Abstract
Calmodulin (Calm), a crucial Ca2+ sensor, plays an important role in calcium-dependent signal transduction cascades. However, the expression and the relevance of Calm in stress and immune response have not been characterized in Megalobrama amblycephala. In this study, we identified the full-length cDNA of Calm (termed MaCalm) in blunt snout bream M. amblycephala, and analyzed MaCalm expression patterns in response to cadmium and Aeromonas hydrophila challenges. MaCalm was 1603 bp long, including a 5′-terminal untranslated region (UTR) of 97 bp, a 3′-terminal UTR of 1056 bp and an open reading frame (ORF) of 450 bp encoding a polypeptide of 149 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight (MW) of 16.84 kDa and an isoelectric point (pI) of 4.09. Usually, MaCalm contains four conservative EF hand motifs. The phylogenetic tree analysis indicated that the nucleotide sequence of MaCalm specifically clustered with Ctenopharyngodon idella with high identity (98.33%). Tissue distribution analysis demonstrated that the ubiquitous expression of MaCalm mRNA was found in all tested tissues, with the highest expression in the brain and the lowest expression in muscle. MaCalm showed significant upregulation at 14 d and 28 d post exposure to varying concentrations of cadmium in the liver; HSP70 transcripts in the liver significantly upregulated at 14 d post exposure to different concentrations of cadmium. Moreover, in response to the A. hydrophila challenge in vivo, MaCalm transcripts in the liver first increased and then decreased, but MaCalm transcripts in the kidney declined gradually with prolonged infection. After the A. hydrophila challenge, the expression level of HSP70 was significantly downregulated at 24 h in the liver and its expression level was notably downregulated at 12 h and at 24 h in the kidney. Collectively, our results suggest that MaCalm possesses vital roles in stress and immune response in M. amblycephala.
Key Contribution:
The first identification and characterization of calmodulin (Calm) was carried out in Megalobrama amblycephala, and Calm could dynamically respond to an Aeromonas hydrophila infection and chronic cadmium exposure in the mRNA level. This research provides valuable insight into Calm-mediated signaling pathways of M. amblycephala in response to bacterial infection and heavy metal exposure, and sheds lights on potential interventions in pathogens’ invasion and heavy-metal-induced toxicity in fish.
1. Introduction
Fishes live in the aquatic environment over their lifetime and inevitably suffer from multitudinous environmental stressors. These stressors can be subdivided into biotic stressors, such as parasitic infection and microbial pathogenic infection, and abiotic stressors, such as ammonia nitrogen, cadmium (Cd) and salinity [1]. To survive and develop under unfavorable environments, fishes have evolved fine-tuned physiological response mechanisms to perceive and properly respond to environmental stimuli. Increasing findings have illustrated that diverse external stressors can bring about an alteration of intracellular calcium ions (Ca2+) concentration, which is then sensed by downstream effectors to trigger a series of physiological–biochemical events, such as gene expression, enzyme activation, protein synthesis and transport and muscular contractions [2,3]. These downstream effectors are also involved in plenty of cellular functions by acting as Ca2+ transporters across cell membranes or as Ca2+-modulated sensors. Calmodulin (Calm) is one of the most representative members of Ca2+-modulated sensors, which is found in all eukaryotic organisms [4]. In vertebrates, the canonical Calm protein contains approximately 150 amino acid residues and the structures of the different Calm proteins exhibit high levels of conservation. Calm carries four EF-hand-type calcium-binding domains and each of the EF-hand domains binds to a Ca2+. Upon binding with Ca2+, a conformational shift of Calm was induced and the activated Ca2+/Calm complex will trigger downstream signal transduction pathways [5].
Until now, Calm has been identified in the mollusks Crassostrea gigas [6] and Anodonta woodiana [7], the crustaceans Eriocheir sinensis [8], Procambarus clarkia [9], Penaeus monodon [10], Litopenaeus vannamei [11] and Portunus trituberculatus [12], the echinoderm Stichopus japonicus [13] and several teleosts Ctenopharyngodon idella [14], Danio rerio [5], Epinephelus akaara [15] and Pagrus major [16]. In aquatic animals, the Calm genes are widely distributed in the cells and there are different levels present in the tissues [5]. Previous studies showed that Calm genes play the crucial role in fish gonad development [15,16], stress response [17,18], hormone synthesis and secretion [14,19] and disease resistance [20]. Furthermore, the Calm gene also plays critical roles in inflammation [21], immune response [8,10], stress response [22], actin cytoskeleton regulation [23], ovarian maturation [24] and spermatogenesis [25] in aquatic invertebrates. Hence, Calm is a multifunctional gene which participates in a multitude of physiological and pathological processes of aquatic animals.
The blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) is a widely distributed and commercially important aquaculture species in China. M. amblycephala is strongly responsive to biotic and abiotic stressors, including Aeromonas hydrophila and Cd, which threatens its culture industry and causes huge economic losses [26,27]. Research into its mechanism of innate immunity to defense pathogens and anti-environment stress is becoming an urgent task that will benefit and improve the immunity of fish in the future. To date, the genome of M. amblycephala has been sequenced (genome assembly No. ASM1881202v1); however, the presence of Calm genes in M. amblycephala has not been identified and characterized. Furthermore, none of the literature has reported the expression and the relevance of Calm in stress and immune responses in M. amblycephala. Hence, this study aims to identify the full-length cDNA of M. amblycephala Calm (termed MaCalm) and then analyze its domain architecture, phylogenetic relationships and mRNA expression in different tissues. Moreover, in this study, differential expression profiles of MaCalm in the liver and (or) kidney were analyzed under the A. hydrophila infection and the Cd stress. Our findings will be important for further investigations of the calcium signal transduction mechanisms under stressful environmental conditions and invading microbes and lay a theoretical foundation for the further exploration of the molecular functions of Calm.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Maintenance and Sample Collection
A total of 145 healthy blunt snout breams (Megalobrama amblycephala) used in the current study were obtained from Changsha pilot research station of Hunan Fisheries Sciences Institute, Changsha, China, and were free of the infection of parasites, bacteria and viruses by our routine diagnostic procedures. To acclimate laboratory environment, fish (32.88 ± 3.42 g in weight and 11.18 ± 0.09 cm of length) were reared for 10 days in a 1.0 × 0.8 × 1.0 m3 aquarium at a water temperature of 20 ± 1 ℃, pH 7.8, photoperiod of 12 h light/12 h dark and dissolved oxygen concentration of 6.0 ± 0.5 mg/L in aerated freshwater. Subsequently, fish (n = 5) were anesthetized by MS-222 (50 mg/L) and their various tissues (brain, gill, liver, spleen, kidney, heart, muscle, intestine and skin) were rapidly dissected, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and then stored at −80 °C. Liver was used for sequence cloning of MaCalm and all sampled tissues were used for follow-up tissue expression analysis of MaCalm.
2.2. Cloning and Sequencing of Calmodulin in M. amblycephala
The total RNA of the M. amblycephala liver was extracted with animal total RNA isolation kit (Foregene, Chengdu, China) and quantified with the NanoPhotometer N60 spectrophotometer (Implen, Munich, BY, Germany) at wavelengths of 260 nm and 280 nm. First-strand cDNA was synthesized from the RNA with PrimeScript™ RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (Takara, Beijing, China) following the manufacturer’s protocol. An alignment of the Calm nucleotide sequences from a variety of species was constructed with ClustalX. To amplify partial cDNA sequence of calmodulin (Calm) gene, primers (CalmF1/CalmR1) were designed to clone conserved nucleotides of Calm in phylogenetically close species C. idella, as mentioned in Table 1. The PCR fragments (381 bp of Calm) were gel purified, ligated into T/A cloning vector pMD-18 T (Takara, Beijing, China) and transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells. The positive clones were screened and sequenced in Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). To obtain the full-length Calm cDNA sequence, the 5′ and 3′ ends were amplified using the SMARTer RACE 5′/3′ Kit (Takara, San Jose, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The primer pairs used for 5′ RACE and 3′ RACE were designed from the newly obtained sequences (Table 1). The amplified PCR products of the cDNA ends were cloned and sequenced as mentioned earlier.

Table 1.
The primer sequences used in this study.
2.3. Bioinformatics Analyses of MaCalm Sequence
The cDNA of Calm was translated into its potential open reading frame (ORF) using the ORF finder algorithm (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/ (accessed on 10 January 2024)). Domain analyses were carried out with Simple Modular Architecture Research Tools (SMART, http://smart.embl.de/ (accessed on 10 January 2024)) and InterPro database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/ (accessed on 10 January 2024)). Identities between Calm and other known Calm amino acid sequences were determined by TBtools software [28]. The predicted molecular weight (MW) and isoelectric point (pI) of the putative protein were also calculated using the TBtools software. Based on amino acid sequence of MaCalm, transmembrane topology prediction and signal peptide were predicted with DeepTMHMM (https://dtu.biolib.com/DeepTMHMM (accessed on 10 January 2024)) and SignaIP 5.0 (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/SignalP-5.0/ (accessed on 10 January 2024)), respectively. Multiple alignments of nucleic acid sequences were performed with the ClustalX program [29]. A phylogenetic tree was constructed with the neighbor-joining (NJ) method in MEGA 11 software [30] and the reliability of the analysis was assessed by 1000 bootstrap replicates.
2.4. Blunt Snout Breams Challenge Experiments
2.4.1. Aeromonas hydrophila Infection
Blunt snout breams were randomly divided into two groups (30 fish per group): control group and infected group. Blunt snout breams in the infected group were injected intraperitoneally with 0.2 mL A. hydrophila; blunt snout breams in the control group were injected intraperitoneally with 0.2 mL stroke-physiological saline solution. Based on our preliminary experiments, the LD50 of A. hydrophila in M. amblycephala challenged with intraperitoneal injection was 4.5 × 106 CFU/mL, which was calculated according to the Reed–Muench method. A. hydrophila was grown overnight in Luria–Bertani medium at 28 °C. Broth cultures were centrifuged at 8000× g for 5 min, washed twice, the turbidity of bacterial suspension was determined by McFarland standard and diluted to 1 × 106 CFU/mL with sterile physiological saline [31,32]. To stimulate infective process of A. hydrophila in aquaculture, a lower concentration (1 × 106 CFU/mL) of bacterial inocula was employed in this study. The conditions in the experimental period (water temperature, water oxygen content, pH and photoperiod) were identical to those in the acclimation period. Fish in the control group (n = 5 per time point; 15 total) and the infected group (n = 5 per time point; 15 total) were euthanized immediately with 50 mg/L MS-222 at 0, 12 and 24 h after challenge and liver and kidney were collected, quickly frozen with liquid nitrogen and then stored at −80 °C until further analysis.
