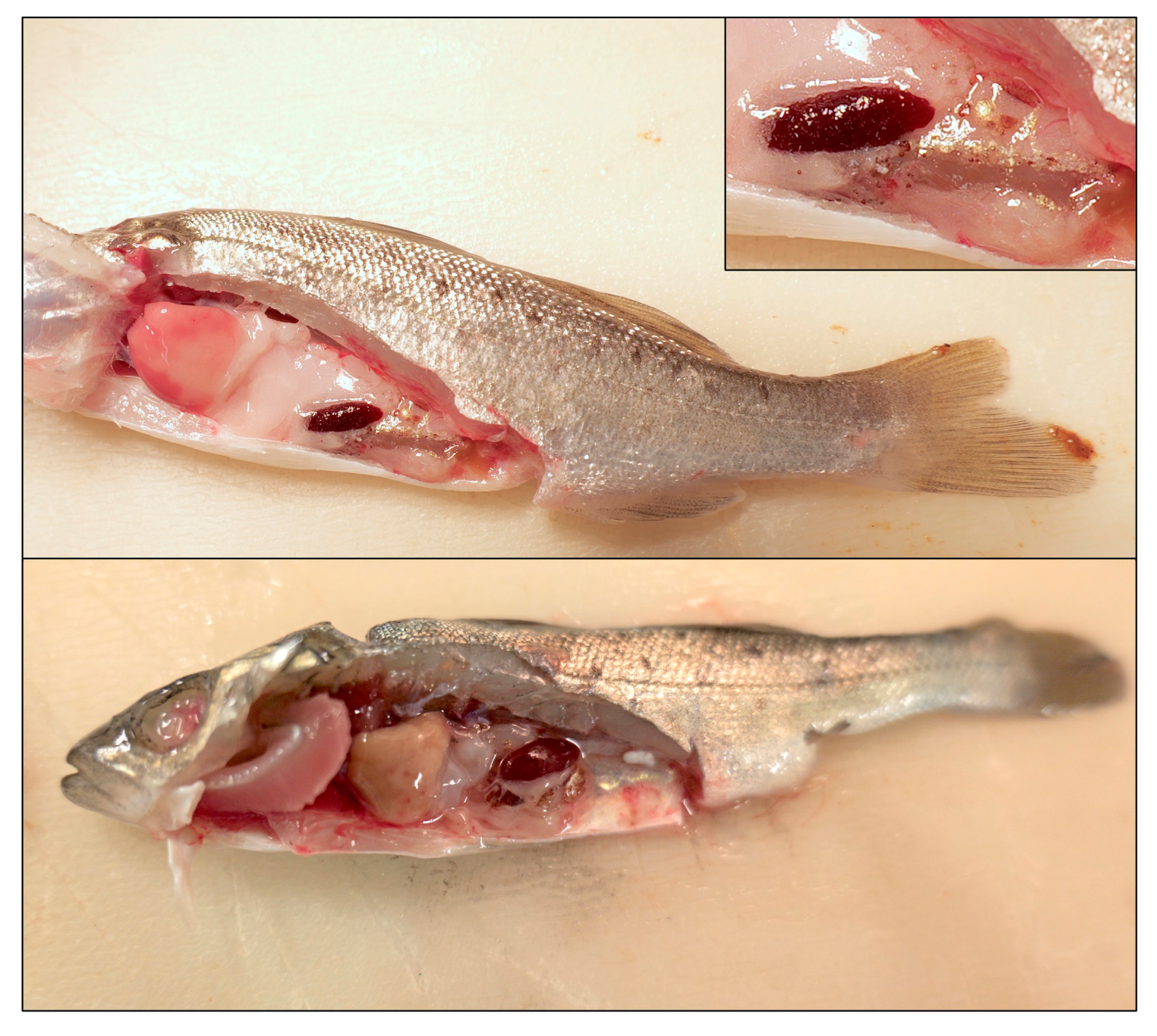
3.1. Study Population and Gross Pathological Findings
3.2. Cytology
3.3. Histopathology
3.3.1. Scaled Skin and Skeletal Muscle
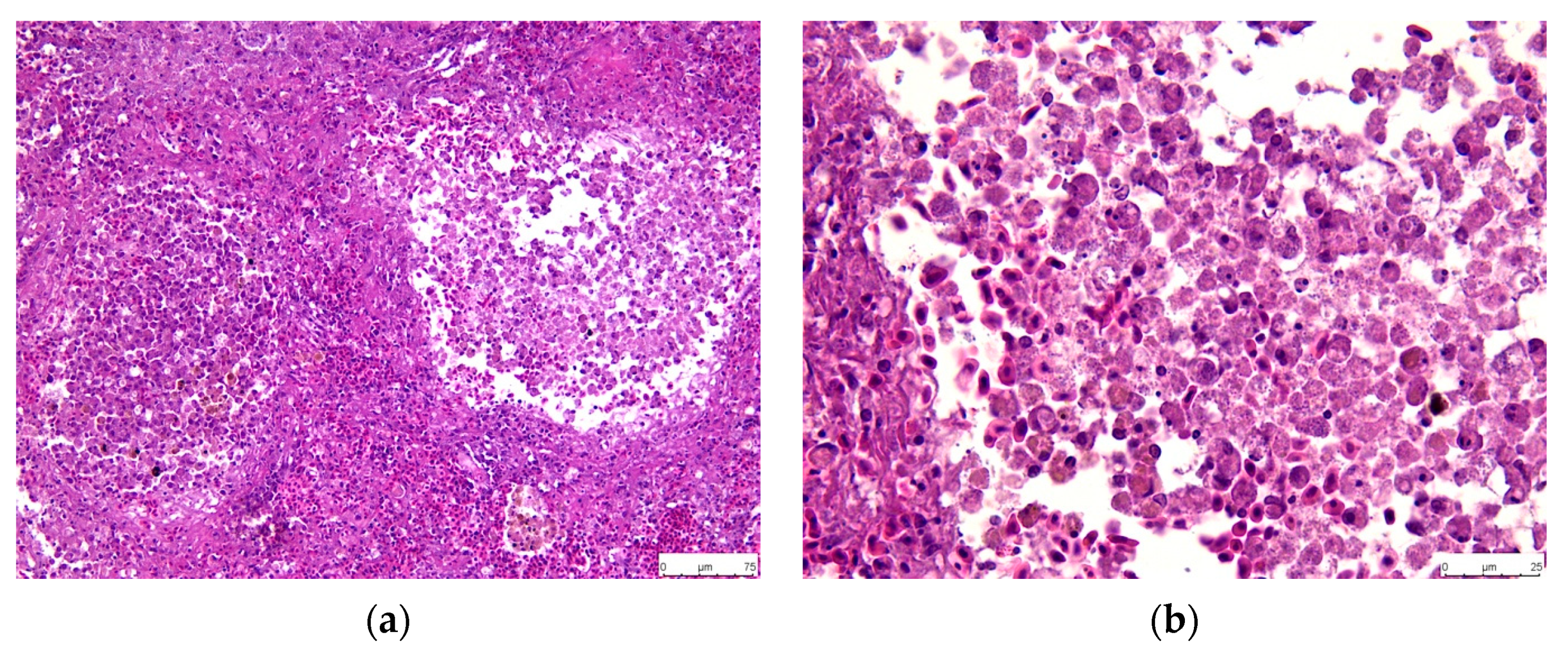
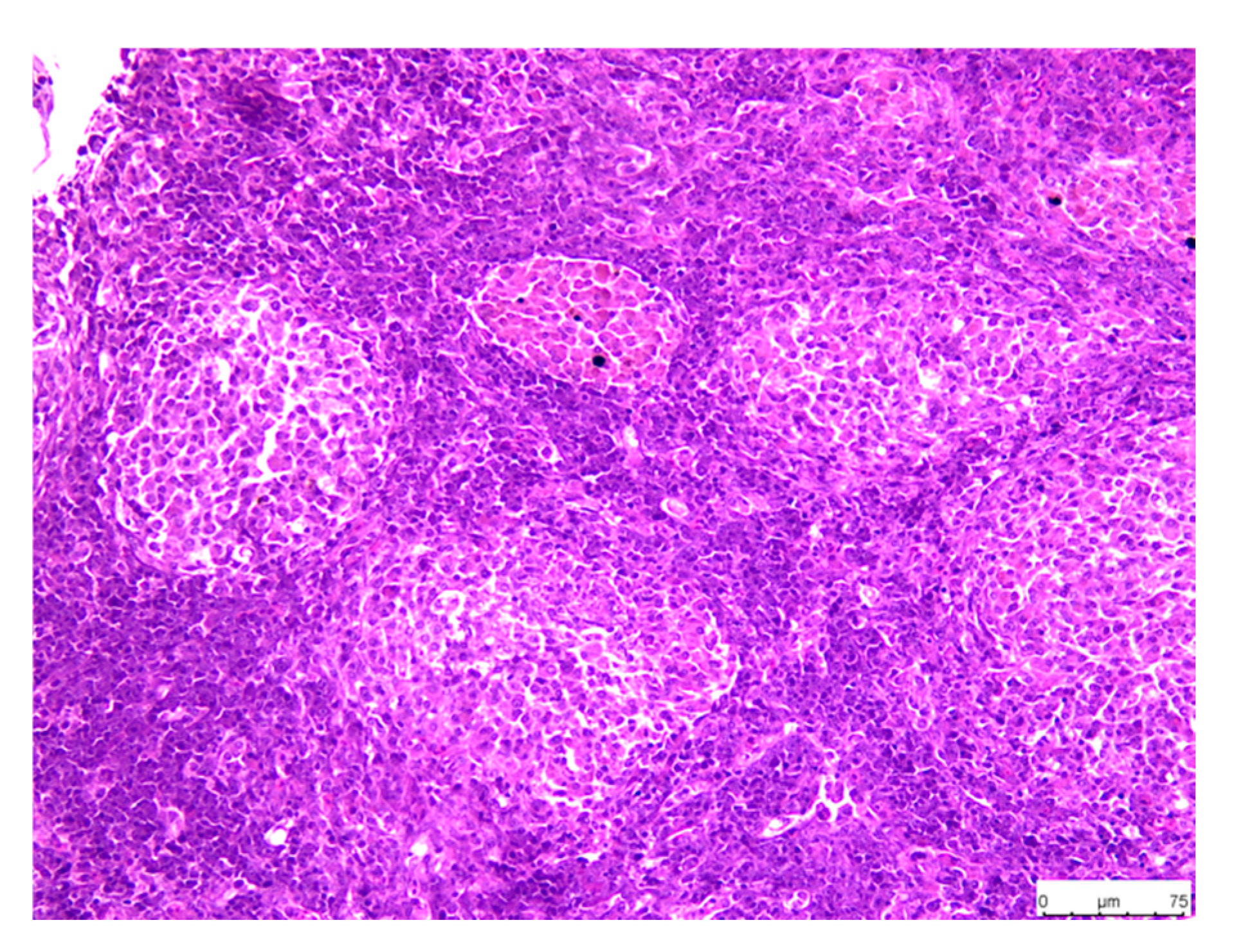
3.3.2. Spleen
3.3.3. Head Kidney
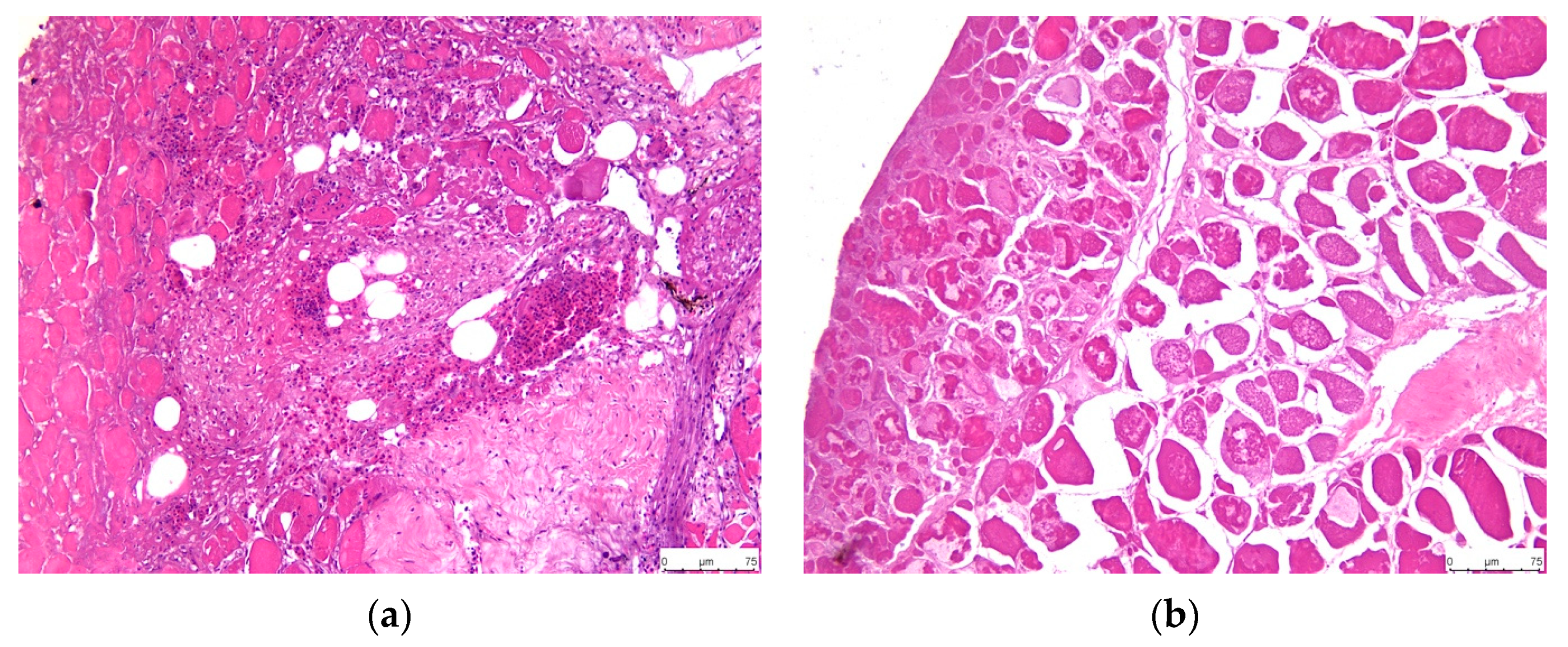
3.3.4. Abdominal Mesentery Fat
3.3.5. Liver
3.4. Isolation and Identification of the Bacterial Pathogens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vandeputte, M.; Gagnaire, P.A.; Allal, F. The European sea bass: A key marine fish model in the wild and in aquaculture. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. FishStatJ Dataset: Global Fishery and Acquaculture Production Statistics. Global Aquaculture Production 1950–2021 (Reales date: March 2021). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United States. 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/statistics/software/fishstatj (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Tziouvas, H.; Varvarigos, P. Intensity scale of side effects in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) post intraperitoneal injection with commercial oil-adjuvanted vaccines. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish. Pathol. 2021, 41, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches-Fernandes, G.M.; Sá-Correia, I.; Costa, R. Vibriosis Outbreaks in Aquaculture: Addressing environmental and public health concerns and preventive therapies using gilthead seabream farming as a model. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 904815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotob, M.H.; Menanteau-Lodouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of co-infections on fish: A review. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramin, N.; Zrncic, S.; Padros, F.; Oraic, D.; Le Breton, A.; Zarza, C.; Olesen, N.J. Fish Health in Mediterranean Aquaculture, Past Mistakes and Future Challenges. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish. Pathol. 2016, 36, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Le Breton, A.D. Mediterranean finfish pathologies. Present status and new developments in prophylactic methods. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish. Pathol. 1999, 19, 250–253. [Google Scholar]
