Effects of Salinity on Growth, Digestive Enzyme Activity, and Antioxidant Capacity of Spotbanded Scat (Selenotoca multifasciata) Juveniles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Rearing Condition and Experimental Design
2.2. Data Processing and Analysis
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Digestive Enzymes Assay
- Amylase: the amount of enzyme that can hydrolyze 10 mg of starch in 30 min at 37 °C in the presence of 1 mg of tissue protein;
- Lipase: the amount of enzyme that can consume 1 µmol of substrate per minute in a reaction system containing 1 g of tissue protein at 37 °C;
- Trypsin: trypsin contained within 1 mg of tissue protein induced a change in absorbance of 0.003 per minute at pH 8.0 and 37 °C;
- Pepsin: the amount of enzyme that can decompose protein to generate an equivalent of 1 µg of amino acids per minute per 1 mg of tissue protein at 37 °C.
2.5. Antioxidant/Oxidant Assays
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Salinity on Juvenile Spotbanded Scat Growth and Survival
3.1.1. Impact of Salinity on Juvenile Spotbanded Scat SR
3.1.2. Impact of Salinity on Juvenile Spotbanded Scat Growth Indices
3.2. Effects of Salinity on Digestive Enzyme Activity of Juvenile Spotbanded Scat
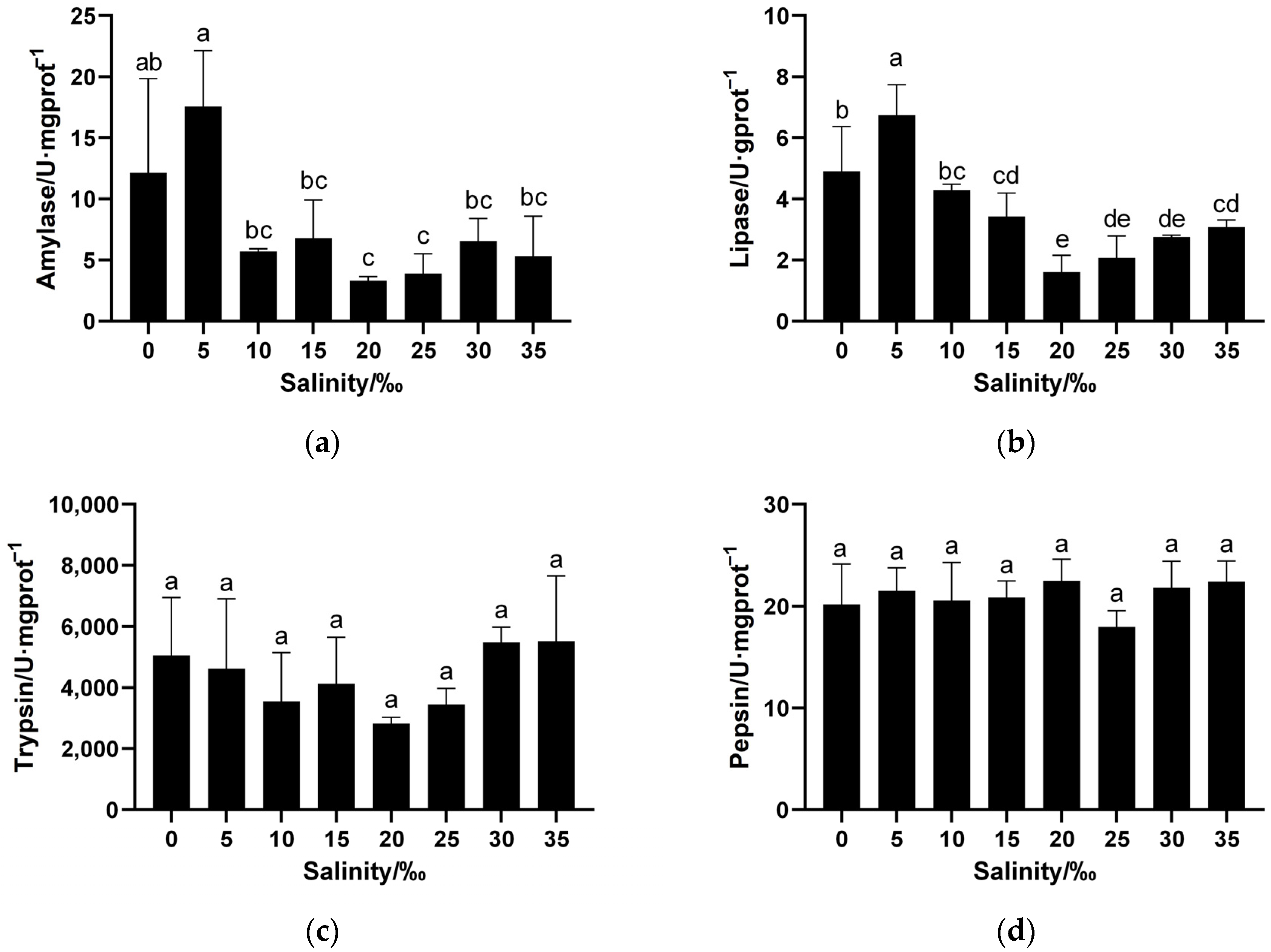
3.2.1. Impact of Salinity on Digestive Enzyme Activity in Juvenile Spotbanded Scat Stomach Tissue
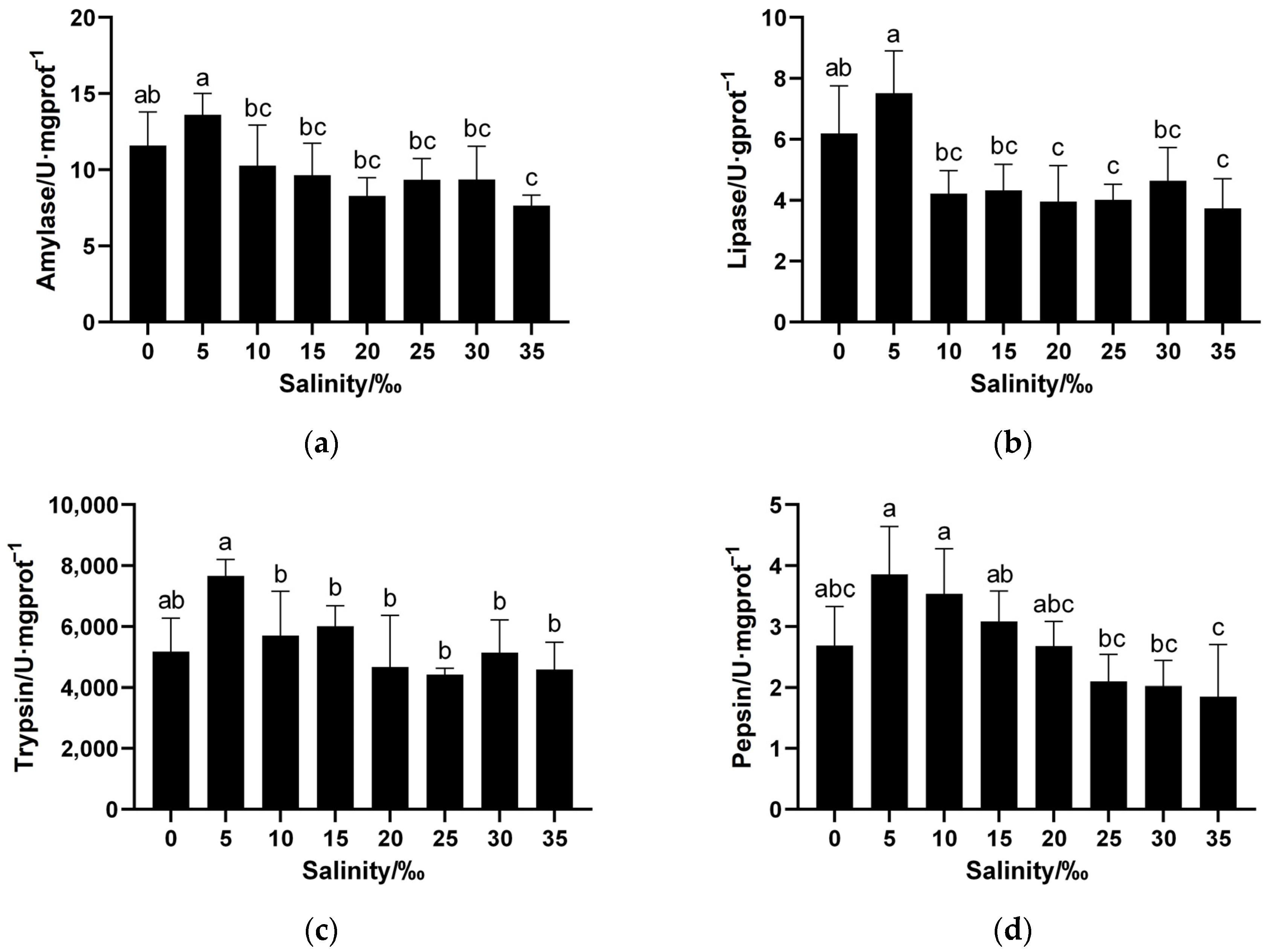
3.2.2. Impact of Salinity on Digestive Enzyme Activity in Juvenile Spotbanded Scat Intestinal Tissue
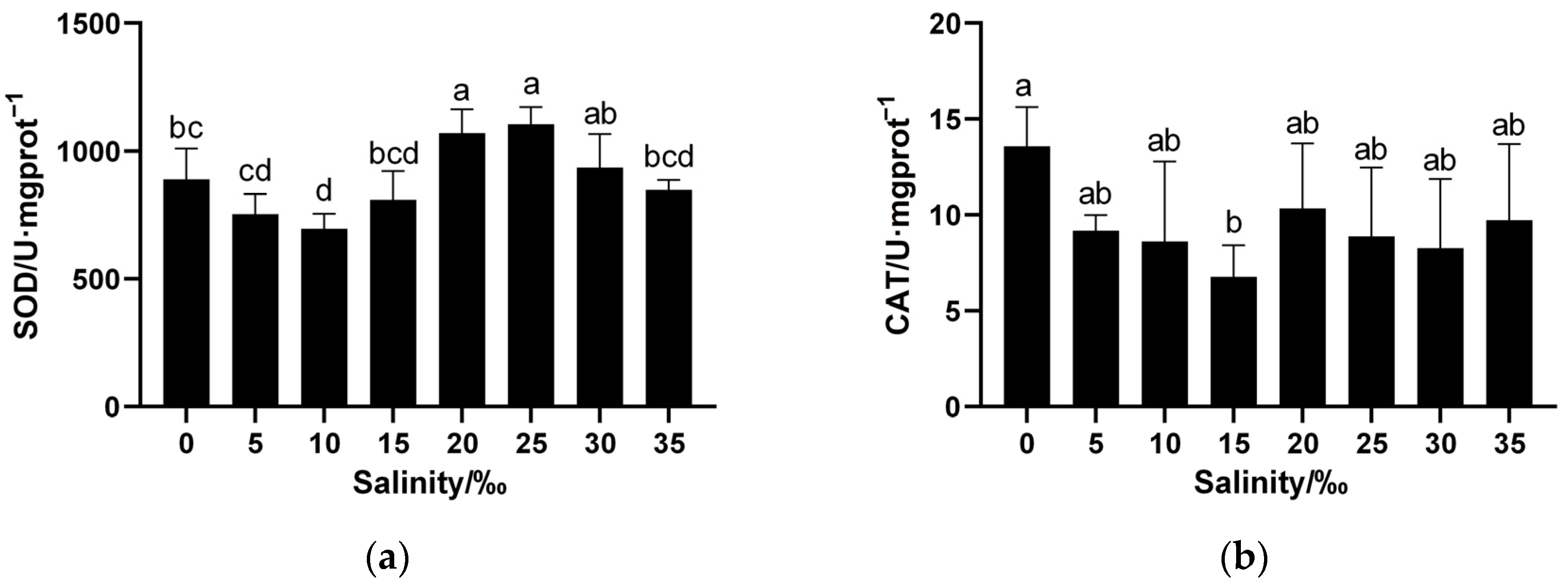
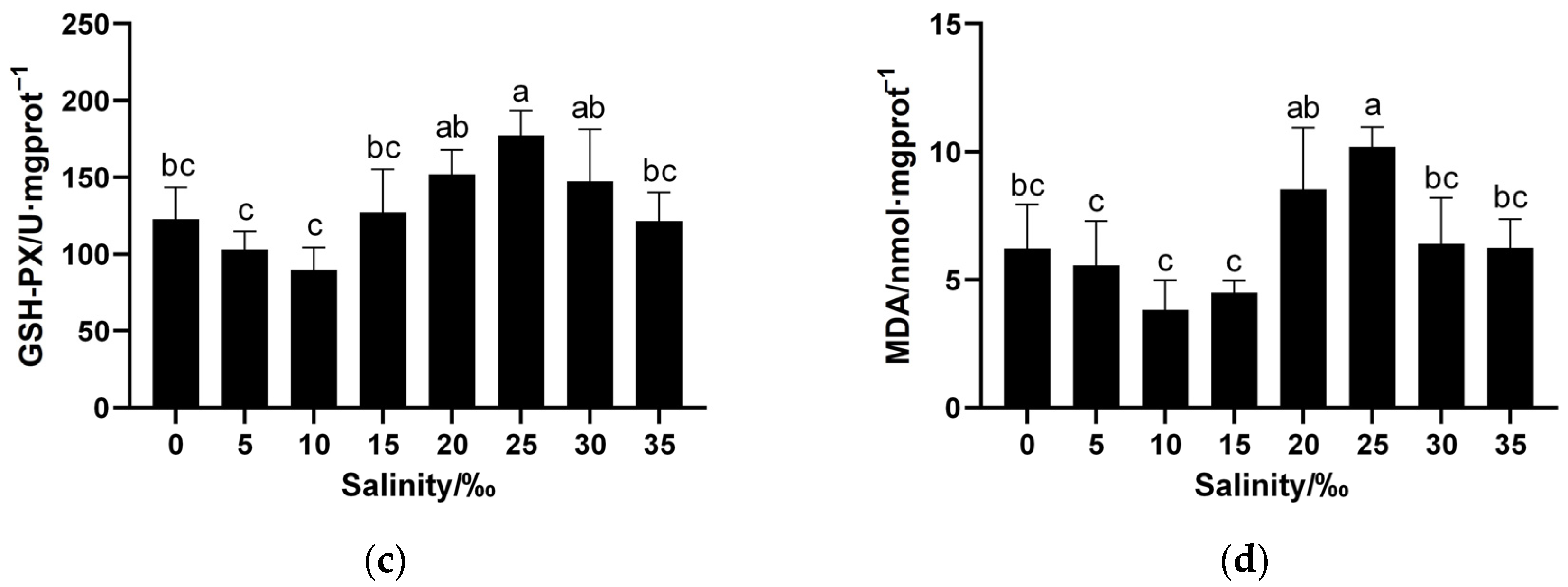
3.3. Effects of Salinity on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and MDA Contents in Juvenile Spotbanded Scat Liver
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhuang, P.; Feng, G.; Zou, X.; Zhao, F.; Yu, Y.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Embryonic and post-embryonic development of Selenotoca multifasciata. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 978–987. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, J.; Han, J.; Xu, Y.; Ma, W.; Feng, S. Isolation and identification of pathogenetic Streptococcus iniae from Selenotoca multifasciata. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2012, 31, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, J.; Kim, B.; Seo, J.; Kim, I.