2.4.2. Waterborne Cd Exposure
Blunt snout breams (n = 80) were randomly divided into four groups and exposed to four different concentrations of Cd for 28 days, respectively. Four concentrations of Cd were as follows: 0 μg/L (control), 5 μg/L (low concentration exposure group, LC), 50 μg/L (medium concentration exposure group, MC) and 500 μg/L (high concentration exposure group, HC). The upper limit of Cd concentration is 5 μg/L according to the national standard for fishery water quality of China made by the Ministry of Environmental Protection. Hence, four concentrations of Cd in four groups correspond to 0×, 1×, 10× and 100× of the upper limit of Cd concentration from the national standard for fishery water quality of China, respectively. Five fish from each group (n = 5) were quickly anesthetized using 50 mg/L of MS-222 and liver were collected at different exposure time points (0, 14 and 28 day). The conditions in the experimental period (water temperature, water oxygen content, pH and photoperiod) were same as those in the acclimation period. Fish were fed twice (8:00 and 16:00) with commercial pellet feed (2% body weight) and excess food and fecal matter were removed from the aquaria to reduce water quality deterioration. To maintain the nominal Cd concentration in experimental water, 50% of water in four groups was renewed daily by adding corresponding dosage of the stock solution (5 g Cd/L) prepared in ultrapure water. During the test period, the monitored Cd concentrations of four treatments were 0.61 ± 0.043 μg/L, 4.86 ± 0.44 μg/L, 49.11 ± 5.73 μg/L and 483.25 ± 23.15 μg/L for the control and 5 μg/L, 50 μg/L and 500 μg/L groups, respectively. The Cd concentrations of water samples from four treatments were determined with atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Expression Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from the M. amblycephala samples using animal total RNA isolation kit (Foregene, Chengdu, China) and RNA quantities and concentrations were determined with the NanoPhotometer N60 spectrophotometer (Implen, Munich, PY, Germany). The RNA concentration of all samples were adjusted to 5 ng/μL and then cDNA was synthesized with PrimeScript™ RT reagent kit with gDNA Eraser (Takara, Beijing, China) following its protocols. The qRT-PCR reaction was carried out with the TB Green® Premix Ex Taq™ (Tli RNaseH Plus) (Takara, Beijing, China) in the LightCycler® 96 instrument (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) with the following procedure: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of amplification (95 °C for 5 s and 60 °C for 20 s). The reaction mixture, containing specific primers (Table 1), was prepared according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Three technological replicates of each sample were assayed. The threshold cycle (Ct) values were determined at the end of each cycle. The relative gene expression levels of Calm were calculated by the 2−ΔΔCt method [33]. With an eye to expression stability of reference genes in the different tissues of M. amblycephala, the RPII gene was chosen as the reference gene in this study [34].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The data of qRT-PCR results were presented as the mean ± standard deviation ( ± S.D.). qRT-PCR data from A. hydrophila infection experiment were analyzed by t test. qRT-PCR data from cadmium exposure experiment were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s post hoc test using SPSS 20.0 software. Differences were considered significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Sequence Characterization of the MaCalm
A 381-bp cDNA fragment was amplified from the M. amblycephala liver cDNA. A BlastX analysis of the fragment showed that it shared high similarity with other reported Calm genes. Based on this conserved sequence, the full-length cDNA of MaCalm (GenBank accession number: OR908926) was obtained. Its complete sequence was 1603 bp and it contained a 450-bp open reading frame (ORF) encoding a polypeptide of 149 amino acids. The 5′ untranslated region (5′-UTR) and 3′ untranslated region (3′-UTR) were 97 bp and 1056 bp, respectively (Figure 1). Like Calm amino acid sequences of other 20 teleost species, MaCalm contains four canonical EF hand motifs (at the 12–40, 48–76, 85–113 and 121–149 amino acids) and each of them has one Ca2+-binding domain (Figure 2). The sequences of the EF hand motif in the MaCalm protein were found to be highly conserved among different species. In the deduced amino acid sequence, none of signal peptides and transmembrane domains were found.

Figure 1.
The complete nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of MaCalm. The start codon (ATG) is boxed. The stop codon (TGA) is marked with an asterisk. The 5′ untranslated region (5′-UTR) and 3′ untranslated region (3′-UTR) are indicated with curved arrows.
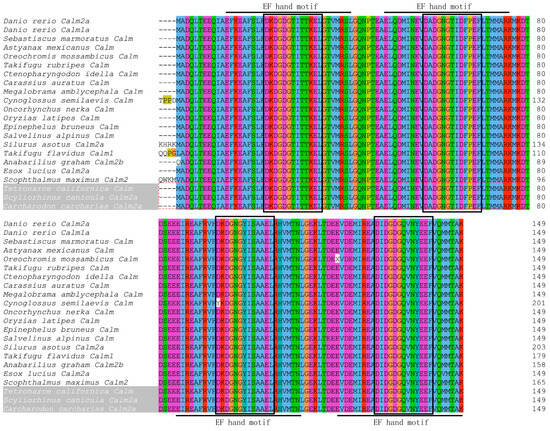
Figure 2.
The amino acid sequences’ alignment of MaCalm with other teleosts’ Calm. The four EF hand domains are marked by solid lines, and these Ca2+-binding domains are denoted with dark boxes. Amino acid residues completely conserved across all species are aligned and shaded in same color. The sequences used for alignment and their GenBank accession numbers were as following: Danio rerio Calm2a: NP_956290.1; Danio rerio Calm1a: AAH97062.1; Sebastiscus marmoratus Calm: ACG50685.1; Astyanax mexicanus Calm: KAG9265857.1; Oreochromis mossambicus Calm: AAS00645.1; Takifugu rubripes Calm: XP_003971505.1; Ctenopharyngodon idella Calm: XP_051724944.1; Carassius auratus Calm: XP_026090521.1; Megalobrama_amblycephala Calm: OR908926 (this study); Cynoglossus_semilaevis Calm: XP_008310981.1; Oncorhynchus nerka Calm: XP_029543691.1; Oryzias latipes Calm: JC1305; Epinephelus bruneus Calm: AEB31285.1; Salvelinus alpinus Calm: XP_023842621.1; Silurus asotus Calm2a: KAI5623426.1; Takifugu flavidus Calm1: TWW78027.1; Anabarilius graham Calm2b: ROI81809.1; Esox lucius Calm2a: NP_001290903.1; Scophthalmus maximus Calm2: AWP19722.1; Tetronarce californica Calm: P62151.2; Scyliorhinus canicular Calm2a: XP_038669580.1; Carcharodon carcharias Calm2a: XP_041067107.1. Fish species of the subclass Chondrichthyes is shaded in light grey and the remaining fish species belong to the subclasss Actinopterygii.