- Evensen, Ø. Development of Fish Vaccines: Focusing on Methods. In Fish Vaccines, Birkhäuser Advances in Infectious Diseases; Adams, A., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, J.; Barber, I.; Boag, B.; Ellison, A.R.; Morgan, E.R.; Murray, K.; Pascoe, E.L.; Sait, S.M.; Wilson, A.J.; Booth, M. Global change, parasite transmission and disease control: Lessons from ecology. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Vibrionaceae representatives. In Bacterial Fish Pathogens: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 357–411. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberghe, J.; Thompson, F.L.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Swings, J. Phenotypic diversity amongst Vibrio isolates from marine aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2003, 219, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniesa, A.; Basurco, B.; Aguilera, C.; Furones, D.; Reverté, C.; Sanjuan-Vilaplana, A.; Jansen, M.D.; Brun, E.; Tavornpanich, S. Mapping the knowledge of the main diseases affecting sea bass and sea bream in Mediterranean. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanayake, T.; Salleh, A.; Noor Azmai Amal, M.; Salwany Md Yasin, I.; Zamri-Saad, M. Pathology and pathogenesis of Vibrio infection in fish: A review. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 28, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, F.J.S.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A. (Eds.) Biology of European Sea Bass; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mougin, J.; Roquigny, R.; Flahaut, C.; Bonnin-Jusserand, M.; Grand, T.; Le Bris, C. Abundance and spatial patterns over time of Vibrionaceae and Vibrio harveyi in water and biofilm from a seabass aquaculture facility. Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmino, J.; Furones, M.D.; Andree, K.B.; Sarasquete, C.; Ortiz-Delgado, J.B.; Asencio-Alcudia, G.; Gisbert, E. Contrasting outcomes of Vibrio harveyi pathogenicity in gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata and European seabass, Dicentrachus labrax. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransangan, J.; Mustafa, S. Identification of Vibrio harveyi isolated from diseased Asian seabass Lates calcarifer by use of 16S ribosomal DNA sequencing. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2009, 21, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iaria, C.; Saoca, C.; Guerrera, M.C.; Ciulli, S.; Brundo, M.V.; Piccione, G.; Lanteri, G. Occurence of diseases in fish used for experimental research. Lab. Anim. 2019, 53, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.; Eissa, A.E.; Hanna, M.; Okada, M.A. Identifying some pathogenic Vibrio/Photobacterium species during mass mortalities of cultured gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) from some Egyptian coastal provinces. Int. J. Veter. Sci. Med. 2013, 1, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avendano-Herrera, R.; Toranzo, A.E.; Magarinos, B. Tenacibaculosis infection in marine fish caused by Tenacibaculum maritimum: A review. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 71, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, F.E. Concomitant infections, parasites and immune responses. Parasitology 2001, 122, S23–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbate, J.M.; Grifò, G.; Capparucci, F.; Arfuso, F.; Savoca, S.; Cicero, L.; Consolo, G.; Lanteri, G. Postmortem electrical conductivity changes of Dicentrarchus labrax skeletal muscle: Root Mean Square (RMS) parameter in estimating time since death. Animals 2022, 12, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Churcher, C.; Scott, C.; Barrett, J.C.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.N.; Clark, T.S.; Kebus, M.J.; Kent, M.L. Specific Pathogen Free—A review of strategies in agriculture, aquaculture, and laboratory mammals and how they inform new recommendations for laboratory zebrafish. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 142, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, T.; Manchanayake, T.; Danial, A.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Azmai, M.N.A.; Md Yasin, I.S.; Mohd Nor, N.; Salleh, A. Evaluating the intestinal immunity of asian seabass (Lates calcarifer, bloch 1790) following field vaccination using a feed-based oral vaccine. Vaccines 2023, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanpichai, P.; Chaweepack, S.; Senapin, S.; Piamsomboon, P.; Wongtavatchai, J. Immune activation following vaccination of Streptococcus iniae bacterin in asian seabass (Lates calcarifer, bloch 1790). Vaccines 2023, 11, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnoy, A.; Thangsunan, P.; Chokmangmeepisarn, P.; Yata, T.; Klongklaew, N.; Pirarat, N.; Kitiyodom, S.; Srisapoome, P.; Rodkhum, C. Mucoadhesive cationic lipid-based Flavobacterium oreochromis nanoencapsulation enhanced the efficacy of mucoadhesive immersion vaccination against columnaris disease and strengthened immunity in Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caipang, C.M.A.; Lucanas, J.B.; Lay-yag, C. Updates on the vaccination against bacterial diseases in tilapia, oreochromis spp. and asian seabass, Lates calcarifer. AACL Bioflux 2014, 7, 184–193. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.R.; Parameswaran, V.; Ishaq Ahmed, V.P.; Syed Musthaq, S.; Sahul Hameed, A.S. Protective efficiency of DNA vaccination in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) against Vibrio anguillarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griot, R.; Allal, F.; Phocas, F.; Brard-Fudulea, S.; Morvezen, R.; Haffray, P.; François, Y.; Morin, T.; Bestin, A.; Bruant, J.S.; et al. Optimization of genomic selection to improve disease resistance in two marine fishes, the european sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 665920. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, B.; Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Coinfection of cage-cultured spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) with Vibrio harveyi and Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida associated with skin ulcer. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 503. [Google Scholar]
- Sulumane Ramachandra, K.S.; Dube, P.N.; Pandikkaden Sundaran, S.; Kalappurakkal Gopalan, P.; Mangottil Ayyappan, M.A.; Nandiath Karayi, S. Coinfection with two strains of Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae and Vibrio harveyi in cage farmed cobia, Rachycentron canadum (Linnaeus, 1766). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Di Francesco, G.; Cammà, C.; Curini, V.; Mazzariol, S.; Proietto, U.; Di Francesco, C.E.; Ferri, N.; Di Provvido, A.; Di Guardo, G. Coinfection by Ureaplasma spp., Photobacterium damselae and an Actinomyces-like microorganism in a bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) with pleuropneumonia stranded along the Adriatic coast of Italy. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 105, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baseggio, L.; Rudenko, O.; Buller, N.; Landos, M.; Englestädter, J.; Barnes, A.C. Complete, closed and curated genome sequences of Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida isolates from Australia indicate mobilome-driven localized evolution and novel pathogenicity determinants. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000562. [Google Scholar]