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J. Cloning of growth hormone, somatolactin, and their receptor mRNAs, their expression in organs, during development, and on salinity stress in the hermaphroditic fish, Kryptolebias marmoratus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2012, 161, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, X. A review on impact of salinity on pactterns of fish ecophysiology. Stud. Mar. Sin. 2002, 41, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Han, L.; Li, G. Growth, osmoregulatory and hypothalamic–pituitary–somatotropic (HPS) axis response of the juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides), reared under different salinities. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, M.N.Y.; Sugai, J.K.; Maciel, J.C.; Francisco, C.J.; Vinícius, R.C. Survival, growth and digestive enzyme activity of juveniles of the fat snook (Centropomus parallelus) reared at different salinities. Aquaculture 2007, 271, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.L.; Ge, X.P.; Huang, J.T.; Wang, A.M.; Lv, F. Effects of Salinity on Digestive Enzyme Activities of Onchidium struma. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 24, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar]
- Na, Y. Effects of Salinity on Digestive Physiology and Osmoregulation Physiology in Grey Mullet Mugil cephalus. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bolasina, S.N.; Tagawa, M.; Yamashita, Y. Changes on cortisol level and digestive enzyme activity in juveniles of Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus, exposed to different salinity regimes. Aquaculture 2007, 266, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.Y.; An, K.W.; An, M.I. Molecular characterization and mRNA expression of glutathione peroxidase and glutathione S-transferase during osmotic stress in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2008, 149, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.P.; Shi, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Jia-Bo, X.U.; Xie, Y.D.; Liu, Y.S.; Shui, C. Effects of salinity on activities of non-specific immune and digestive enzymes in juvenile estuarine tapertail anchovy Coilia nasus. J. Dalian Ocean. Univ. 2016, 31, 533–537. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.; Sun, P.; Peng, S.-M.; Shi, Z.H. Effects of low salinity stress on the antioxidant enzyme activities in juvenile Pampus argenteus liver and the APTase activities in its gill and kidney. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Yin, F.; Peng, S.-M.; Shi, Z.H. Effects of salinity on the activity of antioxidant enzymes in livers of juvenile Oplegnathus fasciatus. Mar. Fish. 2010, 32, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou, E.; Loumbourdis, N. Exposure of the frog Rana ridibunda to copper: Impact on two biomarkers, lipid peroxidation, and glutathione. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 69, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Fan, C.; He, X.; Cheng, K. Effects of three typical sulfonamides on GST activity and MDA content in liver tissue of Oreochromis niloticus. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Brocker, C.; Thompson, D.C.; Vasiliou, V. The role of hyperosmotic stress in inflammation and disease. Biomol. Concepts 2012, 3, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, Q.; Zou, X.; Feng, G.; Zhao, F.; Yu, Y.; Sun, X.; Yang, J. Effects of water temperature, salinity and pH on embryonic development of Selenotoca multifasciata. South China Fish. Sci. 2021, 17, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, A.C.; Takeda, M.; Tanaka, H.; Yoo, M.S. Chromosomes of Scatophagus argus and Selenotoca multifasciata (Scatophagidae). Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1988, 35, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mu, X.; Li, H.; Gui, L.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, J. Complete mitochondrial genome of the striped scat Selenotoca multifasciata (Perciformes: Scatophagidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 2691–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.Z.; Liang, H.F.; Wen, C.Q.; Wang, P.S.; Huang, J.Y. Effect of Salinity on the Growth of Selenotoca multifasciata. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2023, 51, 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Peskin, A.V.; Winterbourn, C.C. Assay of superoxide dismutase activity in a plate assay using WST-1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 103, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoar, W.S.; Randall, D.J. Fish Physiology. Volume VI. In Environmental Relations and Behavior; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1971; pp. 289–290. [Google Scholar]