A comparison among homologous amino acid sequences showed that MaCalm shared a high sequence identity (96.73–100%) with other fish species. It shared the highest identity (100%) with D. rerio, Sebastiscus marmoratus, Astyanax mexicanus, Takifugu rubripes, C. idella, Oncorhynchus nerka, Oryzias latipes, Epinephelus bruneus, Salvelinus alpinus, Tetronarce californica, Carassius auratus, Esox lucius, Scyliorhinus canicular and Carcharodon carcharias (Table 2). Moreover, the theoretical pI of MaCalm was 4.09 and the estimated MW was 16.84 kDa.

Table 2.
Comparison of Megalobrama amblycephala Calm and the Calm amino acid sequence from other fish species. The comparison included the percent identity, isoelectric point (pI) and molecular weight (MW).
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of MaCalm
As shown in Figure 3, the evolutionary relationship was evaluated from the phylogenetic analysis between MaCalm and other species. Besides O. latipes, the species of Actinopterygii (including M. amblycephala) are clustered into one branch and were well separated from C. carcharias and S. canicular (Chondrichthyes). In the light of the phylogenetic tree, MaCalm is most closely clustered with that from C. idella and has a high level of similarity with homologs from C. auratus. It is obvious from the phylogenetic tree that the Calm of teleosts (Actinopterygii and Chondrichthyes) are well divergent from mammals (Mus musculus and Rattus norvegicus). The phylogenetic tree was consistent with traditional taxonomy and phylogenetic transition.
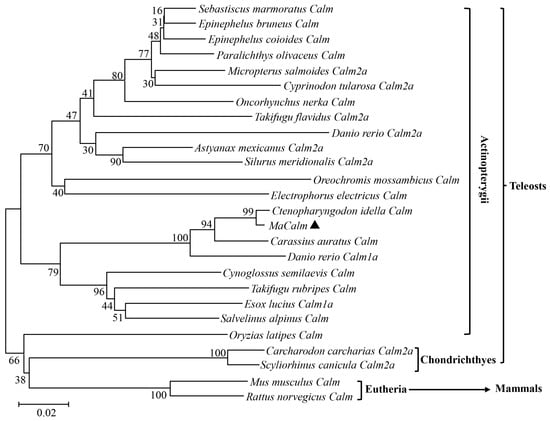
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree of Calm from Megalobrama amblycephala and other species constructed with the neighbor-joining (NJ) method in MEGA 11. These nucleotide sequences used and their GenBank accession numbers are: Carassius auratus Calm (AY656700.1); Ctenopharyngodon idella Calm (AY627883.1); MaCalm (OR908926), marked with ▲; Danio rerio Calm1a (NM_213351.1); Cynoglossus semilaevis Calm (XM_008312759.3); Takifugu rubripes Calm (XM_003971456.3); Esox lucius Calm1a (NM_001304069.1); Salvelinus alpinus Calm (XM_023973836.1); Takifugu flavidus Calm2a (XM_057047918.1); Astyanax mexicanus calm2a (XM_007255786.4); Silurus meridionalis Calm2a (NM_199996.2); Danio rerio Calm2a (XM_046875174.1); Oncorhynchus nerka Calm (XM_029669738.1); Epinephelus bruneus Calm (JF430618.1); Sebastiscus marmoratus Calm (EU871679); Electrophorus electricus Calm (M36168); Oreochromis mossambicus Calm (AY513748.1); Epinephelus coioides Calm (KC540636.1); Paralichthys olivaceus Calm (EU519228.1); Micropterus salmoides Calm2a (XM_038737638.1); Cyprinodon tularosa Calm2a (XM_038299495.1); Oryzias latipes calmodulin Calm (XM_023952043.1); Carcharodon carcharias Calm2a (XM_041211173.1); Scyliorhinus canicula Calm2a (XM_038813652.1); Mus musculus Calm (X61432.1); Rattus norvegicus Calm (AF178845.1). The bootstrap values were marked at each node of the tree. Mus musculus and Rattus norvegicus are set as the out group.
3.3. Tissue Distribution of MaCalm mRNA Transcripts
RT-qPCR was performed to investigate the mRNA expression pattern of MaCalm in the brain, gill, heart, intestine, liver, spleen, kidney, skin and muscle (Figure 4). In M. amblycephala, MaCalm was expressed broadly in all determined tissues. Among these determined tissues, MaCalm was highly expressed in the brain, moderate in the gill, kidney, spleen, intestine and skin and low in the liver, heart and muscle (Figure 4A).
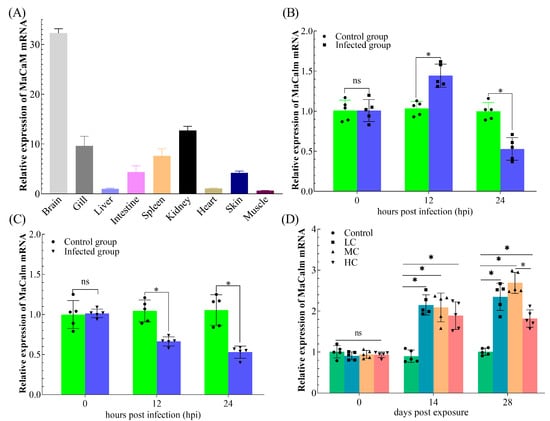
Figure 4.