- Nowlan, J.P.; Britney, S.R.; Lumsden, J.S.; Russel, S. Experimental induction of Tenacibaculosis in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) using Tenacibaculum maritimum, T. dicentrarchi, and T. finnmarkense. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizawa, S.; Tsuruya, Y.; Fukui, Y.; Sawabe, T.; Yokota, A.; Kogure, K.; Higgins, M.; Carson, J.; Thompson, F.L. Vibrio jasicida sp. nov., a member of the Harveyi clade, isolated from marine animals (packhorse lobster, abalone and Atlantic salmon). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Sakane, T.; Suzuki, M.; Hatano, K. Phylogenetic structure of the genera Flexibacter, Flexithrix, and Microscilla deduced from 16S rRNA sequence analysis. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 48, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Dawood, M.A.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; El-Matbouli, M. The nature and consequences of co-infections in tilapia: A review. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, T.T.; Berneking, L.; Rohde, H.; Chistner, M.; Schlickewei, C.; Sena Martins, M.; Schmiedel, S. Wound infection with Vibrio harveyi following a traumatic leg amputation after a motorboat propeller injury in Mallorca, Spain: A case report a review of literature. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, A.G.; Loughland, I.; Seebacher, F. What do warming waters mean for fish physiology and fisheries? J. Fish Biol. 2020, 97, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascarano, M.C.; Stavrakidis-Zachou, O.; Mladineo, I.; Thompson, K.D.; Papandroulakis, N.; Katharios, P. Mediterranean Aquaculture in Changing Climate: Temperature Effects on Pathogens and Diseases of three farmed fish species. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujalte, M.J.; Bobadilla, A.S.; Álvarez-Pellitero, P.; Garay, E. Carriage of potentially fish-pathogenic bacteria in Sparus aurata cultured in Mediterranean fish farms. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 54, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.T.; Taengphu, S.; Sangsuriya, P.; Charoensapsri, W.; Phiwsaiya, K.; Sornwatana, T.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Senapin, S. Recovery of Vibrio harveyi from scale drop and muscle necrosis disease in farmed barramundi, Lates calcarifer in Vietnam. Aquaculture 2017, 473, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Al-saari, N.; Mohamad, A.; Mursidi, F.A.; Mohd-Aris, A.; Amal, M.N.A.; Kasai, H.; Mino, S.; Sawabe, T.; Zamri-Saad, M. Vibriosis in fish: A review on disease development and prevention. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2019, 31, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, E.J. Skin ulcers in fish: Pfiesteria and other etiologies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 28, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadar, M.; Dhama, K.; Vakharia, V.N.