- Imsland, A.K.; Gústavsson, A.; Gunnarsson, S.; Foss, A.; Árnason, J.; Arnarson, I.; Jónsson, A.F.; Smáradóttir, H.; Thorarensen, H. Effects of reduced salinities on growth, feed conversion efficiency and blood physiology of juvenile Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.). Aquaculture 2008, 274, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsamos, S.; Nebel, C.; Charmantier, G. Ontogeny of osmoregulation in postembryonic fish: A review. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2005, 141, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderdice, D.F. 3 Osmotic and Ionic Regulation in Teleost Eggs and Larvae. Fish Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 163–251. [Google Scholar]
- Fridman, S.; Bron, J.; Rana, K. Ontogenic changes in the osmoregulatory capacity of the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus and implications for aquaculture. Aquaculture 2012, 356, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duston, J. Effect of salinity on survival and growth of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) parr and smolts. Aquaculture 1994, 121, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bœuf, G.; Payan, P. How should salinity influence fish growth? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 130, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; You, H.; Jiang, Z.; Ge, Y. Effect of different salinity on food intake and growth for platichthys stellatus juveniles. Feed. Ind. 2008, 29, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yuan, C.G.; Ruan, C.X. Combined effect of temperature and salinity on the growth of Pseudosciaena crocea. J. Guangzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 12, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, L.Y.; Ping, Z.Y.; Min, Z.Q.; Jun, L.I.; Jie, X.Y.; Cai, H.J.; Zhi, Z.Y. Effects of Temperature and Salinity on the Growth and Survivability of Young Epinephelus moara. J. Jimei Univ. 2014, 19, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Mookkan, M.; Muniyandi, K.; Ramasubbu, S.; Raman, V.; Govindarajan, T. Influence of Salinity on Survival and Growth of Early Juveniles of Spotted Scat Scatophagus argus (Linnaeus, 1766). Indian J. Innov. Dev. 2014, 3, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- An, L.; Zhu, S.R.; Dong, X.S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zhang, L.G.; Zhu, Y.A.; Meng, Q.L. Effects of salinity on growth, flesh quality