Relative expression of MaCalm in Megalobrama amblycephala. (A) Tissue-specific expression of MaCalm in nine tissues of M. amblycephala. (B) Expression profiles of MaCalm in liver post infection with Aeromonas hydrophila. (C) Expression profiles of MaCalm in kidney post infection with A. hydrophila. (D) Expression profiles of MaCalm in liver post exposure with different concentrations of cadmium. The asterisk (*): significant differences at the same point of time when compared with control group (p < 0.05); ns: no significant differences at the same point of time when compared with control group (p > 0.05).
3.4. MaCalm Gene Expression in Response to A. hydrophila and Cd Challenge
To investigate the immune role of MaCalm during the pathogen’s infection, MaCalm transcript changes in the liver and kidney of fish infected with A. hydrophila were determined using the RT-qPCR method. In the liver, an A. hydrophila infection markedly upregulated MaCalm mRNA expression at 12 hours post-infection (hpi), but downregulated significantly 24 hpi (Figure 4B). On the contrary, the MaCalm mRNA expression levels in the kidney decreased notably at 12 hpi and continued to decrease at 24 hpi (Figure 4C). The MaCalm gene expression patterns in response to different concentrations of Cd are presented in Figure 4D. Compared to the control group, the MaCalm transcript of the LC, MC and HC groups were remarkably upregulated at 14 d and the elevated expression lasted until the end of the experiment.
3.5. Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70) Gene Expression in Response to A. hydrophila and Cd Challenge
Variations of the stress-related gene HSP70 in response to A. hydrophila and Cd challenges are shown in Figure 5. Compared with control group, fish infected with A. hydrophila showed lower HSP70 transcripts in the liver at 24 hpi (Figure 5A). After an A. hydrophila challenge, a remarkable downregulation of the HSP70 transcripts was observed at 12 hpi and 24 hpi in the kidney with respect to the control group (Figure 5B). After exposure to Cd, the HSP70 transcript of the LC, MC and HC groups increased significantly at 14 days post exposure, and then returned to the control level at 28 days post exposure (Figure 5C).
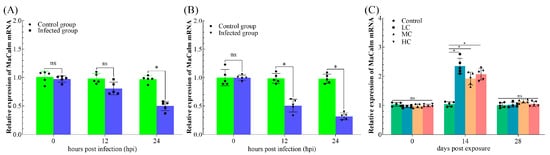
Figure 5.
Relative expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70) in Megalobrama amblycephala. (A) Expression profiles of HSP70 in liver post infection with Aeromonas hydrophila. (B) Expression profiles of HSP70 in kidney post infection with A. hydrophila. (C) Expression profiles of HSP70 in liver post exposure with different concentrations of cadmium. The asterisk (*): significant differences at the same point of time when compared with control group (p < 0.05); ns: no significant differences at the same point of time when compared with control group (p > 0.05).
4. Discussion
Calm, a Ca2+-activated functional protein, participates in a lot of physiological processes in aquatic organisms, including neuroendocrine hormone production, developmental regulation, stress resistance and inflammatory and immunological responses [17,19,20,21,24]. Based on the whole genome data (genome assembly No. ASM1881202v1), four predicted Calm homologous genes, Calm1a, Calm1b, Calm2b and Calm3b, were found in the M. amblycephala genome. The nucleotide sequence identity of MaCalm and four Calm homologous genes was calculated and the sequence identity of MaCalm shared a 99.8%, 69.6%, 53.0% and 47.3% identity to Calm1a, Calm1b, Calm2b and Calm3b, respectively. MaCalm and Calm1a had a high-level identity of greater than 98%, with only a difference of 81 bases. Therefore, MaCalm and Calm1a might be the same genes. In other words, we verified the existence of the Calm transcript in M. amblycephala for the first time. To better understand the functions and mechanism of Calm in fish, the Calm gene from M. amblycephala was then characterized. The MaCalm protein is composed of 149 amino acid residues and shows high sequence similarity (about 96.73–100% sequence identity) with other Calms in teleosts. Especially, MaCalm shared 100% similarity with Calms from D. rerio, S. marmoratus, A. mexicanus, T. rubripes, C. idella, O. nerka, O. latipes, E. bruneus, S. alpinus, T. californica, C. auratus, E. lucius, S. canicular and C. carcharias, implying that the MaCalm protein belongs to the conserved calmodulin family in fish. Similar with previous works [10,11], the MaCalm protein also contains four Ca2+-binding domains, confirming that Calm is the essential sensor of Ca2+ and the key regulatory protein of downstream calcium signaling pathways in M. amblycephala. Besides Cynoglossus semilaevis, the acid amino sequence of the Ca2+-binding domains of MaCalm are identical with that of the other vertebrate and invertebrate species in Figure 2, indicating that the major functions and structures of MaCalm might bear a strong resemblance to the Calm from other teleost species [11]. In this study, one or several different amino acid residues were found among MaCalm and other teleost species, which is similar with the study in Stichopus monotuberculatus [35] and L. vannamei [11]. Therefore, the high similarity of Calm amino acid residue may be the adaptation strategy to environmental conditions during animal evolution. And the amino acid residue mutations of Calm may be related to their living environment. Furthermore, the dendrogram showed that MaCalm shared a close evolutionary relationship with its counterparts from C. idella and C. auratus and all of them were clustered into the Actinopterygii Calm branch. Thus, MaCalm was inferred to be able to bind Ca2+ through Ca2+-binding domains and regulate Ca2+-activated signaling pathways in multiple biochemical and physiological processes [6].