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Karthik, K.; Tiwari, R.; Khandia, R.; Munjal, A.; Salgado-Miranda, C.; Joshi, S.K. Advances in aquaculture vaccines against fish pathogens: Global status and current trends. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aqualc. 2017, 25, 184–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrok, M.; Algammal, A.M.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Hetta, H.F.; Atwah, B.; Alghamdi, S.; Fawzy, A.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Rodkhum, C. Tenacibaculosis caused by Tenacibaculum maritimum: Updated knowledge of this marine bacterial fish pathogen. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 12, 1068000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Failde, L.D.; Losada, A.P.; Bermudez, R.; Santos, Y.; Quiroga, M.I. Tenacibaculum maritimum infection: Pathology and immunohistochemistry in experimentally challenged turbot (Psetta maxima L.). Microb. Pathog. 2013, 65, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, R.H.; Diab, A.M.; Shakweer, M.S.; Ghetas, H.A.; Khallaf, M.M.; Omar, A.A.E.-D. New perspective to control of tenacibaculosis in sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax L. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levipan, H.A.; Tapia-Cammas, D.; Molina, V.; Irgang, R.; Toranzo, A.E.; Magariños, B.; Avendaño-Herrera, R. Biofilm development and cell viability: An undervalued mechanism in the persistence of the fish pathogen Tenacibaculum maritimum. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, F.; Magnani, M. Photobacteriosis: Prevention and diagnosis. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 793817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, J.A.; Hanson, L.A. Health Maintenance and Principal Microbial Diseases of Cultured Fishes; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Essam, H.M.; Abdellrazeq, G.S.; Tayel, S.I.; Torky, H.A.; Fadel, A.H. Pathogenesis of Photobacterium damselae subspecies infections in sea bass and sea bream. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romalde, J.L. Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida: An integrated view of a bacterial fish pathogen. Int. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Micoli, A.; Manni, M.; Picchietti, S.; Scapigliati, G. State-of-the-art vaccine research for aquaculture use: The case of three economically relevant fish species. Vaccines 2021, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miccoli, A.; Saraceni, P.R.; Scapigliati, G. Vaccines and immune protection of principal Mediterranean marine fish species. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2019, 94, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsson, R.; Powell, D.B. Effects of disease risk, vaccine efficacy, and market price on the economics of fish vaccination. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midtlyng, P.J.; Reitan, L.J.; Speilberg, L. Experimental studies on the efficacy and side-effects of intraperitoneal vaccination of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) against furunculosis. Fish Shellfish Immun. 1996, 6, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, M.; Kusuda, R. The effect of various cultivation periods on the efficacy of formalin killed cell vaccine of Pasteurella piscicida in yellowtail. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1988, 54, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, I.; Inoue, S.; Kawai, K.; Oshima, S. Repeatable immersion infection with Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida reproducing clinical signs and moderate mortality. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 707–714. [Google Scholar]
- Afonso, A.; Gomes, S.; da Silva, J.; Marques, F.; Henrique, M. Side effects in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) due to intraperitoneal vaccination against vibriosis and pasteurellosis. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2005, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillehaug, A.; Lunder, T.; Poppe, T.T. Field testing of adjuvanted furunculosis vaccines in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J. Fish Dis. 1992, 15, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, M.T.; Roberts, R.J.; Tatner, M.; Ward, P. The effects of the use of potassium alum adjuvant in vaccines against vibriosis in rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J. Fish Dis. 1984, 7, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, H.; Okano, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Iwai, D.; Mizukami, M.; Akiyama, N.; Matsuura, S. Antibacterial abilities of intestinal bacteria from larval and juvenile Japanese flounder against fish pathogens. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Stuckey, L.F.; Robertson, P.A.W.; Effendi, I.; Griffith, D.R.W. A probiotic strain of Vibrio alginolyticus effective in reducing diseases caused by Aeromonas salmonicida, Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio ordalii. J. Fish Dis. 1995, 18, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, I.; Liu, Y.; Wiegertjes, G.F.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Exploring fish microbial communities to mitigate emerging diseases in aquaculture. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fix161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cámara-Ruiz, M.; Cerezo, I.M.; Guardiola, F.A.; García-Beltrán, J.M.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Esteban, M.Á. Alteration of the Immune Response and the Microbiota of the Skin during a Natural Infection by Vibrio harveyi in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Pascual, D.; Vendrell-Fernandez, S.; Audrain, B.; Bernal-Bayard, J.; Patiño-Navarrete, R.; Petit, V.; Rigaudeau, D.; Ghigo, J.M. Gnotobiotic rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) model reveals endogenous bacteria that protect against Flavobacterium columnare infection. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palazzolo, S.; Gervasi, C.; Abbate, J.M.; Gjurčević, E.; Falleti, R.; Piro, M.G.; Lanteri, G.; Iaria, C.; Marino, F. Natural Bacterial Co-Infection in Farmed European Sea Bass Intended for Experimental Research in Sicily, Southern Italy: Pathological Findings. Fishes 2024, 9, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9090360
Palazzolo S, Gervasi C, Abbate JM, Gjurčević E, Falleti R, Piro MG, Lanteri G, Iaria C, Marino F. Natural Bacterial Co-Infection in Farmed European Sea Bass Intended for Experimental Research in Sicily, Southern Italy: Pathological Findings. Fishes. 2024; 9(9):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9090360
Chicago/Turabian StylePalazzolo, Simone, Claudio Gervasi, Jessica Maria Abbate, Emil Gjurčević, Rosa Falleti, Maria Giovanna Piro, Giovanni Lanteri, Carmelo Iaria, and Fabio Marino. 2024. "Natural Bacterial Co-Infection in Farmed European Sea Bass Intended for Experimental Research in Sicily, Southern Italy: Pathological Findings" Fishes 9, no. 9: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9090360
APA StylePalazzolo, S., Gervasi, C., Abbate, J. M., Gjurčević, E., Falleti, R., Piro, M. G., Lanteri, G., Iaria, C., & Marino, F. (2024). Natural Bacterial Co-Infection in Farmed European Sea Bass Intended for Experimental Research in Sicily, Southern Italy: Pathological Findings. Fishes, 9(9), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9090360