and antioxidant capacity of juveniles Micropterus salmoides. Freshw. Fish. 2023, 53, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Tang, X.; Liu, H.; Tian, J. Effects of salinity on plasma osmolality and gill na~+-k~+-atpase activity of juvinile japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2006, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.J.; Wang, C.G.; Zheng, S.L. Effects of Salinity on Digestive Enzyme Activity of Pagrosomus Major Young Fish. J. Xiamen Univ. 1998, 37, 754–756. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Tian, X.; Dong, S.; Gong, Q. Effects of Different Salinities on the Growth, Osmoregulation and Energy Budget of the Bester(Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus). Period. Ocean. Univ. China 2007, 13, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Gheisvandi, N.; Hajimoradloo, A.; Ghorbani, R.; Hoseinifar, S.H. The effects of gradual or abrupt changes in salinity on digestive enzymes activity of Caspian kutum, Rutilus kutum (Kamensky, 1901) larvae. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 31, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieu, D.Q.; Hang, B.T.B.; Huong, D.T.T.; Kertaoui, N.E.; Farnir, F.; Phuong, N.T.; Kestemont, P. Salinity affects growth performance, physiology, immune responses and temperature resistance in striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) during its early life stages. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 1995–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.F.; Gao, X.Q.; Yu, J.X.; Qian, X.M.; Xue, G.P.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Liu, B.L.; Hong, L. Effects of different salinities on growth performance, survival, digestive enzyme activity, immune response, and muscle fatty acid composition in juvenile American shad (Alosa sapidissima). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 43, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, S.S.; Jiddawi, N.S.; Poj, B. Effect of salinity levels on growth, feed utilization, body composition and digestive enzymes activities of juvenile silver pompano Trachinotus blochii. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2016, 4, 279–283. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Guan, R.; Jin, H. Effects of the salinity on the growth performance and digestive enzyme activities of Anguilla marmorata elver and A. bicolor pacifica elver. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2015, 39, 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Yan, M.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhou, C. Effects of salinity on growth and nonspecific immune enzyme activities of Anguilla japonica. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2011, 30, 528–532. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Zhao, F. Influence of salinity on serum osmolarity, ion content and gill Na+, K+-ATPase activity of Siganus guttatas. Mar. Fish. 2015, 37, 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Chiang, L.; Cisternas, E.; Ponce, O. Partial purification of pepsins from adult and juvenile salmon fish Oncorhynchus keta. Effect of NaCl on proteolytic activities. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1987, 87, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Shui, C.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y. Effect of salinity on survival, growth, body composition, oxygen consumption, and ammonia excretion of juvenile spotted scat. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2020, 82, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, E.J.; Haard, N.; Feltham, L. Gastric proteases of the Greenland cod Gadus ogac. I. Isolation and kinetic properties. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1986, 64, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoud, I.P.; Kreydiyyeh, S.; Chalfoun, A.; Fakih, M. Influence of salinity on survival, growth, plasma osmolality and gill Na+–K+–ATPase activity in the rabbitfish Siganus rivulatus. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 348, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.; Dominique, Y.; Massabuau, J.; Boudou, A.; Bourdineaud, J. Comparative effects of dietary methylmercury on gene expression in liver, skeletal muscle, and brain of the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Chen, B.; Qiu, L.; Fu, X.; Yang, B.; Han, Y. Influence of low salinity stress on the gill Na+/K+-ATPase, liver antioxidase and non-specific immune enzyme in juvenile Pleuronectes yokohama. J. Guangdong Ocean. Univ. 2017, 37, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman AN, A.; Mohamed, A.A.-R.; Dahran, N.; Farag, M.F.M.; Alqahtani, L.S.; Nassan, M.A.; AlThobaiti, S.A.; El-Naseery, N.I. Appraisal of sub-chronic exposure to lambada-cyhalothrin and/or methomyl on the behavior and hepato-renal functioning in Oreochromis niloticus: Supportive role of taurine-supplemented feed. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 250, 106257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansaldo, M.; Luquet, C.M.; Evelson, P.A.; Polo, J.M.; Llesuy, S. Antioxidant levels from different Antarctic fish caught around South Georgia Island and Shag Rocks. Polar Biol. 2000, 23, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, P.-J.; Qiu, C.-G.; Xu, S.-L.; LIN, S.-Z. Effects of salinity on growth, activity of non-specific immune and antioxidant enzymes in obscure puffer Takifugu obscures. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2014, 38, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.-N.; Wu, J.; Su, S.-J. Effects of salinity stress on antioxidant enzymes of Penaeus monodon of two different life stages. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2008, 4, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaweł, S.; Wardas, M.; Niedworok, E.; Wardas, P. Malondialdehyde (MDA) as a lipid peroxidation marker. Wiad. Lek. 2004, 57, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Ma, A.J.; Wang, X.A.; Huang, Z.H.; Yu, H.; Yang, Z. Effects of temperature and salinity on the activities of antioxidant enzymes of juvenile turbot Scophthalmus maximus. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2012, 27, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
| Salinity (‰) | Experimental Day | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | |
| 0 | 96.11 ± 0.96 c | 96.11 ± 0.96 c | 96.11 ± 0.96 c | 96.11 ± 0.96 c | 92.78 ± 0.96 e |
| 5 | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 100.00 a |
| 10 | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 100.00 a |
| 15 | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 100.00 a |
| 20 | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 96.39 ± 0.48 c | 96.39 ± 0.48 c |
| 25 | 100.00 a | 99.16 ± 0.84 a | 99.16 ± 0.84 a | 99.16 ± 0.84 a | 99.16 ± 0.84 a |
| 30 | 100.00 a | 100.00 a | 97.63 ± 0.65 b | 97.63 ± 0.65 b | 97.63 ± 0.65 b |
| 35 | 98.05 ± 0.48 b | 98.05 ± 0.48 b | 98.05 ± 0.48 b | 94.72 ± 0.96 d | 94.72 ± 0.96 d |
| Salinity (‰) | Wt (g) | WGR (%) | SGR (%·Day−1) | FR (%·Day−1) | GR (%) | ADG (g·Day−1) | CF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3.32 ± 1.15 e | 563.20 ± 230.11 e | 4.09 ± 0.73 e | 4.02 ± 0.46 a | 70.84 ± 19.73 e | 0.06 ± 0.03 e | 4.55 ± 0.19 b |