As a vital Ca2+ receptor in various physical processes, Calm is widely distributed and essential in multifarious tissues of aquatic organisms [7,8,10,16]. In the present study, MaCalm transcripts were widely expressed in all examined tissues, with the highest expression levels in the brain and the lowest expression levels in muscle. The brain is thought of as a core center of the nervous system in regulating basic vital functions, such as cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal and sensory activities [36]. Therefore, the highest mRNA expression level of MaCalm in the brain suggests that MaCalm plays crucial roles in maintaining normal brain function and regulating neuronal signal transduction in M. amblycephala. In P. clarkia [37] and L. vannamei [11], the Calm gene was also highly expressed in the nerves (homologous organs of brain). The tissue expression of MaCalm mRNA was similar to that of Calm in the hybrid F1 of Acanthopagrus schlegelii male × Pagrus major female [16] and Drosophila melanogaster [38]. Although the structure of Calm is similar across species, some differences in Calm tissue distribution are found among different animal species [14,15,39,40]. The constitutive distribution and diversified expression patterns of MaCalm in different tissues are likely related to the multiple functions of Calm.
In aquatic organisms, previous works indicate that Calm plays important roles in host immune defense as a multifunctional mediator capable of regulating the antibacterial effect and inflammatory response by interacting with nitric oxide (NO) [6,13] and modulating the activation of phagocytosis [23], as well as partaking in the NO-mediated activation of Calm kinase-dependent signal cascades [21]. However, the involvement of Calm in the immune responses of M. amblycephala remains unclear. In this study, the significant downregulation of MaCalm in the kidney was detected after A. hydrophila infection, suggesting MaCalm played pivotal roles in fish defense against the invasion of pathogens. However, a notable upregulation of Calm in the kidney was observed after Vibrio alginolyticus infection in Epinephelus coioides [39], suggesting that the expression patterns of Calm varied depending on the animal species and microbial strains. Unlike in the kidney, MaCalm mRNA expression in the liver increased notably at 12 hpi after A. hydrophila infection, which might respond to the microbial challenge and neutralize the adverse effects of the Aeromonas infection [39]. Intriguingly, several pieces of research show that Calm could act as a co-factor of virulence factors of bacteria to prevent innate immune activation [20]. Therefore, the downregulation of MaCalm transcripts in the kidney (at 12 hpi and 24 hpi) and liver (at 24 hpi) may be an alternative immune strategy of the host immune system against bacterial infection. MaCalm appears to have divergent mechanisms of interaction with A. hydrophila infection. In addition to the involvement in the immunity response, the functional roles of Calm in the various adversity stresses have been revealed in aquatic animals [7,8,17,18,21,22]. For example, Calm played a principal role in adapting to ammonia-N exposure in L. vannamei [22]. As was shown in this study, MaCalm transcripts presented a steady and significant augment in relation to Cd exposure. A similar observation was reported in A. woodiana after Cd exposure [7]. Previous studies have demonstrated that Cd2+ can lead to Ca2+ overload by blocking the outflow of intracellular Ca2+ and facilitating the release of calcium pool in the endoplasm [41]. As the pivotal intracellular Ca2+-binding protein, the overexpression of the Calm gene is favorable to decrease intracellular Ca2+ concentration, and maintain dynamic balance of intracellular Ca2+. This might be the self-adaptive mechanism of M. amblycephala in response to waterborne Cd exposure. A previous study has shown that Calm activation was mainly mediated in the presence of Cd2+ in Oncorhynchus mykiss and Mytilus sp. [42]. Moreover, the radius of Cd2+ approximate to that of Ca2+ and Cd2+ has a higher affinity for Calm [41]. Cd2+ can combine with Calm by competing with Ca2+, disturb Calm-dependent signaling cascades and bring about cytotoxicity [43]. As a consequence, the upregulation of Calm transcripts might be relevant with Cd-induced toxicity and Calm may be a promising therapeutic target for Cd-aroused diseases.
HSP70, a stress-related gene, is involved in multiple biological functions and immunity responses under both normal and stress conditions, plays crucial roles in protecting fish against adverse stressors and maintains the homeostasis and survival of fish [44,45]. Thus, HSP70 is a potential molecular biomarker for stressful environmental factors and disease conditions in fish. In this study, HSP70 transcripts of M. amblycephala were remarkably suppressed in the liver and kidney at 12 hpi and (or) 24 hpi after infecting with A. hydrophila, suggesting that A. hydrophila infection significantly affected HSP70 expression levels and led to an evident stress response. Similar observations were reported in Opuntia ficus, Microptenus salmoides and Labeo rohita under bacterial challenge by A. hydrophila [46,47,48]. In the present study, Cd brought about the induction of the HSP70 gene expression level in the liver, which was similar to previous findings [41]. These results indicate that HSP70 transcripts could respond differentially to biotic and abiotic stressors. Calm is considered as one of the most important molecular biomarkers in teleost fishes under chronic stressors [39]. Therefore, the combination of the MaCalm and HSP70 expression level in the liver could be regarded as the potential biomarkers of Cd-induced toxicity. Pioneer research has shown that Calm is involved in heat shock signal transduction and regulating the expression of HSP70 transcripts in M. musculus and Homo sapiens [49,50]. In our study, the dynamic changes of HSP70 transcripts were broadly consistent with the alternations of MaCalm gene expression. These data support a role for MaCalm in the induction of HSP70 and the promotion of the stress response during A. hydrophila infection and waterborne Cd expression and in remodeling the Calm-mediated defense signaling cascade, suggesting that Calm regulates remodeling in multiple contexts: bacterial infection and heavy metal exposure. The regulatory mechanism of Calm and its downstream signal transduction pathway in fish need further investigation in response to various stimuli.
5. Conclusions
The full-length cDNA of MaCalm was identified from blunt snout bream M. amblycephala and shown to belong to a conservative calmodulin family. MaCalm had a broad expression in all examined tissues with the highest level in the brain and weakest level in muscle. MaCalm transcripts altered remarkably and dynamically in the liver and kidney under A. hydrophila and cadmium challenges. Moreover, MaCalm and HSP70 could be considered as the combined biomarkers for cadmium toxicity and cadmium pollution monitoring in the water environment. These results revealed that MaCalm is an important multifunctional protein in response to stress and pathological conditions, which would provide the fundamental data to further elucidate the expression and function of Calm and Calm-mediated multiple defense signaling pathways.
Author Contributions
J.G.: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, resources, writing—original draft. H.W.: formal analysis, methodology, resources. X.T. and J.W.: methodology, resources. M.X.: formal analysis, resources. Z.X. (Zhenzhen Xiong): formal analysis, investigation. D.O.: resources, supervision. Z.X. (Zhonggui Xie): funding acquisition, supervision. R.S.: project administration, funding acquisition, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System of the People’s Republic of China (program CARS-45) and the Aquatic Drug Safety Evaluation of the Department of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of Hunan Province.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All fish sampling procedures were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the laboratory animal welfare ethical review and regulations for the administration of affairs concerning experimental animals in China, under the approval and supervision of Hunan Fishery Sciences Institute, Changsha, China (Approval Code: No. HFSI2022-03).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Menon, S.V.; Kumar, A.; Middha, S.K.; Paital, B.; Mathur, S.; Johnson, R.; Kademan, A.; Usha, T.; Hemavathi, K.N.; Dayal, S.; et al. Water physicochemical factors and oxidative stress physiology in fish, a review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science 1980, 207, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapham, D.E. Calcium signaling. Cell 2007, 131, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, D.; Means, A.R. Calmodulin: A prototypical calcium sensor. Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedberg, F.; Rhoads, A.R. Multiple calmodulin genes in fish. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2002, 29, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.R.; Li, J.L.; Wang, W.L.; Li, J.X.; Zhao, Q.; Li, M.J.; Wang, L.L.; Song, L.S. A calmodulin targeted by miRNA scaffold659_26519 regulates IL-17 expression in the early immune response of oyster Crassostrea gigas. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 124, 104180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.X.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, F.J.; Qiu, Y.H.; Feng, W.P.; Shao, X.Y.; Su, C.Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.M.; Wang, M.Q.; et al. Characterization of AwCaM1 from freshwater clam Anodonta woodiana and effect of Ca2+ and Cd2+ on its expressions. Asian J. Ecotox. 2021, 16, 227–238. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Jia, Z.R.; Li, X.J.; Geng, X.Y.; Sun, J.S. Calmodulin is a stress and immune response gene in Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.J.; Yu, Y.Y.; Gao, J.; Feng, Y.Y.; Tang, L.; Sun, Y.X.; Yang, L.L. Characterization and function of a novel calmodulin-like protein from crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengprasert, P.; Amparyup, P.; Tassanakajorn, A.; Wongpanya, R. Characterization and identification of calmodulin and calmodulin binding proteins in hemocyte of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 50, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.F.; Yao, C.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Two types of calmodulin play different roles in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) defenses against Vibrio parahaemolyticus and WSSV infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.T.; Lv, J.J.; Gao, B.Q.; Liu, P. Cloning and expression analysis of Portunus trituberculatus calmodulin cDNA. J. Fish. Sci. Chin. 2015, 22, 1150–1159. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Ren, C.H.; Li, W.H.; Jiang, X.; Xia, J.J.; Wong, N.K.; Hu, C.Q. Calmodulin of the tropical sea cucumber: Gene structure, inducible expression and contribution to nitric oxide production and pathogen clearance during immune response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.F.; Fu, G.D.; Wang, X.Y.; Ko, W.K.W.; Wong, A.O.L. Modulation of calmodulin gene expression as a novel mechanism for growth hormone feedback control by insulin-like growth factor in grass carp pituitary cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3821–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, S.W.; Wen, J.J.; Liu, S.G.; Long, Z.F. Cloning and characterization of a sex-reversal-related gene ECaM in Epinephelus akaara gonads. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 32, 147–153. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ji, H.J.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.W. Cloning and expression analysis of Calmodulin from the hybrid F1 of Acanthopagrus schlegelii male × Pagrus major female and P. major. Mar. Fish. 2018, 40, 435–446. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Patel, D.M.; Brinchmann, M.F.; Hanssen, A.; Iversen, M.H. Changes in the skin proteome and signs of allostatic overload type 2, chronic stress, in response to repeated overcrowding of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 891451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zeng, M. Hexavalent chromium-induced apoptosis in Hep3B cells is accompanied by calcium overload, mitochondrial and AIF translocation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.S.T.; Fuentes, J.; Almeida, O.; Power, D.M.; Canario, A.V.M. Ca2+-Calmodulin regulation of testicular androgen production in Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 162, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanford, J.J.; Odendall, C. Ca2+-calmodulin signalling at the host-pathogen interface. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2023, 72, 102267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xin, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Qiao, X.; Wang, L.; Song, L. Ca2+/Calmodulin-NOS/NO-TNFs pathway hallmarks the inflammation response of oyster during aerial exposure. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 603825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pan, L.Q.; Xu, L.J.; Si, L.J. Effects of ammonia-N exposure on the concentrations of neurotransmitters, hemocyte intracellular signaling pathways and immune responses in white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 75, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Tang, Y.; Sun, S.G.; Kim, T.; Ju, K.; Ri, S.; Du, X.Y.; Zhou, W.S.; Shi, W.; Li, S.G.; et al. Modulatory function of calmodulin on phagocytosis and potential regulation mechanisms in the blood clam Tegillarca granosa. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 116, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.B.; Shui, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhao, C.Y.; Song, C.M.; Liao, X.R. Participation of calmodulin in ovarian maturation induced by eyestalk ablation in red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.X.; Chen, G.Z.; Tu, H.H.; Yao, X.Y.; Peng, X.; Lan, X.; Tang, Q.Y.; Yi, S.K.; Xia, Z.L.; Cai, M.Y.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis and functional gene expression in different stages of gonadal development of Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Fishes 2023, 8, 8020094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.H.; Lin, W.; Yang, L.P.; Qiu, Y.M.; Kuang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Li, D.P.; Tang, R.; et al. Sub-chronic exposure to ammonia inhibits the growth of juvenile Wuchang bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) mainly by downregulation of growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor axis. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.X.; Li, S.N.; Liang, Y.X.; Xu, R.Y.; Qi, Q.; Wang, B.K.; Zhang, C.N. 16S rRNA and transcriptome analysis of the FOS-mediated alleviation of Aeromonas hydrophila-induced intestinal damage in Megalobrama amblycephala. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.W.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.L.; Feng, J.T.; Chen, H.; He, Y.H.; et al. TBtools-II: A "one for all, all for one" bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanmougin, F.; Thompson, J.D.; Gouy, M.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal X. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaji Saganuwan, S. A modified arithmetical method of Reed and Muench for determination of a relatively ideal median lethal dose (LD50). Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F. Identification, Detection and Construction of Green Fluorescent Protein Markers Strains of Pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila Isolated from Megalobrama amblycephala. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2012; pp. 1–78. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=WdAl4K16JyU-4njk9QQnnQ7VlwsH5-tJywpPtueH0phwhOdTiQGpZvnCSONautb8ZJEthsFlEjREQbGg-Z1k1aw6SM5XIGpcoMUFf2cm8L0DZNfw04QqTW3iuLtBboxotPn33yRkwnJ2VUNgKs7LRg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 4 May 2024). (In Chinese).
- Gao, J.W.; Xi, B.W.; Chen, K.; Song, R.; Qin, T.; Xie, J.; Pan, L.K. The stress hormone norepinephrine increases the growth and virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.Y.; Xi, B.W.; Ren, M.C.; Dong, J.J.; Xie, J.; Xu, P. Molecular cloning, tissue expression of gene Muc2 in blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala and regulation after re-feeding. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Ren, C.H.; Hu, C.Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhong, M. cDNA cloning and tissue distribution of calmodulin from sea cucumber (Stichopus monotuberculatus). South China Fish. Sci. 2014, 10, 75–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, W.Y. Role of calmodulin in brain function. Prog. Brain Res. 1982, 56, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Gillen, C.M.; Wheatly, M.G. Cloning and characterization of a calmodulin gene (CaM) in crayfish Procambarus clarkii and expression during molting. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 152, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiman, R.G.; Atkinson, R.C.; Andruss, B.F.; Bolduc, C.; Kovalick, G.E.; Beckingham, K. Spontaneous avoidance behavior in Drosophila null for calmodulin expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2420–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.W.; Xie, F.X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.N. Characterization and expression analysis of Calmodulin (CaM) in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) in response to Vibrio alginolyticus challenge. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.F.; Wong, A.O.L. Genomic structure and transcriptional regulation of grass carp calmodulin gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Bi, L.; Jin, L.; Peng, R. Toxic effects of cadmium on fish. Toxics 2022, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behra, R. In vitro effects of cadmium, zinc and lead on calmodulin-dependent actions in Oncorhynchus mykiss, Mytilus sp., and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1993, 24, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Chao, S.H.; Zysk, J.R.; Cheung, W.Y. Stimulation of calmodulin by cadmium ion. Arch. Toxicol. 1985, 57, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.H.; Xie, J.; Xu, P.; Liu, W.B.; Ge, X.P.; Liu, B.; He, Y.J.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zhou, Q.L.; Pan, L.K. Molecular cloning and expression of two HSP70 genes in the Wuchang bream (Megalobrama amblycephala Yih). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.H.; Guo, Z.X.; Wang, A.L. The protective effects of taurine on oxidative stress, cytoplasmic free-Ca2+ and apoptosis of pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus) under low temperature stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 77, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharloei, M.; Heidari, B.; Zamani, H.; Hadavi, M. Effects of Pro-Tex® on the expression of Hsp70 gene and immune response parameters in the Persian sturgeon fingerlings, Acipenser persicus, infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2020, 36, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.N.; Lu, K.L.; Wang, J.H.; Qian, Q.; Yuan, X.Y.; Pu, C.C. Molecular cloning, expression HSP70 and its response to bacterial challenge and heat stress in Microptenus salmoides. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 2389–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Mohapatra, A.; Sahoo, P.K. Expression analysis of heat shock protein genes during Aeromonas hydrophila infection in rohu, Labeo rohita, with special reference to molecular characterization of Grp78. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Cong, X.; Suo, J.J.; Cao, R.F.; Jiang, Z.L.; Gao, S.S.; Tian, W.R. Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II contributes to HSP70 expression in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica 2012, 27, 213–217. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Wei, J.N.; Peng, W.X.; Liang, J.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Dai, G.; Yuan, J.; Pan, F.Y.; Xue, B.; et al. The association of CaM and Hsp70 regulates S-phase arrest and apoptosis in a spatially and temporally dependent manner in human cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2009, 14, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).