| 5 | 12.67 ± 1.80 a | 2433.80 ± 359.21 a | 7.16 ± 0.33 a | 2.63 ± 0.07 b | 172.97 ± 10.63 a | 0.27 ± 0.04 a | 4.53 ± 0.86 b |
| 10 | 11.31 ± 2.27 b | 2162.40 ± 453.56 b | 6.89 ± 0.41 ab | 2.83 ± 0.22 b | 161.91 ± 15.26 ab | 0.24 ± 0.05 b | 4.52 ± 1.13 b |
| 15 | 11.02 ± 2.01 b | 2104.47 ± 402.57 b | 6.84 ± 0.39 b | 2.55 ± 0.06 b | 155.22 ± 14.80 b | 0.23 ± 0.04 b | 4.93 ± 1.00 b |
| 20 | 8.40 ± 2.67 cd | 1580.60 ± 534.75 cd | 6.16 ± 0.71 cd | 2.78 ± 0.41 b | 135.84 ± 21.44 c | 0.18 ± 0.06 cd | 5.23 ± 0.79 b |
| 25 | 9.14 ± 1.70 c | 1727.29 ± 340.85 c | 6.42 ± 0.40 c | 2.39 ± 0.23 b | 138.72 ± 18.53 c | 0.19 ± 0.04 c | 4.69 ± 1.16 b |
| 30 | 7.33 ± 1.99 d | 1366.00 ± 398.94 d | 5.88 ± 0.66 d | 2.55 ± 0.39 b | 111.82 ± 23.99 d | 0.15 ± 0.04 d | 5.98 ± 1.67 a |
| 35 | 8.22 ± 1.87 cd | 1543.07 ± 373.85 cd | 6.16 ± 0.52 cd | 2.78 ± 0.27 b | 135.19 ± 18.25 c | 0.17 ± 0.04 cd | 4.91 ± 0.96 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Ai, T.; Yang, J.; Shang, M.; Jiang, K.; Yin, Y.; Gao, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, N.; Ju, J.; et al. Effects of Salinity on Growth, Digestive Enzyme Activity, and Antioxidant Capacity of Spotbanded Scat (Selenotoca multifasciata) Juveniles. Fishes 2024, 9, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9080309
Liu J, Ai T, Yang J, Shang M, Jiang K, Yin Y, Gao L, Jiang W, Zhao N, Ju J, et al. Effects of Salinity on Growth, Digestive Enzyme Activity, and Antioxidant Capacity of Spotbanded Scat (Selenotoca multifasciata) Juveniles. Fishes. 2024; 9(8):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9080309
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jianyi, Tongxi Ai, Jun Yang, Meijuan Shang, Keji Jiang, Yane Yin, Lei Gao, Wei Jiang, Na Zhao, Jianfeng Ju, and et al. 2024. "Effects of Salinity on Growth, Digestive Enzyme Activity, and Antioxidant Capacity of Spotbanded Scat (Selenotoca multifasciata) Juveniles" Fishes 9, no. 8: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9080309
APA StyleLiu, J., Ai, T., Yang, J., Shang, M., Jiang, K., Yin, Y., Gao, L., Jiang, W., Zhao, N., Ju, J., & Qin, B. (2024). Effects of Salinity on Growth, Digestive Enzyme Activity, and Antioxidant Capacity of Spotbanded Scat (Selenotoca multifasciata) Juveniles. Fishes, 9(8), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9080309





